-
氮氧化物 (NOx,主要包括NO和NO2) 作为大气污染物,不仅会危害人群健康[1-2],还是造成酸雨、雾霾和光化学烟雾的重要因素[3]。柴油车是我国NOx的重要来源。根据生态环境部最新发布的《中国移动源环境管理年报 (2022) 》,我国柴油车NOx排放占汽车排放总量的88%以上。
目前,NH3选择性催化还原 (NH3-SCR) 技术是柴油车尾气NOx净化的主流技术,其核心是催化剂。以V2O5/TiO2和V2O5-WO3(MoO3)/TiO2催化剂为代表的钒基催化剂被广泛应用于固定源烟气脱硝,其催化效率高、抗硫性能优异,也被引入柴油车NOx催化净化领域,并规模化应用于我国国四和国五阶段柴油车尾气NOx排放控制技术中[4-5]。钒具有生物毒性,且温度窗口较窄、热稳定性较差[6],限制了钒基氧化物催化剂的进一步应用。目前,以Cu-SSZ-13为代表的Cu基小孔分子筛因其良好的催化性能和水热稳定性,在国六柴油车尾气NOx催化净化中广泛应用。开发具有优异NH3-SCR活性的环境友好型催化剂一直是该领域的研究热点。
由于具有优异的氧化还原性能,CeO2作为催化剂的活性组分、助剂和载体得到了广泛应用[7-8],但是纯CeO2催化剂的催化活性和热稳定性较差。在NH3-SCR反应中,氧化还原位点和酸性位点存在协同作用。因此,将同种功能位点高度分散,不同功能位点紧密耦合成为该类催化剂的设计原则[9]。基于该原则,研究者们引入一系列助剂 (Ti[10-11]、W[12-13]、Nb[14-16]、Zr[17]和Sn[18-19]等) ,以改善纯CeO2催化剂的性能。其中,SnO2拥有大量的本征氧缺陷和较强的Lewis酸性[20-22],因此受到了广泛关注。CeO2-SnO2在250~450 ℃可实现大于60%的NOx转化率[18]。该催化剂体系兼具抗水抗硫性能[18]、抗钾中毒[23]和抗铅中毒[19]性能,具有良好应用前景。
研究者们通过助剂掺杂提升了CeO2-SnO2催化剂的催化活性。ZHANG等[24]通过溶剂热法制备得到了Ce-Sn-Ti三元氧化物催化剂,其在180~460 ℃实现了90%的NOx转化率。LIU等[25]发现Ce1W0.24Sn2Ox催化剂具有优异的NH3-SCR性能,W物种通过与Ce物种耦合形成了新的Ce-O-W活性位点,同时提高了催化剂在150~300 ℃下的NO氧化能力,抑制了高温下NH3的氧化。由于Nb2O5中的Nb—OH和Nb=O可作为Brønsted和Lewis酸性位点吸附更多的NH3物种[14,26-28],且有助于增加催化剂的氧空位[28-29],因此可作为活性组分或助剂提高催化剂的NH3-SCR活性。基于对CeO2-SnO2的研究和理解,本研究将Nb引入CeO2-SnO2催化剂开发新型CeSnNbOx金属氧化物催化剂,并结合多种表征手段阐明Nb对催化剂活性的促进作用,以期明确Nb掺杂对于活性提升的作用机制,为开发高效Ce基氧化物催化剂提供参考。
-
本研究以硝酸铈作为Ce源、以四氯化锡作为Sn源、以草酸铌作为Nb源、以氨水作为沉淀剂,采用共沉淀法制备了摩尔比为Ce∶Sn∶Nb = 1∶2∶a (a = 0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5和2.0) 的催化剂。制备过程如下:首先,将一定量的前驱体添加至去离子水中,经搅拌、溶解后,逐滴加入过量的氨水,在室温下搅拌12 h;随后,通过抽滤的方式实现固液分离,得到已洗涤至中性的固体沉淀物,后将其置于100 ℃烘箱内干燥12 h;最后,将干燥的沉淀前体物移至马弗炉中,以5 ℃∙min−1的升温速率线性升温至700 ℃,焙烧3 h,得到最终催化剂,命名为Ce1Sn2NbaOx。同时,通过相同方法制备了Ce1Sn2Ox作为参比样品,以对比考察Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的结构和催化性能。经压片、筛分得到40~60目催化剂,以用于NH3-SCR活性评价。
-
催化剂活性评价实验在多气路固定床反应器中进行,所用模拟气控制如下:0.05% (体积分数) NO、0.05% (体积分数) NH3、5% (体积分数) O2、5% (体积分数) H2O、N2为平衡气,测试温度为150~550 ℃,总气体流量为500 mL∙min−1。采用配有光程气体池的Antaris IGS (Thermo Fisher) 红外气体分析仪,对反应过程中尾气各组分 (NH3、NO、NO2和N2O) 浓度进行实时监测。实验得到的全部数据点均在反应达到稳定状态后的采集的数据经3次平均后得到。
NOx转化率 (X) 和N2选择性 (S) 计算公式见式 (1) 和 (2) 。
式中:
$\left[{\text{NO}}_{{x}}\right]\text{=}\left[\text{NO}\right]\text{+}\left[{\text{NO}}_{\text{2}}\right]$ ,${\left[{\text{NO}}_{{x}}\right]}_{\text{in}}$ 和${\left[{\text{NO}}_{{x}}\right]}_{\text{out}}$ 分别为进气口和出气口处NOx的体积分数。 -
1) N2吸附-脱附分析。使用自动物理吸附装置MicrotracBEL采集样品的N2吸附-脱附等温线。具体实验方法为:首先,对样品进行300 ℃真空脱气1 h,除去其表面的杂质;接着,在-196 ℃液氮温度下测定其N2吸附和脱附等温线。样品的比表面积为P/P0 = 0.05~0.30,以BET公式为依据,计算得到样品的比表面积;以BJH模型为依据,计算得到样品的孔径分布、总孔体积及平均孔径。
2) 粉末X射线衍射 (XRD) 。利用荷兰PANalytical X pert Pro衍射仪采集样品图谱。使用Cu Kα射线 (波长λ = 0.154 06 nm) ,管电流和电压分别为40 mA和40 kV,扫描范围为2θ = 5~90o,扫描步长为0.02o。
X射线光电子能谱 (XPS) :采用AXIS Supra (英国Kratos Analytical Inc.) 测定样品的X射线光电子能谱,以Al Kα (1486.6 eV) 作为X射线靶材,以C 1s结合能 (BE = 284.8 eV) 为基准对所测元素的结合能进行核电位移校正。
3) H2程序升温还原 (H2-TPR) 。本实验在Micromeritics AutoChem 2920化学吸附仪上进行。具体实验步骤如下:首先,在Ar气氛 (气体流量为30 mL∙min−1) 中,将U型石英反应器中的100 mg样品于400 ℃预处理0.5 h,后将其冷却至室温;随后,切换反应气氛为10% (体积分数) H2/Ar (气体流量为50 mL∙min−1) ;最后,待基线平稳后,以10 ℃∙min−1的升温速率线性升温至1 000 ℃,并使用热导检测器 (TCD) 对程序升温过程中的信号进行实时记录。
4) NH3程序升温脱附 (NH3-TPD) 。所用的装置与H2-TPR实验装置相同,具体实验步骤如下:首先,在Ar气氛 (气体流量为30 mL∙min−1) 中,将U型石英反应器中的200 mg样品于400 ℃预处理0.5 h,然后将其冷却至室温,以除去样品表面吸附的杂质;接着,将0.25% (体积分数) NH3/He (气体流量为30 mL∙min−1) 气流通入U型石英反应器中,在NH3吸附饱和之后,将反应气氛转换为Ar吹扫2 h,以去除样品表面吸附的NH3;最后,待基线平稳后,在Ar吹扫下,以10 ℃∙min−1的升温速率线性升温至650 ℃,并使用热导检测器 (TCD) 对程序升温过程中的信号进行实时记录。
5) 原位漫反射傅立叶变换红外光谱 (in situ DRIFTS) 。本实验在Thermo Fisher公司的配备有MCT/A检测器的Nicolet IS50上进行。将20% (体积分数) O2/N2气氛 (气体流量为300 mL∙min−1) 通入装有催化剂的原位反应池中,并于450 ℃预处理0.5 h,以去除催化剂表面的杂质;温度降至200 ℃并使用N2吹扫;待信号稳定后可采集背景谱图,并在后续的光谱中自动扣减该背景谱图。采集谱图的扫描次数为100次,分辨率为4 cm−1。在NH3或NOx吸附的in situ DRIFTS实验中:向装有催化剂的气体池中通入0.05% NH3或0.05% NO+5% O2 (百分数为体积分数,气体流量为300 mL∙min−1) 吸附1 h,然后使用N2吹扫催化剂表面0.5 h,并实时采集反应过程中的谱图。
-
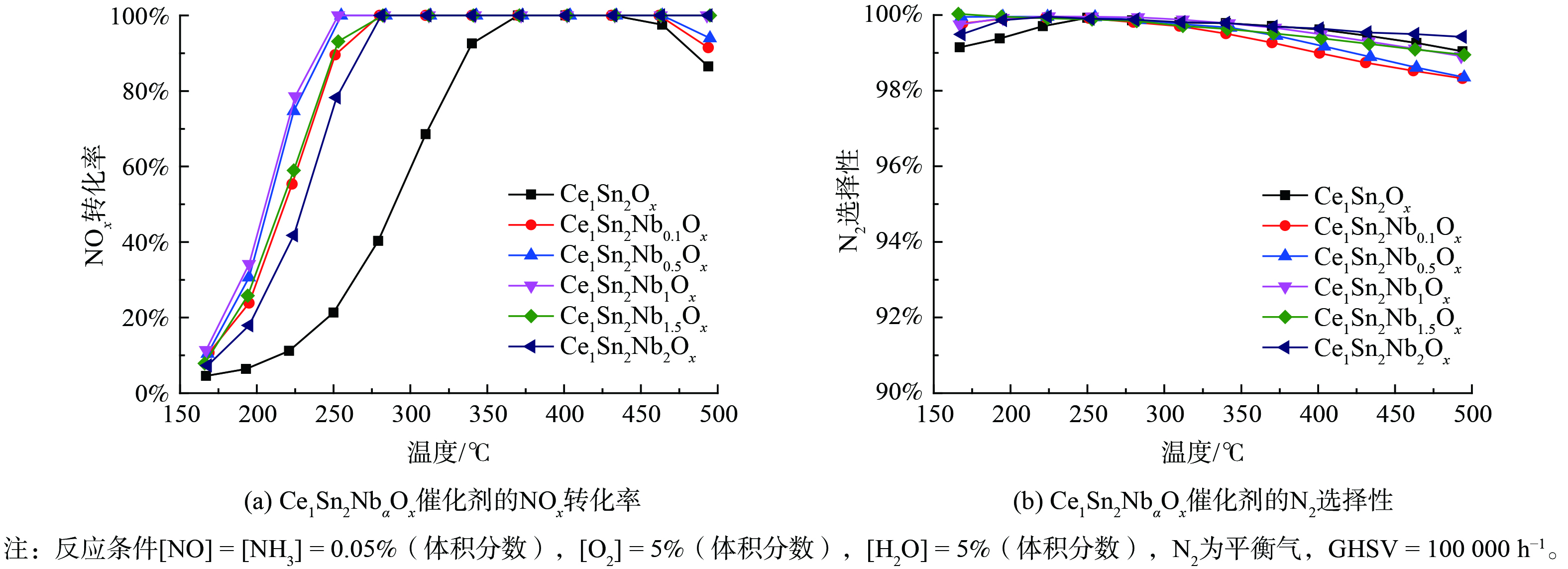
图1展示了Ce1Sn2Ox和不同Nb掺杂量的Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的NOx转化率和N2选择性。Ce1Sn2Ox的温度窗口较窄,掺杂Nb后,随着Nb/Ce摩尔比增加,催化剂的低温和高温活性均得到提升,在250~500 ℃达到接近100%的NOx转化率。然而,随着Nb/Ce摩尔比进一步增加至1.5和2.0时,在150~250 ℃内,催化剂的低温NOx转化率逐渐降低。因此,适量Nb掺杂能有效提高催化剂的NH3-SCR活性。此外,整个温度测试区间内的N2选择性均大于98%。因此,Ce1Sn2Nb1Ox为优选催化剂。
-
由氮气的吸附-脱附等温线计算得到Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的结构参数,如表1所示。Ce1Sn2Ox催化剂的比表面积为50.1 m2∙g−1,总孔体积0.14 cm3∙g−1。在掺杂Nb后,优选的Ce1Sn2Nb1Ox催化剂的比表面积和总孔体积最大,分别为56.9 m2∙g−1和0.27 cm3∙g−1。这表明最优Nb掺杂量有效改善了催化剂的比表面积和总孔体积,有利于反应物和中间体分子的吸附与分散[30-31]。
-
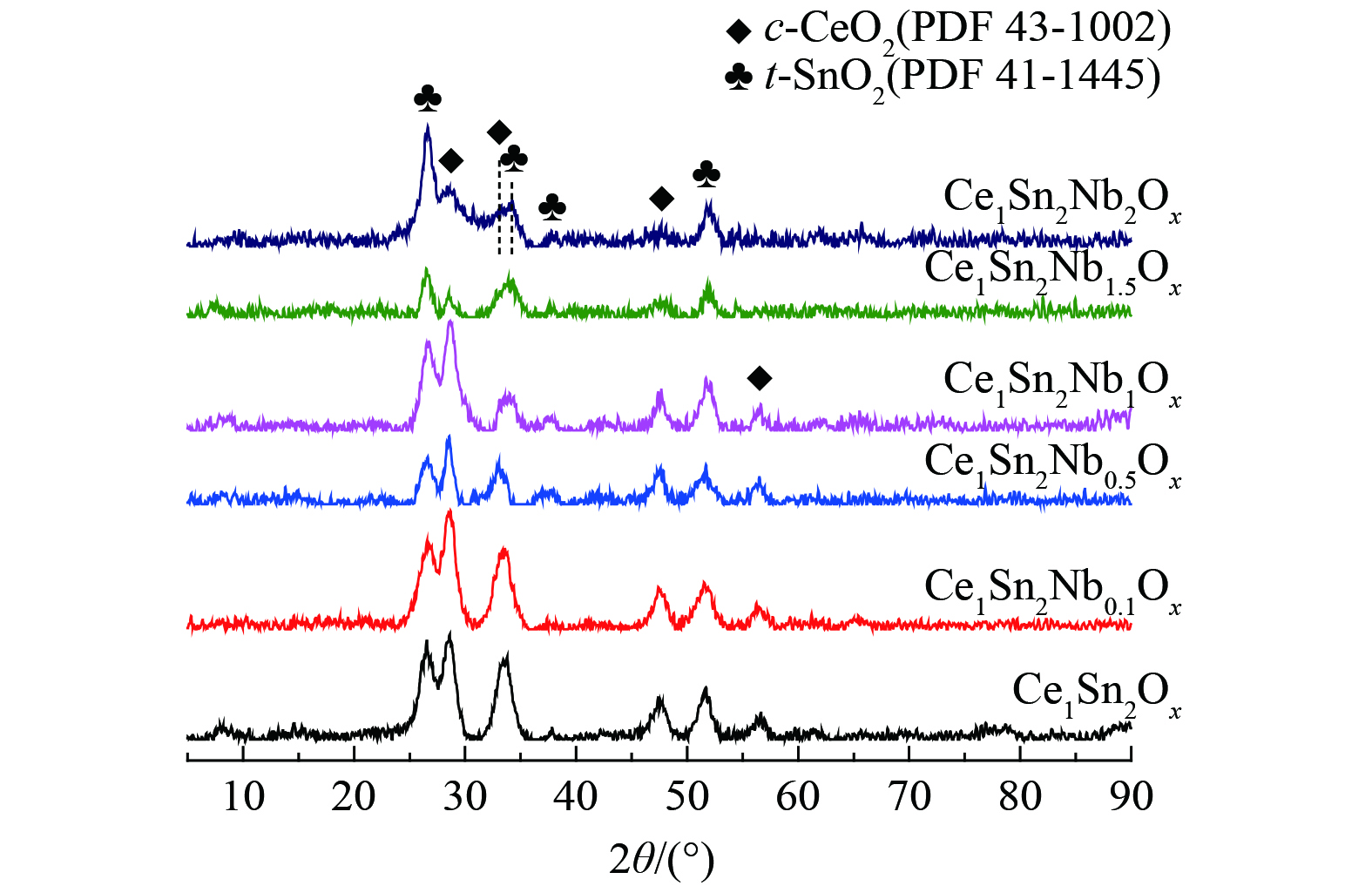
图2显示了Ce1Sn2Ox和不同Nb掺杂量的Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的XRD结果。Ce1Sn2Ox催化剂具有立方相CeO2 (c-CeO2,PDF 43-1002) 和四方相SnO2 (t-SnO2,PDF 41-1445) 晶相。在掺杂Nb后,未见任何含Nb的结晶相,这说明Nb物种以高度分散或无定形状态存在于Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂中。当Nb/Ce摩尔比为0.1~1时,c-CeO2的衍射峰强度大于t-SnO2,而当Nb/Ce摩尔比大于1时,则表明Nb掺杂量影响了催化剂晶相的结晶度。
-
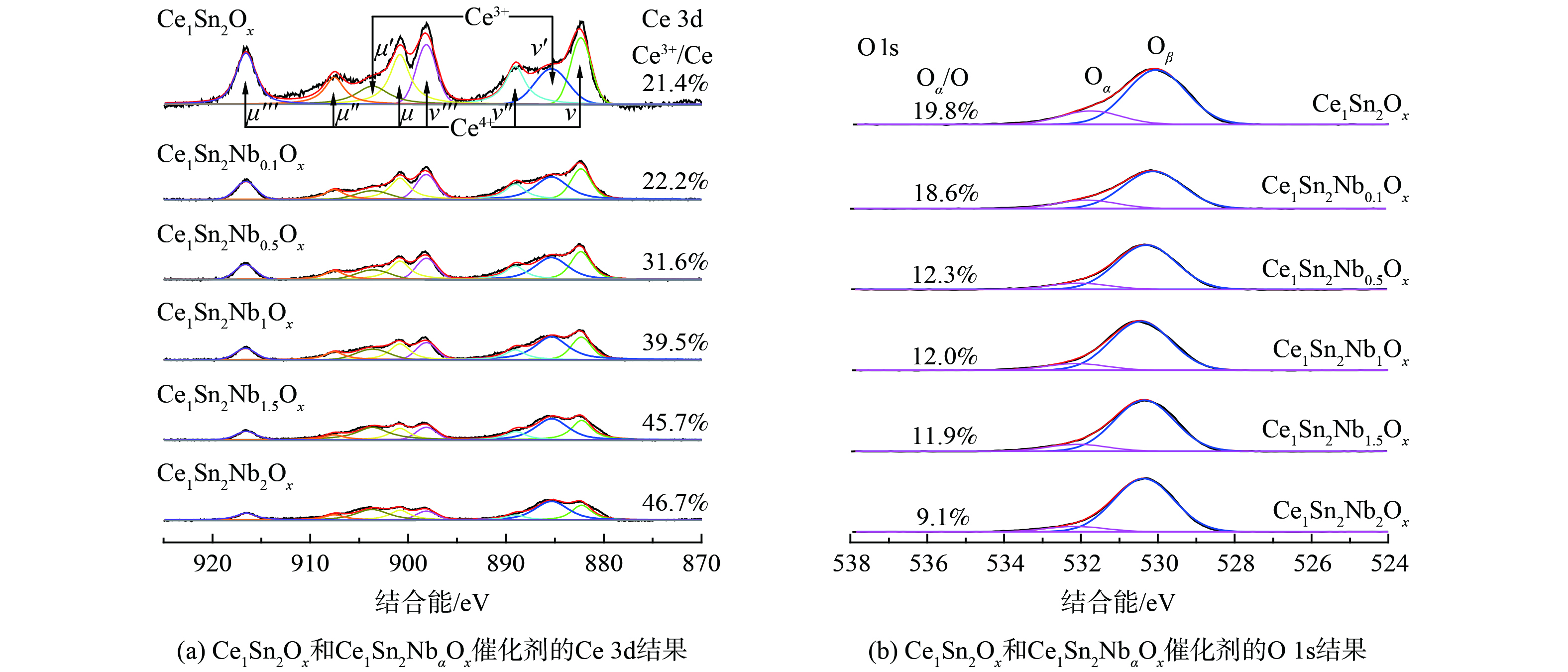
图3 (a) 表明Ce 3d的XPS谱图由8个高斯重叠峰组成,自结合能从低到高分别标记为ν、ν'、ν''、ν'''、μ、μ'、μ''和μ''',其中ν、ν''、ν'''、μ、μ''和μ'''归属于表面Ce4+,ν'和μ'归属于表面Ce3+[18,32]。在Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂表面,Ce3+和Ce4+同时存在,其中Ce4+占主导地位。为了对2种催化剂表面Ce物种中所占的摩尔比进行直观比较,通过高斯分峰拟合处理,计算得到Ce3+/Ce比例,具体见式 (3) 。
式中:S代表峰面积,计算结果标注在图3 (a) 中。Ce1Sn2Ox催化剂Ce3+/Ce比例为21.4%,随着Nb掺杂量的增加,Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的Ce3+/Ce比例也随之增加。
图3 (b) 中O 1s的XPS谱图由2个高斯重叠峰构成,其中具有更高结合能的峰 (531.7~532.1 eV) 归属为表面吸附氧物种 (O22-或O−,标记为Oα) ,结合能较低的峰 (530.0~530.4 eV) 归属为晶格氧物种 (O2−,标记为Oβ) [16,33]。为了直观地比较Oα在2种催化剂表面氧物种中的比例。本研究通过高斯分峰拟合处理,计算得到Oα/O比例,具体见式 (4) 。
式中:S(Oα)和S(Oβ)代表Oα和Oβ的峰面积,计算结果标注在图3 (b) 中。Ce1Sn2Ox催化剂Oα/O比例为19.8%,随着Nb掺杂量的增加,Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的Oα/O比例随之降低。
Ce基催化剂中的Ce3+主要来自本征氧空穴 (Ov) 的形成,因此Ce3+/Ce比例和Oα/O比例通常具有相同的变化趋势[12]。而本研究中,随着Nb掺杂量的增加,催化剂Ce3+/Ce比例增加,但Oα/O的比例却降低。因此,微晶或无定形的Ce3+-O-Nb5+结构可能是Ce3+的另一来源,为NH3-SCR反应提供了可能的Ce-O-Nb活性位点[14]。
-
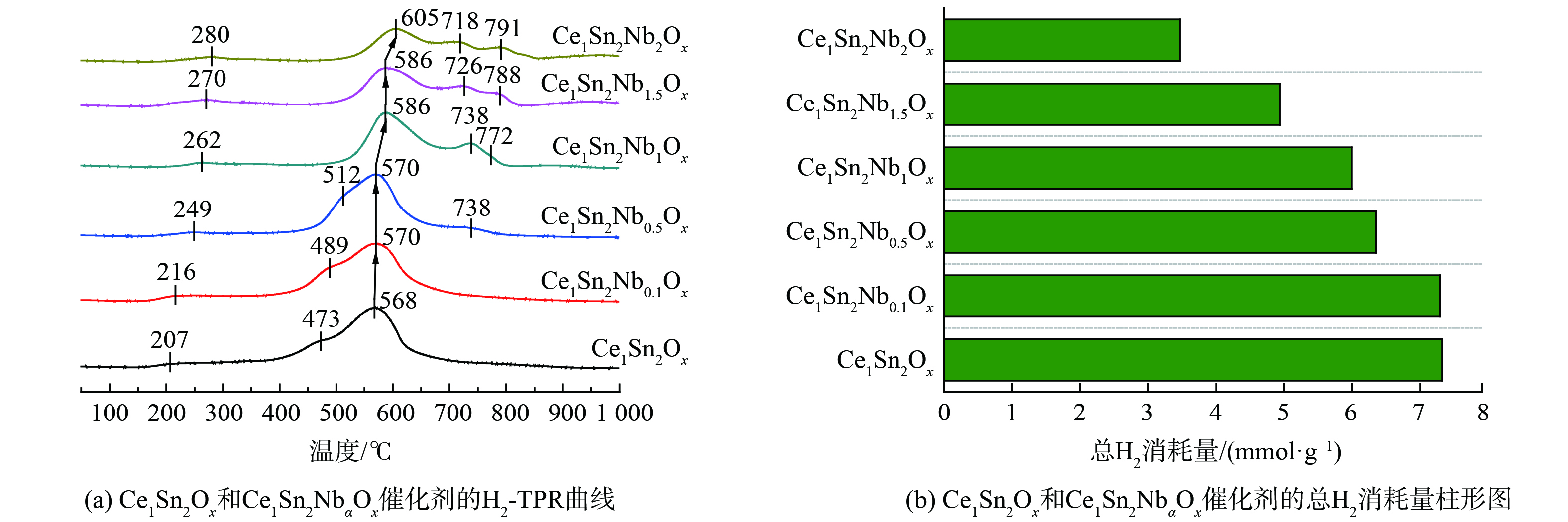
图4为水热老化前后Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的H2-TPR曲线,并通过积分H2消耗峰的峰面积定量不同催化剂的H2消耗量。催化剂的H2-TPR曲线在207~280 ℃和473~791 ℃附近出现H2消耗峰,分别归属为表面和体相氧物种的还原[34]。随着Nb掺杂量的增加,Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂表面和体相氧的还原峰均向高温方向偏移 (图4 (a) ) ,且总H2消耗量逐渐降低 (图4 (b) ) 。这说明Nb掺杂不仅削弱了Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂表面氧和体相氧的流动性,还减少了可还原氧物种的数量,与O 1s的XPS结果一致。由此说明,Nb对氧化还原性的影响并不是Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂活性提升的关键因素。
-
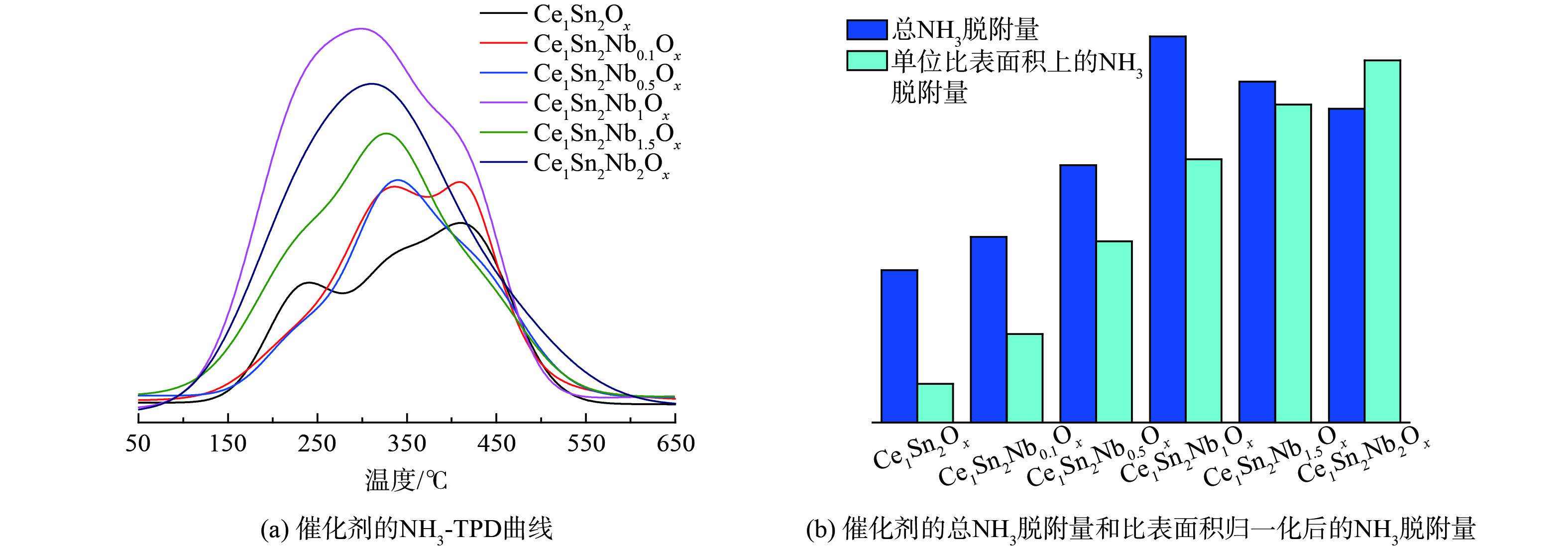
本研究通过NH3-TPD实验探究了Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的表面酸性,并通过积分NH3脱附峰的峰面积定量不同催化剂的NH3脱附量,结果如图5所示。与Ce1Sn2Ox催化剂相较,随着Nb/Ce摩尔比的增加,Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的NH3脱附量呈现先升高后减低的趋势。对NH3脱附量进行比表面积归一化处理后,单位比表面积上的NH3吸附量呈上升趋势。因此,当Nb/Ce摩尔比大于1时,催化剂总NH3脱附量的降低主要是由于比表面积的减小。对比Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的NH3-TPD结果可知,Nb掺杂使Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂表面形成了更丰富的酸性位点,改善了催化剂的表面酸性。具体的Lewis酸性位点和Brønsted酸性位点的变化将在后续的NH3吸附in situ DRIFTS结果说明。
-
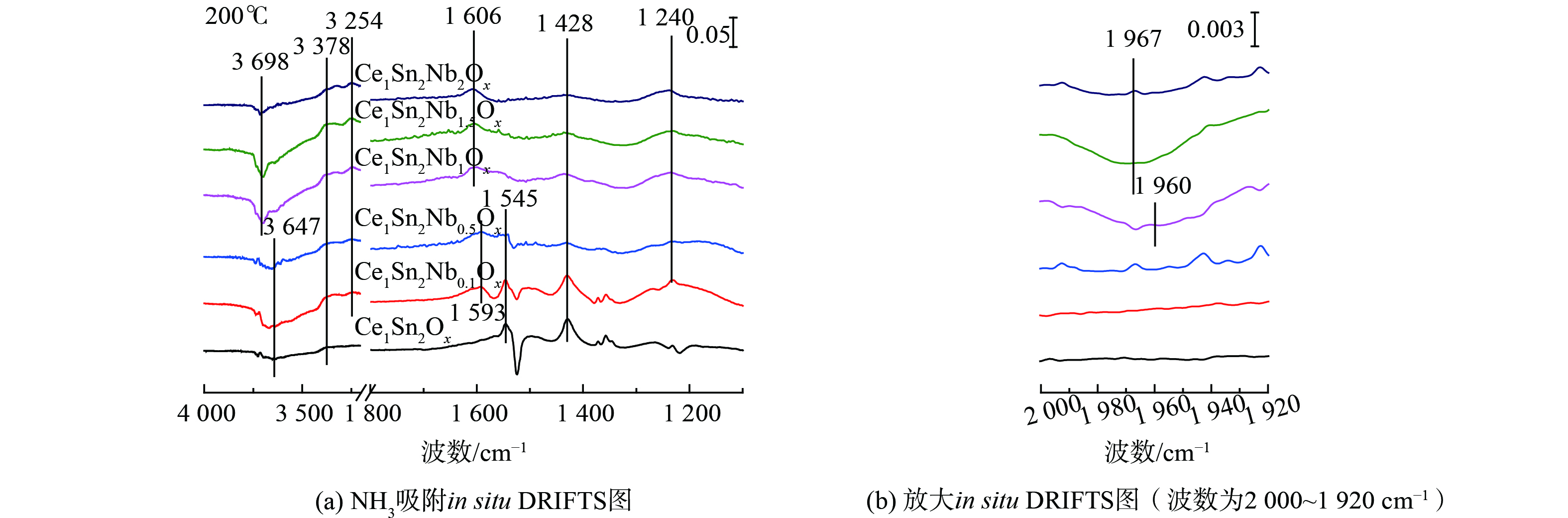
图6为Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂上NH3吸附的in situ DRIFTS结果和2 000~1 920 cm−1的放大图。2种类型的NH3物种吸附在催化剂表面,包括吸附在Lewis酸位上的配位NH3物种 (1 606、1 240 cm−1) [35-37]和Brønsted酸位上的NH4+物种 (1 593、1 428 cm−1) [38-39]。此外,1 967和1 960 cm−1处出现了Nb==O的消耗峰。这说明Nb==O同样可作为催化剂表面的NH3吸附位点[14],且适量Nb掺杂增强了Nb==O对表面NH3物种的吸附。同时观察到了位于3 698和3 647 cm−1处的羟基消耗峰[37]、位于3 378和3 254 cm−1位置处的N—H伸缩振动[40-42]和位于1 545 cm−1位置处的酰胺物种 (NH2) 剪切振动。与Ce1Sn2Ox相较,随着Nb/Ce摩尔比的增加,Brønsted酸位上NH4+物种的吸附逐渐受到抑制,而Lewis酸位上配位NH3物种的吸附逐渐增加。普遍认为,Lewis酸位上吸附的NH3物种较Brønsted酸位上吸附的NH4+物种稳定,因此,Nb掺杂增强了Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂表面酸性位点的强度和稳定性。
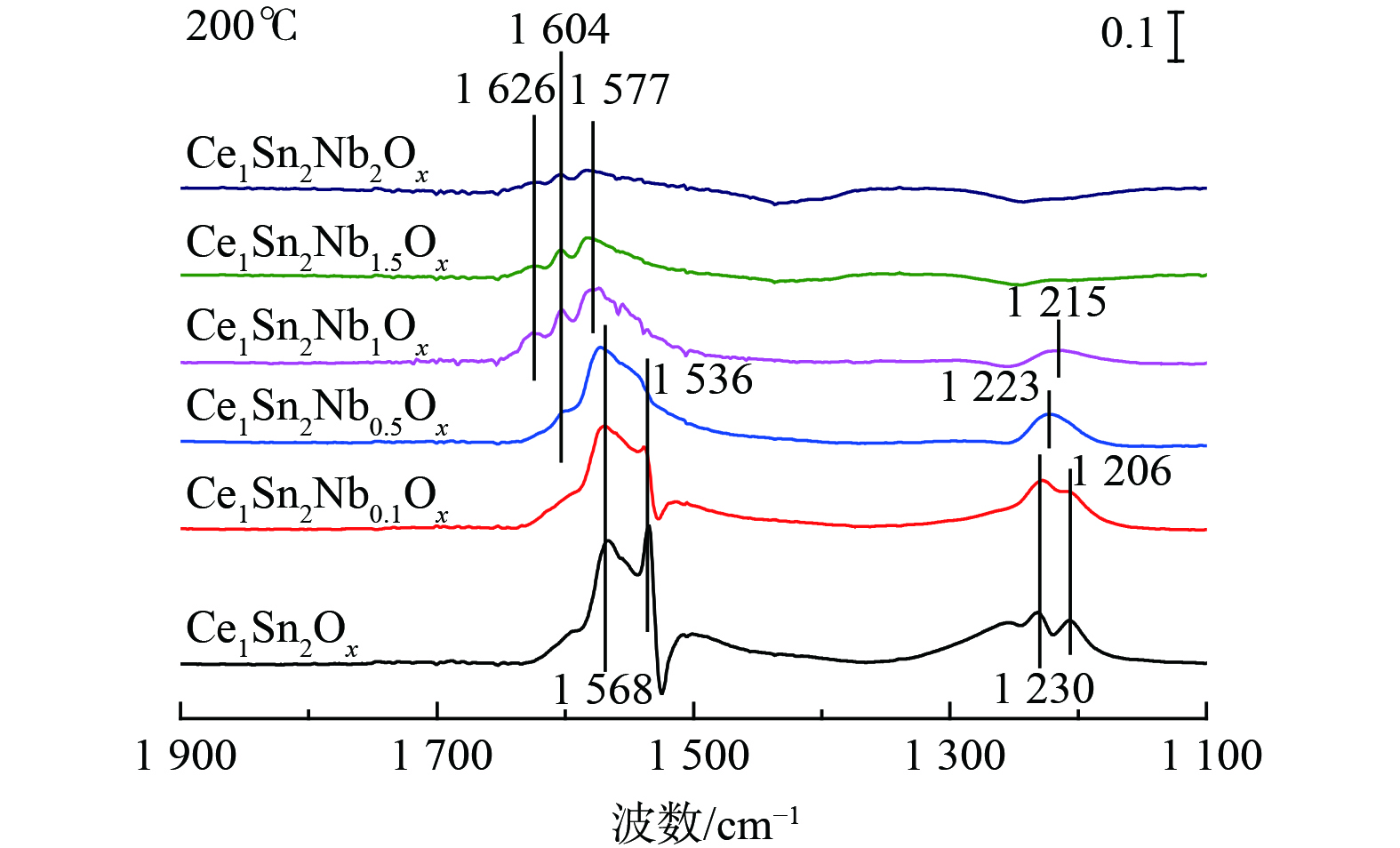
图7为NOx吸附在Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂上的in situ DRIFTS结果,其中1 626和1 604 cm−1位置处的峰可归属为吸附的桥式硝酸盐物种,1 577、1 568和1 206~1 230 cm−1处的红外峰可归属为吸附的双齿硝酸盐,1 536 cm−1处的红外峰可归属为单齿硝酸盐[18,29,43]。与Ce1Sn2Ox相较,Nb掺杂显著抑制了催化剂表面硝酸盐的吸附[33]。
-
1) 优选后的Ce1Sn2Nb1Ox催化剂在体积空速为100 000 h−1的测试条件下,在250~500 ℃内实现了接近100%的NOx转化率,且整个温度测试区间内的N2选择性均大于98%。2) Nb掺杂改善了Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的比表面积和总孔体积,更利于活性位点的暴露和分散;Nb物种在催化剂表面高度分散,可能与Ce物种耦合形成Ce-O-Nb活性位点。Nb掺杂改变了Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的表面吸附行为,使表面NH3物种更倾向于吸附在Lewis酸性位点上,同时抑制了催化剂表面硝酸盐的吸附。3) Nb掺杂减弱了Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的氧化还原性能,但却提升了催化剂表面酸性位点的数量、强度和稳定性。通过对Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂表面酸性位点和氧化还原位点进行合理调控,促进了反应物的吸附与活化,从而达到了高效的NOx净化效率。
Nb掺杂对CeO2-SnO2催化剂NH3-SCR活性的促进作用
Promotional effect of Nb doping on NH3-SCR activity over CeO2-SnO2 oxide catalyst
-
摘要: NH3选择性催化还原 (NH3-SCR) 是柴油车尾气NOx净化的主流技术。将Nb引入CeO2-SnO2得到了一种新型的CeSnNbOx金属氧化物催化剂,考察了Nb掺杂对催化剂结构、元素价态、活性位点、氧化还原性能、表面酸性和吸附性能的影响,并结合BET、XRD、XPS、H2-TPR、NH3-TPD和in situ DRIFTS等多种表征手段明确了Nb对该催化剂活性的促进作用。结果表明,Ce1Sn2Nb1Ox催化剂表现出最佳活性,在温度为250~500 ℃时,达到接近100%的NOx转化率。Nb掺杂改善了催化剂的比表面积和总孔体积,合理调控了催化剂表面酸性和氧化还原性能。此外,催化剂表面高度分散的Nb物种可能与Ce物种耦合形成新的Ce-O-Nb活性位点,有助于催化剂NH3-SCR性能的提升。本研究可为开发高效Ce基氧化物催化剂提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 柴油车尾气净化 /
- 氨选择性催化还原氮氧化物 /
- Ce基氧化物催化剂 /
- 铌物种
Abstract: NOx emissions from diesel vehicles can induce a series of environmental pollution problems, including acid rain, haze and photochemical smog. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 (NH3-SCR) is the dominant technology for NOx abatement from diesel vehicle exhaust. In this study, Nb was introduced to CeO2-SnO2 to obtain a novel CeSnNbOx metal oxide catalyst. The effects of Nb doping on the structure, element valence state, active site, redox performance, surface acidity, and surface adsorption performance of the catalysts were investigated. By combining various characterization methods including BET, XRD, XPS, H2-TPR, NH3-TPD, and in situ DRIFTS, the promoting effect of Nb on the activity of this catalyst was clarified. The results showed that the Ce1Sn2Nb1Ox catalyst exhibited the best activity, achieving nearly 100% NOx conversion in the temperature range of 250~500 ℃. Nb doping improved the specific surface area and total pore volume of the catalyst, and reasonably regulated the surface acidity and redox performance of the catalyst. In addition, the highly dispersed Nb species on the surface of the catalyst may couple with the Ce species to form a new Ce-O-Nb active site, which contributed to improve the NH3-SCR performance of the catalyst. This study can provide reference for the development of efficient Ce-based oxide catalysts. -

-
表 1 Ce1Sn2Ox和Ce1Sn2NbaOx催化剂的结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of Ce1Sn2Ox and Ce1Sn2NbaOx catalysts
样品 比表面积/(m2∙g-1) 平均孔径/nm 总孔体积/(cm3∙g-1) Ce1Sn2Ox 50.1 11.6 0.14 Ce1Sn2Nb0.1Ox 47.9 10.8 0.13 Ce1Sn2Nb0.5Ox 47.5 14.7 0.18 Ce1Sn2Nb1Ox 56.9 19.6 0.27 Ce1Sn2Nb1.5Ox 44.3 19.2 0.21 Ce1Sn2Nb2Ox 37.2 20.8 0.19 -
[1] DUNCAN B N, LAMSAL L N, THOMPSON A M, et al. A space-based, high-resolution view of notable changes in urban NOx pollution around the world (2005-2014)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2016, 121(2): 976-996. doi: 10.1002/2015JD024121 [2] BONINGARI T, SMIRNIOTIS P G. Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOx abatement[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2016, 13: 133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2016.09.004 [3] RICHTER A, BURROWS J P, NÜß H, et al. Increase in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over China observed from space[J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7055): 129-132. doi: 10.1038/nature04092 [4] LIU F D, SHAN W P, PAN D W, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 for heavy-duty diesel vehicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(9): 1438-1445. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60048-6 [5] BUSCA G, LIETTI L, RAMIS G, et al. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 1998, 18(1/2): 1-36. [6] 刘福东, 单文坡, 石晓燕, 等. 用于NH3选择性催化还原NOx的钒基催化剂[J]. 化学进展, 2012, 24(4): 445-455. [7] SHAN W P, LIU F D, YU Y B, et al. The use of ceria for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(8): 1251-1259. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60155-8 [8] LIU F D, YU Y B, HE H. Environmentally-benign catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx from diesel engines: structure-activity relationship and reaction mechanism aspects[J]. Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(62): 8445-8463. doi: 10.1039/C4CC01098A [9] SHAN W P, YU Y B, ZHANG Y, et al. Theory and practice of metal oxide catalyst design for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 376: 292-301. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.05.015 [10] XU W Q, YU Y B, ZHANG C B, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over a Ce/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2008, 9(6): 1453-1457. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2007.12.012 [11] SHAN W P, LIU F D, HE H, et al. The remarkable improvement of a Ce-Ti based catalyst for NOx abatement, prepared by a homogeneous precipitation method[J]. ChemCatChem, 2011, 3(8): 1286-1289. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201000409 [12] SHAN W P, LIU F D, HE H, et al. Novel cerium-tungsten mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(28): 8046-8048. doi: 10.1039/c1cc12168e [13] SHAN W P, GENG Y, CHEN X L, et al. A highly efficient CeWOx catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(4): 1195-1200. [14] QU R Y, GAO X, CEN K F, et al. Relationship between structure and performance of a novel cerium-niobium binary oxide catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 142-143: 290-297. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.035 [15] QU R Y, PENG Y, SUN X X, et al. Identification of the reaction pathway and reactive species for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over cerium-niobium oxide catalysts[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(7): 2136-2142. [16] LIAN Z H, SHAN W P, ZHANG Y, et al. Morphology-dependent catalytic performance of NbOx/CeO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(38): 12736-12741. [17] COLÓN G, VALDIVIESO F, PIJOLAT M, et al. Textural and phase stability of CexZr1-xO2 mixed oxides under high temperature oxidising conditions[J]. Catalysis Today, 1999, 50(2): 271-284. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00509-4 [18] LIU Z M, FENG X, ZHOU Z Z, et al. Ce-Sn binary oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 428: 526-533. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.175 [19] LI X L, LI Y H, DENG S S, et al. A Ce-Sn-Ox catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2013, 40: 47-50. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.05.024 [20] WANG Y L, JIANG X C, XIA Y N. A solution-phase, precursor route to polycrystalline SnO2 nanowires that can be used for gas sensing under ambient conditions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(52): 16176-16177. doi: 10.1021/ja037743f [21] FANG C, SHI L Y, LI H R, et al. Creating hierarchically macro-/mesoporous Sn/CeO2 for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(82): 78727-78736. doi: 10.1039/C6RA18339E [22] ABEE M W, COX D F. NH3 chemisorption on stoichiometric and oxygen-deficient SnO2 (110) surfaces[J]. Surface Science, 2002, 520(1/2): 65-77. [23] ZHAO W X, RONG J, LUO W, et al. Enhancing the K-poisoning resistance of CeO2-SnO2 catalyst by hydrothermal method for NH3-SCR reaction[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 579: 152176. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.152176 [24] ZHANG G D, HAN W L, ZHAO H J, et al. Solvothermal synthesis of well-designed ceria-tin-titanium catalysts with enhanced catalytic performance for wide temperature NH3-SCR reaction[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 226: 117-126. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.12.030 [25] LIU J J, HUO Y L, SHI X Y, et al. Insight into the remarkable enhancement of NH3-SCR performance of Ce-Sn oxide catalyst by tungsten modification[J]. Catalysis Today, 2023, 410: 36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2022.02.001 [26] MA Z R, WU X D, SI Z C, et al. Impacts of niobia loading on active sites and surface acidity in NbOx/CeO2-ZrO2 NH3-SCR catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 179: 380-394. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.038 [27] MA Z R, WENG D, WU X D, et al. A novel Nb-Ce/WOx-TiO2 catalyst with high NH3-SCR activity and stability[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2012, 27: 97-100. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2012.07.006 [28] MA S Y, GAO W Q, YANG Z D, et al. Superior Ce-Nb-Ti oxide catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2021, 94: 73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2020.11.001 [29] DING S P, LIU F D, SHI X Y, et al. Promotional effect of Nb additive on the activity and hydrothermal stability for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over CeZrOx catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 180: 766-774. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.06.055 [30] HAO Z F, JIAO Y L, SHI Q, et al. Improvement of NH3-SCR performance and SO2 resistance over Sn modified CeMoOx electrospun fibers at low temperature[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 327: 37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.07.037 [31] YAO X J, YU Q, JI Z Y, et al. A comparative study of different doped metal cations on the reduction, adsorption and activity of CuO/Ce0.67M0.33O2 (M=Zr4+, Sn4+, Ti4+) catalysts for NO+CO reaction[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 130-131: 293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.11.020 [32] LIU Z M, LIU Y X, CHEN B H, et al. Novel Fe-Ce-Ti catalyst with remarkable performance for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(17): 6688-6696. [33] YAN L J, LIU Y Y, ZHA K W, et al. Deep insight into the structure-activity relationship of Nb modified SnO2-CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2017, 7(2): 502-514. [34] LIU J J, HE G Z, SHAN W P, et al. Introducing tin to develop ternary metal oxides with excellent hydrothermal stability for NH3 selective catalytic reduction of NOx[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021, 291: 120125. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120125 [35] XU H D, WANG Y, CAO Y, et al. Catalytic performance of acidic zirconium-based composite oxides monolithic catalyst on selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 240: 62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.11.053 [36] JIANG B Q, LI Z G, LEE S C. Mechanism study of the promotional effect of O2 on low-temperature SCR reaction on Fe-Mn/TiO2 by DRIFT[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 225: 52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.03.022 [37] CHEN L, LI J H, GE M F. DRIFT study on cerium-tungsten/titiania catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(24): 9590-9596. [38] CHEN L, LI J H, GE M F, et al. Mechanism of selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over CeO2-WO3 catalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2011, 32(5): 836-841. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(10)60195-7 [39] LIU Z M, ZHANG S X, LI J H, et al. Promoting effect of MoO3 on the NOx reduction by NH3 over CeO2/TiO2 catalyst studied with in situ DRIFTS[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 144: 90-95. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.06.036 [40] SHAN W P, LIU F D, HE H, et al. A superior Ce-W-Ti mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 115-116: 100-106. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.12.019 [41] WU Z B, JIANG B Q, LIU Y, et al. DRIFT study of manganese/titania-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(16): 5812-5817. [42] LIU F D, HE H, DING Y, et al. Effect of manganese substitution on the structure and activity of iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2009, 93(1/2): 194-204. [43] LIU F D, SHAN W P, LIAN Z H, et al. The smart surface modification of Fe2O3 by WOx for significantly promoting the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 230: 165-176. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.02.052 -



 下载:
下载: