-
氮是植物生长所需的重要营养元素,也是水体富营养化的主要污染物,水体中的氮素经过悬浮颗粒物或沉积物的吸附、络合、絮凝或共沉淀作用,富集到沉积物中成为“汇”[1 − 2]. 当环境条件发生改变时,沉积物中的氮素会通过解吸、溶解、生物分解等作用再次释放到上覆水中,成为二次污染“源”[3]. 氨氮(NH3-N)作为沉积物氮素向水体释放的主要形态引起了国内外学者的广泛关注[4].
目前对湖泊、水库、河流等水域沉积物中NH3-N的释放动力学特征、释放通量和潜力等方面的研究较多,研究方法包括实验室培养(静态培养、连续流动培养和摇瓶法)和原位测定(原位箱和高分辨孔隙水原位采样)[5 − 7]. 研究发现,不同水域沉积物中NH3-N的释放量存在较大差异:苏青青等[8]通过释放动力学试验和一级动力学模型拟合,测得香溪河沉积物NH3-N的最大释放量为67.1—74.4 mg·kg−1;王圣瑞等[7]测得洱海表层沉积物NH3-N的释放量为120.9—281.0 mg·kg−1;邹航等[9]的研究则发现,珠江河口湿地沉积物对NH3-N表现为吸附作用,吸附量变化范围为267.0—377.5 mg·kg−1.
沉积物NH3-N的释放能力受本底氮含量、水力扰动、DO浓度、pH值、盐度、水土质量比、有机质矿化程度、水生植物等因素的影响[10 − 12]. 李志萍等[13]对汤河水库沉积物NH3-N释放影响因素的研究发现,上覆水NH3-N浓度的变化对沉积物NH3-N释放量的影响不显著,但上覆水温度和pH升高,水力扰动和贫氧条件均能促进沉积物NH3-N的释放[14 − 15]. 上覆水环境对滇池上游和白洋淀沉积物NH3-N释放影响的模拟研究显示[16],酸性或碱性条件有利于NH3-N的释放,而在中性条件下释放量最小. 刘培芳等[17]研究水体盐度对长江口潮滩沉积物NH3-N释放的影响,发现盐度上升可促进离子吸附反应配位键的形成,促进沉积物NH3-N的释放. 上覆水的水化学条件(如pH、IS等)对不同水域沉积物NH3-N释放影响的规律存在差异,沉积物NH3-N本底值的异质性可能导致沉积物NH3-N释放特征表现出与已有研究不同的规律. 人工湿地进水水化学条件的变化程度高于湖泊和水库,且湿地水浅、易受风浪扰动的影响,其沉积物NH3-N释放特征及水化学条件的影响仍不清楚,相关研究鲜见报道.
为此,以云南大理洱海上游的罗时江表流人工湿地为研究对象,通过野外定位观测明确湿地上覆水和表层沉积物中NH3-N的时空分布特征,进一步借助摇瓶试验法测定湿地典型样点表层沉积物的NH3-N释放量,并设置上覆水的pH和IS梯度,研究不同水化学条件对沉积物NH3-N释放的影响. 研究结果可为准确评价表流人工湿地截留污染物效率提供基础数据,为罗时江流域人工湿地沉积物的清淤管理提供科学依据.
-
罗时江湿地位于云南大理洱海上游,是2009年建成的表流人工湿地,用于截留上游种植业、畜禽养殖业、农村生活污水排放的氮磷等污染物[18]. 湿地水域面积44.5 hm2,属北亚热带高原季风气候区,年均气温15.6 ℃,年均降水量为
1000 —1200 mm,干湿季分明,降雨集中时间为湿季(5—10月),其余时间为干季(11月—次年4月). 湿地内人工种植了莲、茭草、芦苇、香蒲、睡莲、海菜花等湿地植物[19]. -
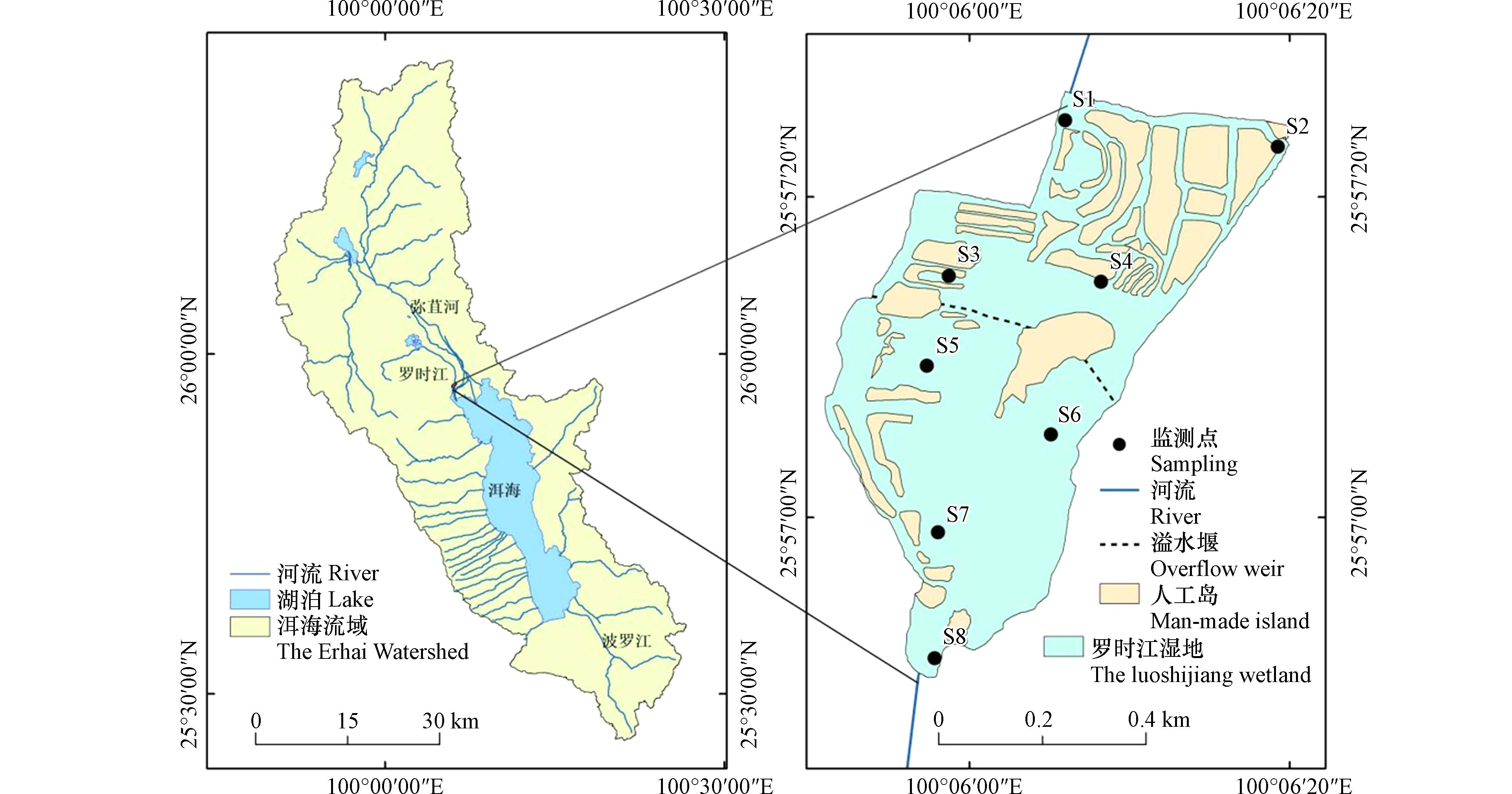
沿水流方向并依据样点空间分布均匀性的原则,在罗时江湿地布设8个采样点(图1),其中S1为罗时江湿地的主要入水口,S8为湿地出水口. 在2019年1—6月期间,每月采集各样点的上覆水和表层沉积物样品(0—5 cm). 表层沉积物采用柱状分层采样器采集,经风干后过2 mm筛备用. 用哈纳便携式多参数水质分析仪(HI98194)现场同步测定水样的温度(T)、pH值、溶解氧浓度(DO)、氧化还原电位(ORP)、总溶解性固体(TDS)等理化指标. 上覆水总氮(TN)和NH3-N浓度分别采用碱性过硫酸钾消解-紫外分光光度法和纳氏试剂分光光度法测定[20],沉积物TN和NH3-N浓度分别用凯氏法和氯化钾溶液提取-分光光度法测定[21].
-
基于课题组前期的研究结果[19],分别以2月和6月代表干季和湿季,选择湿地典型位置(S1、S6和S8)样点的表层沉积物样品,参照王圣瑞等[22]报道的方法测定沉积物NH3-N的释放量. 称取0.15 g沉积物放入15 mL瓶中,加满提取液(0.01 mol·L−1 NaCl,pH=7),密封后恒温(23±1)℃振荡(200 r·min−1)24 h. 提取结束后,
2500 r·min−1离心10 min,采用与1.2节部分相同的方法测定上清液中的NH3-N浓度,并计算为第1次提取的沉积物NH3-N释放量(Q1). 将上清液完全取出,再加入提取液重复上述过程2次,分别得到第2和第3次提取的沉积物NH3-N释放量,3次释放量相加为累积释放量(Q3). NH3-N释放的模拟试验设置2个平行,所有数据误差均<5%.引入参数P并根据式1算得NH3-N释放量随提取次数增加的变化趋势,反映沉积物中NH3-N的释放潜力,数值越大说明沉积物中NH3-N释放的持续能力越强;引入参数F并根据式2计算第1次提取NH3-N释放量在累积释放量中的占比,反映沉积物NH3-N的易释放量,数值越大,快速释放的NH3-N占比越高.
-
因湿地入水口沉积物最先接触上游来水,对水化学条件变化最为敏感,故以S1采样点的表层沉积物为对象,设置提取液的pH和离子强度(IS)梯度开展NH3-N释放的模拟试验. 试验的固液比、提取条件和时长、分离和测定、参数计算等均与1.3部分相同. pH试验背景溶液为0.01 mol·L−1 NaCl,使用NaOH或HCl调节提取液pH为5、7和9;IS试验背景溶液pH为7,分别配制IS为0.01 mol·L−1、0.1 mol·L−1和1 mol·L−1的NaCl溶液.
-
使用Origin 2021软件完成图形绘制,使用SPSS 25软件进行单因素方差分析(Duncan),图表中不同字母表示组内数据存在显著差异(P<0.05).
-
罗时江湿地上覆水理化指标和氮浓度的变化情况如表1所示. 湿地上覆水呈弱碱性且处于弱还原环境,连续半年的监测时间内上覆水DO随T的升高呈下降趋势. 上覆水TDS湿季(650±110)mg·L−1高于干季(500±90)mg·L−1,而TN则呈相反趋势,干季(3.4±1.8)mg·L−1高于湿季(1.3±0.3)mg·L−1. 上覆水TN浓度2月最高,是5月的4.4倍,NH3-N浓度无明显的干湿季差异,但TN中NH3-N的占比湿季37.9%±7.2%高于干季20.9%±4.5%.
罗时江流域内种植大蒜、水稻、玉米、烤烟等作物,冬末春初(2月)农田氮肥施用量增加,氮素流失量大[23],导致湿地上覆水中TN浓度升高并在2月达到峰值,随后下降,总体呈现干季高于湿季的规律. 研究发现,受纳水体中TDS浓度主要受上游径流的影响,湿季降雨量增加,地表径流中携带的离子增多,导致湿地上覆水中TDS浓度升高[24]. 湿地上覆水NH3-N浓度受2个因素影响:上游氮素流失和湿地沉积物释放. 上游氮肥流失是干季湿地上覆水NH3-N的主要来源,而湿季径流的增加会对沉积物造成水力扰动,再加上水温升高、DO下降均会促进沉积物NH3-N向上覆水释放[25]. 这两方面因素在干湿季贡献的不同可能是湿地上覆水NH3-N浓度无季节差异的原因,同时湿季沉积物NH3-N释放量的增加可能解释了上覆水NH3-N比例升高的现象.
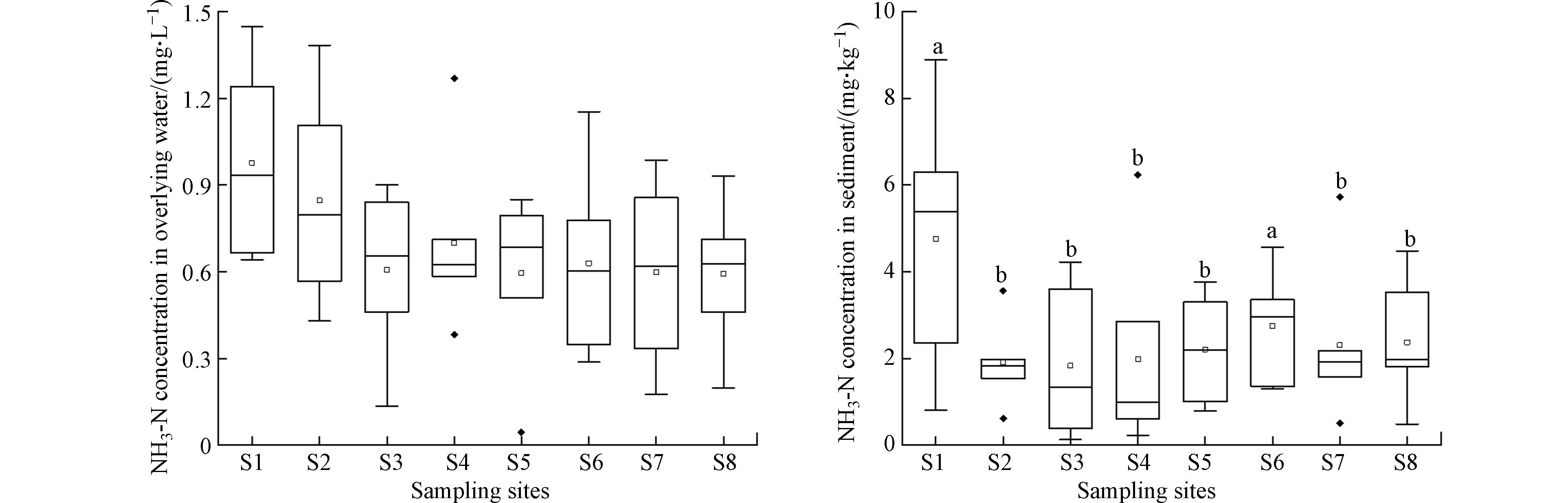
罗时江湿地上覆水和表层沉积物中NH3-N浓度具有空间异质性(图2),变化范围分别为0.14—1.45 mg·L−1和0.23—8.89 mg·kg−1,干湿季差异均不显著(P>0.05). 湿地入水口的上覆水和表层沉积物NH3-N浓度最高,平均浓度分别达(1.0±0.3)mg·L−1和(4.8±3.2)mg·kg−1,出水口NH3-N平均浓度分别是入水口的59.2%和49.9%,沿水流方向上覆水NH3-N浓度呈下降趋势,但差异不显著(P>0.05);而表层沉积物NH3-N浓度显著下降(P<0.05),且在入水口(S1)富集,湿地表现出对水体NH3-N的去除能力. 研究显示,表流人工湿地通过减缓水流促进颗粒物沉积、湿地植物吸收、微生物转化等作用去除水体中的NH3-N. 当水体由罗时江流入湿地,河道迅速变宽、水流变缓,有利于水体中负载NH3-N的颗粒物沉积,导致NH3-N在湿地入水口沉积物中富集. 罗时江湿地内成片种植的湿地植物通过摄取上覆水中的NH3-N作为生长氮源,可提高湿地对氮素的拦截效果[26].
该研究与袁海英等[19]2017—2018年对罗时江湿地上覆水的监测结果相比,TN平均浓度(2.7 mg·L−1)下降28%,但仍超过《地表水环境质量标准》(GB
3838 —2002)V类水限值,而NH3-N平均浓度(0.7 mg·L−1)及其在TN中的占比(25.8%)分别升高65.0%和14.7%. 由此可以推断,罗时江湿地上游氮素污染负荷呈下降趋势,但湿地沉积物向上覆水释放NH3-N的量却呈上升趋势,研究其沉积物NH3-N的释放特征和影响因素具有重要的现实意义. -
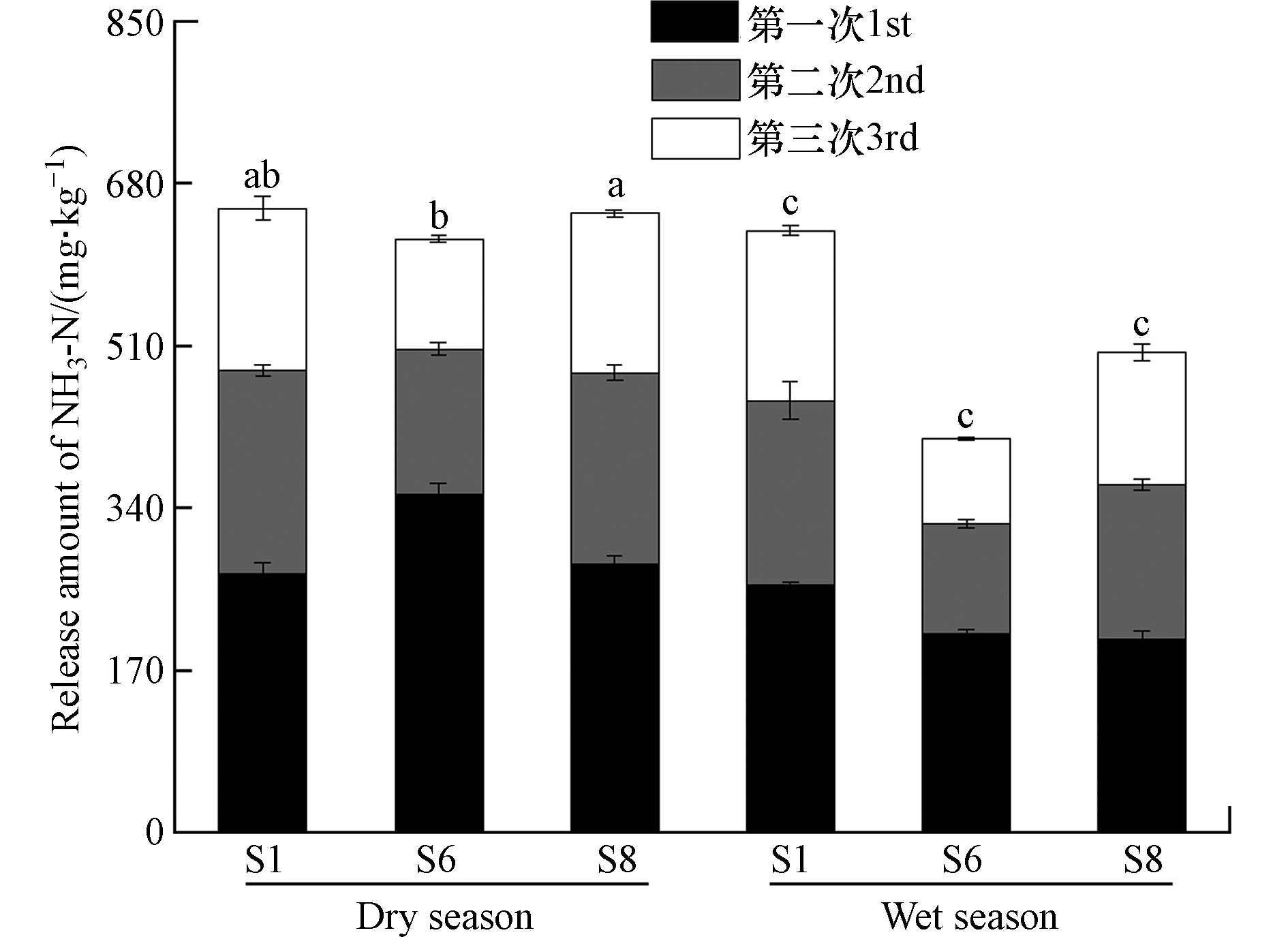
罗时江湿地代表性样点沉积物NH3-N的累积释放量如图3所示,由图3可知,沉积物NH3-N累积释放量变化范围为412.9—653.7 mg·kg−1,在模拟试验条件下均保持释放状态,且随着提取次数的增加单次释放量逐渐降低. 干季湿地内部与出水口沉积物NH3-N释放量存在显著差异(P<0.05),湿季则呈入口>出口>湿地内部的趋势. 所有样点沉积物NH3-N的累积释放量表现为干季显著大于湿季(P<0.05). 该研究测得罗时江湿地沉积物NH3-N的释放量显著高于九龙江口湿地[15](1.6—3.5 mg·kg−1)、三峡水库香溪河[8](67.1—74.4 mg·kg−1)、长江中下游湖泊[27](35.0—109.3 mg·kg−1)及湿地下游洱海[7](120.9—281.0 mg·kg−1),与海河流域汪洋沟[28](258.0—705.0 mg·kg−1)和滇池[5](155.8—667.8 mg·kg−1)沉积物NH3-N释放量相当.
罗时江湿地沉积物具有较高的NH3-N释放风险,但已有研究报道中沉积物NH3-N释放量的估算方法差异较大,涉及多次释放平衡累加法[22]、释放动力学模型拟合法[7]、孔隙水扩散通量估算法[29]等,未形成统一的研究方法,无法准确比较不同研究区沉积物NH3-N释放量的差异,有待进一步研究.
基于累积释放量Q1和Q3计算的,反映各样点和干湿季沉积物NH3-N释放特征的参数如表2所示,由表可知,干季湿地入水口(S1)沉积物NH3-N持续释放能力(P)最强,湿地内部(S6)最低,各样点沉积物NH3-N持续释放能力干季大于湿季;干湿季沉积物快速释放NH3-N占比(F)湿地内部样点最高,各样点沉积物快速释放NH3-N占比也呈干季大于湿季的规律.
研究发现,与沉积物颗粒结合的NH3-N,在水力扰动、温度升高、微生物活性增强等条件下极易向上覆水释放;沉积物中NH3-N含量越高,向上覆水持续释放的能力越强[11]. 湿地入水口处河道变宽、水流减缓,负载NH3-N的颗粒物易发生沉积作用,导致该位置沉积物NH3-N含量显著高于其他样点(图2,P<0.05),持续释放能力也最高. 与其他位置相比,湿地内部水流更平缓,负载NH3-N悬浮颗粒物的沉积量有限,在相对稳定水动力条件下沉积的NH3-N,当发生水力扰动时更容易向上覆水释放,导致湿地内部沉积物NH3-N持续释放能力最低,而快速释放NH3-N量最高. 罗时江湿地沉积物NH3-N持续释放能力及快速释放部分占比的干湿季差异,受到气候和上游污染负荷的共同影响. 与湿季相比,干季降雨量更小、蒸发量更大,径流对湿地上覆水的稀释作用更小,同时干季施肥活动相对集中[30],导致沉积物中NH3-N量更高;而湿季显著增加的径流对湿地沉积物造成水力扰动,温度升高微生物活性增加,这些因素均会促进沉积物NH3-N向上覆水释放[31 − 32],使得沉积物NH3-N总量和易释放比例均低于干季.
叶琳琳等对瓦埠湖沉积物NH3-N释放的研究表明,DO是重要影响因素,厌氧条件(DO<1 mg·L−1)沉积物NH3-N释放量约是好氧条件(5 mg·L−1<DO<7 mg·L−1)释放量(1.5 mg·kg−1)的4.8倍[33],且针对巢湖[34]、九龙江口湿地[15]的研究显示,无论DO水平的高低,沉积物NH3-N均处于释放状态. 结合罗时江湿地野外调查结果,湿地水体常年处于缺氧(2 mg·L−1<DO<4 mg·L−1)或好氧状态,DO未呈现出明显的季节规律. 与之相比,因排污、强降雨、有机物好氧分解等作用[35],湿地上覆水体可能出现pH或IS的波动,由此影响沉积物NH3-N的释放. 此外,王圣瑞等[7]的研究发现,0—5 min内洱海沉积物NH3-N释放速率最大(18.47—40.58 mg·kg−1·min−1),300 min后趋于稳定,故本研究选取的72 h能确保沉积物NH3-N释放达平衡,所有基于释放量的分析讨论可为评估罗时江湿地沉积物NH3-N释放潜力提供有力依据.
-
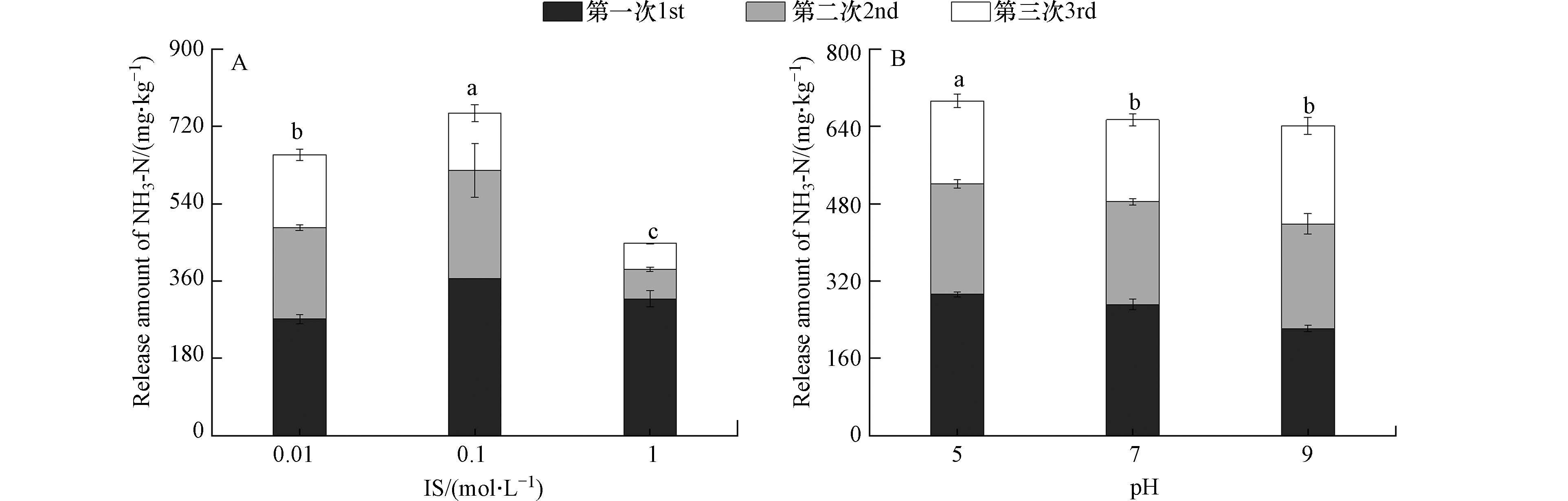
上覆水的水化学条件对湿地入水口表层沉积物NH3-N释放特征的影响如图4所示. 由图4A可知,试验设置的3个IS条件下,沉积物NH3-N均呈释放趋势,且随提取次数的增加,NH3-N单次释放量逐渐下降;中等IS(0.1 mol·L−1)促进NH3-N释放,而高IS(1 mol·L−1)抑制. 基于不同水化学条件沉积物NH3-N释放的Q1和Q3计算的释放特征参数显示(表3),中等IS促进沉积物NH3-N的持续释放,而高IS抑制;随着上覆水IS的升高,可增加沉积物中快速释放NH3-N占比,当IS=1 mol·L−1时,第1次提取NH3-N释放量达累积释放量的71.2%.
上覆水IS主要通过改变沉积物微粒双电层的厚度影响沉积物NH3-N的释放. 中等IS条件下,沉积物微粒双电层结构较稳定,Na+可与扩散层中的NH4+发生离子交换反应,故能促进NH3-N的释放[36];随着IS的升高,上覆水中Na+与沉积物微粒扩散层中NH4+的静电斥力增加,可将扩散层中的NH4+挤压至吸附层中,使扩散层厚度变小,可供交换的NH4+浓度下降[37],从而导致沉积物NH3-N释放量降低. 在IS升高、沉积物微粒扩散层被压缩的过程中,靠近外部更容易发生离子交换反应的NH4+释放量增加,导致第1次提取的NH3-N释放量占比升高. 该研究上覆水最低IS设置为0.01 mol·L−1(等同于TDS为585 mg·L−1),与罗时江湿地上覆水的平均TDS(546±121)mg·L−1相当. 降雨产生的地表径流及湿地上游的排污均可能导致上覆水IS高于该研究的最低值,进而促进沉积物NH3-N的释放,污染风险增加.
由图4B可知,上覆水处于弱酸性、中性和弱碱性条件下,沉积物NH3-N均呈释放趋势,且随着提取次数的增加单次释放量减小;pH的升高显著抑制沉积物NH3-N的释放. 由沉积物NH3-N释放的特征参数可知(表3),弱酸或弱碱性条件下沉积物NH3-N的持续释放能力强,但随着上覆水pH的升高,沉积物快速释放NH3-N占比降低.
上覆水pH主要通过影响离子交换过程或与NH3-N发生化学反应来影响沉积物NH3-N的释放[38]. 酸性条件下,H+浓度较高,通过离子交换释放沉积物微粒扩散层和吸附层中的NH4+[39 − 40],导致沉积物NH3-N释放量最高. 碱性条件下,OH−浓度较高,与NH4+反应转化为气态NH3从水相逸出,且沉积物微粒扩散层靠外的NH4+更容易发生反应,导致沉积物NH3-N释放量及快速释放部分的占比均降低. 罗时江湿地沉积物中有机质分解的耗氧作用、上游排污均可能导致上覆水pH出现弱酸性[41],进而促进沉积物NH3-N释放,增加水体二次污染风险.
-
(1)罗时江湿地上覆水NH3-N浓度无显著干湿季差异(P>0.05),空间上沿水流方向呈下降趋势,湿地表现出对水体NH3-N的截留效果,且主要富集于入水口沉积物中.
(2)湿地沉积物NH3-N累积释放量变化范围为412.9—653.7 mg·kg−1,干季释放量的空间差异不显著(P>0.05),湿季则呈入水口>出水口>湿地内部的趋势;入水口沉积物NH3-N持续释放能力最高,且干季大于湿季.
(3)模拟条件下上覆水IS和pH的改变可显著影响沉积物NH3-N的释放特征,IS升高,pH下降均可促进沉积物NH3-N向上覆水的持续释放,同时提高快速释放NH3-N的占比.
洱海罗时江湿地表层沉积物氨氮释放特征及影响因素
Release characteristics and influencing factors of ammonia nitrogen in the surface sediment of the Luoshijiang Wetland upstream of the Erhai Lake
-
摘要: 以洱海上游的罗时江湿地为研究对象,基于为期半年的野外监测,弄清湿地水体和表层沉积物中氨氮(NH3-N)的时空分异规律,借助摇瓶试验法探究湿地入口沉积物NH3-N的释放特征及水体离子强度(IS)和pH的影响. 结果表明:(1)罗时江湿地上覆水和表层沉积物NH3-N浓度变化范围分别为0.14—1.45 mg·L−1和0.23—8.89 mg·kg−1,干湿季差异均不显著(P>0.05);上覆水和表层沉积物NH3-N浓度均沿水流方向显著下降(P<0.05),出水口NH3-N平均浓度分别是入水口的59.2%和49.9%,湿地对水体NH3-N有截留效果. (2)模拟试验条件下,沉积物NH3-N累积释放量的变化范围为412.9—653.7 mg·kg−1,随提取次数的增加单次释放量逐渐降低;NH3-N累积释放量湿地入口显著高于其他样点,干季高于湿季. (3)上覆水IS升高促进沉积物NH3-N的持续释放,增加快速释放NH3-N占比;上覆水处于弱酸条件下更利于沉积物NH3-N的持续释放,同时提高快速释放NH3-N占比. 研究结果显示,表流湿地入水口沉积物是NH3-N的主要富集场所,水化学条件变化导致NH3-N向上覆水释放可能引起二次污染.
-
关键词:
- 表流人工湿地 /
- 沉积物氨氮 /
- 释放特征 /
- 上覆水pH和离子强度影响.
Abstract: The Luoshijiang Wetland, located in the upstream of the Erhai Lake, was selected as the research object. The spatiotemporal variations of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) in the water body and surface sediment of the wetland were clarified based on the half-year field monitoring, and the release characteristics of NH3-N in the wetland inlet sediment and the effects of water ionic strength (IS) and pH were explored via flask-shaking test. The results showed that: (1) The NH3-N concentrations in the overlying water and surface sediment of the Luoshijiang Wetland varied from 0.14 mg·L−1 to 1.45 mg·L−1 and 0.23 mg·kg−1 to 8.89 mg·kg−1, respectively, with no significant difference in dry and wet seasons (P>0.05). The NH3-N concentrations in the overlying water and surface sediment decreased significantly along the flow direction (P<0.05), and the average NH3-N concentration at the outlet was 59.2% and 49.9% of that at the inlet, respectively. The wetland showed a retention effect towards NH3-N in the water body. (2) Under the simulated test conditions, the cumulative release amount of NH3-N from sediment varied from 412.9 mg·kg−1to 653.7 mg·kg−1, and the single release amount gradually decreased with the increase of extraction times. The cumulative release amount of NH3-N at the wetland inlet was significantly higher than that at other sample sites, and was higher in the dry season than in the wet season. (3) The increase of IS in the overlying water promoted the continuous release of NH3-N from sediment and increased the proportion of rapid release NH3-N. The weak acid condition of the overlying water facilitated the continuous release of NH3-N from sediment, and the proportion of rapid release NH3-N was also increased. The results indicated that the sediment at the inlet of the surface flow wetland was the main enrichment site of NH3-N, and the change of water chemical conditions might lead to the release of NH3-N to the overlying water, resulting in potential secondary pollution. -

-
表 1 罗时江湿地上覆水理化指标和氮浓度的月际变化
Table 1. Inter-monthly variation of physicochemical indicators and nitrogen concentrations in the overlying water of the Luoshijiang Wetland
月份
MonthpH DO/(mg·L−1) ORP/mV T/℃ TDS/(mg·L−1) TN/(mg·L−1) NH3-N/(mg·L−1) 1 7.4±0.2ab 6.6±0.5a 110±60a 10.5±1.1e 500±20c 2.2±0.9bc 0.8±0.4a 2 7.5±0.3ab 4.0±0.6bc 40±20b 13.1±1.3d 500±70c 5.6±2.1a 0.8±0.2a 3 7.6±0.4a 3.3±0.4c 130±50a 15.6±1.6c 440±20c 3.0±0.7b 0.7±0.3a 4 7.4±0.5ab 5.1±2.8b 130±50a 20.9±3.6b 620±130b 3.0±0.7b 0.6±0.1ab 5 7.2±0.3b 3.0±0.7c 120±40a 26.4±1.7a 610±60b 1.3±0.4c 0.4±0.4b 6 7.2±0.1b 2.7±0.2c 120±50a 25.2±0.5a 700±14a 1.4±0.3c 0.9±0.3a 注:不同字母表示季节间差异显著( P <0.05).
Note: Different letters indicate significant differences between seasons at P<0.05.表 2 表层沉积物NH3-N释放特征参数
Table 2. Parameters of NH3-N release characteristics in surface sediment
参数
Parameter干季S1
Dry season S1干季S6
Dry season S6干季S8
Dry season S8湿季S1
Wet season S1湿季S6
Wet season S6湿季S8
Wet season S8P 191.2 133.6 183.6 185.2 102.1 150.1 F 41.5 57.0 43.5 41.2 50.5 40.3 表 3 不同水化学条件下表层沉积物NH3-N释放特征参数
Table 3. Parameters of NH3-N release characteristics in surface sediment in different water chemical conditions
释放条件
Release conditionsIS=0.01 mol·L−1 IS=0.1 mol·L−1 IS=1 mol·L−1 pH=5 pH=7 pH=9 P 191.2 192.6 64.6 200.3 191.2 209.4 F 41.5 48.7 71.2 42.2 41.5 34.6 -
[1] WESTON N B, GIBLIN A E, BANTA G T, et al. The effects of varying salinity on ammonium exchange in estuarine sediments of the parker river, Massachusetts[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2010, 33(4): 985-1003. doi: 10.1007/s12237-010-9282-5 [2] 叶宏萌, 杨浩, 袁旭音, 等. 基于流域沉积物氮磷形态的生态风险评价: 以沙溪流域为例[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(12): 3471-3479. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019111802 YE H M, YANG H, YUAN X Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment based on nitrogen and phosphorus forms in watershed sediments: A case study of the Shaxi Watershed, Fujian[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(12): 3471-3479 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019111802
[3] ZHONG J C, YOU B S, FAN C X, et al. Influence of sediment dredging on chemical forms and release of phosphorus[J]. Pedosphere, 2008, 18(1): 34-44. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60100-3 [4] 何宗健, 吴志强, 倪兆奎, 等. 江湖关系变化对鄱阳湖沉积物氨氮释放风险的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(5): 1277-1284. HE Z J, WU Z Q, NI Z K, et al. The influence of the River-Lake relation changed on the sediments ammonia nitrogen release risk of Poyang Lake[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(5): 1277-1284 (in Chinese).
[5] 邓伟明, 徐晓梅, 陈春瑜, 等. 滇池表层沉积物中氨氮的释放特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(4): 524-531. DENG W M, XU X M, CHEN C Y, et al. Study on release characteristics of ammonium in the surface sediments of Dianchi Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(4): 524-531 (in Chinese).
[6] KUWABARA J S, WOODS P F, BERELSON W M, et al. Importance of sediment-water interactions in Coeur d'Alene Lake, Idaho, USA: management implications[J]. Environmental Management, 2003, 32(3): 348-359. [7] 王圣瑞, 何宗健, 赵海超等. 洱海表层沉积物中总氮含量及氨氮的释放特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(3): 256-261. WANG S R, HE Z J, ZHAO H C, et al. Studying on total nitrogen content and release characteristics of ammonium in the surface sediment of Erhai Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2013(3): 256-261 (in Chinese).
[8] 苏青青, 宋林旭, 刘德富, 等. 三峡水库香溪河沉积物氮含量和氨氮释放特征[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2019, 40(3): 1-7. SU Q Q, SONG L X, LIU D F, et al. Total nitrogen content and ammonia nitrogen release from surface sediments of Xiangxi River, Three Gorges Reservoir region[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2019, 40(3): 1-7 (in Chinese).
[9] 邹航, 王立立, 柳蓉. 珠江河口湿地沉积物吸附氨氮及影响因素研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36(3): 46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2014.03.009 ZOU H, WANG L L, LIU R. Study on the ammonia nitrogen adsorption of sediments in Pearl River estuarine wetlands and its impact factors[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 2014, 36(3): 46-51 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2014.03.009
[10] BOLAEK J, GRACA B. Ammonia nitrogen at the water-sediment interface in Puck bay (Baltic sea)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1996, 43(6): 767-779. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1996.0102 [11] YIN K, HARRISON P. Influences of flood and ebb tides on nutrient fluxes and chlorophyll on an intertidal flat[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2000, 196: 75-85. doi: 10.3354/meps196075 [12] HU W F, LO W, CHUA H, et al. Nutrient release and sediment oxygen demand in a eutrophic land-locked embayment in Hong Kong[J]. Environment International, 2001, 26(5-6): 369-375. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00014-9 [13] 李志萍, 刘攀峰, 韩亚, 等. 汤河水库底泥氨氮释放规律试验研究[J]. 华北水利水电学院学报, 2013, 34(6): 47-49. LI Z P, LIU P F, HAN Y, et al. Experimental study on ammonia nitrogen release in sediment of Tanghe Reservoir[J]. Journal of North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power, 2013, 34(6): 47-49 (in Chinese).
[14] 刘成, 邵世光, 范成新, 等. 巢湖重污染汇流湾区沉积物营养盐分布与释放风险[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(11): 1258-1264. LIU C, SHAO S G, FAN C X, et al. Distribution and release risk of Nutrients in the sediments of heavily polluted confluence bay of Chaohu Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(11): 1258-1264 (in Chinese).
[15] 邱昭政, 颜昌宙, 赵艳玲, 等. 不同溶氧条件下九龙江口湿地沉积物-水界面氨氮释放与氧化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(12): 1902-1908. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.021 QIU Z Z, YAN C Z, ZHAO Y L, et al. The release and oxidation of ammonia at the sediment-water interface of Jiulong River Estuary wetland under different oxygen conditions[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2011, 20(12): 1902-1908 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.021
[16] 龚云辉, 刘云根, 王妍, 等. pH对高原山地农村沟渠底泥氮形态及氨氮释放通量影响模拟研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(3): 378-386. GONG Y H, LIU Y G, WANG Y, et al. Effect of pH on nitrogen forms and ammonia nitrogen release flux in the bottom muddy of plateau rural ditches[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(3): 378-386 (in Chinese).
[17] 刘培芳, 陈振楼, 刘杰, 等. 环境因子对长江口潮滩沉积物中NH4+的释放影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2002, 15(5): 28-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2002.05.008 LIU P F, CHEN Z L, LIU J, et al. Effects of environmental factors on NH4+release in tidal flat sediments along the Yangtze delta[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2002, 15(5): 28-32 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2002.05.008
[18] 项颂, 吴越, 吕兴菊, 等. 洱海流域农业面源污染空间分布特征及分类控制策略[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(11): 2474-2483. XIANG S, WU Y, LÜ X J, et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution of agricultural non-point source pollution in Erhai Lake basin and its classified control strategy[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(11): 2474-2483 (in Chinese).
[19] 袁海英, 梁启斌, 侯磊, 等. 洱海入湖河口湿地沉积物氨氮释放潜力研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(6): 762-769. YUAN H Y, LIANG Q B, HOU L, et al. Research on the release potential of ammonia in the estuarine wetland sediments of Erhai Lake[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2020, 36(6): 762-769 (in Chinese).
[20] 国家环境保护总局《水和废水监测分析方法》编委会. 水和废水监测分析方法(第四版)[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2002. State Environmental Protection Administration, the editorial board of water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods. Water and wastewater monitoring analysis method [M]. Fourth Edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002 (in Chinese).
[21] 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2012. 土壤氨氮、硝酸盐氮、亚硝酸盐氮的测定氯化钾溶液提取-分光光度法: HJ 634-2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-7. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in soil by Potassium Chloride Solution Extraction Spectrophotometry: HJ 634-2012[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-7 (in Chinese).
[22] 王圣瑞, 赵海超, 王娟, 等. 有机质对湖泊沉积物不同形态氮释放动力学影响研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(2): 332-340. WANG S R, ZHAO H C, WANG J, et al. The effects of organic matter on the release kinetics of nitrogen with different forms in the lake sediments[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012, 32(2): 332-340 (in Chinese).
[23] ONGLEY E D, ZHANG X, YU T. Current status of agricultural and rural non-point source pollution assessment in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(5): 1159-1168. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.047 [24] 张子璐, 刘峰, 侯庭钰. 我国稻田氮磷流失现状及影响因素研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(10): 3292-3302. ZHANG Z L, LIU F, HOU T Y. Current status of nitrogen and phosphorus losses and related factors in Chinese paddy fields: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(10): 3292-3302 (in Chinese).
[25] LIANG Z, LIU Z, ZHEN S, et al. Phosphorus speciation and effects of environmental factors on release of phosphorus from sediments obtained from Taihu Lake, Tien Lake, and East Lake[J]. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 97(3-4): 335-348. doi: 10.1080/02772248.2015.1050186 [26] 刘永, 张诗涵, 肖雅元, 等. 红树林人工湿地的脱氮除磷效果研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(8): 1788-1799. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-1478 LIU Y, ZHANG S H, XIAO Y Y, et al. Efficiency of mangrove wetlands in nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(8): 1788-1799 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-1478
[27] 朱辉翔, 张树楠, 彭英湘, 等. 绿狐尾藻湿地对养殖废水中不同污染负荷氮去除效应[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(19): 217-224. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.19.025 ZHU H X, ZHANG S N, PENG Y X, et al. Effect of myriophyllum elatinoides wetland on nitrogen removal from swine wastewater under different pollution loads[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(19): 217-224 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.19.025
[28] 张亚娟, 刘存歧, 古钧, 等. 汪洋沟表层沉积物中总氮含量和氨氮释放特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(2): 519-524. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150204 ZHANG Y J, LIU C Q, GU J, et al. Total nitrogen content and release characteristics of ammonium in surface sediment of Wangyang River[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(2): 519-524 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150204
[29] 李宝, 丁士明, 范成新, 等. 滇池福保湾间隙水氮磷分布及其与底泥微生物和磷酸酶相互关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 2008, 20(4): 420-427. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.04.003 LI B, DING S M, FAN C X, et al. Distributions of nitrogen and phosphorus in interstitial waters in the sediments of Fubao Bay in Lake Dianchi and their relationships with the activities of microbe and alkaline phosphatase in the surface sediments[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2008, 20(4): 420-427 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2008.04.003
[30] 段四喜, 杨文燕, 李锋林, 等. 洱海流域肥料面源污染负荷特征研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2022, 34(1): 193-201. DUAN S X, YANG W Y, LI F L, et al. Research on load characteristics of non-point source pollution of fertilizer in Erhai lake basin[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2022, 34(1): 193-201 (in Chinese).
[31] 袁轶君, 何鹏程, 刘娜娜, 等. 温度与扰动对鄱阳湖沉积物氮释放的影响[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(5): 495-500. YUAN Y J, HE P C, LIU N N, et al. Effects of temperature and disturbance on nitrogen release from sediment of Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of East China university of Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 43(5): 495-500 (in Chinese).
[32] MARTIN S, KRISTENSEN P, JEPPESEN E. Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arresø, Denmark[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1992, 228(1): 91-99. doi: 10.1007/BF00006480 [33] 叶琳琳, 潘成荣, 张之源, 等. 瓦埠湖沉积物氮的赋存特征以及环境因子对NH4+-N释放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(5): 1333-1336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.05.047 YE L L, PAN C R, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Characteristics of N forms in Wabu lake sediments and effects of environmental factors on NH4+-N release[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2006, 25(5): 1333-1336 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.05.047
[34] 刘静静, 汪家权, 徐文炘. 环境因子对巢湖沉积物中NH4+释放的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(29): 12870-12872. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.29.138 LIU J J, WANG J Q, XU W X. Effects of environmental factors on NH4+ release in sediment from Chaohu lake[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 36(29): 12870-12872 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.29.138
[35] 石晓勇, 王修林, 陆茸, 等. 东海赤潮高发区春季溶解氧和pH分布特征及影响因素探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(5): 404-412. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.05.003 SHI X Y, WANG X L, LU R, et al. Distribution of dissolved oxygen and pH in frequent HAB area of the East China Sea in spring 2002[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2005, 36(5): 404-412 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.05.003
[36] 张然, 陈雅丽, 武晓娟, 等. 离子强度和胡敏酸影响下不同土壤胶体稳定性研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(6): 2347-2357. ZHANG R, CHEN Y L, WU X J, et al. Stability of different types of soil colloids under the influence of ionic strength and humic acid[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(6): 2347-2357 (in Chinese).
[37] 孙刘鑫, 王培茗, 杨俊浩, 等. 离子强度对吸附有机污染物影响的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(6): 3239-3257. SUN L X, WANG P M, YANG J H, et al. Research progress on the effect of ionic strength on the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater by adsorbents[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(6): 3239-3257 (in Chinese).
[38] 刘莹, 刘晓晖, 张亚茹, 等. 三种人工湿地填料对低浓度氨氮废水的吸附特性[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(5): 1118-1127. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017082913 LIU Y, LIU X H, ZHANG Y R, et al. Adsorption properties of low concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater by three constructed wetland fillers[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(5): 1118-1127 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017082913
[39] 裴佳瑶, 冯民权. 环境因子对雁鸣湖沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(12): 3447-3459. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201912021 PEI J Y, FENG M Q. Effects of environmental factors on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from the sediment of the Yanming Lake, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(12): 3447-3459 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201912021
[40] LI Z, WANG S R, WU Z H, Coupling effect of pH and dissolved oxygen in water column on nitrogen release at water sediment interface of Erhai Lake, China[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 149: 178-186 (in Chinese). [41] 陈家厚. 松花江流域pH值异常变化的监测分析[J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2008, 32(3): 14-17. CHEN J H. The diagnoses of pH abnormal change in Songhua River Basin[J]. Heilongjiang Environmental Journal, 2008, 32(3): 14-17 (in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: