-
在印染行业,未经处理排出的染料废水会对水生环境及人类健康造成了极大的威胁[1-3]。因此,去除印染废水中的染料十分有必要。目前,诸多方法被用于印染废水的净化,如吸附、膜过滤、电化学、生物法[4-7]等。吸附技术因其操作便捷、绿色环保、经济高效、再生性能良好等优点被广泛使用[3,5,8]。开发一种高效、经济可行的吸附材料已成为研究的热点[9]。此外,传统的吸附剂在吸附−分离−循环的使用过程容易损耗,难以固液分离再利用,并易造成二次污染。引入磁性材料构建磁性吸附剂,利用外磁场快速地将吸附剂从水体中分离,能有效解决这个问题[10]。
海藻酸钠(sodium alginate,SA)分子含有羟基和羧基,可与阳离子发生静电吸附,同时产生螯合作用。除此之外,海藻酸钠还能与金属离子反应形成类似“蛋壳”结构的水凝胶,可作为其他吸附剂的良好骨架[11-12]。氧化石墨烯(graphene oxide,GO)因其具有巨大的比表面积,分子表面含有丰富的含氧官能团,亲水性很强,在水中有着良好的分散性,使得氧化石墨烯在废水处理领域可以作为理想的吸附剂[13]。YANG等[14]使用GO去除废水溶液中的亚甲基蓝(methylene blue,MB),在MB初始质量浓度低于250 mg·L−1时,对MB的去除率可达到99%,溶液基本脱色至无色。
基于此,本研究使用改良的Hummers法制备GO,以海藻酸钠为基结合Fe3O4及GO,制备了Fe3O4@SA/GO凝胶球,并对吸附剂进行了系列表征分析,研究了Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB动力学以及单因素对吸附剂吸附MB的影响及吸附剂的循环利用性;此外,在不同pH下,研究了吸附剂对含MB与碱性品红(basic fuchsin,CB)共存的废水中染料的去除,以期为处理实际印染废水提供参考。
-
1)主要原料及试剂。海藻酸钠SA(AR,西陇科学股份有限公司);氯化钙CaCl2(AR,天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司);四氧化三铁Fe3O4(AR,天津市精细化工研究所);亚甲基蓝染料C16H18ClN3S(AR,济南市历城区明鑫化工);碱性品红染料C20H19N3(AR,济南市历城区明鑫化工);硫酸H2SO4(GR,广州化学试剂厂);石墨粉C(AR,天津市永大化学试剂有限公司)、硝酸钠NaNO3(天津市百世化工有限公司)、高锰酸钾K2MnO4(AR,郑州润祥化工原料有限公司);双氧水H2O2(AR,上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司);乙醇C2H6O(AR,广州化学试剂厂)。
2)主要仪器。紫外分光光度计UV759(上海精密科学仪器有限公司);扫描电子显微镜Sigma HD(卡尔·蔡司股份公司);傅里叶变换红外光谱仪Nicolet6 700(赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司:振动样品磁强计7 407(美国Lake Shore公司);比表面积分析仪ASAP(Micromeritics,USA)。
-
1)GO的制备。采用改良的Hummers法处理石墨粉制备[15]:将盛有150 mL 98%(质量分数)硫酸的烧杯置于冰水中冷却至0 ℃,快速搅拌下加入5.0 g石墨粉、2.5 g硝酸钠以及15.0 g高锰酸钾。随后将烧杯转移至水浴锅中升温至35 ℃。搅拌加入150 mL去离子水,待呈棕色粘稠状时升温至95 ℃。充分反应3.0 h后加入50 mL 5%(质量分数)的双氧水,待颜色变为亮红色时停止加热,冷却至常温后将混合液进行超声1.0 h,然后采用5%(质量分数)的盐酸、无水乙醇以及去离子水进行3次清洗后,移至烘箱中50 ℃干燥后研磨过筛备用。
2)Fe3O4@SA/GO的制备。称取200 mg氧化石墨烯加入到100 mL去离子水中超声4.0 h,分别加入0.5 g四氧化三铁和1.5 g海藻酸钠粉末搅拌4.0 h,将混合液滴加至6%(质量分数)的氯化钙溶液中静置交联24 h后采用去离子水对复合凝胶清洗3~5次,置于真空干燥箱60 ℃下干燥48 h后备用。
-
1)模拟废水和混合废水的吸附实验。取100 mL一定质量浓度的MB溶液于锥形瓶中,使用0.1 mol·L−1的盐酸与0.1 mol·L−1的氢氧化钠调节其pH,加入一定量的吸附剂;于25 ℃,180 r·min−1的条件下恒温振荡一定时间后取上清液,稀释至一定倍数,采用紫外分光光度计于664 nm处测定溶液的吸光度,并计算MB对应的质量浓度。再取100 mL的100 mg·L−1含MB与CB废水于锥形瓶中,后续步骤同上。采用紫外分光光度计于波长664 mm处和542 mm处分别测定MB和CB吸光度,并折算对应的质量浓度。
2)吸附再生实验。在25 ℃、pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液至吸附平衡。取一定体积混合液使用磁铁分离,测定MB质量浓度,剩余混合液过滤后得到固体吸附剂,分别使用乙醇、去离子水清各洗3次后将样品烘干备用。再将一定质量待解吸的Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂投入0.1 mol·L−1的HCl中进行解吸,放置于震荡器中震荡1.0 h后取样使用磁铁分离吸附剂,测定上清液中MB质量浓度;将解吸后样品过滤后分别用乙醇、去离子水各清洗3次后烘干备用[16]。在相同条件下进行上述吸附再生实验,重复5次,测试每次的吸光度,进而计算出每次对应的去除率。
-
1)吸附实验过程中MB的吸附量和吸附去除率分别根据式(1)和式(2)进行计算[17]。
式中:qt为吸附过程t时刻的MB吸附量,mg·g−1;c0、ct、ce为分别为吸附前、吸附某时刻、吸附后溶液MB质量浓度,mg·L−1;v为吸附溶液体积,L;m为吸附剂质量,g;r为去除率,%。
2)本研究使用伪一级动力学(式(3))[18]、伪二级动力学(式(4))[19]和Weber-Moris粒子扩散模型(式(5))[20]对吸附过程进行拟合。
式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qt为吸附过程t时刻的吸附容量,mg·g−1;k1为伪一级吸附速率常数,min−1;k2为伪二级吸附速率常数,min−1;kpi为在阶段内i的颗粒内扩散常数,mg·min1/2·g−1;cid为与边界厚度相关的常数,mg·g−1。
3)本研究使用Langmuir[21](式(6))和Freundlich[22](式(7))等温线模型对吸附过程进行拟合。
式中:qe为平衡时的吸附量,mg·g−1;qm为最大吸附量,mg·g−1;b为Langmuir平衡常数,L·mg−1;ce为吸附平衡质量浓度,mg·L−1;KF为吸附常数;n为吸附强度指数。
-
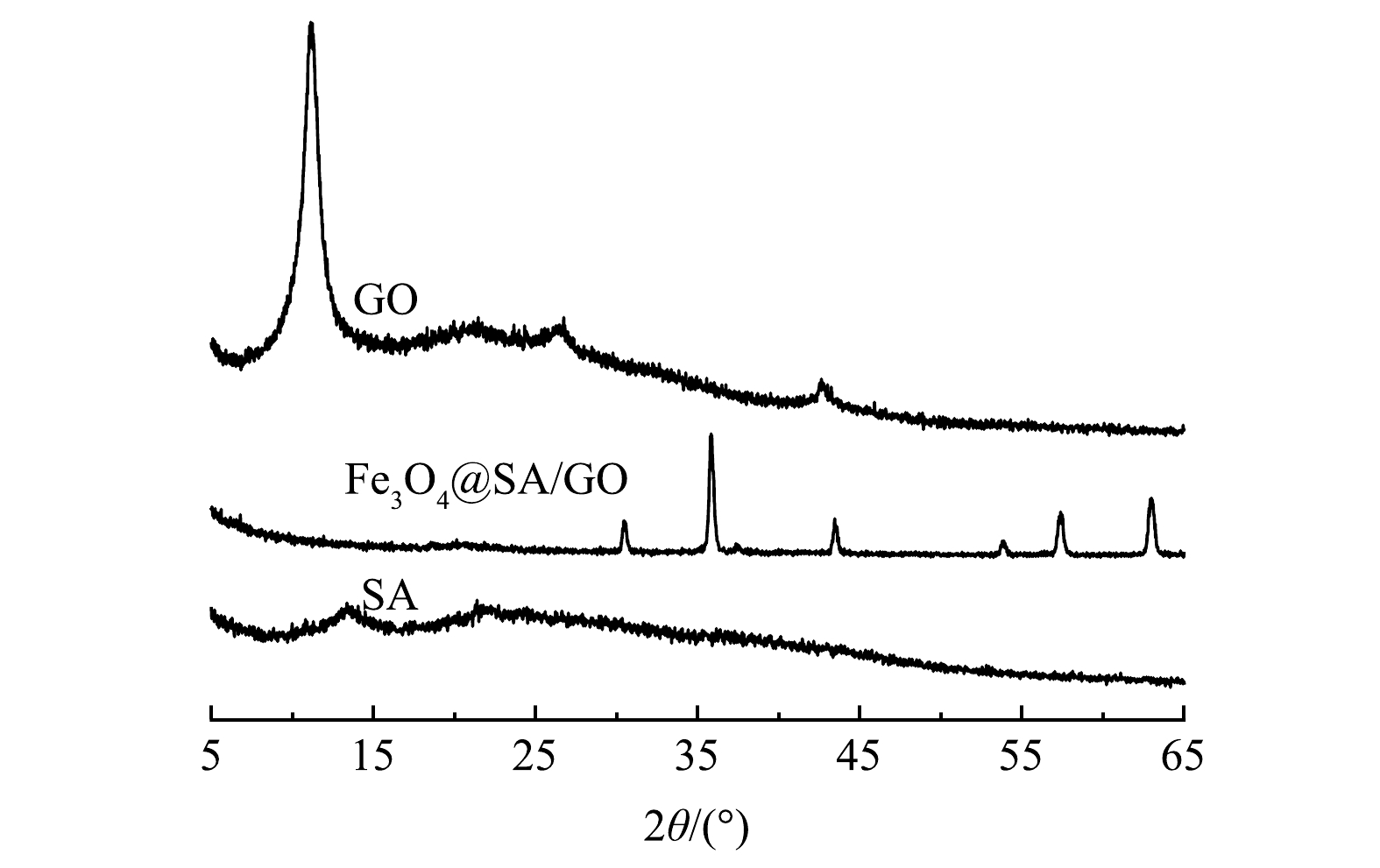
1)晶体结构。本研究采用XRD对所制备的材料的结构以及结晶度进行分析。如图1所示,在GO的图谱中可以看到,在2θ为11.0°出现了较强的衍射峰,属于GO的特征衍射峰[23],表明GO被成功制备并具有完整的晶型。在Fe3O4@SA/GO图谱中,Fe3O4@SA/GO在2θ值为30.0°、35.4°、43.0°、56.9°、62.5°处均出现了Fe3O4的特征衍射峰,说明Fe3O4成功负载到Fe3O4@SA/GO,而GO在2θ为11.0°处的特征衍射峰消失。这可能是因为GO与Fe3O4和SA结合后破坏了GO原有的晶体结构,致使GO的特征衍射峰消失[24]。
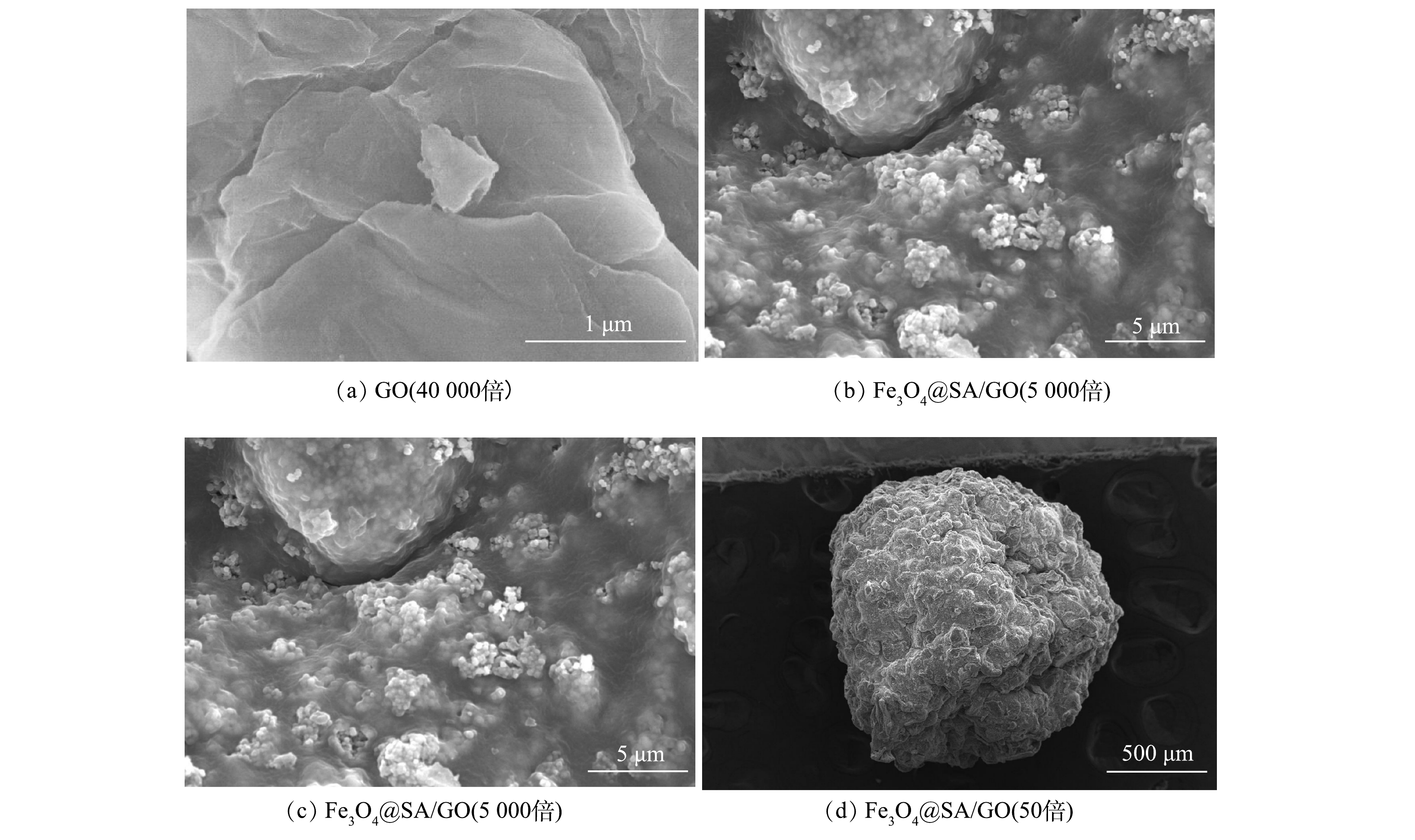
2)材料形貌。本研究采用SEM对制备的GO以及Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂进行扫描拍照,分析表面微观形貌。由图2(a)可以看出,GO为二维片状结构,表面光滑但带一些褶皱,片层之间存在间距;这些结构可以提高GO的比表面积,有利于磁性粒子的负载和提高吸附性能[25]。由图2(b)、图2(c)观测到,在凝胶球表面有明显的Fe3O4与GO片层,Fe3O4与GO通过制备过程被成功负载到凝胶球中。图2(d)中的Fe3O4@SA/GO是在真空干燥箱60 ℃下干燥的扫描电镜图。可以看出,小球表面凹处较多是由于在干燥过程中水分蒸发造成,但整体来看依旧是球形,其表面存在的空隙有利于增加吸附容量。
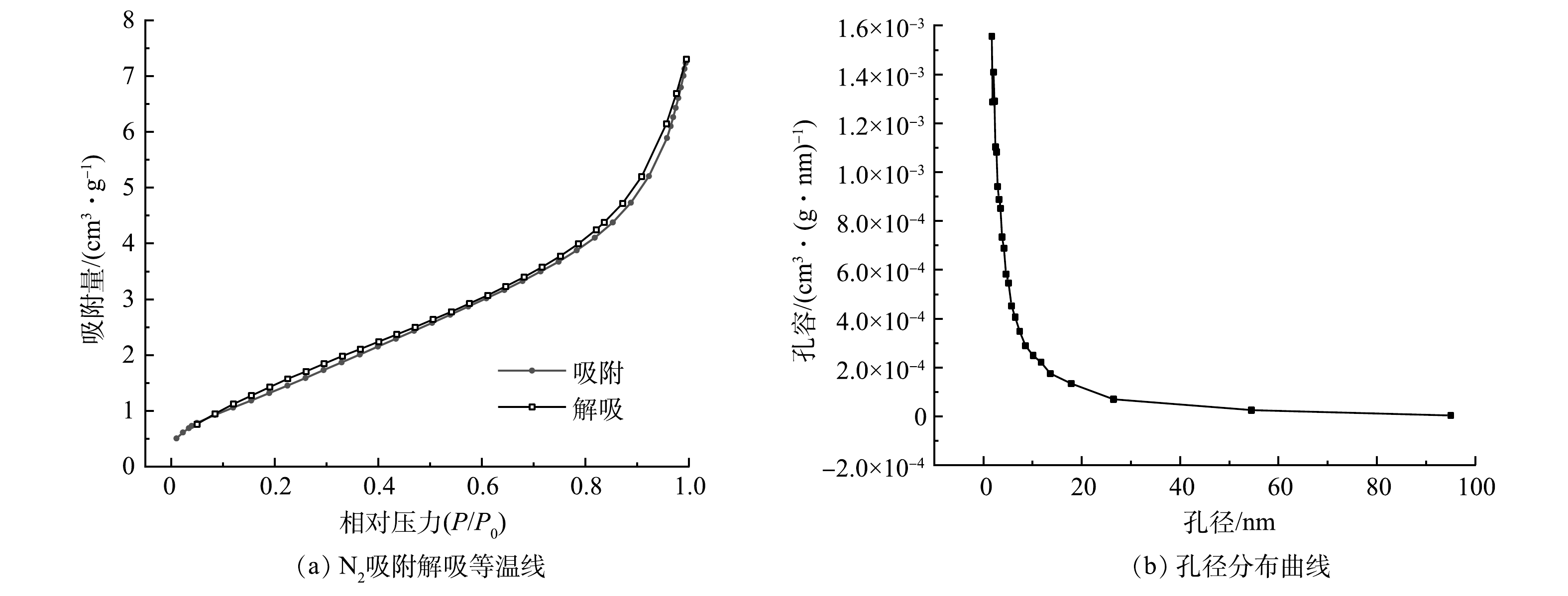
3)比表面积及孔径分析。吸附剂表面是吸附过程的主要场所,吸附剂的吸附能力与其所具有的孔隙结构密切相关。本研究通过使用BET方法取得关于Fe3O4@SA/GO材料结构特征有关参数。由图4可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO的吸附等温线属于IUPAC分类中的IV型等温线[26]。此外,在0.1~1.0的相对压力范围内能够以观察到类似于H1型的滞回环,说明Fe3O4@SA/GO材料是孔径分布很窄的介孔材料,同时也是形状及尺寸较为均匀的球形颗粒。这与SEM的分析结果相对应。Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂的比表面积为5.31 m2·g−1,孔体积为0.01 mL·g−1。由Fe3O4@SA/GO的孔径分布图可以得知,制备的材料孔径主要分布在1.5~19 nm。
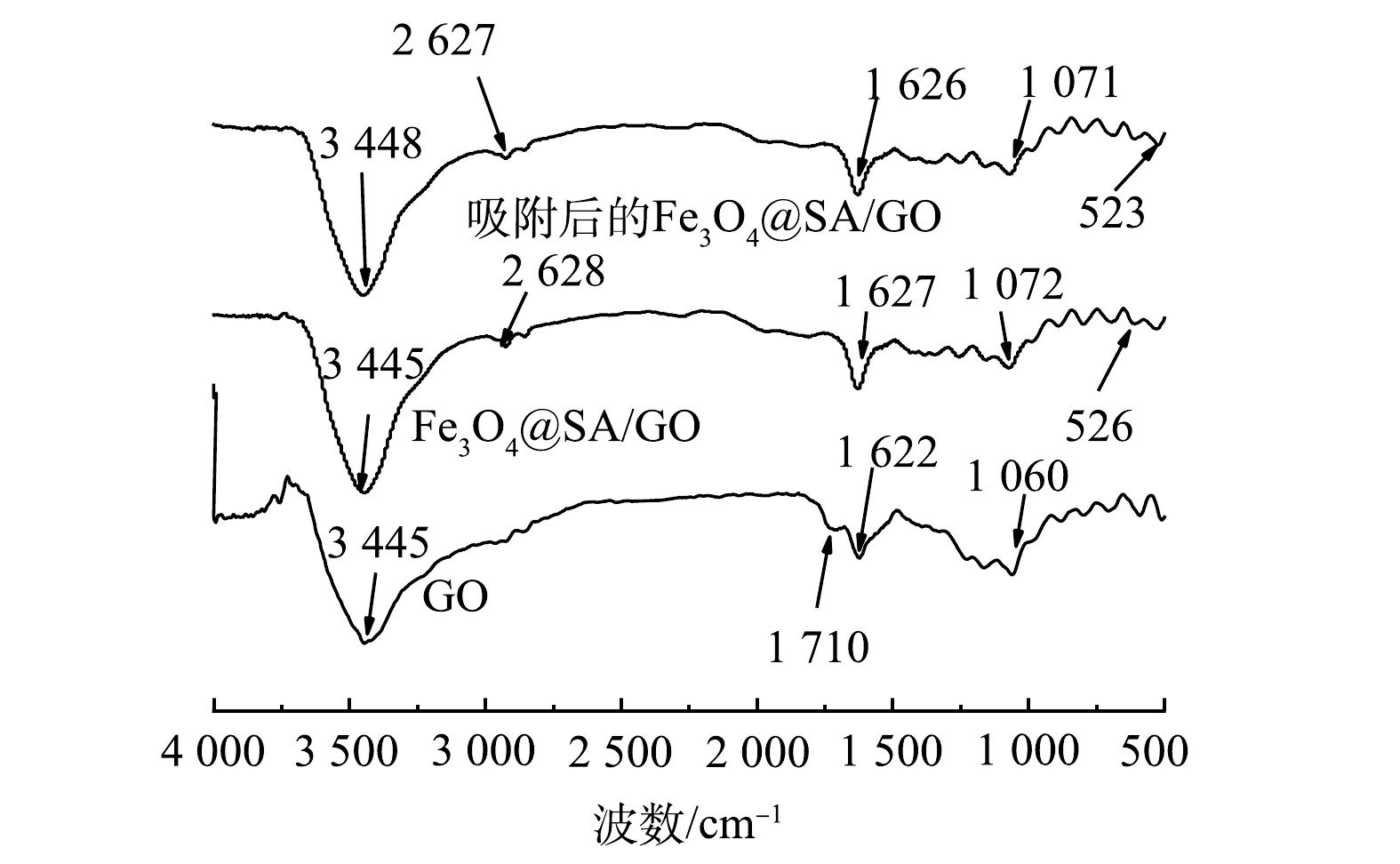
4)吸附剂化学结构的表征。为分析吸附剂中含有的官能团结构,采用FT-IR对其进行表征,结果如图3所示。由图3可见,在GO的图谱中波数为3 445、1 710、1 622、1 060 cm−1有明显的特征峰,其中3 445 cm−1是—OH伸缩所产生的特征峰,1 710 cm−1是由于C=O产生的伸缩振动峰,1 622 cm−1处为C=C产生的伸缩振动峰,在1 060 cm−1处出现的峰为C—O—C振动所形成的吸收峰。由上述结果可以看出,所制备的GO表面含有丰富的官能团,证明GO的制备较理想。在Fe3O4@SA/GO的图谱中,在3 445 cm−1出现的峰是—OH振动所形成的吸收峰,而2 928 cm−1出现的峰是SA的特征峰,526 cm−1出现的峰是Fe—O伸缩振动峰[27],1 627 cm−1和1 072 cm−1可归为—COO−的对称和反对称伸缩振动吸收峰。Fe3O4@SA/GO材料官能团较为丰富,含有大量的含氧官能团,如羟基和羧基等。因此,在吸附MB后,—OH发生红移,其他各键的伸缩振动峰均向低波数方向移动。这说明MB与Fe3O4@SA/GO的各含氧基团发生了配位反应或离子交换[28-29],没有新的吸收峰形成,分子结构没有发生变化,这也进一步地佐证了Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附机制偏向于物理吸附。
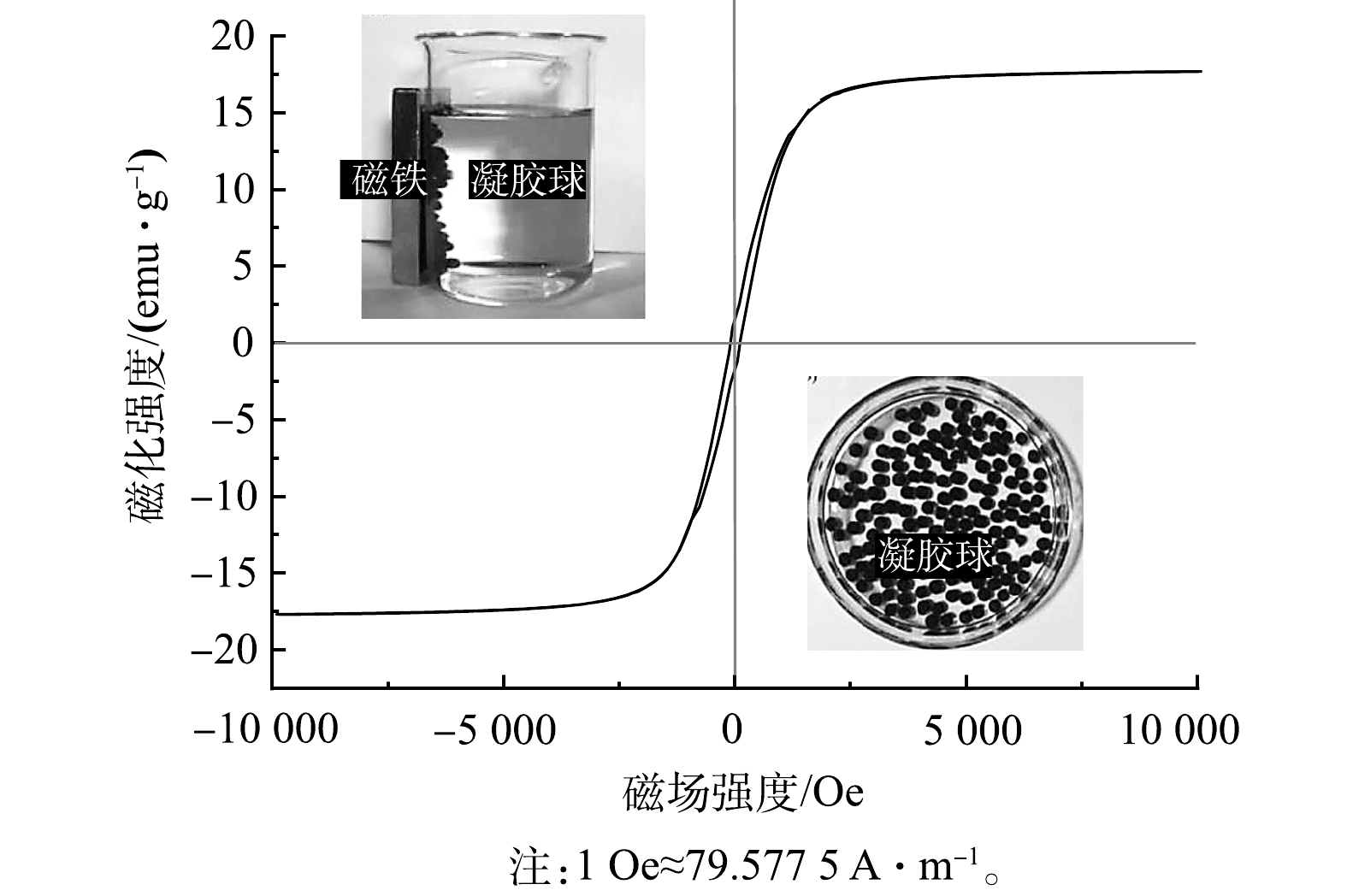
5) Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料的磁性能。本研究中材料负载Fe3O4的目的是使其获得磁性,便于快速回收。为验证Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料的磁学特性,采用VSM对Fe3O4@SA/GO测试,得到其磁滞回线。如图5所示,磁性复合材料Fe3O4@SA/GO的饱和磁化强度达到了17.88 emu·g−1,且其矫顽力(Hc)和剩磁(Mr)几乎接近于0。Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料具有良好的超顺磁性,属于软磁范畴,可实现外加磁场的快速分离回收,为其用于废水处理提供了较大的优势[30]。
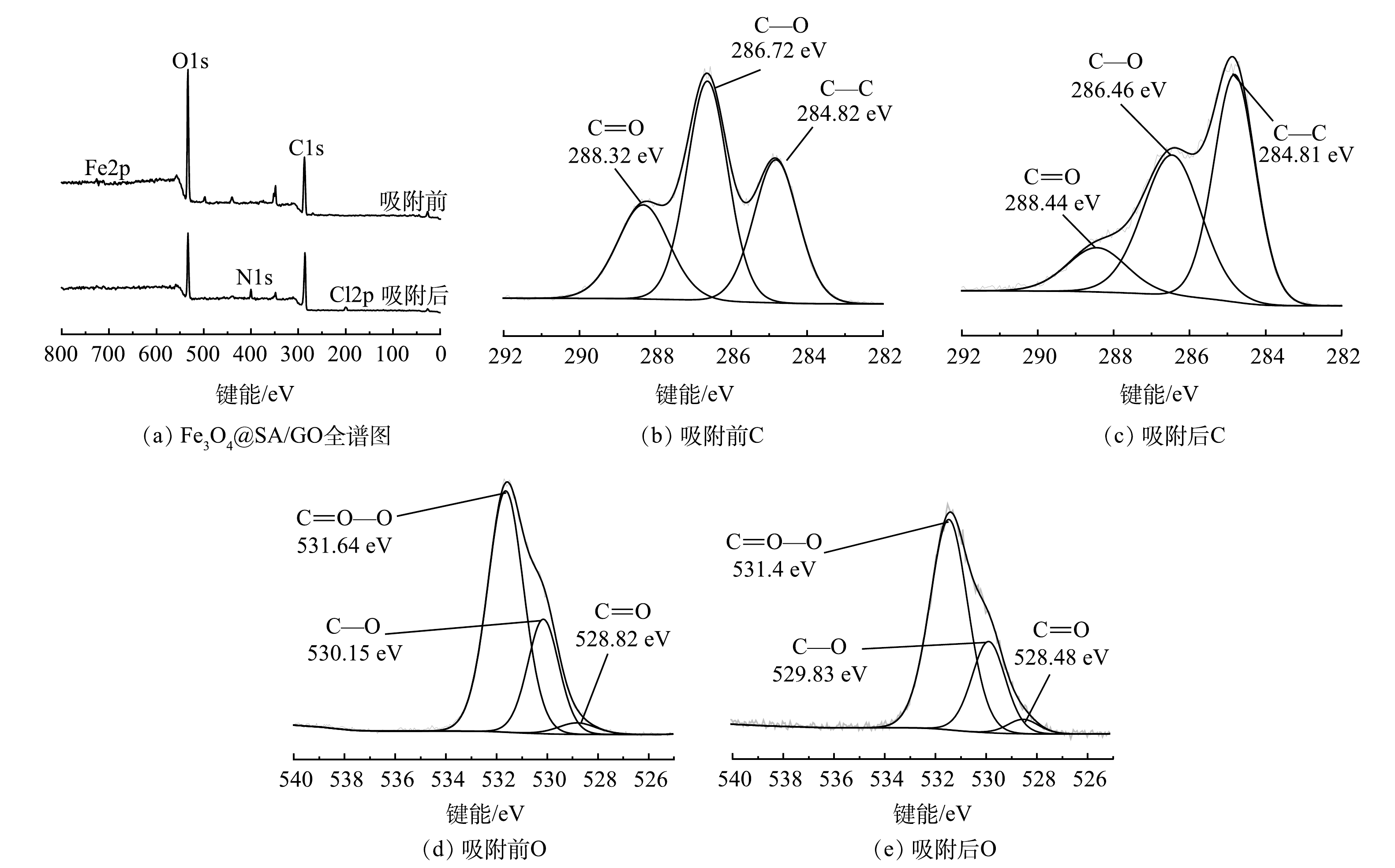
6) Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料表面元素及化学形态分析。XPS表征手段不仅能探Fe3O4@SA/GO材料表面的化学组成,而且可以确定各元素的化学状态,对分析Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB的反应机理有较大帮助[30]。Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂吸附MB前后的XPS图谱见图6。由图6(a)可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附前后都检测出O、C、Fe等元素且在Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB后的全谱图中出现了氮、氯元素。这可能归因于MB已成功吸附至Fe3O4@SA/GO的表面。由图6(b)~(e)可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB前后官能团中C=O、C—O、C—C和C=O—O等的结合能位置均发生了变化,如288.32 eV→288.44 eV、286.72 eV→286.46 eV、284.82 eV→284.81 eV、531.64 eV→531.41 eV、530.15 eV→529.83 eV和528.82 eV→528.48 eV。此外,官能团特别是含氧官能团的相对含量也发生了变化。这些键能大小以及官能团含量的变化进一步说明MB分子被吸附到了Fe3O4@SA/GO表面,且这些官能团可能通过与MB分子上的部分官能团结合,进而参与了吸附过程。
-
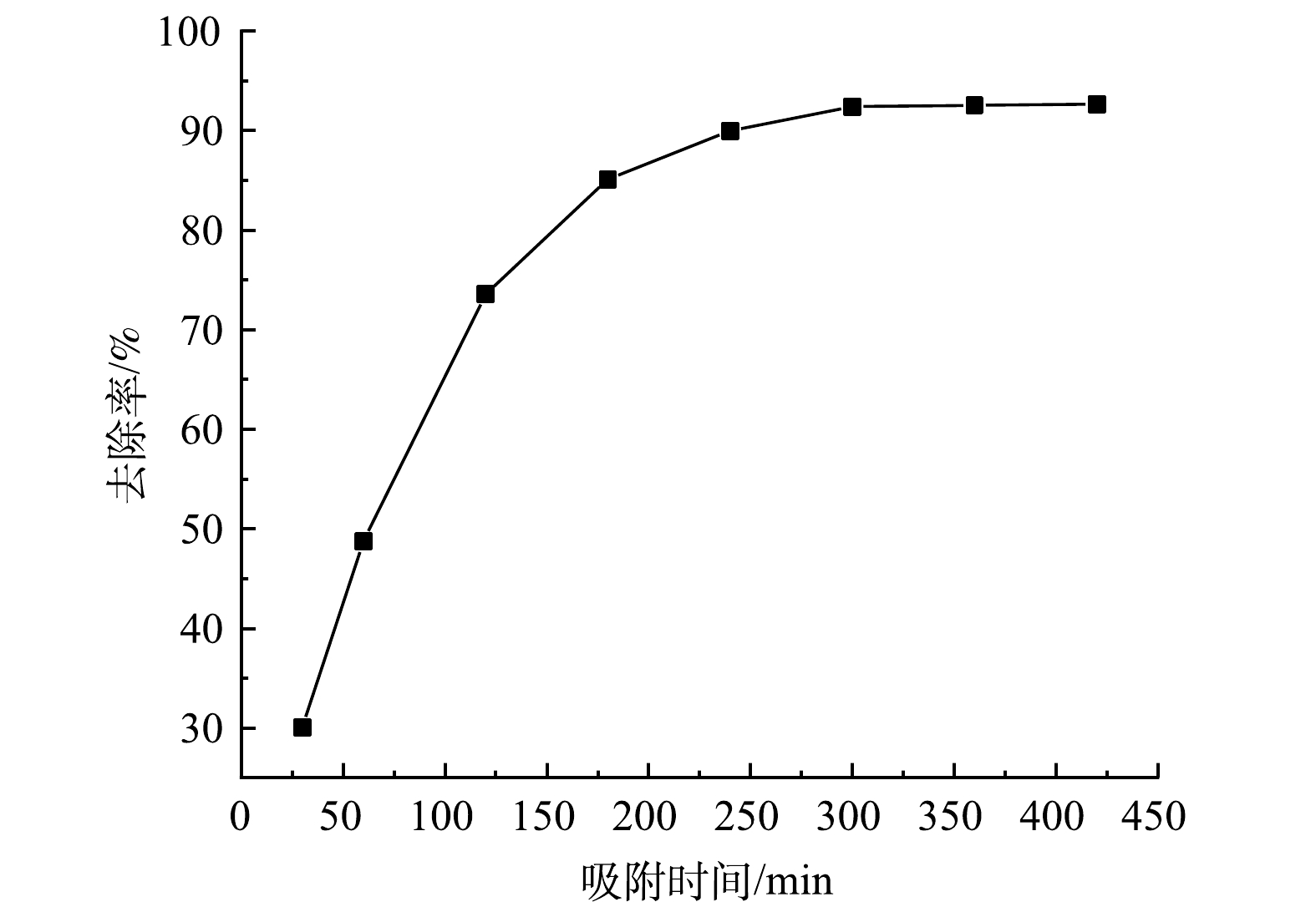
1)吸附时间对吸附性能的影响。在25 ℃、pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液,其处理效果随时间的变化如图7所示。在吸附过程前300 min内,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率随时间的增加而快速上升。在吸附初始阶段,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂表面存在大量的吸附活性位点;但随着吸附继续进行,材料表面吸附点位被MB占据,剩余吸附位点逐渐减少,吸附的速率逐渐变缓,去除率最终也趋向于稳定。在吸附时间为300 min时,吸附几乎达到平衡状态,此时吸附去除率为92.4%。时间进一步延长,则吸附去除率均趋于稳定,后续实验将300 min作为最佳吸附时间。
为进一步研究Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附过程,选用伪一级动力学和伪二级动力学及Weber-Moris粒子内扩散方程模型对实验数据进行拟合,用以了解Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附动力学行为及其吸附机理。
动力学方程拟合结果见图8,拟合得到相关参数如表1所示。由表1可以看出,伪一级模型拟合度优于伪二级模型,伪一级模型得出的平衡吸附量与实验数据所得的平衡吸附量更接近。这表明Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附可以用伪一级吸附动力学方程描述,染料MB在Fe3O4@SA/GO上的吸附过程更偏向于物理吸附。
一般吸附剂对吸附质的吸附过程可以使用表层扩散过程以及颗粒内扩散过程相结合来对吸附-脱附的平衡动态过程描述。本研究采用Weber-Moris粒子内扩散方程模型拟合分析Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB的吸附数据。拟合结果见图9,拟合参数见表2。由图9可见,吸附过程可分为3个阶段:第1阶段表示为MB在Fe3O4@SA/GO表面边界层迅速扩散;第2阶段则表示颗粒的内扩散过程,这时Fe3O4@SA/GO表面的活性位点被MB完全占据,MB逐渐向颗粒内部扩散,占据内部活性位点;随着MB完全占据完Fe3O4@SA/GO活性位点,吸附速率逐渐趋向于0,吸附达到平衡(第3阶段)[31]。颗粒内扩散模型拟合可以很好地拟合Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附,颗粒内扩散是Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB的限速步骤之一。但本研究中拟合曲线均未过原点,这说明吸附速率不仅受到颗粒内扩散的限制,还存在其他影响因素[32]。
2) pH对吸附性能的影响。一般认为,pH通过影响材料表面官能团的性质以及溶液中染料的形态,进而影响吸附效果[33-34]。在25 ℃,pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液3.0 h,结果如图10所示。可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率和吸附量的走势几乎是一致的,pH处于4~9时,均随着pH的增加而增大。在pH为4~5时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB吸附量及去除率均低于20%;当pH为5~6时,吸附剂对MB吸附量及去除率均有显著的提升,MB去除率达到70%左右。这是因为,随着pH的升高,Fe3O4@SA/GO材料表面的—COOH电离程度在增加,—COOH转变成—COO−,对MB的吸附增加,当pH为9时吸附量和去除率均均达到最高,分别为86.3 mg·g−1和82.4%。当溶液为碱性时,MB主要以一价阳离子存在,Fe3O4@SA/GO表面带负电荷,静电作用、内层络合、表面沉淀使得磁性吸附剂对MB有较好的效果。当pH由9增加到10时,可能由于溶液中OH−离子浓度较高,易与MB染料结合,从而降低了MB与Fe3O4@SA/GO凝胶的结合概率,吸附量反而有所减小,故选择pH为9为最佳pH[35]。
3)投加量对吸附性能的影响。吸附剂投加量很大程度上决定了处理成本,过量的吸附剂造成浪费,而过少的吸附剂又达不到处理效果。故针对吸附过程中合理的投加量进行了研究。在25 ℃,pH为9的条件下,分别以不同的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液,结果如图11所示。由随着Fe3O4@SA/GO的投加量从0.2 g·L−1增加至2.0 g·L−1,MB的去除率由38.4%增加至81.8%,去除效果较显著。而对MB的吸附量随着Fe3O4@SA/GO的投加量增加而降低,当吸附剂投加量由0.2 g·L−1增加至2.0 g·L−1时,吸附量由208.41 mg·g−1降低至44.3 mg·g−1;当继续增加吸附剂投加量至3.0 g·L−1,去除率略微上升至86.9%,增幅较小。后续投加量增加至5.0 g·L−1,去除率变化甚微。其主要原因是:吸附残存的MB质量浓度不仅与吸附剂吸附点位数量有关,而且遵循吸附平衡理论,即使投加量增加至5.0 g·L−1,MB去除率也几乎没有变化。因此,从经济效益及去除率的角度考虑,后续实验采用吸附剂投加量为1.0 g·L−1。
4) MB初始质量浓度对吸附性能的影响。在25 ℃、pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理不同质量浓度的MB溶液,结果如图12所示。随着MB的初始质量浓度的增加,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附率下降,但对MB的吸附量一直处于上升趋势,而且去除率依旧保持在74%以上。这是因为:在MB质量浓度较低的时候,吸附剂Fe3O4@SA/GO表面有较多的饱和活性位点,这时MB的初始质量浓度是主要的影响因素。在MB为50 mg·L−1时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率达到92.6%,而吸附量为45.6 mg·g−1;随着MB初始质量浓度的增加,吸附量几乎呈直线上升的趋势,在500 mg·L−1时达到最大,为390.5 mg·g−1,此时Fe3O4@SA/GO表面可能还存在较多的活性位点,吸附平衡后材料表面的吸附点位并没有完全占满,未达到饱和吸附,平衡吸附量远小于饱和吸附量。
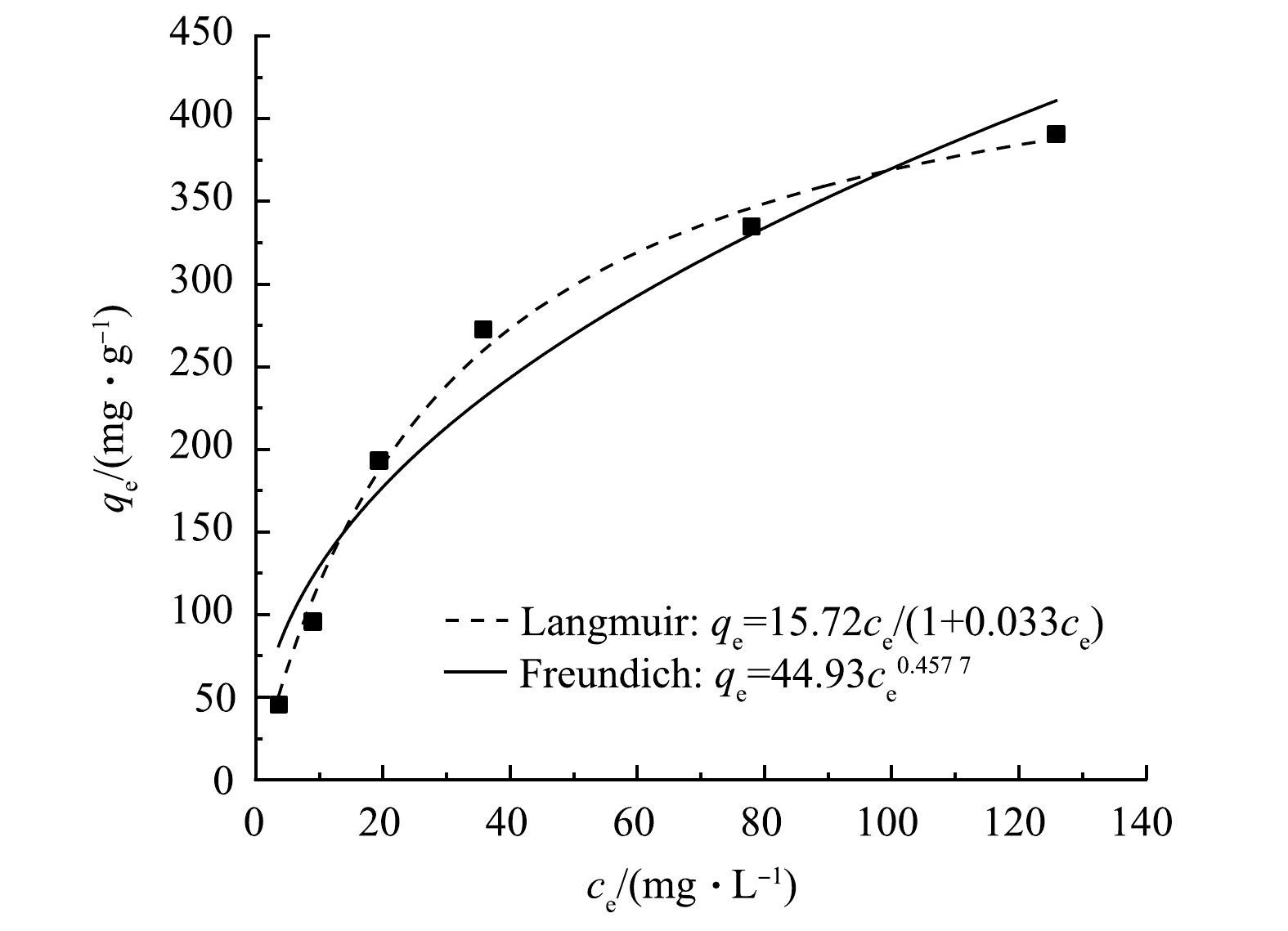
为了进一步分析Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附机理和吸附等温线数据,采用Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型对吸附实验数据进行非线性拟合。拟合结果如图13所示,拟合所得相关参数如表3所示。可见,Langmuir模型拟合度比Freundlich模型拟合度更大,达到了0.975,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB的吸附更符合Langmuir模型,同时也表明MB在吸附剂表面的吸附伴随着MB在吸附剂表面单层的形成[34]。此外,n的值为2.37,当n在1~10内,表明该吸附过程比较容易进行。KF值越大,代表其吸附量越大。在本实验中,KF为52.95,表明Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB具有较强的吸附能力。
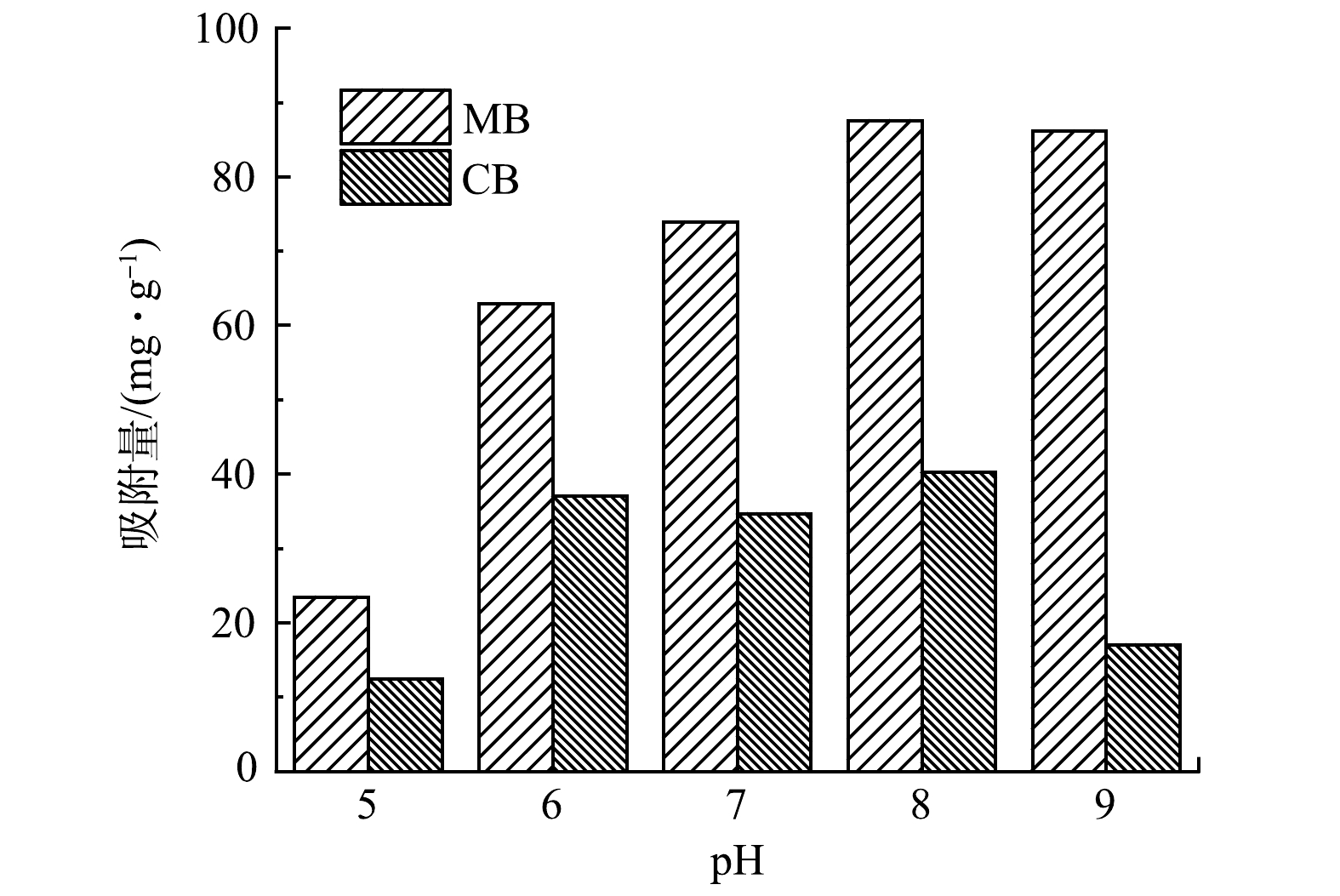
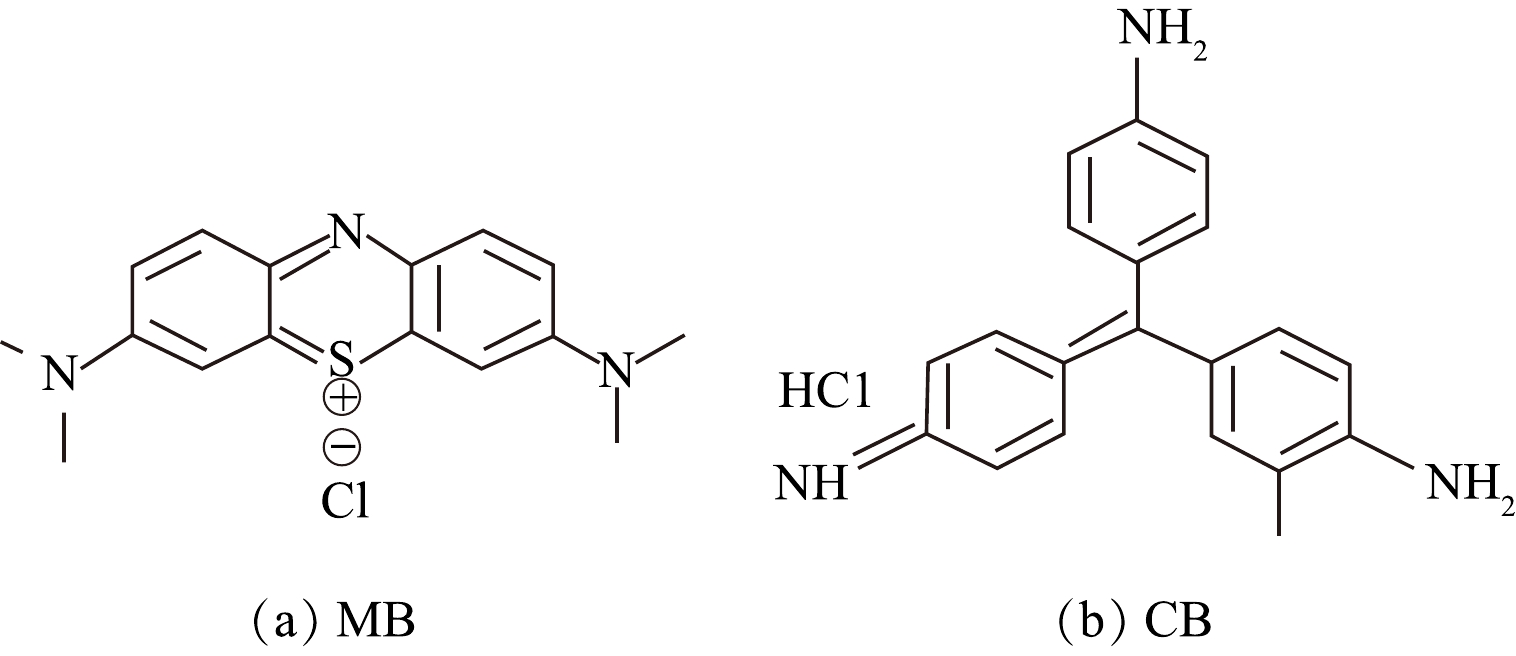
5) pH对Fe3O4@SA/GO在混合染料废水中吸附性能的影响。实际染料废水成分复杂,一般含有多种不同的染料,为探究材料对实际废水的吸附效果以及对不同染料的吸附选择性,选择了碱性品红与亚甲基蓝2种染料作为代表污染物进行混合来模拟实际废水进行研究。在25 ℃、转速180 r·min−1的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量处理100 mg·L−1的MB和CB的混合液5.0 h,并不断调节混合液的pH,结果如图14所示。由图14可以看出,在pH为5时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB和CB吸附量仅分别为23.4 mg·g−1和12.4 mg·g−1。这可能是因为:pH较小时,溶液中H+与染料阳离子产生竞争吸附,H+与Fe3O4@SA/GO上的官能团结合使得Fe3O4@SA/GO上的结合点变少,使得Fe3O4@SA/GO对混合染料的吸附量变小[36]。在pH在6~9时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附量处于上升状态,最大吸附量可达到86.18 mg·g−1;而pH为8时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对CB的吸附量达到最大,为40.24 mg·g−1。这可能是由于:随着pH的升高,Fe3O4@SA/GO表面的—COOH电离程度在增加,—COOH转变成—COO−,对CB的吸附量增加。在pH为9时,材料对CB的吸附量骤降。这可能是由于:CB的结构受溶液pH影响较大,其生色基团(醌式结构)被碱性溶液含有的大量OH−破坏更加彻底,导致褪色,进而对实验结果造成了一定影响[37-38]。由图15可以看出,MB分子结构为“条状”而CB分子结构为 “三角状”。“条状”的MB分子相对于“三角状”的CB分子可能更易于进入材料1.5~1.9 nm的孔隙中被吸附。上述结果表明,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附优于对CB的吸附。
-
实验中采用0.1 mol·L−1的HCl对Fe3O4@SA/GO进行解吸。发现酸性条件有利于从Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂中解吸MB。其原因为,在酸性条件下H+的浓度较高,吸附剂表面正电荷能够质子化基团,这有利于吸附剂的解吸。由图16可见,虽然随循环次数的增加,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率稍微有所下降,但经历5次脱附循环后吸附剂对MB的去除率依旧保持在70%以上。这说明Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂能够有效去除MB,且再生性能良好。
-
1)制备所得的Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料空隙较多,材料表面官能团,尤其是羧基、羟基等含氧官能团丰富;材料具有良好的磁学特性,饱和磁化强度达到了17.88 emu·g−1,具有超顺的磁性,属于软磁的范畴。
2)在25 ℃、pH=9、吸附剂投加量为1.0 g·L−1、MB质量浓度为100 mg·L−1、吸附时间为300 min时,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB的去除率达到92.4%,吸附量达到94 mg·g−1;Fe3O4@SA/GO对混合液中的MB吸附优于CB,在pH为8时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB和CB的吸附量分别为86.18 mg·g−1和40.24 mg·g−1。吸附再生实验结果表明,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂在0.1 mol·L−1 HCl下脱附再生具有良好再生性能。
3) Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB吸附过程的拟合结果与伪一级动力学方程和Langmuir吸附等温线有较好的相关性,说明吸附过程偏向于物理吸附,是单分子层吸附;Weber-Moris粒子内扩散方程模型拟合结果表明,吸附速率除了受到颗粒内扩散的限速作用之外,还受其他因素的影响。
Fe3O4@SA/GO凝胶球的制备及对亚甲基蓝的吸附性能
Preparation of Fe3O4@SA/GO gel ball and its adsorption performance towards methylene blue
-
摘要: 以海藻酸钠为骨架,结合Fe3O4及氧化石墨烯制备了Fe3O4@SA/GO复合凝胶球。采用SEM、FT-IR、XRD、VSM等对制备的材料进行了表征分析,并且考察了Fe3O4@SA/GO对水中亚甲基蓝的吸附性能。结果表明:Fe3O4@SA/GO凝胶球空隙较多,表面含有丰富的羧基、羟基等含氧官能团;材料磁性能良好,饱和磁化强度达到了17.88 emu·g−1,具有超顺的磁性;在25 ℃、pH=9的条件下,投加量为1 g·L−1的吸附剂对100 mg·L−1亚甲基蓝吸附300 min,吸附率达到了92.4%,吸附量可达94 mg·g−1;吸附过程相对符合伪一级动力学方程,吸附过程偏向于物理吸附;Langmuir等温模型能够更好地反应吸附平衡,吸附以表面单层覆盖为主,最大吸附量为452 mg·g−1;在相同条件下,Fe3O4@SA/GO对混合液中亚甲基蓝的吸附效果优于碱性品红;该吸附剂具有良好的循环利用性能,5次脱附循环使用后对亚甲基蓝的吸附率依旧保持在70%以上。以上研究结果可为处理印染废水提供参考。Abstract: Fe3O4@SA/GO gel ball was prepared with sodium alginate as skeleton, in combination with Fe3O4 and graphene oxide. The magnetic composites were characterized by SEM, FT-IR, XRD and VSM, and its adsorption performance towards methylene blue was also studied. The results showed that many pores was in Fe3O4@SA/GO gel spheres, and the surface of these spheres contained rich oxygen-containing functional groups such as carboxyl and hydroxyl groups. Fe3O4@SA/GO gel spheres had good excellent magnetic and superparamagnetic properties, their saturation magnetization reached 17.88 emu·g−1. The adsorption properties and mechanism of methylene blue(MB) from aqueous solution onto the beads were studied. Under the conditions of 25 ℃, pH=9, 100 mg·L−1 methylene blue, 1 g·L−1 adsorbant, the adsorption rate reach 92.4% after 300 min adsorption, and the adsorption capacity reached 94 mg·g−1. The adsorption kinetics accorded with pseudo-first order kinetic equation, and the adsorption process preferred to a physical adsorption. The adsorption isotherm data were well fitted to Langmuir model and the adsorption was a mainly monolayer one, the maximum adsorption capacity was 452 mg·g−1. Under the same conditions, methylene blue adsorption effect by Fe3O4@SA/GO was superior to basic fuchsin in the dye mixture. The adsorption rate of methylene blue still maintained over 70% after 5 recycling, which indicated that this material had a good recycling ability. The above results can provide a new material and technical reference for the adsorption removal of dyeing wastewater.
-
Key words:
- sodium alginate /
- graphene oxide /
- methylene blue /
- coexistence of dyes /
- adsorption /
- magnetic
-
在印染行业,未经处理排出的染料废水会对水生环境及人类健康造成了极大的威胁[1-3]。因此,去除印染废水中的染料十分有必要。目前,诸多方法被用于印染废水的净化,如吸附、膜过滤、电化学、生物法[4-7]等。吸附技术因其操作便捷、绿色环保、经济高效、再生性能良好等优点被广泛使用[3,5,8]。开发一种高效、经济可行的吸附材料已成为研究的热点[9]。此外,传统的吸附剂在吸附−分离−循环的使用过程容易损耗,难以固液分离再利用,并易造成二次污染。引入磁性材料构建磁性吸附剂,利用外磁场快速地将吸附剂从水体中分离,能有效解决这个问题[10]。
海藻酸钠(sodium alginate,SA)分子含有羟基和羧基,可与阳离子发生静电吸附,同时产生螯合作用。除此之外,海藻酸钠还能与金属离子反应形成类似“蛋壳”结构的水凝胶,可作为其他吸附剂的良好骨架[11-12]。氧化石墨烯(graphene oxide,GO)因其具有巨大的比表面积,分子表面含有丰富的含氧官能团,亲水性很强,在水中有着良好的分散性,使得氧化石墨烯在废水处理领域可以作为理想的吸附剂[13]。YANG等[14]使用GO去除废水溶液中的亚甲基蓝(methylene blue,MB),在MB初始质量浓度低于250 mg·L−1时,对MB的去除率可达到99%,溶液基本脱色至无色。
基于此,本研究使用改良的Hummers法制备GO,以海藻酸钠为基结合Fe3O4及GO,制备了Fe3O4@SA/GO凝胶球,并对吸附剂进行了系列表征分析,研究了Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB动力学以及单因素对吸附剂吸附MB的影响及吸附剂的循环利用性;此外,在不同pH下,研究了吸附剂对含MB与碱性品红(basic fuchsin,CB)共存的废水中染料的去除,以期为处理实际印染废水提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试剂及仪器
1)主要原料及试剂。海藻酸钠SA(AR,西陇科学股份有限公司);氯化钙CaCl2(AR,天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司);四氧化三铁Fe3O4(AR,天津市精细化工研究所);亚甲基蓝染料C16H18ClN3S(AR,济南市历城区明鑫化工);碱性品红染料C20H19N3(AR,济南市历城区明鑫化工);硫酸H2SO4(GR,广州化学试剂厂);石墨粉C(AR,天津市永大化学试剂有限公司)、硝酸钠NaNO3(天津市百世化工有限公司)、高锰酸钾K2MnO4(AR,郑州润祥化工原料有限公司);双氧水H2O2(AR,上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司);乙醇C2H6O(AR,广州化学试剂厂)。
2)主要仪器。紫外分光光度计UV759(上海精密科学仪器有限公司);扫描电子显微镜Sigma HD(卡尔·蔡司股份公司);傅里叶变换红外光谱仪Nicolet6 700(赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司:振动样品磁强计7 407(美国Lake Shore公司);比表面积分析仪ASAP(Micromeritics,USA)。
1.2 材料的制备
1)GO的制备。采用改良的Hummers法处理石墨粉制备[15]:将盛有150 mL 98%(质量分数)硫酸的烧杯置于冰水中冷却至0 ℃,快速搅拌下加入5.0 g石墨粉、2.5 g硝酸钠以及15.0 g高锰酸钾。随后将烧杯转移至水浴锅中升温至35 ℃。搅拌加入150 mL去离子水,待呈棕色粘稠状时升温至95 ℃。充分反应3.0 h后加入50 mL 5%(质量分数)的双氧水,待颜色变为亮红色时停止加热,冷却至常温后将混合液进行超声1.0 h,然后采用5%(质量分数)的盐酸、无水乙醇以及去离子水进行3次清洗后,移至烘箱中50 ℃干燥后研磨过筛备用。
2)Fe3O4@SA/GO的制备。称取200 mg氧化石墨烯加入到100 mL去离子水中超声4.0 h,分别加入0.5 g四氧化三铁和1.5 g海藻酸钠粉末搅拌4.0 h,将混合液滴加至6%(质量分数)的氯化钙溶液中静置交联24 h后采用去离子水对复合凝胶清洗3~5次,置于真空干燥箱60 ℃下干燥48 h后备用。
1.3 吸附性能测试实验
1)模拟废水和混合废水的吸附实验。取100 mL一定质量浓度的MB溶液于锥形瓶中,使用0.1 mol·L−1的盐酸与0.1 mol·L−1的氢氧化钠调节其pH,加入一定量的吸附剂;于25 ℃,180 r·min−1的条件下恒温振荡一定时间后取上清液,稀释至一定倍数,采用紫外分光光度计于664 nm处测定溶液的吸光度,并计算MB对应的质量浓度。再取100 mL的100 mg·L−1含MB与CB废水于锥形瓶中,后续步骤同上。采用紫外分光光度计于波长664 mm处和542 mm处分别测定MB和CB吸光度,并折算对应的质量浓度。
2)吸附再生实验。在25 ℃、pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液至吸附平衡。取一定体积混合液使用磁铁分离,测定MB质量浓度,剩余混合液过滤后得到固体吸附剂,分别使用乙醇、去离子水清各洗3次后将样品烘干备用。再将一定质量待解吸的Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂投入0.1 mol·L−1的HCl中进行解吸,放置于震荡器中震荡1.0 h后取样使用磁铁分离吸附剂,测定上清液中MB质量浓度;将解吸后样品过滤后分别用乙醇、去离子水各清洗3次后烘干备用[16]。在相同条件下进行上述吸附再生实验,重复5次,测试每次的吸光度,进而计算出每次对应的去除率。
1.4 实验数据分析方法
1)吸附实验过程中MB的吸附量和吸附去除率分别根据式(1)和式(2)进行计算[17]。
qt=(c0−ct)×vm (1) r=c0−cec0×100% (2) 式中:qt为吸附过程t时刻的MB吸附量,mg·g−1;c0、ct、ce为分别为吸附前、吸附某时刻、吸附后溶液MB质量浓度,mg·L−1;v为吸附溶液体积,L;m为吸附剂质量,g;r为去除率,%。
2)本研究使用伪一级动力学(式(3))[18]、伪二级动力学(式(4))[19]和Weber-Moris粒子扩散模型(式(5))[20]对吸附过程进行拟合。
qt=qe(1−e−k1t) (3) qt=k2q2et1+k2qet (4) qt=kpit1/2+cid (5) 式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qt为吸附过程t时刻的吸附容量,mg·g−1;k1为伪一级吸附速率常数,min−1;k2为伪二级吸附速率常数,min−1;kpi为在阶段内i的颗粒内扩散常数,mg·min1/2·g−1;cid为与边界厚度相关的常数,mg·g−1。
3)本研究使用Langmuir[21](式(6))和Freundlich[22](式(7))等温线模型对吸附过程进行拟合。
qe=qmbce1+bce (6) qe=c1/1nneKF (7) 式中:qe为平衡时的吸附量,mg·g−1;qm为最大吸附量,mg·g−1;b为Langmuir平衡常数,L·mg−1;ce为吸附平衡质量浓度,mg·L−1;KF为吸附常数;n为吸附强度指数。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 材料的表征
1)晶体结构。本研究采用XRD对所制备的材料的结构以及结晶度进行分析。如图1所示,在GO的图谱中可以看到,在2θ为11.0°出现了较强的衍射峰,属于GO的特征衍射峰[23],表明GO被成功制备并具有完整的晶型。在Fe3O4@SA/GO图谱中,Fe3O4@SA/GO在2θ值为30.0°、35.4°、43.0°、56.9°、62.5°处均出现了Fe3O4的特征衍射峰,说明Fe3O4成功负载到Fe3O4@SA/GO,而GO在2θ为11.0°处的特征衍射峰消失。这可能是因为GO与Fe3O4和SA结合后破坏了GO原有的晶体结构,致使GO的特征衍射峰消失[24]。
2)材料形貌。本研究采用SEM对制备的GO以及Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂进行扫描拍照,分析表面微观形貌。由图2(a)可以看出,GO为二维片状结构,表面光滑但带一些褶皱,片层之间存在间距;这些结构可以提高GO的比表面积,有利于磁性粒子的负载和提高吸附性能[25]。由图2(b)、图2(c)观测到,在凝胶球表面有明显的Fe3O4与GO片层,Fe3O4与GO通过制备过程被成功负载到凝胶球中。图2(d)中的Fe3O4@SA/GO是在真空干燥箱60 ℃下干燥的扫描电镜图。可以看出,小球表面凹处较多是由于在干燥过程中水分蒸发造成,但整体来看依旧是球形,其表面存在的空隙有利于增加吸附容量。
3)比表面积及孔径分析。吸附剂表面是吸附过程的主要场所,吸附剂的吸附能力与其所具有的孔隙结构密切相关。本研究通过使用BET方法取得关于Fe3O4@SA/GO材料结构特征有关参数。由图4可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO的吸附等温线属于IUPAC分类中的IV型等温线[26]。此外,在0.1~1.0的相对压力范围内能够以观察到类似于H1型的滞回环,说明Fe3O4@SA/GO材料是孔径分布很窄的介孔材料,同时也是形状及尺寸较为均匀的球形颗粒。这与SEM的分析结果相对应。Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂的比表面积为5.31 m2·g−1,孔体积为0.01 mL·g−1。由Fe3O4@SA/GO的孔径分布图可以得知,制备的材料孔径主要分布在1.5~19 nm。
4)吸附剂化学结构的表征。为分析吸附剂中含有的官能团结构,采用FT-IR对其进行表征,结果如图3所示。由图3可见,在GO的图谱中波数为3 445、1 710、1 622、1 060 cm−1有明显的特征峰,其中3 445 cm−1是—OH伸缩所产生的特征峰,1 710 cm−1是由于C=O产生的伸缩振动峰,1 622 cm−1处为C=C产生的伸缩振动峰,在1 060 cm−1处出现的峰为C—O—C振动所形成的吸收峰。由上述结果可以看出,所制备的GO表面含有丰富的官能团,证明GO的制备较理想。在Fe3O4@SA/GO的图谱中,在3 445 cm−1出现的峰是—OH振动所形成的吸收峰,而2 928 cm−1出现的峰是SA的特征峰,526 cm−1出现的峰是Fe—O伸缩振动峰[27],1 627 cm−1和1 072 cm−1可归为—COO−的对称和反对称伸缩振动吸收峰。Fe3O4@SA/GO材料官能团较为丰富,含有大量的含氧官能团,如羟基和羧基等。因此,在吸附MB后,—OH发生红移,其他各键的伸缩振动峰均向低波数方向移动。这说明MB与Fe3O4@SA/GO的各含氧基团发生了配位反应或离子交换[28-29],没有新的吸收峰形成,分子结构没有发生变化,这也进一步地佐证了Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附机制偏向于物理吸附。
5) Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料的磁性能。本研究中材料负载Fe3O4的目的是使其获得磁性,便于快速回收。为验证Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料的磁学特性,采用VSM对Fe3O4@SA/GO测试,得到其磁滞回线。如图5所示,磁性复合材料Fe3O4@SA/GO的饱和磁化强度达到了17.88 emu·g−1,且其矫顽力(Hc)和剩磁(Mr)几乎接近于0。Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料具有良好的超顺磁性,属于软磁范畴,可实现外加磁场的快速分离回收,为其用于废水处理提供了较大的优势[30]。
6) Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料表面元素及化学形态分析。XPS表征手段不仅能探Fe3O4@SA/GO材料表面的化学组成,而且可以确定各元素的化学状态,对分析Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB的反应机理有较大帮助[30]。Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂吸附MB前后的XPS图谱见图6。由图6(a)可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附前后都检测出O、C、Fe等元素且在Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB后的全谱图中出现了氮、氯元素。这可能归因于MB已成功吸附至Fe3O4@SA/GO的表面。由图6(b)~(e)可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB前后官能团中C=O、C—O、C—C和C=O—O等的结合能位置均发生了变化,如288.32 eV→288.44 eV、286.72 eV→286.46 eV、284.82 eV→284.81 eV、531.64 eV→531.41 eV、530.15 eV→529.83 eV和528.82 eV→528.48 eV。此外,官能团特别是含氧官能团的相对含量也发生了变化。这些键能大小以及官能团含量的变化进一步说明MB分子被吸附到了Fe3O4@SA/GO表面,且这些官能团可能通过与MB分子上的部分官能团结合,进而参与了吸附过程。
2.2 Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB吸附效果的分析
1)吸附时间对吸附性能的影响。在25 ℃、pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液,其处理效果随时间的变化如图7所示。在吸附过程前300 min内,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率随时间的增加而快速上升。在吸附初始阶段,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂表面存在大量的吸附活性位点;但随着吸附继续进行,材料表面吸附点位被MB占据,剩余吸附位点逐渐减少,吸附的速率逐渐变缓,去除率最终也趋向于稳定。在吸附时间为300 min时,吸附几乎达到平衡状态,此时吸附去除率为92.4%。时间进一步延长,则吸附去除率均趋于稳定,后续实验将300 min作为最佳吸附时间。
为进一步研究Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附过程,选用伪一级动力学和伪二级动力学及Weber-Moris粒子内扩散方程模型对实验数据进行拟合,用以了解Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附动力学行为及其吸附机理。
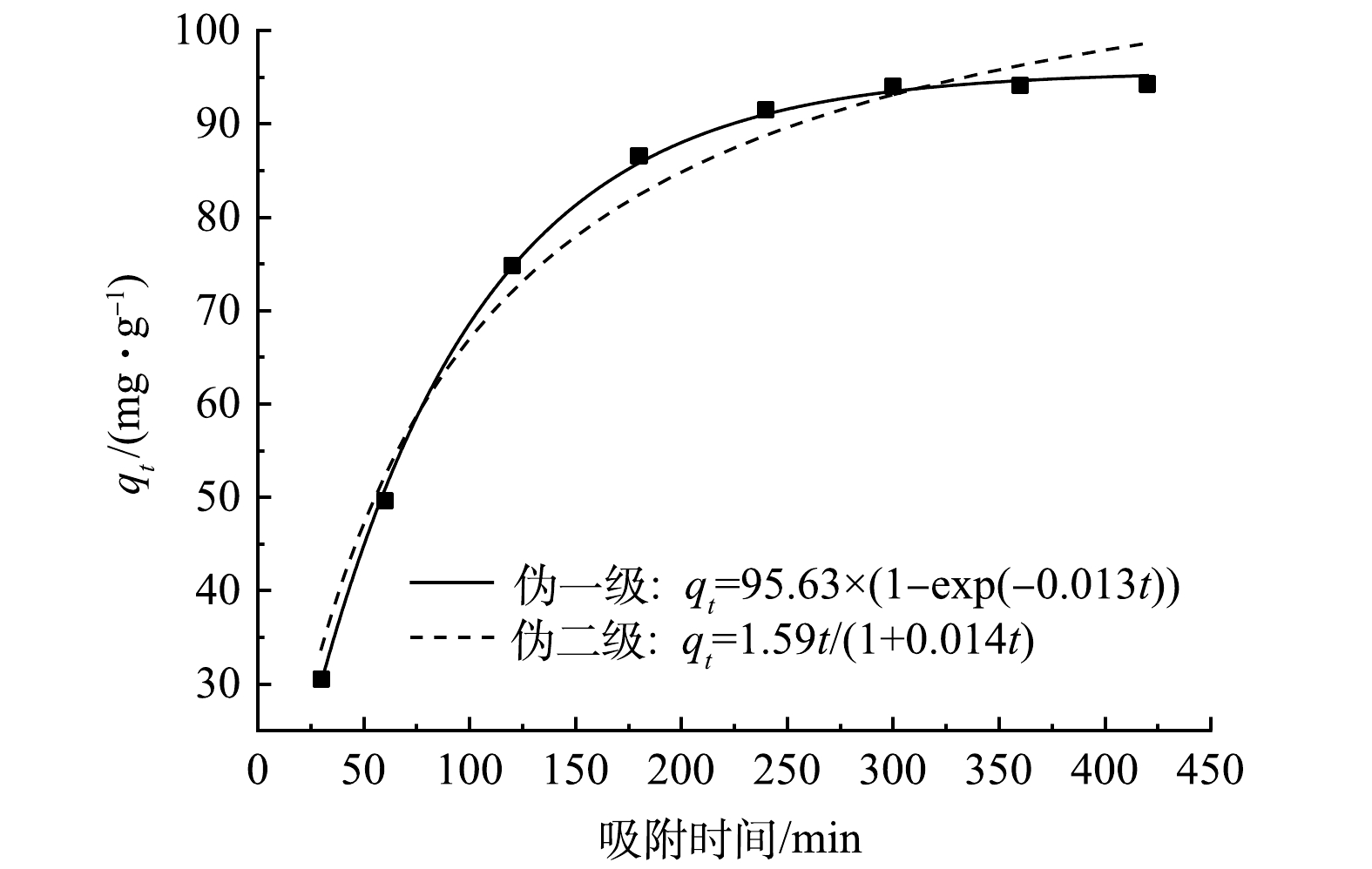
动力学方程拟合结果见图8,拟合得到相关参数如表1所示。由表1可以看出,伪一级模型拟合度优于伪二级模型,伪一级模型得出的平衡吸附量与实验数据所得的平衡吸附量更接近。这表明Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附可以用伪一级吸附动力学方程描述,染料MB在Fe3O4@SA/GO上的吸附过程更偏向于物理吸附。
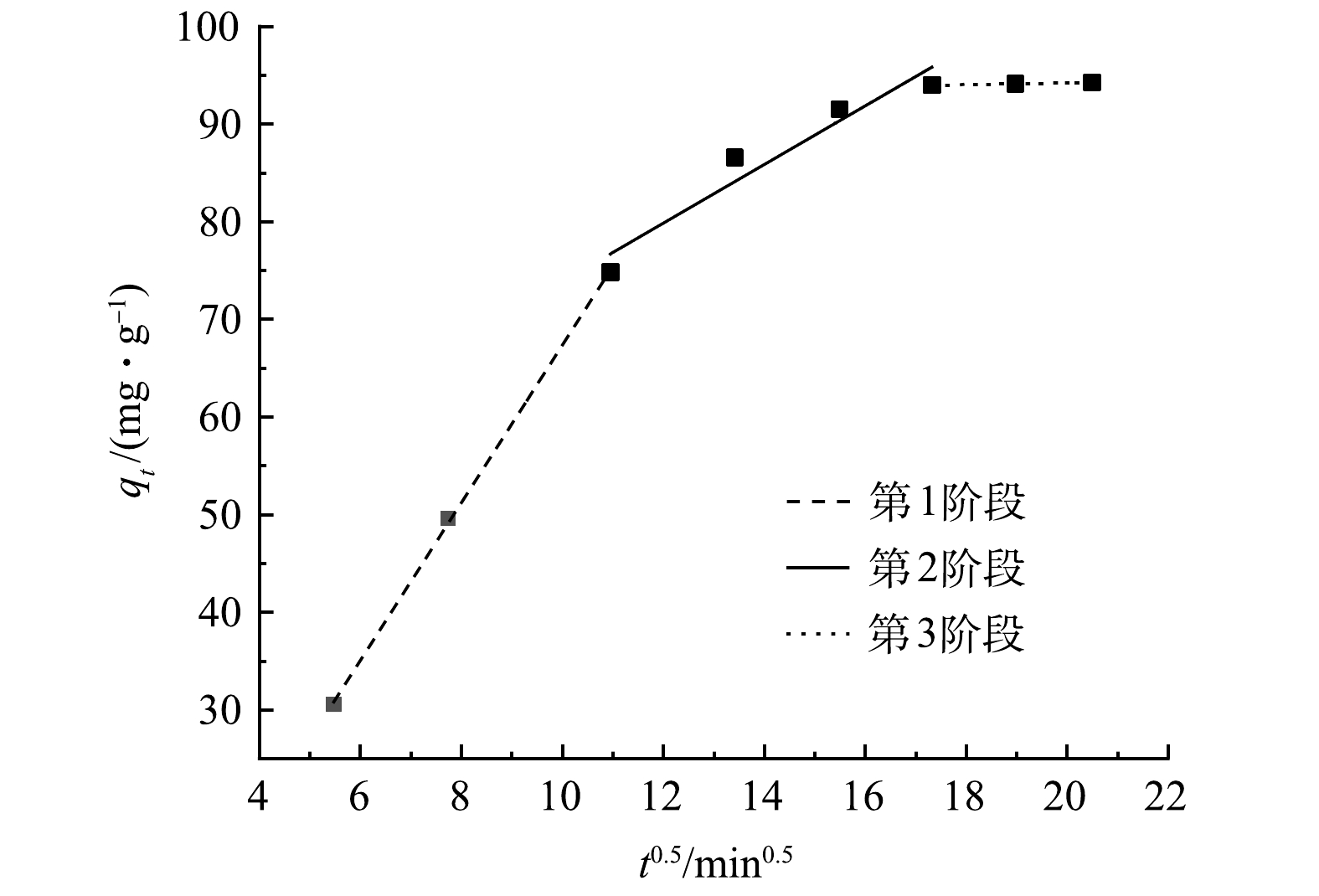
表 1 Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB动力学模型的拟合参数Table 1. Fitting parameters for kinetic models of MB adsorption onto Fe3O4@SA/GO伪一级动力学 伪二级动力学 qe(exp)/(mg·g−1) k1/min−1 qe(cal)/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/min−1 qe(cal)/(mg·g−1) R2 1.263×10−2 95.627 0.998 9 1.186×10−4 115.717 0.978 7 94.261 一般吸附剂对吸附质的吸附过程可以使用表层扩散过程以及颗粒内扩散过程相结合来对吸附-脱附的平衡动态过程描述。本研究采用Weber-Moris粒子内扩散方程模型拟合分析Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB的吸附数据。拟合结果见图9,拟合参数见表2。由图9可见,吸附过程可分为3个阶段:第1阶段表示为MB在Fe3O4@SA/GO表面边界层迅速扩散;第2阶段则表示颗粒的内扩散过程,这时Fe3O4@SA/GO表面的活性位点被MB完全占据,MB逐渐向颗粒内部扩散,占据内部活性位点;随着MB完全占据完Fe3O4@SA/GO活性位点,吸附速率逐渐趋向于0,吸附达到平衡(第3阶段)[31]。颗粒内扩散模型拟合可以很好地拟合Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附,颗粒内扩散是Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB的限速步骤之一。但本研究中拟合曲线均未过原点,这说明吸附速率不仅受到颗粒内扩散的限制,还存在其他影响因素[32]。
表 2 Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB的颗粒内扩散模型拟合参数Table 2. Intra-particle diffusion model parameters of MB on Fe3O4@SA/GO模型 参数 kid/(mg·min1/2·g−1) cid/(mg·g)−1 R2 边界层扩散 8.07 −13.38 0.999 3 颗粒内扩散 2.38 54.60 0.900 5 平衡阶段 0.08 93.58 0.994 7 2) pH对吸附性能的影响。一般认为,pH通过影响材料表面官能团的性质以及溶液中染料的形态,进而影响吸附效果[33-34]。在25 ℃,pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液3.0 h,结果如图10所示。可以看出,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率和吸附量的走势几乎是一致的,pH处于4~9时,均随着pH的增加而增大。在pH为4~5时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB吸附量及去除率均低于20%;当pH为5~6时,吸附剂对MB吸附量及去除率均有显著的提升,MB去除率达到70%左右。这是因为,随着pH的升高,Fe3O4@SA/GO材料表面的—COOH电离程度在增加,—COOH转变成—COO−,对MB的吸附增加,当pH为9时吸附量和去除率均均达到最高,分别为86.3 mg·g−1和82.4%。当溶液为碱性时,MB主要以一价阳离子存在,Fe3O4@SA/GO表面带负电荷,静电作用、内层络合、表面沉淀使得磁性吸附剂对MB有较好的效果。当pH由9增加到10时,可能由于溶液中OH−离子浓度较高,易与MB染料结合,从而降低了MB与Fe3O4@SA/GO凝胶的结合概率,吸附量反而有所减小,故选择pH为9为最佳pH[35]。
3)投加量对吸附性能的影响。吸附剂投加量很大程度上决定了处理成本,过量的吸附剂造成浪费,而过少的吸附剂又达不到处理效果。故针对吸附过程中合理的投加量进行了研究。在25 ℃,pH为9的条件下,分别以不同的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理100 mg·L−1的MB溶液,结果如图11所示。由随着Fe3O4@SA/GO的投加量从0.2 g·L−1增加至2.0 g·L−1,MB的去除率由38.4%增加至81.8%,去除效果较显著。而对MB的吸附量随着Fe3O4@SA/GO的投加量增加而降低,当吸附剂投加量由0.2 g·L−1增加至2.0 g·L−1时,吸附量由208.41 mg·g−1降低至44.3 mg·g−1;当继续增加吸附剂投加量至3.0 g·L−1,去除率略微上升至86.9%,增幅较小。后续投加量增加至5.0 g·L−1,去除率变化甚微。其主要原因是:吸附残存的MB质量浓度不仅与吸附剂吸附点位数量有关,而且遵循吸附平衡理论,即使投加量增加至5.0 g·L−1,MB去除率也几乎没有变化。因此,从经济效益及去除率的角度考虑,后续实验采用吸附剂投加量为1.0 g·L−1。
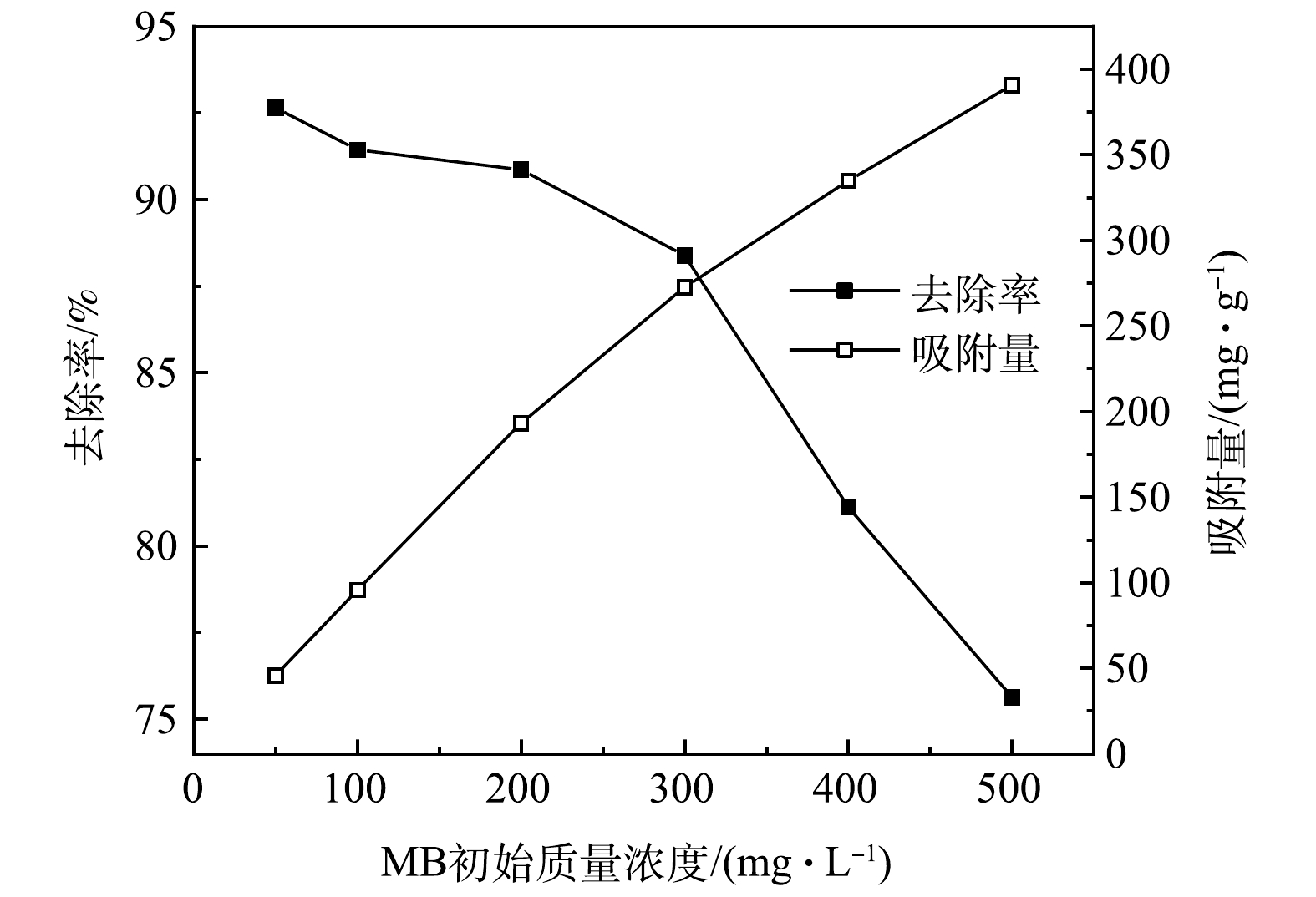
4) MB初始质量浓度对吸附性能的影响。在25 ℃、pH为9的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量吸附处理不同质量浓度的MB溶液,结果如图12所示。随着MB的初始质量浓度的增加,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附率下降,但对MB的吸附量一直处于上升趋势,而且去除率依旧保持在74%以上。这是因为:在MB质量浓度较低的时候,吸附剂Fe3O4@SA/GO表面有较多的饱和活性位点,这时MB的初始质量浓度是主要的影响因素。在MB为50 mg·L−1时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率达到92.6%,而吸附量为45.6 mg·g−1;随着MB初始质量浓度的增加,吸附量几乎呈直线上升的趋势,在500 mg·L−1时达到最大,为390.5 mg·g−1,此时Fe3O4@SA/GO表面可能还存在较多的活性位点,吸附平衡后材料表面的吸附点位并没有完全占满,未达到饱和吸附,平衡吸附量远小于饱和吸附量。
为了进一步分析Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附机理和吸附等温线数据,采用Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型对吸附实验数据进行非线性拟合。拟合结果如图13所示,拟合所得相关参数如表3所示。可见,Langmuir模型拟合度比Freundlich模型拟合度更大,达到了0.975,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB的吸附更符合Langmuir模型,同时也表明MB在吸附剂表面的吸附伴随着MB在吸附剂表面单层的形成[34]。此外,n的值为2.37,当n在1~10内,表明该吸附过程比较容易进行。KF值越大,代表其吸附量越大。在本实验中,KF为52.95,表明Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB具有较强的吸附能力。
表 3 Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB等温线模型的拟合参数Table 3. Fitting parameters for isotherm models of MB adsorption onto Fe3O4@SA/GO朗格缪尔模型 弗朗德力西模型 b/(L·mg−1) qm/(mg·g−1) R2 KF n R2 0.041 81 452.138 0.975 52.95 2.370 0.952 5) pH对Fe3O4@SA/GO在混合染料废水中吸附性能的影响。实际染料废水成分复杂,一般含有多种不同的染料,为探究材料对实际废水的吸附效果以及对不同染料的吸附选择性,选择了碱性品红与亚甲基蓝2种染料作为代表污染物进行混合来模拟实际废水进行研究。在25 ℃、转速180 r·min−1的条件下,以1.0 g·L−1的Fe3O4@SA/GO投加量处理100 mg·L−1的MB和CB的混合液5.0 h,并不断调节混合液的pH,结果如图14所示。由图14可以看出,在pH为5时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB和CB吸附量仅分别为23.4 mg·g−1和12.4 mg·g−1。这可能是因为:pH较小时,溶液中H+与染料阳离子产生竞争吸附,H+与Fe3O4@SA/GO上的官能团结合使得Fe3O4@SA/GO上的结合点变少,使得Fe3O4@SA/GO对混合染料的吸附量变小[36]。在pH在6~9时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附量处于上升状态,最大吸附量可达到86.18 mg·g−1;而pH为8时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对CB的吸附量达到最大,为40.24 mg·g−1。这可能是由于:随着pH的升高,Fe3O4@SA/GO表面的—COOH电离程度在增加,—COOH转变成—COO−,对CB的吸附量增加。在pH为9时,材料对CB的吸附量骤降。这可能是由于:CB的结构受溶液pH影响较大,其生色基团(醌式结构)被碱性溶液含有的大量OH−破坏更加彻底,导致褪色,进而对实验结果造成了一定影响[37-38]。由图15可以看出,MB分子结构为“条状”而CB分子结构为 “三角状”。“条状”的MB分子相对于“三角状”的CB分子可能更易于进入材料1.5~1.9 nm的孔隙中被吸附。上述结果表明,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的吸附优于对CB的吸附。
2.3 吸附再生实验分析
实验中采用0.1 mol·L−1的HCl对Fe3O4@SA/GO进行解吸。发现酸性条件有利于从Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂中解吸MB。其原因为,在酸性条件下H+的浓度较高,吸附剂表面正电荷能够质子化基团,这有利于吸附剂的解吸。由图16可见,虽然随循环次数的增加,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB的去除率稍微有所下降,但经历5次脱附循环后吸附剂对MB的去除率依旧保持在70%以上。这说明Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂能够有效去除MB,且再生性能良好。
3. 结论
1)制备所得的Fe3O4@SA/GO复合材料空隙较多,材料表面官能团,尤其是羧基、羟基等含氧官能团丰富;材料具有良好的磁学特性,饱和磁化强度达到了17.88 emu·g−1,具有超顺的磁性,属于软磁的范畴。
2)在25 ℃、pH=9、吸附剂投加量为1.0 g·L−1、MB质量浓度为100 mg·L−1、吸附时间为300 min时,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂对MB的去除率达到92.4%,吸附量达到94 mg·g−1;Fe3O4@SA/GO对混合液中的MB吸附优于CB,在pH为8时,Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB和CB的吸附量分别为86.18 mg·g−1和40.24 mg·g−1。吸附再生实验结果表明,Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附剂在0.1 mol·L−1 HCl下脱附再生具有良好再生性能。
3) Fe3O4@SA/GO对MB吸附过程的拟合结果与伪一级动力学方程和Langmuir吸附等温线有较好的相关性,说明吸附过程偏向于物理吸附,是单分子层吸附;Weber-Moris粒子内扩散方程模型拟合结果表明,吸附速率除了受到颗粒内扩散的限速作用之外,还受其他因素的影响。
-
表 1 Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB动力学模型的拟合参数
Table 1. Fitting parameters for kinetic models of MB adsorption onto Fe3O4@SA/GO
伪一级动力学 伪二级动力学 qe(exp)/(mg·g−1) k1/min−1 qe(cal)/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/min−1 qe(cal)/(mg·g−1) R2 1.263×10−2 95.627 0.998 9 1.186×10−4 115.717 0.978 7 94.261 表 2 Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB的颗粒内扩散模型拟合参数
Table 2. Intra-particle diffusion model parameters of MB on Fe3O4@SA/GO
模型 参数 kid/(mg·min1/2·g−1) cid/(mg·g)−1 R2 边界层扩散 8.07 −13.38 0.999 3 颗粒内扩散 2.38 54.60 0.900 5 平衡阶段 0.08 93.58 0.994 7 表 3 Fe3O4@SA/GO吸附MB等温线模型的拟合参数
Table 3. Fitting parameters for isotherm models of MB adsorption onto Fe3O4@SA/GO
朗格缪尔模型 弗朗德力西模型 b/(L·mg−1) qm/(mg·g−1) R2 KF n R2 0.041 81 452.138 0.975 52.95 2.370 0.952 -
[1] KONICKI W, ALESKANDRZAK M, MIJOWSKA E. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on adsorption of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2017, 123: 35-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2017.03.036 [2] TKACZYK A, MITROWSKA K, POSYNIAK A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 717: 137222. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137222 [3] OTHMAN N H, ALIAS N H, SHAHRUDDIN M Z, et al. Adsorption kinetics of methylene blue dyes onto magnetic graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 2803-2811. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.024 [4] WANG H, GAO H H, CHEN M X, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/titania nanocomposites as an adsorbent for methylene blue adsorption[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 360: 840-848. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.11.075 [5] YAO X X, JI L L, GUO J, et al. An abundant porous biochar material derived from wakame (undaria pinnatifida) with high adsorption performance for three organic dyes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 318: 124082. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124082 [6] BAYAZIT S S, DANALIOĞLU S T, SALAM M A, et al. Preparation of magnetic MIL-101(Cr) for efficient removal of ciprofloxacin[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(32): 25452-25461. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0121-0 [7] 崔梦娇. 磁性金属-有机骨架复合材料的制备及其对水中有机污染物吸附性能的研究[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2020. [8] LEI J P, QIAN R C, LING P H, et al. Design and sensing applications of metal-organic framework composites[J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 58: 71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2014.02.012 [9] 叶霞, 刘长霞, 韩月, 等. 壳聚糖改性膨润土对有机染料的吸附研究[J]. 广东化工, 2021, 48(12): 26-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2021.12.012 [10] 江湛如, 汤媛媛, 李冰玉, 等. 磁性海藻酸铁介孔碳微球的合成及对水体中砷的去除[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(6): 2382-2392. [11] 曹仕文, 张鸿, 孟驰涵, 等. 海藻酸钠/二氧化硅杂化微球结构与吸附性能[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(9): 3512-3519. [12] 姚温浩, 于飞, 马杰. 海藻酸盐复合凝胶吸附材料的合成及其在水处理中的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2018, 30(11): 1722-1733. [13] KHALILIFARD M, JAVADIAN S. Magnetic superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge loaded with Fe3O4@oleic acid@graphene oxide as high performance adsorbent oil from water[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127369. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127369 [14] YANG S T, CHEN S, CHANG Y, et al. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 359(1): 24-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.02.064 [15] MARCANO D C, KOSYNKIN D V, BERLIN J M, et al. Improved synthesis of graphene oxide[J]. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(8): 4806-4814. doi: 10.1021/nn1006368 [16] 邹成龙, 梁吉艳, 姜伟. 磁性膨润土吸附Cr(Ⅵ)离子解吸再生性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(10): 2127-2135. [17] MAHMOUD M, NABIL G M, KHALIFA M A, et al. Effective removal of crystal violet and methylene blue dyes from water by surface functionalized zirconium silicate nanocomposite[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(2): 103009. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103009 [18] MARŠÁLEK R, ŠVIDRNOCH M. The adsorption of amitriptyline and nortriptyline on activated carbon, diosmectite and titanium dioxide[J]. Environmental Challenges, 2020, 1: 100005. doi: 10.1016/j.envc.2020.100005 [19] MALLAKPOUR S, TABESH F. Tragacanth gum based hydrogel nanocomposites for the adsorption of methylene blue: comparison of linear and non-linear forms of different adsorption isotherm and kinetics models[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 133: 754-766. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.129 [20] ZHAO M, XU Y, ZHANG C, et al. New trends in removing heavy metals from wastewater[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(15): 6509-6518. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7646-x [21] CAO H L, WU X S, SYED-HASSAN S S A, et al. Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphorous adsorption by rape straw-derived biochar functionalized with calcium from eggshell[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 318: 124063. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124063 [22] TANG Y J, YANG R, MA D, et al. Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution by adsorption onto a hydrogel composite[J]. Polymers and Polymer Composites, 2018, 26: 161-168. doi: 10.1177/096739111802600204 [23] 田希双. 氧化石墨烯/聚苯胺复合吸附剂的制备及其性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2020. [24] 陆烨敏. 改性氧化石墨烯去除离子染料和Cr(Ⅵ)的研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2020. [25] 常会, 范文娟, 曾成华, 等. 氨基功能化磁性氧化石墨烯吸附亚甲基蓝的性能探讨[J]. 冶金分析, 2019, 39(8): 52-60. [26] ALQADAMI A A, KHAN M A, OTERO M, et al. A magnetic nanocomposite produced from camel bones for an efficient adsorption of toxic metals from water[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 178: 293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.023 [27] DUAN H M, LI L L, WANG X J, et al. β-Cyclodextrin/chitosan-magnetic graphene oxide-surface molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomplex coupled with chemiluminescence biosensing of bovine serum albumin[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(84): 68397-68403. doi: 10.1039/C5RA11061K [28] 于长江, 王苗, 董心雨, 等. 海藻酸钙@Fe3O4/生物碳磁性复合材料的制备及其对Co(Ⅱ)的吸附性能和机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(6): 1549-1557. [29] 王磊, 白成玲, 朱振亚. 氧化石墨烯/海藻酸钠复合膜对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附性能和机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(3): 681-689. [30] 邹成龙. 磁性膨润土材料制备及吸附重金属离子与再生研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2019. [31] ZHOU X, ZHOU J, LIU Y, et al. Preparation of iminodiacetic acid-modified magnetic biochar by carbonization, magnetization and functional modification for Cd(II) removal in water[J]. Fuel, 2018, 233: 469-479. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.075 [32] 马天行, 杨琛, 江鲜英, 等. 纳米零价铁改性氨基生物炭的制备及对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附和解吸特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(10): 5433-5439. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201603178 [33] CHIU Y H, CHANG T F M, CHEN C Y, et al. Mechanistic insights into photodegradation of organic dyes using heterostructure photocatalysts[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9: 430. doi: 10.3390/catal9050430 [34] SHAMY E, GAMAL A. An efficient removal of methylene blue dye by adsorption onto carbon dot@zinc peroxide embedded poly vinyl alcohol (PVA/CZnO2) nano-composite: A novel reusable adsorbent[J]. Polymer, 2020, 202: 122565. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2020.122565 [35] 王智存, 牛敬业, 王义西, 等. pH响应性纤维素基气凝胶的制备及吸附再生性能[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 35(3): 287-292. [36] 和芹, 陈伟, 舒世立, 等. 海藻酸钠磁球制备及对亚甲基蓝的吸附研究[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2021, 60(4): 532-539. [37] 杨新周, 杨子仙, 段聪丽, 等. 咖啡壳吸附亚甲基蓝和碱性品红的性能研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(5): 957-961. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2017.05.028 [38] 温培娴, 丁伟. 品红褪色机理的实验探究[J]. 化学教育(中英文), 2020, 41(7): 96-100. -






 下载:
下载: