-
自20世纪60年代以来,阻燃剂(flame retardants, FRs)常被添加到塑料材料中阻止燃烧,或者延缓火灾的蔓延. 然而,经过40年的发展,在公共健康领域,溴代阻燃剂(brominated flame retardants, BFRs)成为高度关注的焦点,研究者发现部分BFRs具有高毒性、持久性和长距离迁移性,因此,BFRs被逐步禁用或者限制使用[1]. 有机磷酸酯(organophosphate ester, OPEs)成为BFRs的替代品. 据统计,大约有40种OPEs用作阻燃剂和塑料添加剂,应用于建筑、纺织、化工、电子、交通运输以及家装材料等行业. OPEs以有机磷三酯(主要使用形式)、有机磷二酯(有机磷三酯的分解产物)和聚磷酸盐的形式存在,磷酸三酯根据取代基的不同分为卤代烷基、非卤代烷基和芳香基OPEs,通常氯代OPEs被用作阻燃剂、非卤代烷基OPEs被用作增塑剂和消泡剂[2-4]. 近20年来,全球范围内OPEs的需求和产量显著增加[5-6]. 2001年,全球有机磷类物质(OPs)用量总计1.86 × 105 t,其中70%为OPEs. 2016年,OPEs生产量占阻燃剂市场总量的18%,位居阻燃剂市场第二[7]. 2017年,全球阻燃剂消耗量为2.53 × 106 t,其中30%的消费量与磷相关,而2008年仅为11%. 2001年,日本OPEs的使用量为2.2 × 104 t,2005年则增至3.0 × 104 t[8]. 2006年,欧洲阻燃剂总消耗量约为4.65 × 105 t,其中OPEs占比20%. 多数OPEs可被归为欧盟所认定的高产量化学品(high-production volume, HPV),其产量在欧洲每年超过1000 t[9]. 2007年,我国OPEs的年产量接近7.0 × 104 t,且以每年15%的速度增长[10].
OPEs是一类从亲水强极性到强疏水非极性的有机化合物,其辛醇-水分配系数的对数值(lgKOW)在−0.65—9.43范围内,覆盖了多氯联苯(4 < lgKOW < 7)及有机氯农药等化合物的lgKOW值范围. 拥有不同的取代基表现不同的理化性质,芳基取代的OPEs普遍比另外的两类酯(除磷酸三(2-乙基己基)tris(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate, TEHP以外)的疏水性更强,挥发性小,非氯代烷基类则随着分子量增大,其lgKOW也会有增大的趋势,但溶解度和蒸气压等会相应减小. 氯代类OPEs性质差异变化较大可能由于引入氯代基团的缘故. 某些OPEs在大气中的半衰期较长,大于《斯德哥尔摩公约》中大气持久性的阈值(> 2 d)[11],如磷酸三(2-氯乙基)酯(tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate, TCEP)和磷酸三氯丙酯(tris(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate, TCPP)已经达到欧盟法规中持久或非常持久化合物的筛选标准[12-13]. 而且,一些研究指出,OPEs具有神经毒性、生殖毒性、致癌性和基因毒性,TCEP已经达到了欧盟关于化学物质致癌性的毒性筛选标准[4-5]. OPEs可以通过摄食和皮肤接触等途径,进入人体,产生负面的健康风险[14]. Liu等[1]发表于《Nature》的研究指出,全球18个大城市的大气中均检出了OPEs及其转化产物,转化产物可能会具有比母体化合物更强的毒性,其持久性也可能大1个数量级,因此转化产物的总风险应当高于母体化合物. 综上所述,OPEs与传统的持久性有机污染物(persistent organic pollutants, POPs)相似,具有持久性、生物蓄积性和毒性.
OPEs主要以物理掺杂混合而非化学键合方式加入到聚合物中,二者的作用力弱,在产品使用周期内和固废处理时,易于通过磨损和渗漏等方式从材料里析出而进入环境. OPEs的半挥发性和持久性导致其具有长距离传输的潜力,在远离人类活动的偏远地区(如高山和极地等地区)也监测到OPEs的存在. 目前,较多的研究报道了OPEs在地表水[15]、沉积物[16]、大气[17]、土壤[18]及生物体[19]等多种环境介质以及人类尿液[20]、血浆[21]、血清[22]、母乳[23]和胎盘[24]等组织中OPEs的含量水平. 由此可见,OPEs的分布范围较广,含量和检出频率较高,且具有明确的毒性,研究OPEs的环境行为及其风险水平具有重要的科学和管理意义.
近年来,有研究者对OPEs的分析方法[25]、水体和室内环境中赋存状况[26]及风险水平[27]、在生物体内的迁移和转化以及生物暴露毒性[28]等方面的进展进行了综述,然而对空气中OPEs的研究进展尚未进行系统总结,从而未能清晰地阐明OPEs的环境归趋和长距离迁移等环境行为以及影响因素的作用机制. 本文将综述近20年的相关研究成果,揭示OPEs在国内外大气环境中的赋存状况,探讨在大气中影响OPEs环境行为的关键因素,并对目前存在的科学问题进行展望.
-
为实现区域环境质量管理和保护公众健康的目的,需要了解大气中OPEs的含量水平、排放清单和来源,理解其在大气中的来源、传输、分配和降解等关键的环境行为过程. 与室内空气相比,室外大气具有更强的流动性,OPEs得以快速扩散,总浓度水平迅速下降,在大多数的报道中仅有几纳克每立方米,比室内空气低1—4个数量级[29]. 在德国的莱茵河畔室内空气中OPEs是该地区大气中含量的10倍左右. 北极Zepplin监测站、Ny-Ålesund市和Longyearbyen市室内空气中的OPEs比室外空气中高2—350倍[30]. 表1总结了世界范围大气中OPEs浓度分布,其分布趋势呈现明显的地域性差异. 在人口密集、经济发达的大型城市大气中OPEs浓度明显高于偏远地区、乡村地区和海洋区域. 例如,西班牙拉科鲁尼亚(6.72 ng·m−3)[31]、中国上海(4.07 ng·m−3)[32]、美国休斯敦(3.09 ng·m−3)[33]、意大利仁德(3.17 ng·m−3)[34]以及德国莱伊河流经地区(3.13 ng·m−3)[35]大气中OPEs含量显著高于加拿大北极地区(0.18 ng·m−3)[36]、美国休斯敦的乡村(0.30 ng·m−3)和睡熊沙丘(0.17 ng·m−3)[33]、德国北海(0.38 ng·m−3)[37]以及全球大洋(0.48 ng·m−3)[8]. 由此可见,大气中OPEs的存在状况明显地受人类活动和经济水平的影响.
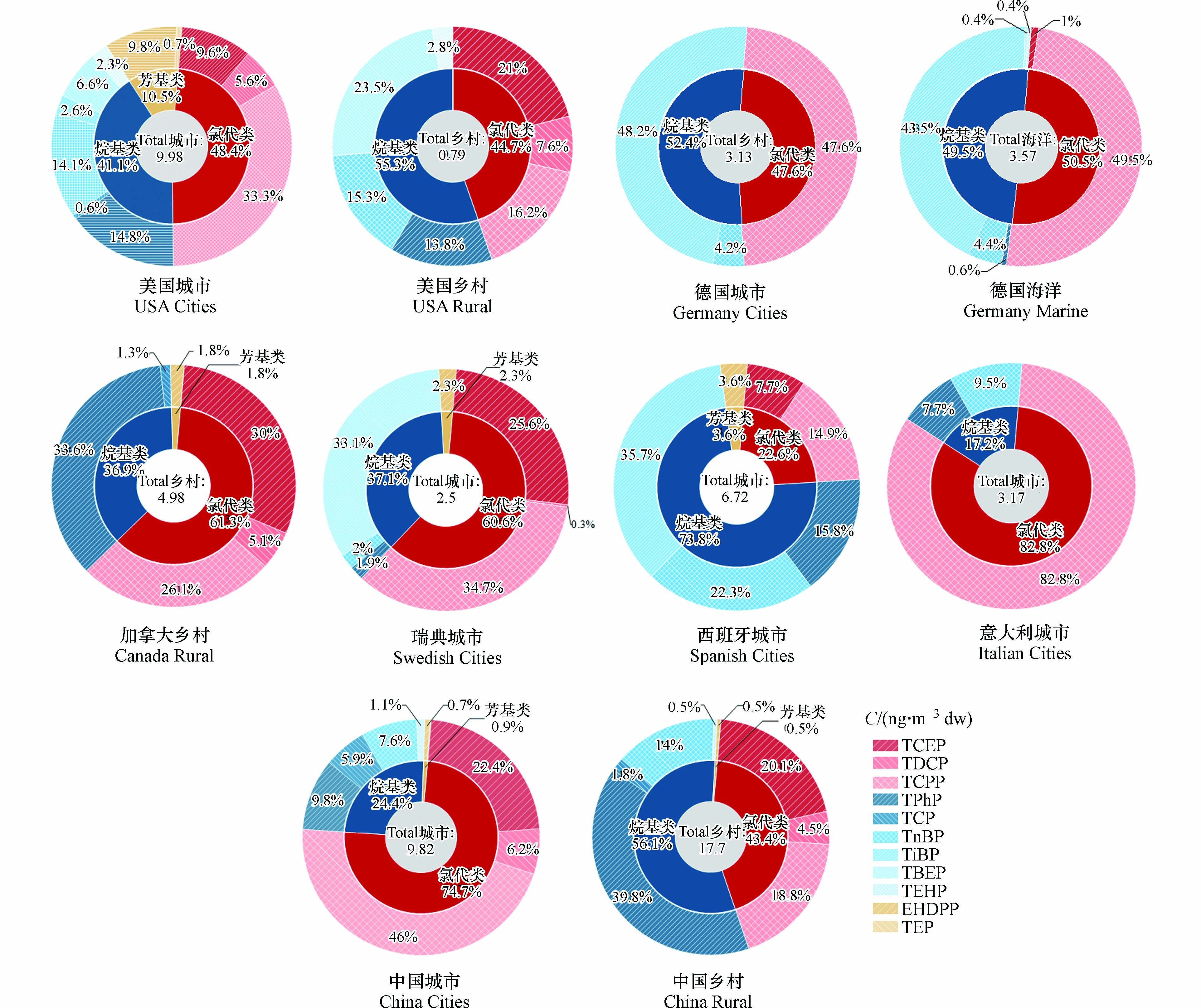
除了OPEs总量的差异外,其组成也呈现明显的地域特征. 图1比较了多个国家的城市与农村大气中OPEs的组成特征. 总体来说,不同种类OPEs的贡献度在各城市间差异较大,主要以氯代类和烷基类为主,少数地区芳基类贡献较高. 就洲际尺度而言,北美洲的美国和加拿大的OPEs的组成较为接近,然而同属欧洲的德国城市、西班牙城市、意大利城市和瑞典城市大气中OPEs的组成相差较大. 就城市而言,意大利城市、加拿大乡村、瑞典城市和中国城市大气中氯代类OPEs显著高于其他两类,而在西班牙城市、土耳其城市和中国农村以及部分城市(成都和大连)大气中烷基类OPEs是主要成分[39, 45];氯代类和烷基类OPEs在美国和德国农村大气中是主要成分,且贡献接近,芳烃类OPEs所占比例低于10.5%. 美国五大湖区的大气调查发现,氯代OPEs是城市地区的主要组成成分,贡献比在50%—80%,偏远地区则主要是由非氯代OPEs主导,贡献比为75%[53]. 氯代OPEs在中国北京和瑞典斯德哥尔摩空气中OPEs贡献比为88%和60%[41, 54]. 此外,在全球(包括印度洋、北极、太平洋和南大洋)海洋大气中3种氯代OPEs贡献率为88%[8]. 同样,通过对加拿大北极地区(2007—2013)和德国北海(2010—2012)等地的观测发现氯代OPEs的浓度均有显著提升,这表明氯代OPEs在大气中排放量逐年上升[36-37, 46].
-
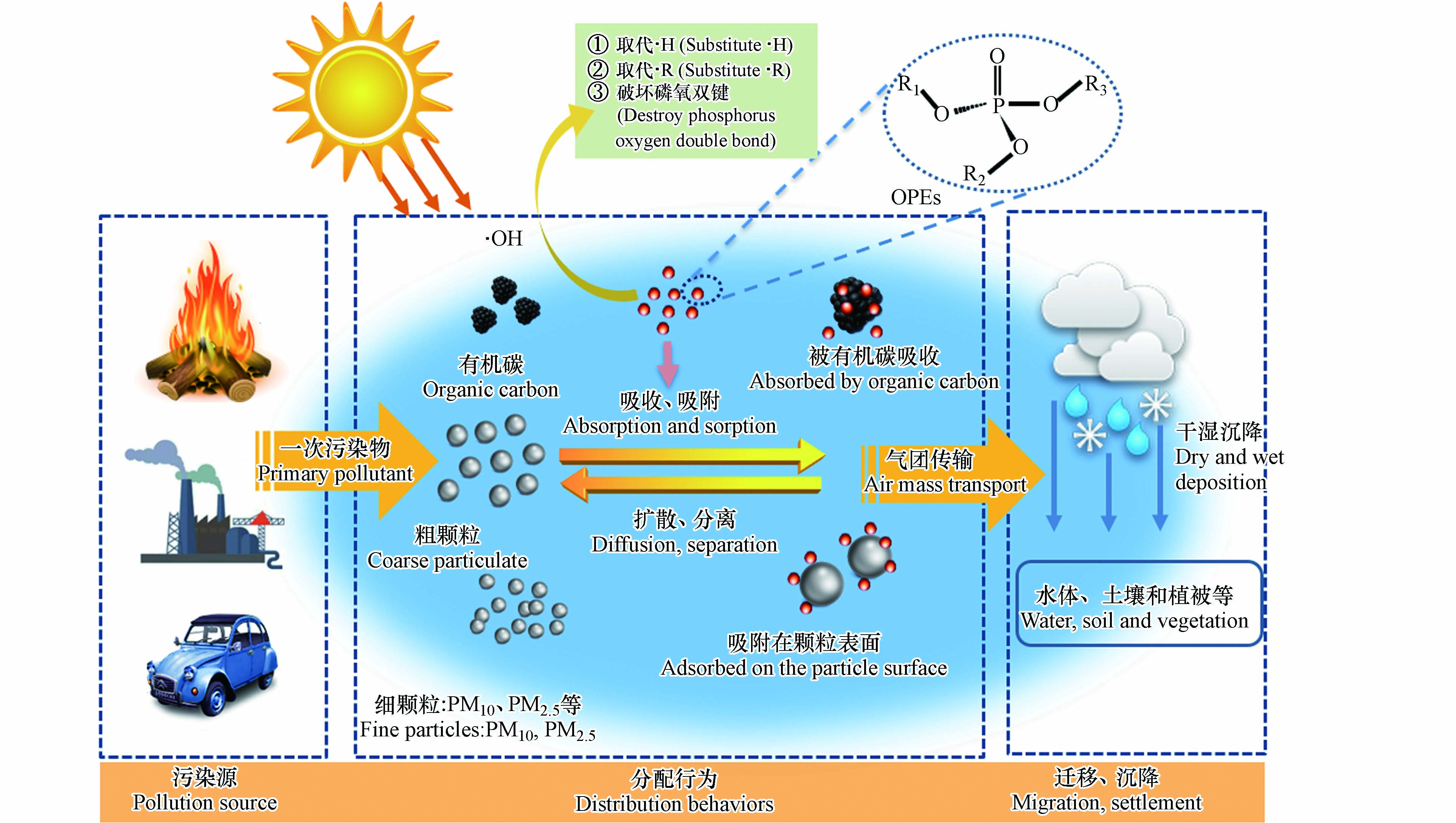
近年来,已有较多的研究报道了世界各地大气环境中OPEs的赋存和来源状况,但是对于OPEs大气环境行为和归趋的研究相对较少. 大气中的OPEs会与燃烧、工业排放和交通运输产生有机碳和颗粒物产生吸附/解吸作用,同时发生一定程度的光解作用. 一部分OPEs随气团运动扩散和迁移,产生区域污染,在干、湿沉降作用下,OPEs降落至土壤、水体和植被表面,从而进入整个生态环境中,如图2所示. 揭示OPEs在大气环境中的分配、迁移和光降解有利于阐明其在大气中的归趋,为污染排放控制提供更好的理论依据.
-
大气中的OPEs可通过吸附/吸收作用进入颗粒相,同样可以通过挥发作用释放至气相,从而达到一定程度的动态平衡. OPEs在气相和颗粒相中的分配特征是决定大气中OPEs的持久性和长距离迁移能力的关键因子之一[55]. 颗粒相OPEs比例的上升是降低OPEs的降解程度、延长持久性和增强长距离大气迁移(LRAT)潜力的一个可能的原因[56]. 而且,气-粒分配影响有机污染物的生物可利用性,具有重要的毒理学和风险控制管理意义. 因此,了解OPEs的气态和颗粒态的相间分布对于理解OPEs的归趋和分配,评估OPEs的生态毒性至关重要.
多数研究者将OPEs的颗粒相结合浓度近似看作整体大气中的总浓度,即认为OPEs主要存在于颗粒相而非气相[8, 50, 57]. Salamova等[58]发现,芝加哥冬季大气环境中OPEs在颗粒相中占比达到95% ± 2%,仅蒸气压较高的TnBP在气态样品中检出. 针对北大西洋和北极[59]、西北太平洋到北冰洋[60]以及北海[37]的研究支持上述结果. 但有学者质疑上述结论,原因为研究所选择的OPEs具有相似的物理化学性质(如仅是卤代OPEs),或者气相OPEs分析方法的检出限比颗粒相高,造成气相的检出率低[36, 53]. 而且,有相反的分配结果报道. 德国海岸大气中气相OPEs占测定总量的55%,且88%的TiBP存在于气相[61]. 采用国际经合组织(OECD)的总持久性(Overall Persistent,POV)和长距离迁移潜力的筛选工具(Screening Tool)模拟大气中OPEs的环境归趋,结果指出至少有半数的受试OPEs应该主要存在气相中[41, 62]. 大规模的监测工作往往受制于财力、人力和能源的限制,目前大气中OPEs调查研究存在着采样范围不够大,数据量不足等缺陷,采用理论模型预测大气SVOCs的环境归趋和长距离传输正日益成为研究污染物大尺度环境行为的一个有效手段. 目前,采用实际监测和理论模型预测的大气中OPEs的气-粒分配特征的研究常常出现相反的结论,表明仍需要从化合物分类以及分配机制和控制因素角度开展深入、细致的研究.
用于定量描述和预测大气中OPEs的颗粒相比例的模型有Junge-Pankow(J-P)模型、Harner-Bidleman(H-B)模型和多参数线性自由能关系模型(pp-LFER)等,基本信息如表2所示. 研究发现分配系数(lgKP(J-P))与过冷饱和蒸汽压的对数值(lgPLº)呈显著负相关,如TCEP和TCPP等高蒸气压(lgPLº > -2)的OPEs在预测模型主要存在于气相中,而高分子量(如TCP和TEHP)蒸气压较小(lgPLº < -3.73)的OPEs在颗粒相中的比例大于50%[63-64]. 相较于模型预测值,KP(J-P)的实测值更高. 挥发性较强的化合物一般对温度的变化较为敏感,因而在不同季节间的分配特征表现出明显差异. 在气温较高的夏季,蒸汽压较大的OPEs(TEP、TCEP和TnBP)挥发性更强,更容易逃逸到周围的空气中,因此,冬季比夏季表现出更高的颗粒相分配[64]. J-P模型与实测值之间的差异化也可能与颗粒物的表面积有关,不同类型的气溶胶会引起θ值发生改变. 空气中粒径较小的粒子具有更大的比表面积,对OPEs具有更强的吸附能力,一些OPEs倾向于与更小尺寸的空气颗粒结合[65]. 因此,大气中OPEs受蒸汽压的影响,挥发性较强组分主要存在于气相,温度降低时粒子中赋存比例有所上升,且更易存在于细颗粒中.
H-B模型认为颗粒物中有机质对半挥发性有机物的吸收作用在分配过程中发挥主要作用,化合物的亲脂性是影响分配的主要因素,辛醇-空气分配系数(KOA)作为关键变量对OPEs的气-粒分配预测的影响最大. 研究表明,OPEs的颗粒相分配系数KP(H-B)与KOA、有机质比例(fOM)呈显著正相关. 这与Khairy等[66]监测埃及室内、外大气中OPEs,所得结论相一致,多种OPEs单体颗粒相分数(Φ)与KOA成显著正相关关系,这也说明了KOA可以作为OPEs气-粒分配预测的关键因素. 在大气环境中,具有较高KOA的OPEs组分向气溶胶中有机质扩散的趋势更强,伴随着大气中TSP浓度的增加,脂溶性较高的OPEs组分主要存在于颗粒相中,而lgKOA < 8.4的大多数组分主要分配在大气气相. Wu等[67]通过分析美国五大湖空气中OPEs的气-粒分配特征发现,虽然模型预测显示TEP、TCEP、TnBP和EHDPP等OPEs的KOA预测值相对较低,但实地观测则发现上述化合物具有较高的气固分配比(26%—63%),表明其KP值可能受其他参数的联合控制[68]. 采用皮尔森线性相关性分析时,H-B模型的颗粒相比例(fpart)与lgPºL之间的关系很弱,J-P模型预测的fpart与lgKOA亦如此. Tool软件预测的fpart与lgKOA二者之间关系曲线呈现S形,当fpart处在0.1—0.9的范围时,其与lgKOA值呈现线性正相关. 基于蒙特卡洛随机数进行模型不确定分析的结果表明,lgKAW、lgKOW和 lgPºL不是导致Tool模型和H-B模型预测气-粒分配比例之间显著差异性的关键因素,应当确定和评估外部驱动力的作用[57]. 例如,颗粒物减弱对羟基自由基(∙OH)的吸收,并且与黑炭的底物效应共同作用阻碍了大气光氧化反应的进行,使得颗粒物结合的OPEs具有更长的大气半衰期. 这些机制的共同作用导致了OPEs优先分配到颗粒相的比例增加[59].
pp-LFER模型将气-粒分配系数(Kp(pp-LFERg/p))和吉布斯自由能联系在一起,描述了极性和非极性SVOCs在颗粒物中的水非溶态有机质(Water Insoluble Organic Matter,WIOM)中的吸附. 预测组分的结构和化学性质决定预测结果,预测分数与电子供体-受体的相互作用呈正相关,适用于极性化合物. Yaman等[63]采用pp-LFER模型预测OPEs颗粒相比例,结果表明TCP、TBEP、TEHP主要存在于颗粒相,预测值稍低;更易挥发的TCEP和TCPP主要存在于气相中,占比范围在18%—43%,与实测值相比,模型高估了其在气相中的比例. 预测的气-粒分配比例与实际监测值之间存在一定的差异,可能是由于气相中OPEs被玻璃纤维滤膜(GFF)所吸附导致颗粒相实测比例升高(气相比例降低). 通过准确性和灵敏度分析比较发现,pp-LFER模型具有全面的模型基础,比单一线性参数模型更可靠,并认为OPEs的分配行为是由化合物与颗粒之间的分子相互作用驱动的,而不是PºL和lgKOA. 因此,为了获取更加准确的检测数据,需要对采样技术的科学性和样品收集材料的干扰性等方面开展更深入的研究.
在实际监测研究中发现,大气中OPEs的气-粒分配存在季节变化. 例如,研究发现天津市夏季(6—8月)大气中气态OPEs浓度较高((1132 ± 1216) pg·m−3)[56]. 在中国华南某地的发达工业区的大气监测发现,颗粒相中OPEs在冬季浓度更高((1049 ± 729) pg·m−3),是由于颗粒结合型OPEs占总浓度的80%[17]. 而在美国五大湖地区,在总体浓度夏季是冬季的5倍,而颗粒相中OPEs占比并未表现出明显季节变化(夏季59%,冬季65%)[67]. Li等[69]对中国黄渤海上空大气的监测发现,颗粒相中OPEs占比为82% ± 17%,且并未表现出明显季节变化;OPEs在气相中浓度为夏季显著高于冬季. 大气温度和相对湿度的随季节改变是影响OPEs分配特征变化的重要因素. 根据Wang等[70]的研究发现,TCPP、TCIPP和TDCIPP在气相和PM2.5中浓度与温度都呈显著相关性.地中海沿岸的突尼斯大气中同样发现TCEP、TnBP、EHDPP与温度呈显著正相关关系(P ≤ 0.002),因此当地大气OPEs浓度夏季高于冬季[71].相对湿度与气相中多数OPEs单体均表现出显著正相关性(P < 0.01),但是对于PM2.5中的浓度变化并无显著影响. 说明大气中水的存在对气态OPEs赋存有积极影响,这与水会阻碍羟基自由基氧化气态OPEs引发降解的发现相一致[72].
-
由于OPEs是人工合成的化合物,在自然界中没有直接来源,内陆地区OPEs大气输送为本地及周边地区和偏远地区主要来源[55, 73]. 利用HYSPLIT模型预测气团轨迹分析我国中原城市群的气团运动发现,多数的气团源于本地(40%—68%),运动缓慢且伴随较高的污染物浓度,少数气团来源于偏远地区(12%—29%)[74]. 内陆城市大气中OPEs的本地来源污染显著,偏远地区贡献值则相对较小,且两地间存在一定的物质交换[55]. 在中国近海(黄海和渤海)OPEs污染主要受到黄海南部气团的影响,主要来自途经长江三角洲等地海洋气团(64%),少数气团来自河北和天津两省(19%),气团受内陆影响显著. OPEs的全球性迁移也吸引了广泛的关注. 研究表明,从亚洲大陆到北太平洋和北冰洋,温度作为驱动因素使大气中OPEs进行长距离迁移到达极地,并在极地地区形成“汇”[60, 75].
大气OPEs浓度的变化与大陆气团有关(特别是工业化地区)[37]. OPEs的浓度从工业化城市地区向近海地区、远洋和极地地区逐渐降低[37, 55, 76]. Wang等[77]通过WRF-CMAQ(weather research and forecast-community multiscale air quality, WRF-CMAQ)模型对中国黄海沿岸冬夏两季大气环境中TCPP的空间浓度梯度进行分析,从内陆的OPEs排放源向近海地区,其浓度在水平方向呈现下降趋势,由此提出陆源输入在近海空气中OPEs的分布中占主导地位,同时气相TCPP倾向于远东地区迁移,颗粒相迁移相对较弱. Zhang等[78]通过OPEs单体与有机碳的相关性分析发现,中国西部、印度半岛和马来半岛是中国南海西部大气颗粒态OPEs的主要源区,同时对大气-海水的界面传输的研究表明,大气挥发过程是OPEs增高的重要因素[79]. Clark等[33]通过相似溯源方法也发现,一些OPEs(如TCPP和EHDPP)的大气浓度与OC/EC(organic carbon/element carbon,有机碳/元素碳)大气浓度间呈强正相关,且源区和下风向监测站表现出相似的组成特征. 因此,作者认为大气颗粒中的含碳成分(OC和EC)可被用作揭示污染物的潜在来源和大气传输过程[33, 71].
干、湿沉降是大气环境中OPEs主要清除方式之一. 已有研究报道降水(雨和雪)中存在OPEs,表明湿沉降可能是大气与土壤和水体等介质进行物质交换的重要过程[18, 55, 80]. 然而,干沉降作为一种缓慢但是稳定的连续过程,涉及的传输范围更广,更受研究者关注[71]. Wu等[81]发现,在中国渤海和黄海北部的干沉降通量在202—1869 ng·m−2·d−1,较为封闭的渤海地区年输入量在(18.3 ± 12.5) t·a−1,贡献度最高为TCPP. Li等[80]在对机场附近多个环境介质(空气、土壤、河水和松针)展开调查发现,土壤和大气中OPEs浓度是显著相关的,利用逸度模型计算结果显示逸度分数处于0.23—0.68之间,说明大气沉降是土壤中的OPEs主要来源之一.
-
OPEs在进入大气环境后,发生光解等光化学行为. OPEs的光降解并不是直接光解形式发生的,而是在阳光照射下使其产生光敏特性,通过大气活性氧自由基的氧化反应进行降解. OPEs的光氧化反应主要有3种方式:第一种是∙OH在磷酸盐的支链上取代氢原子或者卤素原子;第二种为∙OH直接添加至磷酸盐中心基团;第三种为∙OH逐步取代反应[1]. 根据OECD所开发的LRTP筛选工具判断,气相中的OPEs可被·OH迅速降解,导致其降解半衰期低于《斯德哥尔摩公约》所规定化学品的最低阈值(大气中 > 2 d)[55]. 然而,大气环境十分复杂,一些因素反而会延长其降解半衰期. Liu等[72]将多种OPEs包覆在(NH4)2SO4颗粒上于充满∙OH的光化学流量管中观察到,由于∙OH光氧化作用,TPhP发生降解,依据反应速率常数计算其大气留存寿命5.6 d;进一步实验发现,通过外加草酸的包覆后,TPhP的降解寿命增加到14 d. 考虑到环境颗粒物更为复杂的状态,该计算可能较为保守. Li等[82]发现,在298 K下气态TCPP环境寿命为1.7 h,而大气中的水分子能通过形成氢键改变反应前复合物和过渡态的稳定性,显著增强TCPP的大气持久性(0.5—20.2 d). 此外,左旋葡聚糖会降低·OH的反应性,且黑炭的底物效应也可能对OPEs的降解速率产生负面效应[72]. 光氧化降解过程是大气中OPEs消除的主要方式之一,也是造成OPEs的LRTP的重要因素,因此,应当开展深入的研究,筛选多种环境因子对OPEs氧化降解过程的影响,揭示降解路径,合理推测降解产物,以期阐明其最终环境归趋.
-
OPEs是一类热点化合物,针对其环境行为的研究发展迅速,然而目前大多数的研究主要依赖实际监测的数据,研究区域较小,且数据累计较少,从而在其迁移潜力、分配模型以及光降解行为方面的研究深度不够. 因此,为了更好地阐明OPEs在大气环境中的源释放途径、迁移/转化过程和环境归趋,未来的研究重点可以从以下几个方面展开:
(1)目前关于大气OPEs的研究关注点在某一个点位或区域上的污染水平和分布特征,缺乏系统性和时间变化方面的研究. 未来研究可通过建立常态化的大气OPEs监测网络,补充全球范围内赋存水平的数据空缺,揭示排放源强的时空变化过程,了解不同释放源对区域大气污染的贡献,编制OPEs排放清单,为精准的管理提供技术支撑.
(2)当前对于大气OPEs气-粒分配机制的研究仍处于起步阶段,传统预测模型主要考虑单一或少数环境因素,对于更为复杂的大气活动并不适用,预测结果有较大出入. 因此在未来的研究中,需要进一步开展多模型交叉预测,并与实际监测数据比较分析,以评估模型有效性和准确性;针对不具备大气监测条件地区,建立更为完善多因素预测模型以分析OPEs的大气分配、传输等环境行为.
(3)现有研究针对的OPEs化学转化行为的解释并不详细,少数研究仅能解释个别OPEs单体在单一因素下的化学转化机制,在多因素并存大气环境下的反应过程显然更为复杂. 因此,在未来的研究中,应开展更广泛的多因素交叉试验,模拟自然环境下OPEs转化条件,以阐述更为准确的大气转化过程.
(4)目前关于OPEs随大气湍流、气团运动和大气演变的具体过程并不清晰. 为了更好揭示空气中OPEs分布和传输过程,需通过进一步考察大气中水蒸汽、温度、颗粒物和化学要素等因素对OPEs形态变化和化学转化的作用机制,进一步厘清OPEs在气体和颗粒物质之间的交换特征,揭示其在大气环境中从点源释放到全球污染的变化规律和归趋.
大气中有机磷酸酯的赋存状况及环境行为
A review on the occurrence and environmental behavior of organophosphate esters (OPEs) as new pollutants in air
-
摘要: 有机磷酸酯(organophosphate esters,OPEs)作为阻燃剂和增塑剂添加在塑料、织物和建筑材料中,其产量逐年递增. OPEs曾经被认为是溴代阻燃剂(BFRs)的有效替代品;然而,最近的研究指出其在大气中的含量比BFRs高1—3个数量级,且某些OPEs化合物半衰期长,具有显著的毒性效应和长距离迁移潜力,因此,OPEs日益成为一类备受关注的全球性新型有机污染物,“更安全”的替代品的认知被质疑. 本文总结了大气中OPEs的赋存状况、气-粒分配、长距离传输和光氧化等方面的研究. 通过比较世界各地区大气OPEs的含量和组成特征发现,工业排放源、长距离传输和气象条件是影响大气中OPEs空间分布趋势的重要因素. 尽管颗粒态对长距离传输、归趋和风险评价具有重要的科学意义,然而,气-粒分配模型研究和实际监测较为缺乏,模型结果和监测计算结果之间差异较大,推测模型的准确性可能受理化性质、气象条件以及采样技术的影响. OPEs在大气中光氧化降解的研究方兴未艾,仍需继续深入发掘多种环境因素的影响,推测降解路径和产物. 因此,将来亟待发展适合OPEs的预测模型,开发新型的采样技术,揭示其光氧化降解路径和产物,以期更好地理解OPEs在大气中的环境赋存和行为规律,为环境质量管理提供理论支持.Abstract: As flame retardants and plasticizers, organophosphate esters (OPEs) have been widely utilized in plastics, textiles, and building materials, and resulted in a sharp increment on production annually. OPEs were ever regarded as effective substitutes for brominated flame retardants (BFRs); however, some current researches showed that their concentrations in air were 1 to 3 orders of magnitude higher than BFRs. Since their half-lives were relatively long, combing their definite toxicity and long-range transport potential, OPEs have increasingly attracted extensive attention and become a class of global organic contaminants. Besides, the recognition of OPEs being safer substitutes is questioned by some researchers. In present study, the progresses on the atmospheric OPEs were reviewed, including the occurrence, the long-range transport, the air-particle partition and the photooxidation of OPEs in air. The deficiency in recent researches was discussed and the perspectives on future study were proposed. Comparing the concentrations and composition characteristics of OPEs in different areas, the industrial sources, long-range transport and meteorological conditions were the predominant factors controlling the spatial distribution tendencies of OPEs in air. The particle-bound OPEs were of remarkable scientific importance in exploring their long-range transport path, revealing their environmental fate and assessing their health risks. However, the researches focusing on air-particle partitions on the basis of field monitoring and theoretical models were relatively insufficient. There was a significant difference between the model results for predicting the percentages of OPEs in particle phase and the field monitoring. It was speculated that the physicochemical properties, meteorological condition and sampling techniques might have influence on the accuracy of models. Moreover, the influence some environment factors on OPEs photooxidation should be explored in order to reveal the reaction paths and proposed the structure of the photodegradation products. Consequently, optimizing proper models, developing new sampling techniques as well as probing the photo-degradation of OPEs were urgent in future for better understanding their environmental behavior and serving the administration of environmental quality.
-

-
表 1 世界各国大气OPEs浓度水平概况(中位数, ng·m−3 dw)
Table 1. OPEs levels in the atmosphere around the world(median, ng·m−3 dw)
采样点
Location城市/乡村
Urban/ village样品形态
Sample state∑OPEs TCEP TDCPP TCPP TPhP TCP TnBP TiBP TBEP TEHP EHDPP TEP 数据来源
Ref.北京 中国 城市 气+固 2.904 0.202 0.056 2.325 0.165 0.04 0.111 — — — — 0.005 [38] 上海 中国 交通枢纽 TSP 15.5 3.5 0.8 2.9 5.9 — 2.4 — ND — — — [39] 乡村 TSP 4.07 1.8 0.3 1 0.5 0.07 0.4 — ND — — — 广州 中国 工业用地 PM2.5 2.425 0.174 — 1.059 0.298 0.465 0.237 — — 0.111 0.073 0.008 [40] 电子回收区 PM2.5 2.196 0.06 — 0.424 1.143 0.322 0.072 — — 0.085 0.086 0.004 10城市 中国 城市 PM2.5 0.42 0.027 0.257 0.136 — — — — — — — — [41] 南京 中国 城市 TSP 152.63 6.85 2.77 81.99 16.59 2.94 2.82 — 5.35 26.75 2.14 4.43 [42] 乡村 TSP 13.62 1.85 0.8 4.12 1.16 0.12 1.33 — 0.11 1.64 ND 2.49 重庆 中国 乡村 气态 265.58 18.5 0.32 33.6 8.11 — 155 42.5 3.28 4.27 — — [43] 成都 中国 城市 PM2.5 6.4 1.1 0.3 1.0 0.5 — 1.0 — 2.3 0.3 — — [44] 大连 中国 城市 气态 1.05 0.193 0.061 0.681 0.043 — 0.046 — 0.019 0.007 — — [45] 莱茵河畔 德国 城市 气+固 3.13 — — 1.49 — — 0.13 1.51 ND ND — ND [35] 海岸 德国 海洋 气+固 0.056 0.003 0.001 0.01 0.003 0.004 0.006 0.009 0.009 0.011 — — [46] 北海 德国 海洋 气+固 0.389 0.031 — 0.271 0.02 — 0.022 0.035 0.007 0.003 — — [37] 仁德 意大利 乡村 PM10 3.165 — — 2.62 0.244 — 0.301 — — — — — [34] 拉科鲁尼亚 西班牙 城市 PM10 6.72 0.52 ND 1 1.06 ND 1.5 2.4 — ND 0.24 — [47] 斯德哥尔摩 瑞典 城市 气+固 2.504 0.64 0.008 0.87 0.047 — 0.051 — 0.83 ND 0.058 — [48] 纽约 美国 城市(机场) 气+固 2.709 0.373 0.219 0.591 0.493 0.061 0.259 0.261 0.168 0.038 0.172 0.074 [48] 休斯顿 美国 城市 TSP 3.092 0.27 0.064 1.2 0.49 — 0.56 — — 0.038 0.47 — [33] 乡村 PM2.5 0.305 ND ND 0.1 ND — 0.17 — — — 0.035 — 工业用地 TSP 1.563 0.09 0.087 0.7 0.21 — 0.12 — — 0.056 0.3 — 芝加哥 美国 城市 颗粒 1.192 0.118 0.079 0.407 0.108 — 0.176 — 0.262 0.042 — — [49] 克利夫兰
美国城市 颗粒 1.122 0.104 0.106 0.322 0.181 — 0.125 — 0.227 0.057 — — 乡村 颗粒 0.403 0.152 0.028 0.072 0.034 — 0.032 — 0.077 0.008 — — 睡熊沙丘 美国 偏远地区 颗粒 0.17 0.008 ND 0.027 0.044 — 0.028 — 0.058 0.005 — — 伊格尔港 美国 偏远地区 颗粒 0.219 0.006 0.032 0.029 0.031 — 0.061 — 0.051 0.009 — — 多伦多 加拿大 乡村 气+固 2.654 0.766 0.154 0.671 1.063 — — — — — — — [50] 北极地区 加拿大 偏远地区 颗粒 0.184 0.119 0.003 0.055 0.007 — ND — — ND ND — [36] 多伦多 加拿大 乡村 气+固 2.138 0.608 0.097 0.575 0.7 0.066 — — — — 0.092 — [51] 布尔萨 土耳其 城市 气态 6.884 0.081 ND 0.63 0.152 — — — 5.958 0.063 — — [52] 注:ND, 未检出; —, 无数据; TSP, 总悬浮颗粒物.ND, not detected; —, no data; TSP, Total Suspended Particle.
TBEP: 磷酸三(2-丁氧基乙基)酯, TiBP: 磷酸三异丁酯, TEP: 磷酸三乙酯, EHDPP: 磷酸二苯基异辛酯, TnBP: 磷酸三正丁酯, TCP: 磷酸三甲苯基酯, TPhP: 磷酸三苯酯, TDCPP: 磷酸三(1,3-二氯异丙基)酯).
TBEP: tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate, TiBP: tri-iso-butyl phosphate, TEP: trimethyl phosphate, EHDPP: 2-ethylhexyl diphenyl phosphate, TnBP: Tri(n-butyl) phosphate, TCP: tricresyl phosphate, TPhP: triphenyl phosphate, TDCPP: tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate).表 2 三种模型的比较
Table 2. Comparison of three models
名称
Model原理
Theory公式
Formula简要描述
Description影响因素
Factors自变量
Independent
variable参考文献Ref. Junge-Pankow
模型Langmuir吸附
等温线理论$ {\text{ƒ}}_{\text{part}}=\dfrac{\textit{cθ}}{{{P}}_{\rm{L}}^{\rm{o}}+\textit{cθ}} $ ${ {K} }_{\text{P}\left(\text{J-P}\right)}=\dfrac{ {\text{ƒ} }_{\text{part} } }{ \text{TSP}\left(\text{1}-{\text{ƒ} }_{\text{part} }\right)}$ 假设大气半挥发有机物通过表面吸附作用吸附至颗粒物表面,仅受蒸发和和冷凝过程的影响 温度、蒸气压 过冷饱和蒸气压(PLº) [64] Harner-Bidleman
模型Langmuir吸附
等温线理论$ \mathrm{lg}{{K}}_{\text{P(H-B)}}=\mathrm{lg}{{K}}_{\text{OA}}\text{+}\text{lg}{\text{ƒ}}_{\text{OM}}-\text{11.91} $ ${\text{ƒ} }_{\text{part}\left(\text{H-B}\right)}=\dfrac{ { {K} }_{\text{P}\left(\text{H-B}\right)}\times \text{TSP} }{ { {K} }_{\text{P}\left(\text{H-B}\right)}\times \text{TSP}+\text{1} }$ 基于大气颗粒物中的有机物质吸收作用主导的分配机制 有机质含量、
亲脂性辛醇-空气分配系数(KOA) [64] pp-LFER模型 多参数线性的
自由能关系模型$\begin{aligned} \text{lg}{{K}}_{\text{p(pp-LFERg/p)}}= & 1.01{S}+\text{3.17}{A}+\text{0.30}{B}+\\ & \text{0.78}{L}+\text{0.51}{V}-\text{7.42} \end{aligned}$ ${ {f} }_{\text{part}\left(\text{pp-LFERg/p}\right)}=\dfrac{ { {K} }_{\mathrm{p}\left(\text{pp-LFERg/p}\right)}\times \text{TSP} }{ { {K} }_{\mathrm{p}\left(\text{pp-LFERg/p}\right)}\times \text{TSP}+\text{1} }$ 综合考虑发生气粒分配的多种相互作用力的能量贡献率 温度 极化率(S)、电子受体性质(A)、电子供体性质(B)、
气体-十六烷分配比(L)、麦高恩体积(V)[64] 注:KP: 气-粒分配系数; TSP: 总悬浮颗粒物浓度; KOA: 辛醇-空气分配系数; PLº: vapor pressure; KOA: Octanol-air partition coefficient; S: polarizability; A: electron acceptor (= H-bond donor) capability; B: electron donor (H-bond-acceptor) capability; L: logarithm of the hexadecane/air partition coefficient; V: McGowan volume. -
[1] LIU Q F, LI L, ZHANG X M, et al. Uncovering global-scale risks from commercial chemicals in air [J]. Nature, 2021, 600(7889): 456-461. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04134-6 [2] WANG X, ZHU Q Q, YAN X T, et al. A review of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in the environment: Analysis, occurrence and risk assessment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 731: 139071. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139071 [3] 高立红, 厉文辉, 史亚利, 等. 有机磷酸酯阻燃剂分析方法及其污染现状研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(10): 1750-1761. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.10.004 GAO L H, LI W H, SHI Y L, et al. Analytical methods and pollution status of organophosphate flame retardants [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(10): 1750-1761(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.10.004
[4] 高小中, 许宜平, 王子健. 有机磷酸酯阻燃剂的环境暴露与迁移转化研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2): 56-68. GAO X Z, XU Y P, WANG Z J. Progress in environment exposure, transport and transform of organophosphorus flame retardants [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 56-68(in Chinese).
[5] van der VEEN I, de BOER J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 88(10): 1119-1153. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067 [6] 廖梓聪, 李会茹, 杨愿愿, 等. 有机磷酸酯(OPEs)的环境污染特征、毒性和分析方法研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4): 1193-1215. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020121601 LIAO Z C, LI H R, YANG Y Y, et al. The pollution characteristics, toxicity and analytical methods of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in environments: A review [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 1193-1215(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020121601
[7] PANTELAKI I, VOUTSA D. Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs): A review on analytical methods and occurrence in wastewater and aquatic environment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 649: 247-263. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.286 [8] MÖLLER A, STURM R, XIE Z Y, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in airborne particles over the Northern Pacific and Indian Ocean toward the Polar Regions: Evidence for global occurrence [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(6): 3127-3134. [9] LI J H, ZHAO L M, LETCHER R J, et al. A review on organophosphate Ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in foodstuffs: Levels, distribution, human dietary exposure, and future directions [J]. Environment International, 2019, 127: 35-51. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.009 [10] 王晓伟, 刘景富, 阴永光. 有机磷酸酯阻燃剂污染现状与研究进展 [J]. 化学进展, 2010, 22(10): 1983-1992. WANG X W, LIU J F, YIN Y G. The pollution status and research progress on organophosphate ester flame retardants [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2010, 22(10): 1983-1992(in Chinese).
[11] LIU Q F, LIGGIO J, WU D M, et al. Experimental study of OH-initiated heterogeneous oxidation of organophosphate flame retardants: Kinetics, mechanism, and toxicity [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(24): 14398-14408. [12] LAI S C, XIE Z Y, SONG T L, et al. Occurrence and dry deposition of organophosphate esters in atmospheric particles over the northern South China Sea [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 127: 195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.015 [13] WANG Q W, LAM J C W, HAN J, et al. Developmental exposure to the organophosphorus flame retardant tris(1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate: Estrogenic activity, endocrine disruption and reproductive effects on zebrafish [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2015, 160: 163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.01.014 [14] 顾俊婕, 胡曼, 耿阳, 等. 有机磷酸酯阻燃剂的人群暴露和甲状腺毒性的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(1): 31-45. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020090801 GU J J, HU M, GENG Y, et al. A review of organophosphate esters(OPEs): Human exposure and toxicities in thyroid [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(1): 31-45(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020090801
[15] 张恒, 郭昌胜, 吕佳佩, 等. 在线固相萃取-超高效液相色谱法检测水中14种有机磷酸酯 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1047-1054. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019103005 ZHANG H, GUO C S, LYU J P, et al. Determination of 14 organic phosphate esters in water by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with online solid phase extraction [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1047-1054(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019103005
[16] MBUSNUM K G, MALLERET L, DESCHAMPS P, et al. Persistent organic pollutants in sediments of the Wouri Estuary Mangrove, Cameroon: Levels, patterns and ecotoxicological significance [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 160: 111542. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111542 [17] ZENG Y, DING N, WANG T, et al. Organophosphate esters (OPEs) in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in urban, e-waste, and background regions of South China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 385: 121583. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121583 [18] 邓旭, 印红玲, 何婉玲, 等. 有机磷酸酯在成都市市/郊区剖面土壤及农作物中的分布及迁移 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 679-685. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018042803 DENG X, YIN H L, HE W L, et al. Distribution and migration of OPEs in soil profile and crops in urban and suburban areas of Chengdu [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 679-685(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018042803
[19] 魏莱, 黄清辉, 许宜平, 等. 崇明岛小白鹭鸟卵中有机磷阻燃剂污染特征 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(5): 1691-1697. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0007 WEI L, HUANG Q H, XU Y P, et al. Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants in little egret eggs from Chongming Island [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(5): 1691-1697(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0007
[20] PETROPOULOU S S E, PETREAS M, PARK J S. Analytical methodology using ion-pair liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of four di-ester metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants in California human urine [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1434: 70-80. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.01.020 [21] JONSSON O B, DYREMARK E, NILSSON U L. Development of a microporous membrane liquid-liquid extractor for organophosphate esters in human blood plasma: Identification of triphenyl phosphate and octyl diphenyl phosphate in donor plasma [J]. Journal of Chromatography B:Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 2001, 755(1/2): 157-164. [22] 李鹏, 李秋旭, 马玉龙, 等. 凝胶渗透色谱-固相萃取净化-气相色谱-质谱法测定人血清中磷酸三酯类化合物 [J]. 分析化学, 2015, 43(7): 1033-1039. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(15)60840-4 LI P, LI Q X, MA Y L, et al. Determination of organophosphate esters in human serum using gel permeation chromatograph and solid phase extraction coupled with GC-MS [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(7): 1033-1039(in Chinese). doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(15)60840-4
[23] KIM J W, ISOBE T, MUTO M, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants (PFRs) in human breast milk from several Asian countries [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 116: 91-97. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.033 [24] DING J J, XU Z M, HUANG W, et al. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in human placenta in Eastern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 554/555: 211-217. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.171 [25] 胡晓辉, 仇雁翎, 朱志良, 等. 环境中有机磷酸酯阻燃剂分析方法的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(12): 2076-2086. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.12.013 HU X H, QIU Y L, ZHU Z L, et al. Research progress on analytical methods of organophosphate ester flame retardants in the environment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(12): 2076-2086(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.12.013
[26] 张洛红, 朱钰, 李宗睿, 等. 有机磷酸酯污染现状及其生物富集和生物转化研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2355-2370. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020121701 ZHANG L H, ZHU Y, LI Z R, et al. Pollution status, bioaccumulation and biotransformation of organophosphate esters: A review [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2355-2370(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020121701
[27] 张晓华, 赵繁荣, 胡建英. 我国人群有机磷阻燃剂暴露评估及其健康风险 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2021, 16(3): 155-165. ZHANG X H, ZHAO F R, HU J Y. Exposure assessment and health risk of organophosphate flame retardants in general population in China [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2021, 16(3): 155-165(in Chinese).
[28] YAO C, YANG H P, LI Y. A review on organophosphate flame retardants in the environment: Occurrence, accumulation, metabolism and toxicity [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 795: 148837. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148837 [29] FAIZ Y, SIDDIQUE N, HE H, et al. Occurrence and profile of organophosphorus compounds in fine and coarse particulate matter from two urban areas of China and Pakistan [J]. Environmental Pollution (Barking, Essex:1987), 2018, 233: 26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.091 [30] NILU (Norsk institutt for luftforskning). Monitoring of environmental contaminants in air and precipitation, annual report 2020. [EB/OL]. [2021-12-14]. [31] QUINTANA J B, RODIL R, LÓPEZ-MAHÍA P, et al. Optimisation of a selective method for the determination of organophosphorous triesters in outdoor particulate samples by pressurised liquid extraction and large-volume injection gas chromatography-positive chemical ionisation-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, 388(5/6): 1283-1293. [32] REN Y Q, WANG G H, LI J J, et al. Evolution of aerosol chemistry in Xi'an during the spring dust storm periods: Implications for heterogeneous formation of secondary organic aerosols on the dust surface [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 215: 413-421. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.064 [33] CLARK A E, YOON S, SHEESLEY R J, et al. Spatial and temporal distributions of organophosphate ester concentrations from atmospheric particulate matter samples collected across Houston, TX [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(8): 4239-4247. [34] NACCARATO A, TASSONE A, MORETTI S, et al. A green approach for organophosphate ester determination in airborne particulate matter: Microwave-assisted extraction using hydroalcoholic mixture coupled with solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Talanta, 2018, 189: 657-665. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.07.077 [35] ZHOU L L, HILTSCHER M, GRUBER D, et al. Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in indoor and outdoor air in the Rhine/Main area, Germany: Comparison of concentrations and distribution profiles in different microenvironments [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(12): 10992-11005. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6902-z [36] SÜHRING R, DIAMOND M L, SCHERINGER M, et al. Organophosphate esters in Canadian Arctic air: Occurrence, levels and trends [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(14): 7409-7415. [37] MÖLLER A, XIE Z Y, CABA A, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the atmosphere of the North Sea [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(12): 3660-3665. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.022 [38] LIU R R, LIN Y F, LIU R Z, et al. Evaluation of two passive samplers for the analysis of organophosphate esters in the ambient air [J]. Talanta, 2016, 147: 69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.09.034 [39] REN G F, CHEN Z, FENG J L, et al. Organophosphate esters in total suspended particulates of an urban city in East China [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 164: 75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.090 [40] WANG T, DING N, WANG T, et al. Organophosphorus esters (OPEs) in PM2.5 in urban and e-waste recycling regions in Southern China: Concentrations, sources, and emissions [J]. Environmental Research, 2018, 167: 437-444. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.08.015 [41] LIU D, LIN T, SHEN K J, et al. Occurrence and concentrations of halogenated flame retardants in the atmospheric fine particles in Chinese cities [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(18): 9846-9854. [42] CHEN Y Q, ZHANG Q, LUO T W, et al. Occurrence, distribution and health risk assessment of organophosphate esters in outdoor dust in Nanjing, China: Urban vs. rural areas [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 231: 41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.135 [43] HE M J, LU J F, WEI S Q. Organophosphate esters in biota, water, and air from an agricultural area of Chongqing, western China: Concentrations, composition profiles, partition and human exposure [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 244: 388-397. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.085 [44] YIN H L, LIANG J F, WU D, et al. Measurement report: Seasonality, distribution and sources of organophosphate esters in PM2.5 from an inland urban city in Southwest China [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 20(23): 14933-14945. doi: 10.5194/acp-20-14933-2020 [45] WANG Y, LI Z Y, TAN F, et al. Occurrence and air-soil exchange of organophosphate flame retardants in the air and soil of Dalian, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 114850. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114850 [46] WOLSCHKE H, SÜHRING R, MI W Y, et al. Atmospheric occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizer at the German coast [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 137: 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.04.028 [47] QUINTANA J B, RODIL R, REEMTSMA T, et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in water and air Ⅱ. Analytical methodology [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 27(10): 904-915. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2008.08.004 [48] WONG F, de WIT C A, NEWTON S R. Concentrations and variability of organophosphate esters, halogenated flame retardants, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in indoor and outdoor air in Stockholm, Sweden [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 240: 514-522. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.086 [49] SALAMOVA A, MA Y N, VENIER M, et al. High levels of organophosphate flame retardants in the great lakes atmosphere [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2014, 1(1): 8-14. [50] ABDOLLAHI A, ENG A, JANTUNEN L M, et al. Characterization of polyurethane foam (PUF) and sorbent impregnated PUF (SIP) disk passive air samplers for measuring organophosphate flame retardants [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 167: 212-219. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.111 [51] SHOEIB M, AHRENS L, JANTUNEN L, et al. Concentrations in air of organobromine, organochlorine and organophosphate flame retardants in Toronto, Canada [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 99: 140-147. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.09.040 [52] KURT-KARAKUS P, ALEGRIA H, BIRGUL A, et al. Organophosphate ester (OPEs) flame retardants and plasticizers in air and soil from a highly industrialized city in Turkey [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 625: 555-565. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.307 [53] SALAMOVA A, PEVERLY A A, VENIER M, et al. Spatial and temporal trends of particle phase organophosphate ester concentrations in the atmosphere of the great lakes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(24): 13249-13255. [54] HE C, WANG X Y, THAI P, et al. Organophosphate and brominated flame retardants in Australian indoor environments: Levels, sources, and preliminary assessment of human exposure [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 235: 670-679. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.017 [55] FU J, FU K H, CHEN Y, et al. Long-range transport, trophic transfer, and ecological risks of organophosphate esters in remote areas [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(15): 10192-10209. [56] ZHANG W W, WANG P, LI Y M, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of organophosphate esters in the atmosphere of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 244: 182-189. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.131 [57] SÜHRING R, WOLSCHKE H, DIAMOND M L, et al. Distribution of organophosphate esters between the gas and particle phase-model predictions vs measured data [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(13): 6644-6651. [58] SALAMOVA A, HERMANSON M H, HITES R A. Organophosphate and halogenated flame retardants in atmospheric particles from a European Arctic site [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(11): 6133-6140. [59] LI J, XIE Z Y, MI W Y, et al. Organophosphate esters in air, snow, and seawater in the north Atlantic and the Arctic [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(12): 6887-6896. [60] NA G S, HOU C, LI R J, et al. Occurrence, distribution, air-seawater exchange and atmospheric deposition of organophosphate esters (OPEs) from the Northwestern Pacific to the Arctic Ocean [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 157: 111243. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111243 [61] REGNERY J, PÜTTMANN W. Occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in urban and remote surface waters in Germany [J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(14): 4097-4104. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.024 [62] LIAGKOURIDIS I, COUSINS A P, COUSINS I T. Physical-chemical properties and evaluative fate modelling of ‘emerging’ and ‘novel’ brominated and organophosphorus flame retardants in the indoor and outdoor environment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 524/525: 416-426. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.106 [63] YAMAN B, DUMANOGLU Y, ODABASI M. Measurement and modeling the phase partitioning of organophosphate esters using their temperature-dependent octanol-air partition coefficients and vapor pressures [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(13): 8133-8143. [64] OKEME J O, RODGERS T F M, JANTUNEN L M, et al. Examining the gas-particle partitioning of organophosphate esters: How reliable are air measurements? [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(23): 13834-13844. [65] YANG F X, DING J J, HUANG W, et al. Particle size-specific distributions and preliminary exposure assessments of organophosphate flame retardants in office air particulate matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(1): 63-70. [66] KHAIRY M A, LOHMANN R. Organophosphate flame retardants in the indoor and outdoor dust and gas-phase of Alexandria, Egypt [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 220: 275-285. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.140 [67] WU Y, VENIER M, SALAMOVA A. Spatioseasonal variations and partitioning behavior of organophosphate esters in the great lakes atmosphere [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(9): 5400-5408. [68] ZENG Y, CHEN S J, LIANG Y H, et al. Traditional and novel organophosphate esters (OPEs) in PM2.5 of a megacity, Southern China: Spatioseasonal variations, sources, and influencing factors [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 284: 117208. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117208 [69] LI J, TANG J H, MI W Y, et al. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of organophosphate esters in air above the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(1): 89-97. [70] WANG Y, BAO M J, TAN F, et al. Distribution of organophosphate esters between the gas phase and PM2.5 in urban Dalian, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 259: 113882. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113882 [71] CASTRO-JIMÉNEZ J, SEMPÉRÉ R. Atmospheric particle-bound organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in a North African Mediterranean coastal city (Bizerte, Tunisia) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642: 383-393. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.010 [72] LIU Y C, LIGGIO J, HARNER T, et al. Heterogeneous OH initiated oxidation: A possible explanation for the persistence of organophosphate flame retardants in air [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(2): 1041-1048. [73] CASTRO-JIMÉNEZ J, GONZÁLEZ-GAYA B, PIZARRO M, et al. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in the global oceanic atmosphere [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(23): 12831-12839. [74] 杨孔. 中原城市群典型城市大气有机阻燃剂污染特征及来源解析[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学, 2019. YANG K. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of atmospheric organic flame retardants in selected cites in the central Henan urban agglomeration[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Normal University, 2019 (in Chinese).
[75] LI Y M, XIONG S Y, HAO Y F, et al. Organophosphate esters in Arctic air from 2011 to 2019: Concentrations, temporal trends, and potential sources [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 434: 128872. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128872 [76] 房晓静, 杨圣文, 张洪海, 等. 海洋及其上空大气中有机磷酸酯的研究进展 [J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(9): 154-165. FANG X J, YANG S W, ZHANG H H, et al. Review of organophosphate esters in oceans and atmospheres [J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(9): 154-165(in Chinese).
[77] WANG L F, HUANG Y F, ZHANG X D, et al. Mesoscale cycling of organophosphorus flame retardants (OPFRs) in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea biotic and abiotic environment: A WRF-CMAQ modeling [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 298: 118859. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118859 [78] ZHANG L L, XU W H, MI W Y, et al. Atmospheric deposition, seasonal variation, and long-range transport of organophosphate esters on Yongxing Island, South China Sea [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150673. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150673 [79] 吴小伟. 大连近岸多环芳烃和有机阻燃剂的污染特征和水-气交换研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018. WU X W. Characrization and air-water exchange of PAHs and organic flame retardents in the coastal area of Dalian[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018 (in Chinese).
[80] LI W H, WANG Y, KANNAN K. Occurrence, distribution and human exposure to 20 organophosphate esters in air, soil, pine needles, river water, and dust samples collected around an airport in New York state, United States [J]. Environment International, 2019, 131: 105054. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105054 [81] WU J H, ZHANG Y F, SONG L, et al. Occurrence and dry deposition of organophosphate esters in atmospheric particles above the Bohai Sea and northern Yellow Sea, China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2022, 269: 118831. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118831 [82] LI C, CHEN J W, XIE H B, et al. Effects of atmospheric water on ·OH-initiated oxidation of organophosphate flame retardants: A DFT investigation on TCPP [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(9): 5043-5051. -



 下载:
下载: