-
啤酒废水是一种高浓度有机废水,主要污染物为高浓度的糖类、醇类等有机物,COD、BOD5浓度分别为1 000~2 500、600~1 500 mg/L[1],如果不经处理,直接排入自然水体会消耗大量的溶解氧,造成严重的环境污染。我国的啤酒产销量已连续多年位居世界第一[2],啤酒在酿造和罐装等过程中会产生大量废水,我国每年啤酒废水总量可达2.5亿t。啤酒废水处理通常采用厌氧与好氧结合[3]、水解酸化-接触氧化[4]、UASB[5]等工艺,这些工艺可有效地去除废水中的污染物,但会产生大量的剩余污泥,增加下游剩余污泥处置费用。因此,找到一种既可以高效去除啤酒废水中的高浓度有机污染物,又可以实现污染物资源化回收的工艺具有非常重要的现实意义。
光合细菌(Photosynthetic Bacteria,PSB)是一种广泛分布于水、土壤和活性污泥等自然和人工环境的原核生物,可以利用光能和各种碳氮源生长[6]。PSB能够耐受较高的有机负荷,并能实现多种废水中污染物的生物资源化[7],现已在大豆加工[8]、淀粉发酵[9]、养殖业[10]和啤酒生产等行业废水处理中成功应用。袁盈波等[11]从养殖场底泥中分离出一株外硫红螺菌,其对畜禽废水和鱼粉废水中硫化物去除率分别为68.55%和56.15%。戴晓等[12]利用Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides Z08探讨不同光氧条件下啤酒废水的资源化应用。
本文利用1株具有污染物同步去除能力的厌氧光合细菌Ectothiorhodospira sp. SU6,通过调节初始碳源和氮磷含量等参数优化其对模拟啤酒废水中污染物的去除与光合细菌生物质的回收,同时进一步探索了Ectothiorhodospira sp. SU6的潜在功能性,为啤酒废水的处理和资源回收提供新的选择。
全文HTML
-
实验菌种外硫红螺菌 Ectothiorhodospira sp. SU6(KX619404)是1株具有多种污染物的同步去除能力的严格厌氧光合细菌[13],现保存于东北大学环境分子生态学实验室。
-
实验用水参考实际啤酒废水污染物组成,以雪花啤酒稀释后配制,COD、TN、TP浓度分别为1 000~4 500、20~21和1~2 mg/L [14]。菌株SU6对模拟啤酒废水的处理能力和对回收细胞生物量的影响通过批次实验探讨。
种子培养基(乙酸钠 1.0 g/L、谷氨酸钠 1.0 g/L、NH4Cl 1.0 g/L、琥珀酸钠 1.0 g/L、NaHCO3 1.0 g/L、KH2PO4 0.5 g/L、K2HPO4 0.5 g/L、MgCl 0.2 g/L、CaCl 0.08 g/L、NaCl 0.1 g/L、FeSO4·7H2O 0.012 g/L、EDTA-Na2 0.1 g/L、L-半胱氨酸 0.5 g/L)和模拟啤酒废水经分装后,通入高纯氩气3 min以排除残余的氧气,用橡胶塞封瓶保证厌氧环境,121 ℃高压灭菌20 min后静置待用。
单因素条件实验在100 mL厌氧瓶中进行,每个厌氧瓶含50 mL培养基,5%(VSU6/V废水%)接种对数期种子液,初始pH=8.0,2 000 lux光照,30 ℃,120 rpm恒温振荡培养,每个实验设置3组平行实验。
1)最优初始COD条件实验:模拟啤酒废水COD浓度分别为1 000、2 000、3 000和4 500 mg/L,NH3-N浓度50 mg/L、磷浓度0 mg/L;
2)最优初始NH3-N浓度实验:根据最佳初始COD浓度配置模拟啤酒废水,NH3-N浓度分别设置为0、50、100、150和200 mg/L,其余条件同上;
3)最优初始TP浓度实验:根据最优初始COD和NH3-N浓度配置啤酒废水,并添加磷酸盐,TP梯度为0、40、80和120 mg/L,其余条件同上;
上述所有条件实验均以空白培养基为对照,每24 h测定菌液OD600值,96 h取样测定培养基的COD、NH3-N和TP变化。
-
水中CODCr、NH3-N、TP和细胞生物量均采用国家标准的分光光度法测定[15]。其中CODCr、NH3-N和TP分别采用:快速消解法、纳氏试剂法和钼酸铵法,生物量以波长600 nm时的菌液光密度值(OD600)计算,未接种液体培养基为空白对照。
1.1. 菌种来源
1.2. 实验方法
1.3. 检测方法
-
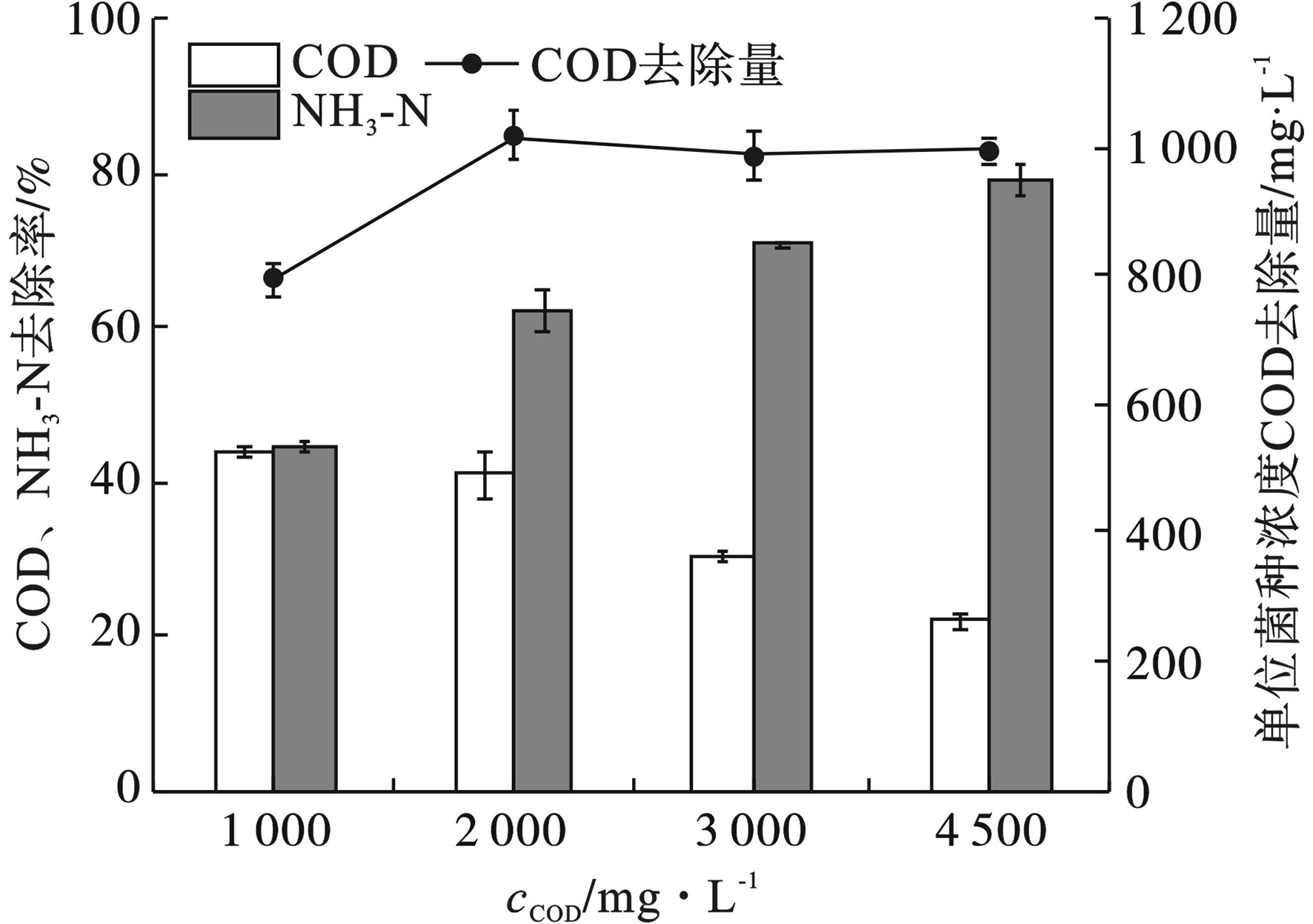
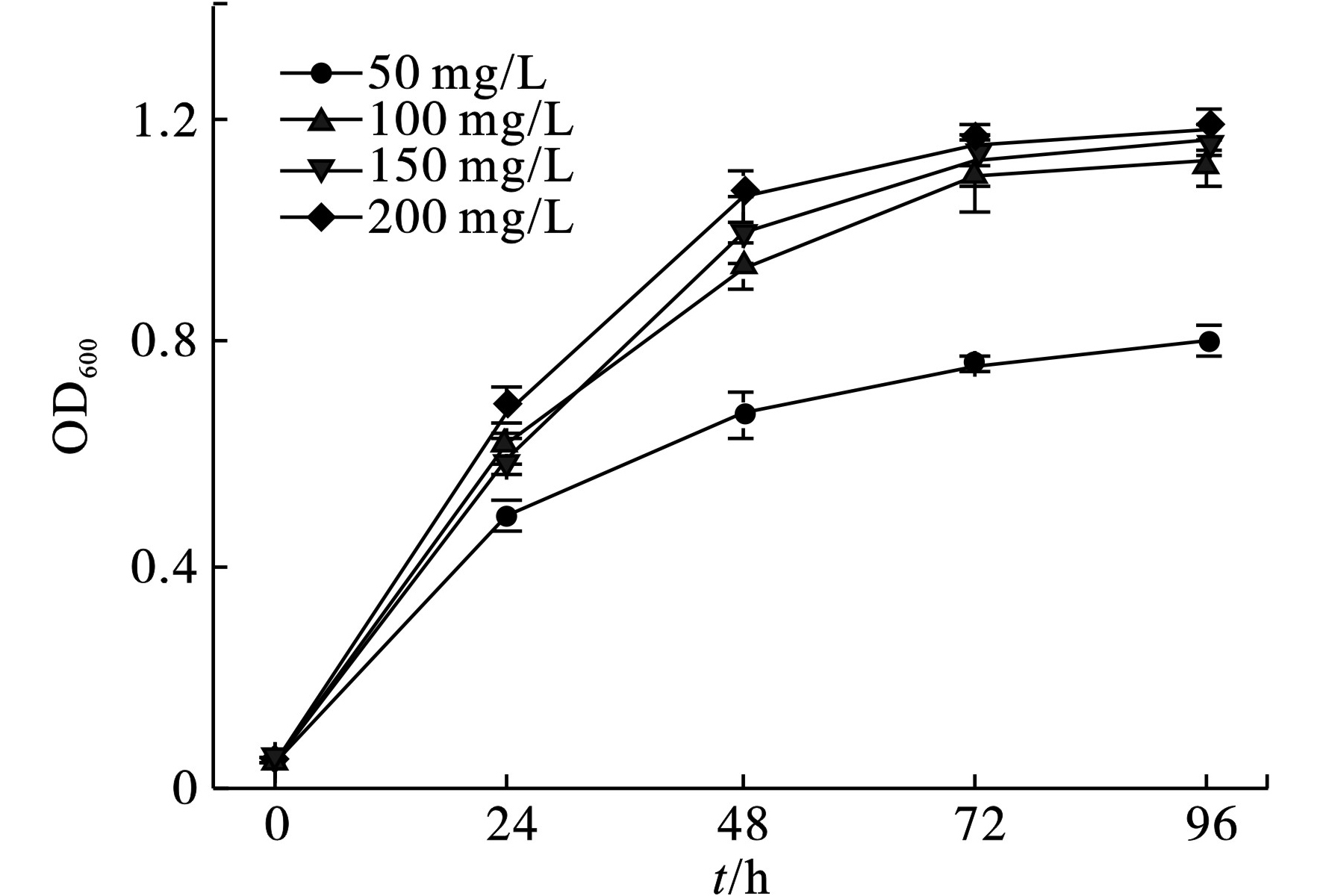
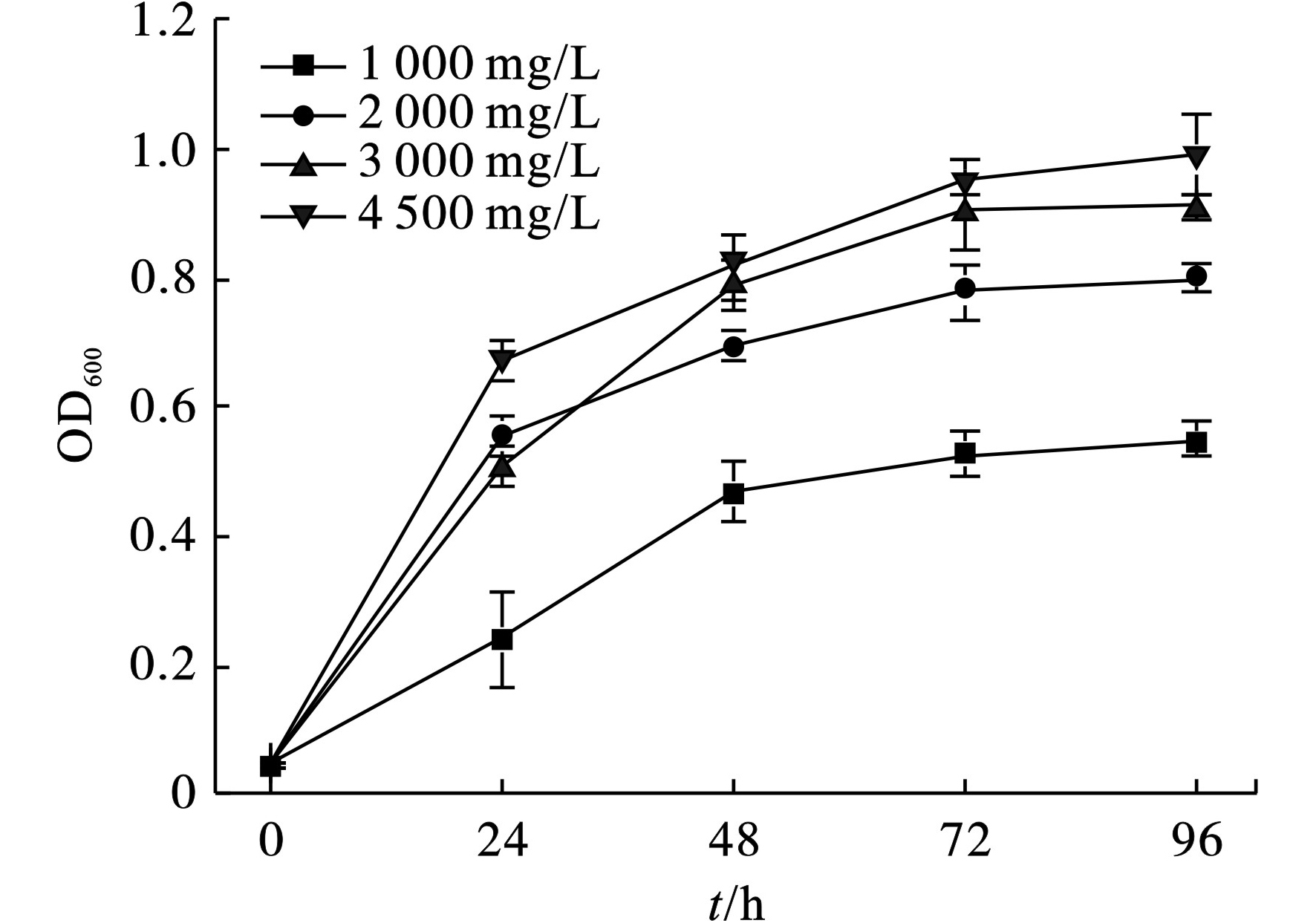
菌株SU6在COD浓度为1 000~4 500 mg/L的培养基中均可迅速生长,见图1。
菌株SU6在前24 h生长速率较快,但是,随着时间的延长,生长速度趋缓,72 h后均进入生长稳定期。在初始COD浓度为3 000和4 500 mg/L时,菌株SU6的细胞生物量较为接近。初始COD浓度为4 500 mg/L时,菌株长势最佳,OD600值为1.00,培养96 h的细胞生物量是COD为1 000 mg/L时的1.82倍。
污染物的去除情况,见图2。
图2可见,随着初始COD浓度增加,菌株SU6对NH3-N的去除率逐渐升高,而对COD的去除率则在20%~45%之间,且整体呈下降趋势。当COD浓度为4 500 mg/L时,细菌SU6的生长状态最佳,增长速度最快,细胞生物质回收量最高,NH3-N去除率为79.1%,但COD去除率低,模拟啤酒废水中剩余大量有机物未能被光合细菌利用。通过计算,在初始COD浓度为2 000 mg/L时,单位细胞生物量对COD的去除效率最高,为1 013.34 mg/L。
模拟废水的组分对菌株SU6的生长和处理效率会产生一定的影响。本研究中,啤酒废水负荷过高,其中残存的乙醇等物质会对光合细菌的生长产生抑制作用,影响细胞生物量的回收。WU et al[16]和ZHOU et al[17] 利用光合细菌处理淀粉发酵废水和制糖废水,此类废水组分更适于光合细菌生长,COD的平均去除率超过60%,最高达95%。另外,啤酒废水C/N/P比例失衡会导致细菌活性下降、生物质回收量降低。虽然增加碳氮比例可以同时提升NH3-N的去除率和光合细菌回收量,但是会导致COD去除效率明显降低。因此,菌株SU6处理模拟啤酒废水的最适初始COD为2 000 mg/L,去除率为40.8%,菌株SU6的OD600值为0.80。
-
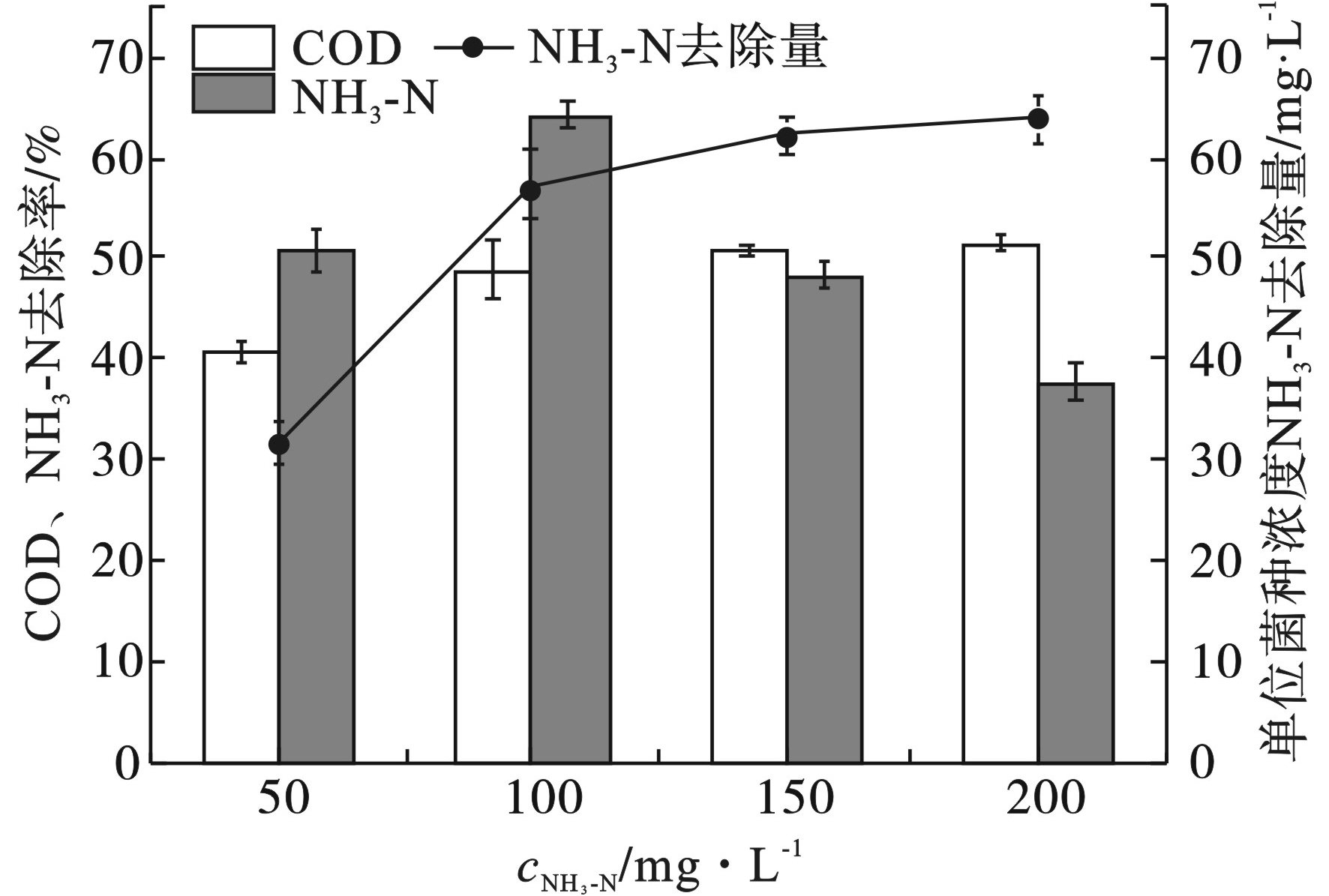
实验证明,额外添加氮源可以促进菌株SU6的细胞生物量增长,并能够提高对COD的去除率,见图3和图4。
图3和图4可见,当NH3-N浓度由50 mg/L增加至100 mg/L时,细胞生物量明显提升,96 h内菌株SU6的OD600由0.80增至1.12,COD的去除率由40.7 %提升至48.8 %,单位细胞生物量对NH3-N的去除率迅速增加。在NH3-N浓度由100增至200 mg/L的过程中,菌株SU6的生物量没有明显增长,COD去除率基本不变,但NH3-N去除率下降,模拟啤酒废水中剩余较多NH3-N未被去除,单位生物量去除NH3-N率没有明显增加,最高为63.87 mg/L。
YANG et al[18]研究发现PSB的氮代谢途径不同于传统处理途径,NH3-N可能被直接氧化为N2或N2O,具备突破现有技术局限性的可能。何春华[6]研究发现C/N比过高或过低均不利于光合细菌生长。本实验额外添加氮源改善C/N比例,有效改善了菌株SU6的生长,提高了啤酒废水的COD去除效率。当添加NH3-N浓度过高时,细胞生物量虽增加,但COD去除率并没有得到提升。因此,光合细菌SU6处理啤酒废水最佳NH3-N浓度为100 mg/L,细胞生物量OD600值为1.12。
-
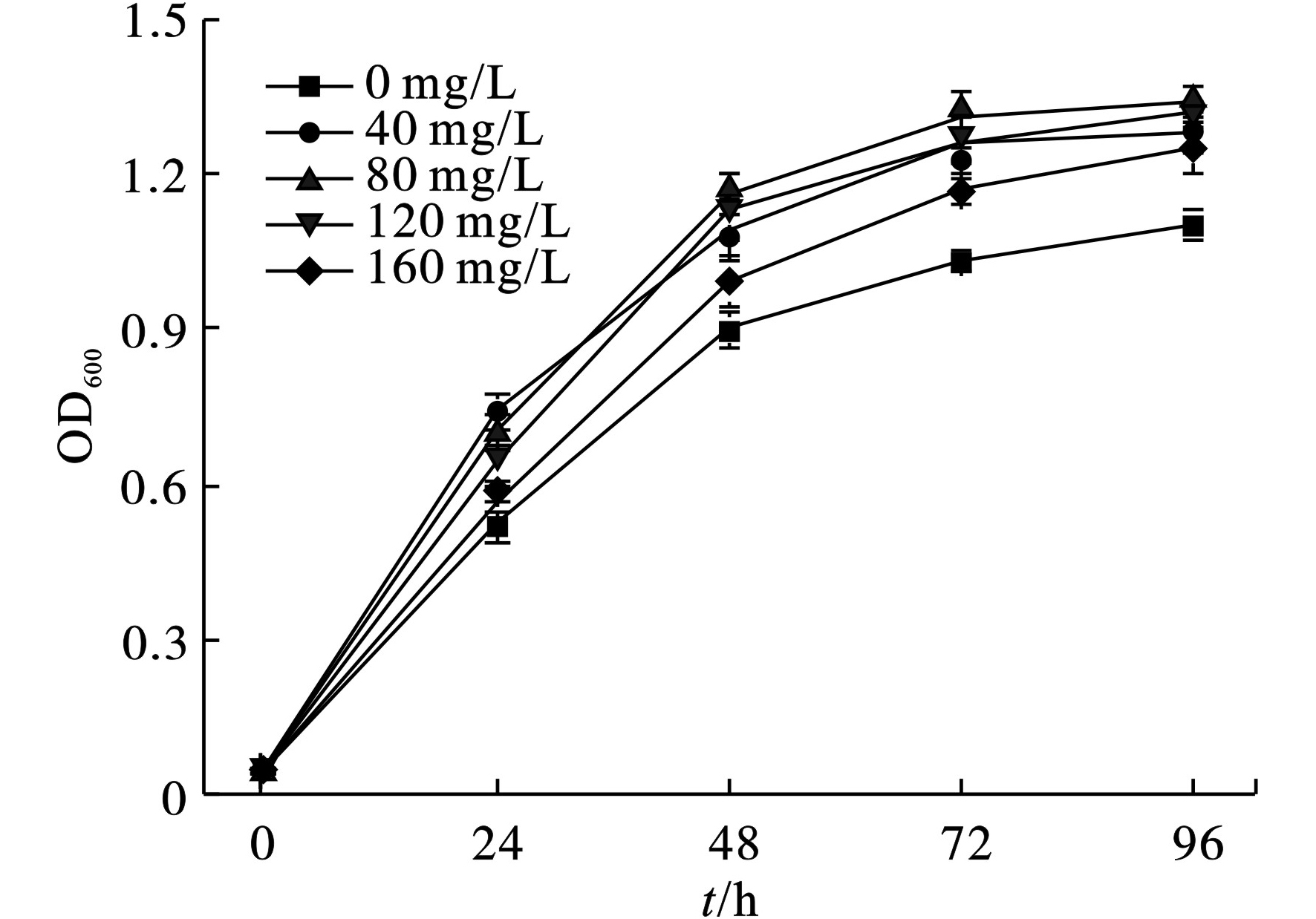
实验表明,光合细菌SU6在没有磷源的培养基中可以正常生长,适当补充磷源可以促进细菌的生长,见图5。
图5可见,在不同浓度磷源培养条件下菌株SU6的生长趋势较为接近,培养72 h后光合细菌均进入稳定期。额外添加40~160 mg/L磷源,均可以略微提升菌株SU6的细胞生物量,实验结束时,添加80 mg/L磷的实验组获得细胞生物量最大值OD600=1.34,较空白对照提高1.21倍。当磷浓度高于80 mg/L时,菌株SU6的生长开始受到抑制。
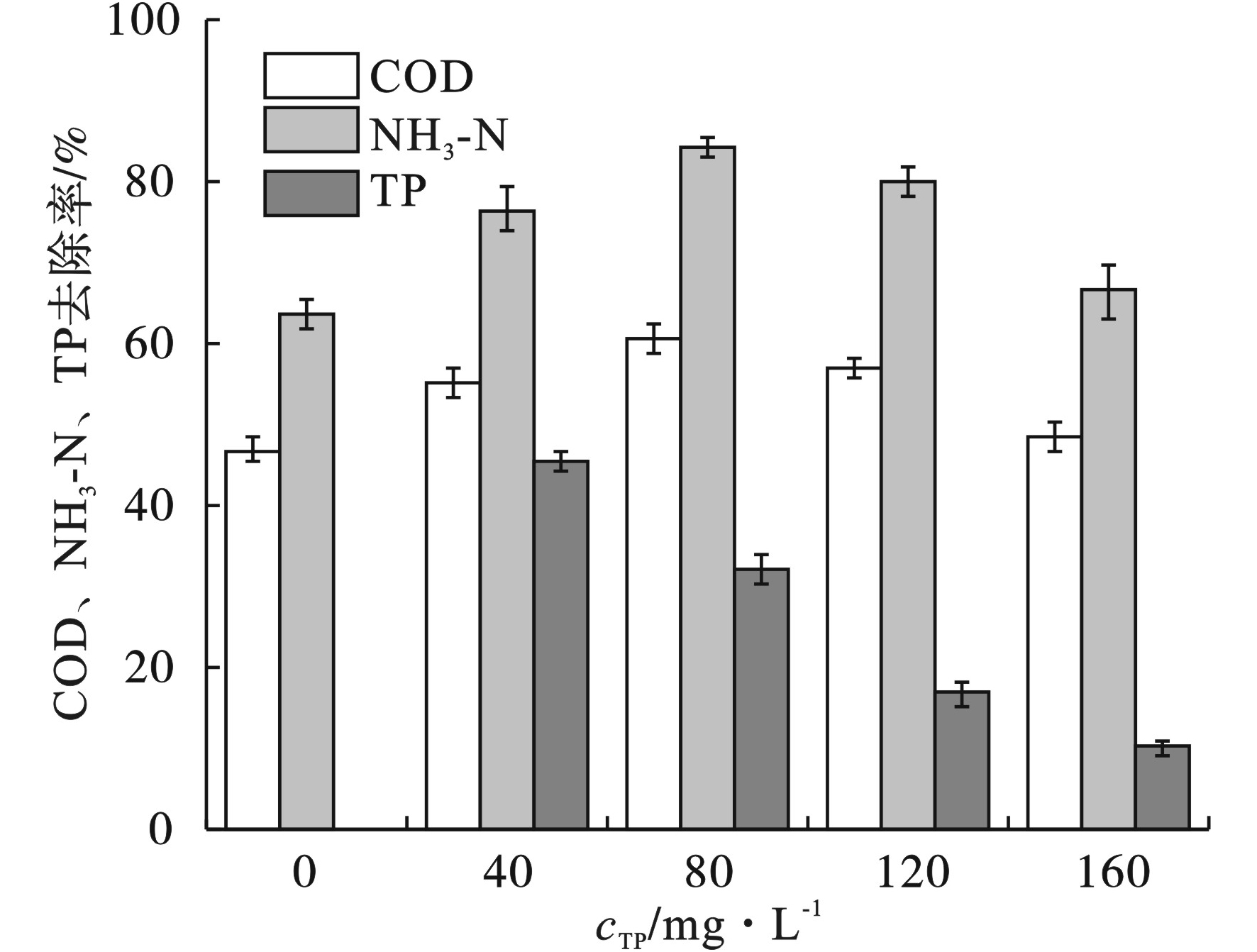
TP浓度对菌株SU6处理啤酒废水生长的影响,见图6。
图6可见,随着外加磷含量的增加,COD和NH3-N去除率也随之提升,在磷浓度为80 mg/L时获得最高去除率分别为60.6%和84.3%,分别较空白对照组提升了13.8%和20.5%。但是,随着磷浓度的继续增加,COD和NH3-N去除率开始逐步降低,在磷浓度为160 mg/L时,降低至48.3%和66.4%。少量磷酸盐,可以促进光合细菌SU6的生长,也可以提高光合细菌对啤酒废水中有机物的转化,收获更多细胞生物量。但是,当补加的磷酸盐过量时,会对光合细菌产生抑制,导致啤酒废水处理效率降低,光合细菌细胞生物质回收率降低,后续除磷成本增加。因此,在使用光合细菌处理啤酒废水时,可以考虑补加少量的磷酸盐以提升效率,本研究建议选择外加磷源40 mg/L,此时菌株SU6可获得生物量OD600=1.28。
2.1. 初始COD对菌株SU6去除效率和生长的影响
2.2. 氮含量对菌株SU6去除效率和生长的影响
2.3. 磷含量对菌株SU6去除效率和生长的影响
-
通过对光合菌Ectothiorhodospira sp. SU6处理模拟啤酒废水的研究,发现菌株SU6在不同初始COD浓度的模拟啤酒废水中均可生长,对不同初始COD浓度处理效果差异明显。适当补加氮源和少量磷源可以有效提高光合菌SU6对COD的去除,并获得更高的细胞生物量。菌株SU6在初始COD、NH3-N和TP浓度分别为2 000、100和40 mg/L的啤酒废水中处理效果最佳,去除效率分别为57.0%、82.7%和50.7%,细胞生物量OD600=1.28。菌株Ectothiorhodospira sp. SU6具有很好的污染物处理和生物质转化能力,可以在后续有机废水的处置中尝试应用。



 下载:
下载: