-
微塑料,即尺寸小于5 mm的塑料,是近年来备受瞩目的新兴污染物[1]。塑料在生产生活中的广泛使用让微塑料的源头无处不在,它们在地表径流、风力、生物等外界因素影响下进入水中,在水中迁移累积并引发各种环境问题[2]。部分微塑料拥有与水生动物食物类似的外形而容易被误食,导致多方面的毒性效应。被水生动物摄食的微塑料随着食物链逐级迁移累积,最终会对人类健康产生威胁[3]。
中国是世界塑料产量第一的国家,微塑料污染问题更加值得关注[4]。研究者们对中国不同类型水域进行监测,在渤海、黄海、东海等海域,长江、黄河、珠江等河流,洞庭湖、鄱阳湖等湖泊中,均发现了不同程度的微塑料污染[5-10]。中国水环境普遍受到微塑料污染的威胁,但不同区域微塑料的污染水平大相径庭[11]。作为一类人造产物,微塑料污染水平与人类活动密切相关,人口密集的城市区域更容易成为微塑料污染的热点区域[12]。目前中国淡水区域微塑料污染相关数据仍然存在空缺,尤其是对于与人类接触频繁的城市湖泊,相关研究十分不足。截至目前为止,只有武汉、长沙、马鞍山等少数城市湖泊有微塑料污染数据可供参考[13-15]。
洞庭湖区是中国重要的农业生产基地和生态基因库,也是享誉中外的旅游胜地。已有研究表明,洞庭湖区广泛受到微塑料污染的威胁。岳阳市是洞庭湖区的最大城市,其生态环境对周边区域影响重大。本研究选取岳阳市内最大的城市湖泊——岳阳南湖作为研究区域,对其表层水体中的微塑料进行调查分析,这是针对洞庭湖区城市湖泊微塑料污染进行的首次研究。本研究将进一步完善城市湖泊微塑料污染基础数据库,为城市区域微塑料污染的防治提供科学依据。
-
南湖位于湖南省岳阳市市中心区域,湖泊面积15.64 km2,平均水深3 m。南湖原属洞庭湖的一部,在人为修建南津港大堤将其与洞庭湖分割开来后形成了一个典型的半封闭城市内湖泊,南湖西侧通过闸口与洞庭湖相连。南湖位于岳阳城市区域内的南湖旅游度假开发区,蜿蜒曲折、总长50 km的湖岸线均属于城市区域。采样点位置如图1所示。南湖湖面上共设置了14个采样点,这些采样点覆盖了南湖的各个区域。
-
采样工作于2019年11月于船只上进行,在每个采样点使用拉式采样器(KLL-S4,SEBA,德国)采集15 L来自0—30 cm深度的表层水体样品,并在船只上当场使用0.045 mm的不锈钢筛网过滤,再将筛网上截留的固体使用去离子水全部冲入采样瓶中保存,所有采样瓶被标放置于冷藏保温箱中进行保存并在采样完成后尽快返回实验室进行处理。基于使用筛网的孔径,本研究仅统计0.045—5 mm范围内的微塑料。
-
样品分析方法参照已有研究进行[16]。采集到的样品在实验室中加入30%过氧化氢溶液和亚铁离子溶液各20 mL进行消解,直至将样品中肉眼可见的生物体清除,使用200 mL密度为1.5 g·cm−3的氯化锌溶液对消解后的样品进行密度分离,去除样品中存在的砂土等杂质。经过24 h静置后提取上清液,将上清液中的固体抽滤到玻璃纤维滤膜上以备镜检。
-
使用体视显微镜来对所有滤膜进行观察(Stemi 508,Zeiss,德国)。根据滤膜上微塑料的表面特征进行分类,并记录它们的形貌特征。微塑料根据其形状划分为纤维、碎片和微球的3种类型,具体分类方法参照已发表的研究进行。为了减少镜检误判带来的误差,本研究采用显微红外光谱仪对微塑料进行进一步的鉴定以确定微塑料的化学成分(Nicolet iN10,Thermo scientific,美国)[17]。
-
本研究使用n·m−3作为单位表达微塑料的丰度,其中n代表微塑料的数量。不同采样点之间的微塑料丰度差异使用单因素方差分析法(ANOVA)进行分析,而南湖不同区域及不同湖泊之间的微塑料丰度对比采用t检验(student-t test)方法进行,当P<0.05时被认为具有统计学意义。所有数据分析使用SPSS Statistics 22.0和Microsoft Excel 365完成。
-
本研究中质量控制方法参照本课题组已发表研究进行设置[18]。在进行样品采集、实验室处理的过程中,所有研究人员均穿戴无粉酚醛手套、穿着天然材料的棉质衣物。所有材料与仪器均使用超纯水清洗3次后使用铝箔纸包裹,仅使用时取出。在进行所有操作时尽量不使用塑料仪器。此外,6个使用去离子水制成的空白样品使用同样方法进行处理,空白实验未发现微塑料存在,说明本研究中来自实验室的背景污染可以忽略。
-
微塑料在南湖表层水体样品中的丰度范围在3050—7100 n·m−3之间,平均丰度为(4664±1742)n·m−3。图2中展示了不同采样位置的微塑料丰度水平。各个采样点之间的丰度水平存在一定差异,但这些差异并没有达到数量级的水平。位于南湖中央的S13采样点污染最为严重,而位于湖泊西北九眼桥的S2采样点污染水平最低。
南湖位于岳阳市中心,是每年吸引大量观光客的著名旅游景点,湖泊部分区域还有养鱼场的存在,人类活动的频繁使潜在的微塑料来源较多[19]。本研究发现南湖存在着较高水平的微塑料污染,且不同区域采样点的丰度水平有一定区别,湖边区域(S1—S10)的微塑料丰度显著低于湖中区域(S11—S14)(P<0.05),这一现象与南湖的水动力特性关系密切。岳阳南湖作为一个典型城市湖泊,其与东洞庭湖连接的闸口除洪水期外均为关闭状态,换言之,南湖在大多数情况下属于封闭性湖泊,水动力特性接近于内陆咸水湖[20]。水流在湖泊中央形成环流区域,导致微塑料在水流的作用下迁移并滞留于湖泊中央。与之相对,这可能是导致微塑料分布展现出“中高边低”的原因[21]。类似的情况在中国青海湖也有出现,根据Xiong等对青海湖表层水体微塑料的调查,环流中央的微塑料污染水平最高可达湖边区域的150多倍[20]。相邻的东洞庭湖则恰好相反,东洞庭湖属于典型自然淡水湖泊,水流集中于南侧鹿角流入,于城陵矶流出而汇入长江,这导致东洞庭湖微塑料丰度水平在入湖口、出湖口较高[9]。南湖与其他湖泊微塑料污染分布特征均可说明水动力因素对微塑料污染的分布起着重要的作用。值得注意的是,南湖水动力特性会在一定时期产生变化。当位于湖泊西侧的闸口开启时,南津港附近水域可能由于水流集中而导致微塑料丰度上升,累积于南湖之中的微塑料也会随之排入洞庭湖,对洞庭湖的环境产生影响[18]。与之类似,南湖北侧王家河水的汇入也可能挟带着微塑料进入南湖。后续研究应该注意对特殊时期的南湖进行调查分析,探明南湖与周边水环境微塑料污染的相互关系。在一些大型湖泊中,风力会对微塑料的分布特征产生影响,但南湖地处岳阳城区最为繁华的区域,周边高楼对风速的削弱效果十分明显,微塑料分布特征没有明显体现出风力的作用效果[22]。
作为一种新兴污染物,微塑料的研究时间较短,采样方法、实验室处理、统计分析等方面均无统一标准,世界上也无任何国家或机构出台微塑料污染水平划分的方法或建议。因此,目前所有微塑料污染水平的确定只能通过已有研究之间的相互对比进行,而这些对比也仅在研究方法类似和丰度单位相同时才有意义[23]。表1中列举了以相似方法进行统计的世界各地湖泊表层水体微塑料污染水平。通过对比可知南湖表层水体中微塑料污染水平显著高于大多数自然湖泊。与南湖相比,意大利的两个旅游湖泊波尔塞纳湖和秋士湖的人流量较小[24];洪湖、鄱阳湖拥有较大的湖面面积,湖中心区域受到人类活动影响较少[9-10]。与之相对,位于中国武汉的北湖、长沙的跃进湖,以及土耳其的库库柯米克泻湖与南湖拥有类似的情况[15,25-26]:位于人口稠密的城市区域、湖泊面积较小等。南湖表层水体中的微塑料污染水平亦显著高于相邻的东洞庭湖(P<0.05),与洞庭湖其他两个区域南洞庭湖、西洞庭湖的差距更为明显,说明人类活动强度对微塑料污染水平的影响显著[27]。
-
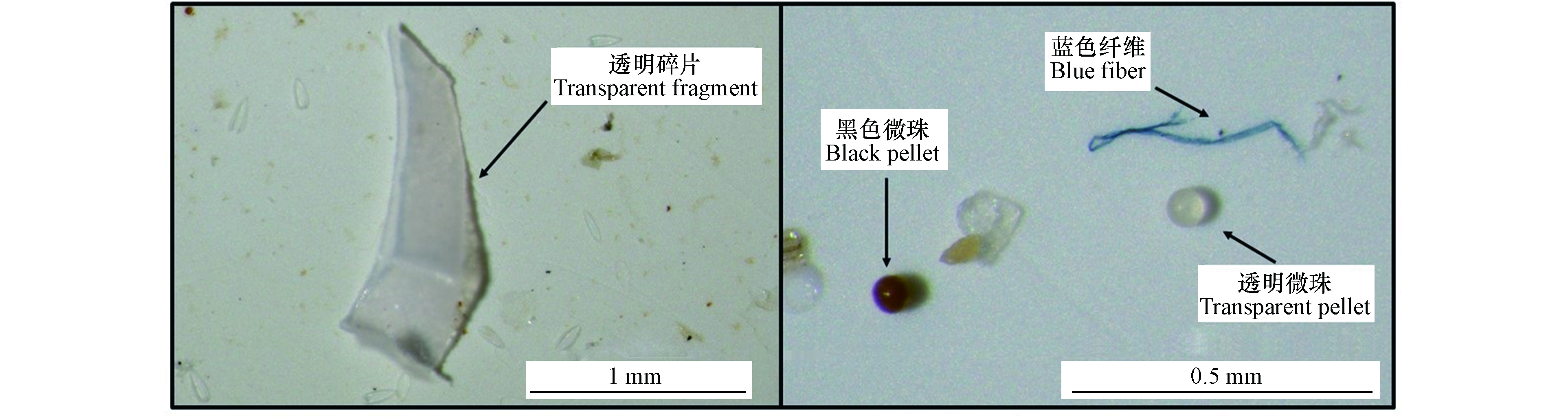
在南湖采集的14个表层水体样品中检测出的微塑料总量为1306个,本研究利用体视显微镜记录了它们的颜色、形状以及尺寸,这些粒子根据其形状被归类到纤维、微球及碎片三类之中(见图3、4)。
从颜色方面来看,透明的微塑料占据了最大的比例,达到了55.8%〔见图3(a)〕。黑色、蓝色是继透明之后较为常见的颜色,分别占比23.6%和14.3%。其余微塑料为红色(3.8%)、黄色(1.9%)、绿色(0.6%)。尺寸方面,微塑料的数量与其尺寸呈反比,尺寸从大到小的占比分别为53.9%、24.9%、19.3%、1.9%,各组数据之间差异显著(P<0.05)〔见图3(b)〕。微塑料形状方面,从南湖采集到的微塑料中纤维占据了90.7%的比例,与之相比,微球和碎片的占比很小,分别为4.8%和4.5%〔见图3(c)〕。
基于微塑料的形貌特征分析其来源是目前相关研究常用的方法。从微塑料的颜色方面来看,本研究与许多已有研究类似,透明微塑料占比较大,透明及简单染色的一次性用品大量使用是导致这一现象的原因。另一方面,在消解过程中使用的强氧化剂也可能导致一些着色粗糙的有色微塑料褪色[32]。用作交通工具中橡胶材料和渔场渔具的黑色、蓝色微塑料也在本研究中数量较多[33-34]。其余红、黄、绿色的微塑料也与日常生活中常见的塑料用品颜色相符。尺寸方面微塑料的数量与其尺寸呈反比。由于较大尺寸的微塑料可以在外界作用下裂解为多个小尺寸微塑料,这一现象是合理且常见的。
本研究从采集的1306个粒子中选择130个具有代表性的微塑料进行检测,检测结果如表2所示,共检测了100个纤维、10个微球和20个碎片,拣选的微塑料涵盖了收集到的不同形状、尺寸、颜色的微塑料,图5中展示了典型微塑料的显微红外光谱。聚酰胺(PA)则在纤维中占比最大,聚乙烯(PE)次之,再次为聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)。微球和碎片均以PE为主。少数微塑料被鉴定为聚丙烯(PP)和聚苯乙烯(PS)。
从FTIR检测结果来看,本研究中的微球和碎片均以聚乙烯为主,其广泛用于制造日用品、渔网及农用薄膜,在研究区域的来源十分广泛,比水更低的密度也使其容易漂浮于湖泊表面。环境中的聚乙烯微塑料可以导致生物毒性效应,也可以作为吸附其他污染物的载体,这一问题在微塑料老化之后更加严重[35-36]。俗称尼龙、涤纶的聚酰胺、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯均属合成纤维最为常见的材料,和聚乙烯的情况类似,它们在南湖区域拥有较多潜在污染源,潜在生态风险亦不可忽视[37-38]。除此之外,少数粒子被鉴定为聚丙烯和聚苯乙烯,没有检出生态风险指数较高的聚氯乙烯等微塑料[39]。结合微塑料外观形态和化学成分分析的结果来看,居民日常生活、旅游业和渔业产生的大量纤维是南湖微塑料最重要的来源,而一次性塑料用品和日常护理品的使用则分别是碎片和微球状微塑料的来源[33,40-41]。
岳阳市近年来在南湖环境保护上举措甚多,如逐步建立生态环境保护管理体制、加强突出生态环境问题整改工作等[42]。南湖排污单位得到了有效管控,建立了南湖水质自动监测项目对南湖水质进行监测,南湖水质断面Ⅲ类达标率由2016年的8.3%提高至2020年的55%。碎片和小球的低丰度也反映出南湖水环境管理措施较为完善。然而,这类措施的效果更多地仅能反映在对微球和碎片微塑料的控制上,固体废物和污水、废水处理条件的改善对纤维微塑料去除率的作用有限,来自附近居民及游客的纺织品脱落、空气中纤维微塑料的沉降暂无有效措施可进行处理[43]。
在实验室环境下进行的动、植物微塑料暴露实验证实了纤维微塑料的毒性。纤维微塑料可以上调斑马鱼的甘油磷脂代谢,加剧氧化损伤和炎症,同时下调与营养缺乏相关的脂肪酰代谢[44];250 μm尺寸的PET纤维微塑料可以引发秀丽隐杆线虫的多代毒性,受到影响的秀丽隐杆线虫出现了运动能力下降、生殖率下降等现象,相关毒性效应需要经过多代才能得以恢复[45]。此外,水环境中赋存的大量纤维微塑料可能使生物体摄入微塑料的量上升,从而加剧微塑料生物累积及食物链转移的风险。目前世界各地已有多项报告证明纤维微塑料在水生生物体内的赋存和累积,其中包括人类经常食用的鱼、虾、蛤蜊等,它们体内的纤维微塑料可以带来生物累积、污染物载体、添加剂释放等多方面的风险,人类作为食物链顶端的存在也会间接被动植物体内的微塑料所影响[46]。因此,南湖微塑料污染的防治在继续严控污废水和固体废弃物排放的同时,也应同时考虑处理工艺的改进以使其具备更强的微塑料处理能力[47]。
-
(1)南湖表层水体中微塑料丰度在3050—7100 n·m−3之间,平均丰度为(4664±1742) n·m−3。相比包括东洞庭湖在内的自然湖泊较高,与其他城市湖泊的微塑料污染丰度接近。表明处于城市中心的岳阳南湖受到了比自然湖泊更加严重的微塑料污染,人类活动是微塑料污染水平的重要影响因素。
(2)南湖表层水体中微塑料的分布方式呈现中心高、周边低的特征。微塑料分布受到水动力条件的影响较为显著,城市内封闭性湖泊中央形成的环流区域成为了微塑料在南湖表层水体中的汇;南湖表层水体中微塑料以纤维状为主,碎片和微球状的微塑料数量较少,最常见的化学成分为聚乙烯,其次为聚酰胺和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯。在水环境保护措施日益完善的背景下,仍需对相关措施进行改进以更加有效地应对微塑料污染威胁。
本研究中尚存在一定局限性需要在未来得到完善:1)综合考虑洪水期开闸等特殊时期的情况,进一步深入探讨水动力环境与南湖微塑料污染的相互关系;2)改进微塑料分析鉴定方式,定量分析南湖微塑料污染生态风险;3)结合最新研究进展和南湖实际情况,为南湖微塑料污染防控措施提供具体有效的科学意见。
典型城市湖泊岳阳南湖表层水体中的微塑料污染特征
Microplastics in surface water of a typical urban lake: A case study from Nanhu Lake, Yueyang City
-
摘要: 微塑料是目前环境领域备受瞩目的新兴污染物,其污染监测基础数据仍存在许多空白亟待填补。本研究选择典型城市湖泊岳阳南湖为研究区域,对其表层水体微塑料污染进行研究。本研究在14个遍布南湖各个区域的采样点采集表层水体样品,基于湿式消解和密度分离方法对样品进行处理,并采用体视显微镜和显微红外光谱仪进行鉴定,对该区域45 μm—5 mm范围的微塑料污染水平、分布特征、潜在来源及风险进行探讨。研究结果表明,南湖表层水体微塑料丰度在3050—7100 n·m−3之间,平均值为(4664±1742)n·m−3,其污染水平高于大多数自然湖泊,与武汉、长沙等城市湖泊相当; 南湖表层水体中的微塑料更容易集中于湖泊中央区域,微塑料在南湖表层水体中的分布呈现“中高边低”的特点;南湖中检测到的微塑料以纤维状为主,其化学成分主要为聚乙烯、聚酰胺和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇脂。由此可知,居民日常生活、旅游业、渔业是南湖微塑料的潜在来源;南湖表层水体微塑料的分布受到水动力条件影响显著;同时,研究区域对于碎片和微球微塑料的管控措施较为有效,而纤维微塑料仍大量赋存于南湖之中,这种情况需要得到重视,微塑料污染防控措施在未来需要进一步完善。Abstract: Microplastic is an emerging pollutant that has attracted wide attention. There still lacks the baseline data of microplastic pollution in many regions, which need to be filled urgently. This paper regarded the typical urban lake-Nanhu Lake in Yueyang City as the research area, and the microplastic pollution level in its surface water was studied. Fourteen sampling sites which were spread across the Nanhu Lake were set to collect surface water samples. Wet digestion oxidation and density separation were choosing as the methods to process water samples. The stereomicroscopy and micro-Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy (μ-FTIR) were applied in identifying microplastics. The pollution levels, distribution characteristics, potential sources, and ecological risk of microplastics with a size range of 45 μm — 5 mm in Nanhu Lake were explored and discussed. The result showed that: 1) Microplastic concentrations of surface water in Nanhu Lake ranged from 3050 — 7100 n·m−3, with an average value at (4664±1742) n·m−3. The pollution level in Nanhu Lake was higher than most natural lakes, and not much different from the urban lakes in other cities, such as Wuhan and Changsha. 2) Microplastic was easier to gather in the central area of Nanhu Lake. The abundance of microplastics in the middle area was higher than that at the edge of this lake. 3) The most common shapes of microplastics in collected surface water samples from Nanhu Lake were fiber. The major polymer compositions were polyethylene (PE), polyamide (PA), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). These findings indicated that surroundings residents’ daily life, tourism, and fisheries made a large contribution to the microplastics pollution in Nanhu Lake. And hydrodynamic characteristic is the critical factor for the distribution of microplastics in this lake. At the same time, we could know that the manage measures for debris and microsphere microplastics in this study area were more effective than fiber microplastics. A large number of fiber microplastics still existed in this urban lake. This phenomenon must be taken seriously and the prevention and control measures for microplastics should be further improved.
-
Key words:
- microplastics /
- lake /
- surface water /
- urban
-

-
表 1 湖泊表层水体中微塑料的分布
Table 1. Occurrence of microplastics in surface water of lakes
地点 Location 国家 Country 采集下限/μm Lower limit 丰度/(n·m−3) Abundance 数据来源 Reference 波尔塞纳湖 意大利 300 0.82—4.42 [24] 秋士湖 意大利 300 2.68—3.36 [24] 巴塔哥尼亚诸湖 阿根廷 38 0.9 [28] 库库柯米克泻湖 土耳其 50 3000—124000 [26] 太湖 中国 47 3400—25800 [29] 北湖 中国 50 8925 [15] 洪湖 中国 50 1250—4650 [9] 滇池 中国 20 800—6000 [30] 跃进湖 中国 45 7050 [25] 鄱阳湖 中国 50 5000—34000 [10] 乌梁素海 中国 75 3120—11250 [31] 南洞庭湖 中国 45 367—1567 [27] 西洞庭湖 中国 45 433—1500 [27] 东洞庭湖 中国 50 900—2800 [9] 南湖 中国 45 3050—7100 本研究 表 2 南湖表层水体中微塑料的化学成分
Table 2. Polymer composition of microplastics in Nanhu Lake
化学成分 Polymer 纤维 Fiber 微球 Pellet 碎片 Fragment 总计 Total 聚乙烯 PE 32 9 11 52 聚酰胺 PA 43 0 0 43 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯 PET 22 0 3 25 聚丙烯 PP 3 0 4 7 聚苯乙烯 PS 0 1 2 3 总计 Total 100 10 20 130 -
[1] KLINGELHÖFER D, BRAUN M, QUARCOO D, et al. Research landscape of a global environmental challenge: Microplastics [J]. Water Research, 2020, 170: 115358. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115358 [2] 王英雪, 徐熳, 王立新, 等. 微塑料在哺乳动物的暴露途径、毒性效应和毒性机制浅述 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(1): 41-54. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020053002 WANG Y X, XU M, WANG L X, et al. The exposure routes, organ damage and related mechanism of the microplastics on the mammal [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(1): 41-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020053002
[3] 张子琪, 高淑红, 康园园, 等. 中国水环境微塑料污染现状及其潜在生态风险 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(10): 3574-3581. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0390 ZHANG Z Q, GAO S H, KANG Y Y, et al. Current status of microplastics contamination in China's water environment and its potential ecological risks [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(10): 3574-3581(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0390
[4] ZHANG Z Y, ZULPIYA·MAMAT, CHEN Y G. Current research and perspective of microplastics (MPs) in soils (dusts), rivers (lakes), and marine environments in China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 202: 110976. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110976 [5] ZHONG M Y, TANG J H, GUO X Y, et al. Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the Bohai, Yellow and East China seas [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140434. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140434 [6] HE D, CHEN X J, ZHAO W, et al. Microplastics contamination in the surface water of the Yangtze River from upstream to estuary based on different sampling methods [J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 196: 110908. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110908 [7] HAN M, NIU X R, TANG M, et al. Distribution of microplastics in surface water of the lower Yellow River near estuary [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 707: 135601. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135601 [8] CHENG Y, MAI L, LU X W, et al. Occurrence and abundance of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) on microplastics (MPs) in Pearl River Estuary (PRE) region: Spatial and temporal variations [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 281: 117025. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117025 [9] WANG W F, YUAN W K, CHEN Y L, et al. Microplastics in surface waters of dongting lake and Hong lake, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 539-545. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.211 [10] YUAN W K, LIU X N, WANG W F, et al. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in water, sediments, and wild fish from Poyang Lake, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 170: 180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.126 [11] 朱莹, 曹淼, 罗景阳, 等. 微塑料的环境影响行为及其在我国的分布状况 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(9): 1437-1447. ZHU Y, CAO M, LUO J Y, et al. Distribution and potential risks of microplastics in China: A review [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(9): 1437-1447(in Chinese).
[12] 徐舟影, 陈奥飞, 赵胤祺, 等. 武汉城市污水中微塑料的分离、鉴定及其微观特征分析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(3): 637-645. XU Z Y, CHEN A F, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Separation, identification and microscopic characteristics analysis of microplastics in Wuhan municipal sewage [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(3): 637-645(in Chinese).
[13] WEN X F, DU C Y, XU P, et al. Microplastic pollution in surface sediments of urban water areas in Changsha, China: Abundance, composition, surface textures [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 136: 414-423. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.043 [14] 王璇, 牛司平, 宋小龙, 等. 城市湖泊沉积物微塑料污染特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(7): 3240-3248. WANG X, NIU S P, SONG X L, et al. Characterization of microplastic pollution of sediments from urban lakes [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(7): 3240-3248(in Chinese).
[15] WANG W F, NDUNGU A W, LI Z, et al. Microplastics pollution in inland freshwaters of China: A case study in urban surface waters of Wuhan, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 575: 1369-1374. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.213 [16] WANG X J, BOLAN N, TSANG D C W, et al. A review of microplastics aggregation in aquatic environment: Influence factors, analytical methods, and environmental implications [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 402: 123496. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123496 [17] WANG C, XING R L, SUN M D, et al. Microplastics profile in a typical urban river in Beijing [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 743: 140708. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140708 [18] YIN L S, WEN X F, DU C Y, et al. Comparison of the abundance of microplastics between rural and urban areas: A case study from East Dongting Lake [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 244: 125486. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125486 [19] GARDON T, EL RAKWE M, PAUL-PONT I, et al. Microplastics contamination in pearl-farming lagoons of French Polynesia [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 419: 126396. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126396 [20] XIONG X, ZHANG K, CHEN X C, et al. Sources and distribution of microplastics in China's largest inland lake - Qinghai Lake [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 235: 899-906. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.081 [21] QUESADAS-ROJAS M, ENRIQUEZ C, VALLE-LEVINSON A. Natural and anthropogenic effects on microplastic distribution in a hypersaline lagoon [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 776: 145803. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145803 [22] BERMÚDEZ M, VILAS C, QUINTANA R, et al. Unravelling spatio-temporal patterns of suspended microplastic concentration in the Natura 2000 Guadalquivir estuary (SW Spain): Observations and model simulations [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 170: 112622. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112622 [23] KUTRALAM-MUNIASAMY G, PÉREZ-GUEVARA F, de MARTÍNEZ I E, et al. Overview of microplastics pollution with heavy metals: Analytical methods, occurrence, transfer risks and call for standardization [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 415: 125755. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125755 [24] FISCHER E K, PAGLIALONGA L, CZECH E, et al. Microplastic pollution in lakes and lake shoreline sediments - A case study on Lake Bolsena and Lake Chiusi (central Italy) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 213: 648-657. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.012 [25] YIN L S, JIANG C B, WEN X F, et al. Microplastic pollution in surface water of urban lakes in Changsha, China [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(9): 1650. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16091650 [26] FARUK ÇULLU A, SÖNMEZ V Z, SIVRI N. Microplastic contamination in surface waters of the Küçükçekmece Lagoon, Marmara Sea (Turkey): Sources and areal distribution [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268: 115801. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115801 [27] JIANG C B, YIN L S, WEN X F, et al. Microplastics in sediment and surface water of west dongting lake and south dongting lake: Abundance, source and composition [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(10): 2164. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15102164 [28] ALFONSO M B, SCORDO F, SEITZ C, et al. First evidence of microplastics in nine lakes across Patagonia (South America) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 733: 139385. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139385 [29] SU L, XUE Y G, LI L Y, et al. Microplastics in Taihu lake, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 216: 711-719. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.036 [30] 袁海英, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 等. 滇池近岸水体微塑料污染与富营养化的相关性 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7): 3166-3175. YUAN H Y, HOU L, LIANG Q B, et al. Correlation between microplastics pollution and eutrophication in the near shore waters of Dianchi lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(7): 3166-3175(in Chinese).
[31] MAO R F, HU Y Y, ZHANG S Y, et al. Microplastics in the surface water of Wuliangsuhai Lake, Northern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 723: 137820. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137820 [32] WANG F, WANG B, DUAN L, et al. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in domestic, industrial, agricultural and aquacultural wastewater sources: A case study in Changzhou, China [J]. Water Research, 2020, 182: 115956. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115956 [33] ZHOU A G, ZHANG Y, XIE S L, et al. Microplastics and their potential effects on the aquaculture systems: A critical review [J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2021, 13(1): 719-733. doi: 10.1111/raq.12496 [34] JÄRLSKOG I, STRÖMVALL A M, MAGNUSSON K, et al. Traffic-related microplastic particles, metals, and organic pollutants in an urban area under reconstruction [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 774: 145503. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145503 [35] LI H, WANG F H, LI J N, et al. Adsorption of three pesticides on polyethylene microplastics in aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, and molecular dynamics simulation [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 264: 128556. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128556 [36] LAN T, WANG T, CAO F, et al. A comparative study on the adsorption behavior of pesticides by pristine and aged microplastics from agricultural polyethylene soil films [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 209: 111781. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111781 [37] de FELICE B, AMBROSINI R, BACCHETTA R, et al. Dietary exposure to polyethylene terephthalate microplastics (PET-MPs) induces faster growth but not oxidative stress in the giant snail Achatina reticulata [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 270: 129430. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129430 [38] KHOSROVYAN A, KAHRU A. Evaluation of the potential toxicity of UV-weathered virgin polyamide microplastics to non-biting midge Chironomus riparius [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 287: 117334. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117334 [39] LITHNER D, LARSSON Å, DAVE G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(18): 3309-3324. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.038 [40] SONG K, DING R R, SUN C Y, et al. Microparticles and microplastics released from daily use of plastic feeding and water bottles and plastic injectors: Potential risks to infants and children in China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021,28: 59813-8. [41] DOWARAH K, DEVIPRIYA S P. Microplastic prevalence in the beaches of Puducherry, India and its correlation with fishing and tourism/recreational activities [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 148: 123-133. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.066 [42] 岳阳市生态环境局南湖新区分局. 南湖新区“十三五”期间和2020年生态环境保护工作总结[EB/OL]. [2020-12-1] http://www.yynanhu.gov.cn/29509/54779/54784/content_1770865.html. [43] SONG Z Y, LIU K, WANG X H, et al. To what extent are we really free from airborne microplastics? [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 754: 142118. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142118 [44] ZHAO Y P, QIAO R X, ZHANG S Y, et al. Metabolomic profiling reveals the intestinal toxicity of different length of microplastic fibers on zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123663. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123663 [45] LIU H L, KWAK J I, WANG D Y, et al. Multigenerational effects of polyethylene terephthalate microfibers in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 193: 110569. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110569 [46] MATEOS-CÁRDENAS A, O'HALLORAN J, van PELT F N A M, et al. Beyond plastic microbeads-Short-term feeding of cellulose and polyester microfibers to the freshwater amphipod Gammarus duebeni [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 753: 141859. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141859 [47] REBELEIN A, INT-VEEN I, KAMMANN U, et al. Microplastic fibers—Underestimated threat to aquatic organisms? [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 777: 146045. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146045 -




 下载:
下载: