-
据中国自行车协会统计,2020年中国电动自行车产量达到4 126.1×104辆[1],截至2020年全社会电动自行车保有量接近3×109辆[2]。由于疫情的影响,外卖、快递的延展变得更加广泛,电动自行车需求量呈爆发式增长,其生产过程产生大量工业废水。其中,电泳涂装废水具有组分复杂、水质水量变化大、难降解等特点[3-5],成为高效处理电泳涂装废水的关键。
芬顿法为通过H2O2与Fe2+在酸性条件下生成强氧化能力的·OH,进而降解废水中有机污染物,同时生成的Fe(OH)3可以通过絮凝以沉淀有机物和磷酸盐。因其不会产生二次污染,被广泛应用于工业废水处理。王小晓等[6]采用Fenton-混凝应急处理汽车涂装废水,在pH=3~5、H2O2为1.7 g·L−1、FeSO4·7H2O为1.75 g·L−1时,反应10 min后,COD、TP、SS及各种金属离子均达到一级排放标准。杨晨曦等[7]在处理涂料废水时发现,在pH=2、H2O2投量为理论投加量的1.5倍、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8时,COD去除率可达60.12%。陈烨等[8]使用Fenton法处理汽车涂装废水时发现,在pH=4、H2O2为2.97 g·L−1、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=3、反应70 min后,COD去除率为71.4%。刘强[9]的研究表明,在H2O2投量为0.6 g·L−1、FeSO4·7H2O投量为0.2 g·L−1、氧化反应60 min后,COD和SS去除率分别为90.0%和98.3%。其他研究者[10-13]采用Fenton方法处理涂装废水,也取得较好的处理效果。但因为不同的生产工艺和原料所产生各废水污染物的组分和浓度不同,以上Fenton处理涂装废水的反应条件和处理效果有差异。因此,针对某种涂装废水,需做小试研究其适宜的Fenton氧化反应条件。因实际涂装废水的水质有波动,研究Fenton氧化涂装废水的反应动力学可指导实际废水处理工程。本研究以某电动自行车生产企业的涂装废水为研究对象,探索了温度、底物对其反应动力学影响的规律,优化了Fenton处理涂装废水的工艺条件,以期为类似涂装废水的处理提供参考.
-
实验原水取自江苏某电动自行车制造企业的涂装车间,该车间生产工序包括脱脂、陶化、电泳和喷涂。其中采用新型陶化工艺取代了传统的磷化工艺,具有不含Fe、Zn、Pb等重金属的优点。原水主要含有苯类、醇类和助剂等,pH=6.0~8.0,COD为1 000~1 500 mg·L−1,TP为10~15 mg·L−1,B/C比约为0.12。实验所用试剂为30%H2O2(质量分数)、NaOH、 H2SO4、七水合硫酸亚铁(FeSO4·7H2O)、聚丙烯酰胺(PAM)。
-
芬顿氧化实验:取100 mL原水于若干个烧杯中,并放于恒温磁力搅拌器上,调节pH,投加H2O2和FeSO4·7H2O,以200 r·min−1进行搅拌,反应结束后将pH调至10,加入适量PAM,搅拌后静置沉淀0.5 h。每组平行实验3次。
pH条件优化。在H2O2为0.6 g·L−1、FeSO4·7H2O为0.8 g·L−1、反应时间为2.5 h的条件下,分别在pH为1、2、3、4、5、6的条件下进行芬顿实验。
H2O2投加量优化。在上述优化后的最佳pH、FeSO4·7H2O为3 g·L−1、反应时间为2.5 h的条件下,H2O2投加量分别为1、2、3、4、5、6 g·L−1,进行芬顿氧化实验。
H2O2的理论投加量按式(1) [7]进行计算。
式中:D为H2O2理论投加量,g·L−1;C(COD)为耗氧有机物(以COD计)的质量浓度,g·L−1;M(H2O2)为H2O2的摩尔质量,g·mol−1;M(O)为O的摩尔质量,g·mol−1。
FeSO4·7H2O投加量优化:在最佳pH、最佳H2O2、氧化反应时间2.5 h的条件下,设置FeSO4·7H2O分别为1、2、3、4、5、6 g·L−1进行芬顿实验。
氧化时间优化:在最佳pH、H2O2、FeSO4·7H2O条件下,设置氧化时间分别为30、60、90、120、150、180、210 min进行芬顿实验。
-
依据Box-Benhnken实验设计原理,固定反应时间,以COD去除率为响应值,以单因素实验中pH(A)、H2O2(B)、FeSO4·7H2O(C)的最优结果为中心水平(0),结合高水平(+1)和低水平(-1),利用响应曲面法优化Fenton氧化条件,各因素水平和编码见表1。
-
分别以零级反应动力学(式(2))、一级反应动力学(式(3))、二级反应动力学(式(4))和三级反应动力学(式(5))对Fenton氧化有机物的降解过程进行拟合。
式中:Ct为t时刻的COD值,mg·L−1;C0为原水COD值,mg·L−1;k为动力学反应速率常数,min−1;t为反应时间,min。
根据Arrhenius方程,建立Fenton完全氧化最优工艺条件时的表观动力学模型,lnk与1/T之间存在线性关系,如式(5)所示。探索Fenton在15、25、35 ℃时完全氧化本涂装废水的动力学特性,获得反应速率常数的温度修正关系。
式中:k为速率常数,min−1;A0为频率因子,min−1;Ea为活化能,J·mol−1;R为通用气体常数,J·(mol·K)−1;T为反应绝对温度,K。
-
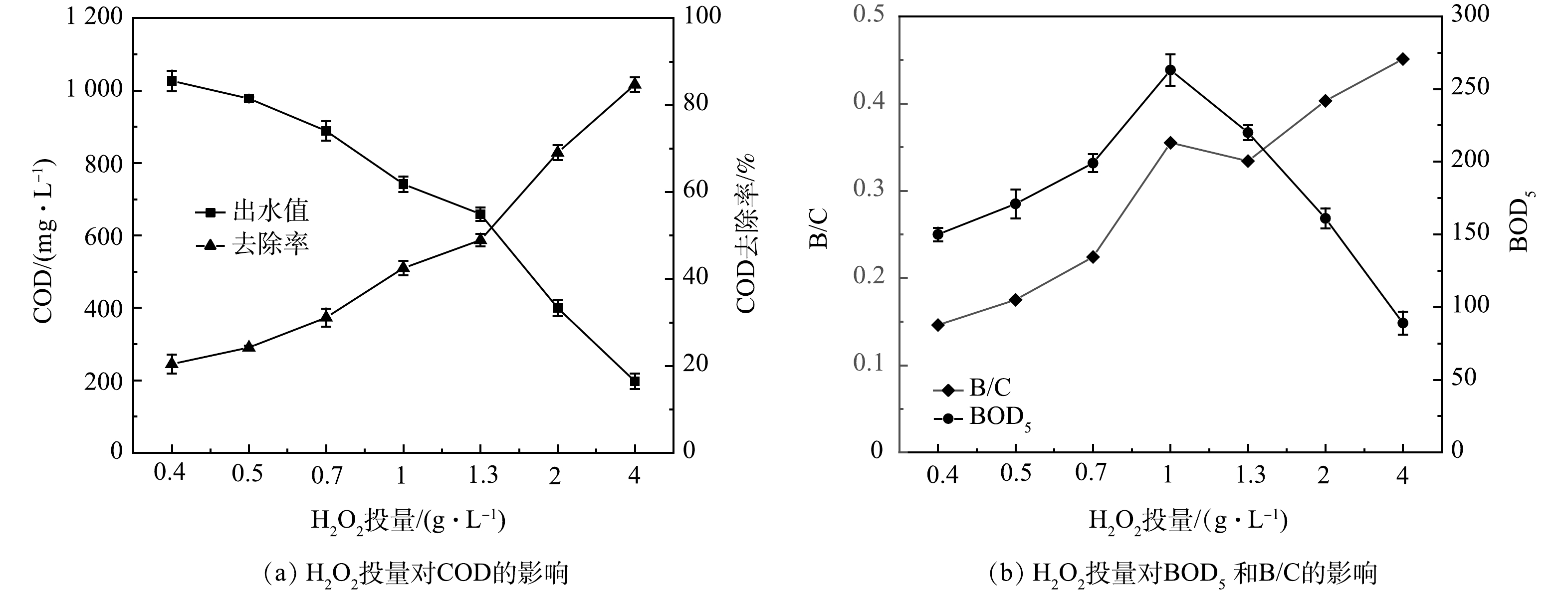
在响应面实验得到的最优pH和n(H2O2/Fe2+)条件下,固定Fenton完全氧化反应时间,改变H2O2投加量分别为0.4、0.5、0.7、1、1.3、2、4 g·L−1,研究其对COD去除率与B/C比的影响,探索Fenton氧化作为电动自行车涂装废水预处理工艺的可能性。
-
COD采用重铬酸盐法测定(HJ 828-2017);TP采用钼酸铵分光光度法测定(GB 11893-89);BOD5采用稀释培养法测定(HJ 505-2009);pH采用玻璃电极法测定(上海仪电PHS-3C)。
-
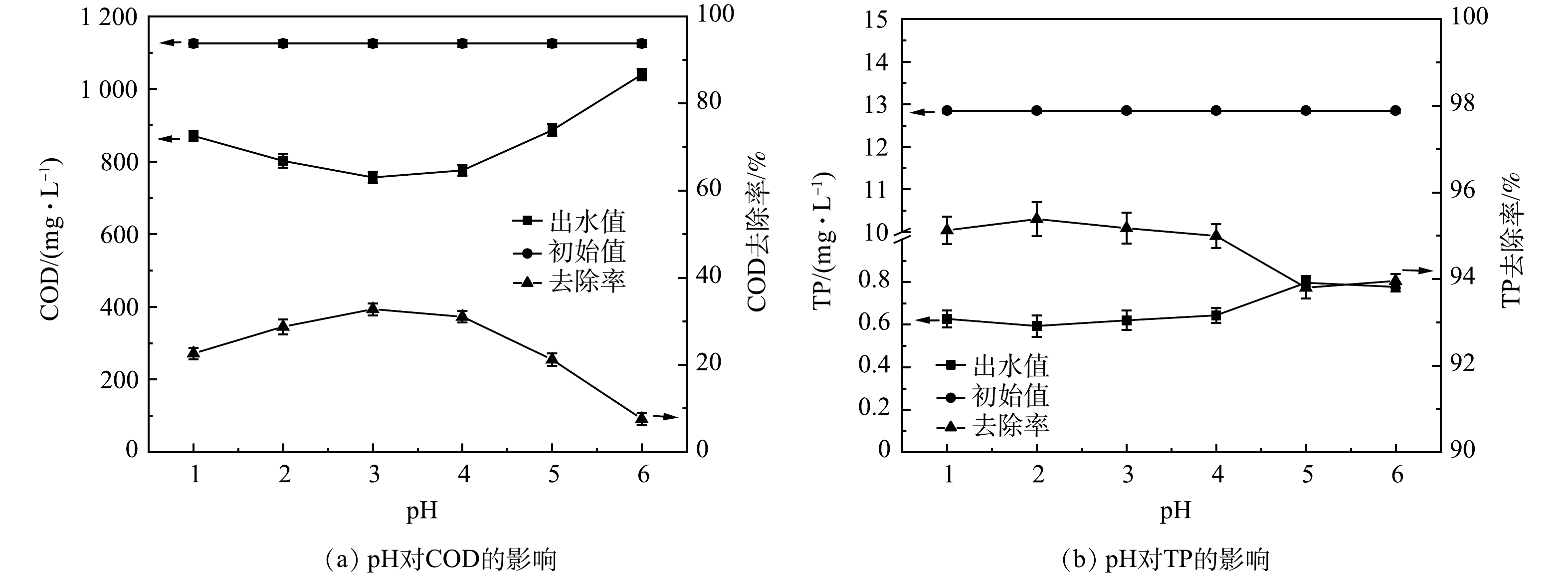
1) pH条件优化。如图1所示,pH从1升至6的过程中,COD去除率先增加再降低。反应体系中过量的H+会阻碍Fe3+转变为Fe2+,抑制催化反应的氧化能力[14],因此,pH并非越低越好。当pH由1增大至3时,随着活性位点数量增加[15],反应速率大幅升高,COD去除率随之升高;当pH 3时,COD去除率达到最高。由式(7)可知,溶液中不断增加的OH−会使(·OH)供应不足,且易造成Fe(OH)3铁盐沉淀,阻断链式反应,H2O2和Fe2+难以形成有效的氧化还原系统[16]。因此,在本研究中,当pH ≥ 5时,COD去除率大幅度降低。溶液中TP含量随着pH的增大而逐渐升高。这是由于当氢氧根离子含量变多时,会优先与Fe3+反应生成铁盐沉淀[17],减少了Fe3+与磷酸盐的结合量,使TP去除率下降。王小晓等[6]采用Fenton工艺应急处理某涂装废水,溶液初始pH为3~5;杨晨曦等[7]研究Fenton氧化处理涂料废水,初始pH为2;LI 等[10]研究表明在酸性条件下,Fenton可以氧化涂装废水中的有机物,但涂装废水中主要有机物组分和浓度的不同导致各研究的最优pH条件略有不同。综合COD和TP的去除效果,本研究中最优pH为3。
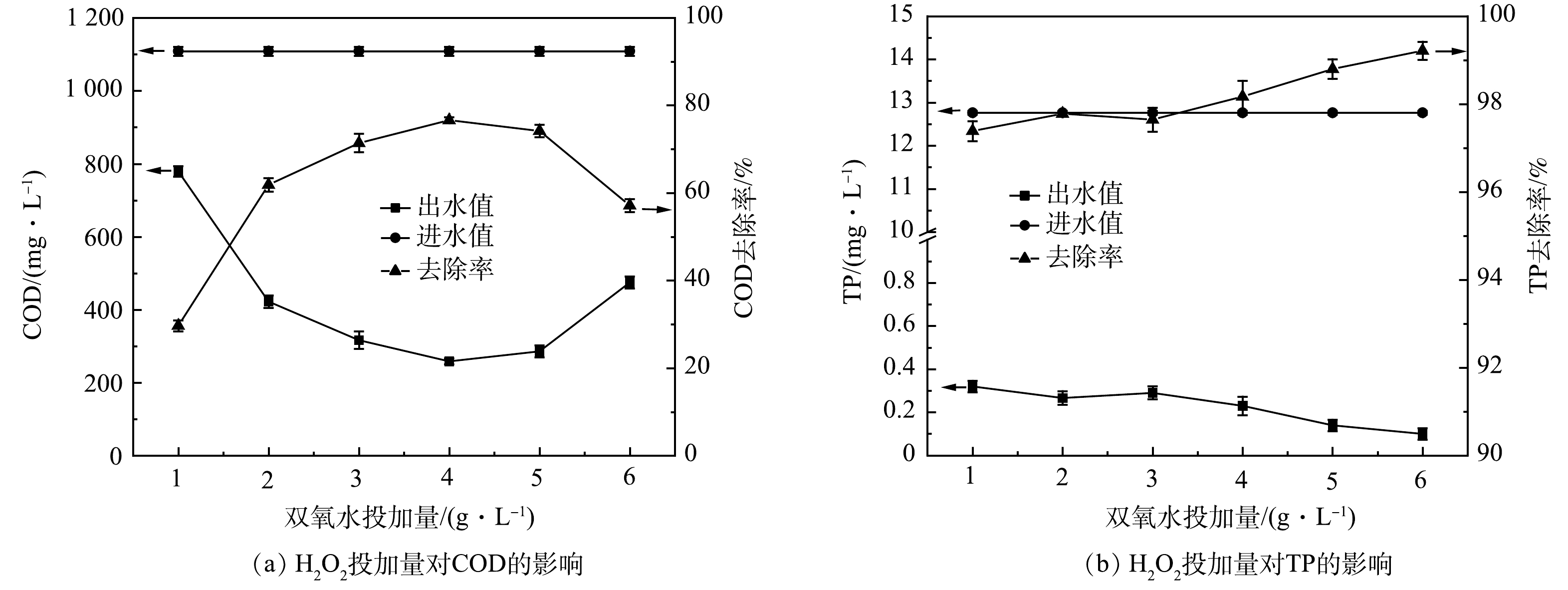
2) H2O2投加量优化。如图2所示,H2O2投加量从1 g·L−1增加到4 g·L−1时,COD最高去除效率达77.75%。增加H2O2能分解产生更多的(·OH)量,有利于提高污染物去除率[18]。但由式(8)可知,H2O2过量会强化(·OH)与H2O2发生复合反应,造成产生的·OH湮灭,导致氧化能力下降;另一方面,过量H2O2分解的O2会携带小絮体上浮,形成浮泥[19]。TP的去除效率无较大波动,为97.50%~99.19%,TP出水浓度稳定在1 mg·L−1以下。故可由COD的去除效果判定H2O2投加量4 g·L−1为宜。由式(1)可得H2O2投加量为1.7 D。于常武等[11]的研究表明,在原水COD为3 280 mg·L−1、pH=3、n(COD/H2O2)=1∶3,即H2O2投加量为6 D时,COD去除率为86%。本研究中COD去除率虽然略低,但H2O2的相对投量比较低。
3) FeSO4·7H2O投加量优化。如图3所示,当催化剂Fe2+含量较少时,COD去除率不高。这是因为活性位点少,有效氧化剂(·OH)产生的速度较慢[20-21]。随着FeSO4·7H2O投加量的加大,产生更多(·OH),使体系内有机物的去除效率逐步提高。当投加量为5 g·L−1时,获得COD最高去除效率达84%。但投加量为4 g·L−1和5 g·L−1时,COD出水浓度只相差4 mg·L−1。氧化后生成的Fe3+是去除PO43-的主要物质,所以FeSO4·7H2O投加量与TP去除率的关系表现为正相关。但溶液中Fe2+过量时,会导致(·OH)不必要消耗,且Fe2+还会被氧化成有色的Fe3+,造成出水溶液偏棕黄色,增加废水的后续处理难度。综合反应效果及经济成本,FeSO4·7H2O投量4 g·L−1(H2O2/Fe2+摩尔比为8.2:1)为宜。陈烨等[8]Fenton氧化某汽车涂装废水,得到n(H2O2/Fe2+)=3时处理效果最优,COD去除率达71.4%;孙水裕等[12]在进水COD为1.5~2.5 g·L−1,n(H2O2/Fe2+)=3时处理效果最优,COD去除率达75%左右;谢永华等[13]得到n(H2O2/Fe2+)=6时处理效果最优,COD去除率达到峰值53%左右。本实验得到的n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8.2,FeSO4·7H2O投药量更少且去除率更高,达80%,更具有优势。
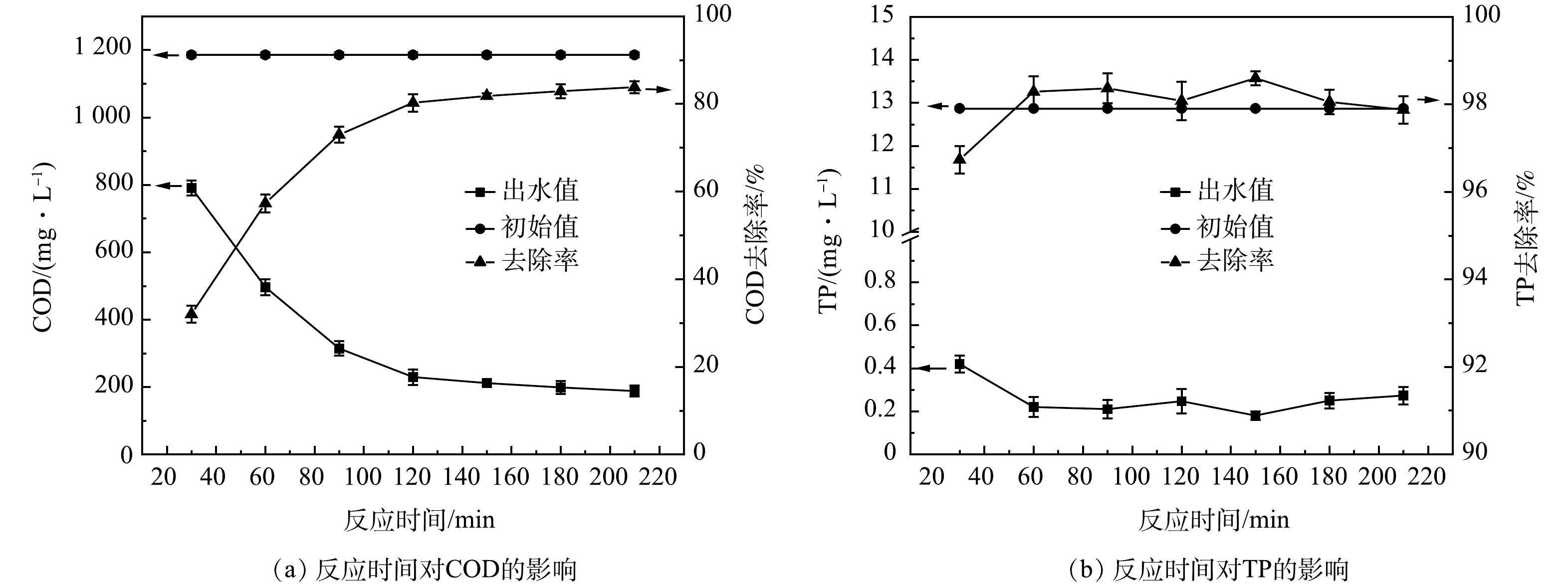
4)反应时间优化。如图4所示,在反应时间0~120 min内,COD去除率呈线性增长趋势,120 min时反应已基本完成,随后的COD去除率曲线逐渐趋于平缓。TP的去除率基本保持稳定,TP出水小于1 mg·L−1。当反应时间足够时,Fenton试剂与原水的分子接触碰撞概率较大,能使工艺处理效能最大化[22]。因此,确定本涂装废水的最佳氧化反应时间为120 min。
-
当反应时间为120 min时,Fenton氧化已基本完成,TP去除率始终高于98%,因此反应时间、TP去除率不作为影响因素。仅以COD去除率为响应值Ƞ,利用响应曲面法研究pH、H2O2和FeSO4·7H2O对Fenton氧化涂装废水的影响,实验结果如表2所示。
通过多元回归拟合,获得关于响应值Ƞ的回归方程(式(9))。其方差分析和显著性检验如表3所示。
COD去除率响应面模型P<0.000 1,有极其显著的统计学差异;而失拟项P>0.05,不显著,回归模型显著可靠。根据模型中P值的显著性分析,A、B、BC、A2、B2、C2对COD响应值的影响为极显著;C、AB为显著影响;AC无显著影响。F值可以判断实验因素对实验结果的影响程度[23-24]。本研究中,各因素对Fenton氧化电动自行车涂装废水的影响显著性为pH>H2O2>FeSO4·7H2O。
等高线可直观呈现反应条件之间交互作用的显著情况,越倾斜椭圆状则交互作用越强烈[25]。如图5(a)所示,当固定FeSO4·7H2O浓度时,响应值随H2O2浓度的增大呈现先升高后降低的明显变化,变化梯度较大。而当H2O2浓度稳定在投量区间时,响应值随FeSO4·7H2O浓度的增大而先升高后降低,但变化幅度小于H2O2。图5(b)的紧密等高线和对角线方向的斜椭圆,表明H2O2和FeSO4·7H2O的交互作用非常显著,说明对Fenton氧化过程至关重要。由图5(c)和图5(d)可见,响应值随着H2O2和pH的升高而先增加后降低,陡峭的曲面证明了H2O2和pH存在一定的交互作用,pH对H2O2生成(·OH)有很大影响。由图5(e)和图5(f)可见,FeSO4·7H2O和pH交互作用的响应面陡峭程度相比于其他2个交互作用略平缓,表3方差分析也表明两者交互作用不突出。
通过响应曲面法得到Fenton完全氧化本涂装废水的最优条件为pH=3.21、H2O2为4.17 g·L−1(H2O2/COD质量比为4.17∶1)、硫酸亚铁为4.29 g·L−1(H2O2/Fe2+摩尔比为8∶1)、反应时间为120 min。对该实验条件进行了验证,得到实际的COD去除率为81.32%,与模型预测值82.15%仅相差1.01%。这表明式(8)可以较好地模拟Fenton完全氧化本废水的处理效果。
-
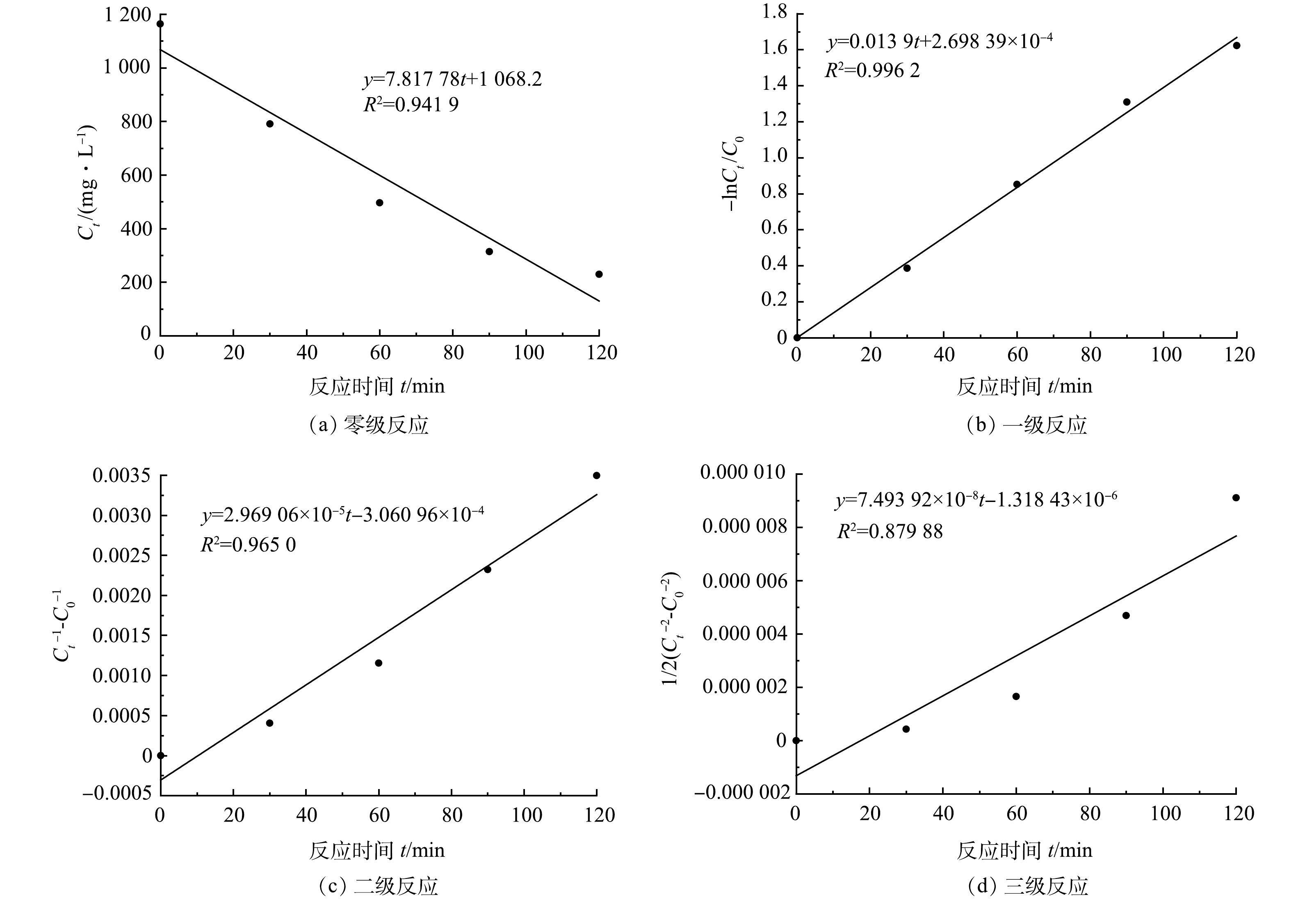
图4反映了涂装废水COD随反应时间的变化,对其进行反应动力学拟合,结果如图6所示。涂装废水的Fenton 完全氧化反应与一级反应动力学拟合度最高,可决系数为0.996,与三级反应动力学拟合度最小,可决系数为0.879。因此,Fenton完全氧化电动自行车涂装废水的反应符合一级反应动力学(式(10))。
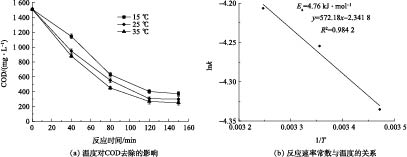
如图7(a)所示,k值随着T的增大而升高,在15、25、35 ℃时,k分别为0.013 0、0.014 2、0.014 9 min−1。这是由于温度升高可提高(·OH)与有机物的碰撞概率,从而强化氧化效果。但在15~35 ℃,COD去除率并没有得到很大提升,仅提高了7%左右,表明季节变化对Fenton去除涂装废水的COD影响并不显著,无需加热措施,可节省运行成本。
依据图7(b)计算可得反应活化能Ea为4.76 kJ·mol−1,频率因子A0为0.10 min−1。Ea较低,说明反应较易进行,且温度对反应影响不大,Fenton降解涂装废水的降解速率的温度修正根据式(11)计算。
-
实际电动自行车涂装废水易受车间生产线等多方面的影响,其水质水量有波动,H2O2的投加量直接关系到废水的处理成本。单一的Fenton完全氧化工艺不仅经济成本高,且不能保证所有时刻的水质指标均稳定达标排放。故在实际工程中常将Fenton氧化作为预处理工艺,与生物方法耦合。Fenton半氧化工艺在去除一部分有机物的同时,改善废水可生化性,为后续生物处理创造有利条件。
由图8可见,当pH=3.21、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8:1、反应时间为120 min时,随着H2O2投量的增加,废水中COD去除率升高,BOD5先升高后降低,废水B/C比升高。这说明芬顿氧化可以有效去除有机物,并且可较好地改善废水的可生化性。当H2O2为0.7 g·L−1时,COD去除率为25.1%,B/C比为0.22;当H2O2为1 g·L−1时,COD值由1 290 mg·L−1降低至742 mg·L−1,COD去除率为42.5%,B/C比从0.12提高至0.35;当H2O2为1.3 g·L−1时,COD去除率为48.9%,B/C比为0.33。一般认为,B/C>0.3的废水可利用生物处理。LI等[10]利用Fenton预处理工业喷涂废水,废水B/C由0.08增加到0.25,可使后续生物法更容易降解有机物。伊学农等[26]在研究Fenton预处理对汽车零部件涂装废水处理的过程中发现,当pH=3~4、FeSO4·7H2O投加量为1.68 g·L−1、H2O2投加量为2.05 g·L−1时,COD去除率为50%,B/C比由0.18提高到0.57,完全满足后续生化处理要求。韩勇刚[27]利用Fenton氧化喷漆废水,初始COD为2 927 mg·L−1,H2O2投加量为0.25 D,H2O2/FeSO4(质量比)为1.6∶1 时,COD去除率为17%,B/C比由0.31提高到0.49。以上研究结果说明,在一定的反应条件下,Fenton处理可以提高废水的B/C值。在本研究中,为节省药剂投加量,对于COD为1 290 mg·L−1的涂装废水,在pH=3.21、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8:1、反应时间120 min,H2O2投加量为1 g·L−1,也即0.36 D(m(H2O2/COD)=0.78:1)时,经Fenton氧化后的出水可满足与生物处理耦合的要求。
-
Fenton全氧化常温降解系数k=0.014 2 min−1,H2O2投加量为1.7 D,根据式(9)可预测当pH=3.21、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8:1、COD去除率为42.5%所需的反应时间为39 min。由2.4节可知,当pH=3.21、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8:1、H2O2投加量为0.36 D ,COD去除率为42.5%的反应时间为120 min。虽然采用Fenton全氧化的条件进行半氧化,可使反应器体积减少67.5%,但投药量增加317%。因此,从长远看,减少投药量比减少反应体积更具经济优势。
以实验所用废水的实际流量165 m3·d−1为例,评估Fenton全氧化处理工艺与Fenton半氧化预处理+生物处理耦合工艺的投资及运行成本。Fenton全氧化工艺的投资费用为53.5×104元,Fenton半氧化预处理+生物处理耦合工艺的投资费用为161.3×104元[28]。
2种工艺的运行费用的差异主要包括电费、药剂费和污泥费,具体比较结果见表4。Fenton全氧化的总装机容量为138.24 kW,电费以0.8元计,则电费为0.76元·t−1;以COD为1 000 mg·L−1计,需688 kg·d−1 H2O2 ,707 kg·d−1 FeSO4·7H2O,药耗成本为7.94元·t−1;每2 d脱泥1次,污泥费用为3.1元·t−1。Fenton全氧化的运行费用合计为11.8元·t−1。吨水处理费用高,受水质波动影响大。
Fenton半氧化耦合生物处理的总装机容量约为273.84 kW,则电费为1.3元·t−1;以COD为1 000 mg·L−1来计,双氧水用量165 kg·d−1,FeSO4·7H2O用量169 kg·d−1,药耗成本为2.1元·t−1;每3 d进行1次脱泥,污泥费用为2元·t−1。Fenton半氧化预处理+生物处理的运行费用合计为5.4元·t−1。日常运行费用低,工艺运行稳定,约2.8 a即可弥补投资高的不足。因此,Fenton半氧化耦合生物处理具有明显优势。
-
1) Fenton完全氧化本涂装废水的最佳条件为pH=3、H2O2为4 g·L−1、FeSO4·7H2O为4 g·L−1、氧化反应时间为120 min,COD去除率达80.1%,TP去除率达98%。
2)各因素对Fenton完全氧化涂装废水COD去除率影响的顺序为pH>H2O2>FeSO4·7H2O,H2O2与FeSO4·7H2O交互极显著,pH与H2O2交互显著,pH与FeSO4·7H2O交互不突出。最优条件为pH=3.21、m(H2O2/COD)为4.17:1、n(H2O2/Fe2+)为8:1、反应时间为120 min,η=81.72+1.79A+1.56B+0.76C+0.78AB+0.48AC+2.25BC-4.93AA-6.85BB-2.17CC,预测电动自行车涂装废水COD去除率为82.15%,实际COD去除率达81.32%,说明预测模型可靠。
3) Fenton完全氧化电动自行车涂装废水符合一级动力学,室温(25 ℃)下降解系数k为0.014 2 min−1,反应活化能Ea为4.76 kJ·mol−1,K=0.10exp(−4.76/RT)。
4)综合经济效益和处理效果,Fenton处理电动自行车涂装废水的最佳反应条件为pH=3.21、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8:1、反应时间120 min、H2O2投加量为理论投加量的0.36倍,在此条件下COD去除率为42.5%,B/C比可提高至0.35,可满足与生物处理耦合,更具经济优势。
Fenton降解涂装废水的因素影响及动力学分析
Influencing factors and kinetic analysis of Fenton degradation of painting wastewater
-
摘要: 以江苏某电动自行车制造企业的涂装废水为研究对象,采用单因素和响应面优化Fenton氧化处理的反应条件,分析了其动力学过程。结果表明:在pH=3.21、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8∶1、m(H2O2/COD)=4.17∶1、氧化反应时间为120 min的条件下,COD和TP的去除率均达到最高,分别为81.32%和98%,其降解过程符合一级反应动力学,室温下降解速率常数k为0.014 2 min−1,活化能为4.76 kJ·mol−1。在pH=3.21、n(H2O2/Fe2+)=8∶1、m(H2O2/COD)=0.78∶1、反应时间120 min的条件下,Fenton半氧化体系对COD去除率可达42.5%左右,处理后废水的B/C比由0.12提高至0.35。综合经济因素,认为Fenton半氧化与生物处理工艺耦合处理实际涂装废水更佳。Abstract: The painting wastewater of an electric bike manufacturing enterprise in Jiangsu was taken as the research object, single factor and response curve tests were conducted to optimize the Fenton oxidation conditions, and the corresponding kinetics of this process was also analyzed. The results show that when pH was 3.21, the molar ratio of H2O2 to Fe2+ was 8∶1 and the mass ratio of H2O2 to COD was 4.17∶1, the removal rates of COD and TP could reach their own highest values of 81.32% and 98% after 120 min Fenton oxidation, respectively. The degradation process accorded with the first-order reaction kinetics, the degradation coefficient k and the activation energy were 0.0142 min−1 and 4.76 kJ·mol−1 at room temperature, respectively. Under the conditions of pH 3.21, n(H2O2/Fe2+) of 8∶1, m(H2O2/COD) of 0.78:1, the Fenton semi-oxidation reaction system could remove about 42.5% of COD within 120 min, and the B/C ratio of the treated wastewater increased from 0.12 to 0.35. Considering the economic factors, it is better to recommend the coupled process of Fenton semi-oxidation and biological treatment to treat the actual painting wastewater.
-
Key words:
- fenton oxidation /
- painting wastewater /
- response surface methodology /
- kinetics
-

-
表 1 响应面设计因素与水平
Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface design
因素 因素编码 因素水平 pH A −1 0 1 H2O2/(g·L−1) B −1 0 1 FeSO4·7H2O/(g·L−1) C −1 0 1 表 2 响应曲面法实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of response surface method
实验号 A(pH) B(H2O2 /
(g·L−1))C(FeSO4·7H2O /
(g·L−1))COD去除率/% 1 2 3 4 67.54 2 3 3 3 72.93 3 3 4 4 81.65 4 4 4 3 74.77 5 3 4 4 81.19 6 3 5 5 76.97 7 3 4 4 82.26 8 4 5 4 73.98 9 3 5 3 71.74 10 4 4 5 78.04 11 3 3 5 69.16 12 3 4 4 81.53 13 2 5 4 68.82 14 3 4 4 81.97 15 2 4 5 73.53 16 4 3 4 69.51 17 2 4 3 72.16 表 3 COD去除率的响应面模型方差分析极显著性检验
Table 3. Analysis of variance and extreme significance test of response surface model based on COD removal rate
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 422.83 9 46.98 163.02 0.000 1 显著 A 25.70 1 25.70 89.19 0.000 1 显著 B 19.41 1 19.41 67.34 0.000 1 显著 C 4.65 1 4.65 16.14 0.005 1 显著 AB 2.40 1 2.40 8.34 0.023 4 显著 AC 0.90 1 0.90 3.13 0.120 1 不显著 BC 20.25 1 20.25 70.27 0.000 1 显著 A2 102.23 1 102.23 354.74 0.000 1 显著 B2 197.71 1 197.71 686.04 0.000 1 显著 C2 19.78 1 19.78 68.64 0.000 1 显著 残差 2.02 7 0.29 失拟 1.34 3 0.45 2.65 0.185 3 不显著 纯误差 0.68 4 0.17 总和 424.85 16 表 4 Fenton全氧化与半氧化-生物处理运行费用比较
Table 4. Comparison of operation cost between Fenton alone treatment and Fenton-biological treatment
元·t−1 处理工艺 电费 药剂费 污泥费 合计 Fenton全氧化 0.76 7.04 3.1 11.8 Fenton半氧化-生物处理 1.3 2.1 2 5.7 -
[1] 智勰. 总体平稳稳中有进——2020年中国自行车行业经济运行分析[J]. 中国自行车, 2021(2): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-999X.2021.02.004 [2] 周晓东, 熊启奎. 电动自行车领域的行业特点及专利保护策略研究[J]. 新能源科技, 2020(7): 21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6936.2020.07.017 [3] 王雪宁, 杨晶晶, 周晓吉, 等. 汽车涂装废水处理技术的研究进展[J]. 涂料工业, 2020, 50(8): 64-70. doi: 10.12020/j.issn.0253-4312.2020.8.64 [4] 刘海宁, 马安明. Fenton氧化技术在难降解工业废水中的应用[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2018, 36(3): 93-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.03.033 [5] 傅银银. 汽车制造企业污水处理工艺研究[J]. 环境与发展, 2020, 32(12): 50-51. doi: 10.16647/j.cnki.cn15-1369/X.2020.12.026 [6] 王小晓, 刘志梅, 雷阳明, 等. Fenton-混凝法应急处理汽车涂装废水的研究[J]. 环境工程, 2013, 31(S1): 147-150. [7] 杨晨曦, 卢垟杰, 李娟, 等. 混凝沉降-Fenton氧化-活性污泥组合法处理水性涂料废水研究[J]. 涂料工业, 2021, 51(1): 62-67. doi: 10.12020/j.issn.0253-4312.2021.1.62 [8] 陈烨, 董菲菲, 陆骏, 等. 混凝芬顿法处理汽车涂装有机废水[J]. 材料保护, 2018, 51(9): 126-129. [9] 刘强. 无人值守序批式Fenton工艺处理电泳废水工程设计[J]. 工业水处理, 2014, 34(2): 84-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2014.02.024 [10] LI X, ZHANG W, LAI S, et al. Efficient organic pollutants removal from industrial paint wastewater plant employing Fenton with integration of oxic/hydrolysis acidification/oxic[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 332: 440-448. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.008 [11] 于常武, 刘春怡. Fenton法处理全自动喷漆线废水的工艺特性及动力学模型[J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(10): 60-63. [12] 孙水裕, 周登健, 罗保全, 等. Fenton工艺在涂装废水中的应用探讨[J]. 中国高新技术企业, 2013(25): 37-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2374.2013.25.020 [13] 谢永华, 杨晨曦. 混凝沉降-Fenton氧化法处理水性涂料废水[J]. 中国涂料, 2020, 35(3): 70-73. [14] VERONICA P N, EMILIO R, MARTA P, et al. Current advances and trends in electro-Fenton process using heterogeneous catalysts: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 201: 399-416. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.002 [15] DBIRA S, BENSALAH N, ZAGHO M M, et al. Oxidative degradation of tannic acid in aqueous solution by UV/S2O82− and UV/H2O2/Fe2+ processes: A comparative study[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(1): 156. doi: 10.3390/app9010156 [16] 梅凤仙. 酸析-芬顿-水解酸化-SBR工艺处理油墨清洗废水的研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2020. [17] 张峰, 詹俊阁, 李学伟, 等. 电芬顿法去除化学镀镍废水中的镍、总磷和COD[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(9): 2428-2435. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201912042 [18] HERMOSILLA D, CORTIJO M, HUANG C P. Optimizing the treatment of landfill leachate by conventional Fenton and photo-Fenton processes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 407(11): 3473-3481. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.02.009 [19] HU H J, TANG Y, YING H S, et al. The effect of copper on iron reduction and its application to the determination of total iron content in iron and copper ores by potassium dichromate titration[J]. Talanta, 2014, 125: 425-431. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.03.008 [20] 赵登, 张安龙, 罗清, 等. Fenton-絮凝工艺深度处理造纸废水[J]. 纸和造纸, 2013, 32(3): 58-61. doi: 10.13472/j.ppm.2013.03.036 [21] 汤优敏, 官宝红, 吴忠标. Fenton去除废水中甲基多巴的机制及动力学[J]. 环境科学, 2008(5): 1271-1276. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.05.022 [22] HUANG T, ZHANG G M, ZHANG N, et al. Pre-magnetization by weak magnetic field enhancing Fe0-Fenton process for wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 346: 120-126. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.009 [23] BERKANT K, BELGIN G. Degradation of Acid Red 274 using H2O2 in subcritical water: Application of response surface methodology[J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 2012, 201-202: 100-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.045 [24] 秦宇, 吴慧芳, 陈文, 等. 响应曲面法优化Fenton氧化处理印染废水[J]. 印染助剂, 2021, 38(6): 38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0439.2021.06.009 [25] MURALIDHAR R. V, CHIRUMAMILA R. R, MARCHANT R, et al. A response surface approach for the comparison of lipase production by Candida cylindracea using two different carbon sources[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2001, 9(1): 17-23. doi: 10.1016/S1369-703X(01)00117-6 [26] 伊学农, 耿成, 董艳玲, 等. Fenton+水解/接触氧化处理涂装废水工程改造与调试[J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(22): 119-124. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2017.22.027 [27] 韩勇刚. Fenton氧化法处理喷漆废水的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008. [28] 翟晶晶, 袁怡, 卜志威, 等. 电动自行车涂装废水处理工程实例及运行分析[J]. 给水排水, 2022, 48(3): 68-74. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2021.11.17.0005 -



 下载:
下载: