-
负压排水技术因具有显著节水、便于污水分质回收利用,以及减少疾病粪口传播等优势,已被规模应用。然而,负压排水系统中的真空便器在使用过程中会产生较大的噪声,严重影响了用户使用体验[1-3]。这在一定程度上阻碍了真空便器在民用建筑中的进一步推广。
负压排水系统主要由负压排水终端、负压排水管网和真空泵站组成。不同于传统重力排水系统,其运输机制是用负压吸力代替重力,将服务区域内的污水输送、收集至中央真空站,之后进行集中处理[4-6]。该技术可应用于多种复杂情形,其管道铺设费用较低,可进行污水源分离并回收利用,对已硬化地面的破坏较小,在节水的同时具有很强密闭性而不易产生异味[7-11]。该技术已在较多领域实现应用,如医院、地铁站内排水,以及高铁、轮船和飞机卫生间排水[12-15]。真空便器是负压排水系统的一种终端,由真空界面阀、配套控制系统与便器组成[16-17]。真空便器在使用中的噪声比传统重力便器大[18]。传统便器在冲水时水流较慢,冲水过程仅混入少量空气。噪声主要为流体的噪声和结构振动噪声,约50~60 dBA[19-21],且在一次冲水的过程中噪音值较为平稳;而真空便器在抽吸时,会连接负压管道系统,污水在负压的抽吸下高速移动,同时会混入大量空气,气动噪声和高速水流造成的结构振动噪声较大,尤其是在界面阀打开和关闭的瞬间[22]。实际测量中,真空便器噪声最大值超过80 dBA,会严重影响用户的使用体验[18]。
ROSE等[18]对真空便器的噪声进行了表征,发现噪声能量为300~2 000 Hz,且在真空便器的一次完整冲洗过程中,其噪声声压级随时间发生较大波动;声压级存在几个较大的峰值,这些峰值比冲洗过程中其他时刻高出10~15 dBA,对使用者的使用体验影响最大。HUFENBACH等[23]研究了真空便器噪声的指向性,发现噪声最大的区域为便盆上方,其他位置噪声均较小;改进便盆底部和管道连接处的几何形状可减小噪声的大小;增加真空界面阀和真空便器之间的管道长度,增大管道的弯曲半径也可减少噪声峰值约10 dBA[22]。ROSE等[18]研究了在真空便器上加装约束阻尼层来降低真空便器噪声的方法,结果显示,阻尼层可使便器振动减弱,但在降低噪声上基本无效果。李静波[24]增加了便器的扩张室结构,可在一定程度上降低便器冲水噪声。梁海波[25]利用逆向工程及PRO/E二次开发技术对坐便器模型进行了构建,使便器性能提升的同时降低了噪声。然而,目前鲜有关于真空便器不同工作参数对其冲水噪声影响的研究。
真空便器冲水量和气液比的改变会影响抽吸时水流的流态。系统真空度升高,则便器抽吸速度会显著增大。这些因素均会影响真空便器产生的噪声强度。本研究通过改变真空便器系统的冲水量、气液比、真空度以及便器类型(坐便器和蹲便器),探究各种因素对真空便器噪声大小的影响,并提出相应参数调整建议,以期为提升用户的使用体验提供参考。
-
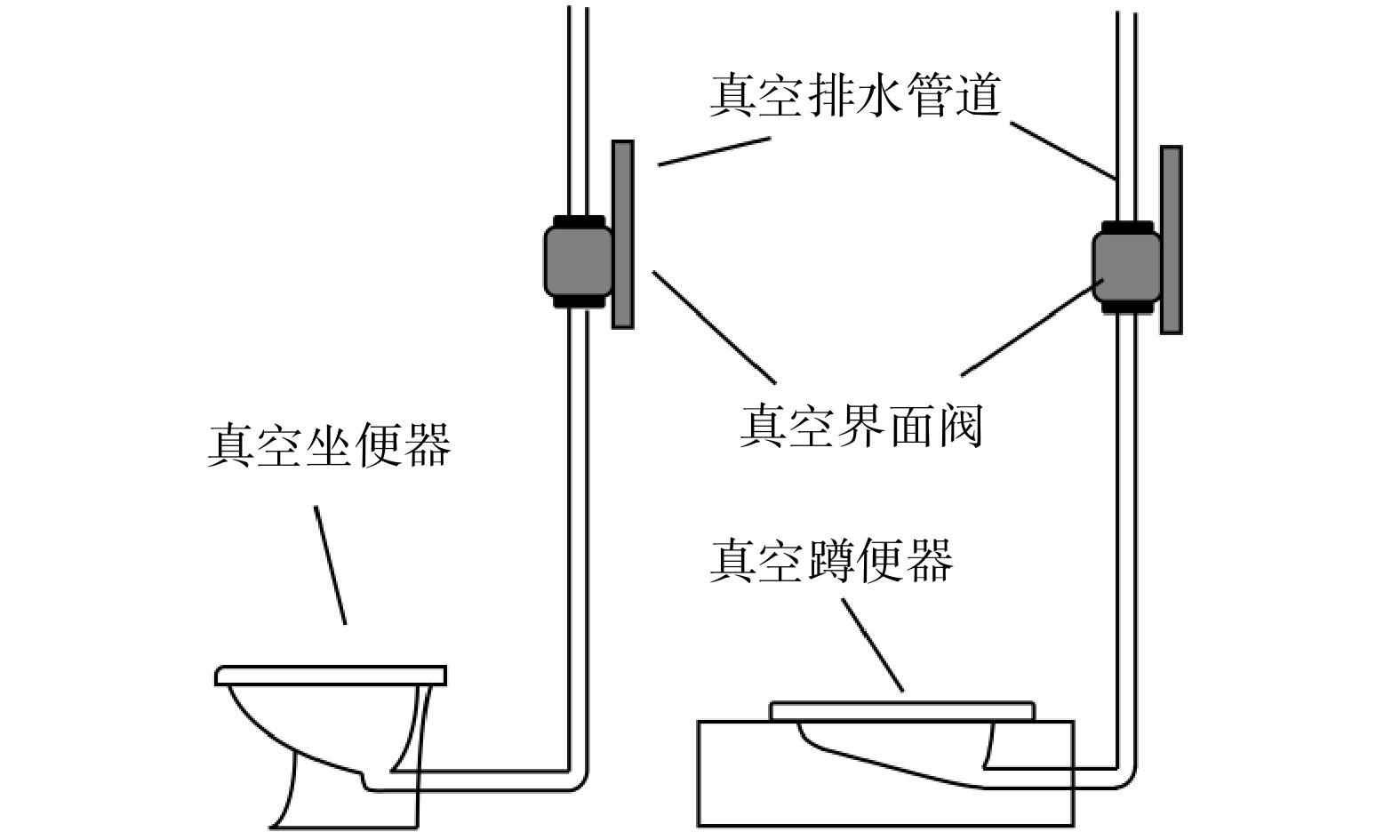
实验平台为山东中车华腾环保科技有限公司实验中心的负压排水系统。系统由BZ30D型真空机组电控柜、GLP2000-P51压力变送器、真空泵站、负压管道、末端洁具和末端控制柜组成。本研究使用的末端洁具为真空蹲便器和真空坐便器(见图1)。泵站与负压管道均安装压力变送器,用以记录一次冲洗过程中各个位置的实时真空度变化。
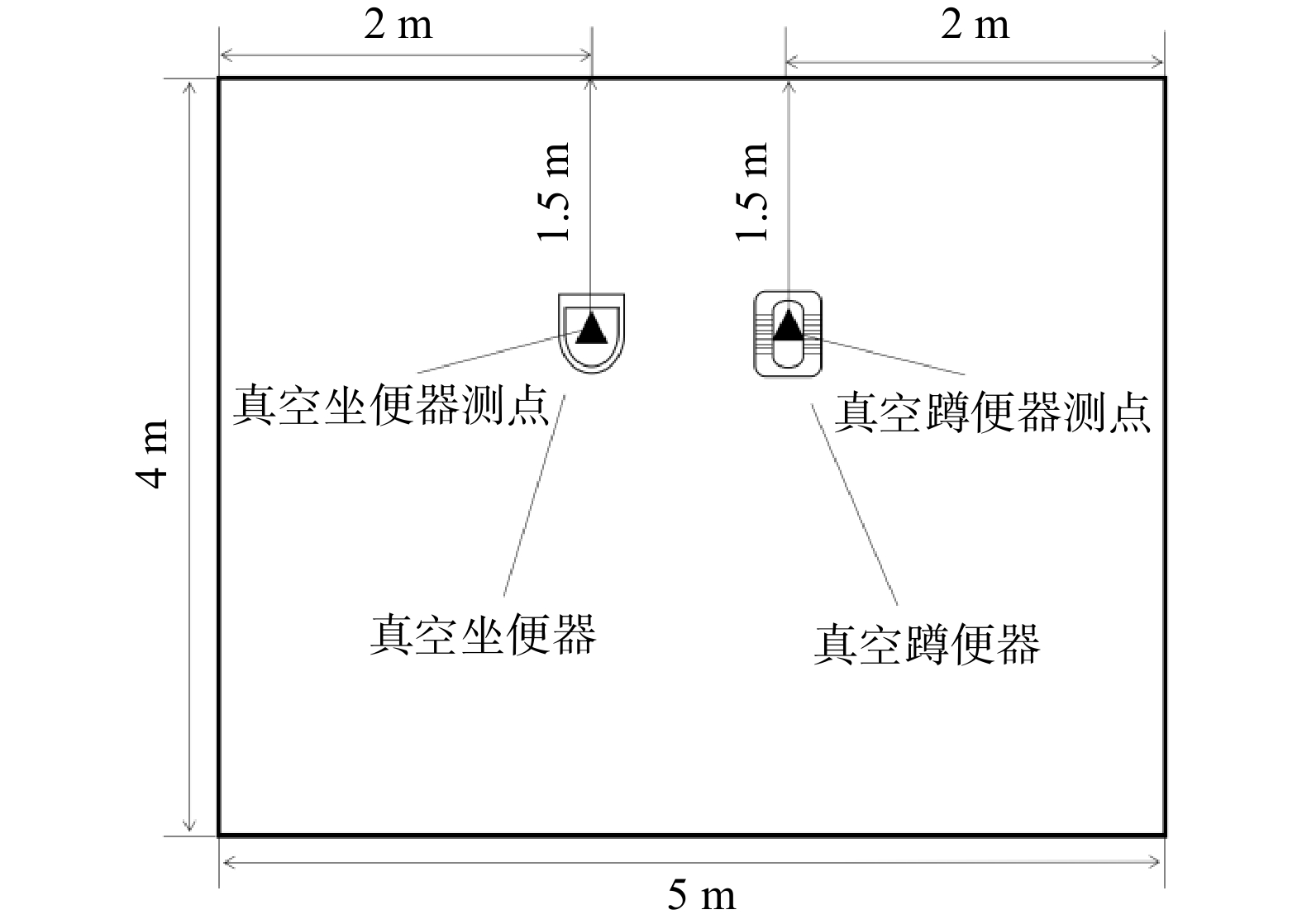
本研究使用的测试室长5 m、宽4 m、高2.8 m(见图2)。背景噪声为35 dBA,测量噪声声级高于背景值10 dBA以上,无需修正。真空便器均靠长边墙体1.5 m处安装,并位于墙体中间位置。测量点位于便器中心正上方1.6 m处。
-
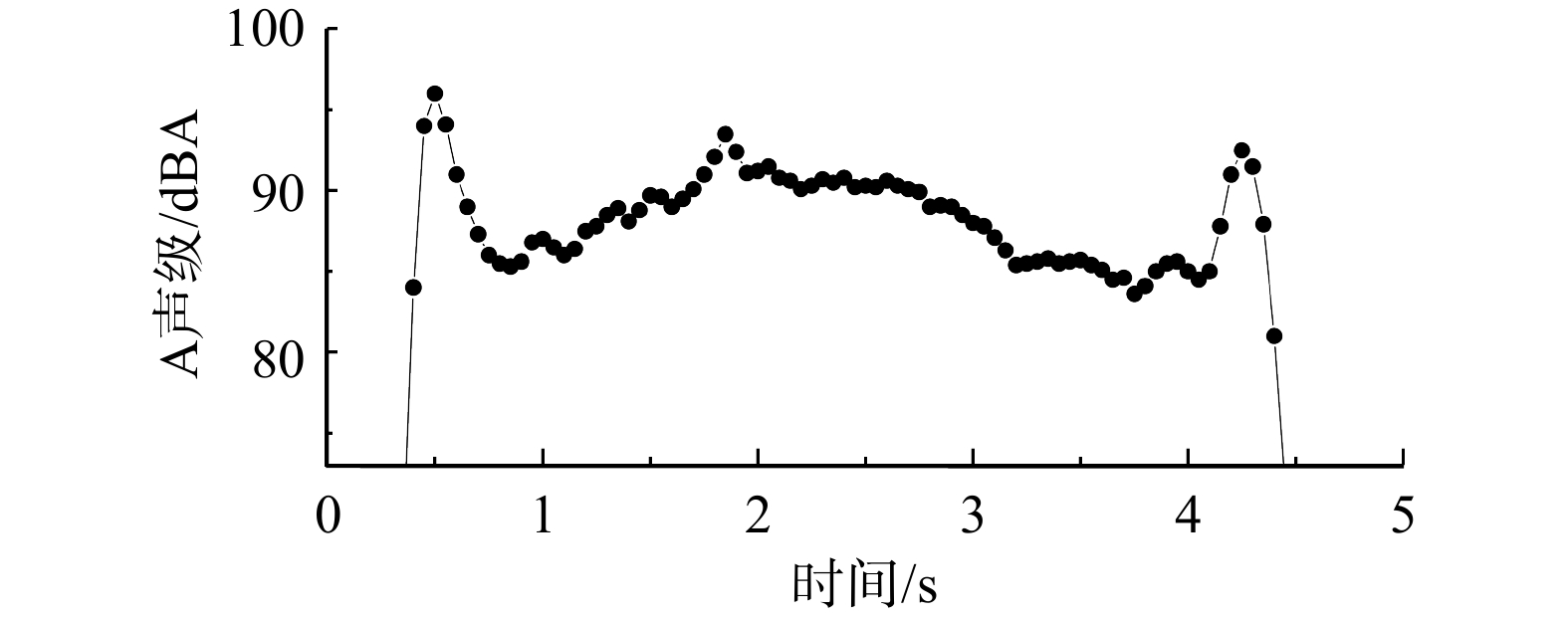
真空便器工作时首先将水阀打开开始冲水,冲洗水冲洗污物,将污物在便池中冲为悬浮状态;之后真空界面阀开启,将便盆连接真空管道系统,污水被抽走,此时水阀保持开启状态;污物被抽走后真空界面阀关闭,水阀继续冲水一段时间后关闭,以保证便盆有余水,防止臭气逸出,也可防止下次使用时污物黏在便器内壁上不易冲洗[16]。水阀在开启时间内排出的水量即为冲水量。图3为真空便器在冲水过程中的时域声级图,表明冲水过程中声压级较高且不稳定。
上述过程中,系统真空度、冲水量、气液比和便器类型等因素都对冲水噪声有直接影响。本研究通过改变上述参数来探究其对一次冲水过程中噪声大小的影响。本实验分别采用了真空蹲便器和真空坐便器。首先参照真空便器标准《铁道客车及动车组集便装置》(TB/T 3338-2013)[26] 进行便盆排污效果实验,以确定实验参数,保证所设置的实验参数均能达到良好的冲洗效果。结果显示,系统真空度低于−0.04 MPa、冲水量低于1.7 L、抽吸时间低于1.0 s时,无法达到排污效果标准。故本研究中真空便器的系统真空度分别设置为−0.04、−0.05、−0.06和−0.07 MPa。在一次冲水过程中冲水量和界面阀开启时间的设置参数见表1。水阀开启后,真空界面阀延后1 s开启以保证污物被冲洗为悬浮状态。真空界面阀关闭后,水阀继续冲水0.5 s保证便盆留有余水。实验分别设置水阀的开启时间为2.5、3.0、3.5和4.0 s。水阀流量为0.7 L·s−1,故冲水量分别为1.75、2.10、2.45和2.80 L;排泄阀开启时间设置为1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 s。通过记录真空泵站的压力传感器在一次冲洗过程中的初末值,结合整套系统的容积,利用理想气体状态方程计算出每次冲洗的进气量(常温常压)。进气量除进水量即可得到气液比[16]。
真空便器在一次冲水中噪声不稳定,噪声峰值处比冲洗过程中的其他时刻高10~15 dBA[18]。该峰值噪声对于使用者的使用体验影响较大。目前,国内针对真空便器的噪声测量标准仅有《铁道客车及动车组集便装置》(TB/T 3338-2013)[26],其对真空便器噪声的测量方法为测量真空便器上方1.6 m处的最大A声级(LAmax),其中坐便器须开盖测量。本研究便使用该测量方法。实验使用TES-1350A声级计,采用A计权,将RESPONSE选在MAX HOLD档,用来记录一次冲水过程中真空便器的最大A声级(LAmax),连续测量10次,最后取平均值。
-
图4反映了真空蹲便器和真空坐便器的噪声随冲水量的变化。对于不同类型真空便器和不同系统真空度,随着冲水量的增加,噪声整体均呈下降趋势。冲水量的增加对真空坐便器噪声的影响较大,可使噪声降低约5 dBA,但对真空蹲便器影响较小,仅降低1~2 dBA。冲水量的增加减少了进气量,空气的振动发出的声音减弱,同时大量的水也会对噪声的传播起到阻挡作用。同时,冲水量较低时冲洗效果会无法达到真空便器的相应标准,冲水量越大冲洗效果越好。因此,当真空便器噪声过大时,可适当增加冲洗水量减小便器噪声,还可提高冲洗效果。
-
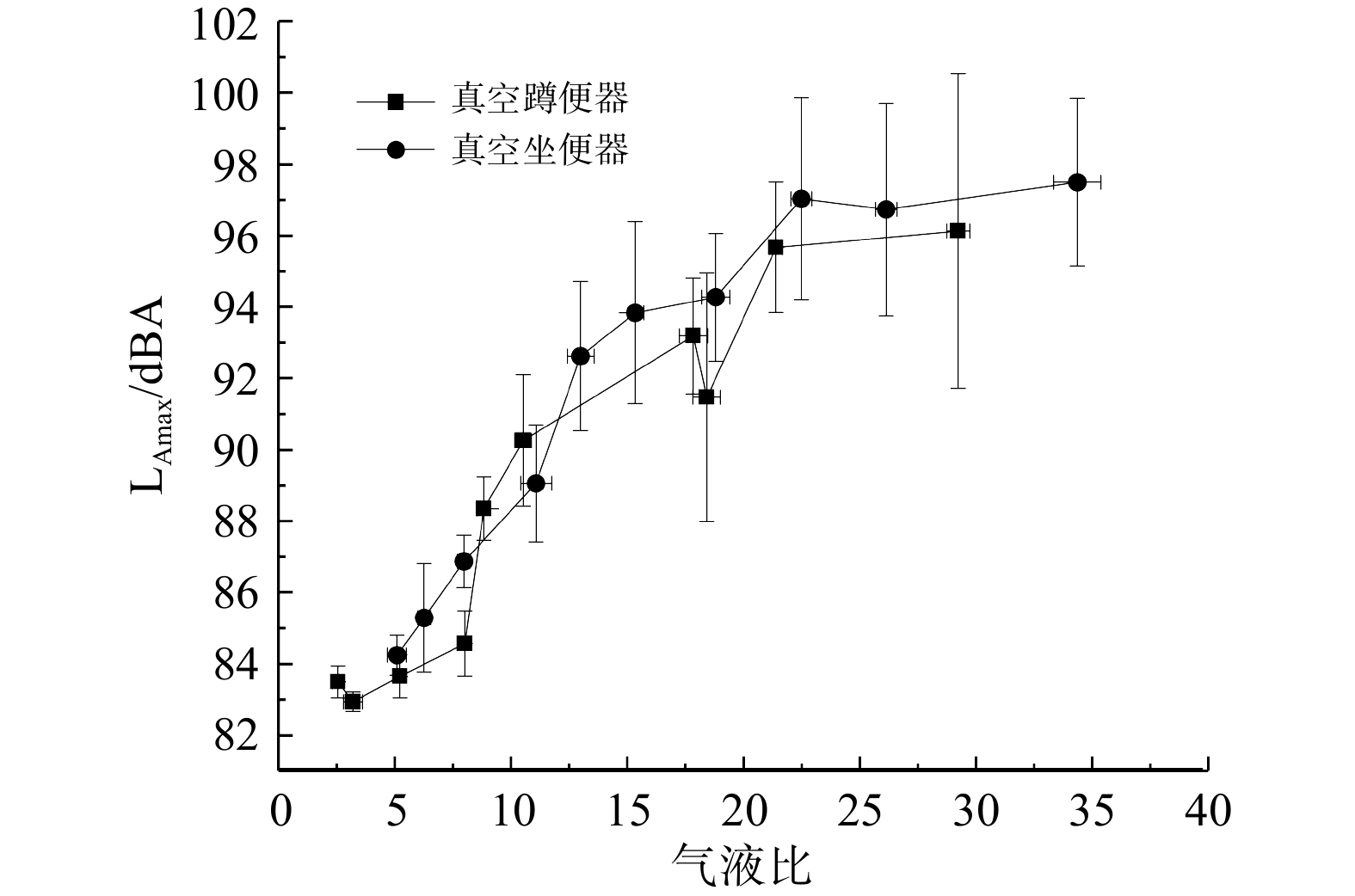
气液比即冲水过程中进气量与进水量的比值。该参数对真空便器的噪声影响较大。图5为系统真空度为−0.05 MPa时,不同气液比下真空蹲便器和真空坐便器噪声大小的变化。不论是真空蹲便器还是真空坐便器,噪声整体随气液比的增加而呈上升趋势。气液比高于23之后,噪声增加减少,趋于平稳。真空蹲便器和真空坐便器的气液比为29.2和34.4时,噪声分别达到了96.1和97.5 dBA。这是由于气液比的增加会导致空气的振动加剧,同时也引起结构振动。经实验发现,气液比低于2.5时,真空便器无法达到冲洗效果标准;气液比越高冲洗效果越好;当真空便器噪声较大时,可通过调整真空界面阀的开启时间和水阀的开启时间来减小气液比从而降低噪声,但气液比不可低于2.5。
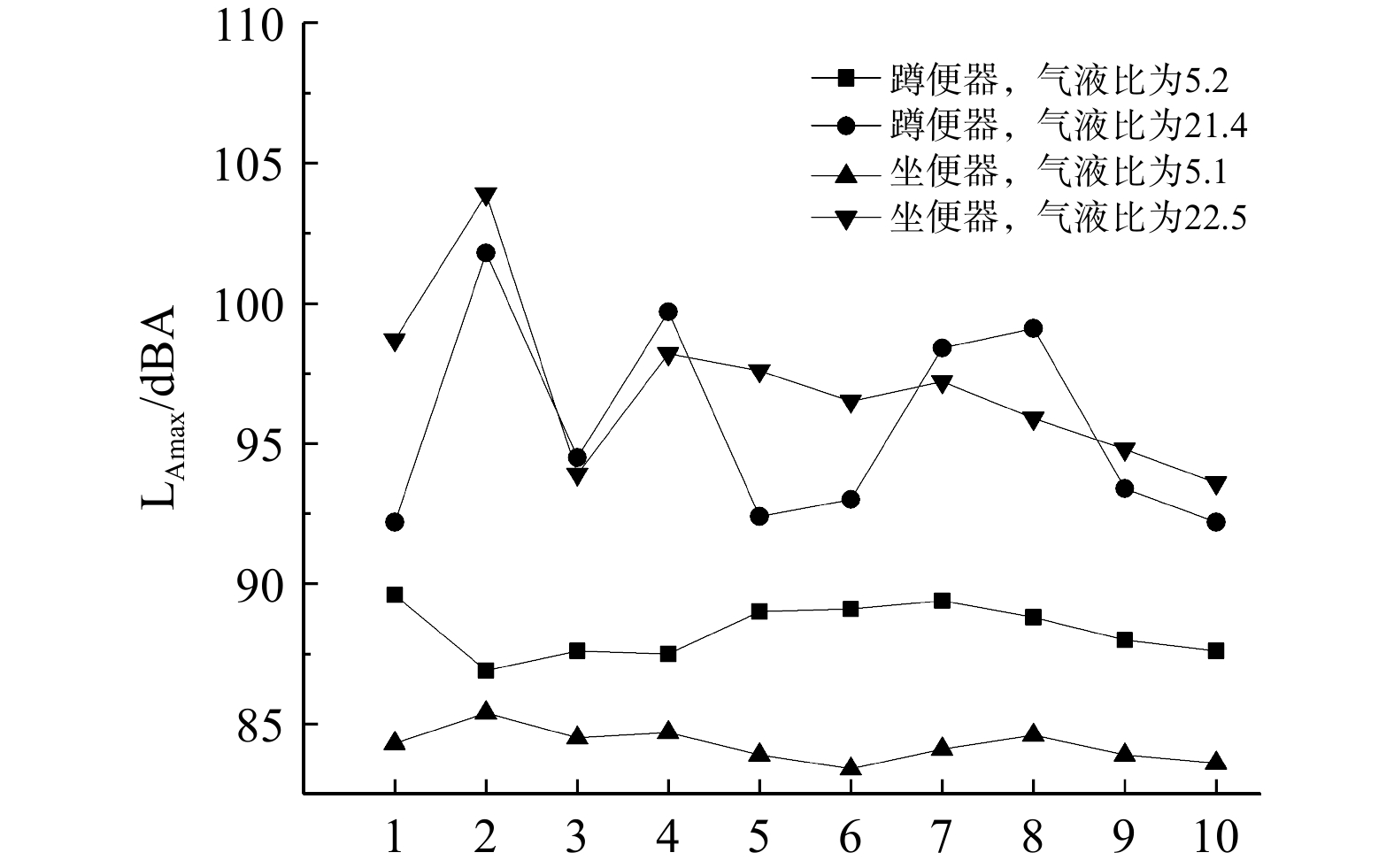
图5中噪声值为10次冲水的均值。在相同情况下,多次冲水噪声的标准偏差随着气液比的增大逐渐增大。这是由于空气量的增大会导致空气振动加剧,真空便器发出的噪声值不稳定,会出现较大波动。图6为在−0.05 MPa下,真空蹲便器的气液比为5.2和21.4、真空坐便器的气液比为5.1和22.5时,便器连续冲水10次的噪声值变化。无论是真空蹲便器还是真空坐便器,气液比越大,便器多次冲水发出的噪声值变化越大。真空蹲便器和真空坐便器的气液比分别为5.2和5.1时,连续冲水10次的噪声值对应的标准偏差仅为0.6和0.56 dBA,极差均为2 dBA;真空蹲便器和真空坐便器的气液比分别为21.4和22.5时,连续10次冲水噪声对应的标准偏差为3.49和2.82 dBA、极差为9.6和10.3 dBA。
-
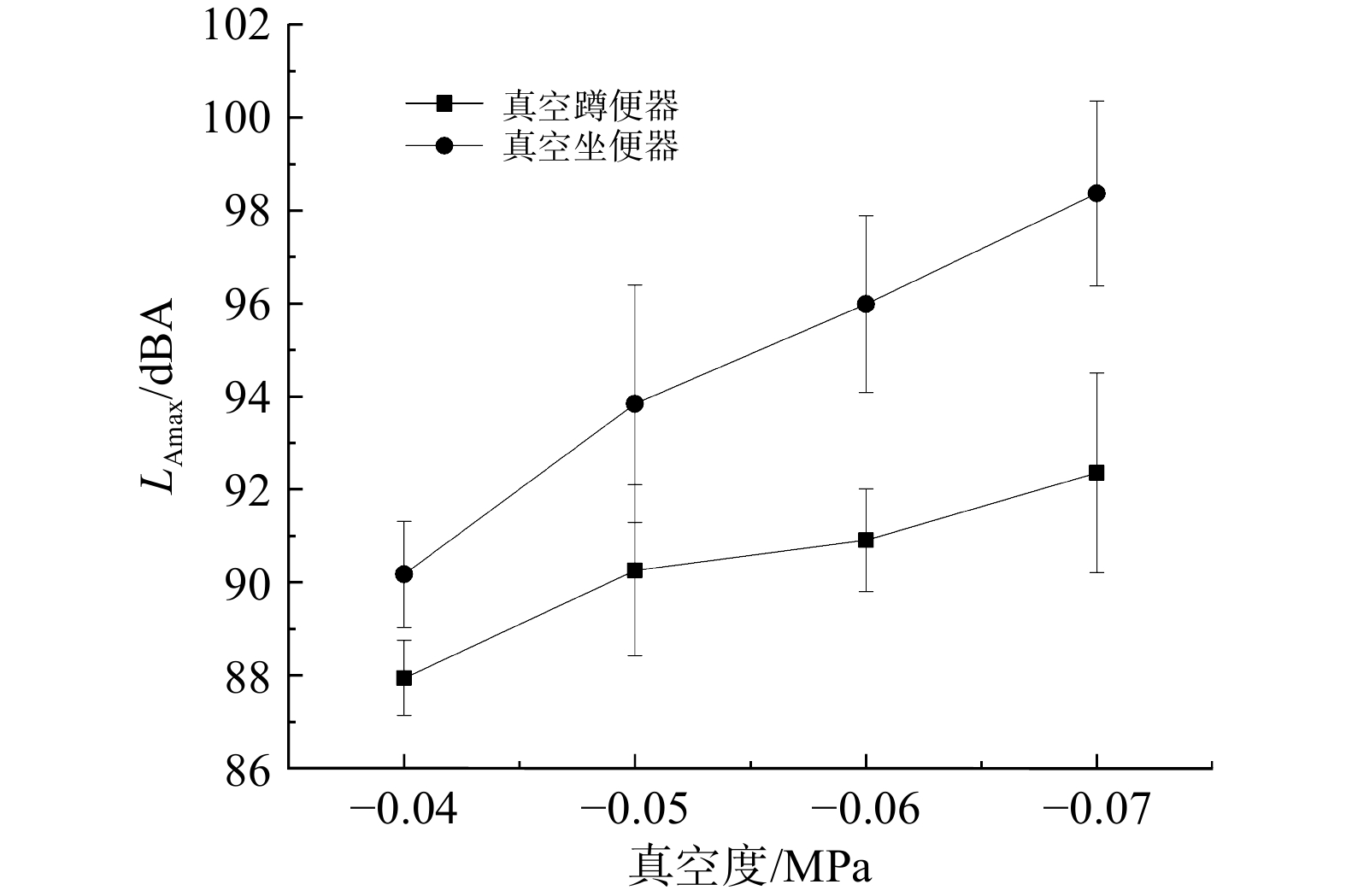
图7反映了随着系统真空度的改变,真空蹲便器和真空坐便器噪声大小的变化。无论是真空蹲便器还是真空坐便器,随着系统真空度的增加,噪声整体呈上升趋势,且多次冲水噪声的标准偏差也在逐渐变大。在系统真空度为−0.04 MPa时,真空蹲便器和真空坐便器噪声值分别为87.9和90.2 dBA;在系统真空度为-0.07 MPa时,真空蹲便器和真空坐便器噪声分别升至92.4和98.4 dBA。系统真空度的增大会导致真空界面阀开启时空气和水的流动速度增大[23],并增加空气的振动;同时,高速水流的冲击也会导致结构振动发声,故系统真空度的增大会提高冲洗过程的噪声值。在系统真空度低于−0.03 MPa时,冲洗效果将达不到真空便器标准,真空度越高冲洗效果越好。因此,当真空便器噪声较大时,建议可适当降低系统真空度,但不可低于−0.03 MPa。
-
以上结果表明,在同一系统真空度下,真空坐便器的噪声普遍高于真空蹲便器,且真空坐便器与真空蹲便器噪声的差值会随着系统真空度的增加逐渐变大,在系统真空度为-0.07 MPa时差值达到6 dBA。这是由于真空坐便器的喇叭形结构,使冲水时的噪声得到了进一步放大,并且真空坐便器冲水时四周旋入式冲水,便盆内的水会形成快速旋转的漩涡,加快了水流的速度;漩涡的中心直接连通真空管道加快了进气速度,导致振动加剧进而使得噪声变大[27-28]。又由于随着冲洗水量的增加,原本噪声值较高的真空坐便器将逐渐与真空蹲便器的噪声大小趋于一致。这是由于随着冲水量的增加,进气量将减小,空气振动造成的声音降低使坐便器与蹲便器噪声大小趋于一致。
将坐便器盖子盖上进行冲水,可比未盖盖时的噪声降低10 dBA。但真空便器依靠外界气压与内部低气压的压差来进行抽吸,盖上盖会影响界面阀等器件的稳定性。因此,可将传统盖子的结构进行优化,使便器盖子盖上时能顺利进入空气;同时,亦可通过改进坐便器便盆的喇叭状构造来降低坐便器噪声。
-
分别针对蹲便器和坐便器利用数学回归方法拟合了真空便器噪声与这些影响因素的定量关系。以噪声为因变量,真空度、冲水量、气液比为自变量,结合多元线性回归方程得到模型方程,见式(1)和式(2)。
式中:LAmaxd为蹲便器最大A声级,dBA;LAmaxz为坐便器最大A声级,dBA;V为冲水量,L;aatm为气液比;P为系统真空度,MPa。
模型参数如表2所示,蹲便器和坐便器模型的P值均小于0.01,确定模型具有预测价值。冲水量、气液比和真空度的P值均远小于0.01,故冲水量、气液比和真空度与真空便器噪声显著相关。即冲水量越少噪声越小,气液比越大噪声越大,系统真空度越低噪声越低。根据该模型中系统真空度、冲水量、气液比和噪声的定量关系,以及前文所述关于这些因素对于冲洗效果的影响,可得出当系统真空度为-0.04 MPa、冲水量为1.7 L、气液比为2.5时噪声最小。代入模型中得到此时真空蹲便器噪声值降为79.8 dBA,真空坐便器噪声值降为81.9 dBA,与实测值基本相同。
-
1)随着冲水量的增加,真空坐便器和真空蹲便器的噪声均呈下降趋势,冲水量的改变对真空坐便器噪声的影响更大。将冲水量降低1 L可分别使真空坐便器和真空蹲便器噪声最大值降低约5 dBA和1.5 dBA。气液比也对真空便器的噪声产生较大影响,且相对于冲水量,气液比对噪声的影响更大。随气液比的增加,真空便器噪声会显著增大。将气液比降低15可使噪声最大值降低约12 dBA。
2)随着系统真空度的增加,不论是真空蹲便器还是真空坐便器,噪声均变大。适当降低系统真空度也可在一定程度上起到降噪效果。将系统真空度调低0.03 MPa可减小真空便器噪声最大值5~8 dBA。
3)真空坐便器因便盆结构原因噪声高于真空蹲便器,高约5 dBA,且在一次冲水过程中,真空坐便器的进气量要高于真空蹲便器。
4)建立了冲水量、气液比和系统真空度与便器噪声的多元线性回归数学模型,并得出真空度设置为−0.04 MPa、冲水量为1.7 L、气液比为2.5时,真空便器的噪声最小。此时,真空蹲便器噪声值为79.8 dBA,真空坐便器噪声值为81.9 dBA。
负压排水真空便器冲水噪声的影响因素
Influencing factors of flushing noise of vacuum toilet with negative pressure drainage
-
摘要: 真空便器噪声问题是影响负压排水用户使用体验的重要因素。通过改变真空便器系统的冲水量、气液比、真空度等工作参数,探究了各因素对真空便器产生噪声大小的影响,并据此提出了参数调整建议。结果表明:增加冲水量可降低真空便器的噪声,且冲水量的改变对真空坐便器噪声的影响更显著,冲水量增加1 L可使真空坐便器噪声最大值降低约5 dBA;真空便器噪声随气液比的增大而增大,气液比降低15可使真空便器噪声最大值降低约12 dBA;系统真空度越高,真空便器噪声越大,将系统真空度调低0.03 MPa,可使真空便器噪声最大值降低5~8 dBA;在相同条件下,真空坐便器噪声高于真空蹲便器。建立了便器噪声与冲水量、气液比和真空度的定量关系模型,得出系统真空度为-0.04 MPa、冲水量为1.7 L、气液比为2.5时噪声最小。此时,真空蹲便器噪声最大值降为79.8 dBA,真空坐便器噪声最大值降为81.9 dBA,噪声得到显著降低。本研究可为降低负压排水真空便器的冲水噪声、提升使用体验提供参考。Abstract: The noise problem of vacuum toilet is an important factor affecting the user experience of negative pressure drainage. By changing the working parameters of the vacuum toilet system, such as flushing volume, gas-liquid ratio, and vacuum degree, the influence of various factors on the noise from vacuum toilet was investigated, and some parameter adjustment suggestions were proposed. The results showed that the noise from vacuum toilet could be reduced by increasing the flushing volume. The influence of the flushing volume on the noise of the vacuum sitting toilet was more significant effect. The maximum noise of the vacuum sitting toilet could be reduced about 5 dBA by increasing the flushing volume by 1 L. The noise of vacuum urinal increased with the increase of gas-liquid ratio, and the maximum noise of vacuum urinal decreased by 12 dBA when the gas-liquid ratio decreased by 15. The higher the vacuum degree of the system was, the greater the noise of the vacuum urinal was. The maximum noise of the vacuum urinal was reduced by 5~8 dBA when the vacuum degree of the system was reduced by 0.03 MPa. Under the same conditions, the noise of vacuum sitting toilet was higher than that of vacuum squatting toilet. The quantitative relationship model of toilet noise with flushing volume, gas-liquid ratio and vacuum degree was established. It was concluded that the minimum noise was obtained when the system vacuum degree was -0.04 MPa, flushing volume was 1.7 L and gas-liquid ratio was 2.5. At this time, the maximum noise of vacuum squatting toilet was reduced to 79.8 dBA and the maximum noise of vacuum sitting toilet was reduced to 81.9 dBA. This study can provide reference for reducing the flushing noise of vacuum urinal with negative pressure drainage and improving the use experience.
-
Key words:
- negative pressure drainage /
- vacuum toilet /
- noise /
- gas-liquid ratio /
- vacuum degree
-

-
表 1 实验参数设置
Table 1. Experimental parameter setting
冲水量/L 抽吸时间/s 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1.75 —— —— —— 2.10 —— —— 2.45 —— 2.80 注:“——”表示真空界面阀关闭后无额外时间补水,导致便盆内无余水,不再进行实验。 表 2 模型参数表
Table 2. Model parameters table
模 型 R R2 调整后
R2标准估算的错误 模型
显著性冲水量显著性 气液比显著性 真空度显著性 蹲便器模型 0.949 0.901 0.891 1.854 0.000 0.001 0.000 0.000 坐便器模型 0.913 0.834 0.819 2.244 0.000 0.001 0.000 0.001 -
[1] 张健, 李孟飞, 李萌, 等. 负压排水技术在乡村污水收集中的应用[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(22): 66-71. [2] PANFIL C, MIREL I, SZIGYARTO I, et al. Technical, economical, social and ecological characteristics of vacuum sewage system[J]. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 2013, 12(5): 1017-1122. doi: 10.30638/eemj.2013.125 [3] TERRYN I C, LAZAR G. Driving forces affecting the adoption of eco-innovation: A survey on vacuum sewer systems[J]. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 2016, 15(3): 589-598. doi: 10.30638/eemj.2016.064 [4] 赫明水, 王长祥, 吕杨, 等. 城市综合管廊真空排水系统模型试验及设计技术研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(24): 66-71. [5] GAO M, GUO B, ZHANG L, et al. Microbial community dynamics in anaerobic digesters treating conventional and vacuum toilet flushed blackwater[J]. Water Research, 2019, 160: 249-258. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.077 [6] MISZTA-KRUK K. Reliability and failure rate analysis of pressure, vacuum and gravity sewer systems based on operating data[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 61: 37-45. [7] 李亚惠, 朱仕坤, 李傲, 等. 农户庭院型生态工艺原位处理源分离后的洗涤废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(6): 2108-2117. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202101015 [8] 李厚禹, 蒯伟, 邵振鲁, 等. 新冠肺炎疫情对农村人居环境整治的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(7): 1579-1588. [9] 严巾堪, 刘晓龙, 王天聪, 等. 真空排水技术在老城区雨污分流工程中的应用[J]. 中国给水排水, 2021, 37(4): 51-55. [10] 李雪, 蒋靖坤, 王东滨, 等. 冠状病毒气溶胶传播及环境影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7): 3091-3098. [11] MULEC A O, MIHELIC R, WALOCHNIK J, et al. Composting of the solid fraction of blackwater from a separation system with vacuum toilets - Effects on the process and quality[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 112: 4683-4690. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.080 [12] 李旻, 徐江, 苏珊珊, 等. 室外真空排水技术在我国应用与发展的若干问题[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(16): 1-5. [13] MOHRA M, BECKETTA M, SCHLIEßMANNA U, et al. Vacuum sewerage systems-A solution for fast growing cities in developing countries?[J]. Water Practice & Technology, 2018, 13(1): 157-163. [14] 幸绍平, 宗法忠. B737NG飞机真空废水排放管路再循环法清洁[J]. 西安航空学院学报, 2014, 32(1): 19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9233.2014.01.005 [15] 温静, 刘勇, 许壮莹, 等. 真空技术在医院排水提升改造中的应用[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2020, 40(3): 262-266. [16] 周敬宣, 李旻. 真空排水系统的原理与设计 [M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2013: 19-21. [17] 王柏和, 王祝, 毕博, 等. 真空技术在钻井平台生活污水收集中的应用[J]. 设备管理与维修, 2019(12): 142-145. [18] ROSE M T, KILTS J F, GEE K L, et al. Noise control of a vacuum-assisted toilet: structural vibration damping//The Acoustical Society of America[J]. 175th Meeting of Acoustical Society of America 2018, Minneapolis, America, 2018: 3aEAa6. [19] 黎巍, 刘子建, 李静波. 基于扩张室消声器的座便器噪声控制研究[J]. 应用声学, 2008, 27(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-310X.2008.01.001 [20] STEWARTND N D. An experience reducing toilet flushing noise reaching adjacent offices[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2011, 129(4): 2605-2605. [21] RYU J, SONG H. Comparison between single-number quantities for rating noises from sanitary installations in residential buildings by objective and subjective methods[J]. Building and Environment, 2019, 164: 106378. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106378 [22] ROSE M T, PIELSTICK B D, JONES Z T, et al. Case study: Noise reduction of a vacuum-assisted toilet[J]. Noise Control Engineering Journal, 2020, 68(4): 294-302. doi: 10.3397/1/376825 [23] HUFENBACH W, DANNEMANN M, KOLBE F, et al. Silent aircraft toilets - different concepts for reducing the sound emission[J]. Heverlee:Katholieke Univ Leuven, Dept Werktuigkunde, 2008: 102-112. [24] 李静波. 扩张室消声器在座便器噪声控制中的应用研究 [D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2007. [25] 梁海波. 逆向工程及PRO/E二次开发技术在坐便器中的应用研究 [D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2010. [26] 济南轨道交通装备有限责任公司, 山东华腾环保科技有限公司, 长春轨道客车股份有限公司. 铁道客车及动车组集便装置TB/T 3338-2013 [S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2013. [27] DAVIES H G, WILLIAMS J. Aerodynamic sound generation in a pipe[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1968, 32(4): 765-778. doi: 10.1017/S0022112068001011 [28] 张鸿煜. 闸前漩涡特性及影响因素试验研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018. -



 下载:
下载: