-
氯代芳构化合物(chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons,CAHs)是一类芳香族化合物,其特征在于苯环上的一个或多个氢原子被氯原子所取代 . 它们在药物生产、汽车尾气以及工业热过程中产生或释放,是一类众所周知的有毒物质. 大部分的CAHs因其高毒性、生物累积性、远距离迁移性和难降解而被认定为持久性有机污染物(persistent organic pollutants,POPs),包括多氯联苯(polychlorinated biphenyls, PCBs),多氯萘(polychlorinated naphthalenes,PCNs)和二恶英(polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans,PCDD/Fs),六氯苯(hexachlorobenzene,HCB)和五氯苯(petachlorobenzene,PeCB)等. 含有三个或更多稠环芳香环的氯代多环芳烃(chlorinated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons,Cl-PAHs)也被证实具有强烈的毒性和致癌突变特性,因此被认为是潜在POPs[1]. 许多研究表明,焚烧过程中产生的烟气中含有大量CAHs,是空气中的CAHs的主要来源[2]. 其中,多氯联苯的生成量与二恶英相当,多氯萘和氯代多环芳烃的生成量总和至少比二恶英高2—3个数量级,氯苯、氯酚类的含量通常比二恶英高3—6个数量级[3].
焚烧过程包括垃圾焚烧、工业固体废弃物焚烧、医疗废物焚烧、燃煤、燃气等人类生产工艺. 在焚烧过程中,烟气环境的特性会显著影响CAHs的生成和去除. 这些特性主要由焚烧过程中的各项参数,如温度、氧浓度以及原料的化学组成,特别是氯和有机物的含量等决定. 当处于高温并有氯源存在时,原始材料(例如废弃物)中的有机物通过热解和氯化反应能生成大量的CAHs[4]. 目前,人们开发了多种破坏CAHs的方法,如电化学法[5]、生物降解法[6 − 7]、光催化法[8]、吸附法[9]、超临界水氧化法[10]、热解法[11]及催化氧化法等. 其中,催化氧化技术备受关注,并取得了一定的研究成果. 催化氧化技术具有反应条件温和、能耗低、效率高、无二次污染、适用范围广等优点[12 − 14]. 本文综述了近年来在焚烧源中氯代芳构化合物催化氧化领域取得的研究成果,主要涵盖催化剂、催化氧化机制、催化剂失活与再生等方面的内容.
-
催化氧化技术的关键在于筛选和制备具有高活性、高稳定性和高选择性的催化剂. 催化剂的活性受到催化剂结构和反应底物特性的影响. 同时,催化剂需要高稳定性以防止反应产物、特别是副产物毒化催化中心. 对于脱氯反应,催化剂的高选择性可以避免产生大量非目标产物或毒性更大的化合物. 催化氧化技术中,常用的催化剂包括贵金属催化剂、过渡金属催化剂、分子筛催化剂. 然而,单一催化剂在应用中常面临效率低下和易中毒失活等问题. 为了优化这些局限性,研究人员通常会通过掺杂其他金属元素或利用分子筛来提升催化剂的反应活性. 总之,催化剂的开发和改进在催化氧化技术中持续扮演着关键角色,同时也面临着诸多挑战.
-
贵金属催化剂,如铂(Pt)、钌(Ru)、钯(Pd)等,广泛应用于各类化学反应中,以其高活性、长使用寿命、高选择性和优异的抗毒性能著称. 表1对比了近年来贵金属催化剂在催化氧化CAHs中的应用研究. 值得注意的是,Ru作为最经济实惠的贵金属催化剂,其催化活性超过了其他贵金属,并且作为迪肯反应的高效催化剂,能有效去除催化剂表面的反应性氯离子物种[15].
为了进一步提高催化效率和稳定性,研究者尝试将贵金属掺杂于过渡金属氧化物中或负载在分子筛上. 例如,Wang等[16]将Ru负载在介孔Fe-Mn氧化物上,成功提高了其催化活性,并发现Ru-O-Mn和Ru-O-Fe分别增加了还原性、表面吸附氧和氧空位的产生,提供了更多的催化活性位点以及更好的反应物扩散条件. Cano等[17]利用分子筛作为载体,制备了Pd/Co-HMOR和Pd/Co-SZ催化剂,研究其对1,2-二氯苯(o-DCB)的催化降解活性. 实验结果显示,Pd/Co-HMOR和Pd/Co-SZ在500 ℃和550 ℃表现出最高活性,而在250—400 ℃的温度范围内,Pd/Co-SZ的催化活性更为突出. XAFS进一步揭示了Pd和Co可在HMOR上形成的高度分散的催化剂活性中心. 这些研究结果均验证了选择合适的载体能显著提高催化剂的活性和稳定性.
催化剂性能的优化也与助催化剂的选择有着密切关系. 例如,向Ru/TiO2催化剂中添加CeO2,不仅可以提高贵金属的活性和分散性,还可以提高COx的产率和无机氯的选择性,同时降低有毒二恶英的生成[18]. 此外,催化剂的晶面选择对催化活性同样有重要影响. 例如,Pt/Mo负载于3种晶面的MnO2纳米棒中,不同MnO2晶面催化活性不同,而Pt和Mo的负载和修饰也有利于活性、多功能性及耐久性的提高[19]. 除此之外,催化剂抗水性也会影响其催化活性. Wu等[20]发现具有疏水性的Ru/TiCeOx催化剂对o-DCB具有良好降解效果,因为水分子占据催化剂表面氧空位从而降低了活性中心利用率. 总之,催化剂载体、助催化剂、晶面的选择以及抗水性都是影响催化性能的关键因素,综合利用这些策略可以显著提升贵金属的活性和稳定性.
-
过渡金属氧化物催化剂因其成本低、资源丰富和良好活性的特性,被视为贵金属催化剂的理想替代品. 常见的过渡金属氧化物催化剂包括铈(Ce)、钛(Ti)、钒(V)、铬(Cr)、锰(Mn)、铜(Cu)等金属氧化物及其复合氧化物. 表2比较了近年来过渡金属氧化物催化剂用于催化氧化CAHs的研究. 研究人员通过引入不同的过渡金属以优化催化剂结构以提高其活性. 例如,将Mn与Co3O4尖晶石结构相结合,可以提高o-DCB和CHCl3的降解率,这是由于Mn增加了尖晶石的分散度和Co2+浓度,提高表面活性氧的氧迁移率[29]. Ce-Zr共改性的锰基氧化物催化剂的活性明显高于单一锰基催化剂,这归因于比表面积的增大、Mn4+阳离子和表面氧物质数量的增加,以及由Ce-Zr改性引起的氧迁移率和锰还原性的增强[30]. WOx/CeO2催化剂在CB和o-DCB催化活性测试中表现出色,这取决于W含量,WOx和CeO2之间的相互作用形成的W-O-Ce增加了氧空位,从而促进了催化剂的还原性和酸性,在350 ℃下,两种污染物的降解率均超过90%[31]. 以Co基氧化物为基底制备了Co/M = 3 (M = Al、Fe、Cr)的催化剂,添加第二种金属能增强了催化剂的酸性和碱性位点的活性,Cr或Fe的添加还提高了原始Co3O4在低温下的表观活性,并有效抑制了多氯代副产物的形成[32].
催化剂的制备方法和金属元素的配比也会影响催化剂的活性. Wu等[33]通过浸渍法调节Ti/Zr物质的量比制备了一系列有序介孔催化剂CeSn/TizZr10-zOx,催化性能随Zr含量呈现先增后降的趋势,其中CeSn/Ti6Zr4Ox催化性能最佳. Wang等[34]采用无模板草酸盐法合成多孔Fe-Mn氧化物催化剂发现,当Fe/Mn为1:1时,催化剂对CB催化活性和选择性也更高,这归因于Fe和Mn间的强烈相互作用使催化剂表面富集Mn4+. Dai等[35]通过溶胶-凝胶法制备Mn(x)-CeLa混合氧化物催化剂,高Mn/(Mn + Ce + La)比率的催化剂表现出高稳定性活性,其中,Mn(0.86)-CeLa催化剂的活性最高. Huang等[36]用湿法浸渍法制备了不同负载量VOx的VOx/CeO2催化剂,发现VOx的加入显著提高了催化活性和稳定性.
此外,催化剂的形貌也被证明对CAHs的降解具有重要影响. Wang等[37]证实了3种形态的Ce-Mn催化剂(纳米片、纳米颗粒和纳米棒)对CB的氧化活性存在显著差异,纳米片催化剂活性最高,可能因其层状结构及高氧空位和Ce3+含量增强了含氯物种的吸附. 另外,Shi等[38]制备了多种纳米结构的VOx/CeO2催化剂,发现纳米棒催化剂活性最强,可能源于其结构和表面特性变化增加了SBET和Oβ/Oα比率,以及通过形成新相CeVO4和增加Ce3+来增加氧空位,从而提高氧迁移率和活性表面氧.
这些研究表明,优化催化剂的性能涉及多方面的调整,包括组成、结构设计、制备方法、元素配比及形态调整. 这些改变能提高催化剂的适应性以及应对多样的环境问题,并在处理CAHs污染物方面表现出更高的效率和效果.
-
分子筛,一种由无机氧化物构成的多孔晶体,具有特定的微孔结构和化学成分,能够在化学反应中充当催化剂. 除了优秀的热稳定性外,分子筛具有较大比表面积并含有大量的酸性位点. 然而,研究发现,分子筛在应用于催化氧化CAHs反应时,相较于贵金属和过渡金属氧化物催化剂并无明显优势. 因此,研究人员通常采用分子筛作为载体,制备金属型复合催化剂以降解CAHs. 这一过程中,分子筛与活性组分之间的协同作用能够提升催化效率和稳定性. 其中,分子筛载体上丰富的酸性位点有助于吸附和脱氯CAHs,活性中心则通常具有出色的氧化能力,可以促进CAHs及其副产物的氧化. 表3列出了近年分子筛催化剂用于催化氧化CAHs的研究.
复合型分子筛催化剂的催化活性依赖于金属的种类、结构、分散程度及制备方法. Zheng等[105]制备的10% CuCe(6:1)/MCM-41纳米级催化剂展示了高催化活性和耐久性,其性能得益于MCM-41载体的大孔径和大比表面积,以及CeO2对CuO分散的增强. Cheng等[106]研究表明,物质的量比及负载组分的相互作用影响催化活性,其制备的10%MnCo(6:1)/MCM-41催化剂展现出优异活性. He等[107]研究制备多种负载金属的介孔分子筛催化剂,结果显示分散性、比表面积和还原性是影响催化活性的主要因素. Zhao等[108]通过后修饰和直接合成两种途径制备了镧系元素修饰的 Co/HMS 催化剂,证实了CeO2形成有利于获得精细的Co3O4晶簇,外骨架Ce修饰催化剂表现出比骨架修饰催化剂更好的催化性能.
另外,分子筛具有大量酸性位点,包括Lewis和Brønsted酸位. 这两种酸位的协同作用有助于提高CAHs的降解活性和稳定性[109 − 110]. 其中,Lewis酸位点可以促进晶格氧的活化,增强氧化还原能力,有利于有机物的氧化和氯的氧化去除. Brønsted酸位则能改变CB的降解路径,促使Cl离子以HCl的形式释放,从根本上抑制了Cl2的生成,降低了含氯副产物和Cl2的选择性. 在金属复合型分子筛催化剂中,还可以通过分子筛中的H·与金属离子交换,调节Brønsted/Lewis(B/L)比,从而优化催化效果. 值得注意的是,H2O与分子筛的相互作用也能显著增加Lewis酸度[14, 111].
总体而言,上述研究强调了分子筛催化剂在降解CAHs方面的重要应用潜力. 虽然在某些情况下,分子筛可能无法与贵金属和过渡金属氧化物催化剂竞争,但其与活性组分的协同作用和丰富的酸性位点赋予了它在这个领域的独特优势.
-
催化剂载体在催化反应过程中的作用至关重要,其功能包括支撑和稳定活性组分、提升催化反应效率和选择性,以及降低催化剂成本等. 载体的性能直接影响到催化反应的效率和经济性,通常需要具备高比表面积、优异的化学稳定性、适当的孔径和孔隙度、良好的可控性等特性.
除分子筛外,常见催化剂载体材料还包括氧化铝、硅胶、TiO2、MgO等. 载体种类、制备方法以及晶体结构,均能影响载体的性质以及与活性组分之间的相互作用. 因此,深入研究载体材料的性能和结构特征至关重要. Zhao等[103]通过调控前体溶液的HCl/(Ti+Si)物质的量比,制备出具有不同性质的CeMn/TiO2-SiO2催化剂,相较于纳米TiO2-SiO2为载体的CeMn/TiO2-SiO2,其具有更大的比表面积. 载体形态也会影响催化氧化反应效率. Deng等[55]发现,Ti的引入和煅烧温度的差异会影响晶体结构,进而影响催化活性. 特别地,萤石型Ce0.9Ti0.1显示出基于Ti归一化的每平方米速率的最高TOF. 再如He等[54]研究发现,煅烧温度显著影响CeOx-MnOx/TiO2催化剂的活性,低温下煅烧的催化剂表现出较高的活性,这主要是由于MnCeOx固溶体的形成以及氧原子迁移率的提高.
催化剂的载体不仅影响催化反应效率,同时也会影响催化降解副产物的生成. Van等[113]对Pt在不同载体上对CB的催化氧化反应进行了研究,发现载体种类会导致多氯副产物的生成水平和分布有所变化. 研究显示,Pt/ZrO2分散度较高(47%),其生成的多氯苯副产物水平较高,而Pt/SiO2的分散度较低(4%),生成的PhClx较少. 不同的载体可能对Pt上发生的反应产生不同的影响,可能是由于其充当吸附在Pt颗粒边缘的芳香环的氯源. 另外,载体上的二次反应也可能导致异构体和同系物模式的变化.
-
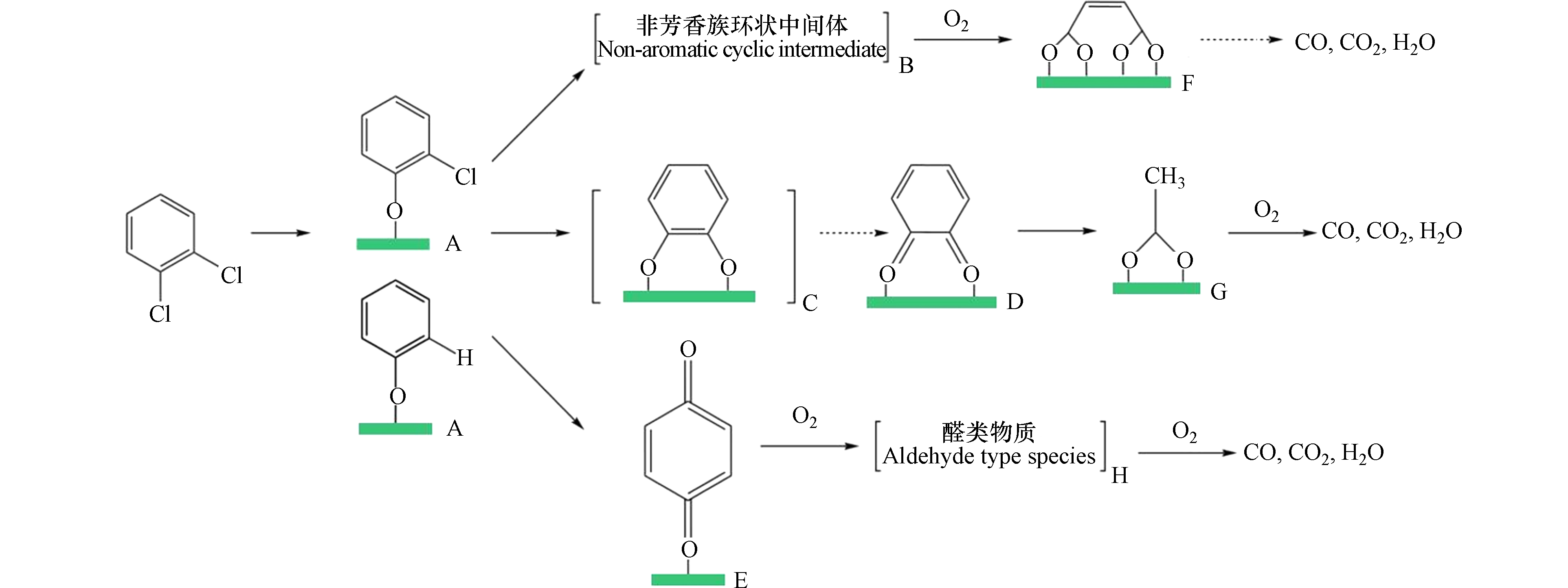
CAHs的催化氧化过程可以分为4个步骤:吸附、活化、键断裂(C—Cl和C—C)、脱附. 即目标有机分子吸附在催化剂的活性位点上,经催化剂表面的氧原子活化发生键断裂,产生一系列降解产物,最后这些产物从催化剂表面脱附并进入反应体系中. 以氯苯和二氯苯在金属氧化物上的催化氧化反应为例[59, 114],如图1所示:首先,污染物分子通过吸附在活性位点上形成π-络合物. 然后,氯被亲核氧[O]捕获,C—Cl键断裂,[O]发生亲核取代,形成表面酚盐. 其次,对吸附的部分脱氯物种进行亲电取代,产生邻苯醌(D) (通过表面儿茶酚酸酯(C)形成)或对苯醌(E). 这些物质可以在随后的步骤中进一步反应,形成表面马来酸盐(F)和醋酸盐(G). 亲电取代也可能导致芳香环的键断裂,得到非芳香中间体(B),该中间体快速反应形成表面马来酸盐(F)、醋酸盐(G)和醛(H). 最后,在表面上形成的一些部分氧化产物发生完全氧化反应,生成最终产物CO、CO2、HCl和H2O. 在这过程中,C—Cl键断裂后Cl会吸附在氧空位或酸性位,然后在羟基存在下通过生成HCl被脱除;同时,HCl也可通过Deacon反应生成作为 Cl2. 因此,增加催化剂中羟基的数量将有助于HCl的快速脱除. 当大量Cl沉积在催化剂表面时,一部分Cl会与催化剂形成金属氯化物影响活性,另一部分Cl会与CB或新生成的中间体结合生成多氯副产物[107, 115 − 117].
-
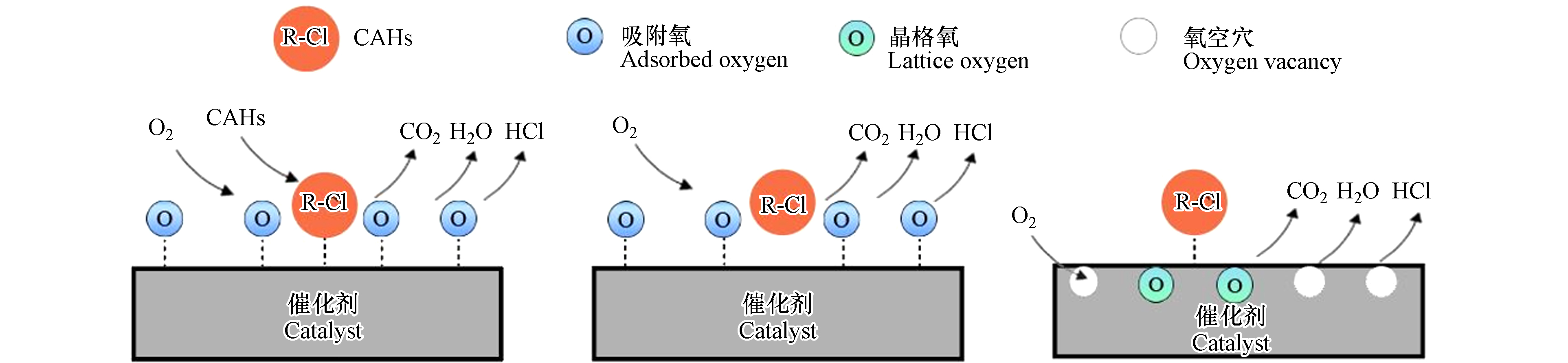
目前主要由3种模型来解释CAHs催化氧化机制,即Langmuir-Hinshelwood(L-H)模型、Eley-Rideal(E-R)模型以及Mars-van Krevelen(MVK)模型(如图2). 其中,L-H模型是基于吸附和脱附原理,如,在贵金属催化剂反应过程中,CAHs通常被吸附在贵金属位点或酸性位点上,然后与吸附的氧物种发生反应,产生CO2、H2O、HCl和其他副产物[117],在L-H机制中,反应速率与吸附能力、表面上反应物之间的相互作用、反应物和产物的解吸能力等因素密切相关,这些因素会影响反应物在催化剂表面上的停留时间和反应的发生速率. E-R模型类似于L-H模型,E-R机制认为CAHs直接与吸附在催化剂表面的氧物种反应,涉及两个不同的分子反应,一种反应物被吸附在某种物质上,生成一种类似配合物的结构,另一种分子与配合物发生反应,进而得到产物[118]. E-R模型中的反应速率取决于吸附的反应物分子的浓度、催化剂表面上的反应活性位点数、反应物分子的解吸速率等因素. MVK模型,也被称为氧化还原模型,该模型认为氧分子在催化剂表面上与反应物分子发生反应,形成氧化产物. 催化剂表面上的氧空位是反应的活性位点,它们可以吸附反应物分子并与其反应. MVK模型包含两个步骤:第一步是氧吸附,氧分子通过表面的空位被吸附到催化剂表面上,并与表面上的反应物分子发生反应;第二步是氧解离,已经被吸附的氧分子通过吸收能量而解离,并释放出氧原子,氧原子与表面上的反应物分子发生反应,生成氧化产物. 催化剂表面上的空位会被反应产物占据,因此需要再次吸附氧分子以维持反应的进行. 当催化剂中的氧被不断消耗后,气氛中的氧会不断进入催化剂,对其进行补充,使催化反应得以持续进行. 然而,氧气对晶格氧的补充能力同时又受到催化剂自身被氧化能力的限制. 当气氛中不存在氧时,催化剂表面依然具有一定活性的晶格氧参与催化反应. 一般来说,贵金属的催化氧化更常用两种经典机制来解释,即L-H机制和E-R机制,分别对应于催化剂表面上两个相邻吸附颗粒之间以及表面吸附颗粒与气体分子之间的反应. 在氧化过程中,贵金属作为界面反应的活性氧化还原中心被认为以其还原态发挥作用[119]. 贵金属活性位点上的L-H机制(见图2a)经过3个步骤:O2在贵金属位点上发生解离,CAHs在没有离解的情况下被吸附在贵金属位点上,解离的O物种攻击吸附的CAH以形成CO2、H2O和其他副产物等,这些副产物在形成后通常遵循E-R机制进入下一个循环[120],或者,CAHs不吸附在催化剂表面上,气态CAHs与吸附在催化剂上的氧直接反应,遵循E-R机制(见图2b)[121]. 大多数过渡金属氧化物催化剂在催化氧化CAHs时,遵循MVK机制(见图2c). 这是因为过渡金属氧化物在表面上具有更多的氧空位. 在此机制中,催化剂的晶格氧物种参与氧化还原过程,当晶格氧被消耗后,催化剂将被部分还原以形成一个氧空位. 随后,空气中的氧会首先吸附在催化剂表面上,形成表面吸附氧. 然后,表面吸附氧进一步填充催化剂中的氧空位,如此往复循环,从而达到催化效果[122].
-
催化剂失活是指催化剂在反应过程中活性下降或完全失去活性的现象,可能多种因素导致,包括催化剂的化学变化、物理变化或结构变化以及反应条件的变化. 失活降低了催化系统的运行能力,增加了未完全氧化物质的产生,包括一系列氯代有机物,甚至可能诱发更危险的化合物如PCDD/Fs或PCBs的产生,这种情况导致包括CAHs在内的多种污染物排放到环境中,从而增加了排放量,并提高了运行成本[124]. 因此,研究催化剂失活和可能的再生对于评估催化剂具有重要意义. 常见的催化剂失活原因通常分为积碳、烧结和中毒. 催化剂积碳是指反应物或反应中间体在催化剂表面吸附和转化时形成碳质物质沉积在催化剂表面的现象. 积炭会覆盖催化剂表面活性中心,减少可利用的表面导致催化剂失活. 另一方面,积炭容易杜塞催化剂孔道,使孔内金属颗粒不能正常发挥催化作用[60]. 催化剂暴露在过高温度下导致结构和性能的变化称为催化剂的烧结或热失活. 它涉及活性元素分散度的降低,比面积、孔体积和孔径的减少、酸度的降低以及结构的破坏. 根据这些结果,很难精确地确定载体或金属在催化剂热失活中的作用[125]. 热失活基本上是不可逆的. 因此,为了避免烧结,有必要提高催化剂的热稳定性并阻碍催化剂中活性元素的流动性,或者开发在较低温度下已经具有活性的催化剂[100].
催化剂中毒主要是由于活性组分吸附了对其有毒性的物质[37],在活性位点上生成稳定且催化活性很低的物种. CAHs催化氧化的研究主要集中在Cl中毒上. 首先,Cl元素的强电负性容易绑定在活性位点内,从而覆盖了活性点,阻碍了CAHs的吸附和活化,导致催化剂失活. 其次,Cl会与金属表面发生相互作用,引起金属组分和载体的腐蚀,导致不可逆的失活. Cl的积累也会导致比表面积减小,微晶尺寸增加,活性相团聚等问题,进而降低催化活性[37, 80,126 − 129]. 贵金属和Cl之间的存在强烈相互作用,因此在反应过程中很容易形成氯化物覆盖活性位点,导致催化剂失活[130 − 132]. 然而,不同的过渡金属氧化物在抗Cl中毒方面表现不同. 例如,在CB催化氧化中,VOx催化剂表面未检测到氯化物种,表现出良好的抗失活性,而MnOx催化剂则深度失活,形成了氯化锰和氧氯化物,证明了通过化学反应形成(氧)氯化物是更为明显和持久的失活类型[51]. 在这种情况下,催化剂的活性可以通过金属氧化物的再氧化,在适当的高温下去除Cl物种得以部分恢复[133]. 除此之外,还可以通过添加其他金属改善催化剂表面性质. 因为引入新的活性组分可以促进沉积在催化剂表面的无机氯物种的解吸,并抑制金属氯化[21,77,79,134 − 135].
-
催化剂再生能力取决于其失活过程的可逆性. 热处理、化学再生、臭氧氧化、汽提或空气处理等手段可以用于恢复失活的催化剂[123]. 在大多数情况下,碳质沉积物可以通过氧气、水蒸气、二氧化碳或氢气的气化完全消除. 然而,催化剂的烧结通常是不可逆的. 此外,挥发性金属氯氧化物的形成也会导致催化剂不可逆失活. 找到有效的再生和再利用方法对于针对CAHs的失活催化剂来说是个挑战. 因此,研究人员正在探索各种催化剂再生方法. Ji等[136]针对V2O5-WO3/TiO2商业催化剂的再生研究,发现在O2环境下50 ℃处理数小时可消除焦炭,使催化剂得到完全再生,并提高了PCDD/F的去除率. Zhu等[137]尝试用盐酸可以部分恢复与o-DCB反应过的Pd/Fe催化剂,部分消除了其表面腐蚀. Sun等[112]研究指出,Brønsted位点的损失主要是由含有芳环的焦炭所致. 针对此,可采用400 ℃的等温空气流再生方法,该方法可将芳香环焦炭转化为更饱和的碳氢化合物或CO2,进而恢复Cu-Nb/HZSM-5催化剂中的大多数Brønsted酸位点. 此外,研究还发现,水可以促进HCl的生成,从而去除表面氯化物并促进碳氧化物形成,有利于焦炭和氯的去除,从而更好地再生催化剂. 但水也会与CAHs竞争活性位点,减少催化剂酸性位点数量[121,138],降低催化效率.
-
催化氧化技术作为处理焚烧烟气中CAHs的有效手段,已经得到了广泛关注. 贵金属催化剂具有高催化活性,但其昂贵的价格、易中毒的特性以及产生大量多氯副产物限制了其实际应用. 相对而言,过渡金属复合氧化物的催化活性虽然不及贵金属催化剂,但是通过改性可以提高其催化活性、稳定性和抗失活性. 此外,分子筛的催化活性依赖于自身酸性,能够有效地抑制多氯副产物的生成,但易受碳沉积的影响. 总体而言,催化氧化技术在处理CAHs方面仍面临诸多挑战和问题. 首先,催化氧化过程机制理解尚不深入. 其次,高反应温度窗口的需求也是一大挑战. 最后,缓解催化剂的失活并找到有效的再生方法亦是迫切的课题. 因此,未来的研究应该全面考虑催化剂的构造、反应机制、失活和再生等因素,以推动高效、经济、环保的催化氧化技术的发展,并推动其在实际应用中的广泛使用.
烟气中氯代芳构化合物催化氧化的研究进展
Research progress on the catalytic oxidation of chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons in flue gas
-
摘要: 焚烧是固体废物处理的重要方式,但由此产生的烟气中含有氯代芳构化合物(chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons,CAHs),对环境和健康构成威胁. 催化氧化技术因其高去除率、低能耗、低二次污染等优点被认为是去除烟气中CAHs最有效的方法之一. 本文系统介绍了常见的催化剂种类,包括贵金属催化剂、过渡金属氧化物催化剂和分子筛催化剂,并比较了它们的优缺点. 同时,深入探讨了催化氧化反应的机制、催化剂失活原因和再生方法,并强调了催化剂的组分、载体、结构和制备方法等对催化剂活性的重要影响. 最后,根据文献研究,对CAHs的催化氧化进行了展望. 未来研究应进一步优化催化剂设计,提高反应效率,并将其应用于实际焚烧烟气治理.
-
关键词:
- 催化氧化 /
- 氯代芳构化合物(CAHs) /
- 催化剂 /
- 催化氧化机制 /
- 催化失活.
Abstract: Incineration is an important method for solid waste treatment, but the resulting flue gas contains Chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons (CAHs), which pose a threat to both the environment and human health. Catalytic oxidation technology is recognized as one of the most effective methods for removing CAHs due to its high removal rate, low energy consumption, and minimal secondary pollution. This paper systematically introduces common catalyst types, including noble metal catalysts, transition metal oxide catalysts, and molecular sieve catalysts, and compares their respective advantages and drawbacks. Furthermore, the mechanism of catalytic oxidation reactions, causes of catalyst deactivation, and regeneration methods are discussed, with an emphasis on the significant impact of catalyst components, structures, supports, and preparation methods on catalyst activity. Finally, based on existing research, the prospects of catalytic oxidation of CAHs are examined. Future research should focus on optimizing catalyst design, enhancing reaction efficiency, and applying the technique to the practical treatment of incineration flue gas. -

-
图 2 催化CAHs氧化的动力学模型
Figure 2. Kinetic models of catalytic CAHs oxidations[123]
表 1 贵金属催化剂用于催化氧化CAHs的研究
Table 1. Research on noble metal catalysts for catalytic oxidation of CAHs
催化剂
CatalystsCAHs污染物
CAHs pollutants转化温度/℃
Conversion temperature转化率/%
Conversion efficiency参考文献
References钌基催化剂 Ru/TiO2 CB 287 90 [15] Ru/Fe1Mn2 197 90 [16] Ru-CeO2,Ru/CeO2-r 250—280 90 [21 − 22] 0.4Ru-1.0Ce/TiO2,Ru/Ti–CeO2 180—250 90—95 [18, 23] Ru/TiCeOx o-DCB 305 90 [20] 铂基催化剂 Pt/γ-Al2O3 CB 210—225 50 [24 − 25] 2Pt- Al-PILC 321 50 [26] PtHFAU(5) 350 95 [27] Pt/CeO-ZrO2 350 97 [28] Pt-110Mn 290 90 [19] 钯基催化剂 Pd/Co-HMOR o-DCB 500 100 [17] 表 2 过渡金属氧化物催化剂用于催化氧化CAHs的研究
Table 2. Research on transition metal catalysts for catalytic oxidation of CAHs
催化剂
CatalystsCAHs污染物
CAHs
pollutants转化温度/℃
Conversion
temperature转化率/%
Conversion
efficiency参考文献
References铈基催化剂 VOx/CeO2 CB 307—325 90 [36, 38] HSiW/CeO2 283 90 [39] MnOx-CeO2,CuO-MnOx-CeO2 236—336 90—100 [40 − 45] ACeOx (A = Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Zr) 328 99 [46] 2.4W/CeO2 CB/o-DCB 339 90 [31] 铈基催化剂 Co3O4-CeO2 1,2,4-TCB 300 96 [47] FexOy-CeO2 HCB 300 100 [48] 钛基催化剂 V2O5/TiO2,TiV10,TiV10Mo,TiV10W,
V2O5-WOx/TiO2CB 247—300 50—100 [49 − 53] CeMn/Ti-400, Ce0.5Ti0.5 198—375 90 [54 − 55] MnOx/TiO2 150—296 90—95 [56 − 57] V2O5/TiO2,V2O5/TiO2-SiO2 DCB 200—400 80—100 [58 − 65] Cr0.1Ti0.9 304 95 [66] MnCe/Ti 275 100 [67] V2O5/TiO2 1,3,5-TCB,1,2,3,4-TeCB,PeCB,HCB,2,3-DCDD,
2-MCDD300—400 25—85 [49, 58] V2O5-TiO2,V2O5-WO3/TiO2,Ce-VxOy/TiO2,
V2O5-CeO2/TiO2PCDD/Fs 180—280 73—98 [68 − 74] V2O5-WO3/TiO2 PCBs 300 98 [75] 锰基催化剂 Fe1Mn1 CB 197 90 [34] CM-R 388 90 [37] LaMnO3,La0.8Sr0.2MnO3,La0.8MnO3 291—410 90 [76] 30Cu/MnOx 290 90 [77] Co9Mn1 o-DCB 347 90 [29] CuO/MnxOy HCB 230 80 [78] Mn-Ce-Mg/Al2O3 315 90 [79] MnxCey/Al2O3 338 100 [80] 铁基催化剂 LaMn0.8Fe0.2O3 CB 500 90 [76] Mn-Ce-Fe DCB 350 98 [81] CaCO3/α-Fe2O3 450 100 [82] CaO/α-Fe2O3 HCB 300 99 [83 − 84] FexOy 300 100 [85] MgFe2O4/Fe3O4 300 100 [86] NiFe2O4 PCBs 300 96 [87] 其他催化剂 Mn-Ce-Zr CB 326 90 [30] CoCr 242 90 [32] LaMn0.8Al0.2O3 380 90 [76] Mn(x)-CeLa 229—279 90 [35, 88] CrCe/Ti-PILC,CrCe(5:1)/AlFe-PILC,MnCe(9:1)/AlZr-PILC 250—290 100 [89 − 91] Mn-Co-Ce-cordierite 325 90 [92] WO3-Nb2O5 350 90 [93] Co3O4-A 310 90 [94] V2O5/TiO2-CNTs,MnOx/TiO2-CNTs,CuOx/CNTs CB,DCB, PCDD/Fs 150—320 78—95 [95 − 98] CeSn/Ti6Zr4Ox o-DCB 343 90 [33] 15CM/TS-1.5 360 100 [99] Fe/AC PCBs 350 100 [100] CuAl2O4, CuxMg1−xAl2O4 HCB,OCDD 300—350 85—99 [101 − 102] γ-Al2O3,La2O3 (MgO,CaO,BaO,La2O3,CeO2,MnO2,Fe2O3,Co3O4)/Al2O3 HCB 300 30—100 [103 − 104] 表 3 分子筛催化剂用于催化氧化CAHs的研究
Table 3. Research on molecular sieve metal catalysts for catalytic oxidation of CAHs
催化剂
CatalystsCAHs污染物
CAHs pollutants转化温度/℃
Conversion temperature转化率/%
Conversion efficiency参考文献
ReferencesCuCe(6:1)/MCM-41 CB 262 100 [105] MnCo (6:1)/MCM-41 270 90 [106] Mn3/KIT-6 211 90 [107] Ce3-Co6/HMS 440 90 [108] Pt0.5Ru0.5/m-HZ 234 50 [110] MnxCe1-xO2/HZSM-5,Mn0.8Ce0.2O2/HZSM-5 230 90 [14, 111] CNH 222 90 [112] Pd/ZSM-5(25) o-DCB 474 90 [109] -
[1] TANG J, MA S T, LIU R R, et al. The pollution profiles and human exposure risks of chlorinated and brominated PAHs in indoor dusts from e-waste dismantling workshops: Comparison of GC-MS, GC-MS/MS and GC×GC-MS/MS determination methods[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 394: 122573. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122573 [2] 刘国瑞, 郑明辉. 非故意产生的持久性有机污染物的生成和排放研究进展[J]. 中国科学:化学, 2013, 43(3): 265-278. doi: 10.1360/032013-12 LIU G R, ZHENG M H. Progress in the studies associated with formation and emission of unintentionally produced persistent organic pollutants[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica), 2013, 43(3): 265-278 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/032013-12
[3] AKAI S, HAYAKAWA K, TAKATSUKI H, et al. Dioxin-like PCBs released from waste incineration and their deposition flux[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(18): 3601-3607. [4] KATAMI T, YASUHARA A, OKUDA T, et al. Formation of PCDDs, PCDFs, and coplanar PCBs from polyvinyl chloride during combustion in an incinerator[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(6): 1320-1324. [5] YIN J J, ZHANG W, ZHANG D M, et al. Electrochemical degradation of chlorobenzene on conductive-diamond electrode[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2016, 68: 71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.06.005 [6] CHENG Z W, LI C, KENNES C, et al. Improved biodegradation potential of chlorobenzene by a mixed fungal-bacterial consortium[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 123: 276-285. [7] WANG B, ZHANG C P, LI S Y, et al. An approach to biodegradation of chlorobenzenes: Combination of Typha angustifolia and bacterial effects on hexachlorobenzene degradation in water[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2016, 74(6): 1409-1416. doi: 10.2166/wst.2016.313 [8] NAGARAJU P, PUTTAIAH S H, WANTALA K, et al. Preparation of modified ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of chlorobenzene[J]. Applied Water Science, 2020, 10(6): 137. doi: 10.1007/s13201-020-01228-w [9] ZHU Q, YAN J R, DAI Q G, et al. Ethylene glycol assisted synthesis of hierarchical Fe-ZSM-5 nanorods assembled microsphere for adsorption Fenton degradation of chlorobenzene[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 385: 121581. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121581 [10] SVISHCHEV I M, PLUGATYR A. Supercritical water oxidation of o-dichlorobenzene: Degradation studies and simulation insights[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2006, 37(1): 94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2005.08.005 [11] VIN N, BATTIN-LECLERC F, Le GALL H, et al. A study of chlorobenzene pyrolysis[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(1): 399-407. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.05.067 [12] EVERAERT K, BAEYENS J. Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2004, 109(1/2/3): 113-139. [13] FINOCCHIO E, BUSCA G, NOTARO M. A review of catalytic processes for the destruction of PCDD and PCDF from waste gases[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2006, 62(1/2): 12-20. [14] WENG X L, SUN P F, LONG Y, et al. Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over Mn xCe1– xO2/HZSM-5 catalysts: A study with practical implications[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(14): 8057-8066. [15] LIU X L, CHEN L, ZHU T Y, et al. Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over noble metals (Pd, Pt, Ru, Rh) and the distributions of polychlorinated by-products[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 363: 90-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.074 [16] WANG G, WANG Y, QIN L B, et al. Efficient and stable degradation of chlorobenzene over a porous iron-manganese oxide supported ruthenium catalyst[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2020, 10(21): 7203-7216. [17] CANO M, GUARÍN F, ARISTIZÁBAL B, et al. Catalytic activity and stability of Pd/Co catalysts in simultaneous selective catalytic reduction of NOx with methane and oxidation of o-dichlorobenzene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 296: 105-117. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.05.049 [18] LIANG W J, ZHU Y X, REN S D, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene at low temperature over Ru-Ce/TiO2: High activity and high selectivity[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2021, 623: 118257. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118257 [19] CHEN G, CAI Y P, ZHANG H, et al. Pt and Mo co-decorated MnO2 nanorods with superior resistance to H2O, sintering, and HCl for catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(20): 14204-14214. [20] WU S L, ZHAO H J, DONG F, et al. Construction of superhydrophobic Ru/TiCeO x catalysts for the enhanced water resistance of o-dichlorobenzene catalytic combustion[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(2): 2610-2621. [21] DAI Q G, BAI S X, WANG Z Y, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over Ru-doped ceria catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 126: 64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.07.008 [22] HUANG H, DAI Q G, WANG X Y. Morphology effect of Ru/CeO2 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 158/159: 96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.062 [23] DAI Q G, BAI S X, WANG J W, et al. The effect of TiO2 doping on catalytic performances of Ru/CeO2 catalysts during catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 142/143: 222-233. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.026 [24] van den BRINK R W, MULDER P, LOUW R. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene on Pt/γ-Al2O3 in the presence of aliphatic hydrocarbons[J]. Catalysis Today, 1999, 54(1): 101-106. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00172-8 [25] van den BRINK R W, LOUW R, MULDER P. Increased combustion rate of chlorobenzene on Pt/γ-Al2O3 in binary mixtures with hydrocarbons and with carbon monoxide[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2000, 25(4): 229-237. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(99)00137-X [26] AZNÁREZ A, DELAIGLE R, ELOY P, et al. Catalysts based on pillared clays for the oxidation of chlorobenzene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 246: 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.07.024 [27] TARALUNGA M, MIJOIN J, MAGNOUX P. Catalytic destruction of chlorinated POPs—Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over PtHFAU catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2005, 60(3/4): 163-171. [28] TOPKA P, DELAIGLE R, KALUŽA L, et al. Performance of platinum and gold catalysts supported on ceria-zirconia mixed oxide in the oxidation of chlorobenzene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 253: 172-177. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.02.032 [29] CAI T, HUANG H, DENG W, et al. Catalytic combustion of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene at low temperature over Mn-modified Co3O4 catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 166/167: 393-405. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.047 [30] LONG G Y, CHEN M X, LI Y J, et al. One-pot synthesis of monolithic Mn-Ce-Zr ternary mixed oxides catalyst for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 360: 964-973. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.091 [31] GU Y F, CAI T, GAO X H, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorinated aromatics over WO x/CeO2 catalysts at low temperature[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 248: 264-276. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.055 [32] DENG W, TANG Q X, HUANG S S, et al. Low temperature catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over cobalt based mixed oxides derived from layered double hydroxides[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 278: 119336. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119336 [33] WU S L, ZHAO H J, TANG Z C, et al. Controlled synthesis of ordered mesoporous TiO2-ZrO2 supported CeSn oxides catalyst for the elimination of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 302: 110214. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110214 [34] WANG Y, WANG G, DENG W, et al. Study on the structure-activity relationship of Fe-Mn oxide catalysts for chlorobenzene catalytic combustion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 395: 125172. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125172 [35] DAI Y, WANG X Y, LI D, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over Mn-Ce-La-O mixed oxide catalysts[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 188(1/2/3): 132-139. [36] HUANG H, GU Y F, ZHAO J, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over VO x/CeO2 catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 326: 54-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.02.016 [37] WANG Y, DENG W, WANG Y F, et al. A comparative study of the catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene and toluene over Ce-Mn oxides[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2018, 459: 61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.08.022 [38] SHI Q, LONG H M, CHUN T J, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene with VOx/CeO2 catalysts: Influence of catalyst synthesis method[J]. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 2019, 17(12): 20190084. [39] ZHANG X J, WEI Y H, SONG Z X, et al. Silicotungstic acid modified CeO2 catalyst with high stability for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 128129. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128129 [40] SONG Z J, YU S X, LIU H, et al. Carbon/chlorinate deposition on MnO x-CeO2 catalyst in chlorobenzene combustion: The effect of SCR flue gas[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133552. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133552 [41] WU L Y, HE F, LUO J Q, et al. Synthesis of three-dimensional ordered mesoporous MnO x/CeO2 bimetal oxides for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(43): 26952-26959. doi: 10.1039/C7RA02299A [42] WANG X Y, KANG Q, LI D. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over MnOx-CeO2 mixed oxide catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2009, 86(3/4): 166-175. [43] WANG X Y, KANG Q, LI D. Low-temperature catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over MnO x-CeO2 mixed oxide catalysts[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2008, 9(13): 2158-2162. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2008.04.021 [44] HE C, MEN G S, YU Y K, et al. Chlorobenzene destruction over mesostructured CuO and MnOx co-modified CeO2 catalyst: Activity and activation route[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2015, 226(3): 57. [45] HE C, YU Y K, SHEN Q, et al. Catalytic behavior and synergistic effect of nanostructured mesoporous CuO-MnO x-CeO2 catalysts for chlorobenzene destruction[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 297: 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.01.076 [46] HE C, XU B T, SHI J W, et al. Catalytic destruction of chlorobenzene over mesoporous ACeO x (a = Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, or Zr) composites prepared by inorganic metal precursor spontaneous precipitation[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2015, 130: 179-187. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.10.008 [47] LIN S J, SU G J, ZHENG M H, et al. Synthesis of flower-like Co3O4-CeO2 composite oxide and its application to catalytic degradation of 1, 2, 4-trichlorobenzene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 123/124: 440-447. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.011 [48] JIA M K, SU G J, ZHENG M H, et al. Synthesis of a magnetic micro/nano Fe xO y-CeO2 composite and its application for degradation of hexachlorobenzene[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2010, 53(6): 1266-1272. doi: 10.1007/s11426-010-3164-3 [49] WANG J, WANG X, LIU X L, et al. Catalytic oxidation of chlorinated benzenes over V2O5/TiO2 catalysts: The effects of chlorine substituents[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 241: 92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.04.002 [50] WANG J, WANG X, LIU X L, et al. Kinetics and mechanism study on catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over V2O5/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2015, 402: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.03.003 [51] BERTINCHAMPS F, POLEUNIS C, GRÉGOIRE C, et al. Elucidation of deactivation or resistance mechanisms of CrOx, VOx and MnOx supported phases in the total oxidation of chlorobenzene via ToF-SIMS and XPS analyses[J]. Surface and Interface Analysis, 2008, 40(3/4): 231-236. [52] BERTINCHAMPS F, GRÉGOIRE C, GAIGNEAUX E M. Systematic investigation of supported transition metal oxide based formulations for the catalytic oxidative elimination of (chloro)-aromatics[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2006, 66(1/2): 1-9. [53] KHALEEL A, AL-NAYLI A. Supported and mixed oxide catalysts based on iron and titanium for the oxidative decomposition of chlorobenzene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2008, 80(1/2): 176-184. [54] HE F, CHEN Y, ZHAO P, et al. Effect of calcination temperature on the structure and performance of CeO x-MnO x/TiO2 nanoparticles for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2016, 18(5): 119. doi: 10.1007/s11051-016-3428-8 [55] DENG W, DAI Q G, LAO Y J, et al. Low temperature catalytic combustion of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene over CeO2-TiO2 mixed oxide catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 181: 848-861. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.053 [56] TIAN W, FAN X Y, YANG H S, et al. Preparation of MnO x/TiO2 composites and their properties for catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177(1/2/3): 887-891. [57] LUO J Q, HE F, LIU S T. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over core-shell Mn/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2017, 24(3): 821-828. doi: 10.1007/s10934-016-0321-x [58] LEE J E, JURNG J. Catalytic conversions of polychlorinated benzenes and dioxins with low-chlorine using V2O5/TiO2[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2008, 120(3): 294-298. [59] LICHTENBERGER J. Catalytic oxidation of chlorinated benzenes over V2O5/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2004, 223(2): 296-308. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2004.01.032 [60] LICHTENBERGER J, AMIRIDIS M D. Deactivation of V2O5/TiO2 catalysts during the oxidation of meta-dichlorobenzene in the presence of methyl-naphthalene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2004, 98(3): 447-453. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2004.08.001 [61] HETRICK C E, PATCAS F, AMIRIDIS M D. Effect of water on the oxidation of dichlorobenzene over V2O5/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2011, 101(3/4): 622-628. [62] CHIN S, JURNG J, LEE J H, et al. Catalytic conversion of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene using V2O5/TiO2 catalysts by a thermal decomposition process[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 75(9): 1206-1209. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.02.015 [63] JUNG K Y, JUNG Y R, JEON J K, et al. Preparation of mesoporous V2O5/TiO2 via spray pyrolysis and its application to the catalytic conversion of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2011, 17(1): 144-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2010.12.013 [64] CHIN S, PARK E, KIM M, et al. Effect of the support material (TiO2) synthesis conditions in chemical vapor condensation on the catalytic oxidation for 1, 2-dichlorobenzene over V2O5/TiO2[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 217: 388-393. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2011.10.055 [65] CHEN N Y, YANG S C, LIU M C, et al. Pellet vanadia catalysts for oxidative destruction of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene: Roles of the grafted TiO2 in vanadia morphology and catalytic reaction[J]. Catalysis Surveys from Asia, 2015, 19(1): 38-56. doi: 10.1007/s10563-015-9184-4 [66] SUN W, GONG B W, PAN J, et al. Catalytic combustion of CVOCs over Cr xTi1- x oxide catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 391: 132-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2020.08.007 [67] LIN F, WANG Q L, HUANG X N, et al. Investigation of chlorine-poisoning mechanism of MnO x/TiO2 and MnO x-CeO2/TiO2 catalysts during o-DCBz catalytic decomposition: Experiment and first-principles calculation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 298: 113454. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113454 [68] JI S S, LI X D, REN Y, et al. Ozone-enhanced oxidation of PCDD/Fs over V2O5-TiO2-based catalyst[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(3): 265-272. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.087 [69] DEBECKER D P, DELAIGLE R, HUNG P C, et al. Evaluation of PCDD/F oxidation catalysts: Confronting studies on model molecules with tests on PCDD/F-containing gas stream[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 82(9): 1337-1342. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.007 [70] YU M F, LIN X Q, LI X D, et al. Catalytic destruction of PCDD/Fs over vanadium oxide-based catalysts[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(16): 16249-16258. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6807-x [71] WEBER R, SAKURAI T, HAGENMAIER H. Low temperature decomposition of PCDD/PCDF, chlorobenzenes and PAHs by TiO2-based V2O5-WO3 catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 1999, 20(4): 249-256. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(98)00115-5 [72] YANG C C, CHANG S H, HONG B Z, et al. Innovative PCDD/F-containing gas stream generating system applied in catalytic decomposition of gaseous dioxins over V2O5-WO3/TiO2-based catalysts[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 73(6): 890-895. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.027 [73] CHEN Y, WU Q, LIU K R. Dual degradation of gaseous 1, 2-dichlorobenzene and PCDD/Fs using Ce doped V xO y/TiO2 immobilized on cordierite[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 154: 472-481. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.012 [74] YU M F, LIN X Q, YAN M, et al. Low temperature destruction of PCDD/Fs over V2O5-CeO2/TiO2 catalyst with ozone[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(17): 17563-17570. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6955-z [75] WEBER R, SAKURAI T. Low temperature decomposition of PCB by TiO2-based V2O5/WO3 catalyst: Evaluation of the relevance of PCDF formation and insights into the first step of oxidative destruction of chlorinated aromatics[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2001, 34(2): 113-127. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(01)00211-9 [76] LU Y J, DAI Q G, WANG X Y. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene on modified LaMnO3 catalysts[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2014, 54: 114-117. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2014.05.018 [77] CHEN X, HE F, LIU S T. CuO/MnO x composites obtained from Mn-MIL-100 precursors as efficient catalysts for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 2020, 130(2): 1063-1076. doi: 10.1007/s11144-020-01816-6 [78] YANG Y, HUANG J, ZHANG S Z, et al. Catalytic removal of gaseous HCBz on Cu doped OMS: Effect of Cu location on catalytic performance[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 150/151: 167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.11.041 [79] WU M, WANG X Y, DAI Q G, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over Mn-Ce/Al2O3 catalyst promoted by Mg[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2010, 11(12): 1022-1025. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2010.04.011 [80] WU M, WANG X Y, DAI Q G, et al. Low temperature catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over Mn-Ce-O/γ-Al2O3 mixed oxides catalyst[J]. Catalysis Today, 2010, 158: 336-342. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.04.006 [81] TANG A D, HU L Q, YANG X H, et al. Promoting effect of the addition of Ce and Fe on manganese oxide catalyst for 1, 2-dichlorobenzene catalytic combustion[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 82: 41-45. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.04.015 [82] MA X D, SUN Q, FENG X, et al. Catalytic oxidation of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene over CaCO3/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2013, 450: 143-151. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.10.019 [83] MA X D, ZHENG M H, LIU W B, et al. Synergic effect of calcium oxide and iron(Ⅲ) oxide on the dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene[J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 60(6): 796-801. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.04.021 [84] MA X D, SUN H W, HE H, et al. Competitive reaction during decomposition of hexachlorobenzene over ultrafine Ca-Fe composite oxide catalyst[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2007, 119(1): 142-147. [85] JIA M K, SU G J, ZHENG M H, et al. Development of self-assembled 3D Fe xO y micro/nano materials for application in hexachlorobenzene degradation[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2011, 11(3): 2100-2106. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2011.3121 [86] SU G J, LIU Y X, HUANG L Y, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical Mg-doped Fe3O4 micro/nano materials for the decomposition of hexachlorobenzene[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 99: 216-223. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.090 [87] HUANG L Y, SU G J, ZHANG A Q, et al. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls using mesoporous iron-based spinels[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 451-462. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.064 [88] WANG X Y, RAN L, DAI Y, et al. Removal of Cl adsorbed on Mn-Ce-La solid solution catalysts during CVOC combustion[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2014, 426: 324-332. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.10.007 [89] FENG B B, WEI Y X, QIU Y N, et al. Ce-modified AlZr pillared clays supported-transition metals for catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2018, 36(11): 1169-1174. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2018.03.026 [90] QIU Y N, YE N, SITU D N, et al. Study of catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene and temperature programmed reactions over CrCeOx/AlFe pillared clay catalysts[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(5): 728. doi: 10.3390/ma12050728 [91] ZUO S F, DING M L, TONG J, et al. Study on the preparation and characterization of a titanium-pillared clay-supported CrCe catalyst and its application to the degradation of a low concentration of chlorobenzene[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2015, 105/106: 118-123. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.12.033 [92] KAN J W, DENG L, LI B, et al. Performance of co-doped Mn-Ce catalysts supported on cordierite for low concentration chlorobenzene oxidation[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2017, 530: 21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2016.11.013 [93] TAO H Y, LI J, MA Q Y, et al. Synthesis of W-Nb-O solid acid for catalytic combustion of low-concentration monochlorobenzene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 123045. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123045 [94] LI Y, CHEN J, HU Z Y, et al. A facile method to synthesize Co3O4 catalyst for efficient chlorobenzene combustion[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2022, 7(17): e202200481. doi: 10.1002/slct.202200481 [95] NIE A M, YANG H S, LI Q A, et al. Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over V2O5/TiO2–carbon nanotubes composites[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(17): 9944-9948. [96] TIAN W, YANG H S, FAN X Y, et al. Low-temperature catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over MnO X/TiO2-CNTs nano-composites prepared by wet synthesis methods[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2010, 11(15): 1185-1188. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2010.06.010 [97] DU C C, WANG Q L, PENG Y Q, et al. Catalytic oxidation of 1, 2-DCBz over V2O5/TiO2-CNTs: Effect of CNT diameter and surface functional groups[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(5): 4894-4901. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8075-1 [98] WANG Q L, HUNG P C, LU S Y, et al. Catalytic decomposition of gaseous PCDD/Fs over V2O5/TiO2-CNTs catalyst: Effect of NO and NH3 addition[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 159: 132-137. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.072 [99] ZHAO H J, HAN W L, DONG F, et al. Highly-efficient catalytic combustion performance of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene over mesoporous TiO2-SiO2 supported CeMn oxides: The effect of acid sites and redox sites[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 64: 194-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2018.03.016 [100] SUN Y F, TAKAOKA M, TAKEDA N, et al. Kinetics on the decomposition of polychlorinated biphenyls with activated carbon-supported iron[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 65(2): 183-189. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.009 [101] FAN Y, LU X B, NI Y W, et al. Destruction of polychlorinated aromatic compounds by spinel-type complex oxides[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(8): 3079-3084. [102] FAN Y, LU X B, NI Y W, et al. Catalytic destruction of chlorinated aromatic pollutants over mesoporous Cu xMg1− xAl2O4 spinel oxides[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2011, 101(3/4): 606-612. [103] ZHANG L F, ZHENG M H, LIU W B, et al. A method for decomposition of hexachlorobenzene by gamma-alumina[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 150(3): 831-834. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.037 [104] ZHANG L F, ZHENG M H, ZHANG B, et al. Decomposition of hexachlorobenzene over Al2O3 supported metal oxide catalysts[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20(12): 1523-1526. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62560-7 [105] ZHENG J, CHEN Z, FANG J F, et al. MCM-41 supported nano-sized CuO-CeO2 for catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(9): 933-940. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2019.06.005 [106] CHENG Z, LI J R, YANG P, et al. Preparation of MnCo/MCM-41 catalysts with high performance for chlorobenzene combustion[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 39(4): 849-856. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(17)62950-4 [107] HE F, LUO J Q, LIU S T. Novel metal loaded KIT-6 catalysts and their applications in the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 294: 362-370. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.068 [108] ZHAO W, CHENG J, WANG L N, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene on the Ln modified Co/HMS[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 127: 246-254. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.08.019 [109] LI N, CHENG J, XING X, et al. Distribution and formation mechanisms of polychlorinated organic by-products upon the catalytic oxidation of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene with palladium-loaded catalysts[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 393: 122412. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122412 [110] WANG Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG L, et al. Total catalytic oxidation of chlorinated aromatics over bimetallic Pt-Ru supported on hierarchical HZSM-5 zeolite[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 308: 110538. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110538 [111] SUN P F, WANG W L, DAI X X, et al. Mechanism study on catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over Mn xCe1- xO2/H-ZSM5 catalysts under dry and humid conditions[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 198: 389-397. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.076 [112] SUN P F, CHEN J K, ZAI S Y, et al. Regeneration mechanism of a deactivated zeolite-supported catalyst for the combustion of chlorinated volatile organic compounds[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, 11(3): 923-933. [113] van den BRINK R W, KRZAN M, FEIJEN-JEURISSEN M M R, et al. The role of the support and dispersion in the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene on noble metal based catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2000, 24(3/4): 255-264. [114] DU C C, LU S Y, WANG Q L, et al. A review on catalytic oxidation of chloroaromatics from flue gas[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 519-544. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.018 [115] GU Y F, SHAO S J, SUN W, et al. The oxidation of chlorinated organic compounds over W-modified Pt/CeO2 catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 380: 375-386. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2019.06.041 [116] SHI Q, DING L, LONG H M, et al. Low-temperature catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over CeOx-VOx/TiO2-graphene oxide catalysts[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2022, 152(12): 3617-3631. doi: 10.1007/s10562-022-03932-5 [117] JIA H Q, XING Y, ZHANG L G, et al. Progress of catalytic oxidation of typical chlorined volatile organic compounds (CVOCs): A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 865: 161063. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161063 [118] BURGOS N, PAULIS M, MIRARI ANTXUSTEGI M, et al. Deep oxidation of VOC mixtures with platinum supported on Al2O3/Al monoliths[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2002, 38(4): 251-258. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(01)00294-6 [119] SU Y, FU K X, PANG C H, et al. Recent advances of chlorinated volatile organic compounds' oxidation catalyzed by multiple catalysts: Reasonable adjustment of acidity and redox properties[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(14): 9854-9871. [120] ZHANG Z X, JIANG Z, SHANGGUAN W F. Low-temperature catalysis for VOCs removal in technology and application: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Catalysis Today, 2016, 264: 270-278. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.10.040 [121] DAI Y, WANG X Y, DAI Q G, et al. Effect of Ce and La on the structure and activity of MnO x catalyst in catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 111/112: 141-149. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.09.028 [122] DAI X X, WANG X W, LONG Y P, et al. Efficient elimination of chlorinated organics on a phosphoric acid modified CeO2 catalyst: A hydrolytic destruction route[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(21): 12697-12705. [123] KIM H S, KIM H J, KIM J H, et al. Noble-metal-based catalytic oxidation technology trends for volatile organic compound (VOC) removal[J]. Catalysts, 2022, 12(1): 63. doi: 10.3390/catal12010063 [124] de JONG V, CIEPLIK M K, LOUW R. Formation of dioxins in the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene and a micropollutant-like mixture on Pt/gamma-Al2O3[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(19): 5217-5223. [125] TARALUNGA M, INNOCENT B, MIJOIN J, et al. Catalytic combustion of benzofuran and of a benzofuran/1, 2-dichlorobenzene binary mixture over zeolite catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2007, 75(1/2): 139-146. [126] LIN F W, XIANG L, ZHANG Z M, et al. Comprehensive review on catalytic degradation of Cl-VOCs under the practical application conditions[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 52: 311-355. [127] HASHEMIKIA S, MONTAZER M. Sodium hypophosphite and nano TiO2 inorganic catalysts along with citric acid on textile producing multi-functional properties[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2012, 417/418: 200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.12.041 [128] ZHANG Z, HUANG J, XIA H Q, et al. Chlorinated volatile organic compound oxidation over SO42−/Fe2O3 catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 360: 277-289. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.11.024 [129] YANG S, ZHAO H J, DONG F, et al. Highly efficient catalytic combustion of o-dichlorobenzene over three-dimensional ordered mesoporous cerium manganese bimetallic oxides: A new concept of chlorine removal mechanism[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2019, 463: 119-129. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.12.006 [130] HASHIMOTO Y, UEMICHI Y, AYAME A. Low-temperature hydrodechlorination mechanism of chlorobenzenes over platinum-supported and palladium-supported alumina catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2005, 287(1): 89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2005.03.039 [131] HATJE U, HAGELSTEIN M, FÖRSTER H. XAS studies on the interaction of with PtY and PdY zeolites[J]. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, 1994, 84: 773-780. [132] van den BRINK R W, LOUW R, MULDER P. Formation of polychlorinated benzenes during the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene using a Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 1998, 16(3): 219-226. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(97)00076-3 [133] YANG Y, HUANG J, WANG S W, et al. Catalytic removal of gaseous unintentional POPs on manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 142/143: 568-578. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.048 [134] HE F, JIAO Y M, WU L Y, et al. Enhancement mechanism of Sn on the catalytic performance of Cu/KIT-6 during the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(21): 6114-6123. [135] DAI Q G, BAI S X, WANG X Y, et al. Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over Ru-doped ceria catalysts: Mechanism study[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 129: 580-588. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.10.006 [136] JI L J, CAO X, LU S Y, et al. Catalytic oxidation of PCDD/F on a V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst: Effect of chlorinated benzenes and chlorinated phenols[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.020 [137] ZHU B W, LIM T T. Catalytic reduction of chlorobenzenes with Pd/Fe nanoparticles: Reactive sites, catalyst stability, particle aging, and regeneration[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(21): 7523-7529. [138] BERTINCHAMPS F, ATTIANESE A, MESTDAGH M M, et al. Catalysts for chlorinated VOCs abatement: Multiple effects of water on the activity of VO x based catalysts for the combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2006, 112(1/2/3/4): 165-168. -



 下载:
下载: