-
纺织工业是我国传统的支柱产业,在织造过程中普遍使用的喷水织机虽然具有质量好、产量高和费用低等优点,但同时也存在着耗水量大(年用水量可达4.5×108 t)和碳组分排放量高(出水COD为200~600 mg·L−1,SS>100 mg·L−1)等环境问题[1],因而会对水体、土壤及生态系统等造成严重伤害[2-3]。横跨江、浙两省的太湖,尽管水资源十分丰沛,但随着近年来两地纺织工业的高速发展,纺织废水排放量及其水污染程度大幅提升,多次频繁暴发的蓝藻表明区域内的水污染治理形势依旧严峻[4-6]。
目前,工业上对织造废水常用的处理技术包括焚烧[7-8]、气浮[9]、混凝[10]、沉淀[11]、好氧和厌氧生物技术[12]等,同时为了达到国家不断严苛的废水排放新标准,膜分离[13-14]、高级氧化技术[15]等强化方法也被应用到织造废水的深度处理过程中。膜分离法由于膜组件需定期更换导致成本较高;传统芬顿氧化技术虽然对污染物的氧化能力强,但其pH=3的最佳工艺条件导致人们在处理进水和出水为pH=6~8的喷织机废水时,不但需要加入大量酸碱调节溶液pH[16],而且还产生大量铁泥二次污染物,增加了水处理的难度与成本[17-18]。
近年来,类芬顿催化氧化法因具有pH使用范围广、催化效率高、催化剂可回收等优点[19-20],已成为高级氧化技术中的研究热点。由于类芬顿反应不再局限于Fe2+与H2O2的组成和均相反应模式,因而在催化剂和氧化剂的组成和反应模式上有更多样性的选择。Cu、Mn、Co等过渡金属氧化物、氢氧化物及其复合物替代Fe2+, PMS、PDS和NaClO替代氧化剂H2O2等[21-24],它们在氧化反应中表现出的强氧化能力和高选择性以及宽pH反应条件,使类芬顿反应在难降解产物的完全去除中被寄予厚望。虽然已有较多类芬顿体系被用于含芳环类结构的难降解有机污染物的去除,但针对喷水织机废水中含有的丙烯酸及其酯这类有机小分子物质,由于它们具有分子结构简单、性质稳定、溶解度大、极性强等特征,并且还可能是经其他水处理方法后所产生的中间产物或最终产物等,因而它们的矿化去除与芳环类物质相比难度更大,有关其高效去除的成功范例也较少[25-27]。
本研究采用共沉淀法合成CuO@Fe3O4非均相类芬顿催化剂,通过构建CuO@Fe3O4/NaClO催化氧化体系,考察其对喷水织机废水中典型有机小分子污染物丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的降解能力,讨论不同反应条件下的丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯矿化效果,探讨CuO@Fe3O4/NaClO体系的催化氧化机理,获得可溶性小分子有机污染物在污水深度处理过程中的特征行为和规律,旨在为水体中有机碳的总量控制和减排提供技术支撑。
-
丙烯酸(CH2CHCOOH)纯度为99%、丙烯酸甲酯(CH2CHCOOCH3)纯度为98.5%、次氯酸钠(NaClO)有效氯含量为4%,均由麦克林集团提供;五水合硫酸铜(CuSO4·5H2O)、七水合硫酸亚铁(FeSO4·7H2O)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、硫酸(H2SO4)均由国药集团提供;自旋捕集剂5,5-二甲基吡咯啉氧化物(DMPO)由Tocris(美国)提供;2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶(TEMP)由Dojindo(日本)提供。以上所有试剂均为分析纯,所有试剂在稀释过程中均使用去离子水作为溶剂。
-
X射线衍射仪(XRD,X`Pert PRO,荷兰帕纳科公司)分析得到样品的晶体衍射谱图;场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM,Gemini SEM 300,德国蔡司公司)表征分析样品的形貌;动态光散射仪(DLS,Zetasizer Nano-ZS90,英国Malvem公司)测定纳米复合物的Zeta电位;光电子能谱仪(XPS,K-Alpha+,美国赛默飞世尔公司)分析样品的组成和价态;电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,X Series II,美国赛默飞世尔公司)分析金属离子含量;全自动比表面和微孔孔径分析仪(Autosorb-IQ2-MP,美国 Quantachrom仪器公司)测定样品的比表面和孔径大小。
-
将FeSO4·7H2O 和CuSO4·5H2O溶于100 mL去离子水中,在50 ℃下缓慢滴入2.5 mol·L−1的NaOH溶液,使体系的pH 值保持在13.0左右;继续反应2 h后,室温静置12 h,再用去离子水重复多次洗涤沉淀物,直至上清液为中性。将滤饼置于真空烘箱中,60 ℃下真空干燥8 h,研磨、60目(孔径为250 μm)筛网过筛。将反应前FeSO4·7H2O 和CuSO4·5H2O投料摩尔比为0:1、2.5:1、5:1、7.5:1、10:1和1:0制备得到的产物分别标记为CuO、2.5CuO@Fe3O4、5CuO@Fe3O4、7.5CuO@Fe3O4和10CuO@Fe3O4和Fe3O4。
-
分别取100 mL不同质量浓度(0.05~0.40 g·L−1)的丙烯酸或丙烯酸甲酯溶液于250 mL 锥形瓶中,加入氧化剂NaClO (6.4~80 mmol·L−1),充分混合之后,调节溶液pH为3.0~11.0,再分别加入已制备得到的各种催化剂 (2~64 mg·L−1),30 ℃下于恒温振荡培养箱中以250 r·min−1 进行降解实验。在设定时间(10~480 min)取水样,用Na2SO3还原残余NaClO后,使用分光光度法(《水质化学需氧量的测定》(HJ 828-2017))测定COD值,计算各样品的COD去除率(式(1))。
式中:η为COD去除率;c0和c分别为丙烯酸及丙烯酸甲酯降解反应前后的COD值,mg·L−1。
氧化反应结束后,将催化剂进行磁力分离,分别用去离子水和无水乙醇各洗涤3次,在60 ℃下真空干燥至恒重。取再生后的催化剂样品,重新加入到丙烯酸或丙烯酸甲酯溶液中进行循环降解实验。
-
在100 mL的0.2 g·L−1丙烯酸溶液中加入48 mg的5CuO@Fe3O4和16 mmol·L−1的NaClO(或是在100 mL的0.2 g·L−1丙烯酸甲酯溶液中加入20 mg的5CuO@Fe3O4和19 mmol·L−1 NaClO),30 ℃下于250 r·min−1的摇床中反应,间隔一定时间后,取样测定COD,对实验数据进行准二级动力学方程(式(2))拟合。
式中:c0和c分别为t0和t时刻反应物中的浓度,mg·L−1;t为反应时间,min;k为拟二级动力学反应速率常数,L·(mg·min)−1。
-
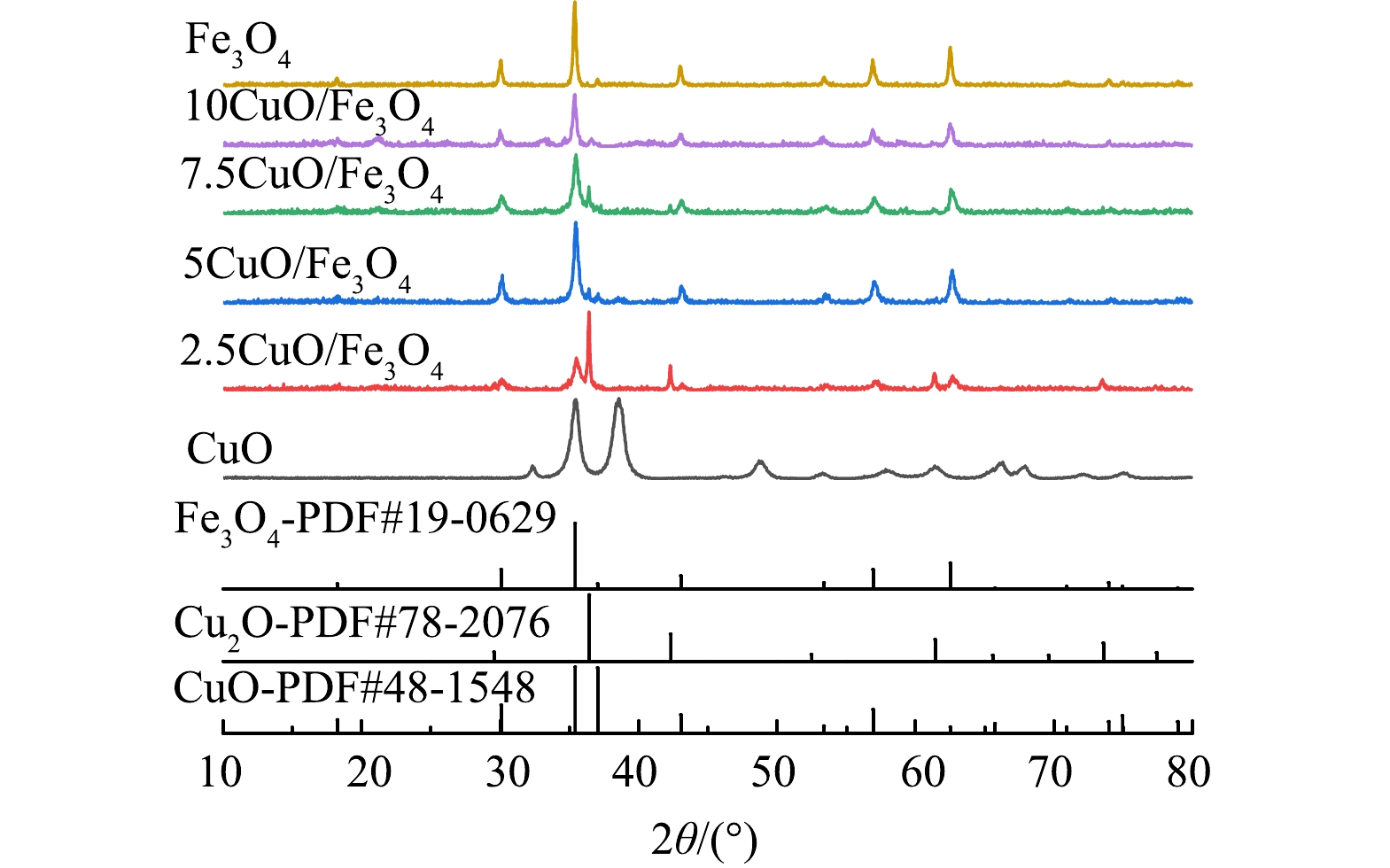
图1为2.5CuO@Fe3O4、5CuO@Fe3O4、7.5CuO@Fe3O4和10CuO@Fe3O4的XRD图谱。可以看出,在2θ=35.4o、37.1o、43.1o、56.9o、75.2o处出现的衍射峰属于CuO (JCPDs 48-1548)的(002)、(111)、(020)、(113)、(222)晶面;而2θ=18.3o、30.1o、35.4o、37.1o、43.1o、53. 4o、56.9o、62.5o、73.9o处出现的衍射峰则属于Fe3O4 (JCPDs 19-0629)的(111)、(220)、(311)、(222)、(400)、(422)、(511)、(440)、(533)晶面反射。已知Fe3O4在2θ=30.1o处出现的强衍射峰对应(220)晶面的特征衍射峰,而CuO在2θ=37.1o的衍射峰则对应(111)晶面的特征衍射峰。比较不同Fe/Cu比下各样品的特征衍射峰,发现随着CuO@Fe3O4中铜含量的增加,复合物中与Fe3O4的(220)晶面对应的衍射峰先增强后降低,并在Fe/Cu比为5:1时结晶性最好;而CuO和Cu2O对应的特征峰则随着Fe/Cu比的变化有不同特点,如CuO的特征衍射峰在Fe/Cu比为7.5:1时最强,而Cu2O的衍射峰是在2.5:1时有强峰等。显然随着Cu含量的增大,各CuO@Fe3O4样品中的Cu存在着在CuO和Cu2O之间的价态转换。
根据SCHERRER方程, 单独制备得到的CuO和Fe3O4粒径分别为11.2 nm和36.4 nm, 而双金属组分催化剂5CuO@Fe3O4中CuO和Fe3O4粒径大小分别为26.2 nm和26.4 nm,2.5CuO@Fe3O4、7.5CuO@Fe3O4和10CuO@Fe3O4中Fe3O4的粒径则分别为18、16.8和22.2 nm, CuO粒径为44.3、58.7和51.2 nm。同5CuO@Fe3O4中CuO和Fe3O4粒径近似相等不同,其他CuO@Fe3O4样品中Fe3O4和CuO相互间粒径差异大。
图2给出了不同CuO@Fe3O4样品的SEM图。可以看出,2.5CuO@Fe3O4、5CuO@Fe3O4、7.5CuO@Fe3O4和10CuO@Fe3O4的微观结构呈现出棒状和颗粒状粒子间相互均匀掺杂的特征。同时随着初始铜含量的降低,即当Fe/Cu在2.5:1~10:1之间变化时,各CuO@Fe3O4样品的粒径尺寸逐渐变大,说明投料时初始铜离子含量的增加对CuO@Fe3O4颗粒的生长有抑制作用。此外,铜离子含量的增加还使CuO@Fe3O4中颗粒状粒子的数量出现先增加再降低的趋势,即5CuO@Fe3O4催化剂中颗粒状粒子最多,而2.5CuO@Fe3O4、7.5CuO@Fe3O4和10CuO@Fe3O4样品中都存在较高比例的棒状粒子。对比相同条件下制备的纯CuO和纯Fe3O4样品SEM图谱,发现它们不但具有单一的片层状或颗粒状形貌,而且其粒径也明显大于各CuO@Fe3O4样品的尺寸。由此可知,在Cu、Fe 2种金属离子共存生成CuO@Fe3O4的过程中,会相互影响自身的颗粒尺度和微观形貌,且加入的Cu离子含量越高,这种粒径减小作用就越大,该结论同前述XRD的粒径表征结果相同。
-
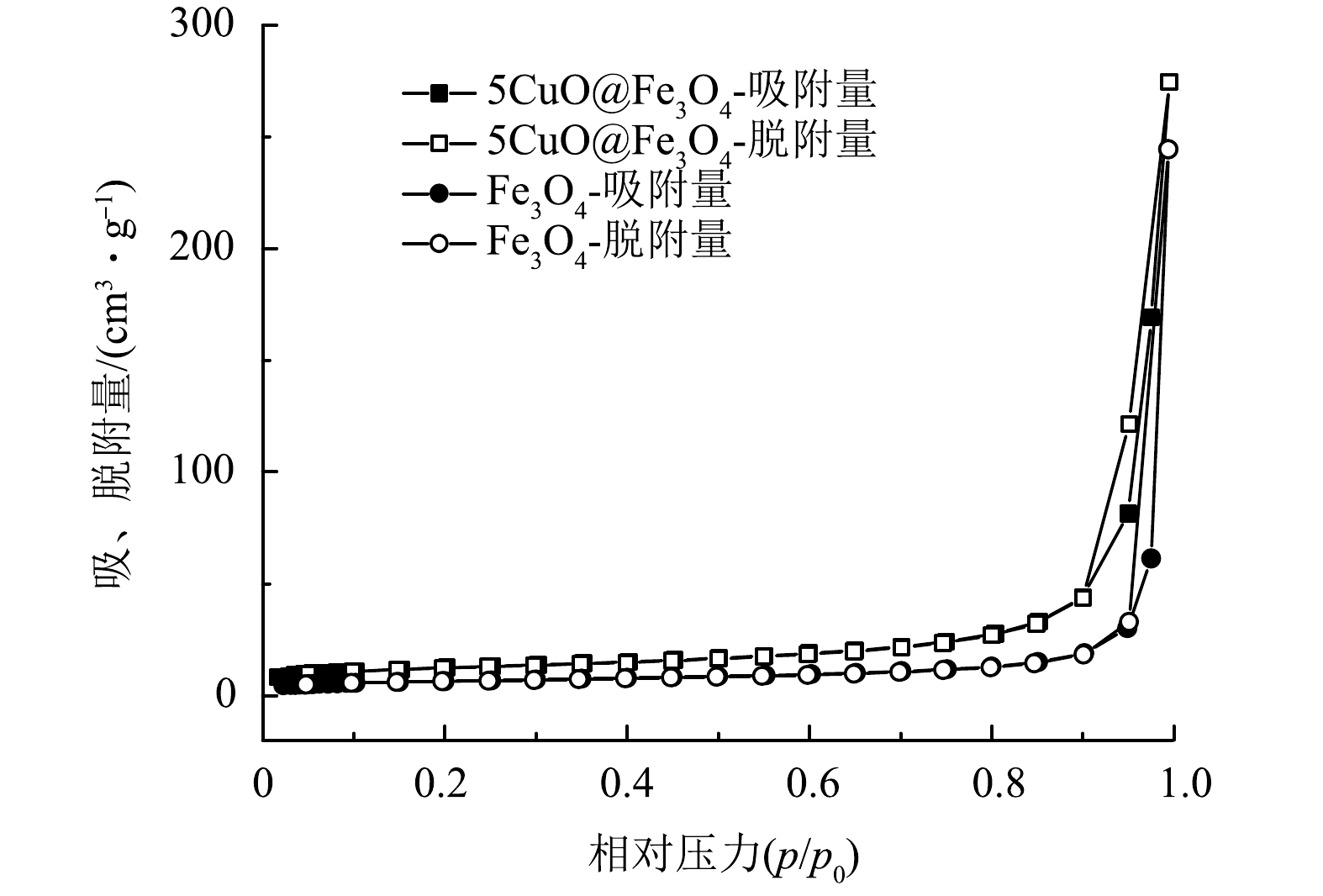
采用N2吸附/解吸等温线研究2.5CuO@Fe3O4、5CuO@Fe3O4、7.5CuO@Fe3O4和10CuO@Fe3O4的表面积、孔径分布等性质(图3),发现各CuO@Fe3O4样品表现出典型的III型吸附特征,吸附线与脱附线不重合,且尾部出现较短的H3型滞后现象[28]。由BET及BJH模型的计算结果可知,5CuO@Fe3O4的比表面积(43.65 m2·g−1)不但比其他CuO@Fe3O4样品的数值小,而且与纯Fe3O4或纯CuO 的比表面积相比也存在明显差异,如计算得到的Fe3O4的比表面积为23.01 m2·g−1,而CuO的比表面积为61.67 m2·g−1。这可能与5CuO@Fe3O4保留了较多纯Fe3O4的典型特征有关,其独特的粒径尺寸和颗粒状形貌为它在后续催化氧化反应中表现出高催化活性创造了条件。
由EDS对5CuO@Fe3O4的元素组成分析结果(图4)可知,它主要由Fe、Cu、O共3种元素组成。由不同元素分布可以看出, Fe、Cu和O 3种元素均匀存在于5CuO@Fe3O4体系内,没有发生聚集现象,且其中的Fe/Cu 比为5.58。对比5CuO@Fe3O4的ICP-MS分析结果(Fe/Cu=4.88),二者的Fe/Cu比都接近理论初始值5∶1。
-
图5(a)为CuO@Fe3O4体系及单独使用Fe3O4和CuO作为催化剂时,在相同反应条件下催化NaClO氧化丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的结果。可以看出,CuO@Fe3O4体系在去除丙烯酸及丙烯酸甲酯时有较好的矿化效果,氧化反应后丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的COD去除率分别介于55%~61%和49%~52%之间,而纯Fe3O4和CuO单独催化时的COD去除率仅为34%和42%。
图5(b)反映了氧化剂NaClO浓度变化对0.2 g·L−1丙烯酸溶液(COD=260 mg·L−1)矿化效果的影响。当NaClO浓度增至16 mmol·L−1时,丙烯酸的COD去除率为61%;继续增加氧化剂NaClO的加入量到48 mmol·L−1,丙烯酸的COD去除率仅增大3%。已知提高NaClO的加入量有助于产生更多·OH等活性物质[29-30],因而氧化反应会表现出随氧化剂加入量增大而增强的矿化反应结果,但氧化剂NaClO浓度过高时会发生自由基淬灭副反应[31],导致活性物质·OH的产生数量不会继续增加[32],从而使丙烯酸的矿化去除率变化不明显。同样,在NaClO浓度增至19 mmol·L−1时,0.2 g·L−1丙烯酸甲酯(COD=300 mg·L−1)在水溶液中的矿化率也能增至52%,但继续增加氧化剂NaClO浓度到57 mmol·L−1,丙烯酸甲酯的矿化去除率仅增加3%。显然,选择同0.2 g·L−1丙烯酸或丙烯酸甲酯COD值等量的16 mmol·L−1或19 mmol·L−1的 NaClO氧化剂进行矿化反应效率高。
图5(c)反映了5CuO@Fe3O4加入量对丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的氧化结果。可以看出,在丙烯酸的降解过程中,当催化剂投加量由0.03 g·L−1增至0.48 g·L−1 时,即氧化剂与催化剂摩尔比为128∶1~8∶1,其矿化效果由37%增至61%;而在丙烯酸甲酯的去除过程,当催化剂投加量由0.02 g·L−1 增至0.2 g·L−1 时,即氧化剂与催化剂摩尔比为228∶1~23∶1,其矿化效果由15%增至52%。有机小分子的矿化效果随着催化剂加入量的增加而提升,这与催化剂用量增大后催化活性中心数量增加有关[33]。再继续增加各催化剂用量,丙烯酸或丙烯酸甲酯的COD去除率变化小,由此可确定的最佳催化剂量应为0.48 g·L−1或0.2 g·L−1。
pH是影响氧化剂NaClO在水中降解有机污染物效果的重要因素[34],同时pH也能影响催化剂的表面电位[35],继而对催化活性产生影响。图5(d)为溶液pH在3.0~11.0时,5CuO@Fe3O4催化NaClO同等COD值丙烯酸氧化反应的结果。可以看出,反应体系的初始pH从3.0增至8.3,溶液中丙烯酸的COD去除率也由39%增至61%。继续增加pH至11.0时,矿化效果下降为35%。图5(e)则为5CuO@Fe3O4催化NaClO同等COD值丙烯酸甲酯氧化反应的结果,即溶液pH从5.0增至9.0时,丙烯酸甲酯的COD去除率由42 %增至53%。pH继续增至11.0,丙烯酸甲酯的COD去除率变为52%。由此可知,在5CuO@Fe3O4催化NaClO氧化丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的反应中,催化剂的pH稳定性好,可在中性及偏碱性条件下均保持较高的COD去除率。
考察Fenton反应对丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的去除效果(图5(d)和5(e)),发现Fenton反应仅在pH=3.0时有73%或51%的丙烯酸或丙烯酸甲酯COD去除率。当调节溶液pH大于7.0后,丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的COD去除率均降到20%左右。显然,5CuO@Fe3O4/NaClO在中性和碱性条件下对丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的矿化去除能力与Fenton反应的效果相比,提高1~2倍。
对5CuO@Fe3O4/NaClO进行重复实验,由图5(f)可以看出,经7次循环后,氧化反应仍能保持较高的去除效果。丙烯酸的COD去除率由第1次反应后的61%,到第4次氧化实验时的51%,再到第7 次氧化后的48%;而丙烯酸甲酯在第7次催化氧化后COD去除率为45%,相比第1次的氧化效果仅下降7%。由此可知,5CuO@Fe3O4在丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的催化氧化过程中稳定性高、重复性好。
-
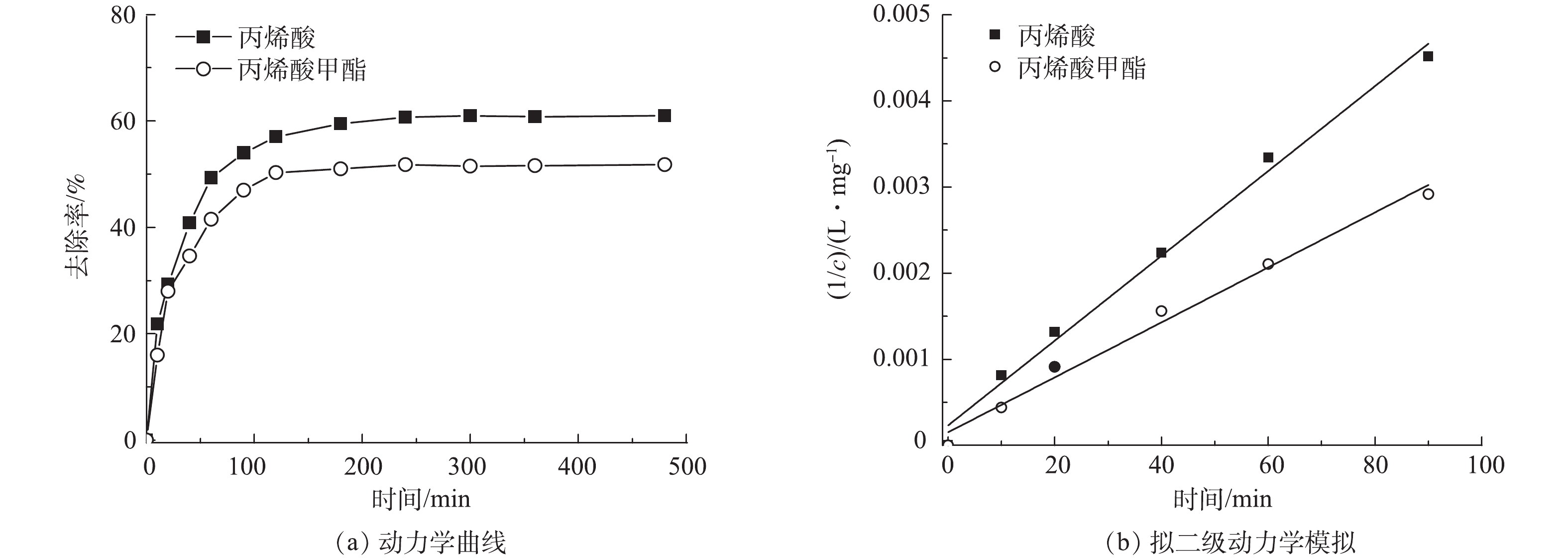
丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的反应动力学曲线如图6(a)所示。可以看出,它们在反应过程中有相同的变化趋势,在0~3 h内,丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的COD去除率快速增长,分别可达 60%和51%;而在3~8 h内,二者的COD去除率仅略有增加。图6(b)为将相关动力学数据(0~3 h)进行拟二级动力学模拟的结果。由丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的拟二级反应速率常数4.93×10−5 L · (mg ·min)−1(R2=0.991)和3.19×10−5 L · (mg ·min)−1(R2=0.988)可以看出,丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯有近似的氧化反应速率。
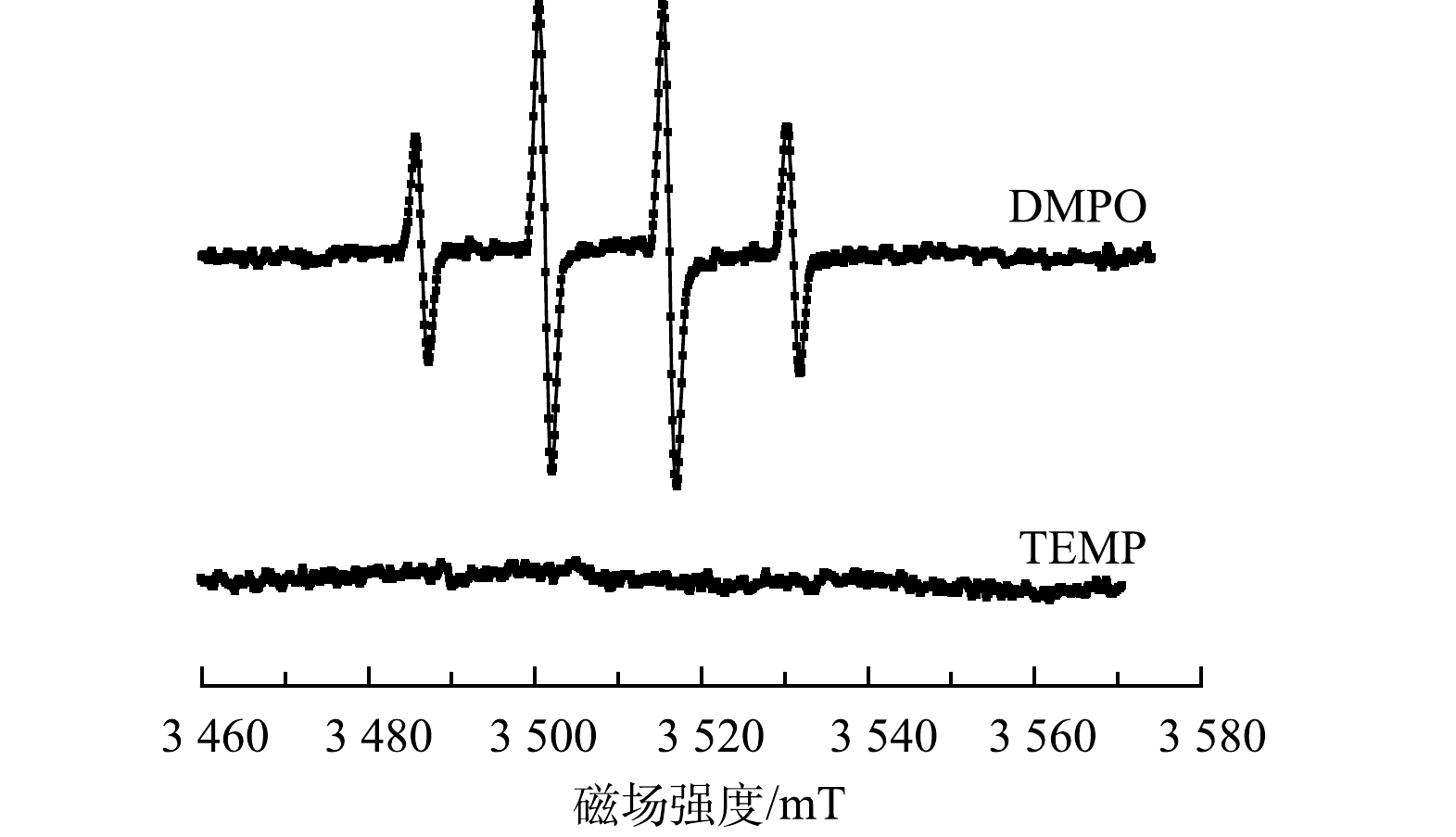
为考察5CuO@Fe3O4体系的主要氧化物种,采用EPR实验来检测降解过程中可能产生的自由基。如图7所示,在NaClO+DMPO+CuO@Fe3O4体系中,出现DMPO捕获羟基自由基的自旋信号DMPO-·OH,即强度比为1:2:2:1的4峰特征峰[36], 表明反应体系中有·OH存在。另一方面,当选择TEMP作为自旋捕捉剂时,NaClO+TMEP+CuO@Fe3O4中未出现1O2自由基的特征3峰光谱[37],因而可以认为反应体系中无1O2活性物质生成。
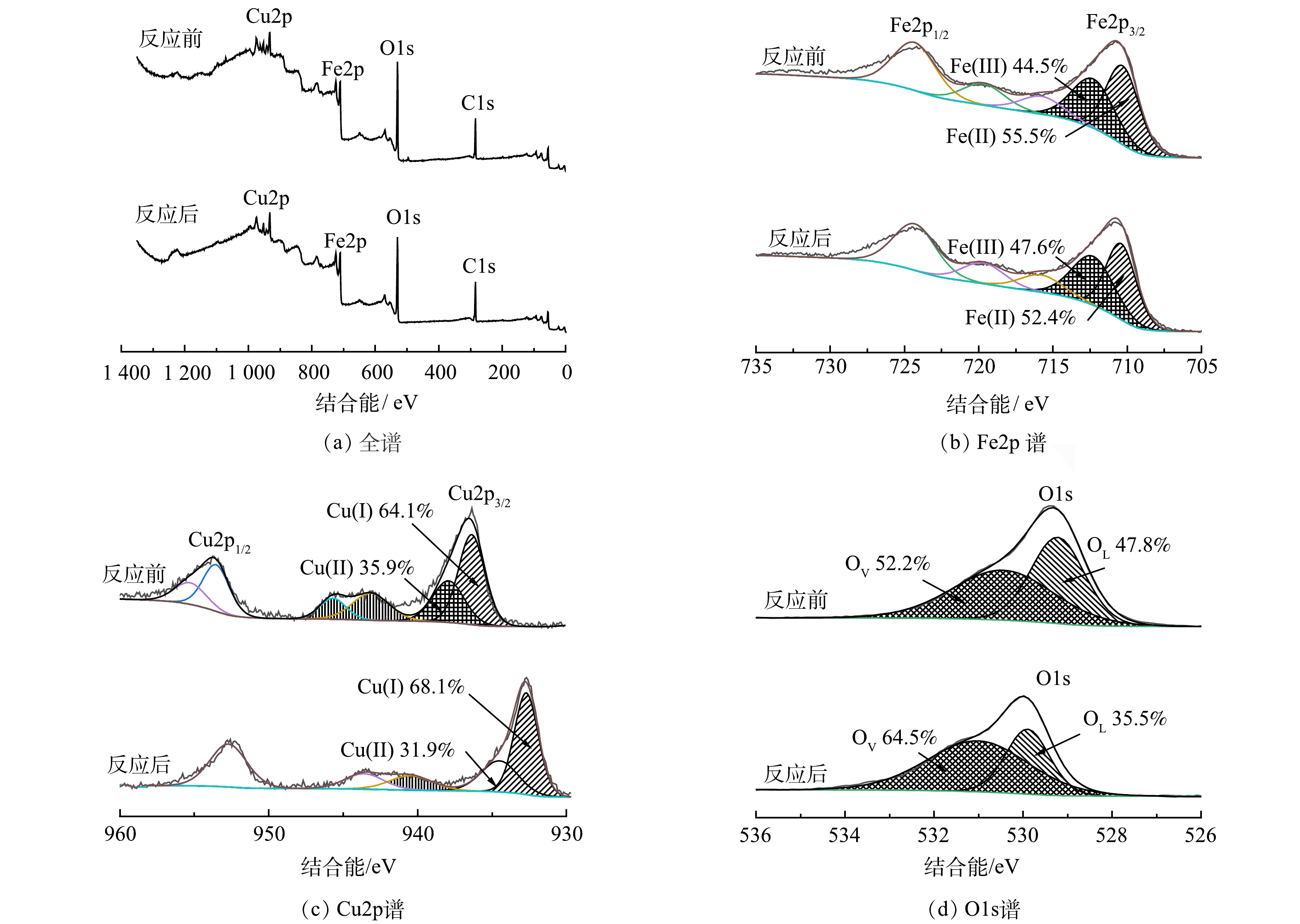
为研究Fe/Cu双金属的协同催化机制,使用XPS 表征了反应前后5CuO@Fe3O4中各金属组分的价态变化。图8(a)中化学结合能284.8、530.8、714.8 和933.0 eV分别对应C1s、O1s、Fe2p和Cu2p轨道,表明样品中包含这4种元素。图8(b)为Fe2p的高分辨XPS谱图。可以看出,在710.3 eV和712.3 eV处是2个主要的Fe2p3/2峰,分别对应Fe2+和Fe3+。反应前它们的相对含量是55.5%和45.5%,反应后则变为47.6%和52.4%;而724.3 eV处的能量峰对应Fe2p1/2,715.7 eV和719.6 eV处的能量峰为Fe2+和Fe3+的振动卫星峰[38-39]。图8(c)中932.7 eV和934.5 eV处是2个主要的Cu2p3/2峰,分别归属于Cu+和Cu2+。反应前它们的含量分别为64.1%和35.9%,反应后其含量则变为68.1%和31.9%;而结合能940.5 eV和943.4 eV处的能量峰是Cu2+卫星峰[35,40]。对比反应前后Fe2+和Cu2+含量变化,可知5CuO@Fe3O4在活化NaClO 的过程中,存在Fe和Cu之间的电荷转移,因而增强了Fe2+/Fe3+、Cu+/Cu2+的循环效率,促进5CuO@Fe3O4表现出较高的活化效率。
图8(d)为反应前后O1s的高分辨XPS谱图。可以看出,529.9 eV和531.0 eV处的2个特征峰分别归属于晶格氧(OL)和来自氧空位的游离氧原子(OV)[41-42]。反应前OL和OV的相对含量分别为47.8%和52.2%,反应后则变为35.5%和64.5%。因为来自氧空位的游离氧原子是有利氧化的,其数量的增加有利于5CuO@Fe3O4/NaClO提高矿化效率。
根据XPS实验结果,5CuO/Fe3O4界面上NaClO可能发生的活化机制见式(3)~式(5)。
-
1) 通过共沉淀法制备双金属氧化物CuO@Fe3O4,采用X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、BET和X射线能谱(EDS)等对其进行组成表征和形貌观察,初始Fe/Cu比为5∶1时制备的5CuO@Fe3O4催化NaClO的活性最高。
2) CuO@Fe3O4/NaClO在pH=8.3或9.0时,对丙烯酸或丙烯酸甲酯COD去除率分别可达61%和53%,反应过程符合拟二级动力学特征。
3) EPR分析表明,·OH是矿化去除反应中的活性物质,无活性物质1O2生成。
4) 在5CuO@Fe3O4中存在Fe和Cu之间的电荷转移,因而增强了Fe2+/Fe3+、Cu+/Cu2+的循环效率,促进5CuO@Fe3O4表现出较高的活化效率。
CuO@Fe3O4催化NaClO 对水中丙烯酸及其酯的矿化去除
Mineralization and removal of acrylic acid and its esters from water by CuO@Fe3O4 catalyzed NaClO
-
摘要: 为实现污水尾端处理中可溶性小分子有机物的完全去除,以克服因它们的大量存在使水体中总有机碳含量增加而引发的严重环境问题,采用氧化剂NaClO和双金属氧化物CuO@Fe3O4组成的催化氧化体系,对喷水织机废水中典型的极性小分子有机物丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯进行矿化去除研究;通过X射线衍射 (XRD) 、扫描电子显微镜 (SEM) 、X射线能谱 (EDS) 和BET分析等方法对催化剂进行结构表征和形貌观察,确定催化剂最佳合成方法,并通过氧化实验考察催化剂双金属组成、氧化剂NaClO浓度、催化剂加入量、溶液初始pH和循环催化氧化等因素对小分子有机污染物矿化去除的效果。结果表明:初始铁铜摩尔比为5∶1时,合成的5CuO@Fe3O4纳米粒子催化活性最高;当5CuO@Fe3O4和NaClO投加量分别为0.48 g·L−1、16 mmol·L−1、pH=8.3时,对0.2 g·L−1丙烯酸的COD去除率可达61%;催化剂经过7次循环操作后,对丙烯酸或丙烯酸甲酯仍能保持48%或45%的COD去除率;EPR实验证明·OH是催化氧化体系中降解丙烯酸和丙烯酸甲酯的主要活性物种。上述研究结果为揭示污染水体中难降解极性小分子有机物的矿化去除规律,实现水体中有机碳的总量控制和减排目标提供了技术支撑。Abstract: Small organic molecules are refractory components in sewage treatment. Their presence in large quantities can increase the total organic carbon content in water and cause serious environmental problems. In this study, the activation of NaClO by CuO@Fe3O4 was evaluated by modeling the mineralization of polar organic molecules acrylic acid and methyl acrylate in jet loom wastewater. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray energy spectroscopy (EDS) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) were used to reveal the morphology and microstructure of CuO@Fe3O4, and determine the optimized synthesis method. The effects of bimetallic composition, NaClO concentration, amount of CuO@Fe3O4, initial pH and cyclic catalytic oxidation on the mineralization of acrylic acid and methyl acrylate were investigated. The results showed that 5CuO@Fe3O4 exhibited a strong catalytic activity in the mineralization process at the initial Fe-Cu molar ratio of 5:1. When the dosages of 5CuO@Fe3O4 and NaClO were 0.48 g·L−1 and 16 mmol·L-1 respectively, the removal rate of COD for 0.2 g·L−1 acrylic acid was 61% at pH =8.3. After seven cycles of operation, the removal rates of COD of acrylic acid and methyl acrylate acid were still 48% and 45%, respectively. EPR experiments showed that ·OH was the main active species for the degradation of acrylic acid and methyl acrylate in the catalytic oxidation system. These results provide a technical support for revealing the rule of mineralization and removal of refractory polar organic molecules in polluted water, so as to achieve the total amount control and emission reduction goal of organic carbon in water.
-
Key words:
- mineralization /
- CuO@Fe3O4 /
- NaClO /
- acrylic acid /
- methyl acrylate
-

-
-
[1] 马慧婕, 沈忱思, 章耀鹏, 等. 纺织工业产排污特征与水污染治理技术进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(11): 2529-2539. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.10.02 [2] 周谨. 无机陶瓷膜在印染废水处理中的应用[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2010, 30(3): 116-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8924.2010.03.023 [3] 陈凤兰, 徐志荣. 《纺织染整工业水污染物排放标准》实施评估: 以浙江省为例[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2019, 39(12): 72-78. [4] 陆茸, 翟康, 徐圃青. 重大环境政策对常州印染行业发展的影响[J]. 江苏科技信息, 2021, 38(22): 72-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7530.2021.22.018 [5] 何锡君, 孙英军, 王贝, 等. 浙江省出入太湖河道水量水质及污染物通量变化(2007—2019年)[J]. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(5): 1425-1435. doi: 10.18307/2021.0527 [6] 翟康, 李嘉义, 袁逸, 等. 常州市太湖流域水生态环境功能区水污染源排放情况分析[J]. 科技创新与生产力, 2021(3): 41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9146.2021.03.041 [7] 宋凯. 丙烯酸装置废水焚烧处理控制方案浅析[J]. 石油化工自动化, 2011, 47(2): 33-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7324.2011.02.008 [8] 王瑞, 李圣强, 赵云海. 高浓度丙烯酸废水处理试验研究[J]. 山东工业技术, 2014(12): 40. [9] 朱又春, 罗爱武, 林美强, 等. 磁分离法处理含油废水研究[J]. 广东工业大学学报, 1998, 15(2): 15-20. [10] BENER S, BULCA Ö, PALAS B, et al. Electrocoagulation process for the treatment of real textile wastewater: Effect of operative conditions on the organic carbon removal and kinetic study[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 129: 47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.06.010 [11] 姚佳伟, 杨庆峰, 陆盛森, 等. 磁性纳米颗粒催化NaClO降解有机废水研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2020, 40(10): 39-43. [12] 庞浩然, 李旭东, 欧文韬, 等. 曝气生物滤池对喷水织机废水BOD5去除效果的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2009, 27(5): 516-519. [13] 何晨曦, 房浩亮, 古丽加衣娜尔·巴合提, 等. 印染废水处理研究进展[J]. 轻纺工业与技术, 2021, 50(8): 130-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0101.2021.08.059 [14] 王双, 张倩, 王薇, 等. 反渗透双膜工艺处理印染废水研究进展[J]. 能源环境保护, 2019, 33(3): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2019.03.001 [15] SUKANYA DEVI R, DHURAI B, SUNDARESAN S, et al. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) : Effective innovative treatment methods to degrade textile dye effluent[M]//MUTHU S S. Advances in Textile Waste Water Treatments. Springer Press, 2021: 173-203. [16] XING M, XU W, DONG C, et al. Metal sulfides as excellent co-catalysts for H2O2 decomposition in advanced oxidation processes[J]. Chemistry, 2018, 4(6): 1359-1372. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2018.03.002 [17] KREMER M L. The Fenton reaction: Dependence of the rate on pH[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2003, 107(11): 1734-1741. doi: 10.1021/jp020654p [18] JAIN B, SINGH A K, KIM H, et al. Treatment of organic pollutants by homogeneous and heterogeneous Fenton reaction processes[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2018, 16(3): 947-967. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-0738-3 [19] SCARIA J, GOPINATH A, NIDHEESH P. A versatile strategy to eliminate emerging contaminants from the aqueous environment: Heterogeneous Fenton process[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 278: 124014. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124014 [20] MA D, YI H, LAI C, et al. Critical review of advanced oxidation processes in organic wastewater treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 275: 130104. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130104 [21] FU W, YI J, CHENG M, et al. When bimetallic oxides and their complexes meet Fenton-like process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 424: 127419. [22] XIE Z H, ZHOU H Y, HE C S, et al. Synthesis, application and catalytic performance of layered double hydroxide based catalysts in advanced oxidation processes for wastewater decontamination: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 414: 128713. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128713 [23] JIA L, JUN S, KUN F, et al. Heterogeneous catalytic persulfate oxidation of organic pollutants in the aquatic environment: Nonradical mechanism[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2021, 33(8): 1311-1322. [24] LUO H, ZENG Y, HE D, et al. Application of iron-based materials in heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 407: 127191. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127191 [25] 刘玥, 赵来群, 龚为进, 等. 硅酸锌铁催化臭氧氧化水体中的丙烯酸[J]. 化工时刊, 2020, 34(3): 16-20. doi: 10.16597/j.cnki.issn.1002-154x.2020.03.005 [26] 高超, 乐清华, 冯杰. Fenton氧化法降解丙烯酸废水的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(7): 1279-1283. [27] 姜晓锋, 高明瑜, 王诗涵, 等. 多相催化氧化-EGSB组合工艺处理丙烯酸废水研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2021, 41(2): 92-96. [28] 何余生, 李忠, 奚红霞, 等. 气固吸附等温线的研究进展[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2004, 20(4): 376-384. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5493.2004.04.012 [29] FANG J, FU Y, SHANG C. The roles of reactive species in micropollutant degradation in the UV/free chlorine system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(3): 1859-1868. [30] 李博强. UV-LED/NaClO高级氧化工艺对典型PPCPs类污染物的降解[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2020. [31] PIZZOLATO T, CARISSIMI E, MACHADO E, et al. Colour removal with NaClO of dye wastewater from an agate-processing plant in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2002, 65(3/4): 203-211. [32] 徐文英, 高浩阳. NiOx(OH)y/NaClO催化氧化体系对模拟印染废水中活性艳红K-2BP的降解脱色效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(3): 835-846. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202006141 [33] PUANGPETCH T, SOMMAKETTARIN P, CHAVADEJ S, et al. Hydrogen production from water splitting over eosin Y-sensitized mesoporous-assembled perovskite titanate nanocrystal photocatalysts under visible light irradiation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(22): 12428-12442. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.08.138 [34] CAO F, ZHANG M T, YUAN S J, et al. Transformation of acetaminophen during water chlorination treatment: Kinetics and transformation products identification[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(12): 12303-12311. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6341-x [35] LEI Y, CHEN C S, TU Y J, et al. Heterogeneous Degradation of organic pollutants by persulfate activated by CuO-Fe3O4: mechanism, stability, and effects of pH and bicarbonate ions[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6838-6845. [36] LI L, ABE Y, KANAGAWA K, et al. Distinguishing the 5, 5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO)-OH radical quenching effect from the hydroxyl radical scavenging effect in the ESR spin-trapping method[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2004, 512(1): 121-124. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2004.02.020 [37] ZHOU X Q, JAWAD A, LUO M Y, et al. Regulating activation pathway of Cu/persulfate through the incorporation of unreducible metal oxides: Pivotal role of surface oxygen vacancies[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021, 286: 119914. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119914 [38] 彭伟, 方振东, 李晨旭, 等. 单组分过渡金属氧化物及其复合材料催化Oxone去除4-氯酚的效能对比研究[J]. 当代化工, 2019, 48(5): 890-894. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2019.05.003 [39] PENG W, LIU J, LI C X, et al. A multipath peroxymonosulfate activation process over supported by magnetic CuO-Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient degradation of 4-chlorophenol[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 35(8): 1662-1672. doi: 10.1007/s11814-018-0074-0 [40] SUN M Y, LEI Y, CHENG H, et al. Mg doped CuO-Fe2O3 composites activated by persulfate as highly active heterogeneous catalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 825: 154036. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154036 [41] 李锋超. 纳米钴锌氧化物活化过硫酸盐(PMS)降解有机污染物研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2020. [42] 李章良, 张国鑫, 潘文斌. Cu/Zn非均相Fenton催化剂的制备及其对环丙沙星的降解效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(3): 806-816. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202006148 -



 下载:
下载: