-
六溴环十二烷(HBCDs)是继多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)和四溴双酚A(TBBPA)之外的全球第三大溴代阻燃剂[1],主要应用于建筑、纺织、电子等行业,作为添加剂加入到发泡聚苯乙烯泡沫塑料(EPS)、挤塑聚苯乙烯泡沫塑料及其阻燃微粒材料中. 2001年,HBCDs全球使用量达16700 t,2006年增至21591 t,2011年达到31000 t,我国作为HBCDs的主要生产国,每年的产量约18000 t. 根据欧洲化学品管理局,每年大约有3141 kg的HBCDs释放到环境中,其中50%存在于废水中,29%进入地表水,21%排放到空气中. HBCDs具有半挥发性、环境持久性、远距离迁移性等特性,使其在各种环境介质中被广泛检出,在2013年,HBCDs被列入斯德哥尔摩公约受控名单[2],我国也于2017年将其列入《优先控制化学品名录(第一批)》. 尽管很多国家禁止或限制HBCDs的使用,但为了给行业足够的时间寻找替代品,HBCDs仍要继续使用到2024年[3],因此其对生态环境及人类健康的不利影响还将持续很长时间.
HBCDs具有6个立体中心,理论上可以形成16种立体异构体. 商用HBCDs主要含有α-、β-和γ-HBCDs等3种异构体,每种异构体含有一对对映体[4]. 不同构型的HBCDs经历生物化学过程时,其异构体或对映体可能发生不同的行为,产生不同的生物学效应和环境效应[5-8]. 与β-和γ-HBCDs相比,α-HBCD具有较高的溶解度和较低的辛醇-水分配系数(lgKow),高温热重排混合物中α-HBCD占比较高[9];在厌氧条件下,α-HBCD的降解速率比γ-HBCD慢[10];高温和日光催化下均可发生γ-HBCD向α-HBCD异构体的转化[11]. 大量研究也发现在生物体中α-HBCD为主要存在的异构体,在适当的条件下,对映体之间亦可发生异构化行为,在玉米根中就曾检测到(±)-β-和(±)-γ-HBCDs向(-)-α-HBCD的对映体选择性转化,其中(-)-γ-HBCD转化率较高[12].
作为疏水型脂肪族溴代阻燃剂,HBCDs易通过挥发、渗出等方式释放到环境中[13]. 1997年,Sellstrom等[14]首次在瑞典河流中检测到HBCDs,之后HBCDs在不同的非生物介质(大气[15]、灰尘[16]、地表水[17]、沉积物[18]和土壤[19]等)中被广泛检出,甚至北极地区也发现了HBCDs的存在[20]. 随之,在生物体(鱼[21]、鸟[22]、植物[23]、小龙虾[24]、牡蛎[25]、蚯蚓[26]、胎盘[27]及母乳[28]等)及食物链中的HBCDs也引起了国内外学者的广泛研究. 目前,关于HBCDs在环境中的富集迁移及动物毒理学研究报道较多[21,29-35],但其在植物中的研究十分有限[36-38]. 有机污染物的植物吸收、累积、转化及毒性研究对于认识其迁移行为、评价其在生态系统的污染风险及其对食物链的潜在危害均有重要意义. 植物是生物圈的重要组成部分,通过呼吸作用及根系的吸收从空气和土壤中获得养分的同时,也会对包括HBCDs在内的污染物进行富集,并通过食物链逐级放大,进而对人类健康及生态安全产生影响. 不同HBCDs异构体和对映体会被陆生[39-42]和水生植物[37,43]吸收富集,在转运和代谢等生理过程中发生选择性降解和构型转化[5,44],从而改变HBCDs异构体和对映体的组成比例,目前植物中关于对映体水平的污染检测研究还很匮乏. HBCDs进入植物体后会对其生长发育产生抑制[45],破坏植物体内氧化平衡,诱导过量活性氧(ROS)产生[45],改变DNA结构,产生基因水平损伤[46]等. 目前关于植物中HBCDs的研究多关注α-、β-和γ-HBCDs,其它异构体很少在环境植物中被检出,也未见其它异构体对植物毒性效应的相关研究. Huang等[42]曾在中国北方塑料垃圾回收地土壤中检测到较低水平的δ-和ε-HBCDs,而在同位点的植物中则均未见检出. 总之,植物中HBCDs的相关研究还需不断探索. 本文对HBCDs的植物提取与分析方法、植物污染现状、传输行为和植物降解以及HBCDs的植物毒性效应进行梳理和分析,并展望了未来的研究方向,为综合评价HBCDs的生物有效性、健康风险评价及环境修复提供科学依据.
-
植物中含有多种干扰物质,如色素、纤维素和水等,因此样品前处理过程非常重要,关系到所得数据的准确性和有效性. 目前环境样品中HBCDs的前处理方法主要包括:索氏提取法[19,23,39-43]、加速溶剂萃取法(ASE)[37]和超声波提取法[47-48](表1).
目前采用索氏提取法处理植物中HBCDs的报道最多,多数研究常用丙酮-正己烷作为提取剂,但因提取剂的比例和提取时间的长短不同,提取率也存在差异,Lü 等[23]、Zhang等[39]和Zhu等[19]使用丙酮-正己烷(1:1,V:V)分别提取了蔬菜和小麦、胡萝卜、芦苇以及冬青、侧柏、马尾松中的HBCDs,提取24 h,提取率分别为93%—128%、76.2%—102.4%和77%—101.1%;Zhu等[40]和Li等[43]分别提取了3种红树林植物和松针中的HBCDs,提取48 h,提取率分别为81.8%—116.6%和77%—101.1%;Hu等[41]提取了树皮中的HBCDs,提取36 h后,加标回收率为61%—86%,也有研究[42]使用正己烷-二氯甲烷(1:1,V:V)为提取剂提取植物中的HBCDs,在65 ℃下提取24 h,5种HBCDs异构体(α-、β-、γ-、δ-和ε-HBCDs)的加标回收率分别为92.6%±9.5%、90.3%±10.5%、88.5%±12.6%、92.6%±10.9%和89.5%±11.8%. 索氏提取法提取成本低,方法简单,但需较长提取时间(>8 h)才能达到较高的提取率. 相比而言,ASE法具有提取时间短、提取剂用量少、回收率高的优点. Li等[37]采用ASE法提取了柏树、芦苇、碱蓬草中的HBCDs,130 ℃下吹扫120 s静置8 min,回收率达到83.5%;Zhu等[49]采用ASE法提取了苔藓、地衣中的HBCDs,两种植物中13C-HBCDs的平均加标回收率分别为83%±16%和93%±14%. 由于设备昂贵,目前采用ASE提取植物中HBCDs的研究还相对较少. 超声波提取法亦具有提取效率高、提取时间短等优点,且操作装置简单,但有研究[50]表明,超声温度过高时,提取剂出现挥发现象,携带提取物质流出,造成损失,另外超声时间过长可能会造成HBCDs降解. 武等[47]使用乙酸乙酯作为提取剂提取了7种陆生植物中的HBCDs,超声提取2次,每次50 min,13C-HBCDs加标回收率为79.0%—81.3%;Zhang等[48]使用丙酮作为提取剂提取藻类中的HBCDs,超声处理10 min以破坏细胞壁促进提取,3种异构体的提取率分别为83%±3%、85%±5%和87%±4%;Kim等[51]使用正己烷-二氯甲烷(1:1,V:V)为提取剂提取了苔藓、地衣中的HBCDs,提取3次,每次30 min,3种异构体的平均回收率为55%、84%和72%;Wu等[45]使用乙酸乙酯提取了玉米中的HBCDs,60 ℃下超声提取2 h,提取率在79.9%—136%之间. 上述提取方法中采用的提取剂各有不同,溶剂配比亦有差异,总体均是选用与HBCDs极性相近,对其溶解度大,对杂质成分溶解度小的溶剂. 从提取效率看,除了溶剂的选择,提取温度和时间也有很大影响,导致各方法的提取率存在差异.
提取后的样品中一般含有复杂的干扰组分,提取液需要经过有效净化后才能进行仪器分析. 目前植物样品的净化方法主要为柱层析法,常用的净化柱有硅胶/氧化铝柱[42,51]、复合硅胶柱[20,37,43,47,49]以及成品活性硅胶柱[19,23,33,40,48],根据分析物的极性不同其在硅胶颗粒上停留时间产生差异而实现分离[52]. 硅胶/氧化铝柱和复合硅胶柱常用填料包括氧化铝、中性硅胶、酸性硅胶、碱性硅胶以及无水硫酸钠等. 氧化铝常用来去除植物中的色素,酸性硅胶用于去除植物中的脂质[19,33,43,49,53],中性硅胶对各种填料起到间隔作用,无水硫酸钠干燥有机相中残留的水分. 研究者往往会根据样品的实际情况来选择上述填料的种类、比例和容量,以达到有效净化的目的. 也有研究[19,23,33,40,48]使用成品活性硅胶柱对植物样品进行净化,多采用德国生产的CNWBOND HC-C18 SPE小柱(500 mg,3 mL/50 pcs),正己烷和丙酮依次进行洗脱,流程简单操作方便,大大减少实验用时,但由于价格昂贵,目前更多研究者[20,37,43,47,49]选择自制复合硅胶柱.
目前植物样品中HBCDs的仪器分析主要采用液相色谱-质谱联用法(LC-MS)[23,41,48]和液相色谱-串联质谱法(LC-MS/MS)[8,23,37,42,47,54-55],电喷雾负电离(ESI-)模式[19,38,40,47]进行测定,常用C18柱[23,37,39,41-43,48-49,51]和Nucleosil β-PM手性柱(德国,MN)[27,39-40,42-43,47,56]分别分离HBCDs异构体和对映体. Li等[43]使用HPLC-MS在XDB-C18柱对HBCDs异构体进行分析,甲醇:水(9:1,V:V)和乙腈为流动相进行梯度洗脱,ESI-源采用选择性反应监测模式(SRM)进行检测,成功实现了α-、β-和γ-HBCDs的基线分离. Zhu等[19]采用LC-MS/MS检测了天津市某EPS原料制造厂附近植物样品中HBCDs,选择在Nucleosil β-PM手性柱得到3对对映体浓度,阐述了HBCDs对映体的植物选择性富集行为. Huang等[42]采用UPLC-MS/MS,Waters Acquity C18柱和Nucleosil β-PM手性柱,分离检测了华北地区塑料垃圾回收场植物中的HBCDs异构体和对映体组成. 目前也有少量研究[57-58]使用气相色谱-质谱联用技术(GC-MS)在石英毛细管色谱柱上检测HBCDs. Salamova等[58]在GC-MS上,使用Rtx-1614熔融石英毛细管色谱柱,在电子捕获负电离源(ECNI),SIM模式下分析检测了全球14个地区树皮样本中的∑HBCDs含量,但在气相色谱分离和质谱定性和定量分析过程中会涉及到较高梯度升温和质子化温度,这将不利于手性构型的分析. 有研究表明,当温度达到160 ℃时,HBCDs的3种异构体间会相互转化,温度超过240 ℃时,HBCDs还会发生脱溴现象,因此,尽管GC-MS具有检出限低、精密度高、便捷有效等优点,但不能用于HBCDs对映体检测,无法全面分析HBCDs立体构型的污染状况. LC-MS可以有效分离HBCDs异构体和对映体,能够获得更多HBCDs在植物中的污染分布信息,该方法更有利于综合全面评估HBCDs的环境风险.
-
目前针对HBCDs生产工厂、电子垃圾拆解地、垃圾堆放场等典型污染源周边的植物污染已有诸多文献报道,通常情况下,生产或使用HBCDs的工厂附近植物中HBCDs浓度水平较高,比非点源或偏远地区环境中至少高出1个数量级以上. Li等[37]调查了莱州湾HBCDs生产基地附近柏树、芦苇和碱蓬草植物组织中的∑HBCDs,其浓度范围分别为80264—148957 ng·g−1 dw、8.88—160241 ng·g−1 dw和207—710 ng·g−1 dw. Zhu等[19]研究了EPS原料制造厂附近的植物中∑HBCDs分布时发现,冬青、柏树和松树叶组织中的浓度范围为3.45—2494 ng·g−1 dw,叶蜡中为126—101855 ng·g−1dw,枝条中为6.7—1049 ng·g−1 dw,树皮中为3.45—165 ng·g−1 dw,且在3种树种的不同组织中观察到显著的∑HBCDs浓度梯度(P<0.01),最高浓度出现在叶蜡中,其次是内叶和枝条,树皮中浓度最低,在L2点位采集的松树组织中,∑HBCDs浓度在松针蜡中高达101855 ng·g−1 dw,内叶中为2238 ng·g−1 dw,枝条中为1049 ng·g−1 dw,树皮中为165 ng·g−1 dw;同时天津市与莱州湾[37]的调查研究结果均显示,植物中∑HBCDs浓度会随距污染源中心距离的增加呈现快速降低趋势,并在1 km左右趋于稳定. 在远离HBCDs产区的华北地区,Huang等[42]调查了部分塑料垃圾回收地的植物样品中∑HBCDs分布和变化特征,结果显示∑HBCDs浓度为3.47—23.4 ng·g−1 dw.
随着气溶胶的输送和沉降,HBCDs能够远距离迁移扩散,导致在距离人群较远的生态保护区甚至极地地区也检测到HBCDs的存在. 深圳福田自然保护区3种红树林植物中∑HBCDs的浓度范围为0.016—194 ng·g−1 dw,其中白骨壤中的浓度(17.99 ng·g−1 dw)显著低于海莲(0.54 ng·g−1 dw)和秋茄(0.40 ng·g−1 dw)[43]. 天津大黄堡湿地自然保护区中心地带的小麦、萝卜和芦苇中∑HBCDs浓度范围为1.46—27.7 ng·g−1 dw,在3种植物的不同组织中HBCDs的总浓度呈现出相同的规律,均为叶部高于根部,且均大于根系土中∑HBCDs的浓度[59]. 河北白洋淀生态旅游区7种陆生植物中也发现浓度范围为n.d.—2.18 ng·g−1 dw的∑HBCDs污染[47],淀区内水生植物中∑HBCDs浓度范围为n.d.—7.26 ng·g−1 dw[38],其中在后塘点位采集的浮萍中∑HBCDs浓度最高(7.26 ng·g−1 dw),其次为南刘庄采集的金鱼藻(6.93 ng·g−1dw). Kim等[51]在南极洲的苔藓、地衣中也检测到了∑HBCDs的存在,浓度范围分别为0.63—960 pg·g−1 dw和0.1—21.1 pg·g−1 dw. 国外对于植物中HBCDs的关注较少,目前仅有Salamova等[58]调查了全球包括挪威、印尼、加拿大和美国等12个城市的40个树皮样本中的∑HBCDs,其中在加拿大安大略省Downsview检测到最高浓度为(21.3±7.7) ng·g−1 lw(脂重)的∑HBCDs,并且发现多地树皮样本中∑HBCDs浓度与当地人口数量显著正相关(P<0.05),说明了人为活动对HBCDs污染的重要贡献.
文献统计结果显示(表2),植物中∑HBCDs的浓度受区域、植物种类、植物组织、环境条件等因素影响显著,不同地区的环境污染水平存在差异,植物对持久性有机污染物的富集能力也存在显著的物种差异性[60]. 这可能是由于不同植物释放的蛋白质、酶、柠檬酸、果酸、葡萄糖、果糖等根系分泌物的种类和数量存在差异,从而影响植物对持久性有机污染物的吸收[61]. 同时,植物根系分泌物形态易受环境温度、湿度、酸碱性等的影响,在不同地区这些环境土壤条件存在明显差异,可能会导致植物对持久性有机污染物的积累不同[62]. 例如,在菠菜对多环芳烃的吸收研究中就发现,气温升高会增强植物光合作用,刺激根际土壤中根系分泌物的释放,同时增加土壤孔隙水中游离污染物的浓度,进而促进植物体内污染物积累,因此不同环境土壤条件也可能会导致植物体内HBCDs的积累出现差异. 此外,植物对包括HBCDs在内的有机物吸收和积累的过程中亦会受到植物代谢和生长稀释等生理过程的影响,这些都会对HBCDs在植物体内的富集分布造成差异[63].
-
商用HBCDs中主要存在的3种异构体,其中γ-HBCD约占总质量的75%—89%,α-HBCD占10%—13%,β-HBCD占1%—12%. 在环境样品检测中,α-HBCD、β-HBCD和γ-HBCD也是植物中主要存在的3种异构体,尽管工业产品中γ-HBCD含量较高,但在多数野外环境研究的植物样本的研究中显示α-异构体占比最高. 例如在上海工业区、商业区和居民区的樟脑树树皮检测中发现3种异构体(α-、β-和γ-HBCDs)均有检出,其平均贡献率分别为44%、18%和38%[64]. 华北地区主要塑料垃圾回收中心的植物样本中,α-、β-和γ-HBCDs组成分别为44.8%—88.1%、8.86%—49.3%和n.d—37.3%[42];在不同植物物种中异构体占比存在显著差异,菠菜根中α-、β-和γ-HBCD的贡献率分别为48.5%、24.4%和27.1%,而大蒜根中的各异构体的贡献率则分别为56.9%、29.4%和13.8%,可见不同的植物物种有着不同的选择性富集代谢能力;白洋淀陆生植物中异构体占比也存在显著的物种差异性,其中α-、β-和γ-HBCDs的平均贡献百分比为44.10%、20.95%和34.95%,荠菜中三者的贡献率分别为56.41%、13.46%和30.14%,而朝天委陵菜中则分别为44.30%、18.01%和37.69%[47];而在白洋淀水生植物中α-、β-和γ-HBCDs平均百分比贡献率分别为35.48%、13.16%、27.36%[38]. Zhu等[40]调查了中国华北、东北、华东、中南、西南、西北和华中7个区域的松针样品中HBCD异构体分布情况,结果显示α-HBCD的平均百分比达到65.1%±15%. 同时,室内模拟试验研究也得到了和采样调研相同的规律. 在菜园土、水稻土和赤红壤3种土壤中添加HBCDs暴露培养玉米,玉米中3种异构体的含量均大致遵循:α-HBCD > γ-HBCD > β-HBCD,地下部的含量大于地上部含量,且积累量随土壤中HBCDs浓度的增加而增加[65]. HBCDs在土壤中的归趋及植物对其行为的影响研究中,单种和混种白菜和萝卜土培暴露8周后发现,HBCDs在白菜和萝卜中的分布均具有异构体特异性,植物地上部组织中α-HBCD含量最高,其次为γ-HBCD,β-HBCD最低[53]. 将小白菜置于低浓度(0.05 ng·mL−1)HBCDs异构体溶液中暴露培养,14 d和30 d时小白菜叶中HBCDs的积累水平均为α-HBCD > β-HBCD > γ-HBCD,这与异构体的水溶性相一致[56]. 黑麦草对HBCDs异构体和对映体的吸收、异构化和代谢研究中,土培暴露黑麦草8周,在地下部和地上部均检测到α-HBCD的优先积累,其次为β-HBCD[5]. 有研究表明生物体内的细胞色素P450会优先代谢β-和γ-HBCDs[66-67],α-HBCD代谢较慢,并且α-异构体能显著抑制玉米细胞色素P450的活性[44],因此更有利于α-HBCD在植物体内的富集. 同时,在黑麦草[5]和小麦[68]的暴露研究中均发现,植物组织中β-和γ-HBCDs可以转化为α-HBCD,而暴露在α-HBCD的黑麦草中则未发现异构化产物,这可能也是α-HBCD在植物体内含量较高的一个重要原因.
迄今为止,也有少量研究发现其他异构体在植物中的优先富集行为. 在南极洲采集的苔藓和地衣中的部分样品[51],珠江三角洲蔬菜农场中的蔬菜[23]样品,以及青藏高原的地衣中[49]均发现γ-HBCD占据绝对优势. 空心菜的室内盆栽暴露实验也检测到γ-HBCD含量最高,α-HBCD次之,β-HBCD最低[65]. 白菜和萝卜暴露HBCDs培养8周后,植物地下部中γ-HBCD的相对丰度远大于α-和β-HBCDs[53]. 在玉米幼苗暴露于不同浓度HBCDs的吸收动力学研究中[45],随着暴露时间的延长,玉米根部和地上部中β-HBCD的占比增加,γ-HBCD的贡献率减少,α-HBCD的占比在根中增加,在地上部中减少. 暴露96 h后,玉米中HBCDs浓度达到平衡,在玉米根部和地上部中不同异构体的积累量为γ-HBCD > β-HBCD > α-HBCD;暴露120 h后,α-和γ-HBCDs的比例比暴露溶液中相对减少了38.87%±1.19%和8.56%±0.67%,β-HBCD相对增加了80.76%±4.56%,表明β-HBCD更易被玉米吸收和向地上部分传输.
综上所述,植物对HBCDs的选择性吸收和转运存在物种差异性,涉及到植物内部的吸收和转运、代谢等生理特征. 这种差异还可能是由于HBCDs不同异构体在空气、水、土壤和沉积物等环境介质中的代谢转化存在差异,致使其在各介质中的占比不同,进而导致其向植物中的传递富集量不同. 在环境中,β-HBCD似乎总是以较小的浓度存在,这可能与工业商品中β-HBCD占比较低和选择性代谢有关. 目前有关植物HBCDs非对映异构体的富集机制尚未完全了解,有待进一步研究.
-
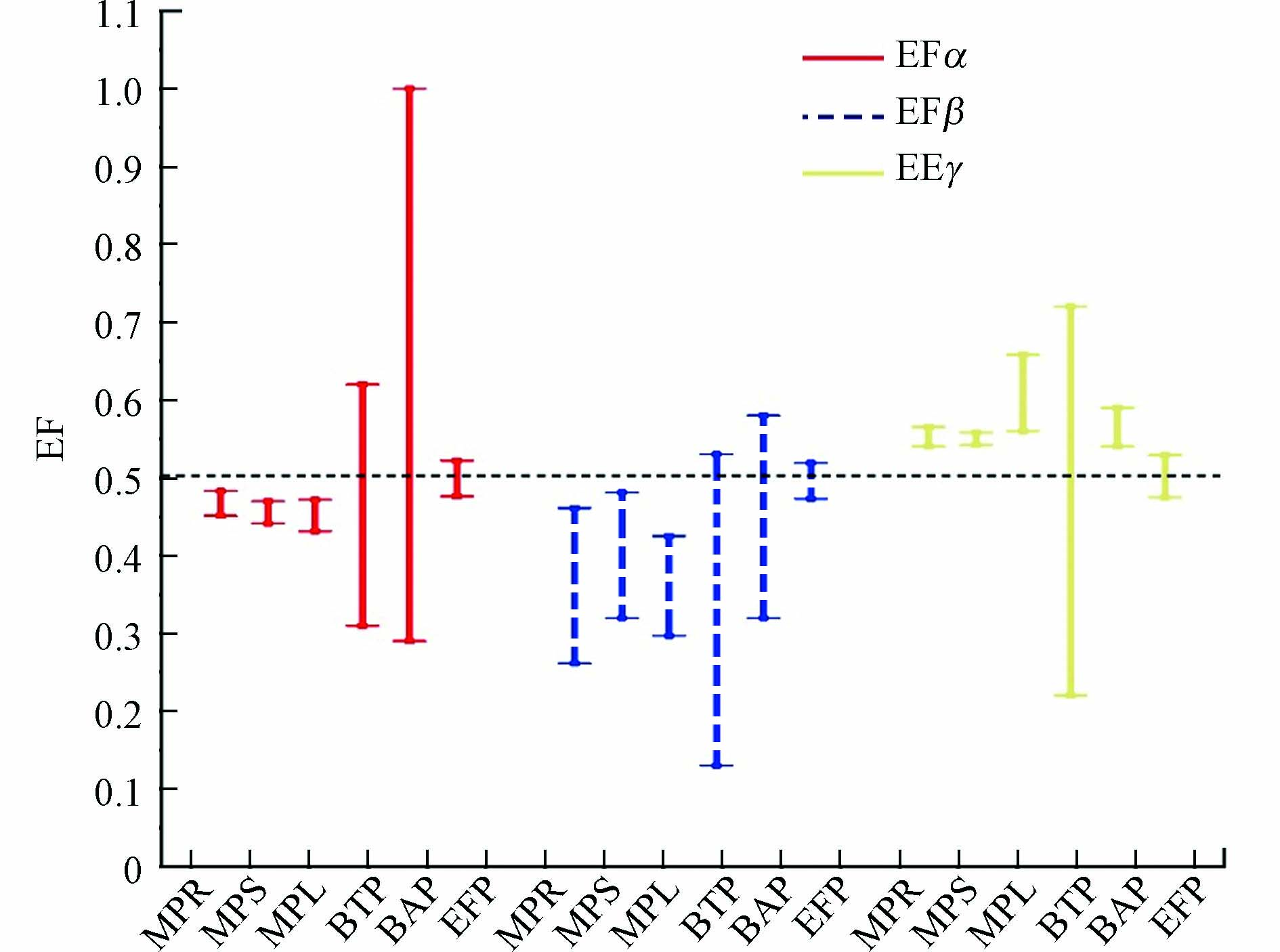
手性有机污染物一般以外消旋体(对映体分数EF=0.5)形式施用并排放到环境,经历了富集、降解、生物吸收和代谢等一系列的物理、化学、生物过程后,其对映体组成往往会发生变化,导致特定对映体占比显著增加,另一对映体占比降低,EF值偏离0.5. 目前关于HBCDs的环境行为在对映体水平上的研究非常有限,而对植物中HBCDs对映体的积累分布考察更是鲜有报道. 目前的研究表明,手性污染物HBCDs在植物中的积累和转运具有对映体选择性[48,69]. Li等[43]研究了深圳福田保护区的红树林植物,在海莲、秋茄和白骨壤的根、茎和叶中α-HBCD的EFs范围分别为0.451—0.483、0.441—0.470和0.431—0.472,β-HBCD的EFs范围分别为:0.261—0.461、0.320—0.481和0.297—0.425,γ-HBCD的EFs范围分别为:0.540—0.565、0.542—0.558和0.560—0.658,显示出(-)-α-、(-)-β-和(+)-γ-HBCDs的优先富集;Wu[70]等在实验室模拟玉米暴露研究也发现,(-)α-、(-)β-和(+)-γ-HBCD的生物积累显著高于其它对映体. 目前植物富集HBCDs对映体的选择性尚无统一的定论,在不同研究中优势富集的对映体存在差异[12](见图1). 在白洋淀的陆生植物中,多数采样点位泥湖草等植物样品中3种异构体的左旋构型富集浓度显著高于右旋构型[47],淀区内的包括荷叶在内的7种水生植物中,则表现出(-)-α-HBCD和(-)-γ-HBCD的选择性富集浓度较高,β-HBCD无显著的对映体选择性[38]. 在中国7个行政区的松针中α-HBCD的EF平均值为0.228±0.076(P < 0.001),表明了(-)-α-HBCD的选择性富集,β-和γ-HBCDs亦无显著的对映体选择性倾向[40]. 天津聚苯乙烯材料制造厂附近的冬青、柏树和松树中,α-和β-HBCDs均为(+)-构型在植物内叶和枝条组织中优先积累(P < 0.05),在冬青和柏树枝条中(-)-γ-HBCD优先富集(P < 0.05)[19]. 天津大黄堡地区的萝卜、小麦和芦苇中,大部分样品的茎和叶组织均呈现出(+)-HBCD的选择性富集优势[59]. Zhu等[5]实验室土培种植黑麦草,暴露培养8周后α-和γ-HBCDs在植物根、茎和叶中的EF值均大于0.5,而β-HBCD则小于0.5,表现出了(+)-α、(-)-β和(+)-γ对映体的选择性富集优势(P < 0.05).
对映体选择性富集是一个复杂的生物化学过程,受多方面因素影响. 通常认为生物介导的过程是影响手性化合物对映体组成的关键因素,在植物体中HBCDs对映体选择性吸收和酶促转化等生物过程,导致了特定对映体的优势累积[4]. 将玉米幼苗水培暴露7 d后发现(-)-α-、(-)-β-和(+)-γ-HBCDs的积累量显著高于其他对映体,且在玉米根中观测到除(+)-α-HBCD外,暴露7 d后所有对映体均发生了不同程度的异构化作用,其中(-)-γ-HBCD转化率最高为90.5%±8.2%,其次为(+)-γ-HBCD[71]. 植物体内HBCDs的对映体选择性降解和代谢亦对其富集水平有着重要影响. Huang等[71]在暴露HBCDs的玉米跟中发现了OH-HBCDs、2-OH-HBCDs、OH-五溴环十二烷醇(OH-PBCDs)和2-OH-PBCDs 4种羟基代谢物,谷胱甘肽(GSH)-HBCD加合物以及五溴环十二碳稀(PBCEe)和四溴环十二碳烯(TBCDe)2种脱溴代谢物,解释了HBCDs在植物体内的羟基化、脱溴和GSH加合物合成代谢途径;并在(+)/(-)-β-或(+)/(-)-γ-HBCDs对映体处理中,检测到(-)-α-HBCD转化产物,证实了其对映体选择性异构化行为. 玉米细胞色素P450酶对HBCDs的体外生物降解研究[44]发现,玉米细胞色素P450酶降解HBCDs的反应遵循一级动力学规律,且具有立体选择性,代谢速率为(-)-γ-HBCD > (+)-γ-HBCD > (+)-α-HBCD > (-)-α-HBCD. HBCDs对映体的选择性植物富集,还可能由物种特异性导致. 在白洋淀地区采集的植物样本中中(-)-HBCDs优先富集[47],而天津大黄堡地区的萝卜、小麦和芦苇中则表现出(+)-HBCDs的选择性富集优势[59]. 此外,HBCDs的对映体选择性植物富集也会受到环境过程的影响,有研究发现高温环境和日光催化均会促使HBCDs立体构型的转化,使得环境中HBCDs对映体组成发生改变[38]. HBCDs在复杂的环境和生物因素影响下发生立体选择性行为,导使不同对映体的富集浓度水平存在差异,这种差异性可以通过食物链转移进入营养水平更高的生物体中,进而产生不同的毒性影响,因此,植物体内HBCDs的立体选择性行为引起越来越多的关注,关于其选择性差异的机理探讨仍需深入探讨.
-
通过气溶胶的沉积、湿沉降等自然过程,各种环境介质中的HBCDs最终将进入土壤环境,土壤是包括HBCDs在内的大多数有机污染物重要的汇. 植物在土壤中普遍存在,是与土壤密切相关的重要生物,HBCDs在土壤—植物系统的传输是其进入食物链的关键途径. 一般来说,植物可以通过两种途径富集土壤中的HBCDs,一种是通过根部吸收进入植物体内,经过蒸腾作用沿木质部向茎叶传输[72],另一种途径是通过叶片吸收大气中的HBCDs[65]. 通常采用植物富集因子和传输系数来评估植物的生物富集能力及污染物在植物体内的传输能力[47]. Zhu等[5]采用土培方式培养黑麦草暴露8周后,分别检测了土壤、植物根部、茎部和叶部HBCDs的累积浓度,核算出HBCDs在黑麦草体内的根富集因子(RCFs)、茎传输系数(SCFs)和叶传输系数(LCFs). 结果表明,HBCDs在黑麦草根部富集能力较强,茎叶传输能力较弱;武彤等[47]研究了白洋淀淀区内6个采样点的土壤和植物样品中HBCDs的富集传输情况,得到RCFs范围为0.12—0.93,根部到地上部的传输系数(TFs)为0.09—0.81,所有RCFs和TFs值均小于1.0,表明HBCDs在白洋淀淀区植物根部的富集以及从根部到地上部的转运均有限,其更倾向于在土壤中积累. 而Lü等[23]研究了珠江三角洲地区的蔬菜样品,采用整株植物中的富集水平核算了HBCDs在各种蔬菜中的生物浓缩因子(BCFs,蔬菜浓度/土壤浓度),其范围为0.29—19.5,平均值为4.90,约90%的植物样本BCFs值大于1.0,这在一定程度上归因于蔬菜物种对HBCDs的强吸收富集能力. Zhu等[69]研究了小麦对HBCDs异构体的吸收途径,通过土壤、空气的单一和混合暴露培养小麦,说明了HBCDs可通过根部和叶部两种途径被小麦吸收. 在混合暴露模式下,将d18-HBCDs添加于土壤中核算了HBCDs从根部到叶部的转运量与叶片积累量的比例(Rt),3种HBCDs异构体的Rt值为14.4%—29.8%,表明叶片中的HBCDs主要是从空气中吸收的. 显然,不同植物物种对HBCDs的富集传输能力存在很大差异.
HBCDs在生产、使用和废弃过程中,会通过工业排污、生活污水等多种途径进入河湖等水—沉积物系统,由于其高疏水性,极易与固体颗粒(如沉淀物)结合. 在水环境中,挺水植物的根或茎扎入底泥中,污染物会随着其生长过程被吸收进入植物体内. Li等[37]报道了莱州湾地区芦苇中HBCDs的植物富集情况,得到其生物累积因子(BAFs,植物浓度/沉积物浓度)为6.37—111,平均值达到32.9,表明芦苇对HBCDs有较强的富集能力. Li等[43]研究了深圳福田保护区的红树林植物以及其根系周围的沉积物,发现植物中的RCFs范围为0.0004—0.43,其中秋茄的RCFs最高,比海莲和白骨壤高出两个数量级,表明相比于海莲和白骨壤,秋茄对HBCDs的富集能力较强;TFr-s(茎浓度/根浓度)为4.11—10.6,均高于1.0,表明HBCDs更易于从根部传输转运到茎部;TFs-l(叶浓度/茎浓度)为0.13—11.7,在白骨壤中TFs-l均大于1.0说明HBCDs优先在其叶中积累,而在海莲和秋茄中TFs-l均低于1,表明HBCDs更倾向于在海莲和秋茄的茎中积累. 迄今为止,不同的陆生和水生环境研究中植物对HBCDs的富集传输情况存在显著的差异,可能是植物对HBCDs积累传输能力的物种差异和环境条件影响共同作用的结果.
HBCDs在植物体系的传输存在立体选择性,尽管相关研究非常有限,但HBCDs各异构体的植物传输探索也受到了研究者们的关注. 一般而言,疏水性较弱的有机化合物更易于在植物中传导,而疏水性较强的有机化合物不易在植物中发生传导,以根系聚积为主. 环境中主要存在的α-、β-和γ-HBCDs的lgKow存在差异,疏水性较弱的α-HBCD在植物中更容易发生特定的传输和转运,从而被输送到地表以上的茎叶组织中,疏水性较强的γ-HBCD则更易在根部累积. Huang等[71]通过水培玉米实验研究了玉米根中HBCDs异构体的富集,发现HBCDs异构体的lg RCFs和lgKow之间呈现显著的正相关性(P < 0.05),说明疏水性更强的γ-HBCD,更容易被植物根部吸收,与上述规律相符. 然而,也有研究得到了不同的结论,在Zhu等[68]小麦吸收HBCDs的研究中,在封闭室内通过土壤和空气暴露HBCDs培养小麦4周后发现,不同异构体的lg RCFs与lg Kow之间呈现显著的负相关关系(P < 0.05),认为疏水性较弱的α-HBCD更易在植物根中富集. 而Li等[43]在福田保护区红树林植物的研究中分析了3种HBCDs异构体的lg RCFs与lg Kow之间的关系,结果发现两者没有显著的相关性(P > 0.05). 白洋淀淀区内的不同植物样本及淀区周边的玉米和小麦中,HBCD富集的RCFs和lg Kow之间均无显著的相关关系[47,73],但在玉米和小麦中发现TFs与lg Kow存在显著的负相关性[73],与疏水性较弱的有机化合物更易于在植物中传导的规律相符. 不同的研究结果差异显著,甚至完全相反. 在实际环境中,HBCDs的高疏水性使其与土壤或沉积物颗粒紧密结合,在土壤-植物体系中土壤与HBCDs的结合会大大削弱植物对其的吸收效率[43],因此实验室水培模拟很可能与土培模拟结果存在差异. 野外环境采样研究揭示了真实环境中长期动态平衡的结果,受到植物种类、植物体组成部分、植物蒸腾作用强度、生长环境和状况等多种环境因素的影响[43,47,73],反映了自然环境中HBCDs传输和转运的复杂性,各种因素的影响途径和机理有待结合现实环境开展更深入的探讨.
-
随着全球工业化和城市化的发展,人们对环境中持久性污染物的担忧日益加剧,进入环境中的HBCDs在短期内无法“自净”,对生态系统及人类造成威胁,目前已有很多研究表明,多种技术可降解环境中的HBCDs[74-83],如超声波降解、光催化降解、生物降解等. 植物吸收和降解技术被认为是保持环境可持续性的一种可行的选择. 土壤-植物体系HBCDs的降解包括3种方式:利用植物根系释放的酶和根系分泌物进行降解;利用植物与根际微生物之间的协同作用进行降解[65];以及HBCDs进入植物体内在酶的作用下被转化和降解,从而降低土壤中HBCDs的浓度.
目前,土壤-植物体系中HBCDs的清除和代谢研究相对较少. 据报道,黑麦草土培暴露8周后,土壤中的HBCDs浓度降低,在植物根、茎和叶中均检测到HBCDs的存在,但黑麦草对土壤中HBCDs的吸收代谢仅占0.57%—3.15%,表明黑麦草能够从土壤中吸收HBCDs,但不是修复HBCDs污染的最佳植物[5]. Zhu等[68]通过土培暴露小麦4周后发现,HBCDs可通过根部被小麦吸收,根际(非根际)土壤中α-、β-和γ-HBCDs的去除率分别为62.4%(39.1%)、61.7%(40.4%)和75.8%(38.2%);表明种植小麦能促进土壤中HBCDs的去除,去除率是非种植区的1.5—2.0倍. 同时,β-或γ-HBCDs在小麦叶片中可转化为α-HBCD,4周后生物异构化效率分别达到0.31%—4.80%和0.92%—8.40%. 李亚宁等[66]将萝卜和白菜单种和混种于含有1000 μg·kg−1 HBCDs的土壤中56 d后发现,单种萝卜组与白菜组土壤中HBCDs的浓度均低于80 μg·kg−1,混种组土壤中HBCDs的浓度约为420 μg·kg−1,且单种组土壤中各异构体的质量浓度均低于混种组(P < 0.001),推断可能是由于植物的种间竞争改变了植物根系分泌物的释放,直接或间接影响了HBCDs的吸附行为,从而改变其生物有效性,致使土壤中HBCDs的浓度变化产生差异.
在土壤-植物系统中添加有机或无机物质以及微生物菌群等可以增加植物对HBCDs的清除和降解效率. Le等[84]在土壤中种植烟草35 d,与对照组土壤相比单独种植烟草可以去除土壤中13%的HBCDs,加入腐殖酸后HBCDs的去除率达到15%,表明腐殖酸对土壤中HBCDs的清除有一定的促进作用;体系加入Pd/Fe纳米颗粒后烟草对土壤中的HBCDs去除率可达41%,表明相比于腐殖酸而言,Pd/Fe纳米颗粒对土壤—烟草体系中HBCDs去除的促进能力更强;腐殖酸和Pd/Fe纳米颗粒同时加入培养体系后发现,其对土壤中HBCDs的联合清除率仅为27%,推测可能是由于腐殖酸能够增强Pd/Fe纳米颗粒的聚集和腐蚀,从而降低了Pd/Fe纳米颗粒的促进效果. 在微生物降解方面,据报道铜绿假单胞菌HS9是一种HBCDs代谢菌[85],可有效促进HBCDs的降解并将其转化为TBCDe、二溴环十二烯(DBCDi)和环十二三烯(CDT). Huang等[86]通过土壤暴露培养玉米,添加HS9菌株10天后使土壤和植物中的HBCDs浓度分别降低了87.6%和25%;微生物多样性分析表明,菌株HS9可以促进植物有益细菌的丰度,从而降低HBCDs对植物的毒性进而促进植物生长. 目前,报道的降解HBCDs的植物种类还不够丰富,对更多类型的植物、植物混种方案研究需要进一步开展,使植物降解HBCDs展现出更大的应用前景. 此外,富集HBCDs的植物需要得到妥善的处理,以免引起二次污染,影响生态系统平衡,进而危害人类自身[87].
-
环境中的HBCDs普遍存在,可通过大气、水、土壤等多种途径进入生物体内,经过食物链中各级消费者的捕食与被捕食关系而逐级积累放大,产生生态毒性,影响人类健康. 植物是生态系统的生产者,食物链的基础,植物对HBCDs有一定的吸收降解能力,同时植物也会受到HBCDs的毒性影响. 目前关于HBCDs的植物毒性研究还相对较少.
据报道,HBCDs会对植物的生长发育产生影响. 周耀红等[6]将植物种子暴露于不同浓度的HBCDs溶液中,2 d后发现HBCDs对萝卜种子发芽率影响不明显,但对白菜种子发芽率有显著抑制作用,随着HBCDs处理浓度的增大,菜心、玉米种子的发芽率出现了下降的弱趋势,总体不明显. 种子萌发需要消耗有机物(包括淀粉、脂肪、蛋白质等),其中种子淀粉是种子中储存最丰富的物质,HBCDs对种子萌发具有抑制作用,很可能是HBCDs破坏了种子中的淀粉或降低了淀粉酶活性[70]所致;5 d后HBCDs对菜心和萝卜的根长有一定的促进作用,而对玉米和白菜的根长则出现低浓度抑制高浓度促进的变化规律,表明HBCDs对不同植物种子的毒性效应存在差异. Wu等[45]将玉米种子浸润于HBCDs溶液中,种子萌发、根部和地上部的生物量以及长度均受到不同程度的抑制,相对抑制率随着HBCDs暴露浓度的增加而增大,当暴露浓度为0.05 mg·L−1时,发芽率、根系生物量、根系长度、地上部生物量及地上部长度的相对抑制率分别为46.54%、32.71%、31.94%、14.04%和11.91%,表明HBCDs对玉米生长的毒性效应大小为发芽率 > 根系生物量 > 根系长度 > 地上部生物量 > 地上部长度. HBCDs具有手性结构,研究表明HBCDs不同异构体和对映体会对植物产生选择性毒性作用[30]. 玉米幼苗经HBCDs溶液暴露培养后,3种异构体均对玉米的发芽率、根长、根重、苗长和苗重产生抑制,其中α-HBCD对玉米的生长抑制率最高[30]. 黑麦草经HBCDs异构体土培暴露8周后[5],其生长受到明显的抑制作用,且相对抑制率随暴露时间的增加而增加,黑麦草的整体生物量和组织生物量显著下降(P < 0.01),其中γ-HBCD抑制率最高,对地上部和地下部的抑制率分别为26.7%±1.1%和30.2%±1.8%;此外HBCDs暴露还导致黑麦草叶绿素含量(叶绿素a和叶绿素b)降低,从而引起植物的生理干扰. 在对映体水平的研究[7]发现,α-HBCD对映体水培玉米幼苗后,幼苗的根部和地上部的生物量和长度均受到选择性抑制,其中(+)-α-HBCD的损伤作用强于外消旋(rac)-α-HBCD和(-)-α-HBCD. γ-HBCD对映体水培暴露玉米幼苗3 d后[88],幼苗根生物量、地上部生物量、根长度、地上部长度等生长指标均受到显著抑制,且抑制率为(+)-γ-HBCD > (rac)-γ-HBCD > (-)-γ-HBCD.
当植物受到HBCDs胁迫时,机体内会产生过量的活性氧(ROS),植物内的氧化平衡被破坏,致使植物遭受损伤. Wu等[45]将玉米水培暴露4 d,当HBCDs浓度低于0.01 mg·L−1时,玉米体内羟基自由基(·OH)水平受到显著诱导(P < 0.05),并随HBCDs暴露浓度的增加呈现先升高后降低的趋势,表明低浓度下玉米ROS的生成致使植物发生氧化应激,在较高浓度下自由基的累积引起植物抗氧化系统失活,细胞受损,使ROS的产生和清除失去活性. 武彤等[89]研究了β-HBCD对玉米的对映体选择性毒性影响,发芽后的玉米水培暴露3 d后,(+)-和(rac)-β-HBCDs可诱导玉米超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)活性随暴露浓度先增后降,推测高浓度下可能植物体内其他抗氧化机制被诱发,从而使得其对SOD和APX活性影响变小;同时发现(+)-β-HBCD对植物的毒性高于(rac)-β-HBCD和(-)-β-HBCD. 崔建升等[88]研究了γ-HBCD对映体对玉米的选择性氧化胁迫,水培暴露3 d后亦检测到玉米组织中SOD和过氧化物酶(POD)活性随暴露浓度先增后降,且损伤强度为(+)-γ-HBCD > (rac)-γ-HBCD > (-)-γ-HBCD. HBCDs对植物不同组织部位的影响存在差异,以上植物发生氧化胁迫的研究中均发现玉米根部的损伤高于地上部.
ROS的累积与植物细胞脂质过氧化和细胞死亡等诸多有害效应有关[45],且有机污染物诱导植物体内产生过量的ROS,可改变植物DNA结构,产生基因水平损伤. Wu等[45]将发芽后的玉米水培暴露HBCDs 4 d后,组蛋白H2AX磷酸化(γ-H2AX)水平受到显著诱导,当HBCDs浓度为0.05 mg·L−1,根部和地上部γ-H2AX含量达到最高,与对照组相比分别增加了23.10%和16.61%,说明DNA的损伤呈现出随着HBCDs浓度的增加而增加的趋势. 武彤等[7]和崔建升等[88]分别研究了α-HBCD对映体和γ-HBCD对映体对玉米的选择性基因损伤,玉米发芽后水培暴露3 d,组织中的γ-H2AX水平均有所增加,其中(+)-α-HBCD的损伤作用强于外消旋(rac)-α-HBCD和(-)-α-HBCD,(+)-γ-HBCD > (rac)-γ-HBCD > (-)-γ-HBCD. 李蝶等[46]提取了植物组织DNA研究了不同HBCDs立体构型对玉米基因的影响,发现HBCDs暴露3 d后,玉米体内的DNA稳定性受到显著影响,基因多态性增加,低浓度下呈现DNA交联损伤为主,高浓度下DNA断裂损伤比例增加,且DNA损伤程度随HBCDs暴露浓度的增加而增加,抗氧化SOD系列基因Cu/Zn-SOD、Fe-SOD和Mn-SOD的表达量也受到不同程度的诱导和抑制作用,3个异构体中α-HBCD对玉米的影响最严重,6个对映体中(+)-α-HBCD的选择性影响最大.
综上所述,HBCDs会引起植物生长发育迟缓、氧化胁迫和基因损伤等毒性效应. POPs物质具有生物放大效应,对于生物链顶端的人类来说,这些毒性被放大了7万倍以上,因此越来越多的研究开始关注植物中存在的HBCDs对人体产生健康危害的风险. 经评估,惠州市、江门市以及广州市的蔬菜中含有的HBCDs水平都存在着一定的致癌危险[65],白洋淀地区种植的玉米中尽管也含有微量HBCDs,但属于低风险水平,可安全的供当地居民食用[73]. 认识手性HBCDs与植物的相互作用为综合评价其环境和健康风险具有重要意义.
-
作为全球第三大溴代阻燃剂,HBCDs已在全球范围的各类环境介质中检出,并对人体健康和生态系统造成了一定影响. 作为新型持久性有机污染物,各国已相继出台相应措施限制或禁止HBCDs的生产和使用,鉴于我国HBCDs的使用还会延续到2024年,HBCDs在环境介质中的累积、转化、迁移以及长期毒性效应仍需进一步研究. 尽管我国关于HBCDs的环境富集和毒性效应已经开展,但关于HBCDs的植物研究还处于起步阶段. 随着研究的深入,人们逐渐认识到HBCDs不同异构体及对映体结构的环境行为及毒性差异,但是到目前为止有关HBCDs环境毒性、迁移转化规律、污染区域的环境修复以及其潜在的长期生态危害性仍存在很多不确定性,尤其关于HBCDs对映体的植物毒性和迁移尚无统一规律. 有关上述问题的工作成果将有利于寻求效率更高的生物治理技术,对评估HBCDs使用和排放、环境生态损伤及健康影响控制提供基础数据,并对制定控制对策、污染治理方案和相关法律法规提供科学依据.
六溴环十二烷(HBCDs)异构体及对映体的植物富集、传输、修复及毒性研究进展
Research progress on plant enrichment, transportation, phytoremediation and toxicity of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDs) diasteresomers and enantiomers
-
摘要: 六溴环十二烷(hexabromocyclododecanes,HBCDs)是一种典型的疏水性脂肪族溴代阻燃剂, 2013年被列入《斯德哥尔摩公约》受控名单中. HBCDs具有手性中心,多个对映异构体,不同的立体构型在环境中会发生选择性富集分布,降解转化和生物毒性等行为. 植物是生态系统能量的生产者,HBCDs可通过植物吸收改变植物生理,影响其在食物链的传递乃至整个生态系统,对环境和人体健康存在潜在危害. 本文对HBCDs异构体和对映体的植物提取分析方法、植物富集和传输、污染土壤的植物修复以及植物毒性效应的最新研究进行梳理. 液相色谱质谱联用技术可有效检测植物中的HBCDs异构体和对映体,对映体水平的检测将成为未来HBCDs立体构型分析的发展方向. HBCDs已在各类植物中被陆续检出,多数研究中α-HBCD是主要的异构体. 目前在HBCDs对映体水平上的研究还非常有限,其在植物体内的传输尚无统一规律. 植物种植可有效清除土壤中的HBCDs,展现出生物修复应用前景. HBCDs会引起植物生长发育迟缓、氧化胁迫和基因损伤等效应,不同构型的HBCDs表现出特异的选择性毒性行为. 鉴于目前关于HBCDs的植物研究还很欠缺,建议今后加强对植物中HBCDs异构体和对映体水平的环境行为和污染治理研究,为综合评价HBCDs的生物有效性、健康风险评价及环境修复提供科学依据.Abstract: Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD), as a typical hydrophobic aliphatic brominated flame retardants was listed in the Stockholm Convention in 2013. HBCDs exists chiral centers and multiple enantiomers. Selective enrichment, distribution, degradation and biotoxicity in the environment may be induced by different stereo configurations of HBCDs. Plants are considered the producers of energy in the ecosystem. Plant physiology might be changed by HBCDs plant uptake, further affects its transmission in the food chain and even the entire ecosystem, and lead to potential hazards to the environment and human health. The latest studies on the plant extraction and analysis methods, plant enrichment and transport, phytoremediation of contaminated soil, and phytotoxicological effects of HBCDs isomers and enantiomers were reviewed in this paper. The liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry could effectively detect HBCDs isomers and enantiomers in plant samples. Detection of enantiomer level will become the development direction in stereoscopic configuration analysis of HBCDs in the future. HBCDs have been successively detected in various plants, with α-HBCD being the dominant isomer. At present, the research on the HBCDs enantiomers level is still very limited, and there is no uniform rule for their transmission in plants. Plant planting can effectively remove HBCDs from soil, showing the application prospect of bioremediation. Toxic effects such as plant growth retardation, oxidative stress and gene damage can be caused by HBCDs, and different configurations showed specific selectivity. The environmental behaviors of HBCDs different configurations are stereoisomer-specific, and plant enrichment, transport, transformation and toxicological effects of HBCDs are selective. So far, plant researches of HBCDs are still insufficient, it is suggested that the environmental behavior and pollution control of HBCDs isomers and enantiomers in plants should be further studied in the future, so as to provide a scientific basis for comprehensive evaluation of bioavailability, health risk assessment and environmental restoration of HBCDs.
-
Key words:
- hexabromocyclododecane /
- enantiomers /
- selective-enrichment /
- phytoremediation /
- phytotoxicity.
-

-
表 1 植物中HBCDs的提取净化及分离分析方法
Table 1. Extraction, purification, separation and analysis of HBCDs in plants
样本
Sample前处理技术
Pretreatment technology提取剂
Extractant提取时间
Time净化方法
Purification method仪器分析方法
Instrumental analysis methods参考文献
Reference大白菜、小白菜、菠菜、芥菜、
莴苣、丝瓜、韭菜、豇豆、萝卜、
红薯、莴苣、香菜索氏提取法 丙酮:正己烷,1:1 24 h 活性硅胶柱(CNW,德国) HPLC-MS [23] 小麦、胡萝卜、芦苇 索氏提取法 丙酮:正己烷,1:1 24 h 活性硅胶柱(CNW,德国) LC-MS/MS [39] 冬青、侧柏、马尾松 索氏提取法 丙酮:正己烷,1:1 24 h 活性硅胶柱(CNW,德国) LC-MS/MS [19] 松针 索氏提取法 丙酮:正己烷,1:1 24 h 硅胶/氧化铝柱 GC-MS [58] 海莲、秋茄、白骨壤 索氏提取法 丙酮:正己烷,1:1 48 h 复合硅胶柱 HPLC-MS/MS [43] 松针 索氏提取法 丙酮:正己烷,1:1 48 h 活性硅胶柱(CNW,德国) HPLC-MS/MS [40] 松树、柏树和垂柳树皮 索氏提取法 丙酮:正己烷,1:3 36 h 硅胶/氧化铝柱 UPLC-MS [41] 玉米、小麦、马铃薯、韭菜、
菠菜、莴苣和大蒜索氏提取法 正己烷:二氯甲烷,1:1 24 h 硅胶/氧化铝柱 UPLC-MS/MS [41] 柏树、芦苇、碱蓬草 加速溶剂萃取法 正己烷 — 复合硅胶柱 HPLC-MS [37] 苔藓、地衣 加速溶剂萃取法 正己烷:丙酮 — 复合硅胶柱 HPLC-MS/MS [49] 泥湖草、牛筋草、朝天委陵菜、
小蓬草、补血草、蓟草和荠菜超声提取法 乙酸乙酯 2次,每次50 min 复合硅胶柱 HPLC-MS/MS [47] 藻类 超声提取法 丙酮 10 min 活性硅胶柱(CNW,德国) LC-MS [48] 苔藓、地衣 超声提取法 正己烷:二氯甲烷,1:1 3次,每次30 min 硅胶/氧化铝柱 LC-MS/MS [51] 玉米 超声提取法 乙酸乙酯 2 h 复合硅胶柱 UPLC-MS/MS [45] 表 2 部分地区植物中∑HBCDs浓度
Table 2. The concentrations of ∑HBCDs in plants in some areas
样品
Sample地区
Area采样地点描述
Description of
sampling location浓度范围/平均浓度
Concentration range/
Average concentration(dw)采样时间
Sample time参考文献
Reference玉米、小麦、马铃薯、韭菜、
菠菜、莴苣、大蒜华北地区 塑料垃圾处理地 3.47—20.2 ng·g−1 — [42] 柏树、芦苇、碱蓬草 中国莱州湾 HBCD生产基地 110—160241 ng·g−1 2010 [37] 冬青、柏树、松树 中国天津 EPS材料制造厂 3.45—160241 ng·g−1 2015 [19] 泥湖草、牛筋草、朝天委陵菜、
小蓬草、补血草、蓟草、荠菜中国白洋淀 天然淡水湖 N.d.—2.18 ng·g−1 2018 [47] 松树、冷杉、云杉 挪威、印尼、南非、尼泊尔、
加拿大、印第安、
爱尔兰、冰岛、美国、
捷克和塔斯纳尼亚远离城市的区域 0.27—21.3 ng·g−1 2009 [58] 玉米、小麦、马铃薯、韭菜、
菠菜、莴苣、大蒜中国天津 大黄堡湿地自然保护区 1.46—27.7 ng·g−1 2011 [59] 大白菜、小白菜、菠菜、芥菜、
丝瓜、韭菜、豇豆、萝卜、
红薯、莴苣、香菜珠江三角洲 蔬菜农场 0.87—32.7/16.6 ng·g−1 2018 [23] 樟脑树皮 中国上海 工业区 280—6600 ng·g−1 — [64] 樟脑树皮 中国上海 商业区 140—2400 ng·g−1 — [64] 樟脑树皮 中国上海 居民区 120—1000 ng·g−1 — [64] 苔藓 南极洲 南设得兰群岛 0.63—960 pg·g−1 2014 [51] 地衣 南极洲 南设得兰群岛 0.1—21.1 pg·g−1 2014 [51] 松树、银杏、刺槐、垂柳、
杨树和柏树树皮中国北京 污染区域附近 26—3400 ng·g−1 2009 [41] 松针 中国 7个行政规划区 6.3—2790 ng·g−1 2013 [40] 荷叶、荷茎、浮萍、金鱼藻、
轮藻、眼子菜、香蒲中国白洋淀 天然淡水湖 N.d.—7.26/1.02 ng·g−1 2018 [38] 海莲、秋茄、白骨壤 深圳 福田保护区 0.016—194 ng·g−1 2015 [43] n.d., 低于检测限或未检出. N.d., Below detection limit or not detected -
[1] MARVIN C H, TOMY G T, ARMITAGE J M, et al. Hexabromocyclododecane: Current understanding of chemistry, environmental fate and toxicology and implications for global management [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(20): 8613-8623. [2] ZHU J, LIU J G, HU J X, et al. Socio-economic analysis of the risk management of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in China in the context of the Stockholm Convention [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 150: 520-527. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.007 [3] KOCH C, SCHMIDT-KÖTTERS T, RUPP R, et al. Review of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) with a focus on legislation and recent publications concerning toxicokinetics and-dynamics [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 199: 26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.011 [4] HEEB N V, SCHWEIZER W B, KOHLER M, et al. Structure elucidation of hexabromocyclododecanes—a class of compounds with a complex stereochemistry [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 61(1): 65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.015 [5] ZHU H K, SUN H W, YAO Y M, et al. Fate and adverse effects of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers (HBCDDs) in a soil-ryegrass pot system [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 184: 452-459. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.166 [6] 周耀红, 马晓净, 吕辉雄. 六溴环十二烷对土壤酶活性、种子发芽率及根伸长的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(1): 100-105. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.01.2016052405 ZHOU Y H, MA X J, LYU H X. Effect of hexabromocyclododecane(HBCDs) on soil enzyme activity, seed germination rate and root elongation [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(1): 100-105(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.01.2016052405
[7] 武彤, 田柳, 崔建升, 等. 六溴环十二烷对映体对玉米的生理和基因损伤研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(12): 4864-4872. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0217 WU T, TIAN L, CUI J S, et al. Physiological and genetic damage of hexabromocyclododecane enantiomers to Maize [J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2018, 38(12): 4864-4872(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0217
[8] WANG X L, SUN R R, CHEN Y D, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and diastereoisomer pattern of hexabromocyclododecane in the vicinity of a chemical plant [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 82: 203-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.03.010 [9] ZHAO Y Y, ZHANG X H, SOJINU O S S. Thermodynamics and photochemical properties of α, β, and γ-hexabromocyclododecanes: A theoretical study [J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 80(2): 150-156. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.002 [10] TANG L, SHAO H Y, ZHU J Y, et al. Hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers in surface sediments from river drainage basins of Shanghai, China: Occurrence, distribution, and mass inventory [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(16): 11993-12000. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4336-7 [11] HEEB N V, GRAF H, BERND SCHWEIZER W, et al. Thermally-induced transformation of hexabromocyclododecanes and isobutoxypenta bromocyclododecanes in flame-proofed polystyrene materials [J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 80(7): 701-708. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.05.034 [12] 黄红林, 王丹, 张淑贞. 实验和理论计算应证玉米体中HBCD的选择性吸收和生物转化[C]//中国化学会第30届学术年会摘要集-第二十六分会: 环境化学. 大连, 2016: 32. HUANG H L, WANG D, ZHANG S Z. Experimental and theoretical calculations should prove the selective absorption and biotransformation of HBCD in maize[C]//Abstracts of the 30th academic annual meeting of the Chinese Chemical Society-Chapter 26. Beijing: Environmental Chemistry, 2016: 3(in Chinese).
[13] 倪涛涛. 六溴环十二烷的分析和光催化降解机制研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2020. NI T T. Analysis of hexabromocyclododecane and photocatalytic degradation mechanism[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[14] SELLSTRÖM U, KIERKEGAARD A, de WIT C, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hexabromocyclododecane in sediment and fish from a Swedish River [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1998, 17(6): 1065-1072. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620170612 [15] LU J F, HE M J, YANG Z H, et al. Occurrence of tetrabromobisphenol a (TBBPA) and hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in soil and road dust in Chongqing, Western China, with emphasis on diastereoisomer profiles, particle size distribution, and human exposure [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 219-228. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.087 [16] ABDALLAH M A E, HARRAD S, COVACI A. Hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol-a in indoor air and dust in Birmingham, U. K: Implications for human exposure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(18): 6855-6861. [17] HE M J, LUO X J, YU L H, et al. Diasteroisomer and enantiomer-specific profiles of hexabromocyclododecane and tetrabromobisphenol A in an aquatic environment in a highly industrialized area, South China: Vertical profile, phase partition, and bioaccumulation [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 179: 105-110. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.04.016 [18] HARRIS B, ABOU-ELWAFA ABDALLAH M. Exploring variations of hexabromocyclododecane concentrations in riverine sediments along the River Medway, UK [J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2021, 23(5): 776-785. [19] ZHU H K, ZHANG K, SUN H W, et al. Spatial and temporal distributions of hexabromocyclododecanes in the vicinity of an expanded polystyrene material manufacturing plant in Tianjin, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 222: 338-347. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.029 [20] de WIT C A, HERZKE D, VORKAMP K. Brominated flame retardants in the Arctic environment—Trends and new candidates [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(15): 2885-2918. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.037 [21] SUN R X, LUO X J, ZHENG X B, et al. Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in fish: Evidence of recent HBCD input into the coastal environment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 126: 357-362. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.040 [22] SUN Y X, LUO X J, MO L, et al. Hexabromocyclododecane in terrestrial passerine birds from e-waste, urban and rural locations in the Pearl River Delta, South China: Levels, biomagnification, diastereoisomer- and enantiomer-specific accumulation [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 171: 191-198. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.07.026 [23] LÜ H X, MA X J, HUANG X J, et al. Distribution, diastereomer-specific accumulation and associated health risks of hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in soil-vegetable system of the Pearl River Delta region, South China [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 248: 109321. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109321 [24] TAVOLONI T, STECCONI T, GALARINI R, et al. BFRs (PBDEs and HBCDs) in freshwater species from Lake Trasimeno (Italy): The singular case of HBCDs in red swamp crayfish [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 758: 143585. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143585 [25] MUKAI Y, GOTO A, TASHIRO Y, et al. Coastal biomonitoring survey on persistent organic pollutants using oysters (Saccostrea mordax) from Okinawa, Japan: Geographical distribution and polystyrene foam as a potential source of hexabromocyclododecanes [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 739: 140049. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140049 [26] LI B, CHEN H, SUN H W, et al. Distribution, isomerization and enantiomer selectivity of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) diastereoisomers in different tissue and subcellular fractions of earthworms [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 139: 326-334. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.004 [27] RAWN D F K, GAERTNER D W, WEBER D, et al. Hexabromocyclododecane concentrations in Canadian human fetal liver and placental tissues [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468/469: 622-629. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.014 [28] HUANG M R, LI J, XIAO Z X, et al. Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane isomers in breast milk from the general population in Beijing, China: Contamination levels, temporal trends, nursing infant’s daily intake, and risk assessment [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 244: 125524. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125524 [29] 耿新华, 李晓, 刘汝锋, 等. 六溴环十二烷在环境中迁移转化的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2012, 35(S1): 144-150. GENG X H, LI X, LIU R F, et al. Advance in researches on the transport and transformation of hexabromocyclododecanes in environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 35(Sup 1): 144-150 (in Chinese).
[30] 武彤, 张淑贞. 六溴环十二烷非对映体的植物吸收和毒性效应[C]//中国化学会第28届学术年会第2分会场摘要集. 成都, 2012. WU T, ZHANG S Z. Plant uptake and toxic effects of hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers [C]//Proceedings of the 28th Annual Academic Conference of the Chinese Chemical Society, Chengdu, 2012 (in Chinese).
[31] 马强, 李文涛, 孙慧媛, 等. 液相色谱-串联质谱法测定食品接触材料中的六溴环十二烷 [J]. 分析测试学报, 2013, 32(1): 133-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2013.01.022 MA Q, LI W T, SUN H Y, et al. Determination of hexabromocyclododecane in food contact materials by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2013, 32(1): 133-137(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2013.01.022
[32] 钱卓真, 汤水粉, 位绍红. 水产品中六溴环十二烷检测技术及污染水平研究进展 [J]. 渔业研究, 2020, 42(6): 642-650. QIAN Z Z, TANG S F, WEI S H. An overview of determination methodologies and pollution levels of hexabromocyclododecane in aquatic products [J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2020, 42(6): 642-650(in Chinese).
[33] ZHANG Y W, RUAN Y F, SUN H W, et al. Hexabromocyclododecanes in surface sediments and a sediment core from Rivers and Harbor in the northern Chinese city of Tianjin [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(5): 1610-1616. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.08.037 [34] WANG X L, ZHANG X, WANG Z F, et al. Determination of hexabromocyclododecane in soil by supercritical fluid extraction and gas chromatography mass spectrometry [J]. Analytical Methods, 2018, 10(10): 1181-1189. doi: 10.1039/C8AY00018B [35] HONG H Z, LV D M, LIU W X, et al. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of three hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicas [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2017, 188: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.04.010 [36] DREYER A, NEUGEBAUER F, RÜDEL H, et al. Halogenated flame retardants in tree samples applied as bioindicators for atmospheric pollution [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 208: 233-240. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.033 [37] LI H H, ZHANG Q H, WANG P, et al. Levels and distribution of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in environmental samples near manufacturing facilities in Laizhou Bay area, East China [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring:JEM, 2012, 14(10): 2591-2597. doi: 10.1039/c2em30231d [38] 尹姗姗. 白洋淀地区六溴环十二烷的环境行为研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2019. YIN S S. Environmental behavior of hexabromocyclododecane in Baiyangdian area[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2019 (in Chinese).
[39] ZHANG Y W, SUN H W, LIU F, et al. Hexabromocyclododecanes in limnic and marine organisms and terrestrial plants from Tianjin, China: Diastereomer- and enantiomer-specific profiles, biomagnification, and human exposure [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 93(8): 1561-1568. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.004 [40] ZHU H K, SUN H W, YAO Y M, et al. Legacy and alternative brominated flame retardants in outdoor dust and pine needles in mainland China: Spatial trends, dust-plant partitioning and human exposure [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 758-765. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.097 [41] HU J C, JIN J, WANG Y, et al. Levels of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hexabromocyclododecane in the atmosphere and tree bark from Beijing, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 84(3): 355-360. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.002 [42] HUANG H L, WANG D, WAN W N, et al. Hexabromocyclododecanes in soils and plants from a plastic waste treatment area in North China: Occurrence, diastereomer- and enantiomer-specific profiles, and metabolization [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(27): 21625-21635. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9792-9 [43] LI H W, HU Y X, SUN Y X, et al. Bioaccumulation and translocation of tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecanes in mangrove plants from a national nature reserve of Shenzhen City, South China [J]. Environment International, 2019, 129: 239-246. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.034 [44] HUANG H L, WANG D, WEN B, et al. Roles of maize cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes in stereo-selective metabolism of hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) as evidenced by in vitro degradation, biological response and in silico studies [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 656: 364-372. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.351 [45] WU T, HUANG H L, ZHANG S Z. Accumulation and phytotoxicity of technical hexabromocyclododecane in maize [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 42: 97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.06.018 [46] 李蝶. 六溴环十二烷对玉米幼苗基因毒性的研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2020. LI D. Dissertation for the master degree genotoxicity of HBCD to maize seedlings [D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[47] 武彤, 尹姗姗, 刘子鑫, 等. 六溴环十二烷(HBCDs)异构体和对映体在白洋淀土壤和植物中的选择性富集与传输 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 1051-1062. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0412 WU T, YIN S S, LIU Z X, et al. Diastereoisomer- and enantiomers-specific enrichment and translocation of Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in soil and plant from Baiyangdian Lake [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(3): 1051-1062(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0412
[48] ZHANG Y W, SUN H W, ZHU H K, et al. Accumulation of hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers and enantiomers in two microalgae, Spirulina subsalsa and Scenedesmus obliquus [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 104: 136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.02.027 [49] ZHU N L, SCHRAMM K W, WANG T, et al. Lichen, moss and soil in resolving the occurrence of semi-volatile organic compounds on the southeastern Tibetan Plateau, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 518/519: 328-336. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.024 [50] 王馨蕾, 崔兆杰. 超声波提取-气相色谱氢火焰测定土壤中六溴环十二烷 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(3): 493-499. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2018.11.10 WANG X L, CUI Z J. Determination of hexabromocyclododecane in soil by an ultrasonic extraction-gas chromatography with FID method [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(3): 493-499(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2018.11.10
[51] KIM J T, CHOI Y J, BARGHI M, et al. Occurrence and distribution of old and new halogenated flame retardants in mosses and lichens from the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 235: 302-311. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.080 [52] 焦艳超. 环境水土样品中有机污染物检测净化方法总结 [J]. 中国标准化, 2021(15): 243-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5944.2021.15.038 JIAO Y C. Overview of the clean-up methods for organic contaminants in environmental wastewater and soil samples [J]. China Standardization, 2021(15): 243-246(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5944.2021.15.038
[53] LI Y N, ZHOU Q X, WANG Y Y, et al. Fate of tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane brominated flame retardants in soil and uptake by plants [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 82(2): 204-209. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.021 [54] GAO S T, HONG J W, YU Z Q, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface soils from e-waste recycling areas and industrial areas in South China: Concentration levels, congener profile, and inventory [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2011, 30(12): 2688-2696. doi: 10.1002/etc.668 [55] ZHAO Y H, LI Q Q, MIAO X, et al. Determination of hexabromocyclododecanes in sediments from the Haihe River in China by an optimized HPLC-MS-MS method [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 55: 174-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.07.013 [56] ZHANG Y W, GUO Q Q, TAN D F, et al. Effects of low-levels of three hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers on the metabolic profiles of pak choi leaves using high-throughput untargeted metabolomics approach [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 1961-1969. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.062 [57] JIA H H, WANG X T, CHENG H X, et al. Pine needles as biomonitors of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and emerging flame retardants in the atmosphere of Shanghai, China: Occurrence, spatial distributions, and possible sources [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(12): 12171-12180. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04558-8 [58] SALAMOVA A, HITES R A. Brominated and chlorinated flame retardants in tree bark from around the globe [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(1): 349-354. [59] 张艳伟. 六溴环十二烷异构体及其对映体的环境分布与生物富集[D]. 天津: 南开大学, 2014. ZHANG Y W. Environmental distribution and bioaccumulation of hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers and enantiomers[D]. Tianjin: Nankai University, 2014 (in Chinese).
[60] WHITE J C. Differential bioavailability of field-weathered p, p’-DDE to plants of the Cucurbita and Cucumis Genera [J]. Chemosphere, 2002, 49(2): 143-152. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00277-1 [61] WHITE J C, KOTTLER B D. Citrate-mediated increase in the uptake of weathered 2, 2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) 1, 1-dichloroethylene residues by plants [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2002, 21(3): 550-556. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620210312 [62] CHEN J, XIA X H, WANG H T, et al. Uptake pathway and accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in spinach affected by warming in enclosed soil/water-air-plant microcosms [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 379: 120831. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120831 [63] ZHU H K, WANG F, LI B, et al. Accumulation and translocation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers into plant under multiple exposure scenarios [J]. Environment International, 2020, 143: 105947. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105947 [64] HAN T, WU M H, ZANG C, et al. Hexabromocyclododecane and tetrabromobisphenol A in tree bark from different functional areas of Shanghai, China: Levels and spatial distributions [J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2017, 19(10): 1346-1354. [65] 马晓净. 土壤—蔬菜系统中六溴环十二烷异构体的迁移与风险评价[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2017. MA X J. Migration and risk evaluation of hexabromocyclododecane isomer in soil and vegetables system[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2017 (in Chinese).
[66] 李亚宁, 冯秀娟, 刘庆余, 等. 六溴环十二烷在土壤中的归趋及植物吸收研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2013, 35(11): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2013.11.002 LI Y N, FENG X J, LIU Q Y, et al. The fate of HBCD in soil and its uptake by plants [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2013, 35(11): 5-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2013.11.002
[67] ZEGERS B N, METS A, van BOMMEL R, et al. Levels of hexabromocyclododecane in harbor porpoises and common dolphins from western European Seas, with evidence for stereoisomer-specific biotransformation by cytochrome p450 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(7): 2095-2100. [68] ZHU H K, SUN H W, ZHANG Y W, et al. Uptake pathway, translocation, and isomerization of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers by wheat in closed chambers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(5): 2652-2659. [69] ZHAI G S, GUTOWSKI S M, LEHMLER H J, et al. Enantioselective transport and biotransformation of chiral hydroxylated metabolites of polychlorinated biphenyls in whole poplar plants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(20): 12213-12220. [70] WU T, WANG S, HUANG H L, et al. Diastereomer-specific uptake, translocation, and toxicity of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers to maize [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2012, 60(34): 8528-8534. doi: 10.1021/jf302682p [71] HUANG H L, ZHANG S Z, LV J T, et al. Experimental and theoretical evidence for diastereomer- and enantiomer-specific accumulation and biotransformation of HBCD in maize roots [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(22): 12205-12213. [72] 王慧芬. 典型污染区土壤—植物中PCBs污染特征及健康风险评价[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008. WANG H F. Contamination and health risk assessment of PCBs in soil-plant system in the typical areas of Zhejiang Province, China[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008 (in Chinese).
[73] 刘子鑫. 溴代阻燃剂六溴环十二烷在白洋淀土壤植物体系的环境行为研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2021. LIU Z X. Study on environmental behavior of brominated flame retardant hexabromocyclododecanes in Baiyangdian Lake soil-plant system[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2021 (in Chinese).
[74] PENG Y H, CHEN Y J, CHANG M, et al. The effect of zerovalent iron on the microbial degradation of hexabromocyclododecane [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 200: 419-426. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.123 [75] SHAH S B, HUANG L, HU H Y, et al. Characterization of environmentally friendly degradation of hexabromocyclododecane by a Bacillus strain HBCD-sjtu [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2019, 145: 104794. [76] LI Y J, LI M H, SHIH Y H. Aerobic degradation and the effect of hexabromocyclododecane by soil microbial communities in Taiwan [J]. Environment International, 2020, 145: 106128. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106128 [77] CHOU T H, LI Y J, KO C F, et al. Efficient hexabromocyclododecane-biodegrading microorganisms isolated in Taiwan [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 271: 129544. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129544 [78] PENG X X, LU Y Y, WANG Q, et al. Kinetics, pathways and toxicity of hexabromocyclododecane biodegradation: Isolation of the novel bacterium Citrobacter sp. Y3 [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 274: 129929. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129929 [79] LI Y J, WANG R, LIN C Y, et al. The degradation mechanisms of Rhodopseudomonas palustris toward hexabromocyclododecane by time-course transcriptome analysis [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 425: 130489. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130489 [80] UKISU Y. Complete catalytic debromination of hexabromocyclododecane using a silica-supported palladium catalyst in alkaline 2-propanol [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 179: 179-184. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.111 [81] 钱翌, 朱晓艳. 环境中六溴环十二烷的修复技术研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(8): 1390-1395. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.08.022 QIAN Y, ZHU X Y. Advances in environmental remediation technologies for hexabromocyclododecane [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(8): 1390-1395(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.08.022
[82] 叶威, 何祥, 柳龙, 等. 超声波降解溴系阻燃剂六溴环十二烷 [J]. 化学与生物工程, 2014, 31(4): 60-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2014.04.016 YE W, HE X, LIU L, et al. Study on ultrasonic degradation of brominated flame retardant hexabromocyclododecane [J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2014, 31(4): 60-63(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2014.04.016
[83] 余飞, 胡忠. 微生物转化六溴环十二烷研究进展 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(5): 1341-1348. YU F, HU Z. Microbial transformation of hexabromocyclododecanes: A review [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(5): 1341-1348(in Chinese).
[84] LE T T, YOON H, SON M H, et al. Treatability of hexabromocyclododecane using Pd/Fe nanoparticles in the soil-plant system: Effects of humic acids [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 689: 444-450. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.290 [85] HUANG L, WANG W W, ZANAROLI G, et al. Hexabromocyclododecanes are dehalogenated by CYP168A1 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain HS9 [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 87(17): e0082621. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00826-21 [86] HUANG L, WANG W W, SHAH S B, et al. The HBCDs biodegradation using a Pseudomonas strain and its application in soil phytoremediation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 380: 120833. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120833 [87] 杨昭, 王莹莹. 农田土壤中六溴环十二烷的污染过程以及生物修复方法研究进展 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(9): 1839-1850. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-0373 YANG Z, WANG Y Y. Contamination and bioremediation of Hexabromocyclododecane(HBCD) in agricultural soils: A review [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(9): 1839-1850(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-0373
[88] 崔建升, 刘颖, 武彤, 等. γ-六溴环十二烷对映体对玉米的氧化损伤 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(9): 1762-1768. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.09.2016012606 CUI J S, LIU Y, WU T, et al. Oxidative damage of γ-hexabromocyclododecane enantiomers to maize [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(9): 1762-1768(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.09.2016012606
[89] 武彤, 李蝶, 田柳, 等. β-六溴环十二烷对玉米生长代谢的对映体选择性影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(3): 909-917. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020102704 WU T, LI D, TIAN L, et al. Enantioselective effects of β-HBCD on the growth metabolism of maize [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(3): 909-917(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020102704
-



 下载:
下载:

