-
近年来,发展高效低耗的挥发性有机化合物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)脱除技术迫在眉睫。目前,已形成系列VOCs排放控制技术,包括物理吸附法[1-2]、等离子体法[3-6]、生物处理法[7-8]、氧化法[9-11]等。其中,等离子体法因其脱除效率高、反应迅速、且无二次污染等优点被认为有一定应用前景。等离子法是利用如滑动电弧、脉冲电晕、介电屏障等对空气放电产生·OH和臭氧等强氧化性物质,将VOCs氧化为清洁小分子碎片(CO2、H2O、H2等),以实现VOCs的脱除。而该方法中,强氧化自由基O3和·OH的含量对VOCs脱除效率有重要影响[12-15]。ZHU等[16]采用介质阻挡放电脱除苯时发现,生成的O3浓度与苯脱除率呈正相关。亦有研究表明,O3和·OH能有效脱除烷烃、苯、甲苯等VOCs[17-19],甚至多环芳烃和二恶英[20-21]。
目前,VOCs脱除领域的研究多较为宏观,对微观层面的温度、浓度、速度场的模拟计算等内容较少。随着计算流体力学(CFD)的发展[22],如Fluent等仿真软件可用于实际工程应用中,以降低设计成本、缩短开发时间等[23]。MOUSAVI等[24]对实验室规模的生物质锅炉进行CFD模拟,研究并确定了氮氧化物形成的不同途径及其贡献。TEODOSIU等[25]将办公设备产生的VOCs排放进行CFD模拟,并分析其健康风险。
O3和·OH对甲苯脱除的反应机理类似[26-27]。由于甲基的活化,O3和·OH均优先攻击甲苯的1,2c—c键位和2碳位,之后在O3和·OH的破坏下,苯环开始断裂。本研究以甲苯作为典型VOCs,利用化学反应耦合CFD方法对VOCs脱除效率的提升进行研究,探索O3/·OH对甲苯的脱除规律,分析影响脱除效率的关键因素,以期确定含甲苯焚烧废气脱除净化的较优反应条件,为实际工业应用提供参考。
-
为利用Fluent软件对污染物分布及脱除效率进行模拟分析,需建立对应网格及模型。如图1(a)所示,本研究将模拟一个长10 m,底面直径为2 m的圆柱形管道。该管道的圆形底面为烟气与含O3/·OH的射流入射面。含O3/·OH的射流入口为直径0.1 m的圆形入口,而底面其余位置均为含污染物的烟气入口,其分布方式如图1(b)所示。为提高计算速度与精度,将整个管道模型对称化切割为4份,单独研究1/4管道的污染物分布情况。而切割面设置为对称面,不会影响后续的模拟计算。对称化处理后的1/4模型如图1(c)所示,底面入口分布情况如图1(d)所示。
网格整体采用配套的ANSYS-ICEM CFD软件进行绘制。整体网格采用O-block结构化网格进行绘制,为提升网格质量,确保计算的精度和速度,绘制为六面体网格。
将模型划分为若干体块(block),整体模型的block体块划分如图1(e)所示。为使体块能满足管道设计需要,应对体块边缘(edge)与射流入口做特定约束,其底面edge如图1(f)所示。绿色边缘edge表示已与某一条曲线固定形成约束,黑色边缘则表示在模型表面普通block体块间的分隔,无特定约束。由此便可利用体块与边缘划分射流入口与烟气入口,并完成对管道壁面、对称面、出口等边界设置。构建完体块后设置整体的网格大小尺寸即可生成模型网格,再对生成网格进行优化加密、平整,最终生成网格(见图1(g)、图1(h))。
-
完成网格绘制后,对生成的网格质量进行检测。经ANSYS-ICEM CFD软件检测,本模型网格总网格数为301 694。通过计算单位网格六面体的雅可比行列式的最小值与最大值之比(雅可比比率)来检测单位网格六面体的变形程度。通常认为比率越接近于1,说明网格质量越好。此外,常见的还有通过计算三维网格的扭曲和坍塌值来判断网格质量好坏[28]。本研究采用的评判标准为雅可比比率。该模型网格质量最小为0.415,网格质量最优为1,约80%的网格质量大于0.8,平均质量0.897。因此,此网格能满足计算需要,以保证计算收敛,并得到准确模拟结果。
-
本次模拟中Fluent模型为瞬态模型Transient,模拟10 s内管道内部的污染物分布情况。时间步长0.01 s,1 000步时间步,每一时间步下至多1 000次迭代或直至收敛。本模型不考虑重力加速度的影响,且开启能量方程。湍流模型为Realizable k-epsilon模型,相较于Standard k-epsilon模型能更好地模拟射流情况。基于前期工作构建的O3/·OH在烟气脱除甲苯的Chemkin反应机理文件及热力学文件[26-27],选择组分输运模型并导入Chemkin反应机理文件及热力学文件,采用有限速率模型(Finite-Rate/No TCI)且组分间相互扩散(inlet diffusion)。设置射流入口与废气入口为速度入口(velocity inlet),管道出口为压力出口(pressure outlet),进行标准初始化(Standard initialization),并设置对应组分及初始温度等参数。
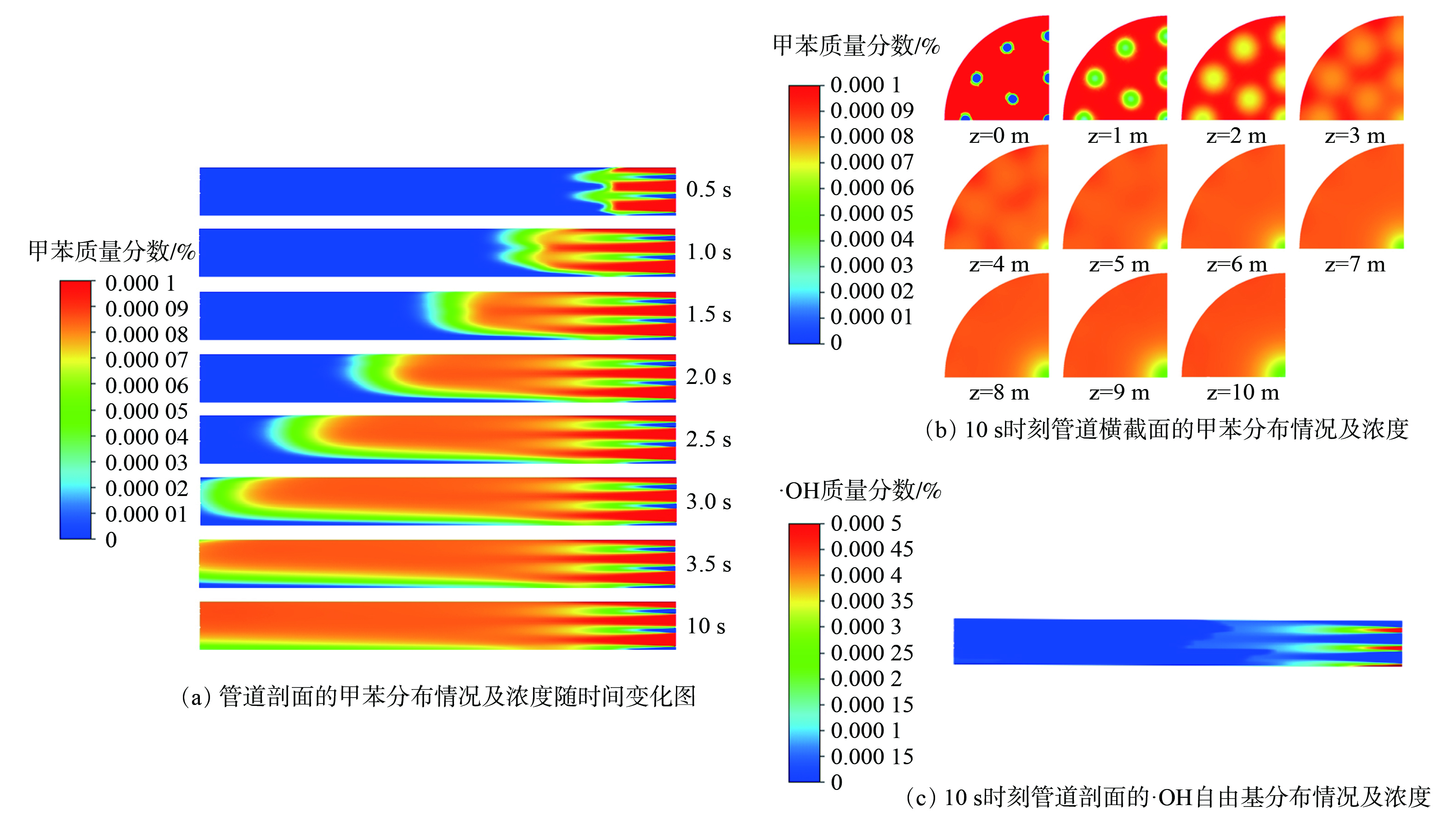
完成初始化后设定每隔0.5 s,即50个时间步后记录管道剖面的甲苯污染物浓度分布。在每个时间步后,记录管道高度每间隔1 m的横截面上,甲苯污染物网格面的平均质量分数和面标准差,用以计算污染物脱除效率和脱除均匀程度。
式中:Ef是甲苯的甲苯脱除效率,%;Cin是烟气入口时甲苯的质量分数,%;Cout是烟气出口时甲苯的质量分数,%。
-
对污染物分布情况进行模拟分析时,入口气体参数为:废气入口速度为3 m·s−1,温度573 K;输入氮气的质量分数为77.849 9%,二氧化碳的质量分数为12%,一氧化碳的质量分数为0.1%,氧气的质量分数为5%,水的质量分数为5%,一氧化氮的质量分数为0.05%,甲苯的质量分数为0.000 1%。射流入口的参数为:速度为10 m·s−1,温度573 K;输入的氮气质量分数为78.999 5%,氧气质量分数为21%,·OH质量分数0.000 5%。每隔1 m取截面数据监测甲苯的平均质量分数。
图2(a)表明,当模拟时间接近10 s时,管道内部气体分布情况基本稳定,甲苯质量分数不再随时间发生大幅度变化。此时,可通过测量管道横截面的甲苯平均质量分数来计算·OH在上述工况下对甲苯的脱除效率。图2(b)中云图颜色表示污染物甲苯的浓度,截面颜色越接近红色,表明该横截面甲苯质量分数越高。反之,云图颜色越接近蓝色,甲苯质量分数越低。通过对比管道横截面及剖面的污染物分布情况发现,管道中部甲苯分布较为均匀,管道后段则稳定。通过图2(c)可观察到管道剖面的·OH分布情况及其质量分数。离射流入口越远,·OH质量分数越低。脱除甲苯的反应大多发生在管道0~5 m处。离入口越远,甲苯质量分数越低,则脱除效率越高。管道长度约10 m,出口处气体中甲苯分布均匀。因此,管道出口处甲苯质量分数可衡量·OH对甲苯的脱除效率。后文中对脱除效率的对比以出口处脱除效率为准,即对比管道出口处的脱除效率。
-
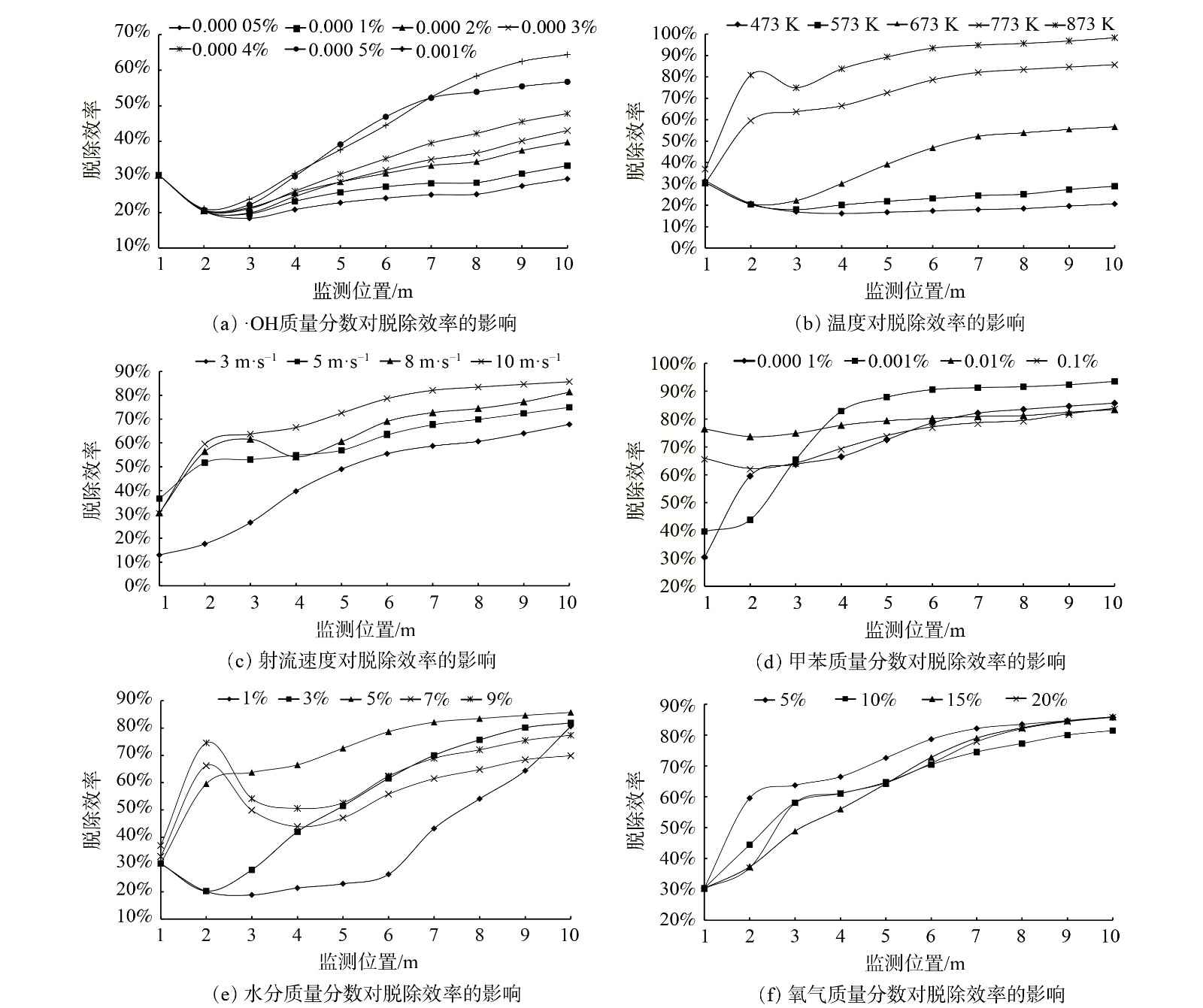
1)·OH质量分数对脱除甲苯的影响。当射流流速10 m·s−1、射流与废气温度为673 K时,改变气体组分,将氮气作为平衡气,模拟当·OH/甲苯质量分数比分别为0.5、1、2、3、4、5、10时,·OH对甲苯的脱除效率。测量时间点为10 s时。图3(a)表明,在该工况下,·OH对甲苯的脱除效率随着·OH/甲苯质量分数比的上升而上升。在质量分数比为1~5时,脱除效率的提升比质量分数比为5~10时更大,可认为当·OH/甲苯质量分数比接近于10时,反应达到一定程度饱和,此时脱除效率提升程度变缓。综上所述,在后续的模拟仿真中选择·OH/甲苯质量分数比为5,既可保证系统对·OH的浓度需求较小,而其脱除效率也较高,应用到工业生产中成本亦较低。
2)温度对脱除甲苯的影响。当·OH/甲苯质量分数比为5、射流流速10 m·s−1时,改变射流入口与废气入口的气体温度,在473~873 K,每升高100 K,模拟1次管道内的污染物脱除状况。图3(b)表明,随着温度升高,·OH对甲苯的脱除效率也逐渐提升。温度在473~673 K时,·OH对甲苯的脱除效率较低;而在温度为773 K时,其脱除效率明显提高,在管道10 m处的脱除效率约85%;而温度为873K时,其脱除效率达到约98%,脱除效率较高。因此,当温度为773 K或873 K时,·OH脱除甲苯效率较高。相较·OH/甲苯质量分数比对脱除效率的影响而言,温度变化对脱除效率的影响更大。
3)射流速度对脱除甲苯的影响。当射流与废气温度均为773 K、·OH/甲苯质量分数比为5时,改变射流入口的射流速度,分别为3、5、8和10 m·s−1时,模拟射流流速对脱除效率的影响。图3(c)表明,随着射流速度变大,·OH对甲苯的脱除效率也逐渐提升。当射流流速为10 m·s−1时,脱除效率最高。但相较其他工况参数而言,射流流速的改变对脱除效率的影响较小。
4)甲苯质量分数对脱除甲苯的影响。图3(d)表明了甲苯质量分数对·OH脱除甲苯效率的影响。当射流速度10 m·s−1、·OH/甲苯质量分数比为5、温度773 K时,改变管道入射的甲苯质量分数,分别模拟甲苯质量分数为0.000 1%、0.001%、0.01%、0.1%,考察系统对甲苯的脱除效率。当甲苯初始质量分数为0.001%时,脱除效率较其他质量分数有一定程度提升,出口处脱除效率约为93.5%。因此,当烟气中甲苯质量分数为0.001%时,系统的脱除效率较高。
5)烟气中水分对脱除甲苯的影响。当射流速度为10 m·s−1、甲苯质量分数为0.000 1%、·OH质量分数为0.000 5%、温度为773 K时,改变烟气入口水分的质量分数分别为1%、3%、5%、7%、9%时,考察·OH对甲苯的脱除效率。图3(e)表明,在改变烟气入口水分时,水分质量分数为5%时脱除效率较高,过高或过低的水分质量分数反而不利于甲苯脱除。但通过与其他因素相比,一定范围内的水分变化对甲苯的脱除效率影响不是很明显。
6)烟气中氧气质量分数对脱除甲苯的影响。当其他的工况参数不变的情况下,即射流速度10 m·s−1、甲苯质量分数0.000 1%、·OH质量分数0.000 5%、温度773 K、烟气入口水分质量分数5%时,改变烟气入口O2质量分数发现,烟气内氧气质量分数对甲苯最终脱除效率影响不大(图3(f)),无明显规律。无论氧气质量分数为5%或20%,其在管道出口10 m处的脱除效率均达到80%以上,其脱除的均匀程度也相差不大。因此,烟气内氧气质量分数对·OH脱除甲苯的影响不大。
-
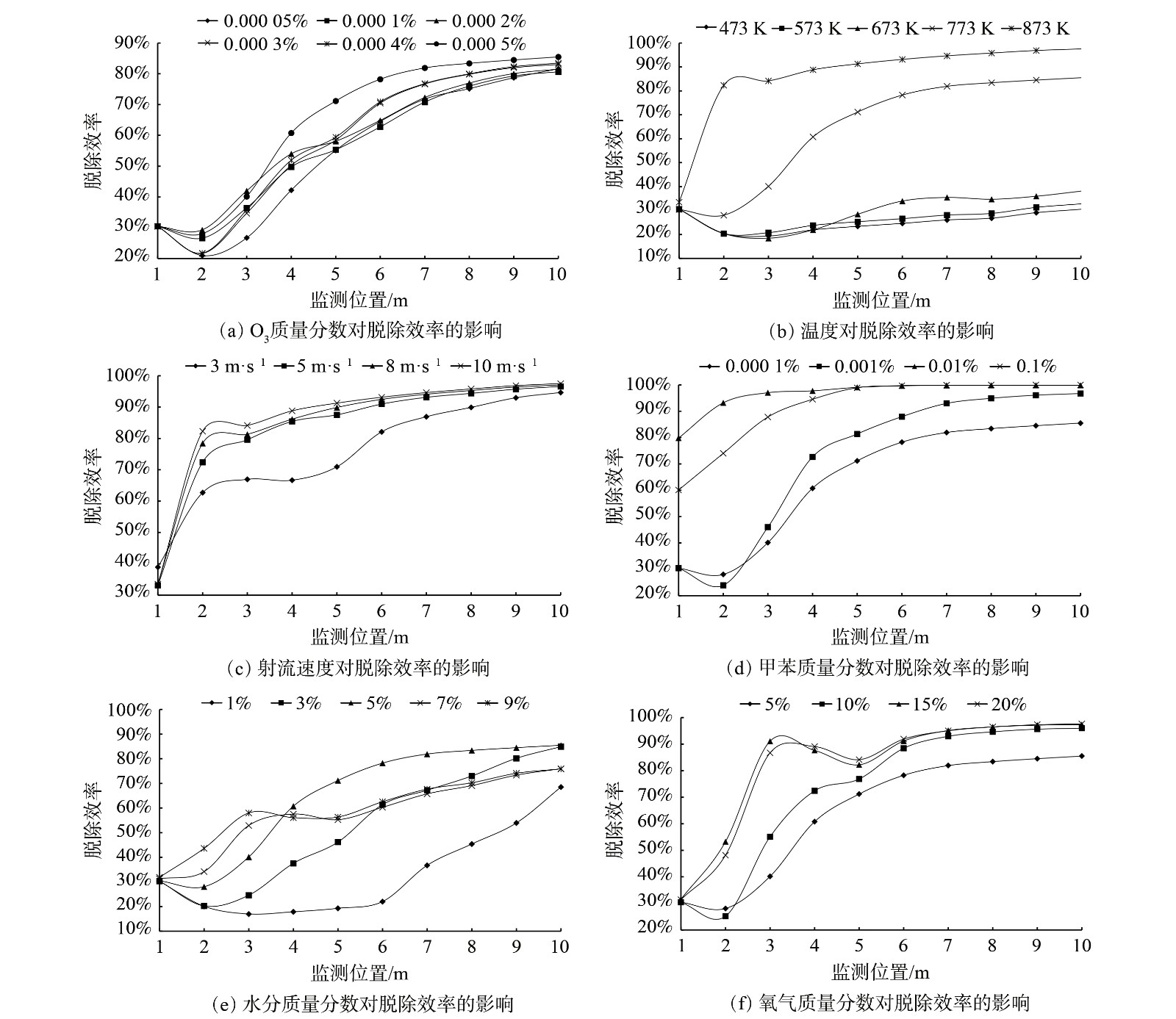
1)臭氧质量分数对脱除甲苯的影响。当射流流速10 m·s−1、射流与废气温度均为773 K时,改变O3/甲苯质量分数比,即分别为0.5、1、2、3、4、5,模拟O3/甲苯质量分数比对污染物脱除效率及均匀性的影响。测量时间点为10 s时。图4(a)表明,O3与·OH脱除甲苯的效果类似,O3对甲苯的脱除效率随·OH/甲苯质量分数比上升而上升。O3/甲苯质量分数比为5时,其脱除效率也较高,且O3质量分数的改变对甲苯脱除效率影响较小,在管道出口10 m处亦可保持80%的脱除效率。
2)温度对脱除甲苯的影响。当O3/甲苯质量分数比为5、射流流速10 m·s−1时,改变射流入口与废气入口的气体温度,在473~873 K内每隔100 K模拟1次管道内的污染物脱除情况。图4(b)表明,随着温度的升高,O3对甲苯的脱除效率也逐渐提升。温度在473~673 K时,O3对甲苯的脱除效率较低,而在温度为773 K时,其脱除效率明显提高。这与·OH脱除甲苯的效果类似,也同样在温度为873 K时,其脱除效率最高约97%。这表明入射的烟气与射流的温度对污染物脱除效率影响较大。
3)射流速度对脱除甲苯的影响。当温度为873 K、不改变气体组分,且O3/甲苯质量分数比为5时,射流入口的射流速度分别为3、5、8和10 m·s−1 4种情况时,如图4(c)所示,可以发现在873 K的环境下随着射流速度的变大,O3对甲苯的脱除效率变化不敏感,管道出口10 m处的甲苯脱除效率均达到了90%以上,且差距不大。这可能是因为射流流速的改变对脱除效率的影响较小,加之在温度为873 K时脱除效率已经处于较高效率,故射流流速的改变所带来的影响较小。因此,为了与·OH做对比,在后续计算中常模拟温度773 K下的工况环境。
4)甲苯质量分数对脱除甲苯的影响。在射流速度10 m·s−1、O3/甲苯质量分数比为5、温度773 K时,改变管道入射的甲苯质量分数,即0.000 1%、0.001%、0.01%、0.1%,考察系统的甲苯脱除效率。图4(d)表明,与·OH降解甲苯的规律不同,随着甲苯质量分数的提升,在保持O3/甲苯质量分数比为5的情况下,甲苯初始质量分数越高,其脱除效率越高。当甲苯质量分数为0.01%或0.1%时,脱除效率接近100%。这与·OH的甲苯脱除规律完全不同。因此,当O3/甲苯质量分数比为5时,在实际应用中,可同时提高烟气中甲苯质量分数与射流中的O3质量分数,可进一步提高甲苯脱除效率。
5)烟气水分质量分数对脱除甲苯的影响。当射流速度10 m·s−1、甲苯质量分数0.000 1%、O3质量分数0.000 5%、温度773 K不变时,改变烟气入口水分的质量分数,即1%、3%、5%、7%、9%,考察O3对甲苯的脱除效率。图4(e)表明,水分质量分数为3%、5%时,脱除效率较高。过高或过低的水分质量分数反而不利于甲苯脱除。同样,一定范围内的水分质量分数对甲苯脱除效率影响并不明显。
6)氧气质量分数对脱除甲苯的影响。当射流速度10 m·s−1、甲苯质量分数0.000 1%、O3质量分数0.000 5%、温度773 K、烟气入口水分质量分数5%时,改变烟气入口的O2质量分数,以考察系统的甲苯脱除效果。图4(f)可表明,与·OH对甲苯的脱除规律不同,烟气中氧气质量分数达到10%时,较氧气质量分数5%的脱除效率有一定程度提升。较高的氧气质量分数有利于O3对甲苯的脱除。而随着氧气质量分数进一步增至15%及20%时,脱除效率接近饱和,达到90%以上,区别不够明显。综上所述,烟气中氧气质量分数为5%并非最优选择,适当提高氧气质量分数有助于污染物脱除,如选取氧气质量分数为10%。
-
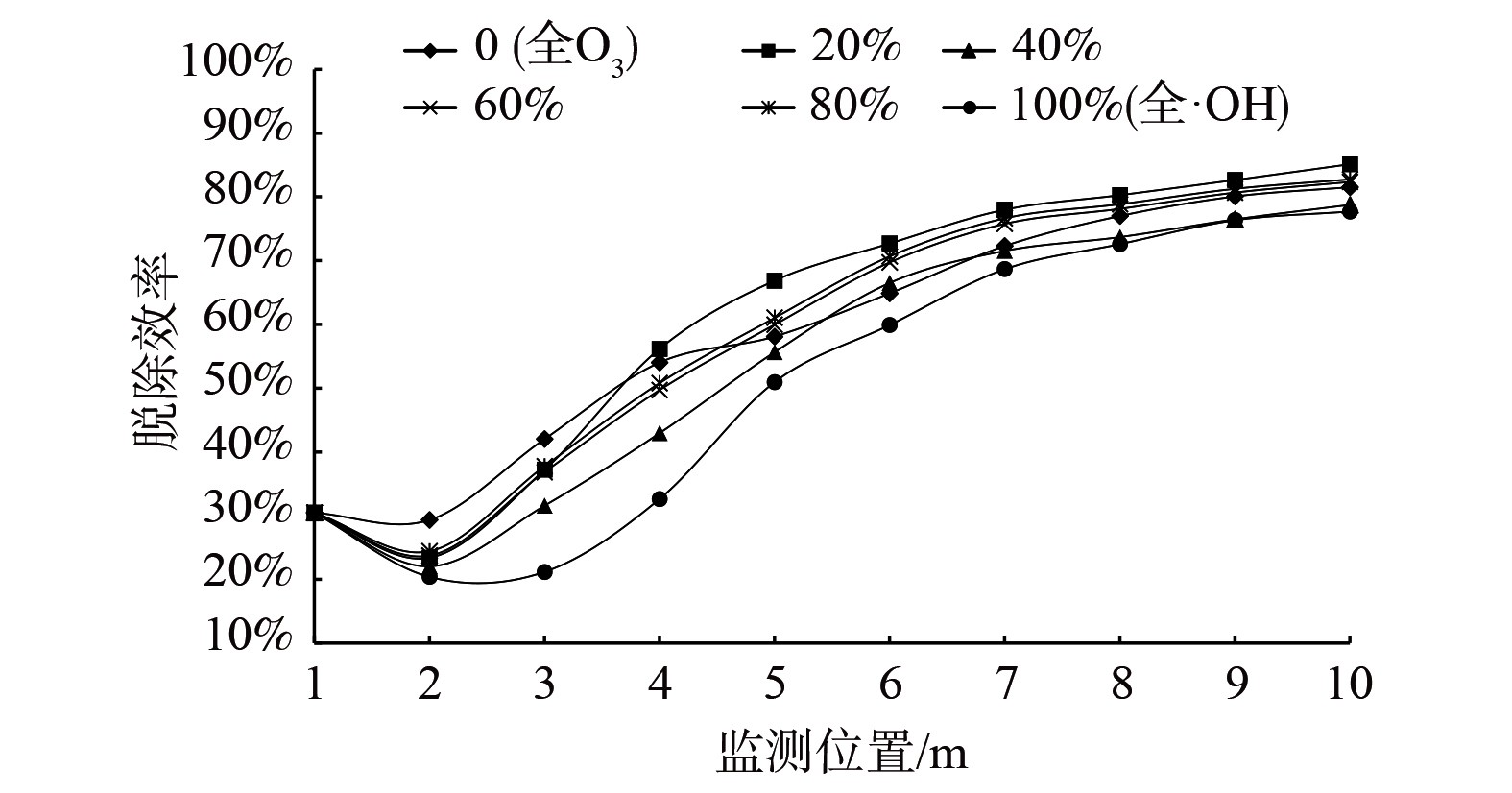
为进一步研究·OH与O3对甲苯脱除效率的影响,模拟·OH与O3混合注入,当射流速度10 m·s−1、甲苯质量分数0.000 1%、温度773 K、(·OH+O3)/甲苯质量分数比为2、烟气入口水分与氧气质量分数之比均为5%时,探究·OH与O3配比对脱除甲苯的影响。
配比百分数即·OH/(·OH+O3)。图5表明,当不同配比的·OH与O3混合注入时,脱除效率会不同,而当·OH质量为(·OH+O3)的20%时,即甲苯质量分数为0.000 1%、·OH质量分数为0.000 04%、O3质量分数0.000 16%时,脱除效率较其他配比条件要高出约5%。因此,混合注入时·OH质量为·OH与O3质量之和20%左右为宜。单一自由基脱除甲苯的效率没有·OH和臭氧共同脱除甲苯的效率高。在此工况条件下,对比·OH与O3单独脱除甲苯的效率发现,O3的脱除效率较·OH高约4%。
文献[29-30]表明,随着注射臭氧质量分数的持续增加,对甲苯的脱除能力逐步提升。此外,使用电晕、紫外线结合在H2O和O2/(空气)存在的情况下反应生成·OH、臭氧混合气体。该混合气体对甲苯的脱除效率可达到98%/(70%)。该结果定性验证了模拟计算与实验结果的一致性。
-
1)在温度为773 K、O3(或·OH)/甲苯质量分数比为5、射流速度10 m·s−1,氧气与水分质量分数均为5%时,O3与·OH对甲苯的脱除效率较高,均可达约85%。温度对脱除效率的影响较大,即温度越高脱除效率越大。在873 K时,其脱除效率可达约97%。而射流速度、甲苯质量分数、水分和氧气质量分数的变化对脱除效率均有影响,但影响的效果较温度变化更小。
2)由模拟仿真结果可知,在温度为773 K、(·OH+O3臭氧)/甲苯质量分数比为2的情况下,O3比·OH有更高的甲苯脱除效率,约高4%。这可能由于在复杂的烟道系统中,·OH有更高泯灭速度,而相比之下O3有更长的活性周期,低质量分数比下O3能更好地脱除甲苯。而在高质量分数比下可忽略泯灭速度影响。
3)当O3与·OH混合射入脱除甲苯时,质量分数配比为20%时脱除效果更优。这表明·OH和O3对甲苯的协同脱除效果较好。
O3/·OH簇射烟气脱除甲苯的数值模拟
Numerical simulation study on toluene removal by O3/·OH radical shower in flue gas
-
摘要: 利用Fluent软件耦合化学反应机理对O3与·OH簇射烟气脱除甲苯进行了数值模拟。针对圆形面为入射面的圆柱形管道,通过模拟计算不同位置截面上的甲苯平均浓度,得到管道各个位置的甲苯脱除效率。在不同温度、射流速度、气体组分、自由基配比等工况条件下,模拟研究O3/·OH对甲苯的脱除规律,分析影响O3/·OH对甲苯脱除效率的关键因素。结果发现,提升温度对脱除效率有较大提升,而自由基浓度、射流速度、水分浓度与氧气浓度等参数均对脱除甲苯效率均有一定影响。由于在复杂的烟道系统中O3具有更长的活性周期,因此,比·OH有更高的甲苯脱除效率,约4%的优势。当O3和·OH混合配比为20%时,脱除效率较其他配比情况要高出约5%,这表明·OH和O3可协同进行甲苯脱除。本研究可为优化含甲苯的焚烧废气脱除净化技术提供参考。Abstract: The removal of toluene by O3/·OH radical shower in flue gas was simulated numerically using Fluent software coupled with chemical reaction mechanism. The removal efficiency of toluene in the different cylindrical pipe was obtained by simulating the average toluene concentration on different sections of the cylindrical pipe with the circular surface as the incident surface. The removal of toluene by O3/·OH was simulated under different operating conditions such as temperature, jet velocity, gas composition and free radical ratio, and the key factors affecting the removal efficiency of toluene by O3/·OH were analyzed. The results showed that the removal efficiency was greatly improved by increasing the temperature, and the free radical, water and oxygen proportion, jet velocity had certain effects on the removal efficiency of toluene. Due to the longer activity cycle of O3 radical in complex flue system, O3 has a higher toluene removal efficiency than ·OH, with an advantage of about 4%. When the ratio of O3 and OH was 20%, the removal efficiency was about 5% higher than that of other ratios, indicating that there was a certain synergistic effect between ·OH and O3 radicals. This study can provide reference for optimizing the removal and purification technology of toluene containing incineration waste gas.
-
Key words:
- ·OH radical /
- ozone O3 /
- reaction mechansim /
- methylbenzene /
- Fluent simulation
-

-
-
[1] 李海龙. 吸附法净化有机废气模拟与实验研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2007. [2] 李守信, 宋剑飞, 李立清, 等. 挥发性有机化合物处理技术的研究进展[J]. 化工环保, 2008, 28(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2008.01.001 [3] ROSOCHA L A. Nonthemal plasma applications to the environment gaseous eletronics and power conditioning[J]. IEEE Transactions On Plasma Science, 2005, 33(1): 129-137. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2004.841800 [4] FUTAMURA S, ZHANG A H, EINAGA H. Involvement of catalyst materials in non-thermal plasma chemical processing of air pollutants[J]. Catalysis Today, 2002, 72(1): 259-265. [5] KANG M, KIM B J, CHO S M. Decomposition of toluene using an atmospheric pressure plasma TiO2 catalytic system[J]. Journal Of Molecular Catalysis A Chemical, 2002, 180(1): l25-132. [6] KIM H H, OH S M, OGATA A, et a1. Decomposition of gas-phase benzene using plasma-driven catalyst(PDC)reactor packed with Ag/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2005, 56: 213-220. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.09.008 [7] 何泽, 李桂英, 安太成, 等. 生物滴滤塔中两种优势菌种对高浓度甲苯废气净化对比实验[J]. 环境工程, 2007, 25(2): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8942.2007.02.012 [8] 张丽, 张小平, 黄伟海. 生物法净化处理挥发性有机化合物技术[J]. 化工环保, 2005, 25(2): 100-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2005.02.006 [9] COX H H J, DESHUSSES M A. Effect of starvation on the performance and re-acclimation of biotrickling filters for air pollution control[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36: 3069-3073. [10] 舒娟娟, 李素媛, 黄雯, 等. 低浓度有机废气纳米TiO2光催化处理技术[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2006, 32(11): 4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2006.11.002 [11] 王宝庆, 马广大, 陈剑宁. 挥发性有机废气净化技术研究进展[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2006, 4(5): 47-51. [12] SON Y S, KIM T H, CHOI C Y, et al. Treatment of toluene and its by-products using an electron beam/ultra-fine bubble hybrid system[J]. Radiation Physics & Chemistry, 2018, 144(3): 367-372. [13] GUO T, LI X S, LI J Q, et al. On-line quantification and human health risk assessment of organic by-products from the removal of toluene in air using non-thermal plasma[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 194(3): 139-146. [14] ZHU F S, LI X D, ZHANG H, et al. Destruction of toluene by rotating gliding arc discharge[J]. Fuel, 2016, 176: 78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.065 [15] CHUN Y N, KIM S C, YOSHIKAWA K. Removal characteristics of tar benzene using the externally oscillated plasma reformer[J]. Chemical Engineering And Processing Process Intensification, 2012, 57/58(1): 65-74. [16] ZHU T, LI J, JIN Y, et al. Decomposition of benzene by non-thermal plasma processing: Photocatalyst and ozone effect[J]. International Journal Of Environmental Science And Technology, 2008, 5(3): 375-384. doi: 10.1007/BF03326032 [17] ATKINSON R, AREY J. Atmospheric degradation of volatile organic compounds[J]. Chemical Review, 2003, 103: 4605-4638. doi: 10.1021/cr0206420 [18] ATKINSON R. Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of organic compounds: A review[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41: 200-240. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.10.068 [19] SHEN X L, ZHAO Y, CHEN Z M, et al. Heterogeneous reactions of volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 68: 297-314. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.027 [20] DANG J, SHI X L, ZHANG Q Z, et al. Mechanism and kinetic properties for the OH-initiated atmospheric oxidation degradation of 9, 10-Dichlorophenanthrene[J]. Science Of The Total Environment, 2015, 505(C): 787-794. [21] WEN Z C, WANG Z H, XU J R, et al. Quantum chemistry study on the destruction mechanism of 2, 3, 7, 8-TCDD by OH and O3 radicals.[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(3): 293-298. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.027 [22] 王兵波. 计算流体力学的发展及应用研究[J]. 南方农机, 2018, 49(9): 145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3872.2018.09.113 [23] 冯良, 刘鲲, 韩国园, 等. 大气式燃气燃烧器引射器的CFD研究[J]. 上海煤气, 2003(2): 13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4709.2003.02.005 [24] MOUSAVI S M, FATEHI H, BAI X S. Numerical study of the combustion and application of SNCR for NOx reduction in a lab-scale biomass boiler[J]. Fuel, 2021, 293: 120154. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120154 [25] TEODOSIU C, ILIE V, TEODOSIU R. Modelling of volatile organic compounds concentrations in rooms due to electronic devices[J]. Process Safety & Environmental Protection, 2016: S0957582016300994. [26] WEN Z C, LIU Y, SHEN H Z, et al. Mechanism and kinetic study on the degradation of typical biomass tar components (Toluene, Phenol and Naphthalene) by ozone[J]. Ozone:Science & Engineering, 2021, 43(1): 78-87. [27] WEN Z C, LIU Y, SHEN H Z, et al. A theoretical study on the destruction of typical biomass tar components (toluene, phenol and naphthalene) by OH radical[J]. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 2021, 98(2): 100015. doi: 10.1016/j.jics.2021.100015 [28] 李海峰, 吴冀川, 刘建波, 等. 有限元网格剖分与网格质量判定指标[J]. 中国机械工程, 2012, 23(3): 368-377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2012.03.026 [29] XI J Y, SAINGAM P, GU F, et al. Effect of continuous ozone injection on performance and biomass accumulation of biofilters treating gaseous toluene[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(1): 33-42. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6248-8 [30] MASUHIRO K, YUJI M, KUNIHITO T, et al. Highly efficient VOC decomposition using a complex system (OH Radical, Ozone-UV, and TiO2)[J]. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 2006, 3(9): 727-733. doi: 10.1002/ppap.200600040 -




 下载:
下载: