-
工业锅炉烟气排入大气后,其中的NOx会造成酸雨、光化学烟雾和臭氧层空洞等环境问题,还会引起呼吸系统疾病[1-2]。NH3的选择性催化还原(selective catalytic reduction, SCR)工艺具有脱硝效率高、无二次污染和SO2中毒敏感性低等优点,广泛用于削减工业锅炉NOx排放[3-4]。V2O5-WO3/TiO2是常用中温SCR催化剂。已有学者实验测量了钒基催化剂脱硝反应的活化能和指前因子等参数[5-6],并在此基础上进行大量数值模拟。 TRONCONI等[7]通过瞬态响应技术研究了钒基催化剂吸附和解析NH3的动力学,并根据实验参数建立SCR蜂窝脱硝数学模型来模拟工业SCR反应器的瞬态行为。该模型考虑了蜂窝催化剂内反应物横向扩散和通道轴向浓度不均匀等因素的影响,预测结果与实验值拟合良好。DHANUSHKODI等[8]将催化剂层视为多孔介质,建立了圆孔蜂窝催化剂SCR脱硝的二维模型,并用它预测了不同温度和氨浓度下的脱硝性能。RODUIT等[9]建立了稳态SCR蜂窝脱硝过程的三维数学模型,研究了蜂窝通道形状、氨氮比和反应物浓度等对脱硝效率的影响。
上述模型没有求解蜂窝通道内烟气流场,催化剂表面对流传质速率依赖于经验关联式。将计算流体动力学(computational fluid dynamics, CFD)方法与催化脱硝数学模型相结合,可提高脱硝过程模拟精度。LEI等[10]假设脱硝反应发生在催化剂层表面,利用商业CFD软件ANSYS Fluent的表面反应模型模拟SCR蜂窝脱硝过程。YAO等[11]将催化剂层视为多孔介质,建立了基于容积反应的SCR蜂窝脱硝CFD模型。为充分考虑多孔催化剂内部组分扩散,可根据实验修正脱硝反应速率。赵大周等[12]考虑内、外扩散以及副反应等因素,建立了SCR催化脱硝的三维模型,研究了工作参数和催化剂层厚度对脱硝效率和SO2转化率的影响。王盛等[13]提出采用扩缩通道来提高SCR蜂窝脱硝性能,并建立了扩缩通道蜂窝SCR反应器的Fluent模型。为减少CFD计算工作量,学者通常提取蜂窝反应器单元结构,建立单元模型。
蓄热式高温空气燃烧技术能通过烟气余热回收有效提高炉窑能源效率,同时促进低热值燃料燃烧利用[14]。这种技术常采用比表面积大、流动阻力小的蜂窝蓄热体来进行烟气-空气换热,学者对其进行了大量的实验和数值模拟研究,以期优化蜂窝蓄热体结构和工艺参数[15-17]。本课题组对蜂窝蓄热体进行了较系统的研究,包括建立了蓄热体复杂非稳态传热CFD模型,提出了新型扩缩通道蜂窝蓄热体,研究了蓄热体结构和工艺参数的影响等[18-20]。鉴于蜂窝蓄热体与SCR反应器结构相容,课题组提出蜂窝蓄热体表面涂覆钒基催化剂的传热-脱硝一体化技术,数值模拟表明该复合蓄热体能实现余热回收和烟气脱硝双重功效。不过,钒基催化剂在烟气出口侧的低温区脱硝效果不太理想[21]。近期,任兆勇等[22]采用廉价原料制备了以新型Popcarbon纳米多孔结构为载体的SCR催化剂5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon,该催化剂在250 ℃以下的低温区有较理想的脱硝性能。
本研究拟通过在现有涂覆单一中温催化剂V2O5-WO3/TiO2的复合蜂窝蓄热体低温侧表面涂覆5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon低温催化剂,同时借助扩缩通道强化传热传质来提高SCR蜂窝蓄热体传热和脱硝性能,在对Fluent软件二次开发的基础上,建立基于多孔介质的SCR蜂窝脱硝与烟气-空气切换的蓄热体非稳态传热相耦合的复合蜂窝蓄热体数值模型,并开展数值模拟,以期探明催化剂涂覆方案和结构参数对复合蓄热体传热和脱硝性能的影响规律,并为蜂窝蓄热与SCR脱硝一体化提供参考。
-
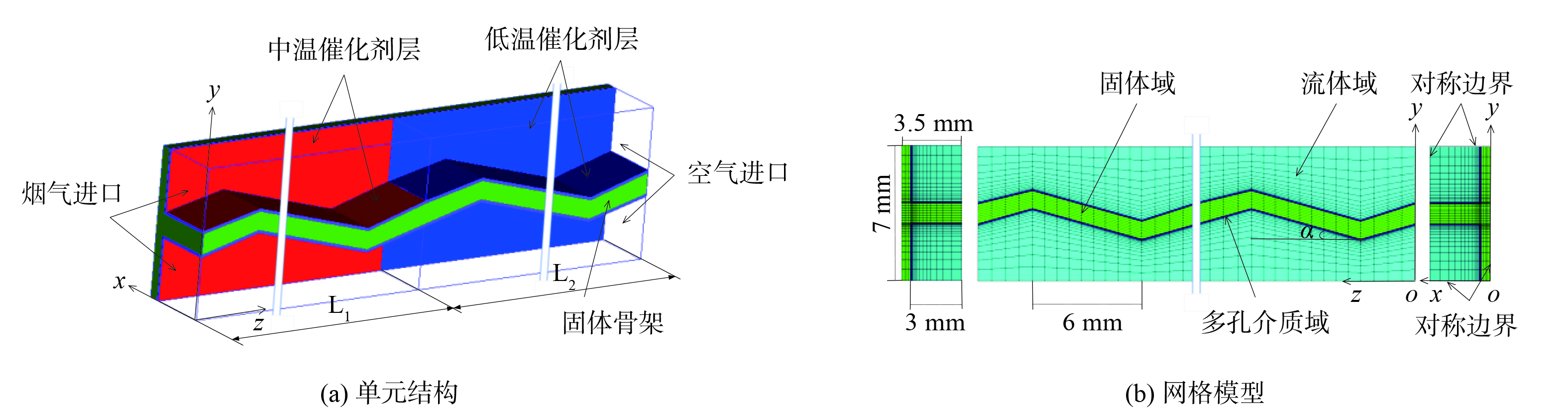
新型复合蓄热体由扩缩通道蓄热体骨架和SCR催化剂组成。工作时,与NH3按照1:1预混均匀的高温烟气和常温空气交替从两侧流过复合蓄热体,实现烟气向空气传热。同时,NH3在蓄热体表面SCR催化剂作用下,将烟气中NOx还原成N2。由于蜂窝结构具有对称性,将复合蓄热体相邻两个流道和骨架的四分之一作为单元结构,如图1(a)所示。
复合蓄热体通道扩张段和收缩段的节距均为6 mm,中间截面特征尺寸为6 mm,扩缩角α取0、5、10、15和20°;烟气进口侧的较高温区骨架表面涂覆V2O5-WO3/TiO2中温催化剂,空气进口侧的较低温区涂覆5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon低温催化剂。2种催化剂层厚度均为110 μm。蓄热体烟气-空气周期切换时间为30 s。表1为复合蓄热体主要结构和工艺参数。
-
鉴于烟气和空气周期的流体雷诺数都小于2 000,蓄热体通道为层流流动[23];另外,假设催化反应在整个催化剂层内发生,飞灰、辐射换热等影响忽略不计[6]。为此,复合蓄热体内烟气-空气通过蓄热骨架的非稳态传热和催化层SCR脱硝过程可用下面的流体质量守恒、动量守恒、能量守恒和组分输运方程及固体能量守恒方程计算。
式中:下标f,s和j分别表示流体、固体和组分索引;u为流体速度,ρ为密度,t为时间;f,p分别为体积力和压强,I为单位矩阵;μ,cp和λ分别为动力粘度,定压比热和热导率;T和h分别为温度和比焓;C,D分别为组分浓度和扩散系数,J为组分扩散通量,由菲克定律计算。为描述催化剂层多孔结构对流动和组分输运的影响,在方程(2)和(4)中分别加入阻力源项Su和组分源项Sj[11,24],得到式 (6) 和(7) 。
式中:K、C2分别为粘滞阻力系数和惯性阻力系数,ω为组分的生成速率,M为摩尔质量。
烟气中NOx的主要成分为NO,其它的NOx含量很少,忽略不计;另外,SOx等其他副反应忽略考虑[21]。基于上述考虑,NH3-SCR脱硝反应如式 (8) 所示。
NH3-SCR脱硝反应速率可用幂函数反应动力学模型描述,即通过各组分反应级数大小描述[25]。经验表明,O2和NH3浓度对SCR脱硝反应的影响很小,其反应级数为0。因此,NO反应速率[22]计算式为式 (9) 。
式中:a表示NO组分的反应级数,对于中温钒基催化剂(V2O5-WO3/TiO2)和低温铜基催化剂(5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon),它分别取1和0.7[22,26];k为反应速率常数(s−1),由阿伦尼乌斯方程计算,k=Ae−E/RT。其中,A、E、R分别为指前因子(s−1)、活化能(kJ·mol−1)和通用气体常数。中温钒基催化剂[5]的A1=1.28×1011 s−1,E1=83.68 kJ·mol−1,而低温铜基催化剂[22]的A2=3.09×104 s−1,E2=24.79 kJ·mol−1。
-
模拟整个复合蜂窝蓄热体的计算网格数量相当大,故提取单元结构作为研究对象。使用ICEM软件建立单元结构几何模型和划分网格,分别见图1(a)和(b)。整个计算域由蓄热体通道(流体域)、骨架(固体域)和催化剂层(多孔介质域)组成。为提高计算速度和精度,采用六面体结构化网格,最小正交质量大于0.9。沿流动方向的温度和浓度梯度较小,采用均匀粗网格,但在垂直于流动方向,多孔介质域和固体域采用均匀的密网格,而流体域则采用向催化剂层逐渐加密的非均匀网格。单元结构侧面为对称边界,流体与固体接触面为耦合传热壁面,烟气进出口边界条件分别设置为质量流量进口和压力出口。
-
在对ANSYS Fluent软件二次开发基础上,模拟新型复合蓄热体非稳态传热和NH3-SCR脱硝过程。计算时,将烟气和空气设为不可压缩理想气体,通过用户自定义函数(user-defined function, UDF)气和空气周期的周期性切换;开启组分输运模型,将催化剂层设置为多孔介质域并激活容积反应[21],其反应速率由UDF计算;蓄热体骨架设为固体,与流体耦合传热。数值方法采用基于压力的分离式求解器,压力速度耦合采用SIMPLE算法。微分方程离散采用二阶迎风格式,迭代计算收敛门槛值为:能量方程10−8,其他方程10−5。
为验证网格无关性,分别使用30、60、90和120万网格对同一复合蓄热体模型进行数值模拟,结果表明相邻网格的能量回收率相差小于2%;网格数量对脱硝效率影响比较大,当网格从30万增加到60万时,脱硝效率提高了5%,继续提高网格数量到90和120万网格,脱硝效率相差不到2%。另外,采用0.25,0.5和1 s三种时间步长进行对比,结果表明0.25 s时计算量太大,1 s的时间步长在模拟切换时比较难收敛,0.5 s能较好地平衡计算量和数值稳定性矛盾。综合前面分析,后续计算使用60万网格和0.5 s时间步长。
-
本研究的复合蓄热体数值模型涉及对ANSYS Fluent软件的二次开发,主要包括基于烟气-空气切换的非稳态蓄热式传热和基于多孔介质容积反应的SCR脱硝等两部分。前者经RAFIDI等[16]的蜂窝蓄热体传热实验验证,并已经用于课题组蜂窝蓄热体传热研究[18,20];后者通过SCR蜂窝脱硝实验的检验,并用于课题组研究扩缩通道强化SCR脱硝。对相关代码进行了改进和优化,以准确再现表面涂覆SCR催化剂时烟气-空气非稳态蓄热式传热与烟气SCR脱硝的耦合行为。
-
经过烟气周期和空气周期若干次切换后,复合蓄热体非稳态传热和脱硝过程达到周期性稳定。周期性稳态传热性能用能量回收率(ERR)表示, 数值等于空气实际回收能量与从烟气中最多可能回收能量的比值,计算式见式 (10) 。
式中:下标ɑ、g和i、o分别代表空气、烟气和进、出口,qm和
$ \overline{h} $ 分别表示气体的质量流量和平均比焓。由于空气出口温度随时间变化,取空气周期平均温度作为空气预热温度[16]。计算式见式 (11)。
复合蓄热体流阻性能用周期性稳态下烟气和空气周期平均压力损失和表示, SCR脱硝性能用脱硝效率(η)表示,等于周期性稳态下烟气周期出口与进口NO平均质量浓度的相对变化,计算式见式 (12) 。
式中:表示标准状况下NO平均质量浓度。
-
钒基SCR催化剂V2O5-WO3/TiO2在中温区(300~400 ℃)有较好的活性,但其在低于250
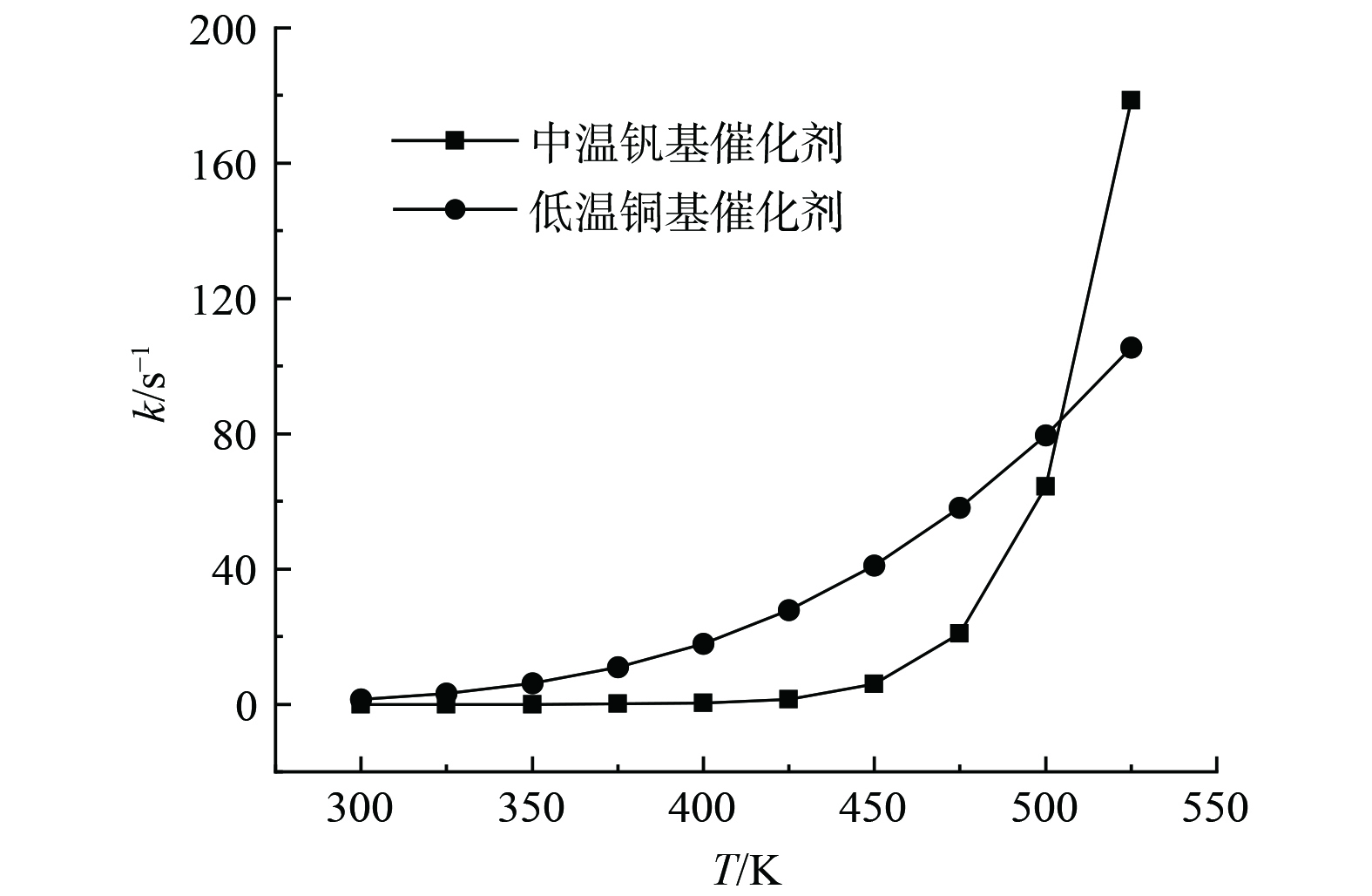
℃时的催化脱硝效果随温度降低并快速衰减。铜基催化剂5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon活性温度较低,在中温区脱硝性能不如钒基催化剂,但在低温区脱硝效果好。因此,组合涂覆钒基和铜基催化剂前,需要合理选择2种催化剂涂覆长度。根据图2中催化剂反应速率常数k曲线,钒基和铜基催化剂k均随温度升高而增大,且在507 K时相等;另外,当温度高于507 K时,钒基催化剂k随温度增加速率远大于铜基催化剂,当温度小于507 K时,其k值随温度降低速度也比铜基催化剂快。这意味着在蓄热体低温侧涂覆钒基催化剂时,局部脱硝反应速率很低,要使蓄热体获得较高的催化反应速率,应在温度大于507 K区域涂覆钒基催化剂,温度低于507 K区域涂覆铜基催化剂。鉴于蓄热体内骨架温度沿轴向单调变化,故以温度等于507 K的骨架位置作为临界点,组合涂覆中、低温催化剂。
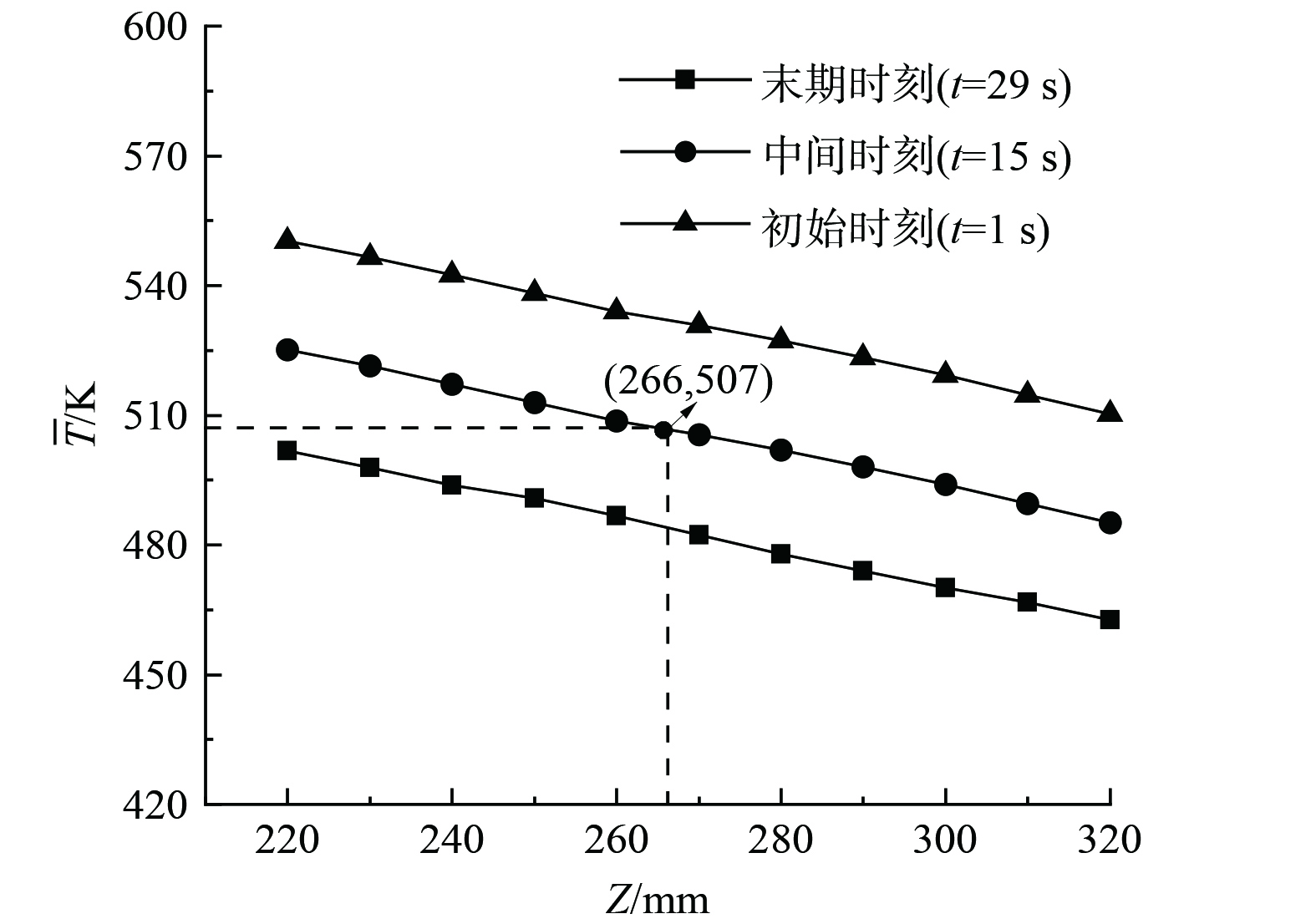
鉴于蓄热体骨架温度随时间显著变化,为保证整个烟气周期均有较好脱硝性能,根据中间时刻骨架温度确定中温和低温催化剂涂层界面。图3为某蓄热体烟气周期不同时刻的骨架温度分布曲线,其中中间时刻(t=15 s)温度为507 K的轴向坐标Z=266 mm。因此,该蓄热体中温催化剂和低温催化剂涂覆长度分别为266 mm和334 mm。
-
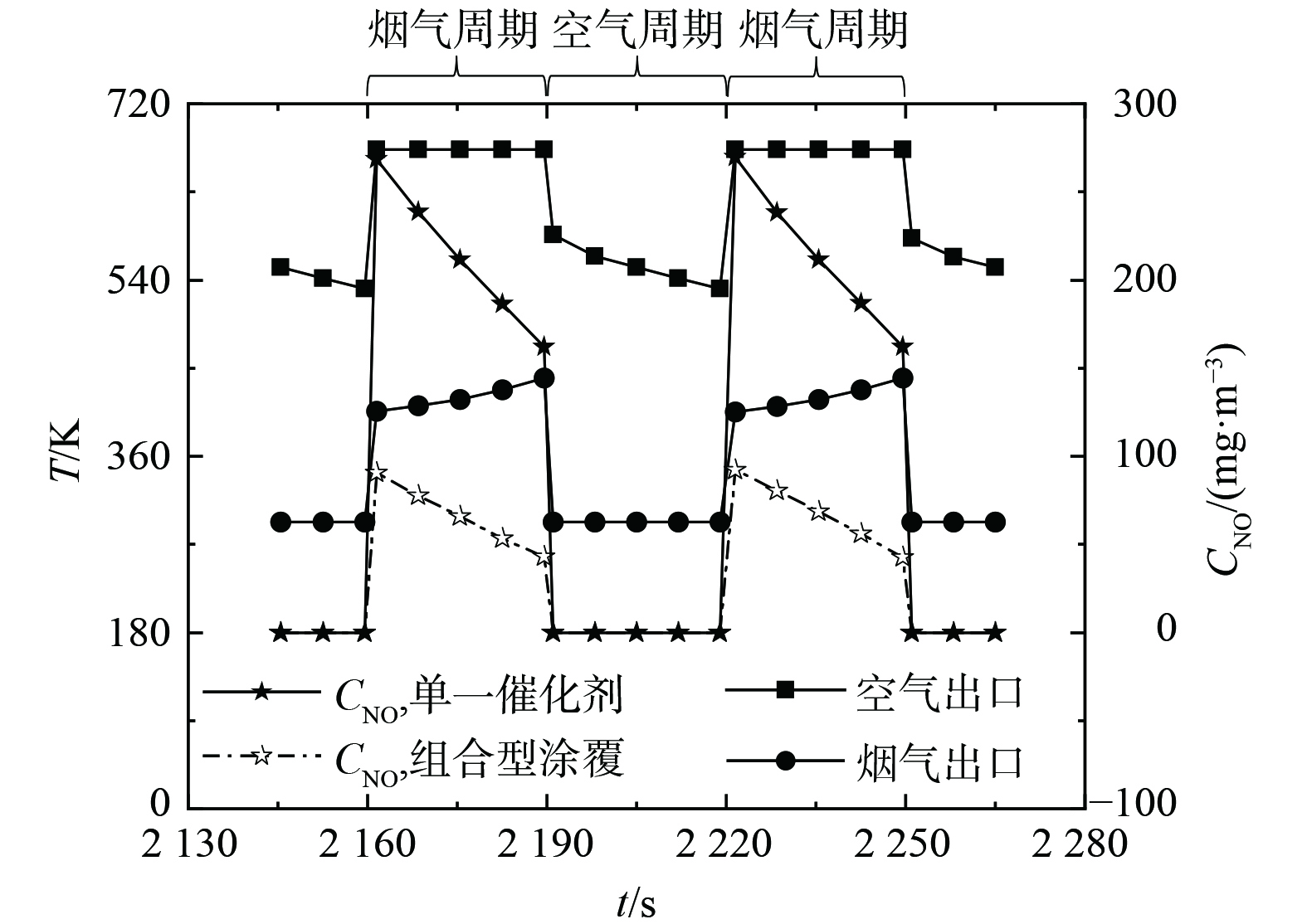
复合蓄热体内部流体和固体温度场随时间和空间不断变化,将显著影响烟气周期NO的转化速率。为深入研究复合蓄热体内部动态脱硝情况,在烟气进口速度5 m·s−1和烟气-空气切换时间30 s条件下对组合涂覆型和单一催化剂型SCR蜂窝蓄热体进行数值模拟,计算的进口和出口流体温度及冷端NO质量浓度随时间的动态变化 (图4) 。2种复合蓄热体的进口和出口温度曲线差异很小,故图4仅有一组温度曲线。烟气周期和空气周期的流体进口温度保持不变,且前者烟气出口温度随时间逐渐升高,后者空气出口温度则随时间不断降低。
上述温度变化曲线与蓄热体非稳态传热密切相关。在烟气周期,由于流体不断向温度较低的蓄热体传热,蓄热体温度随时间不断升高,这导致烟气由于放热量逐渐减少而出口温度不断升高;进入空气周期后,常温空气流过高温的蓄热体,蓄热体由于被空气不断带走热量,温度不断降低,空气则由于吸热量逐渐减少而出口流体温度随时间不断降低。众所周知,SCR脱硝仅发生在烟气周期,根据图4中的五角星曲线,组合涂覆型和单一催化剂型SCR蓄热体的烟气出口NO质量浓度均随时间不断降低。显然,这是由于在烟气周期,蓄热体和流体温度均随时间不断上升,提高了催化剂活性。此外,组合涂覆型SCR蓄热体的烟气出口NO质量浓度显著低于单一催化剂型SCR蓄热体。在整个烟气周期,前者烟气出口NO质量浓度为58.7 mg·m−3,比后者低71.6%。这证实组合型涂覆有效提升了复合SCR蓄热体脱硝性能。定量分析图4动态温度和浓度曲线发现,在典型工况下,组合涂覆型SCR蓄热体空气周期出口流体温度随时间从586.3 K降至531.0 K,对应的蓄热体能量回收率从61.1%降至52.2%;而烟气周期出口烟气NO质量浓度从92.0 mg·m−3降至42.8 mg·m−3,对应的脱硝效率从86.7%升至93.8%。
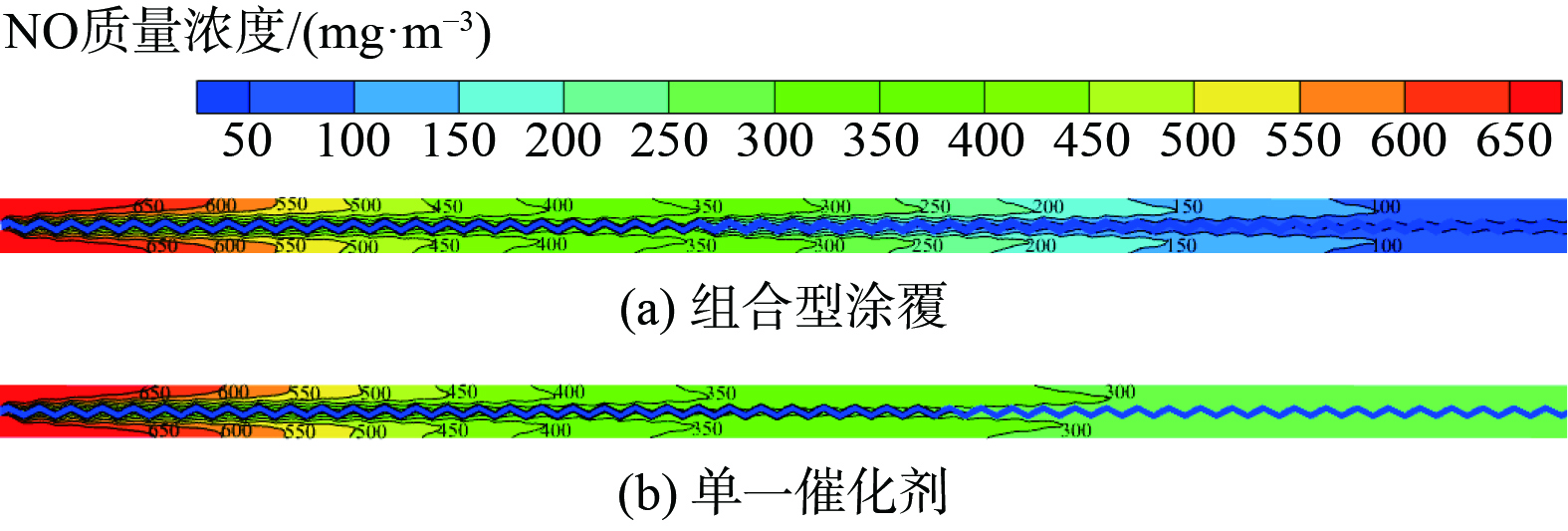
为探究组合涂覆中低温催化剂强化复合蓄热体脱硝性能的物理机理,实验得到组合涂覆型和单一催化剂型SCR蓄热体在烟气周期中间时刻的纵剖面NO质量浓度云图 (图5(a)和(b)) 。根据图5(b),烟气从左端流入单一催化剂型复合蓄热体时,烟气中NO质量浓度不断减小,且浓度等值线云图越来越稀疏。这意味着脱硝速率沿轴向逐渐减慢。组合涂覆型蓄热体纵剖面NO质量浓度(见图5(a))也是沿烟气流动方向(向右)逐渐降低,且其左侧高温区NO质量浓度等值线云图与单一催化剂型蓄热体相同。另外,在蓄热体中间某个位置,组合涂覆型蓄热体NO质量浓度等值线突然加密,且该位置下游的NO质量浓度较单一催化剂蓄热体有显著降低。这表明组合涂覆可有效提高复合蓄热体脱硝性能。
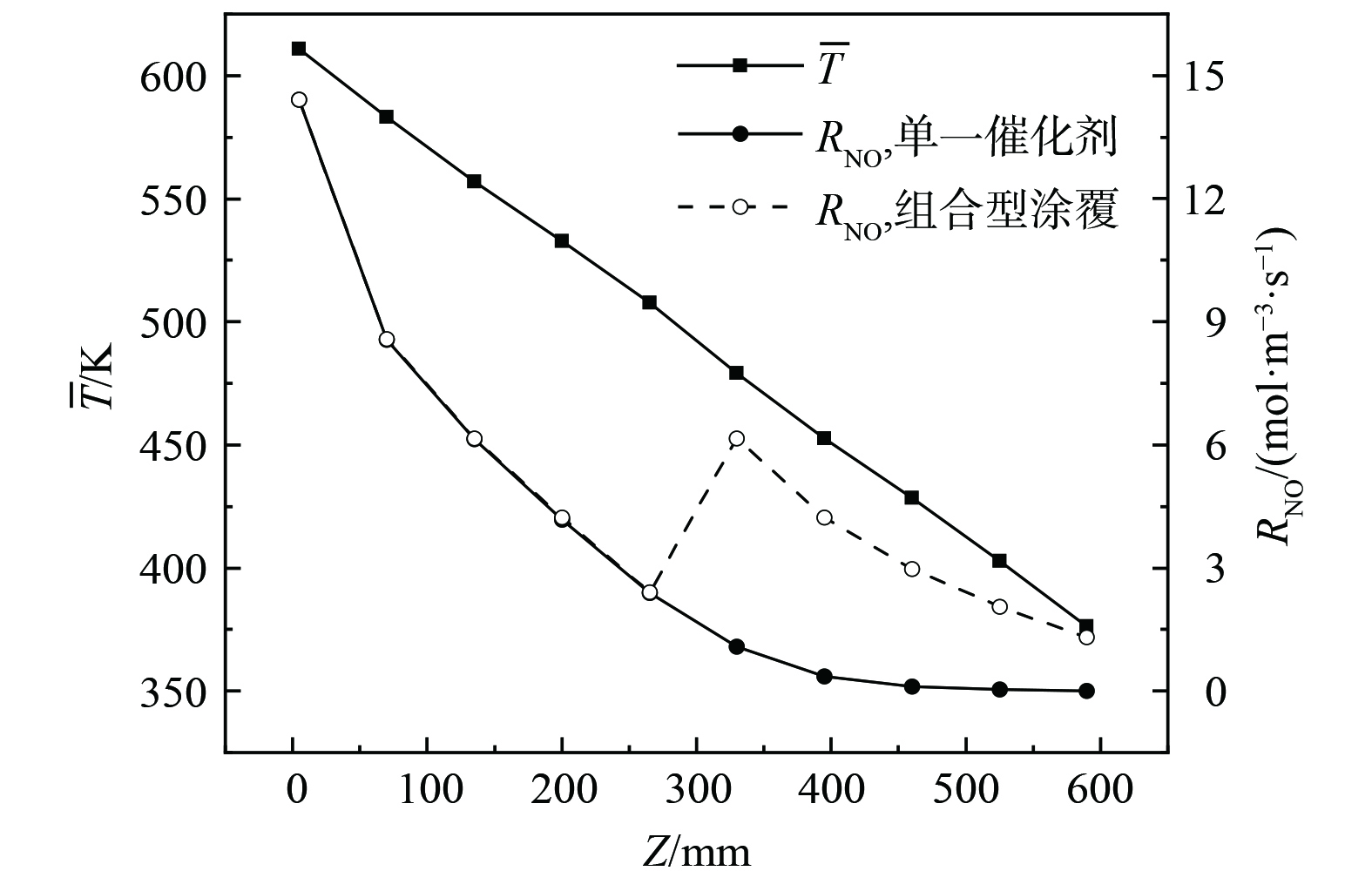
为进一步验证组合涂覆和单一催化剂型复合蓄热体脱硝性能的差异,实验得到在烟气周期中间时刻脱硝反应速率(RNO)和温度沿流动方向(Z向)的变化曲线 (图6) 。在烟气进口侧的较高温区域(Z≤266 mm),组合涂覆型与单一催化剂型蓄热体都涂覆中温钒基催化剂V2O5-WO3/TiO2,故两者RNO曲线基本完全相同;然而,由于组合涂覆型蓄热体在Z>266 mm区域涂覆低温铜基催化剂5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon,在Z=266 mm,RNO突然跃升,且其RNO在整个低温催化剂涂覆区段均显著高于对应位置的单一催化剂型蓄热体。进一步分析图6中催化剂温度曲线发现,Z>266 mm区段对应T<507 K的低温区。根据图2,该低温区铜基催化剂反应速率常数k高于钒基催化剂,这也进一步解释了组合涂覆提高脱硝性能的机理。
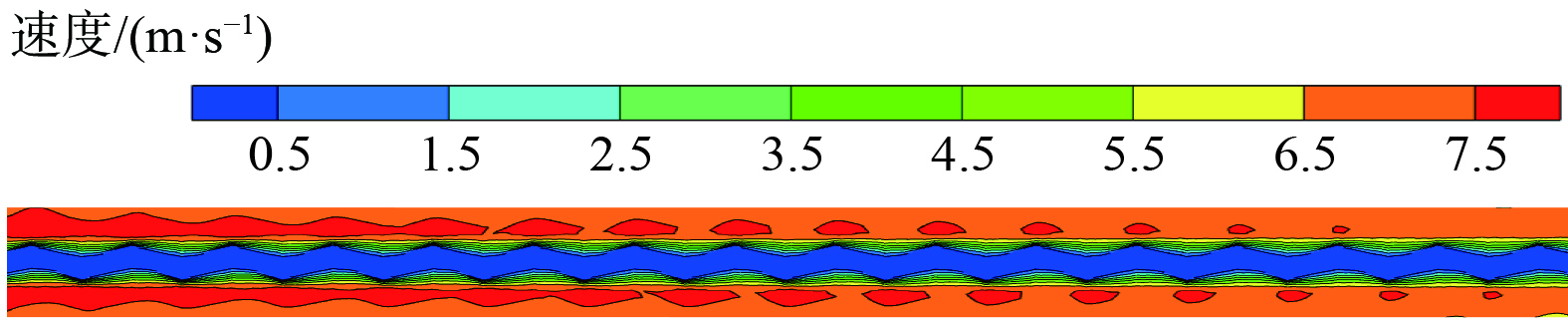
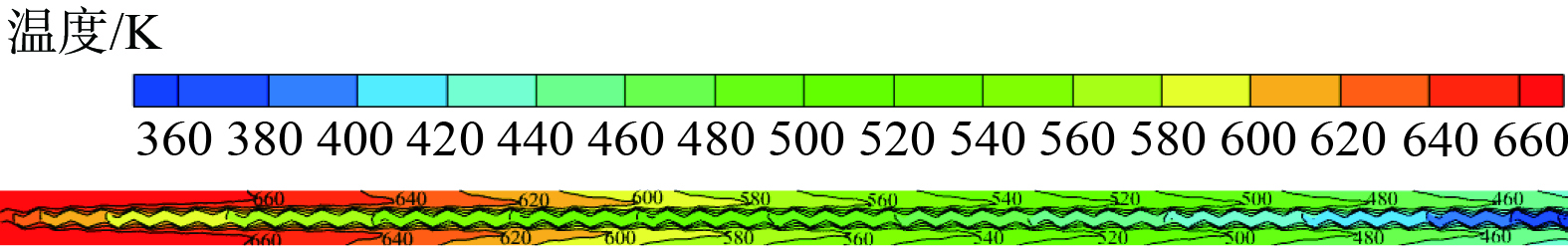
图5表明,复合蓄热体横向NO质量浓度等值线呈现典型的“M”形(由于对称,只显示了一半)。这表明通道中央位置虽然离催化层最远,但其有较快的NO质量浓度削减速度。为理解这一现象,分析得到复合蓄热体烟气周期中间时刻纵剖面流体速度云图 (图7) 。烟气在通道喉部受强烈扰动,在壁面附近形成射流,流体速度横向分布不再是典型的抛物线,通道中央流体速度小于距壁面某个距离处的流体速度。这说明削减后者NO质量浓度比削减通道中央流体更困难,另外,扩缩结构会诱导旋涡,加速横向流体的掺混,这有助于降低中央流体NO质量浓度。显然,在这两方面因素可解释图5中“M”形的NO等值线。上述扩缩通道速度场也将影响通道内部烟气温度场。图8为复合蓄热体烟气周期纵向剖面的温度云图,通道内温度等值线与浓度等值线类似,也呈现“M”形,亦进一步验证了前面的假设。
-
按照3.1节的方法,计算了不同扩缩角(α=0、5、10、15和20°)条件下复合蓄热体组合涂覆时的中温和低温催化剂长度,结果如表2所示。在相同烟气进口速度条件下,随着α从0°增至20°,中温催化剂涂覆长度从258 mm增至274 mm,低温催化剂的涂覆长度则相应减小。中温催化剂涂覆长度随α单调增大的原因与扩缩通道强化传热有关,在本研究设定温度范围内,α越大,扩缩通道对流传热越强,因此,α较大时复合蓄热体下游烟气温度较低,对应的骨架和催化剂等温线(包括临界温度T=507 K)相应朝低温侧出口移动。
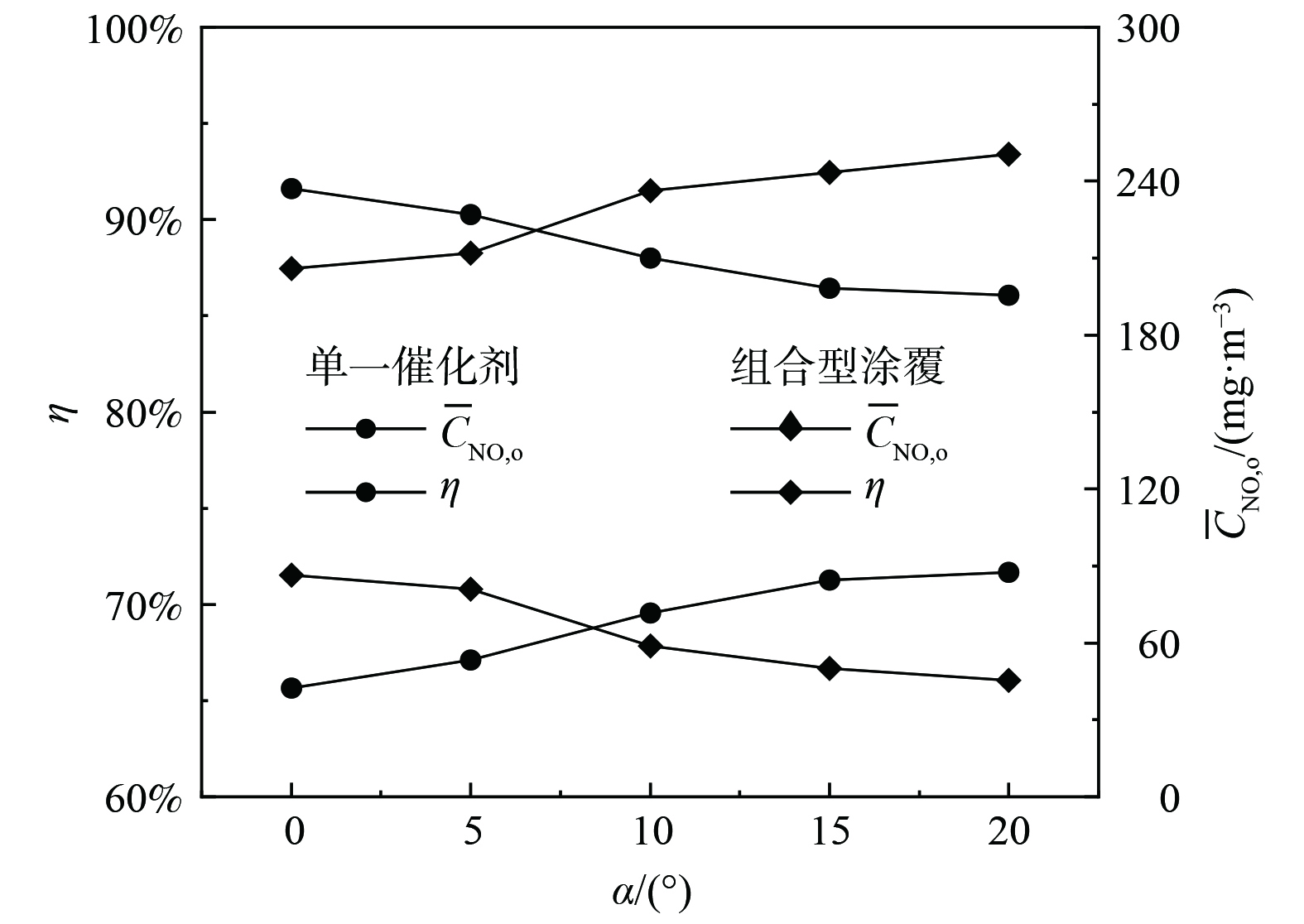
图9为组合涂覆和单一催化剂等两种复合蓄热体脱硝效率(η)和出口NO浓度(
$ \overline{C} $ NO,o)随通道扩缩角(α)的变化情况。2种蓄热体的$ \overline{C} $ NO,o均随α的增加而减小,对应的η则随α的增加而增加。此外,与单一催化剂蓄热体相比,组合涂覆蓄热体脱硝性能更为优越。当从α从0°增加到20°,单一催化剂型复合蓄热体$ \overline{C} $ NO,o从237.0 mg·m−3降至195.5 mg·m−3,η则从65.7%增至71.6%;在相同条件下,组合涂覆型SCR蓄热体的$ \overline{C} $ NO,o从86.5 mg·m−3降至45.5 mg·m−3,η则从87.5%升至93.4%。分析图9发现,当α=5°时,增加α可显著提高(或降低)复合蓄热体的η(或$ \overline{C} $ NO,o)。当α=15°时,继续提高α,单一催化剂型蓄热体η的增加速度显著减慢,与单一催化剂蓄热体相比,组合涂覆型蓄热体在α=10°时就随α增加缓慢增加。当α等于15°时,组合涂覆型的η和$ \overline{C} $ NO,o分别为92.4%和50.1 mg·m−3,分别比单一催化剂型增加21.2%和降低148.3 mg·m−3。由于复合蓄热体脱硝效率主要取决于来流烟气NO浓度、催化层脱硝反应速率和催化层表面NO的对流输运等因素,前面也已讨论了组合涂覆型复合蓄热体通过增大低温区催化层脱硝反应速率提高脱硝性能的物理机理,故结合扩缩通道强化传质来进一步探讨复合蓄热体脱硝效率随扩缩角增大机理。王盛等[13]研究表明,扩缩通道蜂窝对流传质速率随扩缩角α增加而增加。α较小时,扩缩通道强化传质效果较弱,因此,较小α的复合蓄热体的脱硝性能与α的关系较弱;当α较大时,扩缩通道对流传质比较强,在来流烟气NO数量有限的条件下,较大α的复合蓄热体脱硝效率随α增加的速率也比较慢;中等α有中等的对流传热速率,进一步提高其数值,一方面能更有效输运主流烟气NO到催化层进行脱硝反应,另一方面,来流烟气能提供足够NO,故中等α的复合蓄热体脱硝效率随α显著提高。对于组合涂覆型蓄热体,由于其脱硝性能比较好,在来流烟气NO数量一定时,中等α即可能产生相当大的NO反应速率,出现来流烟气NO浓度瓶颈,因此,组合涂覆型蓄热体脱硝效率随α增加速率变慢的临界α比单一催化剂蓄热体小。
-
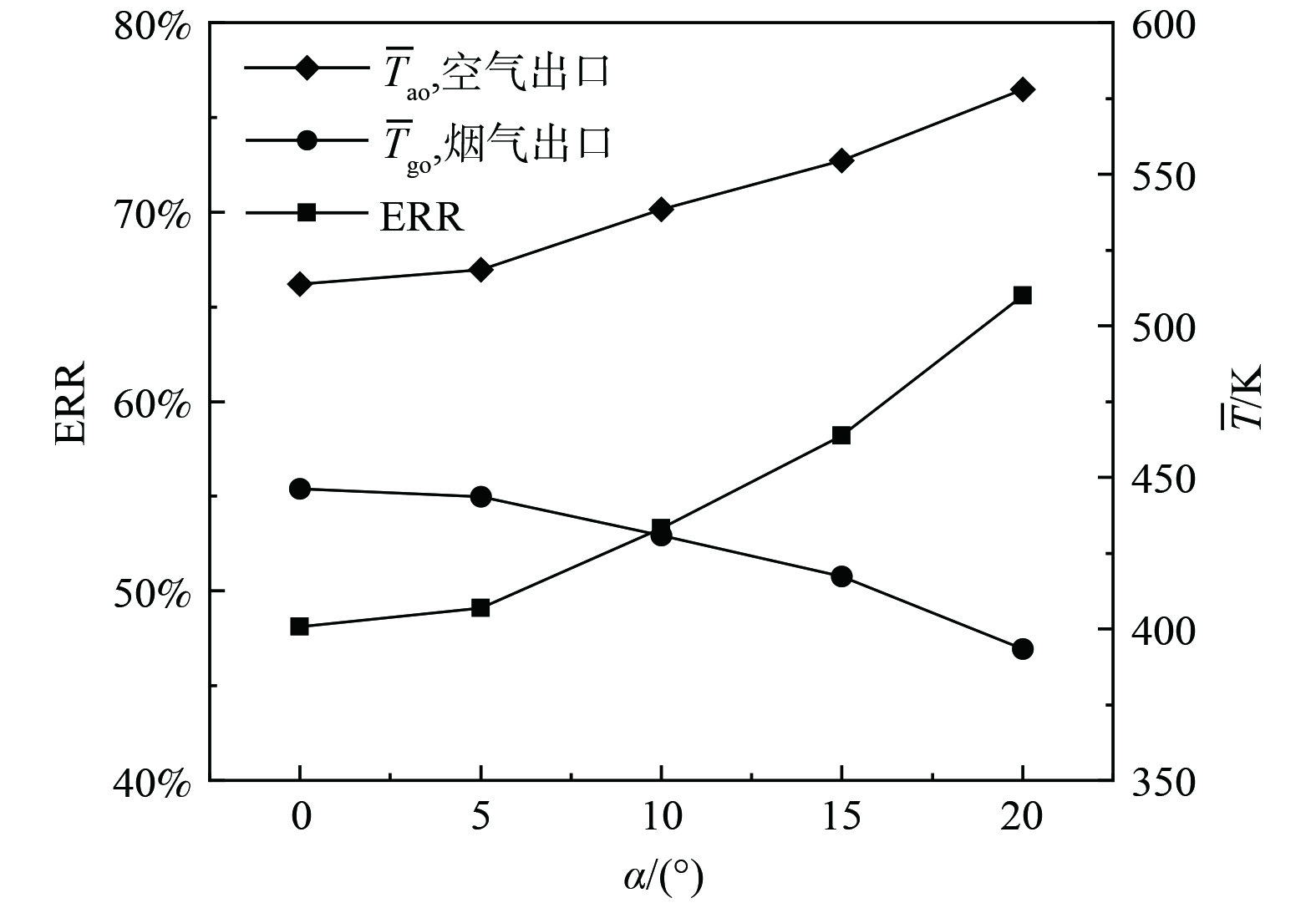
如前所述,催化剂涂覆方案对复合蓄热体传热流动性能影响很小。图10为复合蓄热体在不同扩缩角(α)条件下的能量回收率(ERR)和流体出口平均温度。空气出口温度即空气预热温度(
$ \overline{T} $ ao)和ERR随α增大而提高,而烟气出口温度($ \overline{T} $ go)则随着α增大而减小。在本文扩缩角范围,即α从0°增大到20°,$ \overline{T} $ ao和ERR分别从513.7 ℃,48.1%增大到578.1 ℃和65.6%,而$ \overline{T} $ go从446.3 ℃下降到394.3 ℃。$ \overline{T} $ ao和ERR随α单调增加的原因可能是α较大的蓄热体骨架有较大的表面积和对流换热系数;此外,α越大,蓄热体骨架质量越多,在烟气和空气周期能够吸收和释放更多热量,这也有助于提高蓄热体传热性能。图11为复合蓄热体在不同扩缩角α下烟气和空气的压力损失。因为空气周期流体流量大致为烟气周期的80%,烟气周期压力损失
$ \Delta \stackrel{̄}{p} $ g大于空气压力损失$ \Delta \stackrel{̄}{p} $ a,约为后者的123.9 %。与$ \overline{T} $ ao和ERR类似,复合蓄热体的$ \Delta \stackrel{̄}{p} $ g和$ \Delta \stackrel{̄}{p} $ a也随α增加而增大,这表明扩缩通道强化传热性能时,需考虑压力损失因素的影响。根据图11,$ \Delta \stackrel{̄}{p} $ 随α增加的速度与α数值密切相关:当α小于15°时,$ \Delta \stackrel{̄}{p} $ g和增加较为缓慢,数值均小于100 Pa,但当α大于15°时,其变化明显加剧,数值也成倍增加(20°时$ \Delta \stackrel{̄}{p} $ g增加至197.9 Pa)。这可能是由于α大于15°后,扩缩通道内产生了显著旋涡,这些旋涡迅速耗散流体机械能,导致烟气和空气周期的压力损失急剧增加。 -
1) 在对Fluent软件二次开发的基础上,建立了多孔介质容积反应的SCR蜂窝脱硝与烟气-空气切换的蓄热体非稳态传热相耦合的复合SCR蓄热体数值模型。该模型可用于研究表面涂覆SCR催化剂的新型扩缩通道蓄热体非稳态传热和脱硝性能。
2) 复合蓄热体工作稳定后,其温度场和浓度场周期性变化,空气周期出口温度和烟气周期出口NO质量浓度均随时间降低,烟气周期出口温度则随时间不断升高。组合涂覆型SCR蓄热体典型工况条件下,烟气周期流体进口温度和NO质量浓度分别为673 K和690.2 mg·m−3,出口温度随时间从405.9 K升高至440.1 K,出口NO质量浓度则从92.0 mg·m−3降低到42.8 mg·m−3,对应瞬态脱硝效率随时间从86.7%升高到93.8%。
3) 增加扩缩角可提高复合蓄热体传热和脱硝性能,亦可增大流动阻力。扩缩角为15°的组合涂覆型SCR蓄热体具有良好的整体性能,其时均能量回收率和脱硝效率分别比涂覆单一钒基催化剂的直通道蜂窝蓄热体提升10.1% (58.2% vs 48.1%)和26.7% (92.4% vs 65.7%),而流动阻力则仅比后者增加了57.1 Pa。
组合涂覆SCR催化剂的扩缩通道蓄热体传热脱硝性能的数值模拟
A numerical simulation of on heat transfer and denitrification performances for regenerators with expansion and contraction channels coated by SCR catalysts
-
摘要: 蜂窝蓄热体表面涂覆中温钒基SCR催化剂(V2O5-WO3/TiO2),可实现余热回收和烟气脱硝双重功效,但钒基催化剂在烟气出口侧的低温区脱硝效果不理想。新型纳米多孔结构的铜基SCR催化剂(5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon)能在低温条件下高效工作。通过在现有钒基SCR蜂窝蓄热体低温侧表面涂覆这种铜基催化剂,并借助扩缩通道强化传热传质进一步提高复合蓄热体传热和脱硝性能。在对Fluent软件二次开发基础上,采用多孔介质方法描述催化层烟气SCR脱硝,建立烟气-空气切换条件下复合SCR蜂窝蓄热体内非稳态传热脱硝的数值模型。借助该模型,探究催化剂涂覆方案和结构参数对复合蓄热体传热和脱硝性能的影响。结果表明:扩缩角为15°的组合涂覆型SCR蓄热体具有良好整体性能,其能量回收率(ERR)和脱硝效率(η)分别比涂覆单一钒基催化剂的直通道蜂窝蓄热体提升10.1% (58.2% vs 48.1%)和26.7% (92.4% vs 65.7%)。本研究结果可为工业锅炉的节能和氮氧化物(NOx)减排提供参考。Abstract: The dual effects of waste heat recovery and flue gas denitrification was obtained by coating Vanadium SCR catalysts of medium temperature (V2O5-WO3/TiO2) on honeycomb regenerators, however, the denitrification performance of Vanadium catalysts is unsatisfactory in the low temperature zone approaching flue gas outlet. Novel Copper-based SCR catalysts of nano porous structure (5%CuO-40% HPW/Popcarbon) were reported to work efficiently under the condition of low temperature. In the current work, to obtain better heat transfer and denitrification performances, the novel Copper-based SCR catalysts are applied to the low-temperature surface of honeycomb regenerators coated with Vanadium catalysts, and expansion and contraction channels are employed to strengthen the heat and mass transfer rates in composite regenerators. With the secondary development of Fluent software, the numerical model of novel composite SCR honeycomb regenerators is established, where the SCR denitrification of flue gas in porous catalyst layers is coupled with the unsteady conjugate heat transfer with air and flue gas flowing through regenerators alternately. With the current model, the effects of catalyst coating scheme and structural parameters on the thermal and denitrification performances are explored for the novel composite regenerators. Numerical results show that the composite SCR honeycomb regenerators with an expansion and contraction angle of 15° can generate a good overall performance, whose energy recovery ratio (ERR) and denitrification efficiency (η) are 10.1% (58.2% vs 48.1%) and 26.7% (92.4% vs 65.7%) higher than those of straight-channel regenerators coated with a single Vanadium-based catalyst, respectively. The results of this study can provide a reference for energy saving and reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in industrial boilers.
-

-
表 1 复合蓄热体的结构和工艺参数
Table 1. Structural and technology parameters of composite regenerators
参数 数值/内容 参数 数值 蓄热体长度 600 mm 切换时间 30 s 通道特征尺寸 6 mm 空气进口流速 2.20 m·s−1 骨架壁厚 1 mm 空气进口温度 293 K 扩缩角 0°、5°、10°、15°和20° 烟气进口流速 5 m·s−1 扩缩节距 6 mm 烟气进口温度 673 K 催化层厚度 110 μm 烟气进口O2体积分数 5% 催化剂种类 V2O5−WO3/TiO2 烟气进口NO体积分数 0.05% 5%CuO-40%HPW/Popcarbon 烟气进口NH3体积分数 0.05% 表 2 不同扩缩角条件下组合涂覆型复合蓄热体中温和低温催化剂的涂覆长度
Table 2. Lengths of medium- and low-temperature catalyst layers for composite regenerators with different expansion and contraction angles
扩缩角α/° 中温催化剂层长度L1/mm 低温催化剂层长度L2/mm 0(直通道) 258 342 5 262 338 10 266 334 15 270 330 20 274 326 -
[1] PALASH S M, KALAM M A, MASJUKI H H, et al. Impacts of biodiesel combustion on NOx emissions and their reduction approaches[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 23: 473-490. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.03.003 [2] BONINGARI T, SMIRNIOTIS P G. Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOx abatement[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2016, 13: 133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2016.09.004 [3] OGIDIAMA O V, SHAMIM T. Performance analysis of industrial selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems[J]. Energy Procedia, 2014, 61: 2154-2157. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2014.12.098 [4] ZHANG W B, CHEN J L. Research progress on NH3-SCR mechanism of metal-supported zeolite catalysts[J]. Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2021, 49(9): 1294-1315. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60080-4 [5] SVACHULA J, FERLAZZO N, FORZATTI P, et al. Selective reduction of nitrogen oxides (NOx) by ammonia over honeycomb selective catalytic reduction catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1993, 32(6): 1053-1060. [6] YANG J, MA H T, YAMAMOTO Y, et al. SCR catalyst coated on low-cost monolith support for flue gas denitrification of industrial furnaces[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 230: 513-521. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.114 [7] TRONCONI E, LIETTI L, FORZATTI P, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the dynamics of the SCR-DeNOx reaction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1996, 21(11): 2965-2970. [8] DHANUSHKODI S R, MAHINPEYN, WILSON M, et al. Kinetic and 2D reactor modeling for simulation of the catalytic reduction of NOx in the monolith honeycomb reactor[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2008, 86(4): 303-309. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2008.02.004 [9] RODUIT B, BAIKER A, BETTONI F, et al. 3-D modeling of SCR of NOx by NH3 on vanadia honeycomb catalysts[J]. AIChE J, 1998, 44(12): 2371. [10] LEI Z, LIU X, JIA M. Modeling of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for NO removal using monolithic honeycomb catalyst[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(6): 6146-6151. [11] YAO J, ZHONG Z, ZHU L. Porous medium model in computational fluid dynamics simulation of a honeycombed SCR DeNOx Catalyst[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2015, 38(2): 283-290. [12] 赵大周, 何胜, 司风琪, 等. 选择性催化还原单孔催化剂数值模拟[J]. 热力发电, 2016, 45(4): 100-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2016.04.017 [13] 王盛, 游永华, 邵坤, 等. 扩缩通道强化蜂窝型SCR反应器脱硝性能的数值研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 393-399. [14] GUO K H, SHI W H, WU D H, et al. Experiment research and simulation analysis of regenerative oxygen-enriched combustion technology[J]. Industrial Heating, 2015, 66: 221-224. [15] 王维刚. 蓄热式换热器的优化设计[J]. 化工机械, 2010, 37(4): 412-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6094.2010.04.004 [16] RAFIDI N, BLASIAK W. Thermal performance analysis on a two composite material honeycomb heat regenerators used for HiTAC burners[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2005, 25(17/18): 2966-2982. [17] 封红燕, 冯毅. 新型蜂窝蓄热体热工特性的数值模拟[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2012, 6: 108-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2012.04.040 [18] YOU Y H, HUANG H, SHAO G W, et al. A three-dimensional numerical model of unsteady flow and heat transfer in ceramic honeycomb regenerators[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 108: 1243-1250. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.08.035 [19] YOU Y H, Wu Z D, LI B, et al. 3D numerical simulation and optimization of honeycomb regenerators with parallel or crosswise arrangement of circular holes[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2019, 137: 22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2019.01.010 [20] 吴仲达, 游永华, 王盛, 等. 扩缩方孔蜂窝蓄热体强化传热的数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(12): 1416-1423. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220009 [21] YOU Y H, WU Z D, ZENG W D, et al. CFD modeling of unsteady SCR deNOx coupled with regenerative heat transfer in honeycomb regenerators partly coated by Vanadium catalysts[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2019, 150: 234-245. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2019.07.015 [22] 任兆勇. 基于新型纳米多孔载体的多金属氧酸盐主客体复合体系的构建及NH3-SCR中低温脱硝性能研究[D]青岛 : 山东大学 , 2019 . [23] 祁海鹰, 李伟, 李宇红, 等. 蜂巢蓄热体的稳态传热特性和最佳换向时间[C]. 全国工业炉暨电热学术会议. 2000, 大连: 366-372. [24] STEPHEN R T. An Introduction to Combustion Concepts and Applications[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2018, [25] VANNICE M A. Kinetics of Catalytic Reactions[M]. 2005, New York: Springer Science & Business Media. [26] 王志鹏, 李鹏飞, 陈媛, 等. SCR脱硝反应活化能和指前因子分析[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(10): 86-91. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201810017 -



 下载:
下载: