-
污泥是城市污水处理厂用生物法处理污水的副产物[1]。其中含有大量细菌、病毒及有机物,还含有镉、铬、铜、锌、铅等重金属和多氯联苯等有毒有害物质[2];且含水率高,可达99%[3]。近年来,随着污水处理厂的大量兴建,随之产生的污泥量也在逐年增加,污泥的处理处置问题日益突出[4]。
国内污泥处置方式主要包括填埋、土地利用、焚烧等[5]。然而这些常规的污泥处置方式已无法满足环保需求。近年来,国内外学者已将研究的焦点转向环境友好、资源化利用度高的污泥处理处置新技术[6-8]。其中,污泥热解是受到业界关注的新技术之一。污泥热解是在厌氧环境下,将污泥转换成生物气、生物油、水和生物炭的技术。该技术主要产物中的生物气和生物油,可作为能源使用[9-10];其固相产物——污泥生物炭,因具有丰富的可溶性盐和大量的有机官能团以及合适的孔隙结构[11],常被用作吸附剂和土壤改良剂。如TANG等[12]将酸碱改性的磁性污泥生物炭用于去除废水中有机污染物;MÉNDEZ等[13]研究了污泥生物炭在地中海土壤中施用后对植物金属累积性的影响。WU等[14]发现,污泥生物炭能降低污泥泥饼的含水量,具有作为污泥调理脱水过程中助滤剂的潜力。
目前,许多污水处理厂使用铁盐作为絮凝剂调理污泥,以提高污泥脱水性能;然而,污泥泥饼的高度可压缩性,限制了其进一步脱水的能力。助滤剂的加入能降低污泥泥饼的可压缩性,从而达到提高污泥脱水性能的目的[15]。本研究选用FeCl3单独调理后的含铁污泥泥饼进行热解,并对热解条件进行优化,以制备铁修饰污泥生物炭;将该铁修饰污泥生物炭作为助滤剂,与FeCl3联合调理污泥,探究铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥脱水性能的影响及其机理,并分析联合调理后污泥的化学性质,研究其改善污泥脱水性能的可行性。
全文HTML
-
供试污泥采自重庆市万州区新田镇污水处理厂污泥浓缩池,该厂设计日处理量为3000 m3·d−1。供试污泥基本性质为:污泥固体浓度为8.08~15.05 g·L−1、污泥含水率(moisture content of sludge cake, MC)为98.48%~99.16%、污泥比阻(sludge specific resistance to filtration, SRF)为1.85×1012~5.20×1012 m·kg−1,污泥净产率(net sludge solids yield, YN)为1.79~2.99 kg·(m2·h)−1。
-
1)铁修饰污泥生物炭的制备。将FeCl3·6H2O配置成10 g·L−1的FeCl3溶液,以12.82%的投加量(将128.2 g FeCl3投加到污泥干重为1 kg的供试污泥中)单独调理供试污泥,过滤脱水后获得泥饼备用;将获得的泥饼于105 ℃烘干至恒重,研磨过10目筛,盛于坩埚中压实上盖,并用锡箔纸密封;然后,置于马弗炉中,分别以300、400、500 ℃热解2 h,热解前先通氮气排除炉中空气,并将排气管液封;热解结束后研磨,获得3种粒径小于180目的铁修饰污泥生物炭颗粒,根据热解温度分别命名为SB-300、SB-400、SB-500。
2)污泥调理实验。将铁修饰污泥生物炭颗粒(SB-300、SB-400、SB-500)(投加量为0~90%)与FeCl3溶液(投加量为12.82%),依次加入污泥中进行调理,以YN为主要指标,以SRF和MC为辅助指标,评价污泥的脱水性能;将FeCl3(12.82%)单独调理的污泥记作FeCl3污泥,筛选出FeCl3(12.82%)与3种铁修饰污泥生物炭颗粒(SB-300、SB-400、SB-500)联合调理时,各自的最佳剂量后,将最佳剂量下调理的3种污泥分别记作FeCl3+SB-300污泥、FeCl3+SB-400污泥、FeCl3+SB-500污泥。通过对污泥Zeta电位、污泥泥饼的微观结构、EDS和泥饼可压缩性系数的分析来研究铁修饰污泥生物炭调理污泥的机理;同时,通过测定污泥的胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances, EPS)含量、重金属(Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn)总量及形态、总氯含量,评价其调理污泥可能存在的环境风险。
-
污泥比阻(SRF)是评价污泥脱水性能的常用指标,将100 mL污泥样品倒入具有预先润湿的0.45 μm滤纸的9 cm标准布氏漏斗中;然后,施加恒定的0.03 MPa真空压力,抽滤至真空破裂,或达到6 min,记录滤液体积;根据吴彦等[15]描述的方法计算SRF。当加入助滤剂,使污泥固体通量发生变化时,引入YN评估污泥的脱水性能[16],YN表示每单位过滤面积和单位时间过滤的污泥固体量,并通过公式(1)来计算。
式中:P是实验压力,N·m−2;ω是滤过单位体积的滤液在过滤介质上截留的固体质量,kg·m−3;μ是滤液动力黏滞度,N·s·m−2;t是过滤滤液体积增加到污泥体积的50%所需的时间,s;R是污泥比阻,m·kg−1;F是校正因子,通过公式(2)来计算。
式中:Coriginal是原污泥中的固体含量,g·L−1;Cconditioner是投加至原污泥中的调理剂固体含量,g·L−1。
污泥的Zeta电位用Zeta电位仪(ZEN3690,英国)测定;污泥泥饼的可压缩性系数指污泥泥饼受单位压力作用的体积变化率,根据QI等[17]描述的方法测定并计算;污泥泥饼的微观结构采用环境扫描电镜(ESEM)(Quanta200,美国)进行测定;污泥生物炭表面铁元素含量采用能谱仪(EDS) (EDAX genesisxm-2,美国)进行测定;污泥胞外聚合物(EPS)采用热处理法进行提取[18],将其分为溶解型胞外聚合物(S-EPS)、松散结合型胞外聚合物(LB-EPS)和紧密结合型胞外聚合物(TB-EPS),含量由多糖和蛋白质含量之和表示[19],其中多糖采用蒽酮-硫酸比色法测定[20]、蛋白质采用快速Lowry法蛋白含量测定试剂盒(品牌:LabAide)测定[21];重金属(Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn)形态采用Tessier五步提取法[22],将其分为可交换态(EXC)、碳酸盐结合态(CA)、铁锰氧化物结合态(Fe-Mn)、有机结合态(OM)、残渣态(RES);污泥重金属含量的分析采用微波消解仪(Speedwave Xpert,德国)消解后,用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Optima7000DV,美国)进行测定;重金属生态风险评价采用RAC(Risk Assessment Code)法[23];固体中的总氯采用电位滴定法(GB/T 30729-2014)。
1.1. 实验原料
1.2. 实验方法
1.3. 分析方法
-
图1显示了铁修饰污泥生物炭投加量对污泥脱水性能的影响。由图1可知,3组实验中,SB-500与FeCl3(12.82%)联合调理时污泥的YN值最高,SRF和MC值最低。由此可知,SB-500与FeCl3联合调理污泥脱水性能更佳。而且,随着铁修饰污泥生物炭投加量的变化,3组实验YN、SRF和MC的变化趋势基本一致,随着铁修饰污泥生物炭投加量的增加,YN先逐渐升高,当投加量达到30%时YN达到最大值,之后YN又逐渐减小并趋于平稳;SRF的变化趋势与YN基本相反,MC值随着铁修饰生物炭投加量的增加而不断减小。由图1(c)可以计算出,1 L含固率为9.97 g·L−1的FeCl3单独调理的污泥脱水后,泥饼总质量为91.84 g,而由SB-500(30%)和FeCl3(12.82%)联合调理的污泥脱水后,泥饼总质量为70.60 g。因此,加入铁修饰污泥生物炭后,泥饼总质量下降,后续处理成本降低。综上所述,SB-500(30%)和FeCl3(12.82%)联合调理污泥脱水效果最佳,且与仅用FeCl3(12.82%)调理的污泥相比,YN升高了73.38%、SRF降低了68.75%、MC降低了9.03%。
-
表1为不同调理方式下污泥的Zeta电位。由该表可知,与原污泥和FeCl3单独调理的污泥之Zeta电位相比,FeCl3分别与SB-300、SB-400、SB-500联合调理后污泥的Zeta电位更趋近于零。其中,FeCl3和SB-500联合调理后的污泥Zeta电位值最趋近于零。这表明,此时污泥最不稳定,污泥颗粒之间的吸引力超过了排斥力,污泥颗粒分散被破坏而更容易发生絮凝,脱水性能更好[24]。这一结果与第2.1节报告的结果相吻合。
-
1)铁修饰污泥生物炭的微观结构。图2显示,在SB-300、SB-400、SB-500表面均有明显空隙结构,但各处理下的污泥间存在较明显的差异。其中,SB-500表面微孔数量最多,且结构最为粗糙,这更有利于将细小的污泥颗粒吸附聚集以提高污泥的脱水性能[25-26]。同时,如表2所示,SB-500表面铁元素含量最高,因此将SB-500添加到污泥后,在Fe3+的作用下,会使污泥颗粒更容易发生絮凝[27],这也印证了第2.1节报告的结果。
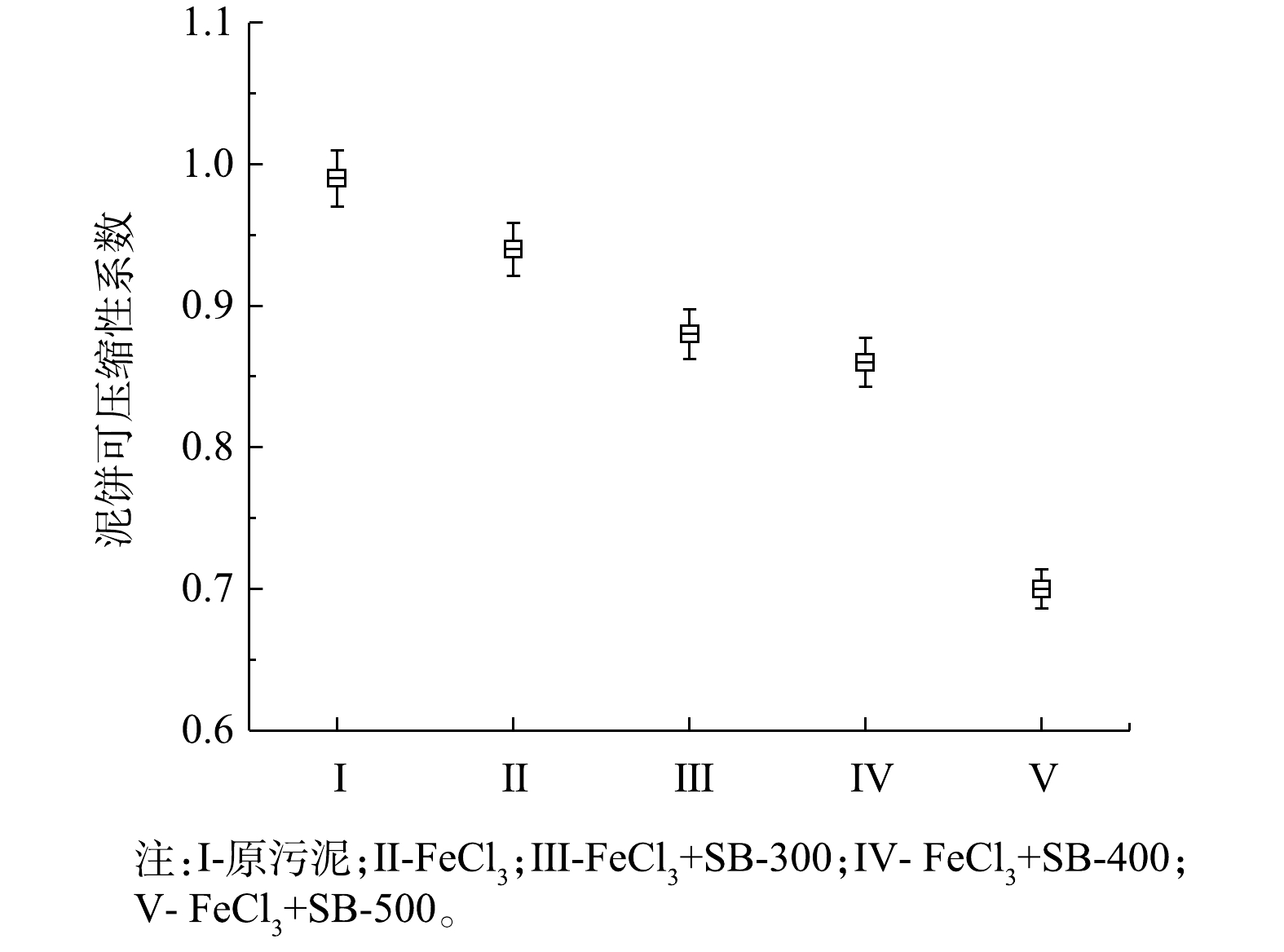
2)铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥泥饼微观结构的影响。由图3可见,3种泥饼中原污泥泥饼最为致密,FeCl3调理的污泥泥饼出现少许裂缝,而投加SB-500之后的泥饼表面出现了较多明显的大裂缝。由图4可知,FeCl3和SB-500联合调理的污泥泥饼可压缩性系数最小,表明加入SB-500后,泥饼不可压缩性最高,不容易发生形变。有研究[15]表明,铁修饰污泥生物炭在污泥脱水过程中起骨架支撑作用,可使泥饼保持较好的渗透性,提高污泥的脱水性能。
-
1)铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥EPS的影响。S-EPS在溶液中处于游离状态,主要包含的是一些高分子物质、胶体和黏液,他们是活性污泥法处理系统中BOD和COD的主要来源[28]。从图5可知,与FeCl3单独调理的污泥相比,FeCl3和SB-500联合调理后的污泥S-EPS明显较低。这可能是因为,SB-500孔隙结构最为发达,因此其比表面积最大,能有效吸附溶液中游离的S-EPS,从而可降低污泥滤液后续的处理成本。
LB-EPS结构松散,具有流动性,会对污泥絮凝、沉降和脱水等性能产生直接影响;而TB-EPS则与细胞壁结合紧密不易脱落,对污泥絮体性质的影响相对较小[28]。与FeCl3单独调理的污泥相比,FeCl3和SB-500联合调理后的污泥LB-EPS、TB-EPS均有明显的降低。这可能是因为,SB-500吸附溶液中的S-EPS后,促使LB-EPS、TB-EPS溶解;同时,对LB-EPS、TB-EPS也有一定的吸附作用,从而降低了污泥中LB-EPS、TB-EPS质量浓度,提高了污泥的脱水性能[29]。
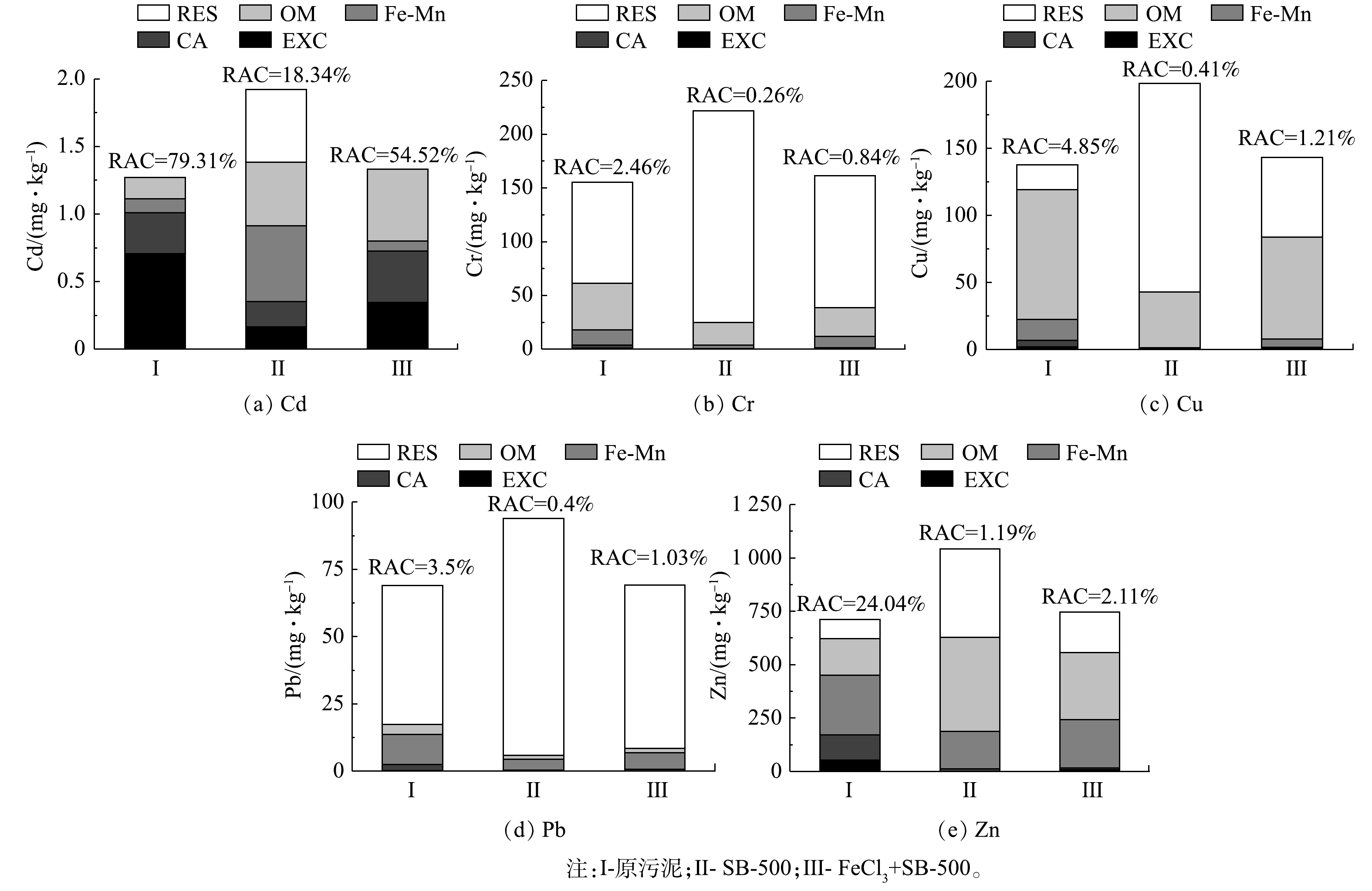
2)铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥泥饼中重金属的影响。图6表示不同调理方式下污泥泥饼中的重金属质量分数,总体而言,泥饼重金属质量分数均未超过《农用污泥污染物控制标准》(GB 4284-2018)中的限值。SB-500中的Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn的质量分数相对原污泥泥饼有所增加。这可能是因为,污泥热解有机物的减少量远大于重金属的减少量[25]。但SB-500中Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn的RAC值均明显小于原污泥。这说明,SB-500中重金属更为稳定,其释放到环境中的风险更低。由图6还可看出,在FeCl3和SB-500联合调理后的污泥泥饼中,Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn的质量分数与原污泥相比,虽有所增加,但增幅较小;而且,Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn的RAC值相较原污泥明显较低。由此可知,经FeCl3和SB-500联合调理污泥后,其重金属的生态风险较小。
3)铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥中氯质量分数的影响。表3为在不同调理方式下,干污泥中总氯的质量分数。由于本研究的污泥为热解处置,因此通过对热解后总氯的归属分布进行分析,可以阐明总氯可能带来的后续环境影响。由表3可知,与单加FeCl3的污泥泥饼相比,加入SB-500的干污泥中所含的总氯质量分数较低。这可能是因为,SB-500进一步提高了污泥的脱水性能,一部分的氯也随水分脱除;而加入SB-500的泥饼热解固相产物和非固相产物(差额)中总氯的质量分数都低于单加FeCl3后的污泥泥饼。因此,加入SB-500之后,氯离子对环境的影响有所降低。
2.1. 铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥脱水性能的影响
2.2. 铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥Zeta电位的影响
2.3. 铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥泥饼微观结构的影响
2.4. 铁修饰污泥生物炭对污泥化学性质的影响
-
1)在500 ℃下制备的铁修饰污泥生物炭(SB-500)(30%)和FeCl3(12.82%)联合调理下,污泥脱水的效果最佳。SB-500的投加,使污泥的Zeta电位更趋近于零,污泥更容易发生絮凝;SB-500表面铁元素含量高,调理后的泥饼孔隙结构发达,其在污泥脱水过程中能使污泥泥饼保持较好的渗透性,从而提高污泥的脱水性能。
2) SB-500的投加,降低了污泥S-EPS、LB-EPS、TB-EPS的含量;且泥饼中Cd、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn形态更为稳定,生态风险较小;氯离子对环境的影响也较FeCl3单独调理时有所降低,且处理成本较低。




 下载:
下载: