-
煤炭作为我国主要能源之一,其燃烧会产生大量颗粒污染物。目前,针对大气中的悬浮颗粒物,我国已采取了多种解决方案[1]。可吸入颗粒物 (PM10) 在污染环境的同时,会影响交通安全[2-3]、人群健康[4-6]。因此,如何有效控制颗粒物排放是当前大气污染治理的重点。目前,工业上主要采用电除尘器来减少颗粒物的排放,但其去除PM2.5能力不足[7-8]。因此,为提高PM2.5的脱除效率,采用电凝并的方法对颗粒物先进行预处理[9],使细颗粒物通过碰撞凝并以增大其粒径,易于被后端电除尘器脱除。
含尘气流通过电晕极中的高压电场时,粉尘颗粒荷电的过程称为粒子荷电。电凝并技术的关键在于提高颗粒的荷电量,使带电粒子以电泳方式达到较大颗粒物的表面,这样便能提高颗粒间的有效碰撞[10],从而促进凝并。WATANABE等[11]、向晓东等[12]的研究表明,加装了预荷电区和凝并区可有效提高电除尘器的效率,而且预荷电技术在钢铁、水泥、锅炉等多个领域均有应用[13]。预荷电效果受多种因素影响,如电极配置、电压、流场风速、颗粒浓度等[14]。王连泽等[15]将含尘气体通过异极性放电电场,随后将其混合进行凝并后发现,施加到电场中正电压和负电压的相互配合对颗粒物的凝并效果影响更大。JI等[16]在直流和交流电场中的粒子充电和团聚的实验中,发现对于给定的电晕电压,在所有大小的颗粒中,负电晕都比正电晕产生更高的电荷,颗粒电荷取决于颗粒质量载荷,质量负荷越大,颗粒的电荷数越低。何剑等[17]提出了一体式双极荷电凝并方法及装置,其颗粒捕集效率有了明显提高。颗粒物的凝并效率与正电晕通道的电场强度成正比,但与负电晕通道的电场强度关系不大。CHANG等[18]对颗粒预荷电特性进行研究,在探讨放电电压对颗粒荷电量的影响时发现正电晕放电时粉尘颗粒的带电量远远大于负电晕的带电量,但使用负电晕放电时则更加稳定。SOBCZYK等[19]对包含有单极静电凝并器的静电除尘器进行了研究,该系统相比单级静电除尘器对PM10的收集效率更高。李雪娥[20]研究双极电袋复合除尘时发现,在相同条件下,双极电袋复合除尘器的伏安特性和除尘效率都高于单级电袋复合除尘器。张江石等[21]对一个电凝并装置安装了双极芒刺预荷电装置后,发现对细微粉尘的凝并效率可提高10%以上。ZHANG等[22]表示通过对电极的优化可以提高离子密度进而加强小颗粒的荷电效果,而通过提高电压增大电场强度可以促进大颗粒的荷电,可见对于不同大小的颗粒影响荷电的因素不同,故应当根据粒径选择不同的参数调整方法。YANG等[23]对电场中粒子荷电过程进行了数值模拟,发现颗粒浓度的变化对电场影响很大,若大到一定程度,电场会被悬浮颗粒上的电荷产生的二次电场严重扭曲,甚至使得下游放电极上所产生的的电晕电流彻底消失,这会使电除尘器的效率大大下降。WANG等[24]同样发现随着PM0.1质量浓度从0增至100.0 mg·m−3,除尘器内离子浓度会下降两个数量级以上,使得颗粒的荷电、传输性能急剧恶化,而加装预荷电器后,该问题得到明显改善。HU等[25]采用多物理耦合验证的数值方法研究了PM2.5在线-板式电除尘器中的荷电和迁移行为和实验参数对除尘效率的影响,结果表明当风速为1.0 m·s−1、电压为50.0 kV时,对2.0 μm的颗粒收集效率达到了100%。以上研究结果表明,预荷电条件的改变会对颗粒物电凝并效果产生很大影响。
然而有关多种因素共同作用下的影响研究仍较为缺乏。本课题组拟探究对预荷电中放电极种类、放电极性、电压值、粉尘浓度、烟道风速5个主要因素对电凝并效果的影响。选取2种典型的放电极:四齿芒刺线和鱼骨线。这2种电极各有优劣:四齿芒刺线尖端密集,电晕电流密度大,利于粉尘荷电,但其正对极板处存在较大范围电流密度盲区;而鱼骨线由于结构简单,产生的盲区没有四齿芒刺线大,但其电流密度小,仅适合处理较小比电阻粉尘[26-27]。基于此,本研究选择这2种电极作为预荷电的放电极,探索其在不同荷电参数下的凝并效果。设计多因素实验研究,通过正交设计从全面实验中选出部分典型性的实验点[28-29],对因素水平进行简化、择优处理,在此基础上进行正交实验,分析结果以得到最佳实验参数组合,以期得到相关因素对电凝并效果的影响,为电除尘技术的应用提供参考。
-
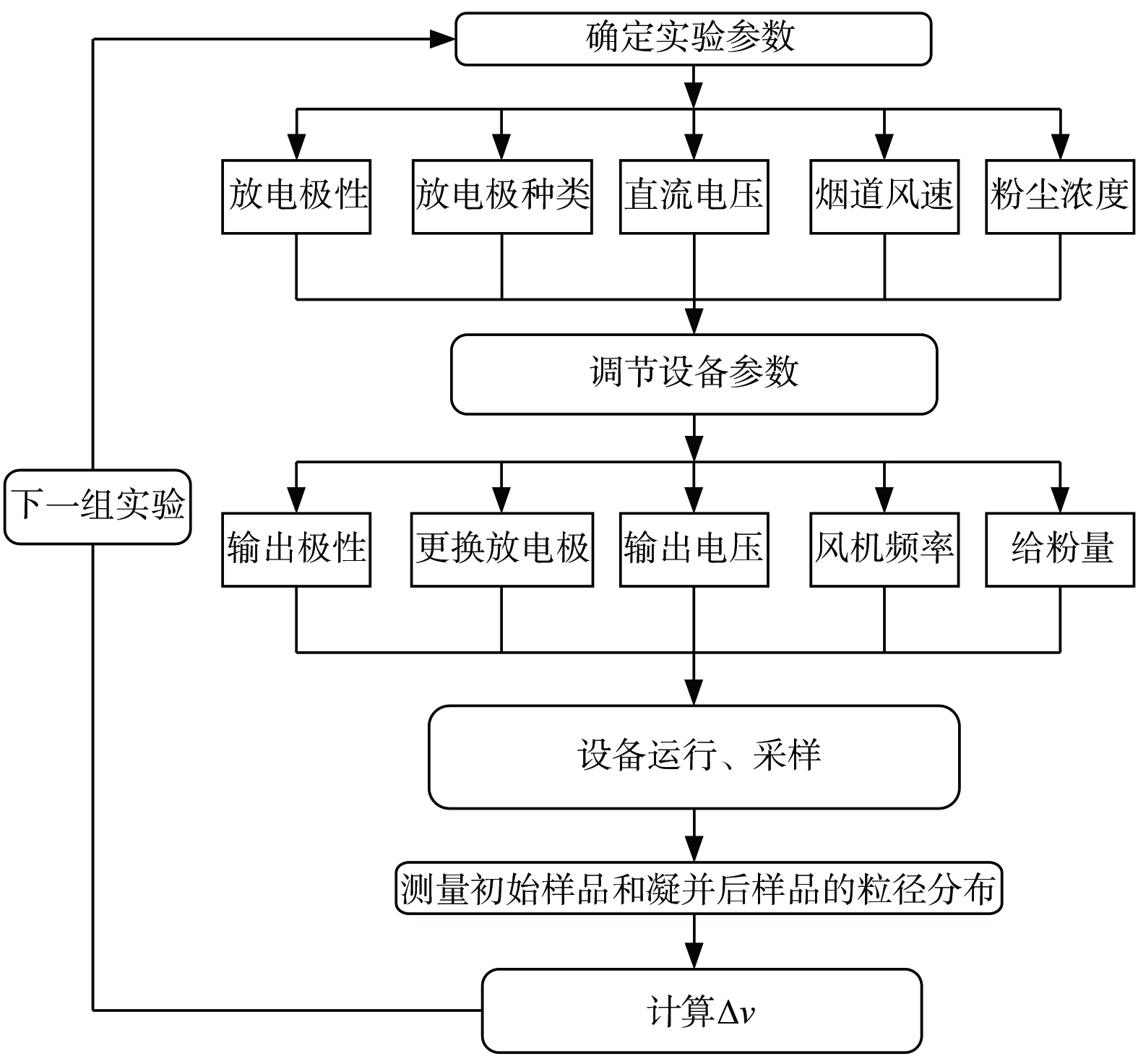
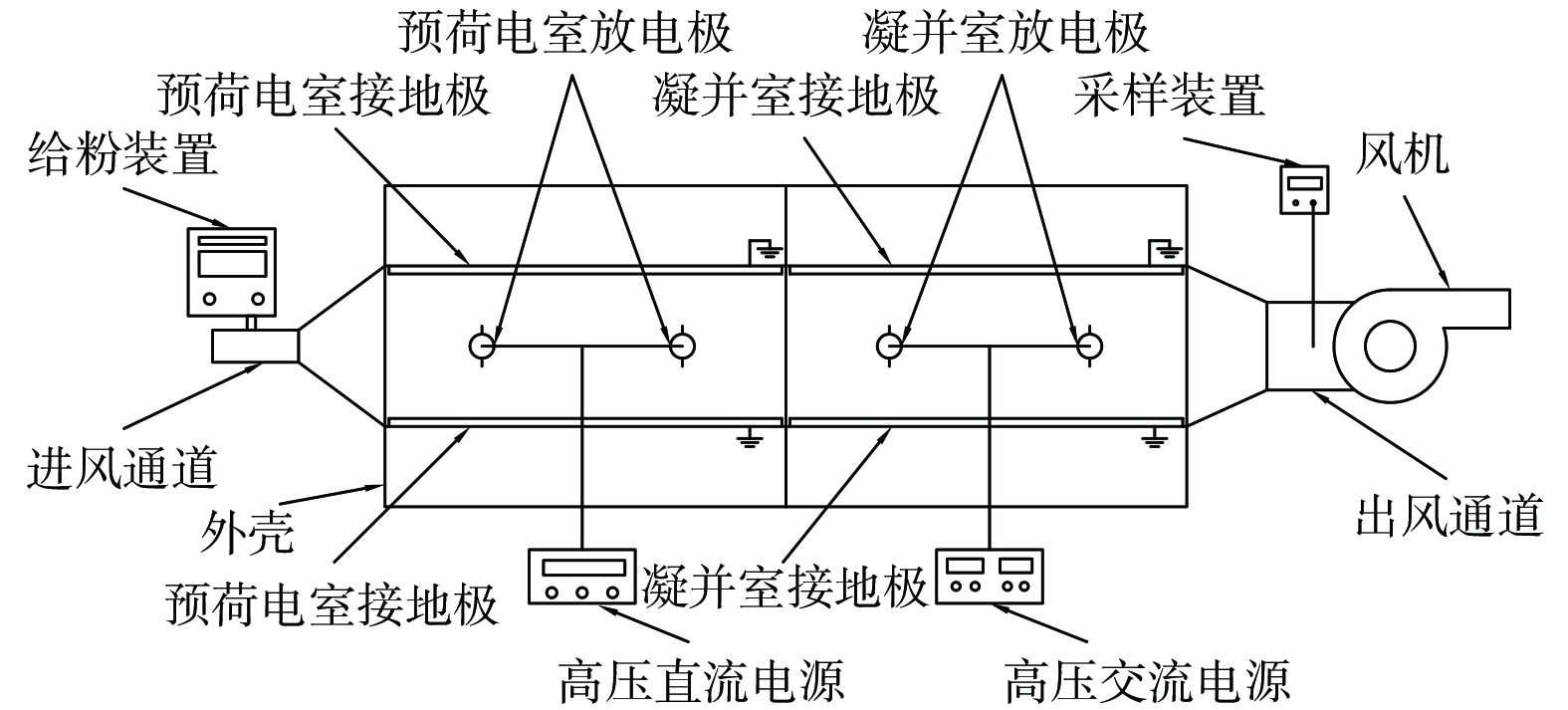
实验系统主要包含给粉系统、预荷电室、凝并室、风机、采样装置等部分 (图1) 。给粉装置使用微粉添加剂机 (DZT-60,天津市大泽科技发展有限公司) ,给粉范围3.0~60.0 g·min−1;预荷电室电源采用高压硅整流器 (GQZC-0.03/100K-T,上海南方电源设备厂) ,频率50.0 Hz,输出电压0~(±100.0 kV) ,输出电流5.0~30.0 mA;凝并室电源采用工频实验变压器 (YDT-5/50,扬州市鑫源电气有限公司),电源频率50.0 Hz,输出电压0~50.0 kV,输出电流0~0.1 A;采样装置选择皮托管平行全自动烟尘采样器 (WJ-60B,青岛崂山电子仪器总厂有限公司) ,采样流量5.0~80.0 L·min−1;变频风机功率为2.2 kW,通过调节频率来控制烟道风速,频率为0~50.0 Hz。
图2为实验流程图。先由粉尘给料机按设定好的粉尘量给粉,随后粉尘被风机吹入风道,依次经过预荷电室和凝并室,完成直流荷电、交流凝并的过程,以实现粉尘粒径的增大,随后被采样器采集,再对其粒度分布进行测量。所用仪器为马尔文激光粒度仪 (Mastersizer 2000,英国马尔文仪器有限公司),采用干法测量,进样器型号为Scirocco 2000,所测结果为粉尘的几何粒径分布。每组实验前,调节好给粉量、风速等参数,在不开启预荷电室和凝并室电源的条件下采样,所测结果为该组实验初始值,即粉尘凝并前的几何粒径分布。再打开预荷电室和凝并室电源,调节电压,其他参数不变。实验进行后,采样测量所得结果为该组实验凝并值,即凝并后的几何粒径分布,与初始值对比计算得出凝并效果。对每组实验进行多次重复实验、测量,直至连续3次的初始值曲线基本重合。该结果即本组实验的最终结果,对凝并后粉尘的测量亦为同样操作。
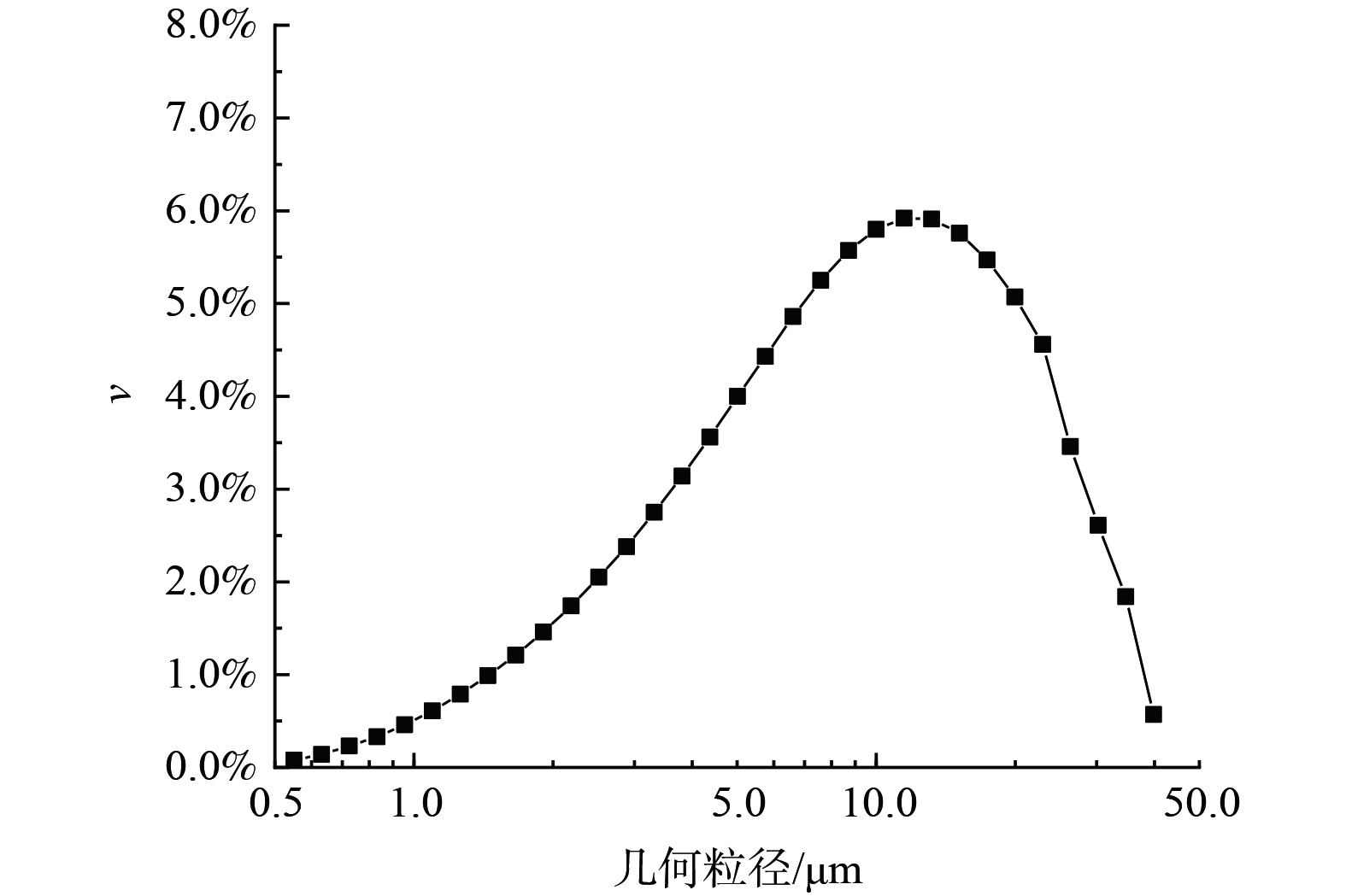
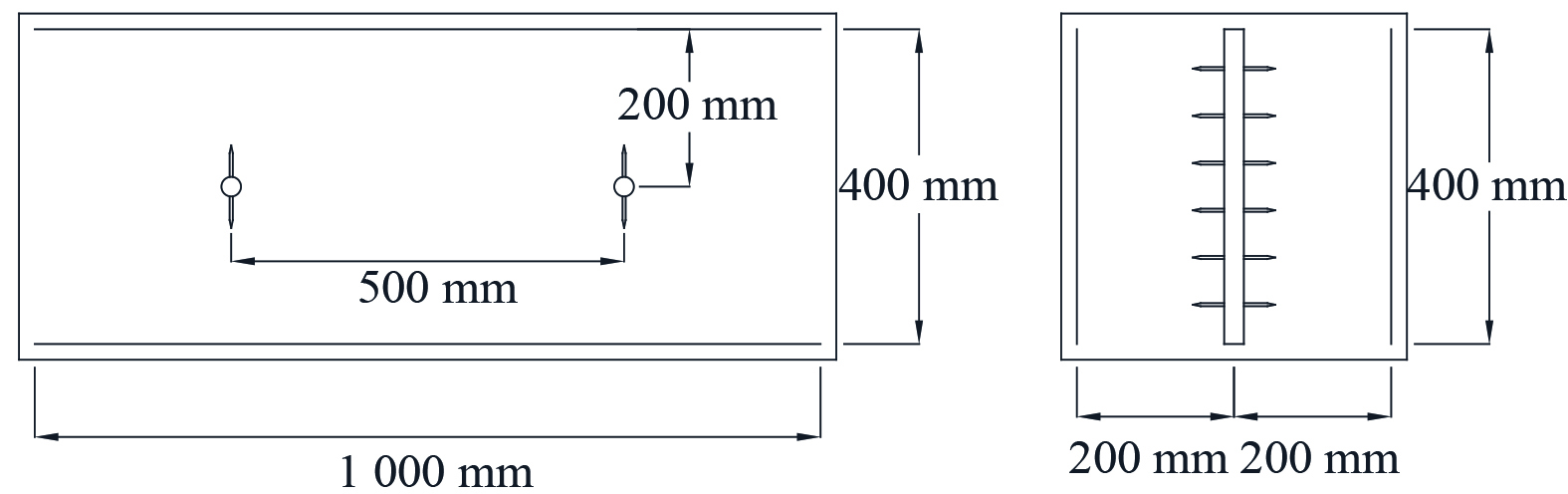
实验对象采用2 000目滑石粉,几何粒径分布如图3所示。粒径为0.5~40 μm,中位径为8.71 μm,密度为2.7 g·cm−3。测得120 ℃时比电阻为9.83×108 Ω·cm。而粉煤灰的几何粒径主要分布在100 μm以下,中位径为4~28 μm[30],密度为1.44~3.21 g·cm−3[31],在120 ℃时比电阻范围为106~1011 Ω·cm[32]。这表明滑石粉与粉煤灰性质相近,适合用于实验。实验前滑石粉在100 ℃烘箱中干燥2 h。预荷电室采用的电源为高压直流电源,可供正、负电压,接地极为金属板,放电极包括鱼骨线、四齿芒刺线 (图4) ,异极距200.0 mm。凝并室采用高压交流电源,接地极为金属板,放电极为四齿芒刺线,异极距200.0 mm,选用电压值35.0 kV。预荷电室和凝并室电极间距相同,具体参数如图5。
-
本实验结果由马尔文激光粒度仪测得的粉尘几何粒径体积分布所得,把凝并后的体积分布与初始值比较,即体积占有率变化来衡量凝并效果[33]
式中:ν为粉尘凝并后某粒径粉尘体积占有率,%;ν0为粉尘凝并前某粒径粉尘体积占有率,%。
当∆ν>0时,该粒径粉尘数增加,这是由于小粒径粉尘通过凝并后变成了大粒径粉尘;当∆ν=0时,该粒径粉尘数不变;当∆ν<0时,该粒径粉尘数减小,这是因为该粒径范围内的小颗粒凝并成了大粒径颗粒。本研究主要探讨粉尘的凝并效果,而小粒径颗粒物体积占有率的减少量是判定凝并效果的主要依据。
本研究对多因素实验采用正交实验。方差分析法是正交实验中分析结果的常用方法之一,能精确地确定各因素对实验结果影响的重要程度,计算步骤及所用公式如下[34]。
用正交表Ln (rm) 来安排实验,则因素的水平数为r,正交表的列数为m,总实验次数为n,设实验结果为yi (i=1,2,…,n) 。
(1) 计算离差平方和
定义P和Q如式 (2) 和 (3) 所示,则总离差平方和如式 (4) 所示。因此,各因素引起的离差平方和如式 (5) 所示。实验误差的离差平方和则如式 (6) 所示。
式中:SSj为第j列因素的离差平方和;Ki为j因素在i水平实验值总和。
(2) 计算自由度
总平方和的总自由度如式 (7) 所示。正交表第j列离差平方和对应的自由度如式 (8) 所示。误差的自由度如式 (9) 所示。
(3) 计算平均离差平方和 (均方)
第j列因素的均方如式 (10) 所示。实验误差的均方如式 (11) 所示。F值则如式 (12) 所示。
(4) 显著性检验和因素分析
如对于因素A,一般认为,若FA> F0.01 (dfA,dfe) ,就称因素A对实验结果有非常显著影响;若F0.05 (dfA,dfe) <FA<F0.01 (dfA,dfe) ,则对实验结果有显著影响;若FA<F0.05 (dfA,dfe) ,则对实验结果影响不显著。最后将方差分析结果列在方差分析表中,进行因素分析及优方案的确定。
-
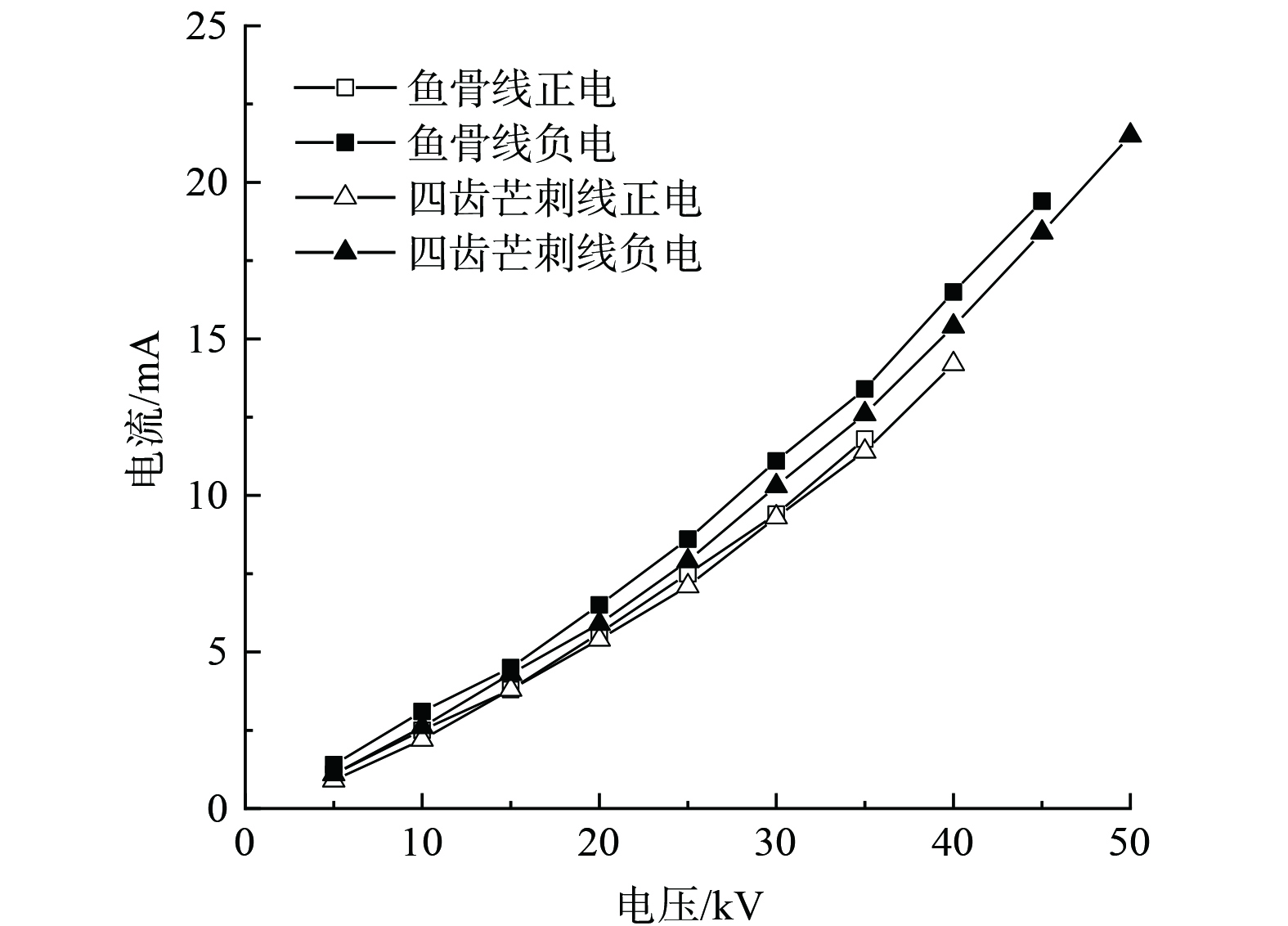
图6为预荷电室在放电极不同的情况下,电压与电流之间的关系,可间接反映粉尘的荷电情况。正、负电流都随电压升高增大,但正电压的电流均低于负电压。这是由于在放电过程中,正电晕放电极间区域只有正离子向极板漂移,而负电晕放电极间不仅存在负离子,而且存在未被附着的自由电子,同时向极板漂移[35]。正负离子对颗粒的荷电规律相同,而自由电子对颗粒的荷电率比离子高的多,这也使得负电晕放电可以使颗粒的荷电量高于正电晕[36-37]。另一方面,正电晕放电的击穿电压较低,且电极形式对电流影响很小;而负电晕击穿电压较高,可达50.0 kV,鱼骨线的电晕电流略大于四齿芒刺线,这是由于芒刺电晕线的支撑部分对电晕电流有很强的屏蔽作用,致使产生的电晕电流减小[38]。
-
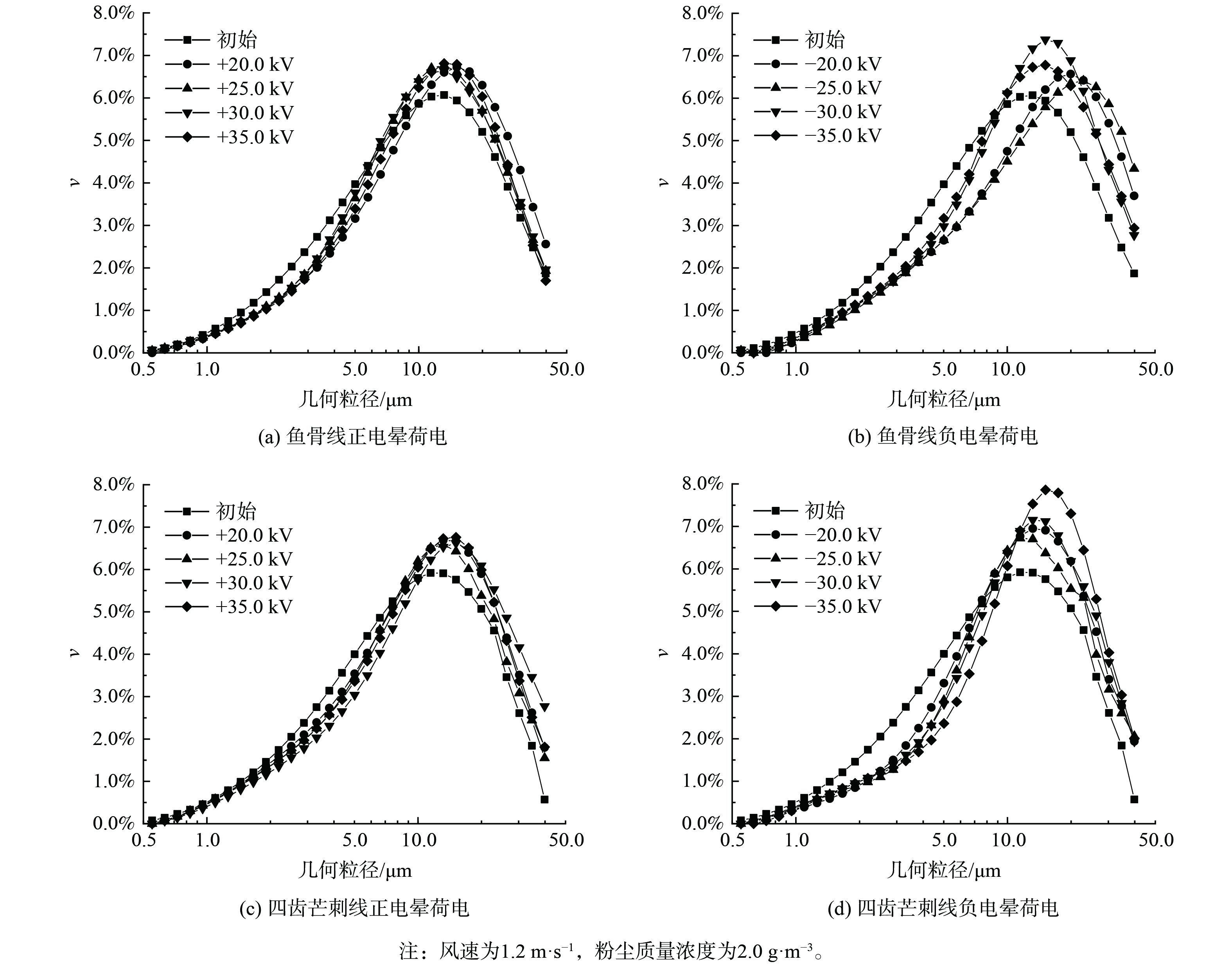
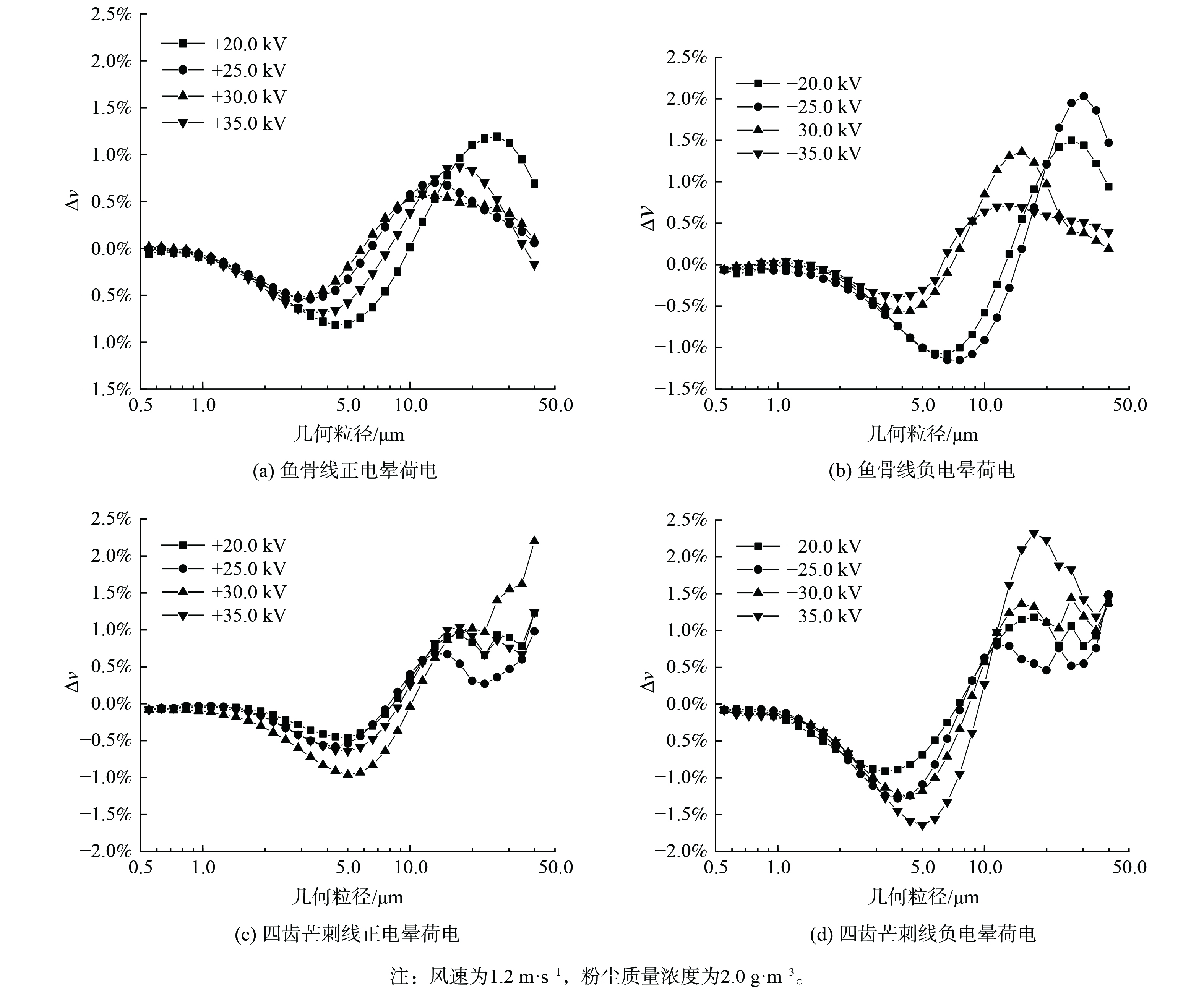
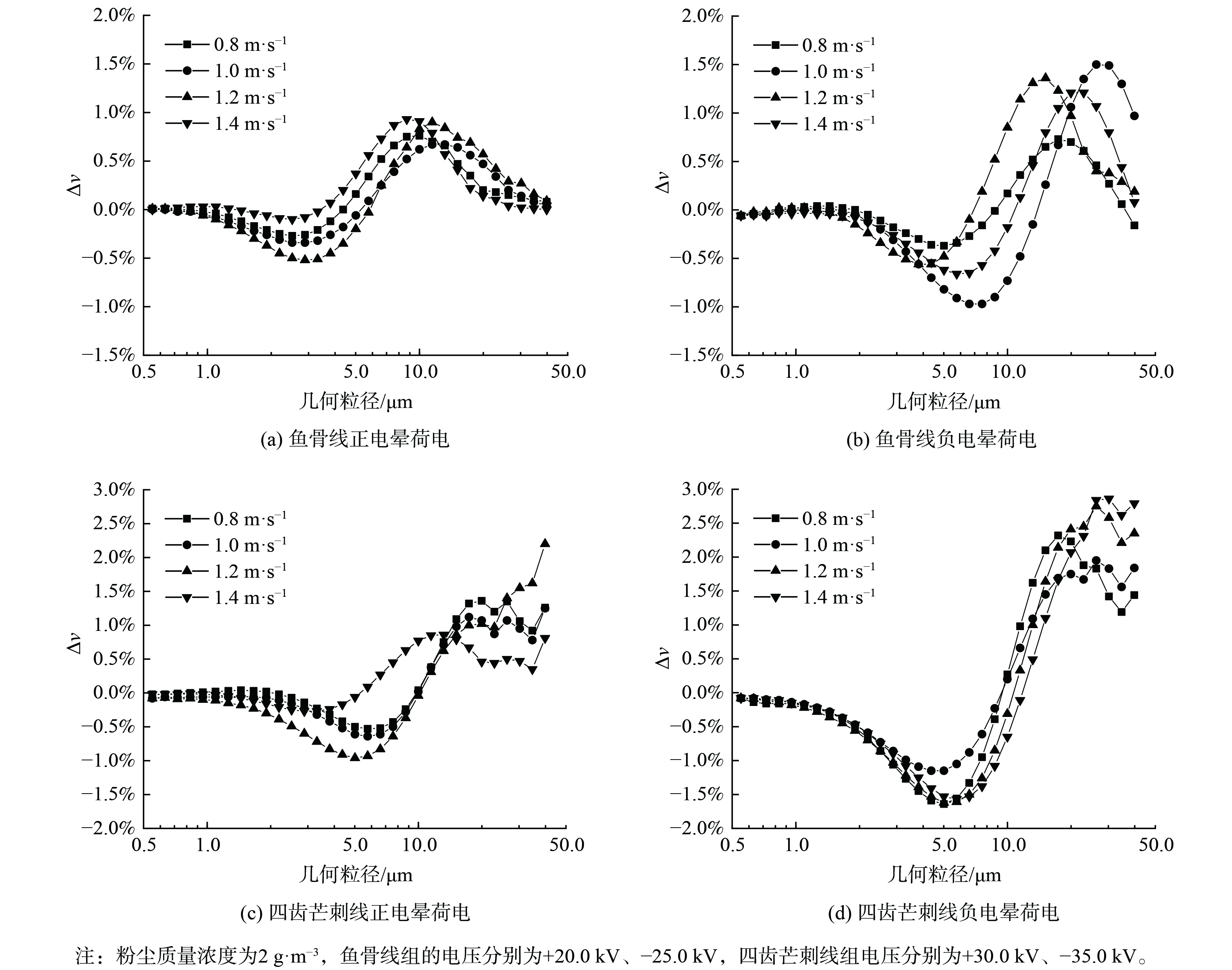
图7为各组实验凝并前后粉尘几何粒径分布的对比图。凝并后曲线峰值右移表明平均几何粒径增大。由图8 (a) 和 (b) 可知,对于鱼骨线,当正电晕放电时,∆ν随电压升高而减小,则凝并效果变差;35.0 kV时又变好;20.0 kV时凝并效果最好,此时∆ν最大为-0.82%。负电晕电压在25.0 kV时效果最佳,此时∆ν的最大值为-1.15%,电压小于25.0 kV。随着电压增大,凝并效果变好,但当电压大于25.0 kV时,凝并效果随电压增大变差,并在30.0 kV时达到了击穿电压,影响了凝并效果。比较两个图的最佳曲线,4 μm以下的颗粒,正电晕荷电的凝并效果比负电晕好,而对于粒径为5~10 μm的颗粒,负电晕荷电效果比正电晕好。
图8 (c) 和 (d) 表明,对于四齿芒刺线,无论是正电晕还是负电晕,随着电压增大,小粒径颗粒物∆ν会增大,且凝并效果变好。正电晕在电压值为35.0 kV 时产生了火花放电,导致凝并效果变差。比较正电晕和负电晕的最佳曲线,即+30.0 kV、−35.0 kV时的凝并效果,负电晕主要对2.8~8.7 μm的颗粒起作用,而正电晕为3.8~7.5 μm,∆ν均在5 μm处达到最低值,分别为−1.46%和−0.96%。因此,四齿芒刺线的负电晕凝并效果比正电晕好,也印证了正电晕和负电晕荷电的原理不一样。无论是正电晕还是负电晕荷电,鱼骨线凝并的最佳电压都比芒刺线小,这说明鱼骨线工作电压的范围较小。
-
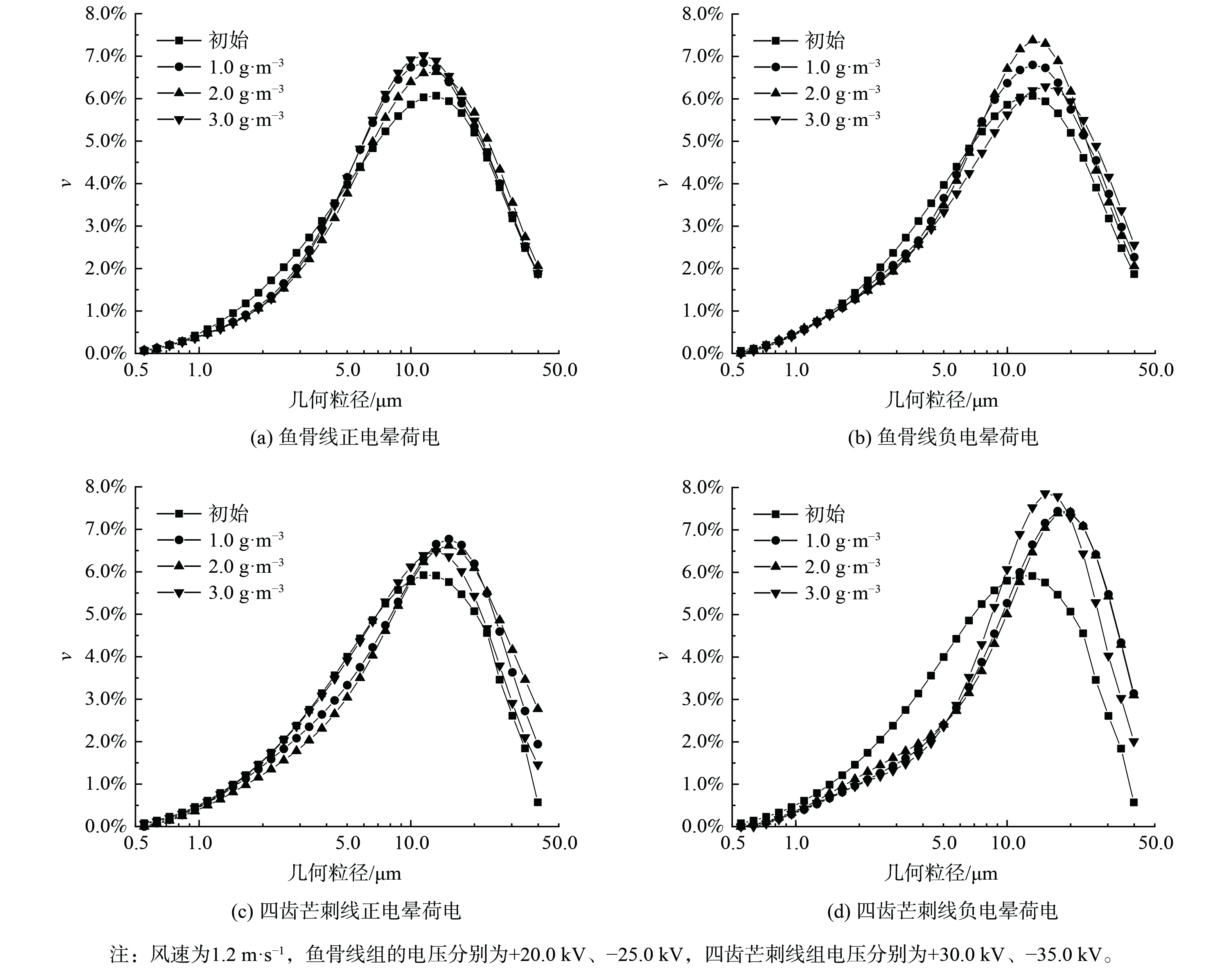
图9为各组实验凝并前后粉尘几何粒径分布的对比结果。与图8类似,凝并后平均粒径增大,曲线峰值右移。如图10 (a) 和 (b) 所示,鱼骨线正电晕荷电时凝并效果最佳的粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3,∆ν在粒径2.5 μm左右降至最低,为-0.52%。粉尘质量浓度较高或较低都会使凝并效果变差,这是由于这两种状态下,粉尘颗粒不能充分碰撞;在负电晕荷电时凝并效果随质量浓度增大而变好,并在3.0 g·m−3时达到最好,∆ν在5 μm处到达了最低,为-0.64%。比较两图中凝并效果的最佳曲线,在粒径3.5 μm处∆ν相同,对于粒径在3.5 μm以下的粉尘颗粒,正电晕荷电凝并效果好,而3.5 μm以上则负电晕荷电效果好。
如图10 (c) 和 (d) 所示,对于四齿芒刺线,正电晕荷电的凝并效果在粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3时达到最佳, ∆ν在5 μm处达到最低值,凝并作用主要发生在粒径为3.8~7.5 μm时。质量浓度小于2.0 g·m−3时颗粒不能充分碰撞,大于2.0 g·m−3则会使颗粒荷电不充分。故在这两种极端状态下,凝并效果均变差。负电晕荷电凝并效果在质量浓度为1.0 g·m−3和2.0 g·m−3时相近,均在5.75 μm处达到∆ν最低值,凝并效应则发生在2.8~8.7 μm。带电粉尘会形成二次电场,在质量浓度过大时会干扰装置内电场使得电晕电流下降,进而造成后续粉尘荷电不充分,使得整体凝并效果变差。另外,负电晕荷电在最佳质量浓度下的凝并效果优于正电晕荷电在最佳质量浓度下的凝并效果。
-
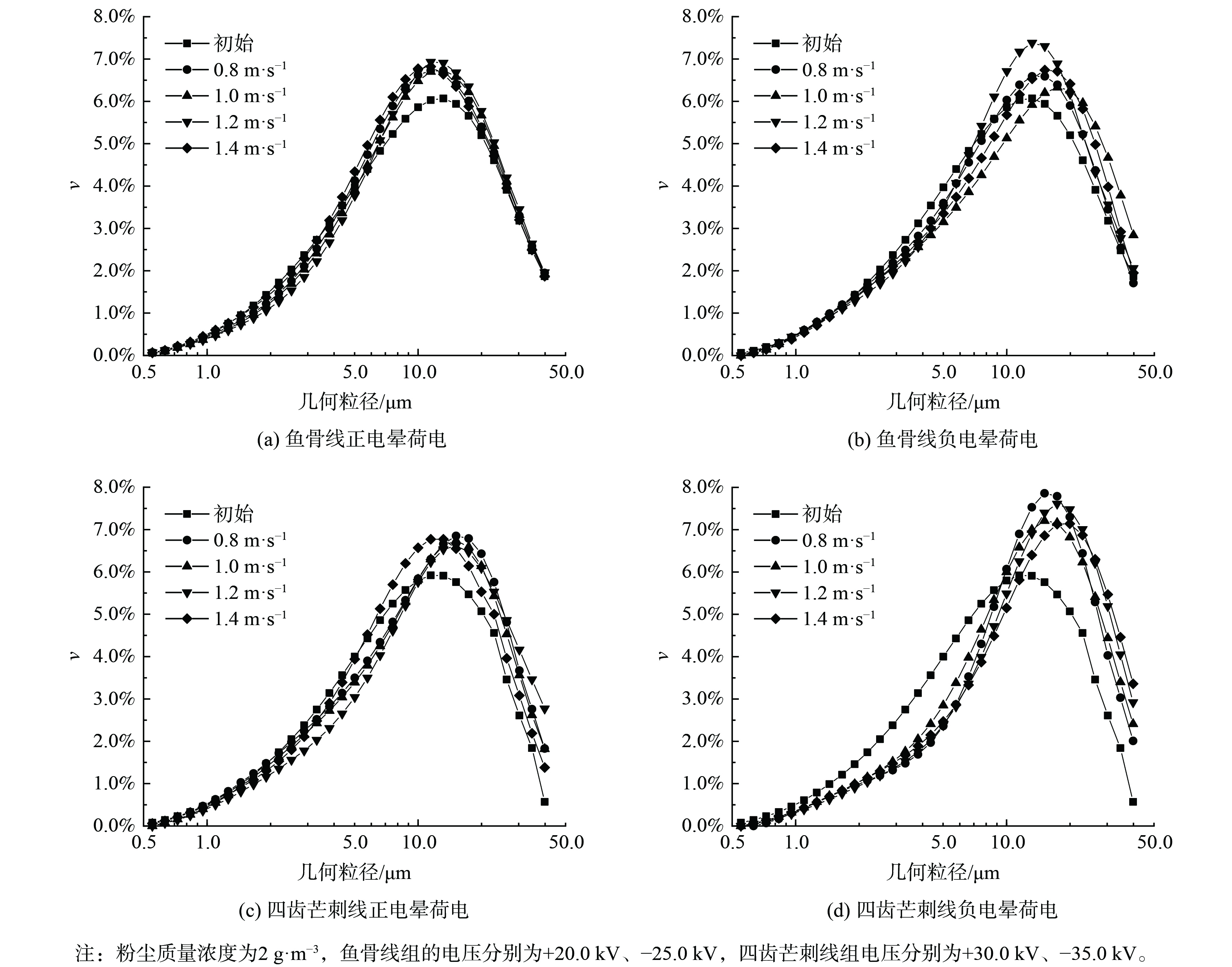
图11为风速影响下凝并前后的几何粒径分布对比结果。对于鱼骨线,如图12 (a) 和 (b) 所示,当正电晕荷电时,凝并效果随风速增大先变好后变差,并在1.2 m·s−1时达到最佳。当负电晕荷电时,风速在1.0 m·s−1时对小粒径颗粒物的凝并效果最佳。对比正、负电晕荷电在各自最佳风速下的凝并效果,正电晕荷电在3.5 μm处∆ν值达到最低点,为−0.52%,负电晕在7 μm左右∆ν达到最低点,为−0.97%。这说明鱼骨线-金属板的正电晕荷电凝并效应主要发生在3.5 μm以下的颗粒物中,而负电晕荷电则主要发生在粒径3.5 μm以上。
如图12 (c) 和 (d) ,对四齿芒刺线,在正电晕荷电时,小粒径颗粒物的∆ν随风速增大而增大,凝并效果变好,在1.2 m·s−1时最好,继续增大则变差。负电晕荷电在风速为0.8、1.2、1.4 m·s−1时,∆ν在0~5 μm内变化基本相同,但在粒径为5~10 μm、风速为1.4 m·s−1时最大,即凝并效果最好,而风速为1.0 m·s−1时的凝并效果比其他风速均更差。对比正、负电晕荷电在各自最佳风速下的凝并效果,正电晕荷电的∆ν在粒径为5 μm时达到最低点,为−0.96%,负电晕荷电在5.7 μm处达到最低点,为−1.57%。这说明负电晕荷电的凝并效果优于正电晕,亦表明凝并效果的主导因素仍然是颗粒荷电的正负性。
-
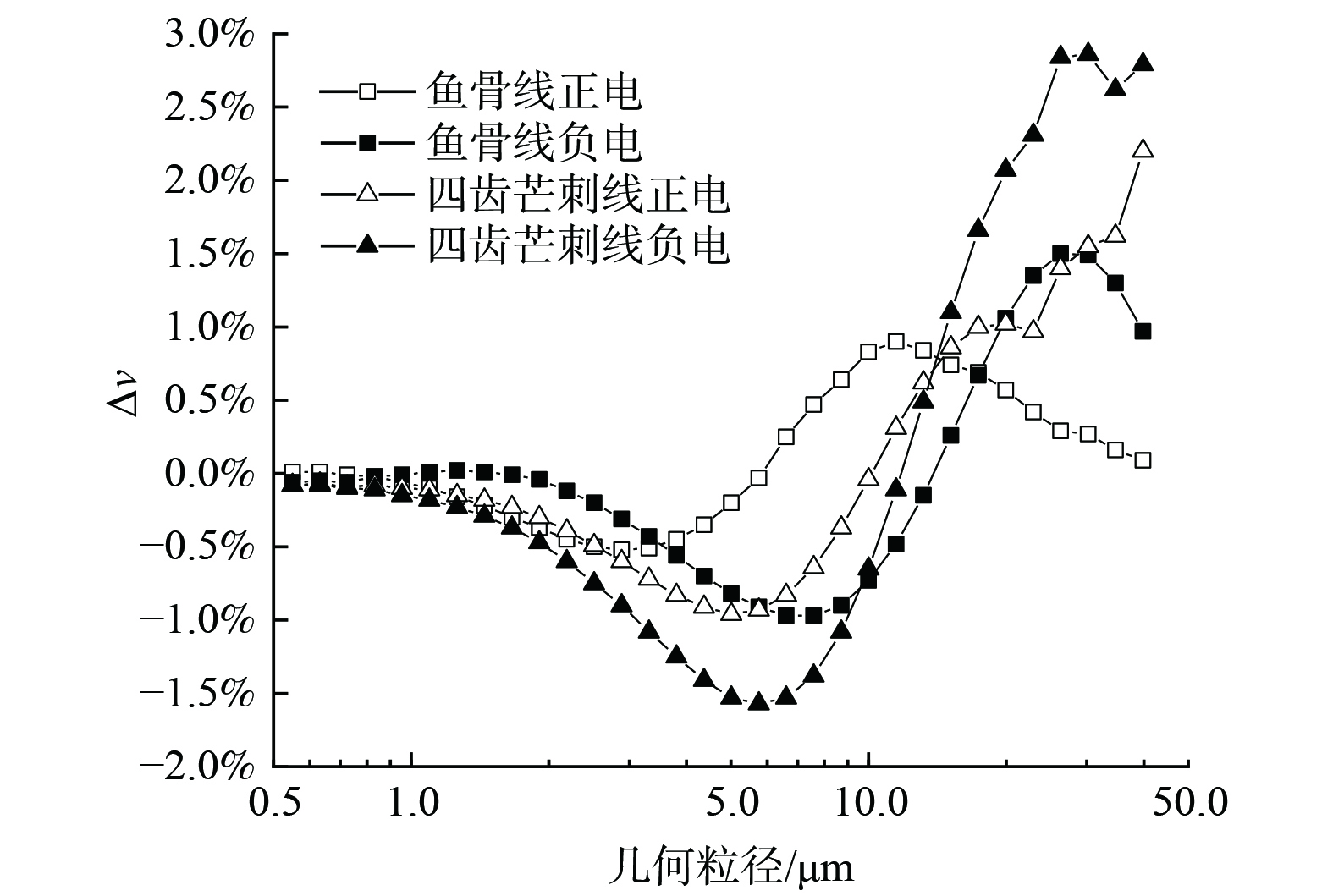
由上述内容得出2种电极凝并效果最佳参数组合:对于鱼骨线-金属板极配形式,正电晕荷电为+20.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电为−25.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.0 m·s−1;对于四齿芒刺线-金属板极配形式,正电晕荷电为+30.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电为−35.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.4 m·s−1。对这4种条件下的凝并效果进行比较,结果如图13所示。在预荷电室为正电晕放电时,2种放电极对小粒径颗粒物的∆ν只有很微小的差别。这表明放电极形式对正电晕荷电的凝并效果影响较小,在2.1节中的V-I特性研究中也得到了证实,其原因是不同放电极的正电晕电流大小区别不大。在预荷电室为负电晕放电时,四齿芒刺线的体积占有率变化比鱼骨线大,凝并效果也是最好的,这说明放电极形式对负电晕荷电的凝并效果影响较大。进而得出凝并效果最佳条件为四齿芒刺线在负电晕荷电时电压为−35.0 kV、粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3、风速为1.4 m·s−1。
-
根据单因素实验结果,负电晕荷电对粉尘的凝并效果比正电晕荷电好,四齿芒刺线比鱼骨线好。因此,正交实验对四齿芒刺线在负电晕荷电下进行,选择电压、风速中在单因素实验中结果较好的3个水平,粉尘浓度3个水平不变,进行3水平3因素正交实验,因素水平见表1。以粉尘体积占有率∆ν的最小值作为评价指标,正交实验分配与测试结果见表2和表3。从极差结果可看出,3个因素的重要程度为:A (电压) >B (浓度) >C (风速) 。方差分析结果如表4所示,从F值大小可看出因素的主次顺序为:电压>浓度,风速对结果无显著影响,结合表2和表3分析该实验的优方案为A1B2C2,即电压为35.0 kV、质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3、风速为1.4 m·s−1。此时的∆ν最小值最小,为−1.57%,即对粉尘的凝并效果最佳,此结果与单因素实验所得结果一致。
-
1) 当预荷电为正电晕放电时,鱼骨线和四齿芒刺线的伏安特性曲线差别很小;当预荷电为负电晕放电时,鱼骨线的电流增长的比四齿芒刺线更快;对于同一种放电极,负电晕放电的电流始终大于正电晕。电极结构对正电晕放电的影响较小,对负电晕放电的影响较大,而负电晕放电时由于自由电子的存在使得电流相对较大,这说明自由电子在荷电过程中起着重要作用。
2) 不同极配形式下,正电晕放电的击穿电压均小于负电晕;对于粉尘的凝并效果,鱼骨线在正电晕荷电下最佳参数为+20.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电下最佳参数为−25.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.0 m·s−1;四齿芒刺线在正电晕荷电下最佳参数为+30.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电下最佳参数为−35.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.4 m·s−1。负电晕荷电对粉尘的凝并效果优于正电晕荷电,四齿芒刺线优于鱼骨线。
3) 正交实验结果表明,凝并效果最优的预荷电条件为负电晕荷电时放电极为四齿芒刺线,电压为−35.0 kV、粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3、风速为1.4 m·s−1;对凝并效果影响最大的因素为电压,粉尘浓度次之,风速影响最小。影响电凝并效果的其他相关因素及因素间的交互作用仍需进一步探索。
预荷电中放电极对交流电场下颗粒物凝并效果的影响
Influence of discharge electrodes in precharging on particle agglomeration effect under AC electric field
-
摘要: 为探索在电凝并过程中,不同预荷电条件对颗粒物凝并效果的影响,选择出最优参数组合,对包含预荷电区和凝并区的实验系统进行了研究。对所选择的鱼骨线和四齿芒刺线2种放电极的伏安特性进行了测量,然后对2种电极分别在正电晕、负电晕荷电条件下,不同电压、粉尘浓度、风速下对粉尘凝并效果的影响进行实验,在此基础上进行正交实验,得出最优水平组合。结果表明,正电晕放电时2种放电极的伏安特性区别很小,负电晕放电鱼骨线电流较大,且负电晕的电流均大于正电晕。单因素实验结果表明,负电晕荷电的凝并效果优于正电晕荷电,四齿芒刺线的凝并效果优于鱼骨线,因此对四齿芒刺线在负电晕荷电的条件下,分别选定电压、粉尘浓度、风速的3个水平进行正交实验,得出凝并效果最佳的因素水平组合为电压35 kV、粉尘质量浓度2.0 g·m−3、风速1.4 m·s−1。本研究提供了一种探究多因素多水平对电凝并效果影响的思路,为颗粒物去除应用中预荷电参数选取提供了参考。Abstract: To explore the effect of different pre-charging conditions on the agglomeration effect of particulate matter in the electric agglomeration process and to select the optimal parameters, an experimental system containing a pre-charging zone and an agglomeration zone was investigated. The V-I characteristics of the discharge electrodes-a fishbone wire and a four-tooth barb wire were measured. Then experiments of the two electrodes under positive corona and negative corona discharge conditions with different voltages, dust concentrations, and airflow velocities were conducted, based on which orthogonal experiments were conducted to derive the best level of each factor. The results showed that the difference between the V-I characteristics of the two electrodes in positive corona discharge was very small. The current of the fishbone wire was larger than that of the four-tooth barb wire in the negative corona discharge. The current of negative corona discharge was larger than that of positive corona discharge. The results of single-factor experiments showed that the agglomeration effect of negative corona discharge was better than that of positive corona discharge, and the agglomeration effect of the four-tooth barb wire was better than that of the fishbone wire. Therefore, three levels of voltage, dust concentration, and airflow velocity were selected for orthogonal experiments with the four-tooth barb wire and negative corona discharge, and the best levels were 35 kV, 2.0 g·m−3, and 1.4 m·s−1 respectively. An idea was proposed for the electric agglomeration experimental research with multi-factor and multi-level, which provided a reference for the selection of pre-charging parameters in practical applications and had certain guiding significance for the removal of particulate matter.
-
煤炭作为我国主要能源之一,其燃烧会产生大量颗粒污染物。目前,针对大气中的悬浮颗粒物,我国已采取了多种解决方案[1]。可吸入颗粒物 (PM10) 在污染环境的同时,会影响交通安全[2-3]、人群健康[4-6]。因此,如何有效控制颗粒物排放是当前大气污染治理的重点。目前,工业上主要采用电除尘器来减少颗粒物的排放,但其去除PM2.5能力不足[7-8]。因此,为提高PM2.5的脱除效率,采用电凝并的方法对颗粒物先进行预处理[9],使细颗粒物通过碰撞凝并以增大其粒径,易于被后端电除尘器脱除。
含尘气流通过电晕极中的高压电场时,粉尘颗粒荷电的过程称为粒子荷电。电凝并技术的关键在于提高颗粒的荷电量,使带电粒子以电泳方式达到较大颗粒物的表面,这样便能提高颗粒间的有效碰撞[10],从而促进凝并。WATANABE等[11]、向晓东等[12]的研究表明,加装了预荷电区和凝并区可有效提高电除尘器的效率,而且预荷电技术在钢铁、水泥、锅炉等多个领域均有应用[13]。预荷电效果受多种因素影响,如电极配置、电压、流场风速、颗粒浓度等[14]。王连泽等[15]将含尘气体通过异极性放电电场,随后将其混合进行凝并后发现,施加到电场中正电压和负电压的相互配合对颗粒物的凝并效果影响更大。JI等[16]在直流和交流电场中的粒子充电和团聚的实验中,发现对于给定的电晕电压,在所有大小的颗粒中,负电晕都比正电晕产生更高的电荷,颗粒电荷取决于颗粒质量载荷,质量负荷越大,颗粒的电荷数越低。何剑等[17]提出了一体式双极荷电凝并方法及装置,其颗粒捕集效率有了明显提高。颗粒物的凝并效率与正电晕通道的电场强度成正比,但与负电晕通道的电场强度关系不大。CHANG等[18]对颗粒预荷电特性进行研究,在探讨放电电压对颗粒荷电量的影响时发现正电晕放电时粉尘颗粒的带电量远远大于负电晕的带电量,但使用负电晕放电时则更加稳定。SOBCZYK等[19]对包含有单极静电凝并器的静电除尘器进行了研究,该系统相比单级静电除尘器对PM10的收集效率更高。李雪娥[20]研究双极电袋复合除尘时发现,在相同条件下,双极电袋复合除尘器的伏安特性和除尘效率都高于单级电袋复合除尘器。张江石等[21]对一个电凝并装置安装了双极芒刺预荷电装置后,发现对细微粉尘的凝并效率可提高10%以上。ZHANG等[22]表示通过对电极的优化可以提高离子密度进而加强小颗粒的荷电效果,而通过提高电压增大电场强度可以促进大颗粒的荷电,可见对于不同大小的颗粒影响荷电的因素不同,故应当根据粒径选择不同的参数调整方法。YANG等[23]对电场中粒子荷电过程进行了数值模拟,发现颗粒浓度的变化对电场影响很大,若大到一定程度,电场会被悬浮颗粒上的电荷产生的二次电场严重扭曲,甚至使得下游放电极上所产生的的电晕电流彻底消失,这会使电除尘器的效率大大下降。WANG等[24]同样发现随着PM0.1质量浓度从0增至100.0 mg·m−3,除尘器内离子浓度会下降两个数量级以上,使得颗粒的荷电、传输性能急剧恶化,而加装预荷电器后,该问题得到明显改善。HU等[25]采用多物理耦合验证的数值方法研究了PM2.5在线-板式电除尘器中的荷电和迁移行为和实验参数对除尘效率的影响,结果表明当风速为1.0 m·s−1、电压为50.0 kV时,对2.0 μm的颗粒收集效率达到了100%。以上研究结果表明,预荷电条件的改变会对颗粒物电凝并效果产生很大影响。
然而有关多种因素共同作用下的影响研究仍较为缺乏。本课题组拟探究对预荷电中放电极种类、放电极性、电压值、粉尘浓度、烟道风速5个主要因素对电凝并效果的影响。选取2种典型的放电极:四齿芒刺线和鱼骨线。这2种电极各有优劣:四齿芒刺线尖端密集,电晕电流密度大,利于粉尘荷电,但其正对极板处存在较大范围电流密度盲区;而鱼骨线由于结构简单,产生的盲区没有四齿芒刺线大,但其电流密度小,仅适合处理较小比电阻粉尘[26-27]。基于此,本研究选择这2种电极作为预荷电的放电极,探索其在不同荷电参数下的凝并效果。设计多因素实验研究,通过正交设计从全面实验中选出部分典型性的实验点[28-29],对因素水平进行简化、择优处理,在此基础上进行正交实验,分析结果以得到最佳实验参数组合,以期得到相关因素对电凝并效果的影响,为电除尘技术的应用提供参考。
1. 实验系统与方法
1.1 实验装置与方法
实验系统主要包含给粉系统、预荷电室、凝并室、风机、采样装置等部分 (图1) 。给粉装置使用微粉添加剂机 (DZT-60,天津市大泽科技发展有限公司) ,给粉范围3.0~60.0 g·min−1;预荷电室电源采用高压硅整流器 (GQZC-0.03/100K-T,上海南方电源设备厂) ,频率50.0 Hz,输出电压0~(±100.0 kV) ,输出电流5.0~30.0 mA;凝并室电源采用工频实验变压器 (YDT-5/50,扬州市鑫源电气有限公司),电源频率50.0 Hz,输出电压0~50.0 kV,输出电流0~0.1 A;采样装置选择皮托管平行全自动烟尘采样器 (WJ-60B,青岛崂山电子仪器总厂有限公司) ,采样流量5.0~80.0 L·min−1;变频风机功率为2.2 kW,通过调节频率来控制烟道风速,频率为0~50.0 Hz。
图2为实验流程图。先由粉尘给料机按设定好的粉尘量给粉,随后粉尘被风机吹入风道,依次经过预荷电室和凝并室,完成直流荷电、交流凝并的过程,以实现粉尘粒径的增大,随后被采样器采集,再对其粒度分布进行测量。所用仪器为马尔文激光粒度仪 (Mastersizer 2000,英国马尔文仪器有限公司),采用干法测量,进样器型号为Scirocco 2000,所测结果为粉尘的几何粒径分布。每组实验前,调节好给粉量、风速等参数,在不开启预荷电室和凝并室电源的条件下采样,所测结果为该组实验初始值,即粉尘凝并前的几何粒径分布。再打开预荷电室和凝并室电源,调节电压,其他参数不变。实验进行后,采样测量所得结果为该组实验凝并值,即凝并后的几何粒径分布,与初始值对比计算得出凝并效果。对每组实验进行多次重复实验、测量,直至连续3次的初始值曲线基本重合。该结果即本组实验的最终结果,对凝并后粉尘的测量亦为同样操作。
实验对象采用2 000目滑石粉,几何粒径分布如图3所示。粒径为0.5~40 μm,中位径为8.71 μm,密度为2.7 g·cm−3。测得120 ℃时比电阻为9.83×108 Ω·cm。而粉煤灰的几何粒径主要分布在100 μm以下,中位径为4~28 μm[30],密度为1.44~3.21 g·cm−3[31],在120 ℃时比电阻范围为106~1011 Ω·cm[32]。这表明滑石粉与粉煤灰性质相近,适合用于实验。实验前滑石粉在100 ℃烘箱中干燥2 h。预荷电室采用的电源为高压直流电源,可供正、负电压,接地极为金属板,放电极包括鱼骨线、四齿芒刺线 (图4) ,异极距200.0 mm。凝并室采用高压交流电源,接地极为金属板,放电极为四齿芒刺线,异极距200.0 mm,选用电压值35.0 kV。预荷电室和凝并室电极间距相同,具体参数如图5。
1.2 分析方法
本实验结果由马尔文激光粒度仪测得的粉尘几何粒径体积分布所得,把凝并后的体积分布与初始值比较,即体积占有率变化来衡量凝并效果[33]
Δv=v−v0 (1) 式中:ν为粉尘凝并后某粒径粉尘体积占有率,%;ν0为粉尘凝并前某粒径粉尘体积占有率,%。
当∆ν>0时,该粒径粉尘数增加,这是由于小粒径粉尘通过凝并后变成了大粒径粉尘;当∆ν=0时,该粒径粉尘数不变;当∆ν<0时,该粒径粉尘数减小,这是因为该粒径范围内的小颗粒凝并成了大粒径颗粒。本研究主要探讨粉尘的凝并效果,而小粒径颗粒物体积占有率的减少量是判定凝并效果的主要依据。
本研究对多因素实验采用正交实验。方差分析法是正交实验中分析结果的常用方法之一,能精确地确定各因素对实验结果影响的重要程度,计算步骤及所用公式如下[34]。
用正交表Ln (rm) 来安排实验,则因素的水平数为r,正交表的列数为m,总实验次数为n,设实验结果为yi (i=1,2,…,n) 。
(1) 计算离差平方和
定义P和Q如式 (2) 和 (3) 所示,则总离差平方和如式 (4) 所示。因此,各因素引起的离差平方和如式 (5) 所示。实验误差的离差平方和则如式 (6) 所示。
P=1n(n∑i=1yi)2 (2) Q=n∑i=1y2i (3) SST=Q−P (4) SSj=rn(r∑i=1K2i)−P (5) SSe=∑SS空列 (6) 式中:SSj为第j列因素的离差平方和;Ki为j因素在i水平实验值总和。
(2) 计算自由度
总平方和的总自由度如式 (7) 所示。正交表第j列离差平方和对应的自由度如式 (8) 所示。误差的自由度如式 (9) 所示。
dfT=n−1 (7) dfj=r−1 (8) dfe=∑df空列 (9) (3) 计算平均离差平方和 (均方)
第j列因素的均方如式 (10) 所示。实验误差的均方如式 (11) 所示。F值则如式 (12) 所示。
MSj=SSjdfj (10) MSe=SSedfe (11) Fj=MSjMSe (12) (4) 显著性检验和因素分析
如对于因素A,一般认为,若FA> F0.01 (dfA,dfe) ,就称因素A对实验结果有非常显著影响;若F0.05 (dfA,dfe) <FA<F0.01 (dfA,dfe) ,则对实验结果有显著影响;若FA<F0.05 (dfA,dfe) ,则对实验结果影响不显著。最后将方差分析结果列在方差分析表中,进行因素分析及优方案的确定。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 V-I特性
图6为预荷电室在放电极不同的情况下,电压与电流之间的关系,可间接反映粉尘的荷电情况。正、负电流都随电压升高增大,但正电压的电流均低于负电压。这是由于在放电过程中,正电晕放电极间区域只有正离子向极板漂移,而负电晕放电极间不仅存在负离子,而且存在未被附着的自由电子,同时向极板漂移[35]。正负离子对颗粒的荷电规律相同,而自由电子对颗粒的荷电率比离子高的多,这也使得负电晕放电可以使颗粒的荷电量高于正电晕[36-37]。另一方面,正电晕放电的击穿电压较低,且电极形式对电流影响很小;而负电晕击穿电压较高,可达50.0 kV,鱼骨线的电晕电流略大于四齿芒刺线,这是由于芒刺电晕线的支撑部分对电晕电流有很强的屏蔽作用,致使产生的电晕电流减小[38]。
2.2 预荷电室电压对粉尘凝并效果的影响
图7为各组实验凝并前后粉尘几何粒径分布的对比图。凝并后曲线峰值右移表明平均几何粒径增大。由图8 (a) 和 (b) 可知,对于鱼骨线,当正电晕放电时,∆ν随电压升高而减小,则凝并效果变差;35.0 kV时又变好;20.0 kV时凝并效果最好,此时∆ν最大为-0.82%。负电晕电压在25.0 kV时效果最佳,此时∆ν的最大值为-1.15%,电压小于25.0 kV。随着电压增大,凝并效果变好,但当电压大于25.0 kV时,凝并效果随电压增大变差,并在30.0 kV时达到了击穿电压,影响了凝并效果。比较两个图的最佳曲线,4 μm以下的颗粒,正电晕荷电的凝并效果比负电晕好,而对于粒径为5~10 μm的颗粒,负电晕荷电效果比正电晕好。
图8 (c) 和 (d) 表明,对于四齿芒刺线,无论是正电晕还是负电晕,随着电压增大,小粒径颗粒物∆ν会增大,且凝并效果变好。正电晕在电压值为35.0 kV 时产生了火花放电,导致凝并效果变差。比较正电晕和负电晕的最佳曲线,即+30.0 kV、−35.0 kV时的凝并效果,负电晕主要对2.8~8.7 μm的颗粒起作用,而正电晕为3.8~7.5 μm,∆ν均在5 μm处达到最低值,分别为−1.46%和−0.96%。因此,四齿芒刺线的负电晕凝并效果比正电晕好,也印证了正电晕和负电晕荷电的原理不一样。无论是正电晕还是负电晕荷电,鱼骨线凝并的最佳电压都比芒刺线小,这说明鱼骨线工作电压的范围较小。
2.3 粉尘浓度对凝并效果的影响
图9为各组实验凝并前后粉尘几何粒径分布的对比结果。与图8类似,凝并后平均粒径增大,曲线峰值右移。如图10 (a) 和 (b) 所示,鱼骨线正电晕荷电时凝并效果最佳的粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3,∆ν在粒径2.5 μm左右降至最低,为-0.52%。粉尘质量浓度较高或较低都会使凝并效果变差,这是由于这两种状态下,粉尘颗粒不能充分碰撞;在负电晕荷电时凝并效果随质量浓度增大而变好,并在3.0 g·m−3时达到最好,∆ν在5 μm处到达了最低,为-0.64%。比较两图中凝并效果的最佳曲线,在粒径3.5 μm处∆ν相同,对于粒径在3.5 μm以下的粉尘颗粒,正电晕荷电凝并效果好,而3.5 μm以上则负电晕荷电效果好。
如图10 (c) 和 (d) 所示,对于四齿芒刺线,正电晕荷电的凝并效果在粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3时达到最佳, ∆ν在5 μm处达到最低值,凝并作用主要发生在粒径为3.8~7.5 μm时。质量浓度小于2.0 g·m−3时颗粒不能充分碰撞,大于2.0 g·m−3则会使颗粒荷电不充分。故在这两种极端状态下,凝并效果均变差。负电晕荷电凝并效果在质量浓度为1.0 g·m−3和2.0 g·m−3时相近,均在5.75 μm处达到∆ν最低值,凝并效应则发生在2.8~8.7 μm。带电粉尘会形成二次电场,在质量浓度过大时会干扰装置内电场使得电晕电流下降,进而造成后续粉尘荷电不充分,使得整体凝并效果变差。另外,负电晕荷电在最佳质量浓度下的凝并效果优于正电晕荷电在最佳质量浓度下的凝并效果。
2.4 风速对粉尘凝并效果的影响
图11为风速影响下凝并前后的几何粒径分布对比结果。对于鱼骨线,如图12 (a) 和 (b) 所示,当正电晕荷电时,凝并效果随风速增大先变好后变差,并在1.2 m·s−1时达到最佳。当负电晕荷电时,风速在1.0 m·s−1时对小粒径颗粒物的凝并效果最佳。对比正、负电晕荷电在各自最佳风速下的凝并效果,正电晕荷电在3.5 μm处∆ν值达到最低点,为−0.52%,负电晕在7 μm左右∆ν达到最低点,为−0.97%。这说明鱼骨线-金属板的正电晕荷电凝并效应主要发生在3.5 μm以下的颗粒物中,而负电晕荷电则主要发生在粒径3.5 μm以上。
如图12 (c) 和 (d) ,对四齿芒刺线,在正电晕荷电时,小粒径颗粒物的∆ν随风速增大而增大,凝并效果变好,在1.2 m·s−1时最好,继续增大则变差。负电晕荷电在风速为0.8、1.2、1.4 m·s−1时,∆ν在0~5 μm内变化基本相同,但在粒径为5~10 μm、风速为1.4 m·s−1时最大,即凝并效果最好,而风速为1.0 m·s−1时的凝并效果比其他风速均更差。对比正、负电晕荷电在各自最佳风速下的凝并效果,正电晕荷电的∆ν在粒径为5 μm时达到最低点,为−0.96%,负电晕荷电在5.7 μm处达到最低点,为−1.57%。这说明负电晕荷电的凝并效果优于正电晕,亦表明凝并效果的主导因素仍然是颗粒荷电的正负性。
2.5 放电极形式对粉尘凝并效果的影响
由上述内容得出2种电极凝并效果最佳参数组合:对于鱼骨线-金属板极配形式,正电晕荷电为+20.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电为−25.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.0 m·s−1;对于四齿芒刺线-金属板极配形式,正电晕荷电为+30.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电为−35.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.4 m·s−1。对这4种条件下的凝并效果进行比较,结果如图13所示。在预荷电室为正电晕放电时,2种放电极对小粒径颗粒物的∆ν只有很微小的差别。这表明放电极形式对正电晕荷电的凝并效果影响较小,在2.1节中的V-I特性研究中也得到了证实,其原因是不同放电极的正电晕电流大小区别不大。在预荷电室为负电晕放电时,四齿芒刺线的体积占有率变化比鱼骨线大,凝并效果也是最好的,这说明放电极形式对负电晕荷电的凝并效果影响较大。进而得出凝并效果最佳条件为四齿芒刺线在负电晕荷电时电压为−35.0 kV、粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3、风速为1.4 m·s−1。
2.6 正交实验
根据单因素实验结果,负电晕荷电对粉尘的凝并效果比正电晕荷电好,四齿芒刺线比鱼骨线好。因此,正交实验对四齿芒刺线在负电晕荷电下进行,选择电压、风速中在单因素实验中结果较好的3个水平,粉尘浓度3个水平不变,进行3水平3因素正交实验,因素水平见表1。以粉尘体积占有率∆ν的最小值作为评价指标,正交实验分配与测试结果见表2和表3。从极差结果可看出,3个因素的重要程度为:A (电压) >B (浓度) >C (风速) 。方差分析结果如表4所示,从F值大小可看出因素的主次顺序为:电压>浓度,风速对结果无显著影响,结合表2和表3分析该实验的优方案为A1B2C2,即电压为35.0 kV、质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3、风速为1.4 m·s−1。此时的∆ν最小值最小,为−1.57%,即对粉尘的凝并效果最佳,此结果与单因素实验所得结果一致。
表 1 因素水平表Table 1. Factor-level table水平 A电压/kV B浓度/( g·m−3) C风速/( m·s−1) 1 35.0 1.0 1.2 2 30.0 2.0 1.4 3 25.0 3.0 1.0 表 2 实验分配与结果Table 2. Test allocation and results实验号 A1 B2 C3 空列4 ∆ν最小值/% 1 1 1 1 1 −1.46 2 1 2 2 2 −1.57 3 1 3 3 3 −1.53 4 2 1 2 3 −1.41 5 2 2 3 1 −1.48 6 2 3 1 2 −1.39 7 3 1 3 2 −1.15 8 3 2 1 3 −1.28 9 3 3 2 1 −1.23 表 3 极差结果Table 3. Range results实验号 A1 B2 C3 空列4 测试结果 K1 −4.56 −4.02 −4.13 −4.17 T=−12.50P=17.36Q=173.77 K2 −4.28 −4.33 −4.21 −4.11 K3 −3.66 −4.15 −4.16 −4.22 极差R 0.90 0.13 0.03 0.05 表 4 方差分析表Table 4. Analysis of variance table因素与项目 SS df MS F 显著性 A电压 0.141 5 2 0.070 7 88.375 ** B风速 0.016 3 2 0.008 2 10.250 * C浓度 0.001 2 2 0.000 6 误差e 0.002 1 2 0.001 1 总和 0.161 1 8 注:显著性“**”表示非常显著,“*”表示显著,空表示不显著;SS的误差eΔ为0.003 3,df的误差eΔ为4。 3. 结论
1) 当预荷电为正电晕放电时,鱼骨线和四齿芒刺线的伏安特性曲线差别很小;当预荷电为负电晕放电时,鱼骨线的电流增长的比四齿芒刺线更快;对于同一种放电极,负电晕放电的电流始终大于正电晕。电极结构对正电晕放电的影响较小,对负电晕放电的影响较大,而负电晕放电时由于自由电子的存在使得电流相对较大,这说明自由电子在荷电过程中起着重要作用。
2) 不同极配形式下,正电晕放电的击穿电压均小于负电晕;对于粉尘的凝并效果,鱼骨线在正电晕荷电下最佳参数为+20.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电下最佳参数为−25.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.0 m·s−1;四齿芒刺线在正电晕荷电下最佳参数为+30.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.2 m·s−1,负电晕荷电下最佳参数为−35.0 kV、2.0 g·m−3、1.4 m·s−1。负电晕荷电对粉尘的凝并效果优于正电晕荷电,四齿芒刺线优于鱼骨线。
3) 正交实验结果表明,凝并效果最优的预荷电条件为负电晕荷电时放电极为四齿芒刺线,电压为−35.0 kV、粉尘质量浓度为2.0 g·m−3、风速为1.4 m·s−1;对凝并效果影响最大的因素为电压,粉尘浓度次之,风速影响最小。影响电凝并效果的其他相关因素及因素间的交互作用仍需进一步探索。
-
表 1 因素水平表
Table 1. Factor-level table
水平 A电压/kV B浓度/( g·m−3) C风速/( m·s−1) 1 35.0 1.0 1.2 2 30.0 2.0 1.4 3 25.0 3.0 1.0 表 2 实验分配与结果
Table 2. Test allocation and results
实验号 A1 B2 C3 空列4 ∆ν最小值/% 1 1 1 1 1 −1.46 2 1 2 2 2 −1.57 3 1 3 3 3 −1.53 4 2 1 2 3 −1.41 5 2 2 3 1 −1.48 6 2 3 1 2 −1.39 7 3 1 3 2 −1.15 8 3 2 1 3 −1.28 9 3 3 2 1 −1.23 表 3 极差结果
Table 3. Range results
实验号 A1 B2 C3 空列4 测试结果 K1 −4.56 −4.02 −4.13 −4.17 T=−12.50P=17.36Q=173.77 K2 −4.28 −4.33 −4.21 −4.11 K3 −3.66 −4.15 −4.16 −4.22 极差R 0.90 0.13 0.03 0.05 表 4 方差分析表
Table 4. Analysis of variance table
因素与项目 SS df MS F 显著性 A电压 0.141 5 2 0.070 7 88.375 ** B风速 0.016 3 2 0.008 2 10.250 * C浓度 0.001 2 2 0.000 6 误差e 0.002 1 2 0.001 1 总和 0.161 1 8 注:显著性“**”表示非常显著,“*”表示显著,空表示不显著;SS的误差eΔ为0.003 3,df的误差eΔ为4。 -
[1] 张丹. 我国城市大气污染现状及防治对策[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(12): 156-158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.12.046 [2] 张楠. 浅谈雾霾的危害及防治[J]. 能源与节能, 2020(2): 71-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2020.02.030 [3] 刘志强, 王玲, 张爱红, 等. 基于贝叶斯模型的雾霾天高速公路交通事故发生机理研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2018, 32(1): 43-49. [4] 邢黎明, 贾继霞, 张艳红. 大气可吸入颗粒物对环境和人体健康的危害[J]. 安阳工学院学报, 2009(4): 48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2928.2009.04.016 [5] 李丽珍, 曹露, 王磊, 等. 谈中国PM2.5的污染来源及危害[J]. 能源与节能, 2013(4): 77-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2013.04.034 [6] MATHILDE P, FALQ G, WAGNER V, et al. Short-term impacts of particulate matter (PM10, PM10–2.5, PM2.5) on mortality in nine French cities[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 95: 175-184. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.06.030 [7] JAWOREK A, KRUPA A, CZECH T. Modern electrostatic devices and methods for exhaust gas cleaning: A brief review[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2007, 65(3): 133-155. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2006.07.012 [8] 徐明厚, 王文煜, 温昶, 等. 燃煤电厂细微颗粒物脱除技术研究新进展[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(22): 6627-6640. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.190489 [9] 石零, 陈红梅, 杨成武. 微细粉尘治理技术的研究进展[J]. 江汉大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(2): 40-46. [10] 王雪, 吕韩雷, 朱廷钰, 等. 细颗粒物电凝并技术研究进展[J]. 煤化工, 2016, 44(3): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9598.2016.03.014 [11] WATANABE T, TOCHIKUBO F, KOIZURNI Y, et al. Submicron particle agglomeration by an electrostatic agglomerator[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 1995, 34(4): 367-383. doi: 10.1016/0304-3886(95)93833-5 [12] 向晓东, 陈旺生, 幸福堂, 等. 交变电场中电凝并收尘理论与实验研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2000, 20(2): 61-65. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2000.02.012 [13] 向轶, 孟刚, 宋波等. 预荷电强化烟气除尘技术的研究进展及应用现状[J]. 现代化工, 2022, 42(11): 82-86. doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2022.11.016 [14] JAWOREK A, MARCHEWICZ A, SOBCZYK A T, et al. Two-stage electrostatic precipitators for the reduction of PM2.5 particle emission[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2018, 67(4): 206-233. [15] 王连泽, 贺美陆, 孟亚力. 双极荷电粉尘颗粒凝聚的初步研究[J]. 环境工程, 2002, 20(3): 31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8942.2002.03.010 [16] JI J H, HWANG J, BAE G N, et al. Particle charging and agglomeration in DC and AC electric fields[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2004, 61(1): 57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2003.12.003 [17] 何剑, 刘道清, 徐国胜. 一体式双极荷电凝并器试验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(17): 45-50. [18] CHANG Q Y, ZHENG C H, YANG Z D, et al. Electric agglomeration modes of coal-fired fly-ash particles with water droplet humidification[J]. Fuel, 2017, 200: 134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.03.033 [19] SOBCZYK A T, MARCHEWICZ A, KRUPA A, et al. Enhancement of collection efficiency for fly ash particles (PM2.5) by unipolar agglomerator in two-stage electrostatic precipitator[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 187: 91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.06.039 [20] 李雪娥. 双极电袋复合除尘器的双极荷电机理与增效特性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2019 [21] 张江石, 周和军. 双区式电凝并技术对提高细微粉尘凝并效率的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(5): 1304-1310. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201907074 [22] ZHANG H, SHAO L Y, GAO W C, et al. Particle charging in electric field under simulated SO3-containing flue gas at low temperature[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122291. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122291 [23] YANG D, Guo B Y, YE X L, et al. Numerical simulation of electrostatic precipitator considering the dust particle space charge[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 354: 552-560. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.06.013 [24] WANG Y F, GAO W C, ZHANG H, et al. Enhanced particle precipitation from flue gas containing ultrafine particles through precharging[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 144: 111-122. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.07.005 [25] HU J, WEN J P, LI H, et al. Experiment and numerical simulation on the fine particle migration behaviors for the collection efficiency enhancement of a wire-plate electrostatic precipitator in pig house[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2022, 199: 107145. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2022.107145 [26] 王新, 刘赫, 肖立春, 等. 气化炉粉尘在电除尘器中的凝并性能//中国环境科学学会环境工程分会[J]. 中国环境科学学会2021年科学技术年会——环境工程技术创新与应用分会场论文集(三). 工业建筑杂志社有限公司, 2021: 6. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2021.021916 [27] 党小庆, 杨春方, 王迪, 等. 电除尘器收尘极板表面电流密度分布实验研究[J]. 重型机械, 2005(2): 32-35. [28] LI W, DAI S L, WANG H Q, et al. Numerical study on the performance of swirl tube based on orthogonal design[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2022, 33(8): 103620. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2022.103620 [29] LIU S B, ZHANG H Y, XU X B. A study on the transient heat generation rate of lithium-ion battery based on full matrix orthogonal experimental design with mixed levels[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 36: 102446. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2021.102446 [30] 刘含笑, 刘美玲, 刘毅, 等. 燃煤飞灰几何粒径分布测试方法及其分布特征[J]. 冶金能源, 2020, 39(2): 52-54. [31] 刘全, 白志民, 王东, 等. 我国粉煤灰化学成分与理化性能及其应用分析[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2021(1): 1-9. [32] 刘含笑, 罗水源, 刘毅, 等. 燃煤电厂飞灰试验室比电阻测试方法及其分布特征[J]. 锅炉技术, 2022, 53(5): 69-74. [33] HUANG C, MA X Q, SUN Y S, et al. Particle agglomeration in bipolar barb agglomerator under AC electric field[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2015, 17(4): 317-320. doi: 10.1088/1009-0630/17/4/10 [34] 李云雁, 胡传荣. 试验设计与数据处理[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005. [35] 许德玄. 静电除尘预荷电的研究[J]. 环境工程, 1997, 15(6): 25-28. [36] WHITE H J. Particle charging in electrostatic precipitation[J]. Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, 1951, 70(2): 1186-1191. doi: 10.1109/T-AIEE.1951.5060545 [37] O'HARA D B, CLEMENTS J S, FINNEY W C, et al. Aerosol particle charging by free electrons[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 1989, 20(3): 313-330. doi: 10.1016/0021-8502(89)90007-4 [38] 李庆, 熊焱青, 李娇娇, 等. 四种芒刺极线负高压电晕放电实验[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(15): 134-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.15.026 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘文静,张金刚,乔治,赵建新. 除尘风机故障分析与技术改造. 当代化工研究. 2024(10): 74-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载: