-
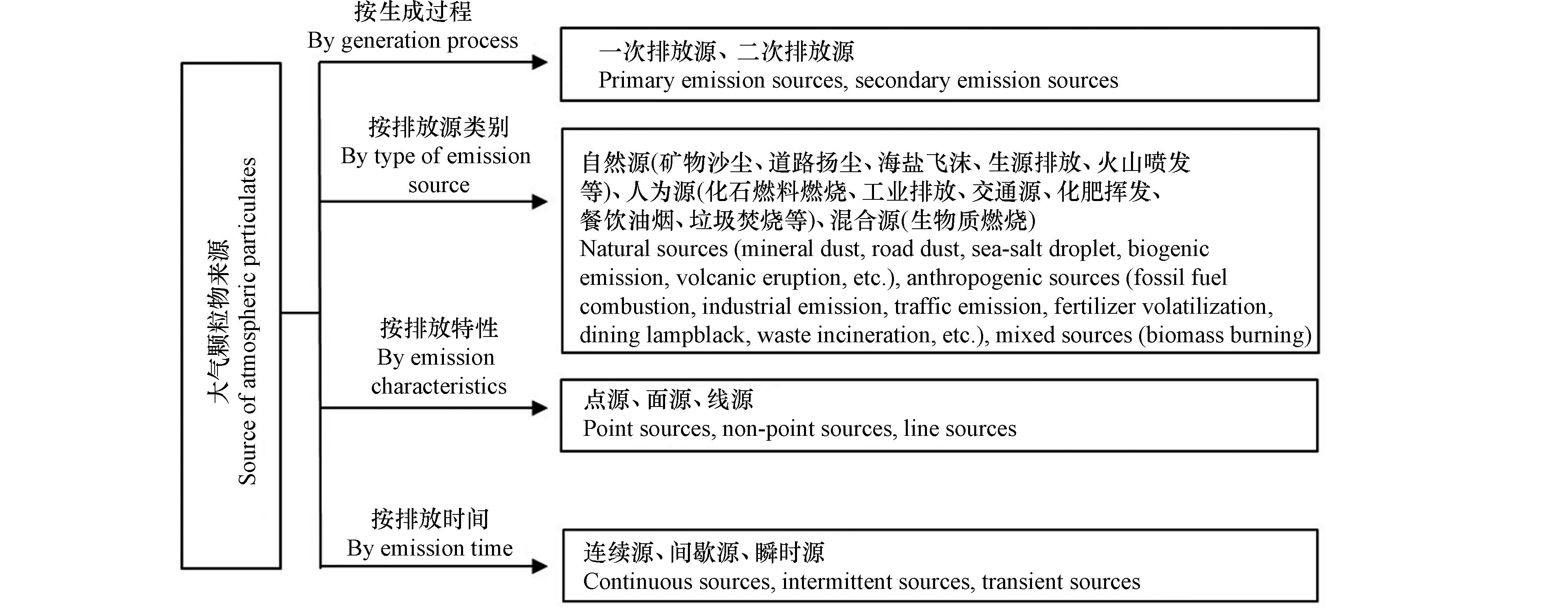
大气气溶胶是指悬浮在大气中的固态或液态微粒所组成的多相分散体系。海洋气溶胶颗粒物的粒径范围通常在0.001—100 μm之间,以超过1 μm粒径的颗粒物居多,由小到大依次可划分为四个模态:核模态、爱根核模态、集聚模态和粗粒子模态[1]. 大气颗粒物的主要化学成分包括无机物、有机物和有生命物质三大类,其中无机物主要包括各类微痕量元素如Al、Fe、Ca、K、Si、Zn、Cu、Pb、Se等,还包括各类离子、化合物及二次源成分(硫酸盐、硝酸盐、铵盐)等;有机物种类繁多、来源广泛且结构复杂,主要包括芳香烃、含氮杂环有机物、脂肪烃、醇、酯、醛、酮类等,而有生命物质则为主要包括细菌、霉菌、真菌、病毒等在内的生物气溶胶. 大气颗粒物复杂的化学组成主要取决于其来源. 根据不同的分类方法,大气颗粒物可以划分为多种类型的来源(图1),其中二次源颗粒物不同于一次排放源直接排放的污染物,其是在一次排放源的基础上,通过光化学反应、液相反应以及气-粒转化等复杂的大气反应过程生成的二次气溶胶. 二次气溶胶颗粒物的成分组成及物理化学性质有很大差异,与参与二次反应过程的气态污染物有关. 一般而言,二次颗粒物硫酸铵、硝酸铵是细颗粒物(PM2.5)的主要成分,可占PM2.5质量浓度的30%—50%[2]. 大气颗粒物中主要无机成分如氮、磷、硅、铁等元素的沉降可为水域生态系统提供营养成分,而重金属元素的沉降则会产生毒性效应,抑制水域生态系统初级生产力的增长[3-5]. 此外,大气中的重金属元素(如Hg)和持久性有机污染物具有致癌、致畸、致突变作用[4,6],会对人体健康产生严重危害. 因此,大气颗粒物具有成分复杂、来源广泛的特征,是一个极为复杂的多相体系,对生态系统和人类生命健康均具有很大影响.
大气沉降是指气溶胶中的营养物质和污染成分通过重力沉降(干沉降)或随降水(湿沉降)等过程沉降至地表和水体的过程. 大气沉降不仅是大气清除自身污染物质的主要方式,也是沙尘和人为污染物质向海洋输送的重要途径之一. 沉降至海洋表层的陆源营养物质和有害成分势必会对海洋生态系统产生复杂的生态效应,这一影响程度与大气颗粒物粒径、成分、含量以及溶解度密切相关[7-9],而气溶胶颗粒物的成分取决于来源及其在大气传输过程中发生的一系列物理化学变化. 大气颗粒物来源解析是指通过物理、化学以及数学模型等技术方法定性或定量识别环境受体中各类大气成分的来源. 由于气溶胶颗粒物的粒径大小、化学组成及在大气化学中的各种效应均与其来源密切相关,追溯并量化大气颗粒物中各类化学成分的来源可为评估陆源输入对海洋大气气溶胶颗粒物和海洋生态系统的影响提供科学依据. 同时,源解析结果对深入揭示大气颗粒物成分的迁移转化机制和服务于政府部门科学制定大气污染物减排措施具有重要参考和实用价值. 因此,大气颗粒物源解析研究得到了科学家、政府和社会公众的极大关注,也是当前海洋科学与大气环境科学交叉研究的热点. 大气颗粒物源解析技术是有效开展大气颗粒物及其化学组分源解析研究的基础. 自20世纪60年代以来,国内外学者对大气颗粒物污染源的鉴别及其贡献大小进行了广泛深入地研究,发展并形成了诸多有效的技术方法体系,取得了一系列创新性成果,进一步加深了对生态系统物质循环的理解,并有力地推动和指导了大气污染精准化防控措施的制定和实施. 由于与人体健康关系密切,目前的大气颗粒物源解析研究多集中在城市[10-12],对海洋大气颗粒物源解析的研究相对较少且缺乏系统性,这极大地限制了对通过大气沉降输入海洋的污染物来源的甄别和防控. 据此,本文在系统梳理、归纳目前主流的大气颗粒物源解析方法发展水平基础上,综述了近40年来各类源解析方法在我国近海大气颗粒物源解析中的应用,并展望了未来海洋大气颗粒物源解析的发展方向,可为进一步阐明各类化学物质的生物地球化学循环过程、科学制定精准化大气污染防控措施提供理论参考和技术支持.
-
大气颗粒物源解析技术自20世纪60年代中期发展至今,已形成了诸多不同类型的方法. 目前较为成熟且使用较为普遍的方法大致可以归纳为以下三类:源清单法、源模型法和受体模型法. 源清单法(Emission inventory)是应用最早的大气成分源解析方法,其根据不同排放源类型的活动水平和排放因子模型评估区域内各类源的排放量,建立污染源清单数据库,并据此识别对相应大气成分有贡献的主要排放源[12]. 源清单法是其它两类源解析方法的重要基础,主要为定性分析,其结果简单清晰,但应用存在较大的局限性,如活动水平资料缺乏、排放因子的不确定性大、开放源(如扬尘)和自然源排放量统计困难等,从而极大地限制了这一方法的应用. 源模型法(Source-oriented model),又称扩散模型法(Diffusion model)或空气质量模型法,是以不同尺度数值模式方法定量描述各类大气成分从源到受体所经历的一系列物理化学过程,包括大气传输、扩散、化学转化以及沉降等,定量估算不同区域和不同类别污染源排放对受体的贡献值[12]. 受体模型法(Receptor model)是指从受体出发,根据污染源样品和受体颗粒物的化学、物理特征等信息,识别污染源类型,并利用数学模型方法定量解析各类型污染源对大气颗粒物中不同化学成分的贡献大小. 受体模型的主要优点是其不需要知晓详细的源强信息,不依赖于排放源的排放条件、气象以及地形等资料,解决了扩散模型一直以来难以解决的问题,且操作简便[10]. 因此,受体模型自20世纪80年代以来得到了极为迅速的发展并在大气颗粒物源解析研究中得到了极为广泛的应用. 上述三类源解析方法各有自身优势和特点,三者之间可以互为补充、相互佐证,力求突破单一源解析方法的缺陷和瓶颈,发展多技术耦合的源解析方法,如受体模型与源清单耦合以及受体模型与源模型耦合的方法等,已逐步形成了较为系统和成熟的大气污染物成分源解析技术体系[2,10,13]. 此外,受体模型还可以与源追踪模型耦合,并结合源排放清单,利用源模型同化空间网格上的受体数据,在此基础上利用三维受体模型进一步解析多点位受体数据,借以实现“时间、空间、组分”多维度上的大气颗粒物精细化源解析[10,14].
-
源清单法可通过详细摸底区域内所有的排放源,统计分析占比较大的排放源,为下一步的精细控制提供基础. 污染源排放量计算可参考生态环境部分别于2014年8月和2015年1月发布的两批次大气污染物源排放清单编制技术指南,涉及PM2.5、大气挥发性有机物、大气氨、扬尘颗粒物、大气可吸入颗粒物(PM10)、道路机动车、非道路移动源、生物质燃烧源等方面[15]. 源清单法的最终结果可以获得点源和面源的排放清单以及最终的排放量统计.
目前我国多数城市和区域已开展了本地区或重点行业污染源排放清单的研究,而在近海的研究还极为薄弱. 我国多数沿海城市已开展了工业源、机动车、港口船舶废气、畜禽养殖、秸秆焚烧、挥发性有机物等的排放清单研究. 沿海港口装卸和船舶航运排放是近海大气污染物的一个重要来源. 在一些沿海港口区域,如青岛港、上海港和厦门港等开展了船舶排放清单研究,对PM10、PM2.5、氮氧化物(NOx)、硫氧化物(SOx)、CO、CO2、挥发性有机物(VOCs)和烃类(HC)的排放总量做了统计(表1). 空间分布上,厦门港各类大气污染物的排放量相对较小,上海港船舶各类大气污染物的排放量最大,远高于青岛港和厦门港(表1). 船舶与港区排放清单的不确定性主要来自污染源活动水平数据和排放因子的不确定性. 因此,对排放因子本地化的深入研究可进一步降低排放清单的不确定度.
排放清单的建立可以直观地反映不同来源的排放情况,为大气污染物精准溯源和科学制定大气污染物减排措施提供了强有力的数据支持. 尽管如此,源清单法也存在一些固有的缺陷,如采集全面可靠的源排放数据存在较大困难,且由于污染物排放源与大气质量之间存在较为复杂的关系,因而排放源的排放量与其受体之间并非单纯的线性关系,即尽管其排放量大但对大气颗粒物的贡献不一定大[10]. 此外,大气污染源极为广泛,源清单法很难对大气污染物实际排放通量进行精准地评估[10,12]. 随着我国经济社会的持续快速发展,单独依靠源清单法已显然不能满足对大气污染物精准溯源的要求,必须结合其它源解析方法的综合应用. 目前,源清单法更多地应用于为源模型法和受体模型法提供数据支撑. 因此,可以认为源清单法是大气颗粒物源解析的重要辅助手段.
-
源模型法,又称扩散模型法或空气质量模型法,其核心部分为大气扩散模型,用于模拟大气颗粒物的输送、扩散以及过程中的转化等. 大气扩散模型的发展历程分为三代,第一代为高斯扩散模型和拉格朗日轨迹模型,代表性模型有工业源综合体(ISC)、经验动力学模拟方法(EKMA)等,其数学形式简单,通过大气数据获取计算所需各类参数,适于各种气象条件,适用于对惰性污染物传输范围和污染状况的模拟评价[12,19];第二代模型为欧拉网格模型,以国外的城市光化学氧化模型(UAM)、区域酸沉降模型(RADM)、区域光化学氧化模型(ROM)为代表,主要针对单一污染问题如臭氧、酸沉降等[12];第三代模型为空气质量模型,称为Models-3,即基于“一个大气”的理念,突破了传统模式针对单一物种或单相物种的模拟,综合考虑了实际大气中不同成分之间的相互转化和影响,开创了模式发展的新理念[12,19]. Models-3模型建立在各污染源排放量或排放强度确定的前提下,对大气颗粒物在大气中的扩散、生成、迁移、转化以及清除等物理化学过程进行全方位模拟,其中的代表模型有Models-3/CMAQ(区域空气质量模式)[19]、WRF-CHEM(耦合化学输送模式)[20]、ISCST-3(稳态高斯烟羽模型)[21]以及我国科学家自主开发的嵌套网格空气质量预报模式(NAQPMS)等[22].
扩散模型应用于大气颗粒物源解析研究存在较强的优势,主要体现在:①扩散模型不局限于观测点位,可以得到源解析结果的空间分布;②扩散模型可区分本地排放源和外来传输源,并能较准确地分析得到不同地区的分担率;③通过情景模拟,源解析结果对科学制定大气污染物防控措施具有重要指导意义和现实意义[12]. 当然,扩散模型的应用也存在一定的不确定性,这主要表现在源清单、大气边界层气象过程以及颗粒物迁移转化过程中复杂的大气化学反应,这些过程和参数的获取极为困难且难以把握其规律,尤其是在重污染天气条件下扩散模型源解析结果的不确定性更为明显[10,12,14]. 因此,目前应用扩散模型开展大气颗粒物源解析的研究工作相对较少. 这方面比较有代表性的工作是Chow等[23]采用ISCST-3扩散模型解析了美国Las Vegas大气PM10的来源,以及Baek等[24]采用CMAQ模型解析了美国Atlanta大气PM2.5的来源,并均获得了较好的效果.
在我国近海,源模型的应用也较少. 如研究人员基于WRF-CMAQ空气质量模型,定量模拟出2014年我国近周边海域船舶运输排放对NOx、SO2、PM2.5和PM10年度平均贡献率分别为5.95%、2.20%、1.46%和1.41%[25]. 船舶排放对空气质量的影响具有显著的季节性差异,我国近周边海域船舶活动对NOx、SO2、PM2.5和PM10年均浓度的贡献率低于6%,由此得出沿海船舶营运对我国近周边海域环境空气质量的影响总体较小[25]. 在中国近海,利用WRF-CMAQ空气质量模型,采用情景模拟“归零法”,得出2016年1月灰霾天气期间,渤海总无机氮沉降主要来自京津冀及山东西北部地区,占比74.6%,而来自长江三角洲及其周边地区的贡献仅为1.14%;上述两个地区对黄海大气总无机氮沉降的贡献分别为38.7%和3.60%,对东海的贡献分别为42.6%和12.1%[26],表明中国东部近海总无机氮沉降的主要来源区域均为京津冀及山东西北部地区. 此外,在珠江三角洲地区采用WRF-CMAQ模式,结合CMAQ的源解析方法对大气硫、氮干沉降的来源也开展了研究[27]. 综上,源模型的优势明显,其应用对于科学认识中国近海不同排放源和区域传输对大气污染物的贡献提供了重要参考. 由于受到精细化源排放清单、气象条件以及化学机制等因素的影响,源模型法对源强不确定的排放源类解析的准确性有待提高,这在一定程度上限制了其应用.
-
受体模型应用的前提是假设污染物从源到受体质量守恒并呈线性关系. 由于受体模型不依赖于气象条件以及污染源排放清单,从而突破了源模型方法的局限性,是现阶段所有源解析方法中最具价值的模型,也是目前国内外最常用的大气颗粒物源解析方法[11]. 至今,受体模型已发展出诸多种类,但归纳起来大致可分为两类:源已知受体模型和源未知受体模型. 受体模型的不确定性主要源自于大气颗粒物采样和其中化学成分测定过程中的不确定性、源成分谱的共线性以及对二次来源的准确判定等[28]. 自20世纪70年代开始,美国和日本等发达国家已经应用受体模型开展了大量的大气颗粒物源解析研究,获得了很好的效果. 相比之下,我国的大气颗粒物源解析研究起步较晚,尤其是对于海洋大气颗粒物,直至20世纪80年代中后期才开始逐步开展源解析的相关研究[29],但发展较快,整体上对我国近海大气颗粒物的来源有了一个较为清晰的认识,取得的成绩有目共睹. 目前,我国科研人员已经在渤海[29-32]、黄海[33-37]、东海[38-42]、南海[43-46]以及热带西太平洋部分海域[47]应用多种受体模型方法开展了卓有成效的大气颗粒物源解析研究,并获得了一系列的新认知和新发现.
-
源已知受体模型,顾名思义,即模型的计算需要输入详细的本地源成分谱信息,但对样品的数量没有要求,此类模型的代表即为化学质量平衡模型(CMB). CMB模型于1972年首次被提出,1980年正式被命名为化学质量平衡法. CMB法是目前在城市大气颗粒物源解析研究中应用最多、最广的受体模型,也是美国环境保护署推荐使用的模型.
其中,X表示给定受体站点的大气化学成分浓度,G代表源对受体站点的贡献,F代表化学成分在源中的质量分数,即源成分谱,E为残差.
CMB法需要输入源成分谱信息(F)和受体点成分谱信息(X),解出相应的源贡献量(G),即某化学成分的受体浓度等于源贡献浓度值与源成分谱中该成分质量分数乘积的线性和,并利用有效方差最小二乘法进行求解. 本地化源成分谱的输入是CMB法能够科学合理应用的一个重要前提。遗憾的是,目前我国的本土源成分谱相当缺乏[12,48],这在很大程度上限制了CMB法的应用及其准确性.
尽管CMB法在中国城市大气颗粒物源解析中得到了较为广泛的应用,然而在中国近海却应用极少,可能与相应的可用源成分谱极为缺乏有关. 早在1984年,即有研究人员运用CMB法解析出渤海的大气颗粒物来自大陆和海洋源的比例近乎2:1,首次证实陆源排放对渤海大气颗粒物的贡献显著高于海洋;而在黄海,海洋源(56.7%)对大气颗粒物的贡献则高于陆源排放(43.3%)[29]. 在天津近海,利用CMB法对大气总悬浮颗粒物(TSP)的来源分析结果显示,燃煤飞灰所代表的人为源对TSP贡献最大(36.14%),其次是地壳源类(33.26%)以及海盐粒子(1.58%),其它未识别的源贡献为30.58%[30]. 这些源解析结果共同表明,在受人为影响显著的渤海及其近岸海域,大气颗粒物的人为源特征明显高于其它形式的源,凸显了渤海大气颗粒物的显著性陆源特征.
针对CMB模型应用过程中的“一组数据多种结果”以及扬尘源与土壤风沙尘和建筑尘之间的严重共线性问题,冯银厂等[49]在国际上首次提出大气颗粒物二重源解析技术,得到了各单一尘源类进入扬尘中的比例及各单一尘源类在扬尘中的分担率,丰富和发展了大气污染物源解析理论,为环境中各类污染物的源解析提供了新的技术方法和视角. 未来,发展并建立精细化源成分谱,结合空气质量模型开发新一代CMB模型将是一个重要的发展方向. 如有研究人员针对受体模型对大气PM2.5中二次无机、有机气溶胶不能给出有效源贡献的问题,建立了一种基于污染源清单的化学质量平衡(Inventory-CMB)源解析受体模型,并将其实际应用于大气PM2.5的源解析研究,取得了很好的效果[50]. 相比于传统的化学质量平衡法,Inventory-CMB的源解析过程对源成分谱的要求较低且抗干扰性更强,同时新模型的计算结果均衡、详尽,比较适合我国当前各类大气PM2.5的防控需求[50].
-
源未知受体模型即广义上的因子分析,主要包括主成分分析、正定矩阵因子分解和多元线性模型等方法. 由于此类模型在使用时无需输入详细的源成分谱信息,故称为源未知受体模型,但需要有能对源类别进行指征的示踪物种(表2、表3)[11-12]. 它基于一些先进的科学手段对在同一受体上测得的大量数据进行解析,提取多个因子,从而推出源的数目和成分谱,然后再与源类型一一对应识别,进而估算出源对受体的贡献大小. 由于模型运行过程中需要进行较为复杂的统计,故对样品数量的要求较高,且不同解析方法要求的样品数量存在较大差异. 源未知类受体模型种类很多,其中比较有代表性的模型有主成分分析(PCA)、正定矩阵因子分解(PMF)模型等. 现阶段对海洋大气颗粒物源解析方面应用较多的当属PCA和PMF模型. 部分源解析模型使用的主要示踪物及解析出的主要源类详见表4.
-
广义上的因子分析法是一种多元统计方法,包括相关性分析、富集因子法、主成分分析和正定矩阵因子分解法等. 因子分析法通过将一些具有复杂关系的变量经过多种数学变换转变为少数几个线性不相关的具有较好代表性的综合指标或因子,从而简化了数据处理程序,揭示实测数据多个变量之间的因果关系. 目前在海洋大气颗粒物源解析中,相关性分析法、富集因子法、主成分分析法的应用非常多.
相关性分析(Correlation analysis)是一种统计学方法,用于分析变量与变量之间是否存在某种随机的共同变化的关系,以及这样的关系的强烈程度,即两个或数个变量共同变化的程度. 相关性分析的变量之间大多具有不完全的相关关系,根据相关的性质和形式不同,可分为正相关和负相关以及线性相关和非线性相关. 在符合所有变量服从正态分布的前提下,二元相关分析一般使用Pearson相关系数,而多元相关分析可以使用偏相关系数或复相关系数. 在有变量不符合正态分布的情况下,二元相关分析多使用Spearman秩相关系数或Kendall秩相关系数,多元相关分析则使用相应的Kendall偏秩相关系数或Kendall和谐系数. 从统计学角度,两个或数个大气成分之间呈显著性正相关关系,则说明它们具有相似的来源或共同的形成机制. 本质上讲,在大气颗粒物源解析中,相关性分析是所有因子分析法的基础.
在胶州湾,利用相关性分析得出气溶胶和降水中的氮主要来源于以农业活动为主的人类生产活动排放,磷具有自然源(沙尘、岩石风化)和人为源(工农业生产)的混合源,而矿物沙尘和建筑扬尘是大气硅的主要来源[3,5,54]. 对于气溶胶和降水中的水溶性常量离子和有机碳,Na+、Mg2+、Cl−均主要来自于海盐颗粒,K+为生物质燃烧源,NH4+、SO42−、NO3−、F−则主要来自于化肥、煤燃烧以及汽车尾气排放等,化石燃料燃烧尤其是煤燃烧是胶州湾大气降水溶解有机碳(DOC)的主导性来源[33,55]. 尽管如此,不同种类离子成分之间的较强线性关系不一定总是表明它们具有相同或相似的来源,也有可能暗示它们在大气中发生反应后以某种化合物的形式共同存在. 如NH4+、SO42−、NO3−的显著正相关表明它们在大气颗粒物中可能以硫酸氢铵(NH4HSO4)和硝酸铵(NH4NO3)的形式存在. 同理,对于Ca2+,其在胶州湾气溶胶中的存在形式可为硝酸钙(Ca(NO3)2)、硫酸钙(CaSO4)、氯化钙(CaCl2)以及氟化钙(CaF2)[33].
在黄渤海,利用相关性分析发现冬季As/TSP与K+/TSP存在显著的相关性. 由于K+通常被用作生物质燃烧的示踪剂,因此,二者之间的强相关性表明生物质燃烧可能是黄渤海冬季大气As的重要来源;在夏季,生物质燃烧排放较小,相应的气溶胶中As/TSP与K+/TSP的相关性也较差[56],从而得到了进一步证实. 在台湾海峡,大气金属元素Na、K、Mg、Ca之间相关性明显,表明这些元素主要源自于海盐飞沫;Na与Pb、Cu、Cd、V、Zn、Fe、Al的相关性不明显,表明海盐不是这些元素的来源[57]. 进一步研究发现,Zn、Fe与Al的相关性较强,而Al一般被认为是地壳尘土的主要成分和示踪元素,因此台湾海峡大气Fe、Zn可认为主要源自于地壳尘土[57]. 此外,大气中的Pb与Cu、Zn、Fe含量之间呈现较好的正相关. 由于大气中的Pb一般被认为具有污染物特征,因此,Cu、Zn、Fe可能部分来自于人为污染物的排放,或者污染物在远距离大气输送过程中与矿物尘土经历了充分的混合, 因而它们之间呈现出了一定的相关性[57]. 相关性分析也应用于大洋海区如西北太平洋气溶胶成分源解析的研究[58]. 由于大气成分来源的多样性以及大气输送过程的复杂性,仅靠相关性分析还难以定量判别各类大气成分的来源,即使定性分析有时也存在较大误差,具有较大的局限性.
富集因子(Enrichment factors, EF),用以表示元素或成分在大气颗粒物中的富集程度,这一方法最早于1974年开始应用于大气颗粒物的源解析研究. 富集因子可以消除采样过程中的各种可变因素(如气象条件)及与污染源距离远近的影响,是一种简便的双重归一化处理方法,其原理是选择满足一定条件的元素作为参比元素(或参比成分),样品中污染元素/成分浓度与参考元素/成分浓度的比值与背景区中二者浓度比值的比率即为富集因子. 计算公式如下:
式中,Ci为元素/成分i的浓度,Cr为选定的参考元素/成分的浓度. 对于大气颗粒物,(Ci/Cr)颗粒即为大气中i相对于参比元素/成分r的相对浓度;同理,(Ci/Cr)背景则为地壳或海水中相应元素/成分的相对浓度,两者的比值即得到富集因子值[59]. 一般而言,如果某一元素/成分的EF值远远小于或远远大于1,则表明该元素/成分相对于参考源被稀释或富集[33].
在天津近海,通过富集因子分析得到渤海湾大气TSP主要有人为源、地壳源和海盐源[30]. 因子分析结果也表明,煤燃烧是中国边缘海气溶胶硫酸盐的主导性来源,油料燃烧是中国东海气溶胶硫酸盐的另一个重要来源,而在南海这一来源则不明显;此外,中国近海气溶胶硫酸盐的另一重要来源为有色金属冶炼[60]. 在胶州湾,富集因子法得出大气Cl−主要来自于海洋,Mg2+同时具有海洋源与地壳源,而SO42−主要为人为源,K+、Na+、NO3−分别主要来源于地壳土壤风化、海洋源以及人为活动排放[33]. 为识别胶州湾大气降水中溶解态微量元素的潜在来源,将降水中各元素同参考元素的比率与其在地壳中的比率对比,并将Al作为地壳源的参考元素计算获得了降水溶解态微量元素的富集因子. 结果表明大部分微量元素相对于地壳土壤呈现显著富集,表明它们均主要来自于海湾周边区域高强度的人类活动排放,尤其是Se通常被看作是煤燃烧的示踪元素. Mn的富集因子高达102.5,结合元素示踪法计算表明工业废气排放是胶州湾大气Mn的主要来源,地壳源占比较低[4]. 利用富集因子法对黄海千里岩岛气溶胶金属元素的源解析研究发现,气溶胶中海盐元素 K、Na、Ca、Mg的富集因子很低而其它元素的富集因子较高,说明黄海上空气溶胶的化学成分有相当部分来源于陆地[61]. 在台湾海峡,利用富集因子确定海盐飞沫不是大气Al、Fe、Zn、Cu、Pb、Cd、V元素的主要来源,Fe和 Zn可能主要来源于地壳尘土,同时,V也可能部分源于地壳,而Pb、Cu、Cd可能主要为人为源[57]. 大气颗粒物中元素浓度和富集系数随大气悬浮颗粒物的粒径而变化,被富集的元素趋于在小粒径颗粒物中富集. 此外,在东海[38]和南海北部[62]等海域也普遍应用富集因子法开展了大气颗粒物源解析研究.
在因子分析法的基础上,发展形成了主成分分析法(PCA). PCA是利用方差最大旋转法将原来众多具有一定相关性的变量重新组合成一组新的互相无关的综合指标来代替原来的指标,同时根据实际需要从中可以取出几个较少的总和变量尽可能多地反映原变量,是一种降维的统计方法. PCA法用于源解析仅能够实现定性判定,其结合绝对主因子-多元线性回归模型(APCS-MLR)之后可实现对大气颗粒物的定量源解析[63]. APCS-MLR由Thurston和Spengler首先提出,这一方法的基本原理为先期将获得的原始数据进行标准化的因子分析,在此基础上得到相关因子的绝对真实得分(APCS),并结合多元线性回归模型(MLR)计算得到各主因子对大气颗粒物的贡献率[63-64]. 目前,PCA是广泛应用于识别海洋大气颗粒物来源的方法,在我国近海得到了较多地应用.
在胶州湾,利用方差最大旋转PCA法来分析大气微量元素的来源,识别出了两个特征值大于1的主成分,解释了大约75.4%的总方差. 第一个主成分与Mn、Co、Zn、Se、Cr等元素密切相关. 显然,该主成分主要代表了人为源,如煤燃烧、垃圾焚烧、钢铁制造甚至农药及其类似物. 第二个主成分解释了全部样品总变量的33.6%,其对应于高负荷的Al、Fe、Pb、Cd,代表了矿物沙尘、有色金属冶炼以及机动车尾气排放的混合源[4]. 采用PCA法对东海气溶胶总态和溶解态微量元素的源解析结果表明,东海气溶胶微量金属元素主要存在3个源类型,分别为矿物尘土和人为污染物的远距离传输、海盐飞沫,其中人为污染物还包括生物燃料/煤燃烧、重油燃烧、金属冶炼业等[7]. 中国近海大气颗粒物主要存在3类来源:人为污染源(NO3−、NH4+、SO42−载荷较高)、海洋源(Na+、Cl−、Mg2+、Br−载荷较高)、地表扬尘源(TSP和Ca2+载荷较高). 3个因子分别解释了52.4%、22.5%、20.8%的方差,其中有机氮在3个因子中的载荷分别为0.82、0.33、0.41,表明中国边缘海气溶胶中的有机氮主要来自于人为排放源,而海洋源和地表扬尘/矿物气溶胶的贡献较小[65]. 在深圳近海,运用PCA法对降水中金属元素的源解析发现[66],重金属污染来源除受近20%的海洋源及10%的地壳源共同影响外,宝安点位还受周边工业生产排放、发电场燃料废气、机动车为期排放的影响,贡献率高达46.3%;大鹏新区点位与海上船舶排放、垃圾焚烧释放及生物质燃烧关系密切,这一来源的贡献率达51.9%;而盐田点位受盐田港码头燃料燃烧、交通源排放以及焚烧释放影响较大,贡献率达38.1%[66],表明不同区域周边排放源的不同导致了大气颗粒物来源的差异.
-
正定矩阵因子分解法(PMF)是在传统的因子分析法基础上进一步发展而来的一种新型大气颗粒物源解析方法[12]. PMF法的基本原理也是质量平衡(同公式1),但其仅需输入受体点的成分谱信息(X),即可利用最小二乘法解出源贡献量(G)和源成分谱信息(F). 由于其相比传统因子分析法可实现大气颗粒物的定量源解析,故此处将其单列. 同CMB相比,尽管不需要输入源成分谱信息,但需要有能对源类别进行指征的示踪物种(表2、表3),且需要的样品量较大(通常大于100个),以便于统计计算[11-12]. 此外,PMF法对源类型数目的确定和源类型的甄别有一定的主观性和不确定性. 在原理上,尽管PMF和PCA均是基于矩阵分解来进行污染物溯源的方法,但PMF较之PCA法在进行迭代运算中可同时确定污染源谱和贡献率,避免了矩阵分解的因子载荷和得分出现负值,使结果更具可解释性,也是美国国家环保署推荐的大气颗粒物源解析方法.
基于PMF模型,解析出渤海湾湿沉降样品中元素的主要污染源为燃煤、扬尘、工业和航运源,4种类型的源分别贡献了湿沉降样品中金属元素的12.8%、25.9%、33.1%和28.2%[31]. 运用PMF源解析方法,识别出青岛近岸海域气溶胶中OC的主要来源为二次生成,占比34%,其次为燃烧和其它不确定源(22%)、地壳源(17%)、机动车排放(14%)以及海洋源(13%)[37]. 也有研究同时运用两种受体模型——PMF和PCA,对北黄海大气气溶胶的化学成分谱进行分析[34],最终鉴别出6类来源:二次气溶胶(硝酸盐和硫酸盐)、土壤源、生物质燃烧、燃油排放、海盐飞沫和工业源,各自的贡献比例分别为42.4%、24.2%、11.5%、10.0%、9.3%和2.6%,其中二次气溶胶和土壤源是北黄海大气颗粒物的主要来源. 这一结果表明,北黄海气溶胶受到附近海域过往轮船排放和我国北方农业生产活动排放的影响明显,而且各类源的相对贡献季节变化较大. 在春、秋季,土壤源和生物质燃烧是主要来源,夏季残渣油的燃烧是主导性来源,而冬季则以二次气溶胶和工业源为主[34]. 目前在中国近海应用PMF法解析大气颗粒物来源的研究相比PCA法还不多,可能的原因是受到了样品数量的限制. 因此,如何在确保源解析精度的情况下降低样品数量是下一步需要解决的重点问题之一.
综上,以因子分析和PMF为代表的源未知受体模型在中国近海大气颗粒物源解析研究中均得到了较为广泛的应用,实现了从定性到半定量-定量的不同层次源解析目标. 尽管上述方法均存在某些不足和局限性,但其广泛应用对深入认识我国近海大气不同成分的来源仍然发挥了重要作用.
-
除上述源解析方法以外,目前在海洋大气颗粒物成分源解析中应用较多的还有特征比值法、指示因子法、同位素示踪法、气团后向轨迹法、潜在源贡献函数模型法等.
-
NH4-N/NO3-N法在中国近海大气干湿沉降营养盐源解析中得到了广泛的应用. 一般认为大气中的NH4-N主要来源于农业活动,包括氮肥NH3挥发,畜牧业以及人畜粪便等有机肥的使用等[67-68];而NO3-N则被认为与工业生产和交通排放密切相关[68]. 因此,在区域尺度上,NH4-N/NO3-N摩尔比被认为是评价大气氮沉降中农业源和工业源排放相对贡献的一个有用的指标[69]. 判定标准为:如果大气氮沉降中NH4-N/NO3-N<1,表明工业源排放是大气氮的主要来源;反之,则以农业源排放为主. 胶州湾大气气溶胶和降水中NH4-N/NO3-N值均大于1,表明来自农业源排放的还原性氮即NH4-N构成了胶州湾大气氮的主要来源[3,5],这与目前中国整体的氮沉降状况一致.
二甲基硫(DMS)在海洋与大气相互作用以及全球气候变化中扮演重要角色. 由于海洋浮游植物释放的DMS氧化可形成甲基磺酸盐(MSA)并进一步转化为非海盐源硫酸盐(nss-SO42−),因此,假设海洋大气中的nss-SO42−全部由浮游植物释放的DMS转化形成,则气溶胶中MSA/nss-SO42−的比值应稳定在0.065上下;而如果人为排放对海域大气nss-SO42−有显著贡献,则MSA/nss-SO42−的比值会显著降低. 因此,海洋大气中MSA/nss-SO42−的比值可作为海洋生源SO42−的一个很好的示踪物,并可指示生源排放和人为源对海洋大气总SO42−的相对贡献,如果这一比值相对较高,则指示海洋生源贡献较大. 据此,在西太平洋的研究发现,海洋气溶胶中MSA/nss-SO42−的比值均小于0.060. 由此得出,海洋生源排放对西太平洋边缘海域大气总nss-SO42−的平均贡献分别为24.6%±19.6%(夏季)和32.3%±61.5%(冬季),显著高于黄、东海的水平[47]. 在此基础上,进一步计算得出人为源、生源排放以及海洋飞沫对夏季西太平洋大气总SO42−的贡献率分别为45.7%、15.0%和39.3%,对冬季的贡献分别为30.1%、14.4%和55.5%[47]. 总体来看,夏季人为排放的贡献率高,冬季海洋飞沫具有较高的贡献,而生源排放的季节差异不大.
大气气溶胶中的NO3−与nss-SO42−的质量比值(NO3−/nss-SO42−)常被用来表征移动污染源(机动车尾气排放)和固定污染源(含硫煤燃烧)对大气中氮和硫相对贡献的大小. 若比值较高,说明移动污染源贡献较大,反之,则以固定污染源的贡献为主. 在我国,汽油和柴油燃烧释放的NOx和SOx的比值分别为13:1和8:1,而煤燃烧释放的NOx和SOx的质量比为1:2. 因此,气溶胶中NO3−/nss-SO42−的值较高代表移动污染源对大气中氮、硫的贡献大于固定污染源;反之,则表明固定污染源的贡献较高. 东海大气气溶胶中NO3−/nss-SO42−的比值为0.02—0.98,平均值为0.45±0.25[42],明显低于黄海[70],这表明移动污染源对黄海大气中氮和硫的贡献较大,而东海则以固定污染源的贡献较大. 需要指出的是,由于当今我国对于煤脱硫燃烧的要求逐渐提高,煤燃烧释放的NOx和SOx的比值可能会有所升高,从而导致这一方法的局限性日益凸显. 尽管如此,这一方法在对某些缺乏污染源排放清单和实测数据的海域定性判定固定污染源和移动污染源相对贡献的大小仍具有一定的实用意义.
气溶胶中的OC/EC比值可用来指示碳质气溶胶的来源[71-72]. 此外,木炭/烟灰(Char/soot)的比值也可作为指示因子用来判定碳质气溶胶的来源. 研究表明,气溶胶中Char/soot的比值在0.6左右可用于指示机动车尾气排放,比值在1.31和22.6可分别用于指示煤燃烧和生物质燃烧[73],也有认为比值为1.9和11.6可分别用于指示煤燃烧和生物质燃烧[74]. 基于此,在东海花鸟岛的研究表明,冬季气溶胶中较高的木炭/烟灰比值指示生物质燃烧和煤燃烧对碳质气溶胶的贡献占主导地位,而夏秋季比值较低,指示机动车尾气排放的贡献较大[75]. 由于OC/EC这一指标不仅受燃料类型(即一次排放)的影响,还受到二次有机气溶胶的制约. 相比之下,Char/soot比值这一指标对判定碳质气溶胶的来源更准确有效[75].
对于持久性有机污染物多环芳烃(PAHs),存在以下特征比值:①若荧蒽/(荧蒽+芘)(Flu/(Flu+Pyr))比值<0.4,表明PAHs主要源于石油类成分的挥发;Flu/(Flu+Pyr)处于0.4和0.5之间,表明PAHs源于石油类的燃烧;而当Flu/(Flu+Pyr)>0.5时,则说明PAHs来源于煤炭和生物质燃烧;②若茚并[1,2,3-cd]芘/(茚并[1,2,3-cd]芘+苯并[g,h,i]䓛)(InP/(InP+BghiP))比值<0.2,指示PAHs主要来源于石油类的泄漏和挥发;比值在0.2和0.5之间指示石油类燃烧,而在大于0.5时说明PAHs主要源于煤和木材的燃烧[76]. 选用上述特征比值进行判断,发现煤和生物质燃烧是环渤海西部地区大气PAHs的主要来源,燃油源在非采暖期有一定贡献[77]. 采用特征比值法和主成分分析-多元线性回归分析法(PCA-MLA)的分析结果也表明生物质燃烧和煤燃烧是渤海砣矶岛大气PAHs的主要贡献源[78],与上述结果一致.
-
海盐示踪法是一类较为常用的大气颗粒物源解析方法,一般将Na+作为海盐源的参考元素. 为区分海盐和人为源对气溶胶主要水溶性离子的贡献,参考如下公式计算:
式中,[K+]、[Ca2+]、[SO42−]、[Na+]分别是实际测得的样品中相应离子的质量浓度(μg·m3). 然而,这种计算方法可能引起一些降水成分的非海盐源浓度值为负数. 基于此,肖辉等[79]总结出一套较为合理的选取海盐源参考元素的方法:①如湿沉降中Cl−/Na+和Mg2+/Na+的当量浓度比值均大于或等于海水中的相应值1.167和0.227,则选用Na+作为海盐源的参考元素;②如Na+/Cl−和Mg2+/Cl−的当量浓度比值均大于或等于海水中的相应值0.859和0.195,则Cl−更适合作为海盐源的参考元素;③如Na+/Mg2+和Cl−/Mg2+的当量浓度比值均大于或等于海水中的相应值4.403和5.126,则选用Mg2+作为海盐源参考元素更为合适.
运用指示因子法,分别以Al和Si作为矿物气溶胶的指示元素,由公式计算得出矿物沙尘可占东海气溶胶TSP总质量浓度的50%和61%[80],表明东海气溶胶至少有一半来自于矿物气溶胶的贡献. 胶州湾大气水溶性离子主要存在三类来源,即人为源、地壳源和海洋源. 大气降水的化学组成可用来反映上述三类来源对大气各个水溶性离子的相对贡献. 海洋源、地壳源和人为源的相对贡献可以根据如下公式计算[81]:
式中,%SSF、%CF、%AF分别指代海洋源、地壳源以及人为源贡献的百分比;X为目标离子,[X/Na+]seawater和[X/Na+]sample分别代表海水和样品中目标离子与Na+的比值,[X/Ca2+]soil和[X/Ca2+]sample则分别指代土壤和样品中目标离子与Ca2+的比值. 源解析结果见表5.
为进一步总结三类来源对大气总离子的相对贡献,根据表5和胶州湾大气降水各类主要水溶性离子浓度的统计结果,运用如下公式定量估算了海洋源、地壳源以及人为源的贡献[33]:
式中,SSF%、CF%、AF%分别指代海盐源、地壳源和人为源的贡献百分数,ss-代表海盐源,nss-为非海盐源,∑ion代表所有测定的离子.
据此,估算出海洋源、地壳源以及人为源对胶州湾大气降水总水溶性离子的贡献比例分别为28.7%,14.5%和56.8%[33]. 整体而言,胶州湾大气水溶性离子以人为源排放占主导,凸显了高强度人类活动对近岸典型海域大气环境的显著影响. 需要指出的是,由于上述方法忽略了海洋浮游植物(生源)的贡献,可能导致海洋源(包括海洋生物源)对降水SO42−贡献的低估,这是由于海洋浮游植物生长释放的DMS可通过与羟基的反应生成SO2,并进一步氧化形成SO42−. 胶州湾生源硫化物对大气SO42−的平均贡献为6.9%[33],高于济州岛(3.6%)[82]. 因此,来自海洋的生源硫排放对胶州湾大气SO42−的贡献不容忽视. 尽管这一方法存在一定的局限性,但它仍一定程度上提供了海洋源、地壳源以及人为源对典型海湾大气水溶性离子的相对定量贡献,具有一定的积极意义.
-
同位素分为稳定同位素和放射性同位素. 目前在源解析研究中应用较多的稳定同位素包括δ13C、δ15N、δ18O、δ34S、204Pb/207Pb、87Sr/86Sr等,此外还包括单体碳、氮同位素等;而放射性同位素主要为Δ14C和Δ17O. 稳定和放射性同位素技术作为源解析与示踪手段,已广泛应用于大气污染物的源解析研究.
碳同位素示踪法是利用稳定性碳同位素的分馏效应和放射性碳同位素的衰变特征指示含碳物质的来源以及大气过程的一类方法[83]. 放射性碳同位素(14C)不仅能定性区分生物源和化石源,还能定量分析不同来源对OC和EC的贡献比率[84]. 利用放射性14C同位素(Δ14C)源解析结果表明,生物质燃烧和非燃烧排放对渤海大气OC的贡献为60.6%,而生物质燃烧排放对渤海大气EC的贡献为44.3%. 相比之下,由PMF法解析出的生物质燃烧排放对气溶胶OC和EC的贡献比Δ14C的解析结果分别低估了8.3%和9.6%[78]. 碳双同位素(14C和13C)可实现气溶胶水溶性有机碳(WSOC)的定量源解析. 理论而言,通过14C同位素定年,可以推断降水中OC的年龄,进而定量判定降水中老碳(化石燃料源OC)与现代碳(新生植被源OC)对大气颗粒物DOC的贡献值. 在山东沿海,降水中的DOC具有相对较老的14C年龄(平均为2841年)和贫化的13C值(平均值-24.4‰),表明大气中当代有机碳与14C贫化的化石燃料源DOC的混合[35]. 进一步,运用14C和13C双端元模型估算出山东沿海7%—52%的降水DOC来源于化石燃料燃烧[35]. 稳定碳同位素的应用方面,在冲绳附近海域,由同位素质量平衡估算春、冬季较高的δ13C值可能主要源自于东亚大陆冬季燃煤取暖带来的大量有机气溶胶的远距离传输,同时矿物沙尘对春季δ13C高值也有较大贡献,而夏季则更多来自于海洋浮游植物和大型藻类的释放[85].
氮稳定同位素的应用方面,大亚湾降水δ15N-NO3−丰度、离子组成以及气团后向轨迹均表明,煤燃烧、汽车尾气以及东北季风带来的中国大陆风尘输入是冬季大亚湾降水中氮的主要来源,而化石燃料燃烧(煤燃烧、汽车尾气)和西南季风输送的珠三角和东南亚扬尘则是春季降水氮的主导来源,而夏季的主要来源则为海洋源、汽车尾气和闪电[43]. 针对鉴别降水中NO3−来源提出的δ15N-δ18O双稳定同位素法,避免了使用单一的δ15N稳定同位素带来的误差和不确定性. 该方法不仅可较为精确地示踪降水中NO3−的来源,还可用于对NO3−的具体形成路径、迁移转化过程的探讨. 然而,稳定同位素方法精确使用的前提是明确当地硫、氮、氧的释放源,确定硫、氮、氧同位素的来源端元及贡献大小. 此外,进行硫、氮、氧稳定同位素分析的前处理过程复杂、费用昂贵,在一定程度上限制了该方法的推广应用[86]. 南海北部东沙岛的监测表明[44],干沉降中δ15N-NO3−和δ18O-NO3−的均值分别为-2.8‰和+58.8‰. 尽管湿沉降的样品有限,δ15N-NO3−依然呈现了一个与干沉降近似的均值-2.6‰,而δ18O-NO3−的均值却显著偏高(+78.8‰). 双同位素比值呈反相关和反季节性变化特征. δ15N-NO3−值夏季较高,冬季较低,而δ18O-NO3−值却恰好与之相反. 在冬季,不仅NO3-N的双同位素组成相对均匀,NH4-N和NO3-N的干沉降通量也相对均匀,反映了来自亚洲大陆的化石燃料燃烧的持续影响. 同位素值在夏季的较大变化可能表明干沉降硝酸盐的来源和动力形成过程存在差异,且夏季δ15N-NO3−的高值与生物质燃烧和闪电有关. 南海西沙群岛海域大气TSP中NO3−的δ15N和δ18O的高值均出现在寒冷月份,表明不同季节NOx的来源和氧化剂存在差异. 在冬季,NOx主要为人为源,特别是中国华南地区的煤炭燃烧,由此产生的高氮沉降又被O3氧化为NO3−. 在夏季,自然源如闪电固氮、生物土壤释放等占比增加,羟基的氧化效率也增长,表明自然源排放是该区域夏季大气NOx的重要来源. 综合来看,南海北部的大气颗粒物中NO3−的浓度和δ15N的值与西沙永兴岛相比较高,而δ18O的值则较低,表明大气理化过程(如与卤素反应生成粗颗粒NO3−)在NOx由沿岸地区向偏远海域传输的过程中引起了NO3−浓度和δ15N值的降低以及δ18O值的增长[45]. 在南海北部西沙永兴岛,由大气颗粒物δ15N和δ13C的值及其季节变化来看,海洋生物活动是大气颗粒物总氮的一个重要来源,南海周边化石燃料和生物质燃烧形成的陆源气团则是总碳的主导性来源. 二次气溶胶的形成和气溶胶化学上的远距离传输也改变了永兴岛大气总氮和总碳的浓度和同位素组成. 总碳和总氮的浓度以及同位素组成的季节性变化显著,表明它们受到不同来源和同位素分馏过程的影响[46]. 在大亚湾也开展了大气降水溶解有机物的δ13C、δ15N双同位素溯源研究[87]. 同位素分馏作用对氮同位素具有一定影响. NH3挥发和反硝化作用是氮损失的两种重要途径. 大气中NH3挥发作用中氮的同位素分馏效应明显,这一过程通常伴随15N贫化的NH3的产生和15N富集的NH4+库的形成. 反硝化作用亦可产生15N贫化的气体,同时导致剩余的NO3−库富集15N. 最新研究发现,由于轻同位素(14NH3)和重同位素(15NH3)在空气中不同的扩散速率导致了氨中氮同位素的分馏,使得15NH3贫化了17.7‰,与在北京实测得到的差异值(15.4‰)非常接近,并最终确认15.4‰可以作为校正被动采样氨氮同位素分馏效应的参数[88]. 在大气NO3−形成过程中,NOx循环导致的同位素分馏作用对δ15N-NO3−的影响很小,几乎可以忽略;煤燃烧和土壤排放的季节性差异导致了δ15N-NO3−的夏季低冬季高的季节分布特征[89].
Pb在自然界中存在4种稳定同位素:204Pb、206Pb、207Pb、208Pb。由于Pb同位素变化可用质谱精确测量,故这种变化通常可作为环境过程的示踪物[90]. Pb同位素组成具有明显的“指纹特征”,环境污染物质与其来源区具有相同的Pb同位素比值,用其研究污染来源能够得到理想的结果. 因此,Pb同位素被广泛运用于不同环境介质中污染源的示踪. 泉州湾大气降尘中204Pb/207Pb、206Pb/207Pb和208Pb/207Pb比值分别为0.0638—0.0640、1.1620—1.1696和2.4436—2.4546. 其中,206Pb/207Pb和208Pb/207Pb的比值介于自然源和汽车尾气之间,与五金、塑料厂及水泥中Pb同位素比值接近,说明人类生产活动可能是大气沉降中Pb的主要来源,也不排除人为源与自然源的混合作用[91]. 与国内其它城市气溶胶中的Pb同位素比值对比也发现了类似特征,反映了近几十年来我国的工业化和城市化发展带来的负面影响. 同样,与之邻近的兴化湾大气降尘206Pb/207Pb和208Pb/207Pb的比值低于自然源,高于汽车尾气,而与五金、塑料厂及水泥中Pb同位素比值相接近[92],再次表明人类生产活动可能是大气降尘中Pb的主要来源. 由Pb同位素识别出兴化湾大气气溶胶中的重金属主要来源于当地及附近区域的工业活动,而非天然污染[93]. 因此,Pb稳定同位素广泛应用于海洋大气重金属源解析,并取得了很好的效果.
-
气团后向轨迹模式(HYSPLIT)是由美国国家大气与海洋局空气资源实验室和澳大利亚气象局联合开发的一种应用于分析大气污染物传输和扩散轨迹的模型,其主要用于解释源的问题,即目标区域大气污染物是由于何种来源导致的影响[14]. HYSPLIT模型基于若干小时内的气象资料计算气团传输轨迹,据此综合分析获得目标区域不同时期内各个气团的来向和传输特征[94]. HYSPLIT模型普遍用来分析气团来源方向及传输路径对气溶胶成分浓度和干沉降通量的影响,对识别气溶胶成分的来源区域和传输过程具有重要价值. 利用HYSPLIT模式分析发现,黄渤海冬季以受西北气团影响为主,受京津冀、山东半岛和辽东半岛地区高强度人类活动产生的大气污染物输送的影响明显,而夏季以东海沿岸气团为主,受中国东部和东南沿海城市排放的影响较为明显,且来自日本和朝鲜半岛的气团中含有最高浓度的As. 春季,影响黄渤海的气团主要来自西伯利亚、我国西北内陆和东南沿海,大气As的浓度偏低[56]. 在胶州湾,气团来源方向和途经区域对气溶胶和降水中的主要化学成分含量有很大影响. 来自西北地区的气团对采样区域的影响频率最高,这一气团主要途经黄土高原、华北平原和京津冀等人口密集区域,其影响下的气溶胶和降水中人为源污染物和矿物成分的浓度最高,而来自东南方向的气团主要受洁净的海洋气流影响,气溶胶和降水中污染成分的浓度很低[3,5,55]. 在我国黄东海[36,95]、青岛南部近海[37,96]、大亚湾[43,97]、南海北部[81,98]以及西太平洋[47]等海区也开展了类似的研究,证实区域外气团来源对相关海区大气成分的输送有很大影响.
-
潜在源贡献函数模型(PSCF)的基本原理是条件概率函数,并据此识别可能的污染源的位置. 该方法通过在气团后向轨迹模拟结果的基础上,创建一定分辨率的矩形网格(i,j)覆盖研究区域,并对污染物浓度设定阀值. PSCF值是经过网格ij的污染轨迹数(mij)与该网格上经过的所有轨迹数(nij)的比值,即PSCFij = mij /nij. PSCF的值越大表明该网格点对该污染物的浓度贡献越大. PSCF值所对应网格组成的区域就是影响该污染物浓度的潜在源区. 由于PSCF是条件概率,当nij较小时,PSCF计算结果的不确定性较大. 此时,可引入权重函数Wij来降低计算的不确定性,即:WPSCF = Wij × PSCF. PSCF模型操作简便,易于实现,能解析出对受体点有显著贡献的所有源,可以定性指示大气污染物的源区并验证由因子分析解析出的来源. 这一方法的局限性体现在目前尚无参数来指示模型的不确定性[1]. 在渤海湾,利用PSCF法分别选择燃煤、扬尘、工业和航运源的指示元素Se、Fe、V、Sb进行潜在源贡献分析,发现Se元素的潜在源区主要分布在天津西南部、北京南部以及河北中部(京津冀工业区),这些区域是燃煤消耗量较大的典型工业区. Fe元素(扬尘源指示元素)的PSCF高值主要分布在距离观测点较近的区域和西北地区,反映了局地扬尘和西北沙尘远距离传输的贡献. 作为工业源指示元素,V的潜在源区分布较广,包括环渤海湾区域、河北中东部和山东西北部,这和华北的工业区分布较为吻合. Sb元素(航运源指示元素)的PSCF高值集中分布在渤海海域及海岸沿线[31],印证了海洋航运对近海和沿海区域大气重金属污染的影响. Yu等[32]利用PSCF法识别出京津冀、内蒙古和蒙古国对秦皇岛沿海地区大气N、P的贡献最大,这三个区域对秦皇岛沿海地区大气N、P的贡献约为70%. 总之,气团后向轨迹法和潜在源贡献因子分析法可用于外来源贡献较大海区的颗粒物源解析研究中.
除此之外,还有一些新型源解析方法如单颗粒气溶胶质谱[99]、显微分析与PMF模型结合[100]、扫描核探针技术与人工神经网络模式集成技术[101]等方法,但是,这些用于城市大气污染物源解析的方法在海洋大气颗粒物源解析研究中尚未见报道.
-
尽管受体模型发展至今已出现了十余种方法,但依然没有一种方法是十全十美的,或多或少都存在一定的缺陷和不足. 由于一种或一类源解析方法的局限性,往往在源解析结果上存在较多的不确定性,而多种源解析方法的应用则可在很大程度上规避这一缺陷. 因此,近年来,多方法集成/耦合使用成为了大气颗粒物源解析研究发展的一大趋势,并在海洋大气成分源解析研究中得到了较多的应用.
综合应用因子分析、回归分析及比值分析法对气溶胶物质来源进行鉴别,结果表明,大连海域(北黄海沿岸)大气气溶胶物质可分为三类:海盐源、地壳源、污染源. 集成分析结果表明,北黄海沿岸海域气溶胶中物质主要来自海水、气态物(SO2、NOx)、土壤尘、煤烟尘、燃油灰和工业废料[102]. 对于碳质气溶胶,运用滑动相关分析表明,PM2.5、OC和EC存在3个时段的污染来源明显差异,究其原因主要受渤海区域风场和污染来源时空变化的影响;集成运用气团后向轨迹和卫星火点分析结果发现,夏季特别是6月份山东半岛秸秆露天焚烧是渤海区域大气碳质气溶胶成分的主要贡献源[78]. 综合应用因子分析和相关回归分析,台湾海峡西部海域大气颗粒物中的Fe主要来自地壳风化尘土,少量来自污染物;Pb和Cd主要来自污染源,少量来自尘土和海水;Cu主要来自尘土,部分来自污染物,少量来自海水[40]. 综合运用PMF和PSCF方法,识别出东海花鸟岛气溶胶来源主要由6个因子构成,分别为一次工业排放(11.3%)、二次气溶胶(22%)、草酸盐相关气溶胶(15.7%)、海盐(36.7%)、船舶排放(6.3%)和矿物粉尘(8.1%). 人为源对可分辨气溶胶质量的贡献在2013年1月和2012年8月分别达到最高(76.6%)和最低(18%). 受东亚季风的强烈影响,二次气溶胶的主要来源区域为河北东南部和山东,这与该地区火力发电厂分布最为密集,并由此导致的前体物排放量最多相一致. 草酸盐相关气溶胶主要由海岸带产生,而初级工业排放这主要来源于鲁西南和长三角地区[39]. 类似地,综合利用水溶性离子的化学计量学关系、相关性分析以及主成分分析,得出东海南部彭佳屿春季TSP中Na+、Cl−和Mg2+全部来源于海盐飞沫;K+来源较多,其中海盐、生物质和煤燃烧是其主要来源;60%的Ca2+来源于当地建筑粉尘;77%的SO42−来源于煤和生物质燃烧;NO3−主要来源于汽车尾气、生物质和煤燃烧等;NH4+主要受二次气溶胶和生物质燃烧的影响[41].
-
大气颗粒物源解析研究是科学有效地开展大气污染防治工作的基础和前提. 在高强度人为排放的影响之下,我国近岸海域大气颗粒物呈现出了较为明显的陆源特点,同大洋海区大气颗粒物的组成区别很大. 经过几十年的发展,大气颗粒物源解析技术从无到有、由简单到复杂逐渐发展起来,创建了包含源清单法、源模型法和受体模型法在内的三大类技术方法体系. 三类方法体系由于原理或假设不同,源解析结果存在一定的差异,表现出各自在实际应用上的优势和局限性. 至今,发展最为完善、应用最为广泛的当属受体模型. 由于无需输入详细的源排放清单和源成分谱信息,以因子分析为代表的源未知受体模型得到了越来越普遍的应用. 尽管CMB和PMF模型是美国环保署推荐的源解析模型,但在中国近海大气颗粒物源解析中,由于缺乏精细化源成分谱信息,CMB法的应用受到很大限制,而以相关性分析、富集因子法、PCA以及PMF为典型代表的因子分析方法得到了广泛应用. 同时,还有其它一些受体模型方法如特征比值法、指示因子法、稳定/放射性同位素示踪法以及气团后向轨迹、潜在源贡献函数模型等应用也较为普遍. 此外,为了得到更为准确的源解析结果,也为了相互验证,多方法集成联用的源解析研究也有开展,在很大程度上提高了大气颗粒物源解析结果的精准度和可靠性.
通过近几十年对大气沉降颗粒物源解析的分析可知,中国近海大气颗粒物的来源主要为人为源,如煤燃烧、工业排放、生物质燃烧、农业化肥使用、城市垃圾焚烧以及二次生成等,还有部分来自矿物沙尘、建筑扬尘、海盐飞沫以及生源释放等的自然源排放,一定程度上实现了来源量化解析. 各类来源的相对贡献大小与海域位置、陆源输入强度、气象因素以及浮游植物生物量等因素有关,导致不同海区、不同季节的大气颗粒物来源存在较大差异. 大气颗粒物源解析结果具有动态性、分层次和相对稳定三个显著特征,其功能主要体现在为本地化大气污染防控提供依据,为重污染天气过程应急响应提供决策依据和筛选最优防控措施等. 遗憾的是,由于各类源解析方法的局限性和不确定性,至今对我国近海各海区大气颗粒物的源解析还很初步,难以实现排放源的精准识别和精确量化,这是我国开展精准化大气污染防治和针对性污染物减排面临的重要挑战. 针对上述问题,今后我国海洋大气颗粒物源解析技术的发展可从以下三方面发力. 一是注重发展精细化源解析技术,开展多种源解析方法的集成和耦合,研发混合源解析模型技术,发挥各自优势,精确识别并量化各类源贡献及其空间分布和传输规律,以实现早预防、早治理. 目前世界各国都在积极探索大气颗粒物源解析的新方法,而将不同的受体模型和扩散模型有机结合,如建立集合模型或混合模型等将成为未来大气颗粒物源解析的重要发展方向. 二是基于受体模型和空气质量模型,开发在线实时快速源解析技术,满足源解析结果的时效性要求. 三是研发二次颗粒物源解析技术,明确二次颗粒物的一次排放源贡献. 如此,不断发展和完善适合于我国近海的大气颗粒物成分源解析技术方法体系,并重点在受人为影响显著的海湾、近岸区域以及生态脆弱区开展精准化大气污染物源解析研究,一方面可提供大气污染物的空间分布和传输途径信息,服务于国家近海大气污染预测预警体系的构建,为海岸带区域颗粒物污染联防联控提供决策依据;另一方面,结合大气污染物浓度和沉降通量的常态化监测,基于“陆海统筹”视角减轻陆源大气成分远距离传输对近海生态环境的负面影响,维护海洋生态系统健康,促进海洋生态系统的可持续发展和海洋资源的可持续利用.
中国近海大气颗粒物来源解析研究进展
Source apportionment of atmospheric particulates in China sea: A review
-
摘要: 大气颗粒物成分复杂、来源广泛,其通过干湿沉降的方式向海洋的输送是海洋营养物质和一些有害成分的重要来源之一,会对海洋生态系统产生重要影响. 大气颗粒物源解析可追溯并量化各类大气成分的排放源信息,为科学防控大气污染和评估海洋大气沉降的生态环境效应提供科学依据. 目前的大气颗粒物源解析研究多聚焦城市,对海洋的研究相对不足. 本文系统梳理了目前各类源解析方法的发展现状,综述了其在我国海洋大气颗粒物源解析中的应用,并展望了未来的研究方向. 结果表明,1)源清单法、源模型法和受体模型三大类技术方法体系在我国海洋大气颗粒物源解析中均有应用,但由于各类方法的适用性和局限性,以因子分析为代表的源未知受体模型得到了最广泛地应用;2)以指示因子法和同位素示踪法为代表的新方法不断涌现,多方法联用源解析技术实现了海洋大气颗粒物来源的准确识别;3)中国近海大气颗粒物的主要来源为化石燃料燃烧、工业排放、生物质燃烧、农业化肥使用、城市垃圾焚烧以及二次生成等的人为源,也有部分来自矿物沙尘、建筑扬尘、海盐飞沫以及生源释放等自然源,其贡献的相对大小与海域位置、陆源输入强度、气象条件以及浮游植物生物量等因素有关. 今后应首先从完善源成分谱入手,注重开展多种源解析方法的集成与耦合,研发混合源解析技术模型,开发在线实时快速源解析和二次颗粒物源解析技术,并重点在受人为影响显著的海湾、近岸区域以及生态脆弱区开展精准化大气污染物源解析研究. 不断发展适合我国近海的大气颗粒物源解析方法体系,对实现陆海统筹下的海洋生态保护战略目标意义重大.Abstract: The composition of atmospheric particulates is complex with a various of sources. Its transport to the ocean via dry and wet deposition is one of the important sources of marine nutrients and some harmful components, which will have important impacts on the marine ecosystem. Source apportionment of atmospheric particulates can trace and quantify the emission sources of various atmospheric components, and provide scientific basis for prevention and control of air pollution and assessment of the ecological environmental effects of marine atmospheric deposition. So far, the study on the source apportionment of atmospheric particulates mainly focuses on cities, whereas, the research of marine aerosol is relatively insufficient. In view of this situation, we summarized the current development of various source apportionment methods, reviewed their application in the study of source apportionment of marine atmospheric particulates, and proposed the future research directions. The results show that (1) the emission inventory, source-oriented model and receptor model have been applied in the source apportionment of marine atmospheric particulates in China. However, due to the applicability and limitations of various methods, the source-unknown receptor model represented by factor analysis has been widely used; (2) new methods such as indicator factor method and isotopic tracing are emerging constantly, the source analysis technology combined with multiple methods has realized the accurate source identification of marine atmospheric particulates; (3) the main sources of chemical components in atmospheric particulates in China sea are anthropogenic sources such as fossil fuel combustion, industrial emissions, biomass combustion, agricultural fertilizer use, municipal waste incineration and secondary formation of pollutants, etc. In addition, the contributions of natural sources such as mineral dust, construction dust, sea salt droplets and biogenic release, etc. cannot be neglected. The relative contributions of these sources are related to the location of the sea, the intensity of terrestrial input, meteorological conditions and phytoplankton biomass. In the future, firstly, perfecting the source component spectrum, emphasizing on the integration and coupling of multiple source analysis methods, developing mixed source analysis technology models, developing online real-time fast source identification and secondary particle source apportionment techniques. On this basis, the research on precise source apportionment technique should be mostly applied in the significantly anthropogenic-influenced bays, nearshore waters and ecological fragile areas in China sea. It is of great significance for realizing the strategic goal of marine ecological protection under the land-sea coordination to continuously develop the method system of atmospheric particulate source apportionment that suitable for China's offshore waters.
-

-
表 1 沿海主要港口大气污染物排放量清单
Table 1. The emission inventory of air pollutants in major coastal ports of China
表 2 大气颗粒物源解析研究中常用的主要无机示踪物[4,11]
Table 2. The main inorganic tracers used in source apportionment of atmospheric particulates
排放源类型
Types of emission sources无机示踪物
Inorganic tracers风起扬尘The wind dust Al、Si、Ca、非海盐源钙离子(nss-Ca2+)、Mn、Ti 建筑尘Construction dust Ca、nss-Ca2+、Mg 冶炼尘Smelting dust Fe、Mn、Zn、Co、Cu 机动车尾气Vehicle exhaust Ni、Co、Cu、Zn、Pb、有机碳(OC) 煤燃烧Coal combustion As、Se、S、非海盐源硫酸根离子(nss-SO42-)、Cl、元素碳(EC) 燃油排放Fuel emissions Ni、V、Cu 生物质燃烧Biomass burning K、非海盐源钾离子(nss-K+)、Zn、Cl 二次无机盐Secondary inorganic salts nss-SO42-、NO3-、NH4+ 注:nss-指代non-sea salt,即非海盐源,下文同此. 表 3 大气颗粒物源解析研究中常用的主要有机示踪物[11]
Table 3. The main organic tracers used in source apportionment of atmospheric particulates
排放源类型
Types of emission sources有机示踪物
Organic tracers机动车尾气Vehicle exhaust 藿烷、甾烷、晕苯、荧蒽、芘 煤燃烧Coal combustion 藿烷、甾烷、烷基芘、多环芳烃 生物质燃烧Biomass burning 左旋葡聚糖、植物甾醇、萜类物质 餐饮排放Dining lampblack 胆固醇、十六烷酸、十八烷酸、豆甾醇、β-谷甾醇、壬醛、9-十六烯酸 香烟排放Cigarette smoke 反异三十烷、反异三十二烷、异三十一烷、异三十二烷、异三十三烷 天然气燃烧Natural gas combustion 苯并(k)荧蒽、苯并(b)荧蒽、苯并(e)芘、茚并(1,2,3-cd)荧蒽、茚并(1,2,3-cd)芘、苯并(g,h,i)苝 植物碎屑Phytodetritus 高分子量的奇碳烷烃 轮胎磨损Tyre wear 高分子量偶碳烷烃、苯并噻唑 表 4 部分源解析方法信息汇总
Table 4. Summary of partial source apportionment methods
源解析方法
Source apportionment methods主要示踪物
The primary tracers大气颗粒物源类型
Types of atmospheric particulate sourcesCMAQ[24] — 9类,包括柴油车排放、汽油车排放、生物质燃烧、煤燃烧、道路扬尘、二次离子(硫酸盐、硝酸盐、铵盐)、二次有机物 CMB-无机CMB-Inorganic[51] SO42-、NO3-、NH4+、EC、有机碳(OC)、Al、As、Ba、Br、Ca、Cu、Fe、K、Mn、Pb、Se、Si、Ti、Zn 8类,包括机动车排放、生物质燃烧、煤燃烧、道路扬尘、二次硫酸盐、二次硝酸盐、二次铵盐)、二次有机碳 CMB-有机CMB-Organic[52] EC、Al、Si、9种烷烃、7种藿烷和甾烷、3种树脂酸、6种多环芳烃、2种不饱和脂肪酸、4种其它有机物 10类,包括柴油车排放、汽油车排放、生物质燃烧、道路尘、二次硫酸盐、二次硝酸盐、二次铵盐、肉类烹饪、天然气燃烧、植物碎屑 PMF[53] SO42-、NO3-、NH4+、As、Ba、Br、Cu、Mn、Pb、Se、Ti、Zn、Al、Si、K、Ca、Fe、OC1、OC2、OC3、OC4、OP、EC1、EC2、EC3以及气体CO、SO2、NO、HNO3、NOx 9类,包括柴油车排放、汽油车排放、生物质燃烧、煤燃烧、道路扬尘、硫酸盐、硝酸盐、两类工业排放 表 5 胶州湾大气降水中不同离子来源的相对贡献[33]
Table 5. Relative contributions of different sources to ions of atmospheric precipitation in Jiaozhou Bay
离子
Ion species海盐源/%
Sea-salt source非海盐源 Non sea-salt source 地壳源/%
Crust source人为源/%
Anthropogenic sourceSO42− 7.1 1.3 91.6 NO3− 0 0.2 99.8 Cl− 96.2 0.3 3.5 Ca2+ 3.8 96.2 0 Mg2+ 56.6 43.4 0 K+ 7.0 93.0 -
[1] 胡敏, 郭庆丰, 郭松, 等. 我国沿海大气颗粒物特征及陆源影响研究[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2018: 1-225. HU M, GUO Q F, GUO S, et al. Study on characteristics of atmospheric particulates and its influence from terrigenous source in coastal China[M]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group, 2018: 1-225 (in Chinese).
[2] 邓小文, 冯银厂, 陈魁, 等. 大气颗粒物精细化源解析技术研究及应用[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2018: 1-188. DENG X W, FENG Y C, CHEN K, et al. Study and application of refined source apportionment technology for atmospheric particulates[M]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing Group, 2018: 1-188 (in Chinese).
[3] XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Fluxes, seasonal patterns and sources of various nutrient species (nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon) in atmospheric wet deposition and their ecological effects on Jiaozhou Bay, North China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 576: 617-627. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.134 [4] XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Atmospheric wet deposition of dissolved trace elements to Jiaozhou Bay, North China: Fluxes, sources and potential effects on aquatic environments [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 174: 428-436. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.004 [5] XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Water-soluble nitrogen and phosphorus in aerosols and dry deposition in Jiaozhou Bay, North China: Deposition velocities, origins and biogeochemical implications [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2018, 207: 90-99. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.03.001 [6] 阿米拉, 耿柠波, 曹蓉, 等. 大气颗粒物中典型有机物的分析方法和污染特征研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(12): 3774-3786. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020081204 A M L, GENG N B, CAO R, et al. Research progress of analytical methods and pollution characteristics of typical organic pollutant in atmospheric particulate matter [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(12): 3774-3786(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020081204
[7] HSU S C, WONG G T F, GONG G C, et al. Sources, solubility, and dry deposition of aerosol trace elements over the East China Sea [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2010, 120: 116-127. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2008.10.003 [8] SONG J M. Biogeochemical processes of biogenic elements in China Marginal Sea[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2010, 1-662. [9] 宋金明, 李学刚, 袁华茂, 等. 海洋生物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 1-690. SONG J M, LI X G, YUAN H M, et al. Marine biogeochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020: 1-690 (in Chinese).
[10] 冯银厂. 我国大气颗粒物来源解析研究工作的进展 [J]. 环境保护, 2017, 45(21): 17-20. FENG Y C. Research progress of source apportionment of atmospheric particulates in China [J]. Environmental Protection, 2017, 45(21): 17-20(in Chinese).
[11] 郑玫, 张延君, 闫才青, 等. 中国PM2.5来源解析方法综述 [J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 50(6): 1141-1154. ZHENG M, ZHANG Y J, YAN C Q, et al. Review of PM2.5 source apportionment methods in China [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2014, 50(6): 1141-1154(in Chinese).
[12] 张延君, 郑玫, 蔡靖, 等. PM2.5源解析方法的比较与评述 [J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(2): 109-121. doi: 10.1360/N972014-00975 ZHANG Y J, ZHENG M, CAI J, et al. Comparison and overview of PM2.5 source apportionment methods [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(2): 109-121(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972014-00975
[13] 朱坦, 冯银厂. 大气颗粒物来源解析原理、技术及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 1-220. ZHU T, FENG Y C. Principle, technology and application of source apportionment of atmospheric particulates[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012: 1-220 (in Chinese).
[14] 高健, 李慧, 史国良, 等. 颗粒物动态源解析方法综述与应用展望 [J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(27): 3002-3021. doi: 10.1360/N972016-00363 GAO J, LI H, SHI G L, et al. Overview of the development and application of multi-time resolution source apportionment for particulate matters [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(27): 3002-3021(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972016-00363
[15] 童克难. 新一批大气污染物源排放清单编制技术指南发布[N]. 北京: 中国环境报, 2015. [16] 吕建华, 付飞, 左华, 等. 青岛市船舶废气排放清单及应用[J]. 环境保护科学. 2019, 45(5): 107-115. LÜ J H, FU F, ZUO H, et al. Ship emission inventory and its application in Qingdao[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2019, 45(5): 107-115 (in Chinese).
[17] 伏晴艳, 沈寅, 张健. 上海港船舶大气污染物排放清单研究 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2012, 12(5): 57-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2012.05.013 FU Q Y, SHEN Y, ZHANG J. On the ship pollutant emission inventory in Shanghai port [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2012, 12(5): 57-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2012.05.013
[18] 曾凡涛, 吕靖. 厦门港船舶排放清单及港口生态效率评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(5): 2304-2311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.05.054 ZENG F T, LÜ J. Ship emission inventory and valuation of eco-efficiency in Xiamen Port [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(5): 2304-2311(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.05.054
[19] 王占山, 李晓倩, 王宗爽, 等. 空气质量模型CMAQ的国内外研究现状 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(6L): 386-391. WANG Z S, LI X Q, WANG Z S, et al. Application status of models-3/CMAQ in environmental management [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 36(6L): 386-391(in Chinese).
[20] 王君悦, 刘朝顺. 基于WRF-Chem的长三角地区PM2.5和O3污染协同控制研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(7): 32-42. WANG J Y, LIU C S. Study on the synergistic control of PM2.5 and O3 pollution in the Yangtze River Delta region based on WRF-Chem model [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2022, 42(7): 32-42(in Chinese).
[21] 吕兆丰, 魏巍, 杨干, 等. 某石油炼制企业VOCs排放源强反演研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(10): 2958-2963. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.10.010 LÜ Z F, WEI W, YANG G, et al. Inversion research in VOCs source emission of a petroleum refinery [J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(10): 2958-2963(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.10.010
[22] 王自发, 谢付莹, 王喜全, 等. 嵌套网格空气质量预报模式系统的发展与应用 [J]. 大气科学, 2006, 30(5): 778-790. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2006.05.07 WANG Z F, XIE F Y, WANG X Q, et al. Development and Application of Nested Air Quality Prediction Modeling System [J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2006, 30(5): 778-790(in Chinese). doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2006.05.07
[23] CHOW J C, WATSON J G, GREEN M C, et al. Middle-and neighborhood-scale variations of PM10 source contributions in Las Vegas, Nevada [J]. Journal of Air Waste Manage, 1999, 49: 641-654. doi: 10.1080/10473289.1999.10463837 [24] BAEK J, PARK S K, HU Y, et al. Source apportionment of fine organic aerosol using CMAQ tracers[A]. In: Proceedings of the Models-3 Use’s workshop[C]. North Carolina: Research Triangle Park, 2005: 1-6. [25] 王征, 秦翠红, 张卫, 等. 中国近周边海域船舶活动对陆域空气质量的影响 [J]. 交通节能与环保, 2019, 15(6): 36-38,53. WANG Z, QIN C H, ZHANG W, et al. Impact of ship activities in the surrounding waters of China on land air quality [J]. Transport Energy Conservation & Environmental Protection, 2019, 15(6): 36-38,53(in Chinese).
[26] 陈春强, 张强, 关晓东, 等. 沙尘和灰霾期间中国近海大气氮沉降通量估算 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(6): 2596-2605. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.06.043 CHEN C Q, ZHANG Q, GUAN X D, et al. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition fluxes during dust and haze events over China Seas [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(6): 2596-2605(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.06.043
[27] 沈傲, 周慧娴, 樊琦, 等. 珠江三角洲地区冬季硫、氮干沉降的来源解析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(12): 5142-5151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.12.005 SHEN A, ZHOU H X, FAN Q, et al. Source apportionment to dry deposition of sulfur and nitrogen in winter in the Pearl River Delta region [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(12): 5142-5151(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.12.005
[28] 廖乾邑, 陈建文, 罗彬, 等. 颗粒物源解析研究进展与展望 [J]. 资源节约与环保, 2015(11): 136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2015.11.106 LIAO Q Y, CHEN J W, LUO B, et al. Progress and prospect of source apportionment of atmospheric particulate matter [J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2015(11): 136(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2015.11.106
[29] 戴树桂, 朱坦, 曾幼生, 等. 从元素组成看渤海、黄海海域大气气溶胶的特征与来源 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 1987, 6(3): 9-13. DAI S G, ZHU T, ZENG Y S, et al. Characteristics and sources of atmospheric aerosols in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea from elemental composition [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1987, 6(3): 9-13(in Chinese).
[30] 韩斌, 白志鹏, 解以扬, 等. 天津近海夏季大气颗粒物元素特征及来源解析 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2010, 29(6): 829-833. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.06.012 HAN B, BAI Z P, XIE Y Y, et al. Characterization of elements and source apportionment in atmospheric particulate matter in Tianjin offshore area in summer [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2010, 29(6): 829-833(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.06.012
[31] 张国忠, 崔阳, 潘月鹏, 等. 渤海湾大气金属元素沉降和来源解析研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(8): 2708-2716. ZHANG G Z, CUI Y, PAN Y P, et al. Deposition fluxes and source apportionment of atmospheric trace metals in the Bohai Bay[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(8): 2708-2716 (in Chinese).
[32] YU L, MA X, GAO H, et al. Distribution and source identification of nitrogen and phosphorus in aerosols in the Qinhuangdao coast, north China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2020, 234: 117475. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117475 [33] XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Chemical characteristics, deposition fluxes and source apportionment of precipitation in the Jiaozhou Bay, North China [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 190: 10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.02.001 [34] 王琳, 祁建华. 北黄海大气气溶胶来源解析[C]//中国环境科学学会大气环境分会. 第19届中国大气环境科学与技术大会暨中国环境科学学会大气环境分会学术年会论文集: 2012年卷. 青岛, 2012: 154. WANG L, QI J H. Source apportionment of atmospheric aerosols over the North Yellow Sea[C]//Atmospheric Environment Branch, Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences. Proceedings of the 19th Chinese Conference on Atmospheric Environment Science and Technology and the 2012 Academic Annual Conference of Atmospheric Environment Branch of Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences: 2012. Qingdao, 2012: 154 (in Chinese).
[35] WANG X, GE T, XU C, et al. Carbon isotopic (14C and 13C) characterization of fossil-fuel derived dissolved organic carbon in wet precipitation in Shandong Province, China [J]. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 2016, 73: 207-221. doi: 10.1007/s10874-015-9323-3 [36] WANG L, QI J, SHI J, et al. Source apportionment of particulate pollutants in the atmosphere over the Northern Yellow Sea [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 70: 425-434. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.12.041 [37] DING X, QI J, MENG X. Characteristics and sources of organic carbon in coastal and marine atmospheric particulates over East China [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2019, 228: 281-291. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.06.015 [38] 秦晓光, 程祥圣, 刘富平. 东海海洋大气颗粒物中重金属的来源及入海通量 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(8): 2193-2196. QIN X G, CHENG X S, LIU F P. Source and air-sea fluxes of heavy metals in the atmospheric particles of East China Sea [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(8): 2193-2196(in Chinese).
[39] WANG F, CHEN Y, MENG X, et al. The contribution of anthropogenic sources to the aerosols over East China Sea [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 127: 22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.12.002 [40] 陈立奇, 王志红, 杨绪林, 等. 台湾海峡西部海域大气中金属的特征II. 大气颗粒金属的来源和入海通量 [J]. 海洋学报, 1999, 21(1): 23-31. CHEN L Q, WANG Z H, YANG X L, et al. Characteristics of metals in atmosphere over the western Taiwan Strait II. Sources and flux [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1999, 21(1): 23-31(in Chinese).
[41] 罗笠, 高树基, 肖化云, 等. 台湾彭佳屿岛春季TSP中水溶性离子源解析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(12): 4452-4459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.12.006 LUO L, GAO S J, XIAO H Y, et al. Source apportionment of water-soluble ions in spring TSP of Pengjia Islet, Taiwan [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(12): 4452-4459(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.12.006
[42] 石金辉, 张云, 高会旺, 等. 东海大气气溶胶的化学特征及来源 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(8): 1750-1757. SHI J H, ZHANG Y, GAO H W, et al. Characteristics and sources of atmospheric aerosols over the East China Sea [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(8): 1750-1757(in Chinese).
[43] WU Y C, ZHANG J P, LIU S L, et al. Nitrogen deposition in precipitation to a monsoon-affected eutrophic embayment: Fluxes, sources, and processes [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 182: 75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.03.037 [44] YANG J Y T, HSU S C, DAI M H, et al. Isotopic composition of water-soluble nitrate in bulk atmospheric deposition at Dongsha Island: sources and implications of external N supply to the northern South China Sea [J]. Biogeosciences, 2014, 11: 1833-1846. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-1833-2014 [45] XIAO H W, XIE L H, LONG A M, et al. Use of isotopic compositions of nitrate in TSP to identify sources and chemistry in South China Sea [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 109: 70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.03.006 [46] XIAO H W, XIAO H Y, LUO L, et al. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope compositions of bulk aerosol samples over the South China Sea [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 193: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.09.006 [47] WANG Q D, SONG J M, LI X G, et al. Geochemical characteristics and potential biogeochemical effect of water-soluble ions in atmospheric aerosols over the western boundary regions of Pacific Ocean [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2019, 227: 101-111. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.04.024 [48] 郑玫, 张延君, 闫才青, 等. 上海PM2.5工业源谱的建立 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(8): 1354-1359. ZHENG M, ZHANG Y J, YAN C Q, et al. Establishing PM2.5 industrial source profiles in Shanghai [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(8): 1354-1359(in Chinese).
[49] 冯银厂, 白志鹏, 朱坦. 大气颗粒物二重源解析技术原理与应用[J]. 环境科学, 2002, 23(S1): 106-108. FENG Y C, BAI Z P, ZHU T. The principle and application of improved-source-apportionment technique of atmospheric particulate matter[J]. Environmental Science, 2002, 23(Sup 1): 106-108 (in Chinese).
[50] 张玉梅, 张卫东, 王军玲. 大气PM2.5源解析“源清单化学质量平衡法(I-CMB) ”模型的建立与应用. 大气科学学报, 2015, 38(2): 279-284. ZHANG Y M, ZHANG W D, WANG J L. Establishment and application of pollutant Inventory-Chemical Mass Balance (I-CMB) model for source apportionment of PM2.5[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2015, 38(2): 279-284 (in Chinese).
[51] YAN B. Characterization and source apportionment of ambient PM2.5 in Atlanta, Georgia: On-road emission, biomass combustion and SOA impact[D]. Atlanta: Georgia Institute of Technology, 2009. [52] ZHENG M, CASS G R, KE L, et al. Source apportionment of daily fine particulate matter at Jefferson street, Atlanta, GA, during summer and winter [J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2007, 57: 228-242. [53] KE L, LIU W, WANG Y, et al. Comparison of PM2.5 source apportionment using positive matrix factorization and molecular marker-based chemical mass balance [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 394: 290-302. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.01.030 [54] 邢建伟, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等. 胶州湾大气活性硅酸盐干沉降特征及其生态效应 [J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9): 3096-3104. XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Dry deposition characteristics of atmospheric reactive silicate at Jiaozhou Bay and its potential ecological effects on marine ecosystem [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 3096-3104(in Chinese).
[55] XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Atmospheric wet deposition of dissolved organic carbon to a typical anthropogenic-influenced semi-enclosed bay in the western Yellow Sea, China: Flux, sources and potential ecological environmental effects [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 182: 109371. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109371 [56] 袁帅, 王艳, 刘汝海, 等. 黄渤海气溶胶中砷的分布特征和季节变化 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9): 4151-4157. YUAN S, WANG Y, LIU R H, et al. Distribution characteristics and seasonal variations of arsenic in atmospheric aerosols over the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(9): 4151-4157(in Chinese).
[57] 张远辉, 詹建琼, 陈立奇, 等. 台湾海峡大气微量金属的化学特征及其入海通量 [J]. 台湾海峡, 2009, 28(4): 447-454. ZHANG Y H, ZHAN J Q, CHEN L Q, et al. Chemical characteristics of atmospheric trace metal and input to Taiwan Strait [J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2009, 28(4): 447-454(in Chinese).
[58] FU J P, WANG B, CHEN Y, et al. The influence of continental air masses on the aerosols and nutrients deposition over the western North Pacific [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 172: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.10.041 [59] 殷美雪. 中国中东部地区大气湿沉降中的离子化学特征[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2015. YIN M X. Chemical characteristics of ions in atmospheric wet deposition over central and eastern China[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2015 (in Chinese).
[60] GAO Y, ARIMOTO R, DUCE R A, et al. Atmospheric non-sea-salt sulfate, nitrate and methanesulfonate over the China Sea [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 1996, 101(D7): 12601-12611. doi: 10.1029/96JD00866 [61] 刘昌岭, 张经, 于志刚. 黄海海域大气气溶胶特征及重金属的大气输入量研究 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 1998, 17(4): 1-6. LIU C L, ZHANG J, YU Z G. Study on the characteristics of the aerosol and atmospheric flux of the heavy metals over the Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1998, 17(4): 1-6(in Chinese).
[62] WU Y C, ZHANG J P, NI Z X, et al. Atmospheric deposition of trace elements to Daya Bay, South China Sea: Fluxes and sources [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 127: 672-683. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.12.046 [63] GUO H, WANG T, LOUIE P K K. Source apportionment of ambient non-methane hydrocarbons in Hong Kong: Application of a principal component analysis/absolute principal component scores (PCA/APCS) receptor model [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2004, 129(3): 489-498. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2003.11.006 [64] 邱立民, 刘淼, 王菊, 等. 绝对主因子分析法解析龙岩市大气中的可吸入颗粒物来源 [J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版), 2012, 50(2): 371-376. QIU L M, LIU M, WANG J, et al. Sources apportionment of atmospheric particles PM10 in Longyan with absolute principal component analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Science Edition), 2012, 50(2): 371-376(in Chinese).
[65] 石金辉. 中国近海大气沉降中氮组分的分布特征及对春季水华事件的影响分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011. SHI J H. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen species over the China Sea and its impact on a spring bloom[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2011 (in Chinese).
[66] 蒋冰艳, 何龙, 陈德华, 等. 深圳近海区域降水中重金属湿沉降通量及源解析 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(7): 1460-1473. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017091901 JIANG B Y, HE L, CHEN D H, et al. Wet deposition flux and sources of heavy metals in precipitation in the coastal area of Shenzhen [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(7): 1460-1473(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017091901
[67] FAHEY T J, WILLIAMS C J, ROONEY-VARGA J N, et al. Nitrogen deposition in and around an intensive agricultural district in central New York [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1999, 28(5): 1585-1600. [68] GU B J, GE Y, REN Y, et al. Atmospheric reactive nitrogen in China: sources, recent trends, and damage costs [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(17): 9420-9427. [69] PAN Y P, WANG Y S, TANG G Q, et al. Wet and dry deposition of atmospheric nitrogen at ten sites in Northern China [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(14): 6515-6535. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-6515-2012 [70] 于丽敏, 祁建华, 孙娜娜, 等. 南、黄海及青岛地区大气气溶胶中无机氮组分的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2007, 27(2): 319-325. YU L M, QI J H, SUN N N, et al. Study on inorganic nitrogen of aerosol in the Qingdao area and over the Yellow Sea and the South China Sea[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 27(2): 319-325 (in Chinese).
[71] WANG F W, GUO Z G, LIN T, et al. Characterization of carbonaceous aerosols over the East China Sea: The impact of the East Asian continental outflow [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 110: 163-173. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.03.059 [72] WANG J Z, HO S S, CAO J J, et al. Characteristics and major sources of carbonaceous aerosols in PM2.5 from Sanya, China [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2015, 530-531: 110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.005 [73] CHOW J C, WATSON J G, KUHNS H D, et al. Source profiles for industrial, mobile, and area sources in the Big Bend regional aerosol visibility and observational (BRAVO) study [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 54: 185-208. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.07.004 [74] CAO J J, ZHU C S, TIE X X, et al. Characteristics and sources of carbonaceous aerosols from Shanghai, China [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13(2): 803-817. doi: 10.5194/acp-13-803-2013 [75] WANG F, FENG T, GUO Z, et al. Sources and dry deposition of carbonaceous aerosols over the coastal East China Sea: Implications for anthropogenic pollutant pathways and deposition [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 245: 771-779. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.059 [76] LUO X J, CHEN S J, MAI B X, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in suspended particulate matter and sediments from the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent coastal areas, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 139(1): 9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.05.001 [77] 刘书臻. 环渤海西部地区大气中的PAHs污染[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2008. LIU S Z. Atmospheric PAH contamination in the Western Watershed of Bohai Sea, China[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2008 (in Chinese).
[78] 王晓平. 渤海区域PM2.5来源及多环芳烃沉降通量[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2015. WANG X P. Sources of PM2.5 and deposition fluxes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Bohai Sea[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015 (in Chinese).
[79] 肖辉, 沈志来, 黄美元. 西太平洋热带海域降水学特征 [J]. 环境科学学报, 1993, 13(2): 143-149. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.1993.02.015 XIAO H, SHEN Z L, HUANG M Y. Chemical characteristics of tropical Western Pacific precipitation [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1993, 13(2): 143-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.1993.02.015
[80] GUO L, CHEN Y, WANG F J, et al. Effects of Asian dust on the atmospheric input of trace elements to the East China Sea [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2014, 163: 19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.04.003 [81] ZHANG X, ZHUANG G, GUO J, et al. Characterization of aerosol over the Northern South China Sea during two cruises in 2003 [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(36): 7821-7836. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.06.031 [82] ARIMOTO R, DUCE R A, SAVOIE D L, et al. Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 1996, 101: 2011-2023. doi: 10.1029/95JD01071 [83] 耿晓飞. 南海与东印度洋热带海洋碳质气溶胶的地球化学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020. GENG X F. Geochemistry study on tropical marine carbonaceous aerosols over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020 (in Chinese).
[84] 曹芳, 章炎麟. 碳质气溶胶的放射性碳同位素(14C)源解析: 原理、方法和研究进展 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(4): 425-432. CAO F, ZHANG Y L. Principle, method development and application of radiocarbon (14C)—Based source apportionment of carbonaceous aerosols: A review [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(4): 425-432(in Chinese).
[85] KUNWAR B, KAWAMURA K, ZHU C. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of ambient aerosols collected from Okinawa Island in the western North Pacific Rim, an outflow region of Asian dusts and pollutants [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 131: 243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.01.035 [86] 邢建伟, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等. 青岛近岸区域典型海陆人为交互作用下酸雨的化学特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(2): 296-308. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.02.2016061706 XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Chemical characteristics of acid rain under the representative interaction among sea, land and anthropogenic activities in the coastal area of Qingdao [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(2): 296-308(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.02.2016061706
[87] WU Y C, LI J L, JIANG Z J, et al. Shifting of dissolved organic matter components and sources in precipitation into an intensified anthropogenic influenced embayment: Interpretation from spectral characteristics and dual stable isotopes [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2022, 270: 106089. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106089 [88] PAN Y P, GU M N, SONG L L, et al. Systematic low bias of passive samplers in characterizing nitrogen isotopic composition of atmospheric ammonia [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2020, 243: 105018. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105018 [89] LI Z J, WALTERS W W, HASTINGS M G, et al. Nitrate isotopic composition in precipitation at a Chinese megacity: seasonal variations, atmospheric processes, and implications for sources [J]. Earth and Space Science, 2019, 6(11): 2200-2213. doi: 10.1029/2019EA000759 [90] 陈成祥, 庄峙厦, 刘海波, 等. 不同赋存形态土壤铅同位素比值用于判别地域性差异的研究 [J]. 分析化学, 2007, 35(1): 103-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2007.01.021 CHEN C X, ZHUANG Z X, LIU H B, et al. Source differentiation by lead isotope ratios in total digests of soil fractions and residual fractions [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 35(1): 103-105(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2007.01.021
[91] 吴辰熙, 祁士华, 方敏, 等. 福建省泉州湾大气降尘中的重金属元素的沉降特征 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2006, 19(6): 27-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2006.06.005 WU C X, QI S H, FANG M, et al. Precipitation characteristics of heavy metal in dustfall to Quanzhou Bay of Fujian Province [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 19(6): 27-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2006.06.005
[92] 吴辰熙, 祁士华, 苏秋克, 等. 福建省兴化湾大气沉降中重金属的测定 [J]. 环境化学, 2006, 25(6): 781-784. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.06.027 WU C X, QI S H, SU Q K, et al. Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals to Xinghua Bay, Fujian Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2006, 25(6): 781-784(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.06.027
[93] 龚香宜, 祁士华, 吕春玲, 等. 福建省兴化湾大气重金属的干湿沉降 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2006, 19(6): 31-34. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2006.06.006 GONG X Y, QI S H, LV C L, et al. Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals to Xinghua Bay, Fujian Province [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 19(6): 31-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2006.06.006
[94] STOHL A. Trajectory statistics: A new method to establish source-receptor relationships of air pollutants and its application to the transport of particulate sulfate in Europe [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1996, 30: 579-587. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(95)00314-2 [95] ZHU L, CHEN Y, GUO L, et al. Estimate of dry deposition fluxes of nutrients over the East China Sea: The implication of aerosol ammonium to non-sea-salt sulfate ratio to nutrient deposition of coastal oceans [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 69: 131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.12.028 [96] QI J H, LIU X H, YAO X H, et al. The concentration, source and deposition flux of ammonium and nitrate in atmospheric particles during dust events at a coastal site in northern China [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18: 571-586. doi: 10.5194/acp-18-571-2018 [97] WU Y C, ZHANG J P, LIU S L, et al. Aerosol concentrations and atmospheric dry deposition fluxes of nutrients over Daya Bay, South China Sea [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 128: 106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.019 [98] LAI S C, XIE Z Y, SONG T L, et al. Occurrence and dry deposition of organophosphate esters in atmospheric particles over the northern South China Sea [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 127: 195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.015 [99] 徐娇, 张邓毅, 张英磊, 等. 基于单颗粒气溶胶质谱技术的源解析新算法 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2): 575-584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.02.009 XU J, ZHANG D Y, ZHANG Y L, et al. A new particle source apportionment method based on single particle mass spectrometry dataset [J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(2): 575-584(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.02.009
[100] 李晓璐, 耿红, 张辰, 等. 显微分析与PMF模型结合用于大气颗粒物源解析的方法探索[C]//中国环境科学学会. 第二十五届大气污染防治技术研讨会论文集. 西安, 2021: 439. LI X L, GENG H, ZHANG C, et al. Study on the method of source apportionment of atmospheric particulate matter by combining microscopic analysis and PMF model[C]//Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences. Proceedings of the 25th Symposium on Air Pollution Control Technology. Xi’an, 2021: 439 (in Chinese).
[101] 李晓林, 朱节清, 郭盘林, 等. 基于扫描核探针技术的大气气溶胶单颗粒物源识别与解析方法研究与应用 [J]. 核技术, 2004, 27(1): 27-34. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3219.2004.01.006 LI X L, ZHU J Q, GUO P L, et al. The source identification and apportionment of aerosol particles in the atmosphere by scanning nuclear microprobes [J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2004, 27(1): 27-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3219.2004.01.006
[102] 李连科, 栗俊, 范国全, 等. 大连海域大气气溶胶物质来源分析 [J]. 重庆环境科学, 1997, 19(5): 18-23. LI L K, LI J, FAN G Q, et al. Sources analysis of marine aerosol in the atmosphere at Dalian sea area [J]. Chongqing Environmental Science, 1997, 19(5): 18-23(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载:

