-
纺织行业中棉织物活性印花工艺一般包括印花、洗网、洗筒、水洗、皂洗等工序,生产过程中会产生大量的工艺废水[1-2]。活性印花废水具有浆料浓度高、活性染料残留多、可生化性相对较好等特点[3]。除此之外,印花废水中残留大量尿素,使印花废水含氮量非常高,从而导致碳氮比失调的问题[4-5]。一般的生化工艺经过厌氧反应器处理,可去除印花废水中部分COD,同时也会将有机氮转化为氨氮,加剧碳氮失调比例,增加了后续的生物脱氮难度。为了解决活性印花废水中高氮问题,行业迫切需要开发一种既高效又经济的生物脱氮技术[6]。
近年来开发出的厌氧氨氧化技术(anaerobic ammonium oxidation, ANAMMOX)为低碳高氮废水提供了高效经济的方法[7]。与传统硝化反硝化相比,ANAMMOX工艺具有节省曝气量和碳源、脱氮效率高、剩余污泥泥少等优点[8]。目前,ANAMMOX工艺已经成功应用于实验室处理高氨氮(>300 mg·L−1)废水,如垃圾渗滤液[9]等。由于厌氧氨氧化工艺以氨氮和亚硝态氮为基质,因此,工艺前段须匹配短程亚硝化工艺来提供亚硝态氮[10-11]。在此基础上,开发出二阶段厌氧氨氧化工艺(如短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化(SHARON-ANAMMOX)工艺[12-13])和平阶段厌氧氨氧化工艺(如完全自养脱氮(completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite, CANON)工艺[14-15])。
由于工业废水中存在大量化学品或其中间产物(如染料)可能会抑制厌氧氨氧化菌的生长,因此,目前主流厌氧氨氧化工艺应用于处理印花废水方面的研究未见报导。本研究旨在探讨厌氧氨氧化工艺处理高氨氮工业废水的实验应用可行性,以典型的高氮印花废水作为处理目标,将UASB工艺和主流厌氧氨氧化MBR-CANON工艺进行串联,来处理活性印花废水,考察了UASB/MBR-CANON工艺对印染废水COD、高氮和色度去除的效率,验证了该工艺处理高氮活性印花废水的可行性。
全文HTML
-
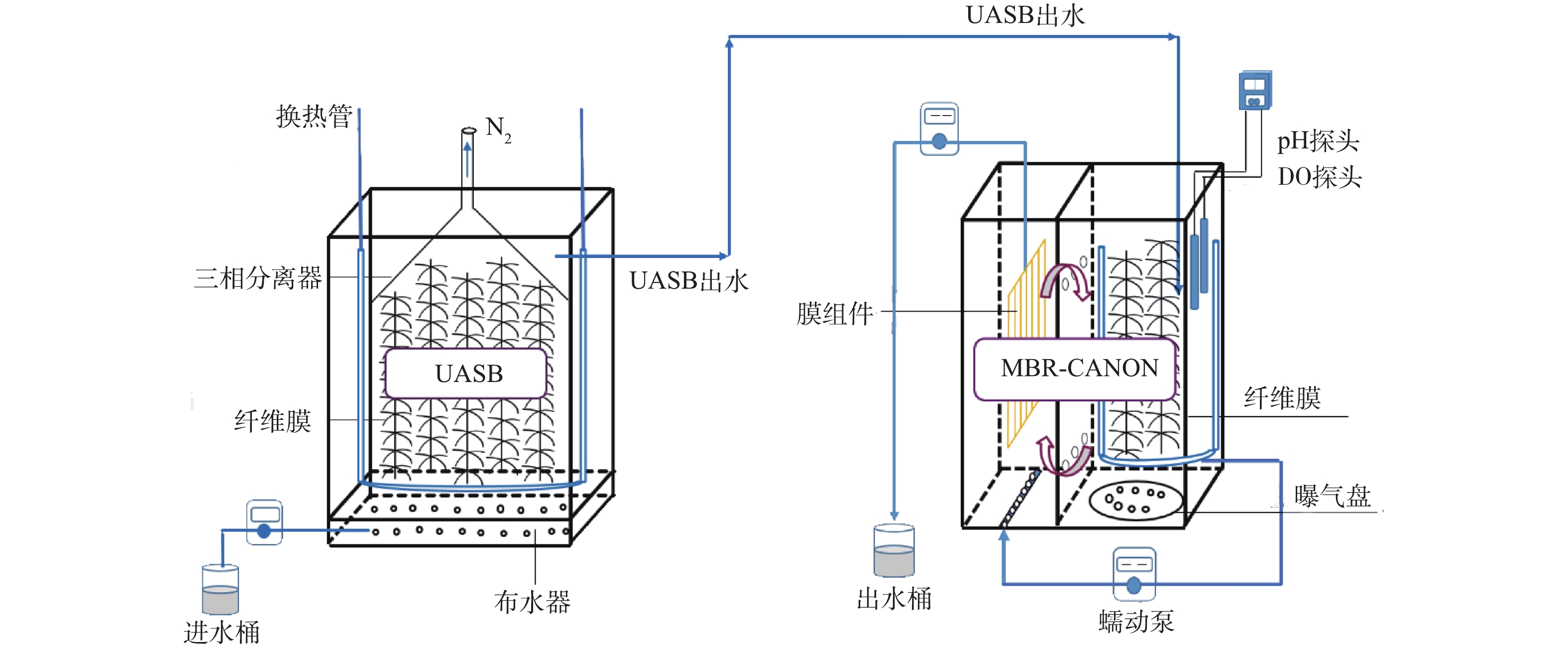
UASB/MBR-CANON工艺通过前置的UASB反应器去除废水中浆料等可生化降解的有机物,同时实现尿素的氨化,为后续的MBR-CANON提供适合的反应条件。CANON采用MBR工艺,反应器内置填料可以通过截留生物量来提高污泥浓度,但生物膜的脱落仍会造成部分污泥流失,因此,本研究采用MBR工艺以加强污泥截留,增加污泥浓度,同时可以过滤悬浮颗粒,优化出水水质。
实验装置系统由厌氧反应器和脱氮反应器组成,分别采用UASB和MBR-CANON反应器形式,如图1所示。其中UASB反应器有效体积为36 L,内部填充软性纤维填料,顶端封闭并设置排气口。MBR-CANON反应器有效体积为12 L,使用隔板平分为左右2部分,左边装填中空纤维膜组件(PVDF膜面积0.144 m2),右边填充软性纤维填料,底部设置曝气盘为微生物提供溶解氧,并放置溶解氧探头和pH计进行实时监测。通过蠕动泵抽取右侧混合液循环至左侧实现膜组件冲刷,使其达到减轻膜污染的目的。当跨膜压力达到−10 kPa时进行膜组件反冲洗。2个反应器均采用连续运行方式,并通过恒温水浴锅和加热管控制反应器内环境温度。
-
UASB反应器接种污泥来自本实验室印染废水的中试厌氧反应器[16],接种污泥浓度为15.6 g·L−1,污泥体积为15 L。MBR-CANON反应器接种污泥来自正在运行的河北某畜牧场厌氧氨氧化污泥,其污泥浓度为10.0 g·L−1,污泥体积为0.5 L。
-
系统运行共200 d,分为2个阶段。UASB反应器和MBR-CANON反应器的独立启动阶段:UASB反应器启动运行共40 d,在此阶段中,水力停留时间为72 h,pH为7.0~8.5,温度为(25±1) ℃。淀粉是活性印花工艺中常用的浆料之一[17],通过将进水中淀粉浓度由500 mg·L−1增加到1 000 mg·L−1,使COD容积负荷由0.17 kg·(m3·d)−1逐渐提高至0.34 kg·(m3·d)−1。染料为活性黄,分子式为C28H20ClN9O16S5·4Na。进水尿素浓度保持在1 070 mg·L−1,其总氮浓度为500 mg·L−1,总氮容积负荷为0.17 kg·(m3·d)−1。MBR-CANON反应器启动共140 d,在此阶段中,水力停留时间为24 h,水力循环中出水与回流比为1∶100。通过将氯化铵浓度由191 mg·L−1依次提高至382、573、764、1 146 mg·L−1的方式,使氨氮容积负荷由0.05 kg·(m3·d)−1逐渐提高至0.10、0.15、0.20、0.30 kg·(m3·d)−1。控制pH为7.5~8.5,温度为(35±1)℃,溶解氧为0.1~0.5 mg·L−1;系统运行140 d后,UASB反应器和MBR-CANON反应器均启动成功并运行稳定,此时将UASB反应器出水逐步添加进入MBR-CANON反应器的进水中进行串联,其他条件保持不变。2个反应器在启动和串联运行中均不排泥。本研究中UASB反应器和MBR-CANON反应器均配制与实际废水相仿的模拟印花废水,具体如表1和表2所示,并添加适量磷、钙镁离子及微量元素[18]。
-
实验在线监测并记录DO和pH(LDO101,Hach,可在线监测并记录数据)。COD采用微波消解法,氨氮采用纳氏试剂分光光度法,亚硝态氮采用N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺分光光度法,硝态氮采用氨基磺酸紫外分光光度法,总氮采用碱性过硫酸钾分光光度法,以上均采用文献中的方法[19]进行测定。
活性黄染料浓度采用分光光度法:取一定量染料溶于去离子水中,在波长200~800 nm范围内,进行紫外-可见全波段扫描,确定染料最大吸收波长。配制梯度浓度的染料标准溶液,在最大吸收波长下测定其吸光度,并绘制吸光度与染料浓度标准曲线。测得水样吸光度,根据标准曲线计算水样染料浓度,染料脱色率计算如式(1)和式(2)所示。
式中:R1为亚硝酸盐积累率;R2为染料脱色率;C为浓度,mg·L−1。
-
在本实验中,膜污染分析测试指标包括膜通量和膜表面滤饼层EPS中的多糖和蛋白质。EPS采用热提取法[20]:将膜表面滤饼层刮至50 mL离心管后,放入摇床中至污泥完全溶解并提取EPS,通过改进Lowry法和蒽酮-硫酸法测定其蛋白质和多糖。
1.1. 实验材料与装置
1.2. 接种污泥
1.3. 实验运行方法
1.4. 分析项目与测试方法
1.5. 膜污染分析方法
-
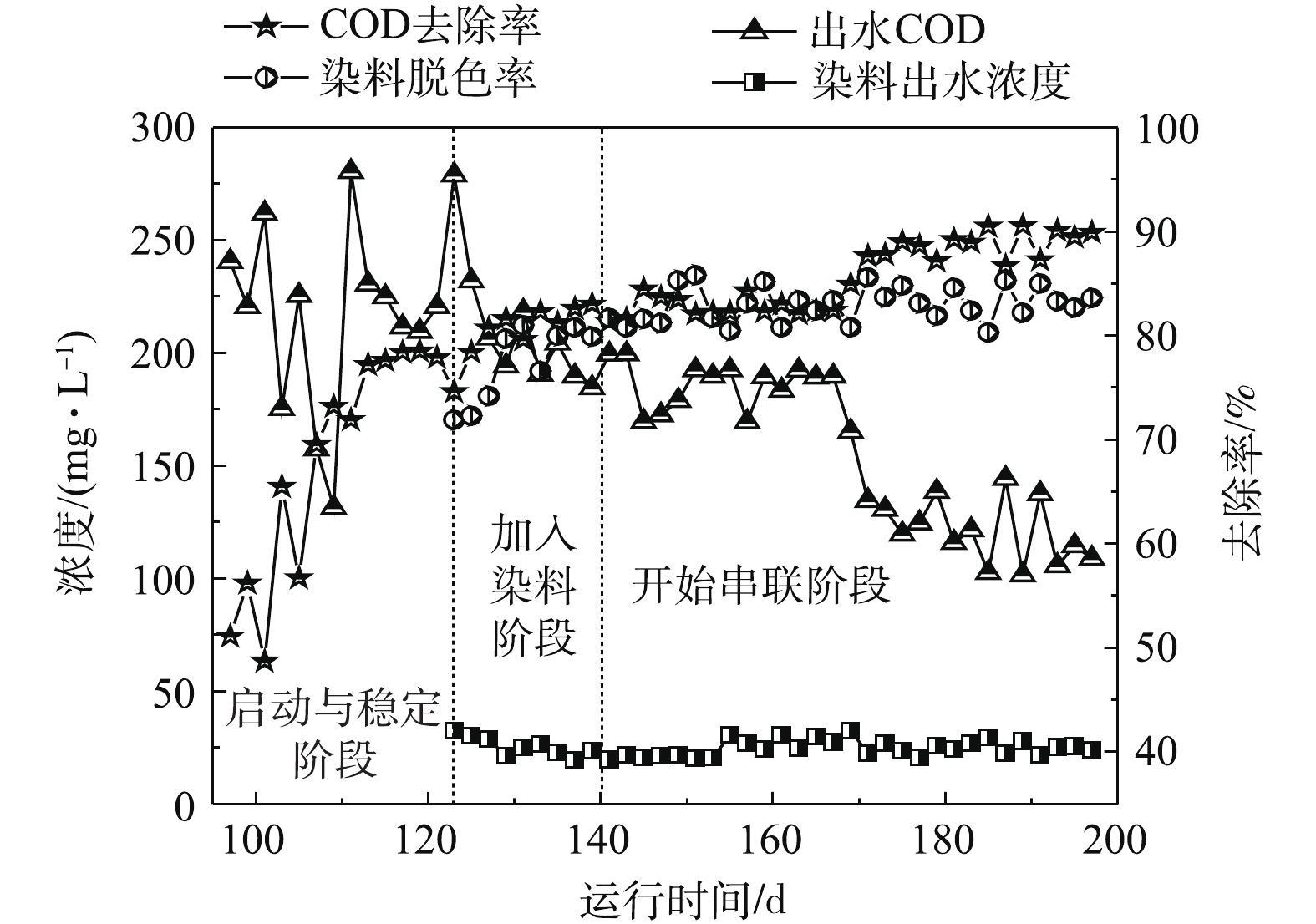
1) UASB反应器启动与运行。UASB反应器可将模拟印花废水中的尿素水解为氨氮,降解大部分淀粉,分解染料,从而降低色度。当MBR-CANON反应器运行至97 d时,开始启动UASB反应器。UASB反应器启动运行结果如图2所示。由图2可知,在UASB反应器运行的第97~109天中,出水COD值平均为201 mg·L−1左右,COD去除率接近60%。当进水继续提高淀粉浓度至1 000 mg·L−1左右时,反应器内微生物浓度与活性不断提高,COD去除率逐渐上升至78%左右。从第123天开始向反应器中加入100 mg·L−1活性黄染料,由图2可知,随着反应器的运行,染料不断被降解,到第140天时,出水染料浓度为25 mg·L−1左右,染料的脱色率缓慢升高至80%左右,此时认为UASB启动成功。由于反应器内接种污泥为处理印染废水中试装置中的污泥,因此,反应器启动所需时间较短。
随着UASB反应器的运行,微生物不断增殖,出水COD去除率和染料脱色率均在80%以上,最高分别可达到85%和86%。运行15 d左右后,提高UASB反应器进水染料浓度至150 mg·L−1,此时出水染料浓度为30 mg·L−1左右,染料的脱色率为80%左右。从第171天开始,反应器出水COD由189 mg·L−1逐渐降低至109 mg·L−1左右,COD去除率平均值为89%,同时,此阶段UASB反应器的染料降解效果相对比较稳定,出水染料浓度和染料脱色率分别为25 mg·L−1和84%左右。以上研究结果表明,UASB反应器对印花废水中COD和活性黄染料均有较好的去除效果。
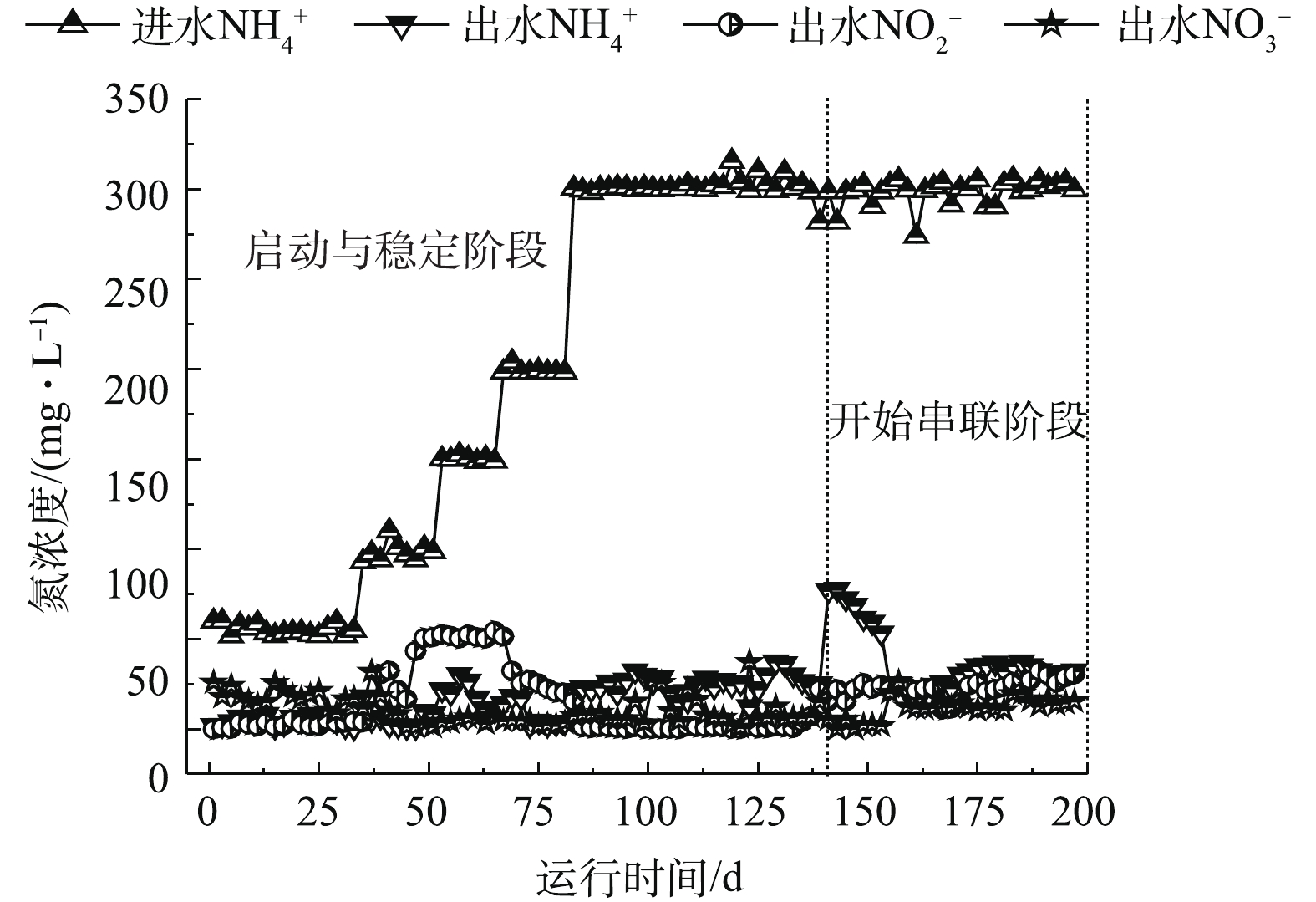
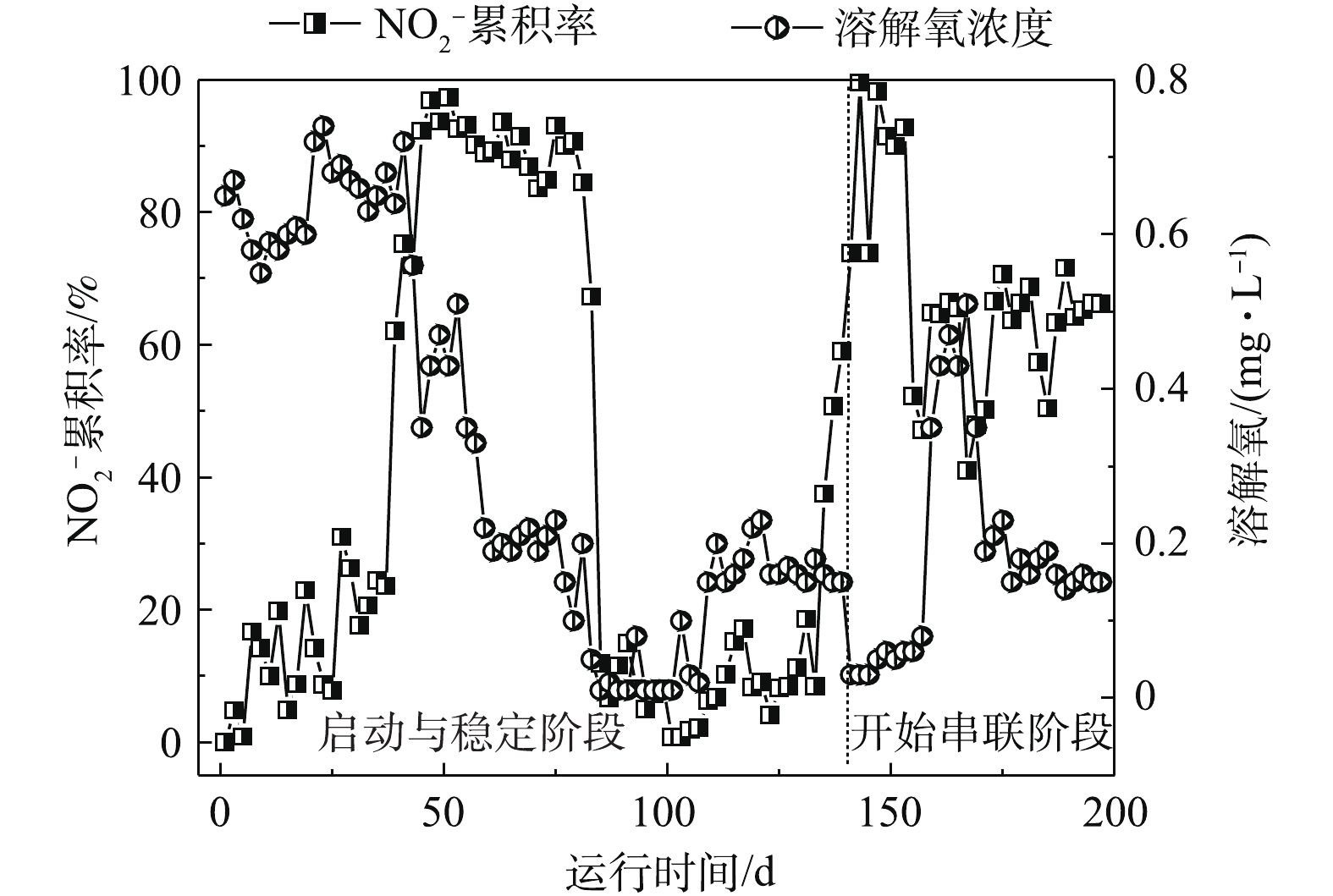
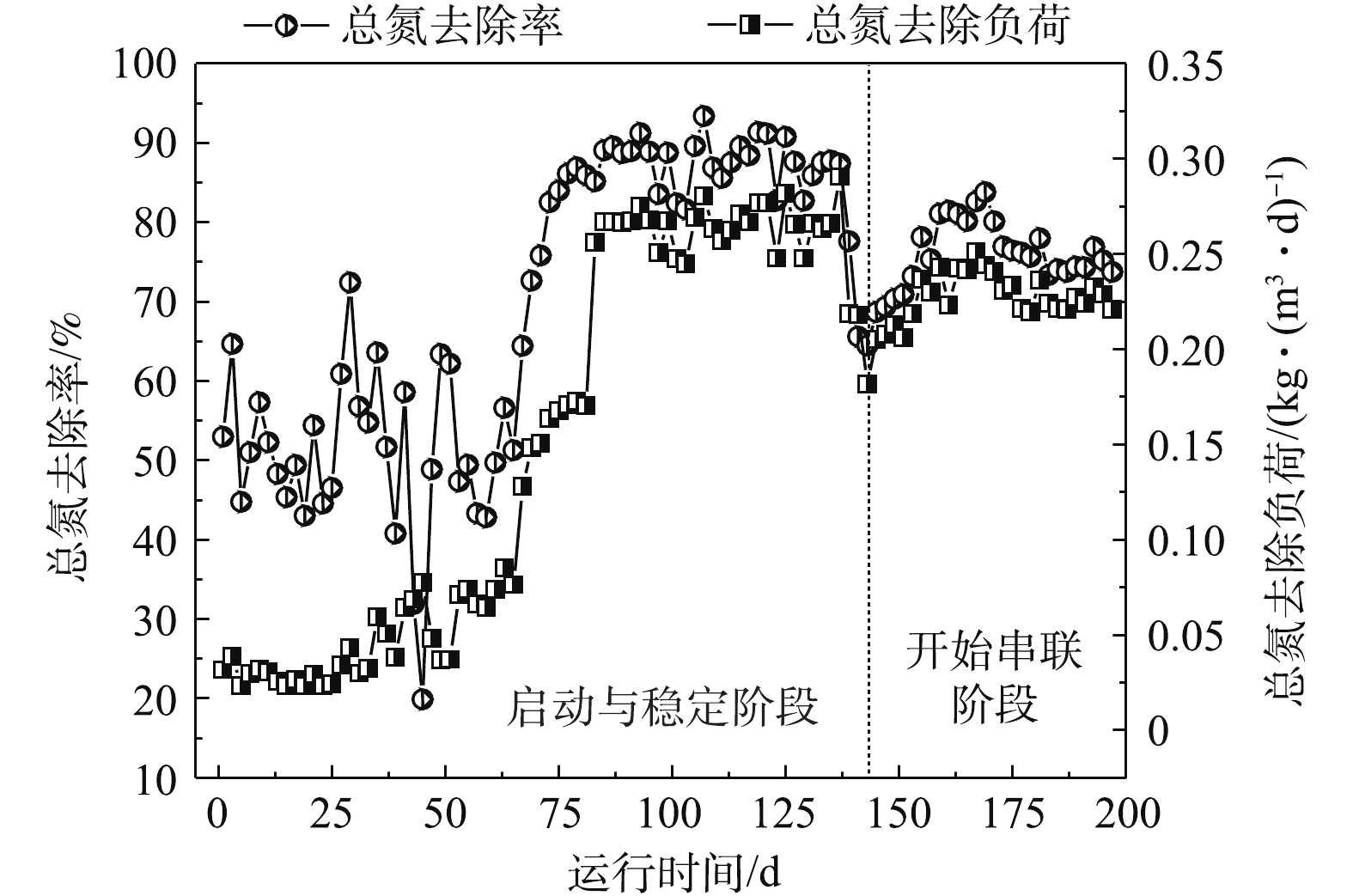
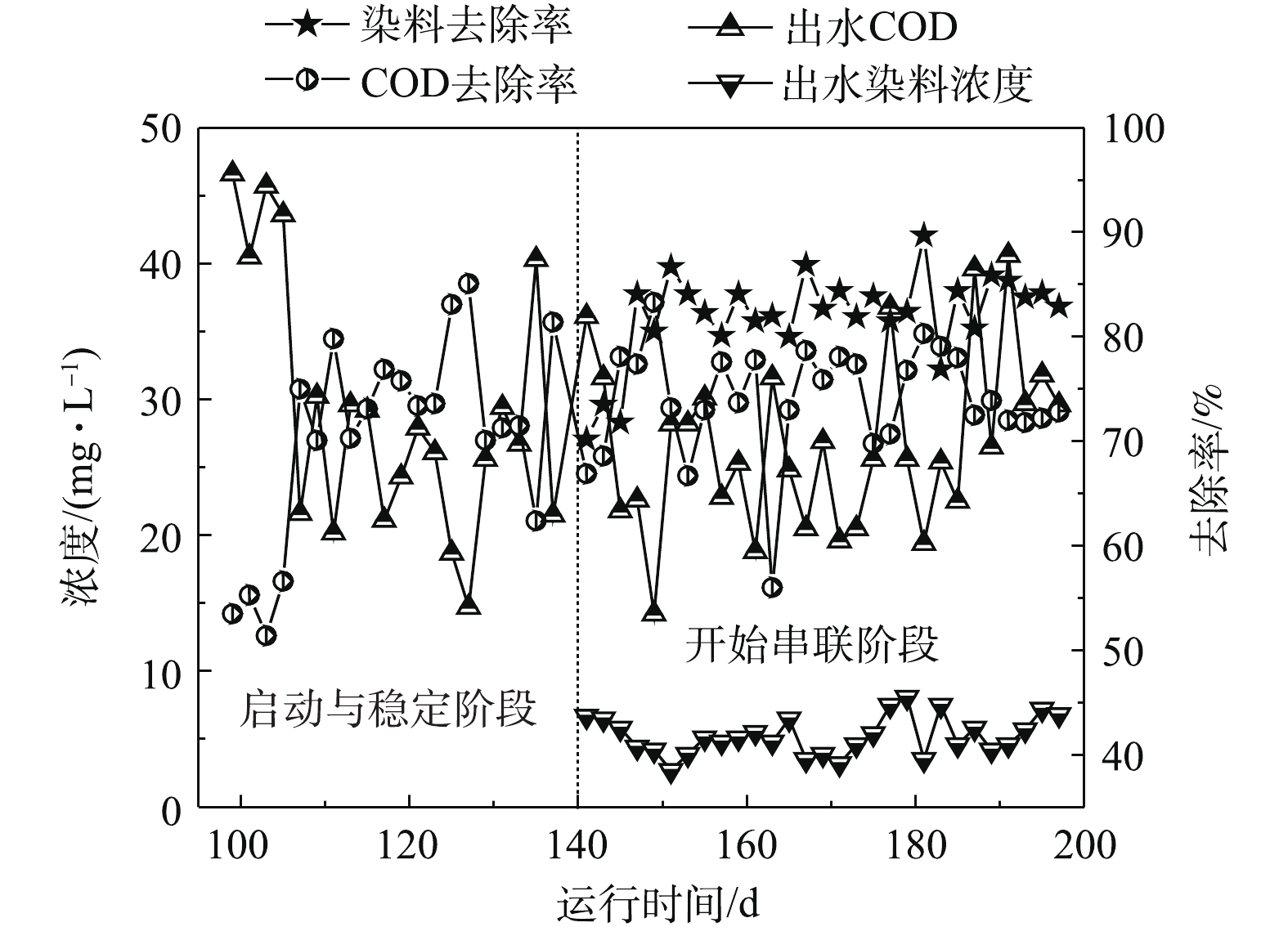
2) MBR-CANON反应器启动与运行。MBR-CANON反应器运行分为2个阶段。第1阶段为启动与稳定阶段,共运行140 d;第2阶段为与UASB串联阶段,共运行60 d,处理效果如图3~图6所示。在MBR-CANON反应器启动与稳定阶段,逐渐将反应器进水氨氮浓度由50 mg·L−1提高至100 mg·L−1,系统中生物量逐渐增多并且微生物逐渐适应水质。在第49天时,亚硝酸盐累积率增长至97%左右,此时亚硝化阶段出现并且趋于稳定。AOB比NOB的氧半饱和常数大,因此,在较低的溶解氧水平下,NOB难以和AOB竞争有限的氧气,从而抑制NOB活性。将反应器进水氨氮浓度提高为200 mg·L−1,此时反应器内溶解氧为0.2 mg·L−1左右,亚硝酸盐累积率逐渐下降,出水氨氮浓度持续降低,厌氧氨氧化反应逐渐出现,在第69天时,反应器总氮去除负荷达到0.15 kg·(m3·d)−1(大于0.10 kg·(m3·d)−1),标志着MBR-CANON反应器正式启动成功[21]。为了提高氨氮容积负荷,继续将反应器进水氨氮浓度提升至300 mg·L−1,反应器总氮去除率不断增高,到第140天时,总氮去除率最高达到91%,总氮去除负荷最高达到了0.29 kg·(m3·d)−1。为了强化MBR-CANON反应器去除COD的能力,在第99天时,开始向MBR-CANON反应器进水中加入100 mg·L−1淀粉。有研究[22]表明,加入少量COD并不会抑制AOB的活性,是因为反应器内COD过低或者溶解氧充足并未引起AOB和NOB对基质的竞争。而当C/N比为1.8~3.5时,AOB的活性将下降70%[23],本实验中也发现COD的加入并未抑制MBR-CANON反应器内AOB的活性。经过40 d运行后,反应器出水COD为29 mg·L−1左右,COD平均去除率最高达到85%以上。
MBR-CANON反应器运行140 d后,将UASB出水逐步添加至MBR-CANON进水中,正式进入UASB与MBR-CANON串联运行阶段。由图3可知,在第140天时,UASB出水接入MBR-CANON反应器后,微生物无法立刻适应进水水质的变化,导致其活性下降,反应器中总氮去除率和总氮去除负荷分别降到了约57%和0.18 kg·(m3·d)−1。在运行30 d后,增大反应器曝气量,使溶解氧升高,反应器内微生物逐渐适应进水水质条件,总氮去除率逐渐上升至82%以上。由图6可知,随着MBR-CANON反应器的不断运行,反应器出水COD平均值为26 mg·L−1左右,COD去除率缓慢上升并稳定在73%。MBR-CANON反应器对染料去除效果相对比较稳定,出水染料浓度平均为5 mg·L−1,染料的脱色率最高达到87%以上。
综上所述,在本实验条件下,接种厌氧氨氧化污泥的MBR-CANON反应器可在69 d内启动成功,并在140 d内达到稳定运行的状态,同时说明UASB/MBR-CANON串联工艺对高氮活性印花废水有良好的降解作用。
-
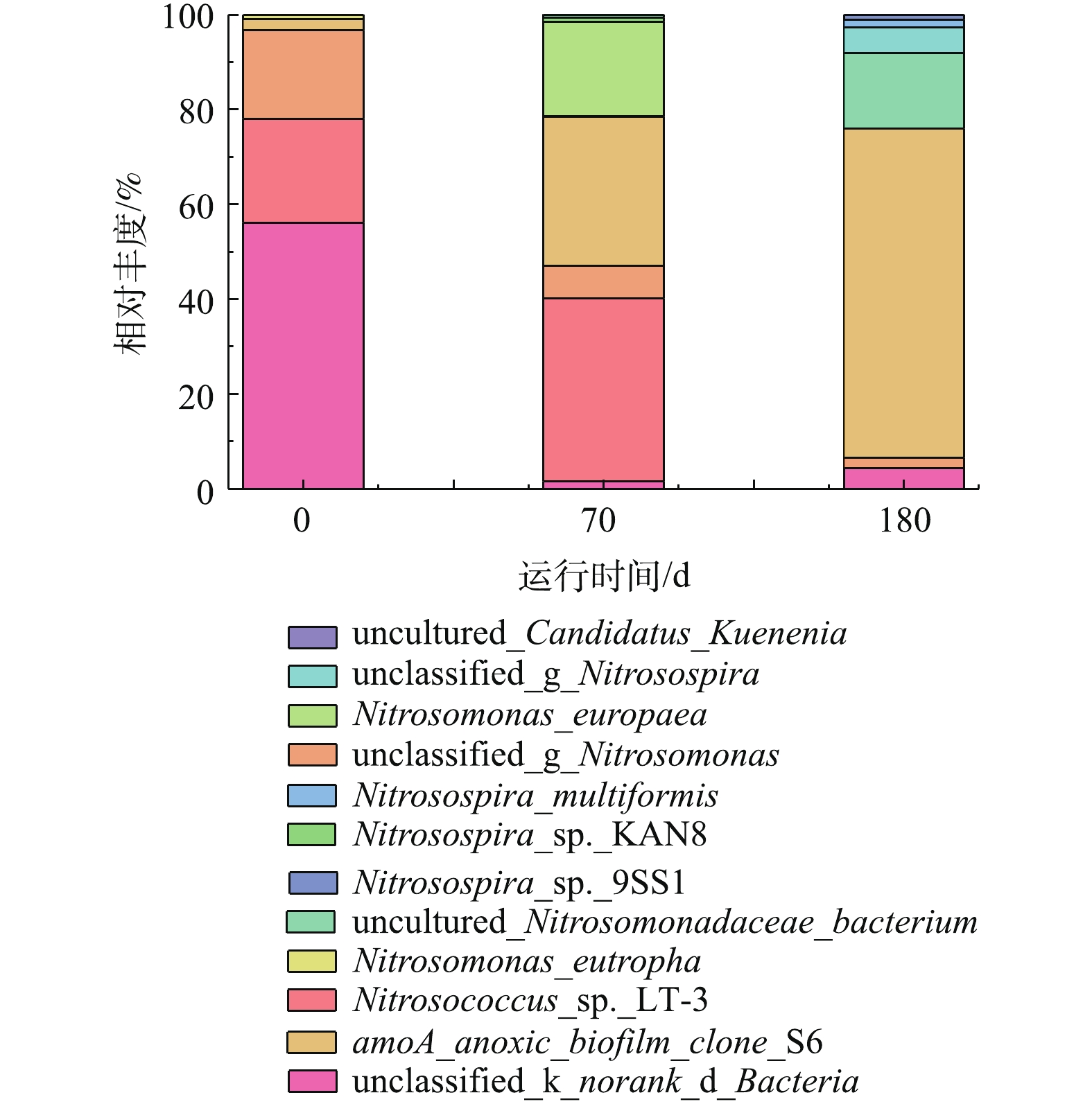
为了考察UASB/MBR-CANON串联工艺处理印花废水过程中MBR-CANON反应器中功能菌的种类及丰度变化情况,分别对反应器接种污泥、第70天和第180天污泥进行高通量测序,分析结果如图7所示。由图7可知,当MBR-CANON反应器启动成功后,亚硝化球菌的丰度由接种时的21.96%增长为38.54%,亚硝化单胞菌(Nitrosomonas_eutropha)的丰度由18.68%降为6.83%,同时出现了一种新的亚硝化单胞菌(Nitrosomonas_europaea,20%),说明随着反应器的运行,系统内亚硝化细菌种类和总相对丰度逐渐增多。此外,缺氧氨氧化菌[24](AmoA_anoxic_biofilm_clone_S6)的丰度由2.34%迅速增长到31.52%,同时出现了厌氧氨氧化菌(Candidatus_Kuenenia,0.001 9%),此时MBR-CANON反应器的脱氮效率在85%左右。这说明2种功能菌在脱氮中起着重要的作用,并且随着反应器的运行,功能菌种类也发生了变化。当UASB和MBR-CANON反应器串联运行稳定后,在第180天,测得系统内出现了大量的亚硝化螺旋菌,而亚硝化菌的总相对丰度逐渐降低。此外生物膜上生长的菌群中缺氧氨氧化菌(AmoA_anoxic_biofilm_clone_S6)和厌氧氨氧化菌(Candidatus_Kuenenia)的相对丰度分别增长至69.48%和0.32%,说明系统中起脱氮作用的氨氧化菌得到了增长。综上研究结果可知,在本研究条件下,印花废水中的污染物并未对系统内脱氮微生物的生长造成严重抑制。
-
为了进一步探究活性黄染料的降解途径,本研究对活性黄染料、UASB反应器出水和MBR-CANON反应器出水进行紫外-可见全波段(UV-vis)扫描,扫描结果如图8所示。由图8可知,活性黄染料有4个特征吸收峰,其中224 nm处为苯环结构吸收峰,254 nm处为三嗪吸收峰,288 nm处为萘环吸收峰,而424 nm处为偶氮双键吸收峰,偶氮双键是形成发色体的主要基团[25]。经过UASB反应器厌氧降解后,位于424、254和288 nm的吸收峰基本消失,说明提供色度的偶氮双键被打开,同时三嗪结构和萘环结构可能被破坏。位于224 nm的苯环吸收峰只是降低但并未消失,可能是由于染料本身结构中的苯环已经被破坏,但三嗪和萘环在厌氧条件下可降解为含有苯环结构的物质,因此,苯环吸收峰仍然存在。接着经过MBR-CANON反应器处理之后,吸收峰位置基本未发生变化但吸光度降低,其原因可能是因为MBR-CANON反应器内生物膜的吸附作用和膜组件的过滤作用使染料进一步截留。
-
图9反映了MBR-CANON反应器中胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances, EPS)中多糖和蛋白质浓度变化及膜通量的衰减情况。由图9可知,膜表面滤饼层EPS中多糖和蛋白质含量在第40天时分别为30.53 mg·L−1和3.70 mg·L−1,第80天为15.30 mg·L−1和6.06 mg·L−1,第180天时为52.14 mg·L−1和17.40 mg·L−1。以上结果表明,多糖和蛋白质含量在膜清洗后有所下降,但总体呈现上升趋势,这可能是因为EPS作为形成生物膜的重要组成部分[26],混合液中的浓度与污泥浓度成正相关关系,随着反应器中微生物的浓度不断升高,污泥混合液中多糖和蛋白质含量不断增加,分离过程中被膜表面截留并不断累积。
膜表面的EPS累积会造成膜通量的衰减[27],MBR-CANON反应器运行200 d期间,膜通量由最初5.79 L·(m2·h)−1衰减至0.96 L·(m2·h)−1,经过清洗后,膜通量可迅速恢复初始通量的80%~90%。同时由于较大的膜出水通量会加速膜污染,污泥容易堵塞膜孔,从而造成更严重的膜污染[28],因此,经过分析验证,本实验中将膜通量控制在6 L·(m2·h)−1以下,此时过滤阻力较小,可有效减缓膜污染。
2.1. UASB/MBR-CANON反应器的启动
2.2. 微生物多样性分析
2.3. 全波段扫描分析
2.4. MBR-CANON反应器膜污染分析
-
1) 采用逐渐提高COD容积负荷的方式启动UASB反应器,其在运行40 d后成功启动,印花废水中COD去除率最高可达到90%,染料的脱色率最高可达到88%;采用逐渐提高进水氨氮容积负荷的方式启动MBR-CANON反应器,其在运行69 d后成功启动,总氮去除率最高达到90%以上,总氮去除负荷最高达到0.29 kg·(m3·d)−1。
2) UASB/MBR-CANON串联运行后,该工艺处理活性印花废水总氮去除率达到70%以上,COD去除率和染料脱色率均达到90%以上。
3) 在MBR-CANON反应器处理活性印花废水过程中,功能菌AmoA_anoxic_biofilm_clone_S6的相对丰度由2.34%逐渐增高至69.48%,并且培养出了Candidatus_Kuenenia,其相对丰度增长至0.32%。
4) UASB/MBR-CANON反应器采用水力循环方式连续冲刷膜组件,经过清洗后,膜通量可恢复至原始通量的80%~90%,可有效减缓膜污染。



 下载:
下载: