-
垃圾填埋场填埋作业及开采治理过程中会释放大量恶臭气体[1]。硫化氢和氨气为其主要组分,常采用生物脱臭技术对其进行处理[2]。生物脱臭法即利用填料上附着微生物的代谢作用去除臭气中污染物分子[3],主要有生物过滤和生物滴滤两种工艺形式,二者均操作便捷、运维费用低[4]。常用填料一般分为两类。一类是纤维物质,如泥炭土、树皮、干草等,多用于生物滤池技术,从而形成一种有利于透气的疏松结构,为微生物提供适当的生存环境,然而此类填料在长期运行后会产生透气性变差、填料堵塞、在大风量情况下通风阻力较强等问题[5];第二类为金属、陶瓷、塑料类填料,如陶粒、多孔空心球、鲍尔环等,多用于生物滴滤池技术,可承受较大污染负荷、不用更换滤料,但该类填料自身无法提供营养物质,需不断喷洒营养液提升微生物对臭气的处理效果[6]。腐殖土由存量垃圾筛分后得到,具有有机质质量分数高、比表面积大、生物量高的特点,已在填埋场覆盖材料与水处理填料等资源化应用方面表现优异[7-9],但运用于恶臭气体处理研究较少,多以与其他疏松生物土壤或蛭石混合的运用方式为主[10]。此外, 腐殖土作为填埋场覆盖土时除吸附作用外,对H2S、CH4等污染物也具有较高的生物降解能力[11-12]。但在实际运用中,由于腐殖土中存在大量粒径较小的细颗粒,作为填料时在大风量情况下,气体通过细颗粒的能量损失较大、通风阻力较高,会使得设备能耗增加。
本研究拟构建多级串联腐殖土固定床,采用存量生活垃圾筛下腐殖土作为固定床生物滤池的填料,针对小气量、高浓度的氨气与硫化氢气体进行处理,研究工艺处理效能及去除机理,以期为多级串联腐殖土固定床生物脱臭技术发展提供参考。
-
腐殖土来源于安徽省亳州市利辛县生活垃圾开挖分选后得到的20 mm筛下腐殖土,其pH为7.88,EC为1.53 mS·cm−3,AT4为12.13 mg·g−1,TOC为56.7 g·kg−1;臭气由南京市天井洼填埋场渗滤液处理站生化池上方逸散的气体混入氨气与硫化氢标准气体进行配制;正常情况下填埋场氨气与硫化氢的质量浓度分别为1~6 mg·m−3与0.1~0.5 mg·m−3,为验证腐殖土固定床对高浓度臭气的去除效果,将处理对象的质量浓度进行扩大,设置氨气质量浓度为1~12 mg·m−3,硫化氢质量浓度为0.2~2 mg·m−3;渗滤液为填埋场自身产生的老龄渗滤液,呈深褐色,其pH为7~8,COD为793.75~1 485.46 mg·L−1,[NH4+-N]为592.84~923.98 mg·L−1,TN为660.48~956.73 mg·L−1。
-
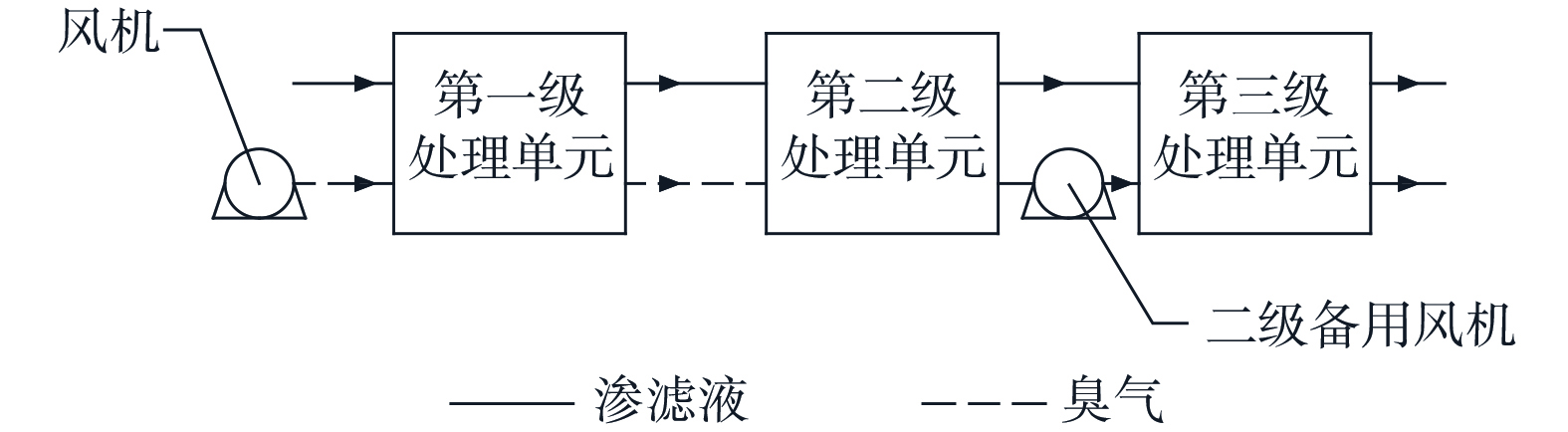
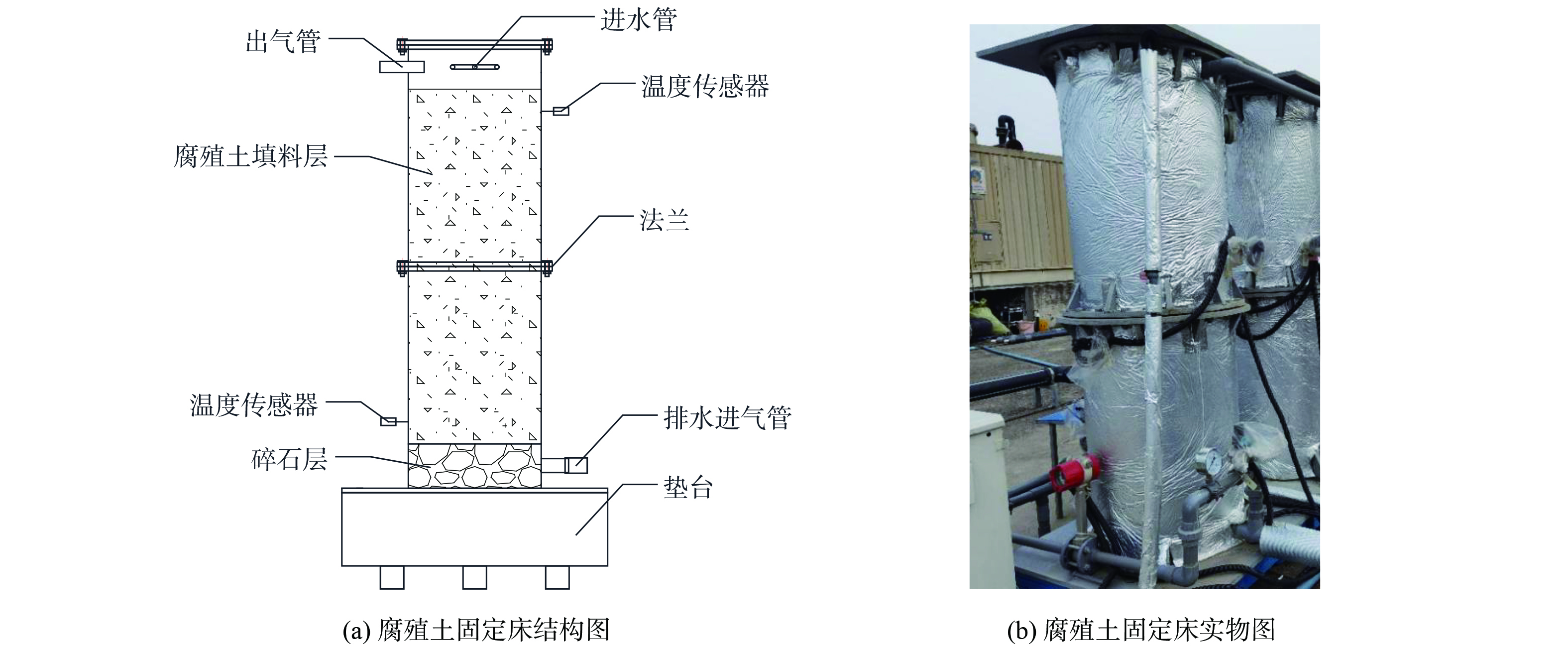
实验为中试规模,装置安装于江苏省南京市天井洼有机废弃物处理场生化池天台排气口附近,主体设为三级腐殖土固定床。恶臭气体来源于生化池天台排气口,为调节气体浓度将氨气与硫化氢标准气体进行调配,由风机进行收集与运送后经三级串联腐殖土固定床处理,净化后排空。承担臭气处理的部分主要为三级串联腐殖土固定床。三级固定床大小、结构相同,每级总高2 m、直径600 mm,其中填料层高1.50 m,体积为0.441 m3,为存量垃圾开挖后分选得到的20 mm筛下腐殖土,填料层顶端与底端设置温度传感器,便于实时监测填料层的温度变化。固定床底部铺设有碎石层,高0.20 m,用于排水与均匀布气。固定床上部设有进水管与出气管,进水管与天台下方SBR反应器出水管及水泵相联通,渗滤液进入固定床后由de20的PVC穿孔管进行布水;出气管采用de50的PVC管,联通下一级腐殖土固定床进气管。臭气进气与渗滤液出水共用一个管道,采用de63的PVC管,铺设于碎石层底部,臭气从下部进入与出水逆流接触。腐殖土固定床结构与实物如图1所示。
以单个腐殖土固定床及其配套装置为一个处理单元,如图2所示。处理单元包括:腐殖土固定床、缺氧SBR反应器、压力过滤器等实验装置,为避免气体从出水口泄露,出水口与水封管相连通。固定床用于气液协同处理,与缺氧SBR反应器有高差,缺氧SBR反应器用于渗滤液的处理,压力过滤器用于SBR反应器的泥水分离、防止SBR内污泥进入固定床。
中试实验装置为3个单元串联运行的系统,如图3所示。主要流程为恶臭气体主要由三级串联腐殖土固定床进行处理。从第一级固定床下方进入,自下而上的经过填料层,从固定床上方出风口排出,并进入下方进入第二级固定床,并依照该流程通过第二级、第三级固定床后排空;在此过程中,渗滤液经第一级缺氧SBR反应器处理后泵入第一级腐殖土固定床上方进水口进行布水,凭借重力自流经过填料进入第二级缺氧SBR反应器,并依照该流程依次通过第二级腐殖土固定床、第三级腐殖土固定床,得到净化。
-
1) 实验与指标分析方法。中试实验采用半连续通风、间歇进水的方式。半连续通风指固定床进水期间不通风,确保渗滤液能够正常进入填料,进水完毕后立刻开启风机通入臭气,其中氨气与硫化氢标准气体通入稳压罐稳压后恒速释放;不通风期间关闭稳压罐与风机,停止收集臭气;间歇进水指渗滤液的进水周期为24 h,每次进水时间为1.5~6 min,此外固定床进水后自流进入下一级缺氧SBR反应器。实验主体为正交实验,根据实验设计条件选取气体表面负荷、水力负荷、污染物负荷为影响因素;考虑到实际工程运用,压力损失 (与气体表面负荷相关) 对腐殖土固定床能耗影响较大,也需评估固定床协同处理的渗滤液总量以及适用的污染物条件,故选取三者为影响因素。腐殖土固定床除进水时间外连续通入臭气,并每隔1 h对进气与各固定床出口臭气中的氨气、硫化氢浓度进行检测,缺氧SBR进水时间为0~2 h,出水时间为0~6 min,出水前1 h进入沉淀阶段,其余时间为反应时间,每隔24 h通过取样口对进出水进行检测,测定COD、[NH4+-N]和TN。此外,根据实验结果,分别以氨气与硫化氢的去除率为指标,选取气体表面负荷、水力负荷、污染物负荷为影响因素,每个因素各选取3个水平进行相关性分析,优化实验条件。
氨气、硫化氢体积分数采用深圳市杰恩凯电子科技有限公司JEK500XT-OU-KJ2型号恶臭在线监测仪进行监测;COD采用重铬酸钾快速消解法(HJ 828-2017),[NH4+-N]的测定参照国标纳氏试剂分光光度法(HJ 535-2009)。
2) 去除机理数学模型推导方法。去除机理方面主要针对各级固定床的传质过程进行研究,分析影响氨气传质的原因。多级串联腐殖土固定床对氨气的去除主要分为5个步骤[13]:氨气分子从气相主体扩散穿过气膜到达相界面;氨气分子穿过相界面到达液膜;氨气分子扩散穿过液膜到达液相主体;液相主体中的氨气分子水解为铵根离子;液相中的铵根离子部分被生物降解。由于本实验中渗滤液提供的氨氮总量远大于氨气总量,此外渗滤液氨氮去除率大于90%,即液相中铵根离子通过微生物硝化作用降解的量远高于气相中氨气组分通过双膜传质进入液相的量,故将氨气转化为铵根离子视为氨气组分的去除。根据双膜理论得到气液传质速率的方程为式 (1) 。
在氨气向渗滤液传质过程中,渗滤液可看成含有氨氮等物质的水溶液。由于氨气属于易溶气体,传质阻力主要源于气膜传质过程,因此其传质过程属于气膜控制。在稳态下,总传质系数近似等于气相传质系数[14],见式 (2) 。
式中:
$ {N}_{\mathrm{A}} $ 为传质通量,mol·(m2·h)−1;$ {p}^{*} $ 为气相主体中的氨气的分压,Pa;$ {p}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 为与液相主体浓度$ {c}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 呈平衡状态时的氨气的气相分压,Pa;$ {K}_{\mathrm{g}} $ 为总传质系数,mol·(m2·h·Pa)−1;$ {k}_{\mathrm{g}} $ 为气相传质系数,mol·(m2·h·Pa)−1。遵守气体实验定律,氨气由标准气体配制。气相主体中的氨气分压可由理想气体状态方程 (式 (3) ) 求得。
式中:
$ {p}^{*} $ 为气相主体中氨气的分压,Pa;$ V $ 为气体体积,m3;$ T $ 为温度,K;$ n $ 为氨气的物质的量,mol;$ R $ 为摩尔气体常数,8.314 472 J·(mol·K)−1;$ Q $ 为气体流量,m3·h−1;$ m $ 为单位时间内氨气的物质的量,mol·h−1;$ {c}^{*} $ 为气相主体中氨气浓度,mol·m−3。腐殖土固定床运行过程中,配制含氨气的试验气体由底部进气顶部出气。实验气体氨气浓度随固定床填料高度增加而降低,即填料底部浓度为固定床进气浓度、填料顶部浓度为固定床出气浓度,假设氨气浓度随固定床高度的变化呈线性关系,见式 (4) 。
当
$ h=0 $ 时,$ {c}_{\mathrm{g}}={c}_{0} $ ,即填料底部浓度为固定床进气浓度;当$ h={h}_{0} $ 时,$ {c}_{\mathrm{g}}={c}_{1} $ ,即填料顶部浓度为固定床出气浓度。代入后计算得到式 (5) 。由于固定床各高度上氨气的浓度不同,将固定床视为整体,根据单位时间固定床的总体氨气负荷,可得到固定床内平均氨气浓度,即为气相主体中等效氨气浓度
$ {c}^{*} $ ,设气相主体中等效氨气浓度$ {c}^{*} $ 对应的高度为$ {h}_{1} $ ,得到式 (6) 。式中:
$ {c}^{*} $ 为气相主体中氨气浓度,mol·m−3;$ {c}_{\mathrm{g}} $ 为固定床各高度氨气浓度,mol·m−3;$ h $ 为固定床填料某位置的对应高度,m;$ {h}_{0} $ 为固定床填料总高度,m;$ {h}_{1} $ 为气相主体中等效氨气浓度$ {c}^{*} $ 对应的高度,m;$ {c}_{0} $ 为固定床进气浓度,mol·m−3;$ {c}_{1} $ 为固定床出气浓度,mol·m−3;$ \alpha 、b $ 为方程式系数。由亨利定律可得,在一定温度和平衡状态下,气体在液体里的溶解度 (用摩尔分数表示) 和该气体的平衡分压成正比,由于受实验装置与实验条件的影响,3台固定床的亨利常数不同[15],计算式见式 (7) 。
式中:
$ {p}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 为与液相主体浓度$ {c}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 呈平衡状态时的氨气的气相分压,Pa;$ {c}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 为液相主体氨氮摩尔浓度,mol·m−3;$ H $ 为亨利常数,mol·(m3·Pa)−1。在腐殖土固定床中,由于渗滤液是顶部进水、底部出水,导致氨氮浓度在固定床的高度上形成梯度,随高度降低而下降;填料顶部浓度即为固定床进水氨氮浓度,假设渗滤液中氨氮浓度随固定床高度的变化呈线性关系,如式 (8) 所示。
当
$ h=0 $ 时,$ {c}_{l}={c}_{\beta } $ ,即填料底部浓度为固定床出水氨氮浓度;当$ h={h}_{0} $ 时,$ {c}_{l}={c}_{\alpha } $ ,即填料顶部浓度为固定床进水氨氮浓度。代入后得式 (9) 。由于固定床各高度上渗滤液氨氮的浓度不同,将固定床视为整体,根据单位时间固定床的进出口渗滤液中的氨氮浓度,可得到固定床内渗滤液的平均氨氮浓度,即为液相主体中等效氨氮摩尔浓度
$ {c}_{\mathrm{a}} $ ,设液相主体等效氨氮摩尔浓度$ {c}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 对应的高度为$ {h}_{2} $ ,则得到式 (10) 。式中:
$ {c}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 为液相主体氨氮摩尔浓度,mol·m−3;$ {c}_{l} $ 为固定床各高度的渗滤液氨氮的浓度,mol·m−3;$ h $ 为固定床填料某位置的对应高度,m;$ {h}_{0} $ 为固定床填料总高度,m;$ {h}_{2} $ 为液相主体等效氨氮摩尔浓度$ {c}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 对应的高度,m;$ {c}_{\alpha } $ 为固定床进水氨氮浓度,mol·m−3;$ {c}_{\beta } $ 为固定床出水氨氮浓度,mol·m−3;$ c、d $ 为方程式系数。在多级串联腐殖土固定床中,氨气吸收速率计算公式为式 (11) 。
式中:
$ {m}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 为氨气吸收速率,mol·h−1;$ {c}_{1} $ 为固定床出气氨气浓度,mol·m−3;$ {c}_{0} $ 为固定床进气氨气浓度,mol·m−3;$ Q $ 为气体流量,m3·h−1。氨气气液传质过程中,传质通量指单位时间通过单位有效传质面积传递的物质的量,根据定义得到式 (12) 。
式中:
$ {N}_{\mathrm{A}} $ 为氨气传质通量,mol·(m2·h)−1;$ {m}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 为氨气吸收速率,mol·h−1;$ A $ 为有效传质面积,m2。此外,由于各固定床工况不同,有效传质面积也不相同。将上述方程式进行联立,即可得到氨气出口浓度与氨气进口浓度、进出口渗滤液中氨氮浓度的关系如式 (13) 所示。
即变形得到式 (14) 。
通过计算各级固定床氨气出口浓度与氨气进口浓度、进出口渗滤液中氨氮浓度的关系对传质过程进行分析,确定多级串联腐殖土固定床对氨气的去除机理,推测影响固定床中氨气传质的因素。
-
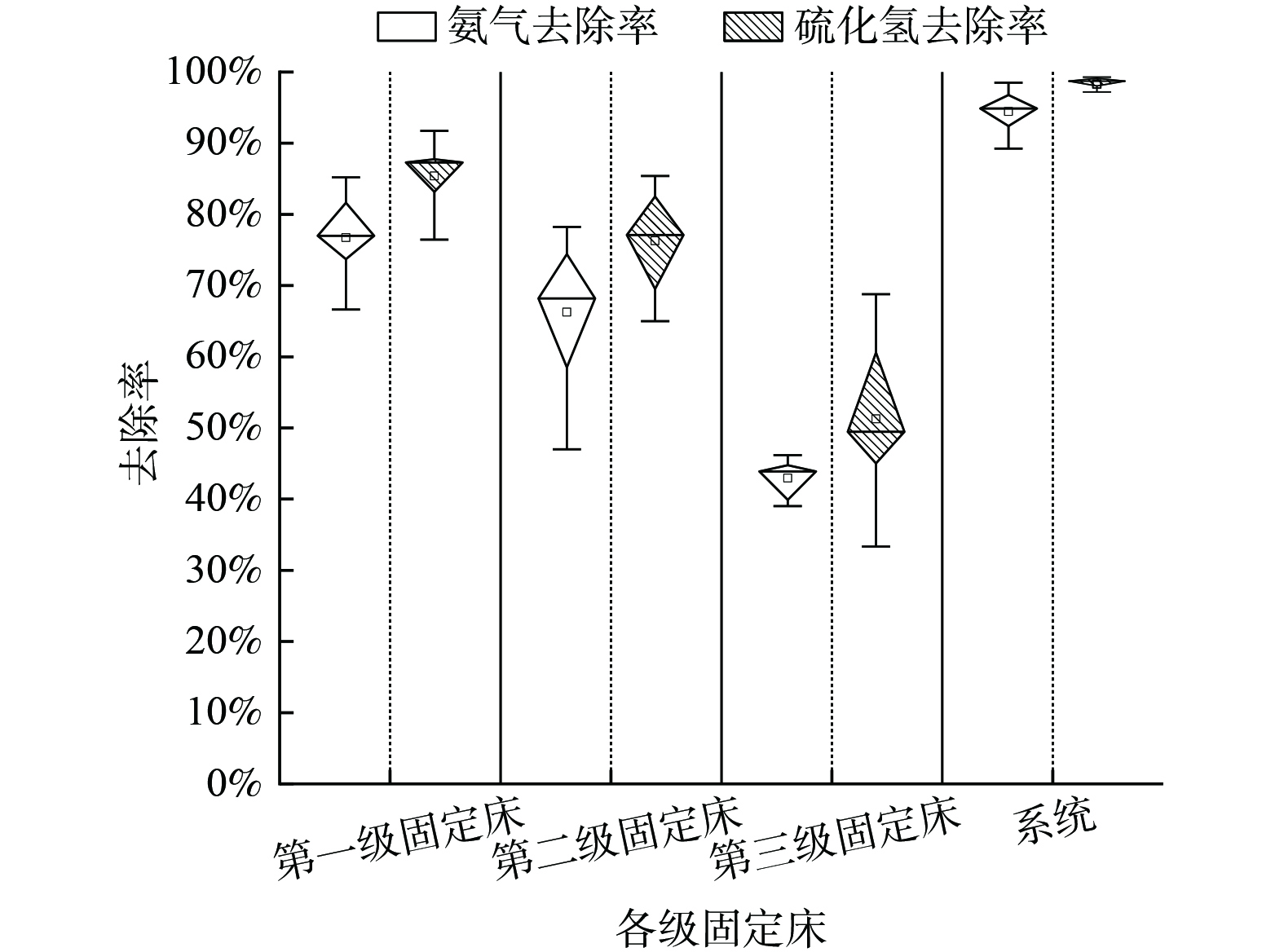
图4为各级固定床对氨气与硫化氢的处理效能。系统对氨气与硫化氢具有较好的处理效能,经三级串联腐殖土固定床处理后,氨气与硫化氢的平均去除率可达95%与98%。三级固定床对氨气与硫化氢的去除率逐级递减:第一级固定床氨气平均去除率为77%,而第二级与第三级固定床氨气平均去除率分别下降至68%与44%;第一级固定床硫化氢平均去除率为87%,而第二级与第三级固定床氨气平均去除率分别下降至77%与48%。这表明第一级固定床承担了主要的氨气、硫化氢处理效能;推测是由于实验处理的氨气与硫化氢具有小气量高浓度特点,气体通过固定床时,由于气量较小,在固定床中停留时间较长、与固定床接触充分,此外腐殖土具有较大的比表面积,可吸附与处理高浓度的氨气与硫化氢,因此氨气与硫化氢大部分在第一级固定床中得到去除,使得进入第二级、第三级固定床中的氨气、硫化氢浓度降低、气液传质效率下降。各级固定床中,硫化氢的去除率均高于氨气的去除率,这是由于固定床渗滤液中氨氮浓度较高、影响氨气的传质,同时也说明腐殖土固定床对硫化氢有更好的处理效果。
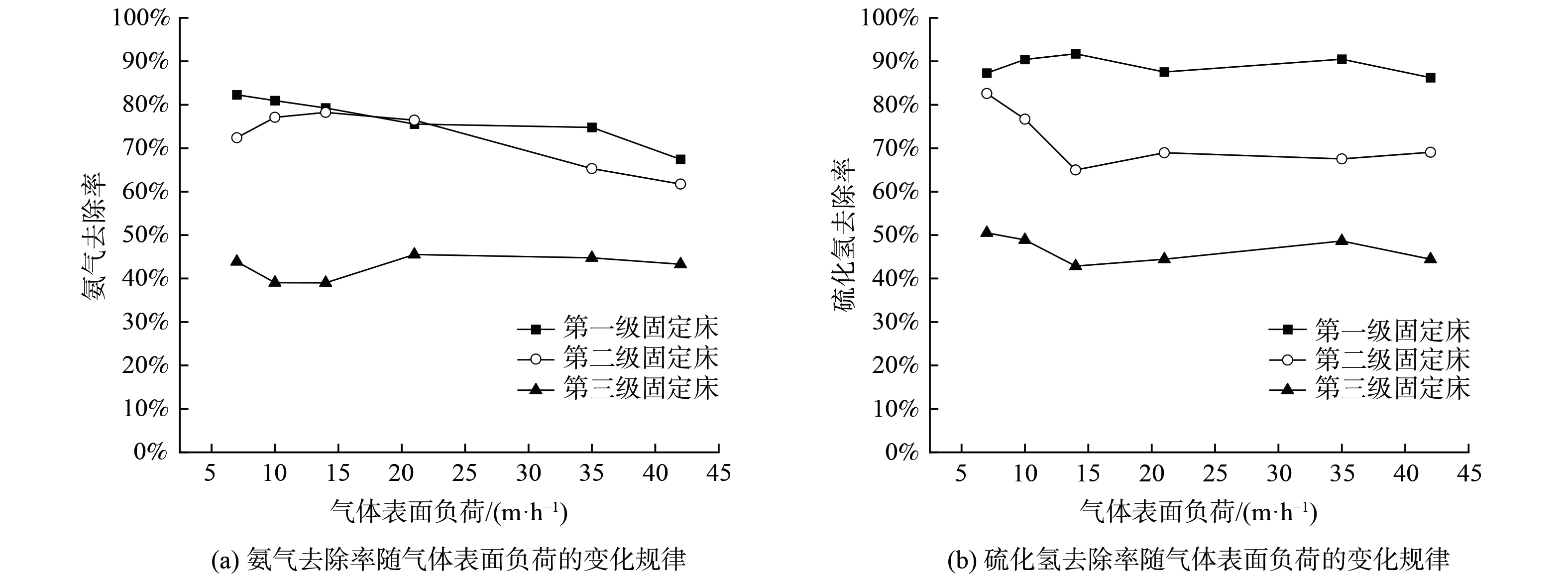
图5为气体表面负荷对各级固定床处理效能的影响。第一级固定床氨气去除率随着气体表面负荷的升高呈下降趋势,由83.30%降至62.43%,其原因是由于在气体表面负荷较高的情况下,氨气分子在固定床内部停留时间较短,从气相与液相之间的传质时间不充分,故溶解量较少、去除率降低。第二级固定床氨气去除率随着气体表面负荷的升高呈先上升后下降趋势,推测原因为第一级固定床气去除率随着气体表面负荷的升高而下降,进入第二级固定床的氨气负荷增加,使得第二级固定床氨气分子的气液传质量增加,故去除率会短暂上升。当气体表面负荷上升到14 m·h−1 时,停留时间对去除率的影响强于氨气负荷对去除率的影响,故氨气去除率下降。第三级固定床氨气去除率随着气体表面负荷的升高呈下降-升高-下降趋势。这是由于在较小的表面负荷的情况下第三级固定床氨气去除率受氨气负荷的影响,即去除率与氨气负荷变化趋势相同,在较高的表面负荷下第三级固定床氨气去除率受气体表面负荷的影响,即气体表面负荷越大、去除率越低。而气体表面负荷对各级固定床硫化氢去除率的影响呈波动趋势,处理效能的影响不明显。
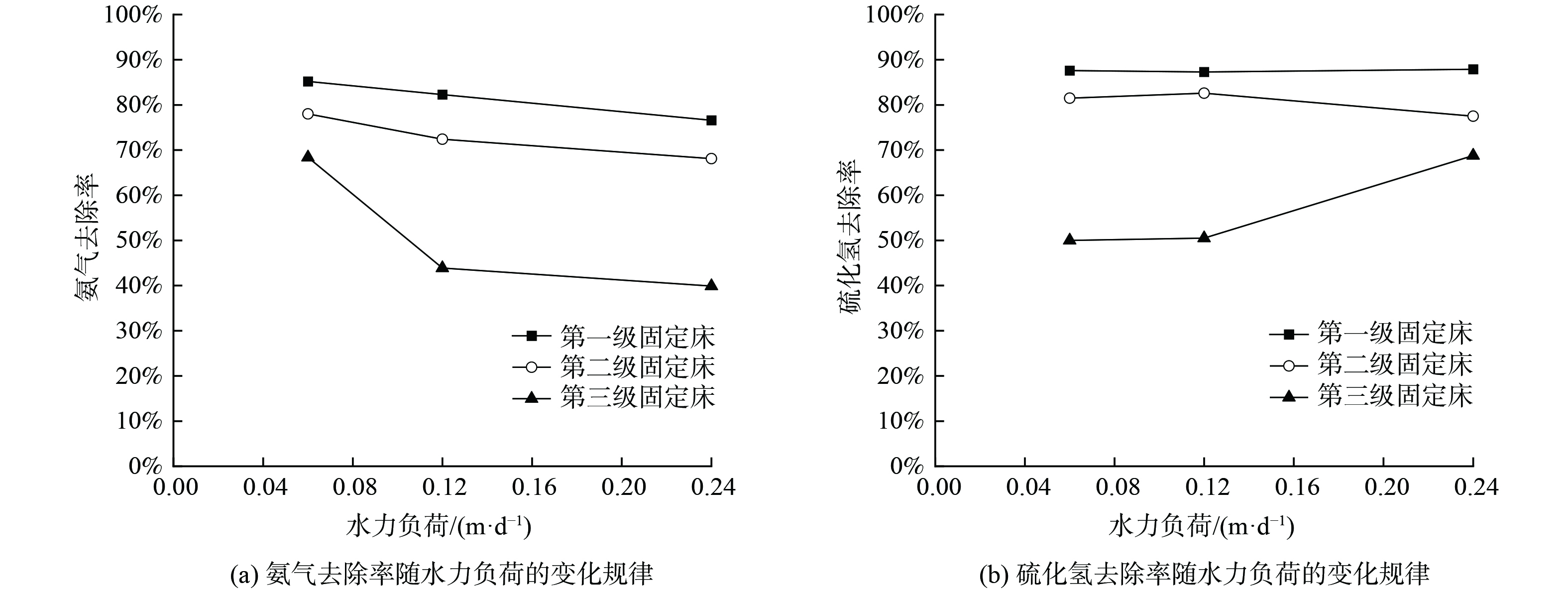
图6为水力负荷对各级固定床处理效能的影响。三级级固定床氨气去除率随着水力负荷的升高呈下降趋势,推测是由于固定床需同时处理渗滤液中的氨氮与臭气中的氨气,在水力负荷较高的情况下,氨氮总量较高,微生物对氨氮的处理效能不足,故氨气的处理效率下降。第三级固定床氨气去除率随水力负荷的变化较为明显,这说明氨气负荷越低,去除率受水力负荷影响越大。硫化氢去除率随着水力负荷的升高变化不明显,推测是由于渗滤液中硫元素质量浓度不高,此外第一级固定床对硫化氢就有较好的去除效果 (87%) ,后两级固定床处理效能中硫化氢负荷的影响大于水力负荷的影响。因此,处理效能主要受固定床硫化氢进口浓度的影响,水力负荷的影响较小。
图7为污染物负荷对各级固定床处理效能的影响。第一、二级固定床氨气去除率与硫化氢去除率随着污染物负荷的升高呈上升趋势,其原因是腐殖土固定床比表面积与生物量较大,对较高浓度的污染物有更好的去除效率。第三级固定床氨气去除率随着氨气负荷的升高呈先上升后下降趋势,推测是由于一、二两级固定床的处理效能随氨气负荷的升高而增强,使得进入第三级固定床的氨气浓度下降,故第三级固定床去除效能下降。由于在较高的硫化氢负荷下,绝大部分硫化氢在一、二两级固定床中得到去除,进入第三级固定床硫化氢浓度较低,去除率主要受第三级进口除硫化氢浓度的影响。
-
1) 氨气显著性分析。依据实验结果,以氨气去除率为指标,选取气体表面负荷、水力负荷、污染物负荷3个因素,按照L9 (34) 正交表进行显著性分析,气体表面负荷水平来源于前期实验中腐殖土固定床气液逆流特性的探索,当气体表面负荷超过14 m·h−1,渗滤液无法正常下渗;水力负荷水平来源于腐殖填料生物滴滤池的适宜范围;氨气负荷水平包括填埋场氨气浓度的由低到高。因素水平见表1。
从氨气显著性分析设计及结果表可知:根据极差的大小,各因素对氨气去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为:A>C>B,即气体表面负荷>污染物负荷>水力负荷。根据每一因素实验结果的均值 (K1、K2、K3) 可判断因素的最优水平。A1B1C3为腐殖土固定床处理氨气的最佳条件,即气体表面负荷为7 m·h−1,水力负荷为0.06 m·d−1,氨气负荷为10 mg·(m3·h)−1。分析结果见表2。
方差分析结果表明:根据方差的大小,各因素对氨气去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为气体表面负荷>污染物负荷>水力负荷。三者对实验结果的影响均有统计学差异 (p<0.05),其中气体表面负荷的影响性较为显著,其F值远远高于污染物负荷与水力负荷,故气体表面负荷为主要影响因素。结合上文的分析,提高污染物浓度与降低气体表面负荷均可提升氨气的去除率,从而证明腐殖土固定床适合小气量高浓度氨气的处理。分析结果见表3。
2) 硫化氢显著性分析。依据实验结果,以硫化氢去除率为指标,选取气体表面负荷、水力负荷、污染物负荷3个因素,按照L9 (34) 正交表进行显著性分析,硫化氢负荷水平包括填埋场硫化氢浓度的由低到高。因素水平见表4。
从显著性分析设计及结果可知:根据极差的大小,各因素对硫化氢去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为C>A=B,即污染物负荷>气体表面负荷=水力负荷。根据每一因素实验结果的均值 (K1、K2、K3) 可判断因素的最优水平。A1B2C3为腐殖土固定床处理硫化氢的最佳条件,即气体表面负荷为7 m·h−1、水力负荷为0.12 m·d−1、硫化氢负荷为2 mg·(m3·h)−1。分析结果见表5。
方差分析结果表明,根据方差的大小,各因素对硫化氢去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为:污染物负荷>气体表面负荷>水力负荷,但仅污染物负荷有统计学差异 (p<0.05) 。气体表面负荷、水力负荷的p均大于0.05,可认为气体表面负荷与水力负荷对硫化氢的去除没有明显影响。结合上文分析,可在保证去除率的前提下,提高污染物浓度、降低气体表面负荷,实现小气量高浓度硫化氢的处理,以达到更经济的处理效果。分析结果见表6。
综合显著性分析的结果得出:气体表面负荷为7 m·h−1、水力负荷为0.06 m·d−1、氨气负荷为10 mg·(m3·h)−1、硫化氢负荷为2 mg·(m3·h)−1为腐殖土固定床的适宜工况,从而证明其对于小气量高浓度臭气有良好的处理效果。此外,较低的气体表面负荷下固定床通风阻力较小、能量损失较低,能以低能耗达到更好的处理效果,适合大规模工程化运用。
-
用X、Y、Z取代系数,式 (14) 变化为式 (15) 。
式中:
$X=1-\dfrac{ART{k}_{\mathrm{g}}{h}_{0}}{Q{h}_{0}+ART{h}_{1}{k}_{\mathrm{g}}}$ ;$ Y= $ $\dfrac{A{k}_{\mathrm{g}}{h}_{2}}{H\left(Q{h}_{0}+ART{h}_{1}{k}_{\mathrm{g}}\right)}$ ;$Z=\dfrac{{h}_{0}-A{k}_{\mathrm{g}}{h}_{2}}{H(Q{h}_{0}+ART{h}_{1}{k}_{\mathrm{g}})}$ 。在单级固定床中,由于工况相同,气液有效传质面积A与亨利系数H保持不变。根据实验结果可得到式中3台固定床在共同运行时的系数数据见表7~9。将数据带入式 (15),得到第一级、第二级、第三级固定床的浓度关系式分别为式 (16)~(18) 。
在同一级固定床中,对比参数X、Y、Z可发现
$ X\gg Z \gt Y $ ,这说明进口氨气浓度、即氨气气相分压对氨气去除的影响远远大于渗滤液中氨氮浓度的影响,因此氨气传质阻力主要来源于气膜、液相传质阻力相对较小,从而证明氨气组分去除过程为气膜控制过程。三级固定床对氨气的去除率可分别表示为式 (19)~(20) 。在三级固定床中,随着级数的增加,
$ X $ 的值逐渐增大、$ 1-X $ 的值逐渐减小,即氨气去除率逐级减小;带入实验数值后可发现渗滤液氨氮浓度对出口氨气浓度的影响也逐级减小,其原因为气相与液相的分压差 (浓度差) 逐级减小,使得传质推动力降低,去除率下降,且腐殖土固定床对渗滤液中氨氮的生物降解效果较好、各级固定床液相氨氮等效形成的分压差距较小。此外,由$ X=1-\dfrac{ART{k}_{\mathrm{g}}{h}_{0}}{Q{h}_{0}+ART{h}_{1}{k}_{\mathrm{g}}} $ 可得,由于等式右边只有气液有效传质面积A为变量,$ X $ 值越大,A值越小,在三级固定床中$ X $ 值逐级增大、A值逐级减小。这说明系统运行时气液有效传质面积逐级减小,第一级最大、第二级次之、第三级最小。因此,多级串联腐殖土固定床对氨气去除主要是靠气相与液相的分压差 (浓度差) ,各级液相氨氮等效形成的分压差距较小、气相与液相的分压差 (浓度差) 与气液有效传质面积逐级减小。 -
本研究使用多级串联腐殖土固定床,在协同渗滤液处理的情况下对恶臭气体进行净化脱臭,探究腐殖土固定床对氨气与硫化氢的处理效能与去除机理,通过显著性分析对腐殖土固定床处理氨气与硫化氢的条件进行优化,并运用物料衡算的方法对腐殖土固定床去除氨气的机理进行分析。实验表明,在合适的气体表面负荷、水力负荷、污染物负荷下,氨气与硫化氢的平均去除率分别为95%与98%,各因素对氨气去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为气体表面负荷>污染物负荷>水力负荷,各因素对硫化氢去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为污染物负荷>气体表面负荷=水力负荷,最佳实验条件为气体表面负荷为7 m·h−1,水力负荷为0.12 m·d−1,氨气负荷为10 mg·(m3·h)−1,硫化氢负荷为2 mg·(m3·h)−1。机理分析的结果表明多级串联腐殖土固定床对氨气去除主要是靠气相与液相的分压差 (浓度差) ,传质受进口氨气浓度、即氨气气相分压影响,此过程中气膜阻力远大于液膜阻力,近似于气膜控制过程,且各级液相氨氮等效形成的分压差距较小、气相与液相的分压差 (浓度差) 与气液有效传质面积逐级减小。
多级串联腐殖土固定床处理氨气硫化氢恶臭气体的机理
Mechanism study on the treatment of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide odor gas by multistage humus soil fixed beds
-
摘要: 设计了腐殖土固定床串联缺氧SBR多级反应器对填埋场臭气与渗滤液进行协同处理,以气体表面负荷、水力负荷、污染物负荷为影响因素进行正交实验,探究腐殖土固定床对氨气与硫化氢的处理效能与去除机理,并运用物料衡算的方法对腐殖土固定床去除氨气的机理进行分析。结果表明:腐殖土固定床对氨气与硫化氢的平均去除率分别为95%与98%,各因素对氨气去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为气体表面负荷>污染物负荷>水力负荷,各因素对硫化氢去除率的影响大小的依次顺序为污染物负荷>气体表面负荷=水力负荷,最佳实验条件为气体表面负荷为7 m·h−1,水力负荷为0.12 m·d−1,氨气负荷为10 mg·(m3·h)−1,硫化氢负荷为2 mg·(m3·h)−1。机理分析的结果表明多级串联腐殖土固定床对氨气去除主要是靠气相与液相的分压差 (浓度差) ,传质受进口氨气浓度、即氨气气相分压影响,此过程中气膜阻力远大于液膜阻力,近似于气膜控制过程,且各级液相氨氮等效形成的分压差距较小、气相与液相的分压差 (浓度差) 与气液有效传质面积逐级减。本研究结果可为现有的填埋场臭气处理技术上发展腐殖土固定床协同处理臭气渗滤液工艺提供参考。Abstract: A humus soil fixed bed series anoxic SBR multistage reactor was designed to carry out collaborative treatment of odor and leachate in landfill. Orthogonal experiments were conducted with gas surface load, hydraulic load and pollutant load as influencing factors to explore the treatment efficiency and removal mechanism of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide by humus soil fixed bed. The mechanism of ammonia removal by humus soil fixed bed was analyzed by means of material balance. The results show that: The average removal rates of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide in humus fixed bed were 95% and 98%, respectively. The order of influence of each factor on ammonia removal rate was gas surface load > pollutant load > hydraulic load, and the order of influence of each factor on hydrogen sulfide removal rate was pollutant load > gas surface load = hydraulic load. The optimal experimental conditions are 7 m·h gas surface load, 0.12 m·d hydraulic load, 10 mg·(m 3·h)−1 ammonia load and 2 mg·(m3·h)−1 hydrogen sulfide load. The results of mechanism analysis show that the removal of ammonia by multistage humus soils fixed bed mainly depends on the partial pressure difference (concentration difference) between the gas phase and the liquid phase, and the mass transfer is affected by the concentration of imported ammonia, namely the partial pressure of ammonia gas phase. In this process, the resistance of gas film is much greater than that of liquid film, which is similar to the control process of gas film. Moreover, the partial pressure difference formed by the equivalent ammonia nitrogen at all levels in the liquid phase is small, and the partial pressure difference (concentration difference) between the gas phase and the liquid phase and the effective mass transfer area of the gas are gradually reduced.
-
Key words:
- humus soil fixed bed /
- biological filter /
- odor gas /
- removal mechanism
-

-
表 1 氨气显著性因素水平
Table 1. Significance factor level of ammonia
水平 A (气体表面
负荷 m·h−1)B (水力
负荷 m·d−1)C (氨气
负荷 mg·(m3·h)−1)1 7 0.06 2 2 10 0.12 5 3 14 0.24 10 表 2 氨气显著性分析设计及结果
Table 2. Design and results of ammonia significance analysis
编号和项目 A B C 氨气去除率 1 1 1 1 98.5% 2 1 2 2 98.9% 3 1 3 3 97.3% 4 2 1 2 95.5% 5 2 2 3 97% 6 2 3 1 94.3% 7 3 1 3 94.4% 8 3 2 1 91.7% 9 3 3 2 93.4% K1 98.2 96.1 94.8 K2 95.6 95.9 95.9 K3 93.2 95.0 96.2 R 5.1 1.1 1.4 优水平 A1 B1 C3 表 3 氨气方差分析结果
Table 3. Results of ammonia variance analysis
方差来源 偏差平方和 自由度 均方 F 统计学差异 A 35.449 2.000 17.725 50.570 0.002 B 1.234 2.000 0.617 7.423 0.024 C 4.470 2.000 2.235 13.767 0.006 表 4 硫化氢显著性因素水平表
Table 4. Significance factor level of hydrogen sulfide
水平 A (气体表面
负荷 m·h−1)B (水力
负荷 m·d−1)C (硫化氢
负荷mg·(m3·h)−1)1 7 0.06 0.5 2 10 0.12 1 3 14 0.24 2 表 5 硫化氢显著性分析设计及结果表
Table 5. Design and results of hydrogen sulfide significance analysis
编号和项目 A B C 硫化氢去除率 1 1 1 1 98.1% 2 1 2 2 98.9% 3 1 3 3 99.1% 4 2 1 2 98.3% 5 2 2 3 98.8% 6 2 3 1 97.9% 7 3 1 3 98.6% 8 3 2 1 98.4% 9 3 3 2 98.5% K1 98.7 98.3 98.1 K2 98.3 98.7 98.6 K3 98.5 98.5 98.8 R 0.4 0.4 0.7 优水平 A1 B2 C3 表 6 硫化氢方差分析结果
Table 6. Results of hydrogen sulfide variance analysis
方差来源 偏差平方和 自由度 均方 F 统计学差异 A 0.427 2 0.214 2.177 0.195 B 0.382 2 0.191 2.122 0.201 C 0.882 2 0.441 10.730 0.010 表 7 第一级固定床实验数据
Table 7. Experimental data of the first stage fixed bed
$ {c}_{0} $ $ {c}_{1} $ $ {c}_{\alpha } $ $ {c}_{\beta } $ 0.351 2 0.062 2 53 978 1 734.3 0.525 9 0.078 8 56 395 1 452.9 0.637 1 0.092 9 53 263 1 689.3 表 8 第二级固定床实验数据
Table 8. Experimental data of the second stage fixed bed
$ {c}_{0} $ $ {c}_{1} $ $ {c}_{\alpha } $ $ {c}_{\beta } $ 0.062 2 0.022 1 287.86 155.00 0.078 8 0.024 9 246.43 143.57 0.092 9 0.030 0 375.71 179.29 表 9 第三级固定床实验数据
Table 9. Experimental data of the third stage fixed bed
$ {c}_{0} $ $ {c}_{1} $ $ {c}_{\alpha } $ $ {c}_{\beta } $ 0.022 1 0.005 9 117.86 96.429 0.024 9 0.006 5 155.00 80.714 0.030 0 0.008 2 240.71 167.14 -
[1] 史炜, 王军民, 曹江林. 垃圾填埋场臭气理论研究进展[J]. 山东化工, 2018, 47(19): 189. [2] 周正伟, 张椰鸣, 夏金雨, 等. 生活垃圾填埋场恶臭污染的测定与控制技术研究进展[J]. 常州大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 34(4): 26-34. [3] 郭瑞, 郑国砥, 陈同斌, 等. 生物滤池去除臭气及VOCs的研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2012, 28(23): 138-142. [4] 潘桂珉, 金红航, 赵秀岩. 废气生物处理[J]. 哈尔滨建筑大学学报, 1996(2): 61-67. [5] 肖作义, 段耀庭, 赵鑫, 等混合填料在生物滤池中除臭效果研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2020, 27(6): 88-94. [6] 余鹏举, 曹先贺, 王宏志, 等. 微生物在恶臭污染治理中的研究及应用[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(1): 165-179. [7] 耿晓梦, 魏然, 伍娜, 等. 存余垃圾挖采筛分与资源化利用现状及发展趋势[J]. 山东化工, 2020, 49(1): 50-51. [8] 赵由才, 柴晓利, 牛冬杰. 矿化垃圾基本特性研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2006(10): 1360-1364. [9] 周正伟, 吴军, 曹丽华, 等. 腐殖填料生物滤池处理生活污水的效能研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2010, 26(7): 22-26. [10] 邓素芳, 杨有泉, 陈敏. 生物土壤滤体除臭装置处理猪粪恶臭效果研究[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2011, 47(12): 33-36. [11] 夏芳芳. 垃圾生物覆盖土对填埋气中H2S的净化作用及机理研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学, 2014. [12] 岳波, 晏卓逸, 黄启飞, 吴小卉, 高红. 准好氧填埋场中间覆盖层CH4释放及减排潜力[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(2): 636-645. [13] 王凯玥, 马永丽, 李琛, 等. 气液固微型流化床的气液传质系数[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3529-3540. [14] 谷德银, 刘有智, 祁贵生, 等. 新型旋转填料床强化气膜控制传质过程[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(9): 2315-2320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6613.2014.09.014 [15] 刘铁军, 王光华, 李文兵, 等. 温度对氨吹脱工艺中氨扩散传质的影响[J]. 武汉科技大学学报, 2012, 35(6): 422-426. -



 下载:
下载: