-
塑料自20世纪初诞生以来,已广泛用于人类社会各个领域. 目前全球已生产了超过8.3亿t的塑料制品[1],大部分塑料制品使用后成为了废物进入自然环境,并造成了极大的环境污染. 塑料废物在进入自然环境过程中,在机械磨损、光照、氧化、水力、微生物和其他风化作用下不断发生老化、裂解(降解)、剥离[2-3],并产生粒径小于5 mm且形态各异的次生微塑料[4]. 微塑料已在大气、土壤、河流和海洋等自然环境中不断被检测出来,并有研究证实其对自然生态环境、生物生长繁殖和人类生命健康存在潜在风险. 微塑料可通过大气沉降和雨水径流进入河流[5-6],且海洋中有70%—80%的微塑料通过河流输入[7]. 可见,河流不仅是微塑料进入水环境的汇,也是微塑料输入海洋环境的源. 由于微塑料具有疏水表面、较大比表面积和稳定结构等特性[8],在环境介质迁移过程中易与重金属、有机污染物等多种污染物发生吸附作用,成为污染物传输载体,并产生联合毒理效应[9],显著增加河流中的污染负荷,进一步危害河流生态系统.
微塑料在河流中的迁移行为受到水温、流速、水位等水文特征的影响,尤其是与河流水动力变化密切相关[10]. 掌握微塑料在河流中的时空分布特征、沉积与迁移规律、吸附/释放污染物行为,对全面评估河流中微塑料的污染负荷与安全风险,实现精准溯源与高效防控均具有重要意义. 鉴于此,本文首先对河流中微塑料赋存形态、丰度和污染特征进行了总结分析,围绕微塑料在河流中的迁移行为详细阐述了水动力条件对微塑料赋存行为、迁移过程及其对污染物吸附/释放影响的研究进展,并提出未来研究方向,皆在为全面了解微塑料在河流中的环境行为提供依据.
-
河流中常见的微塑料类型主要包括聚乙烯(PE)、聚丙烯(PP)、聚酰胺(PA)、聚酯(PET)、聚氯乙烯(PVC)和聚苯乙烯(PS)[11],且占比最多的微塑料类型以塑料制品产量最高的PE和PP为主,如表1所示. 微塑料在河流中赋存形状主要有纤维、颗粒、片状和薄膜4种,且形状的不同可能会影响微塑料在河流环境中的运移过程[20]. 相关研究证实,河流中微塑料的赋存形态与人类活动密切相关. 如珠江广州段上覆水的微塑料以纤维状为主,占比高达80.9%,其次是碎片(18.9%)和薄膜(2.2%)[14],分析认为纤维状微塑料可能来自生活污水中的衣物洗涤的脱落颗粒[21-22]. 同样,相关调查发现长江口和东海近岸水体中悬浮微塑料以纤维状为主,占比分别为79.1%和83.2%[23]. 沿海水域中纤维状微塑料占比较高,可能是因为微塑料不仅来自长江的输送,还可能来自海上航运和渔业活动中废弃绳索产生的纤维颗粒. 但Bian等[15]在渭河秦岭山区段向平原段的过渡区域中发现,河流中的薄膜微塑料占比高达41.19%,这可能是由于该地区人类活动以农业为主,在农田中广泛采用的薄膜成为了该区域微塑料的主要污染源.
由于河流中的微塑料污染多样化[24],导致其赋存的颜色丰富,甚至存在彩色微塑料,如红色、蓝色、绿色等,但以白色、透明和黑色为主(表1). 其中,白色和透明微塑料可能来源于包装袋、塑料容器和鱼线等,黑色微塑料则可能来源于汽车轮胎在路面上磨损而形成,而彩色微塑料主要来源于为了特殊功能需求和提高市场吸引力而着色的彩色塑料制品. 虽然彩色微塑料占比低,但因其颗粒大小与浮游生物的幼虫相似[25],极易被水生生物误食[5],较其他颜色微塑料对生物的危害性大. 长江流域中的微塑料以透明/白色和黑/灰色为主,而其他颜色占比较低(表1). 其中,透明/白色所占比例较大,这与大多数河流的微塑料调查结果一致,可能是自然风化作用导致其他颜色的塑料发生褪色[15,26]. 此外,紫外线引发的光降解是一种非常有效的降解机制,微塑料颜色越深,越容易吸收光照导致塑料表面温度升高进而加速塑料的分解[19]. 由于塑料在河流运输过程中,还可通过水力磨损、微生物降解等作用加速微塑料的破碎,使得多数检测样品中的微塑料粒径低于1.0 mm. 但微塑料尺寸越小,产生的环境毒理效应也将更明显.Choi等[27]将海洋桡足类生物暴露于50 nm和10 μm的PS微珠中,发现较小粒径的微塑料更能显著提高细胞内的活性氧(ROS)水平,从而产生更大的氧化应激效应.
-
微塑料在河流中赋存数量的剧增,及其在食物链中的转移已引起了广泛关注[28]. 因此,研究微塑料在河流中的赋存丰度与时空分布对于评估微塑料对人类健康的根本影响,并确保生态系统安全至关重要. 基于染料染色和荧光定量的荧光染色技术因其操作方便、检测高效和成本经济,常用于微塑料的量化与示踪[29-30]. 如Simmerman和Wasi[31]利用尼罗红染料染色和荧光显微镜观察的方法对美国威斯康星州西部的某小溪水体中的微塑料丰度进行检测,该方法较光学显微镜手动计数法可有效增加粒子检测的概率. 荧光染色技术还可用于跟踪微塑料在河流中的运移与分布规律. 如Cook等[32]检测了经荧光染色后的PE微塑料在实验水槽中不同时空下的赋存丰度,研究证实PE微塑料的迁移行为符合均匀流下的分散理论. 由此可见,荧光染色技术可成为开展微塑料在河流中的赋存丰度与时空分布特性研究的一种有效监测手段.
不同河流中检测到的微塑料丰度存在显著差异,上覆水中微塑料丰度为0.1—105 n·m−3,而沉积物中微塑料丰度为10—104 n·kg−1(表1). 尤其是我国海河和渭河上覆水中微塑料丰度相比于国外河流的赋存丰度偏高,跨越了2—5个数量级,这也反映了微塑料在河流中的赋存丰度明显受空间分布和陆域环境污染状况的影响. 总体而言,城市段河流上覆水中微塑料丰度明显高于非城市段,且下游高于上游,这与Yuan等[12]研究认为长江中微塑料丰度与采样点的海拔高度和城市距离呈负相关,而与采样点所处人口密度和城市化率呈正相关结论相一致. 分析认为,微塑料是由废弃塑料在各种环境作用下不断受径流或河流水流携带从高海拔地区迁移累积至低海拔地区中,从而表现出低海拔地区的城市段河流丰度较高. 如Zhou等[33]在对长江流域沿岸土壤中微塑料污染水平的调查中发现,微塑料丰度随海拔高度的降低而显著升高. 此外,河流中微塑料的赋存丰度还受季节时间的影响,尤其是受河流季节性变化引起的水体扰动(如强降雨和季风)和水文条件改变(如水位、流量和流速)所影响[12],从而使微塑料赋存丰度的变异性较大,甚至可达1—2个数量级的差异,如表1所示.
不同采样时间和地区下淡水河流中的微塑料丰度存在显著的时空变异性,可能是由于河流水文特征(如流速、水位、流量等)和地貌特征(如河床形态、植被强度、坡度、拦水坝、水库等)影响了微塑料在河流中的迁移过程和归趋[34],进而影响微塑料在河流中横向和垂向分布特征. 如湍流和底流的消退与出现不断使微塑料发生下沉和上浮,水生生物的误食与排泄也使微塑料不断发生垂向转移[14]. 支流的汇入是影响微塑料横向分布的主要原因[35],尤其是在汇流处产生复杂的水动力条件,使沉积于河床底部的微塑料发生再悬浮,进而导致上覆水中微塑料丰度的增加[14].
-
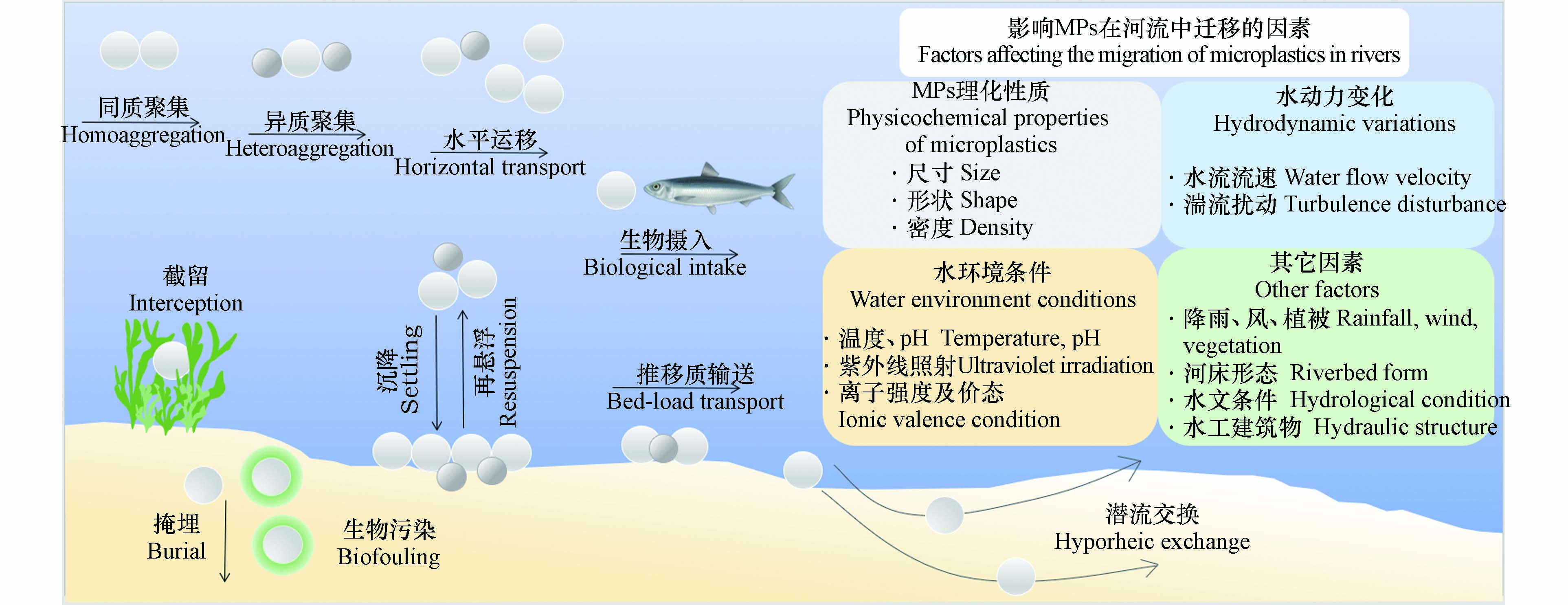
微塑料进入河流后会发生聚集、水平运移、沉降、掩埋、再悬浮、推移质输送和潜流交换等类似于颗粒物在水环境中的典型迁移过程(图1),且这一环境迁移过程可循环发生,也可自发终止[36]. 其中,聚集是微塑料环境行为的一个关键过程,其不仅决定微塑料在天然水域中的水平运移和垂向运移行为[34],进而影响微塑料在水体中的分布[37],而且还可通过改变微塑料的粒径、密度和比表面积而影响微塑料中添加剂的释放及其对污染物的吸附迁移过程[38]. 微塑料在河流中可发生同质聚集和异质聚集[3],但通常而言,微塑料在天然水环境中会大概率通过表面吸附作用与河流中的微生物、粘土矿物、有机污染物和金属氧化物等物质发生异质聚集,使得微塑料密度发生显著改变而影响其在天然水域中的垂向分布[38-39]. 相关研究表明,pH、紫外线照射、离子强度及价态等水环境条件在微塑料聚集过程中起主导作用[3,40]. 由于位于不同水深的微塑料通常受风化程度不同,使得聚集过程的主导影响因素不尽相同. 如位于河流表面的微塑料聚集体主要受光照影响,紫外线照射产生的羟基和羧基等自由基不仅会促进微塑料的聚集行为[40],还可导致微塑料降解成更低分子量的小碎片[41]. 而位于河床的微塑料不易受光照影响,但复杂的水动力条件和微生物作用可显著影响微塑料的聚集行为[38,41]. 此外,微塑料的小聚集体相较于大聚集体具有更大的比表面积和更多的反应位点,从而可能会释放更多的污染物,进而对河流生态环境产生更显著的负面影响[42].
河流中的部分微塑料可通过水平运移作用流向下游,最终进入海洋[44]. 微塑料在河流中的运移过程受水动力条件的影响较大,如水流速度、水深和水流的季节性变化[45].Xia等[46]发现雨季条件下河流水流速度较大,可形成较强的水动力加强微塑料的水平运移作用,使得沉积物中的微塑料丰度低于旱季. 微塑料在河流中的垂向分布不仅受重力沉降行为的直接影响,还受潜流交换的影响,尤其是粒径小于100 μm的微塑料颗粒[47]. 微塑料的沉降行为主要受微塑料的密度、大小、形状等理化性质所影响,如在瑞典的Gota河中大多数密度较高、尺寸较大的微塑料会在河流中发生沉降,而密度接近于水的较小微塑料则漂浮于水面,并向河流下游运移直至海洋[48]. 同时微塑料形状表面越光滑,受到的阻力就越小,沉降速率较表面不规则的颗粒要大. 此外,微塑料的沉降还受河道水工建筑物和气候事件的间接影响,如河流中的拦水坝、水库群、防波堤和丁顺坝等水工建筑物会降低河流流速,进而加强微塑料在河床中的沉降行为[34];而暴雨、洪水和飓风事件可导致河流产生足够的湍流和较大的流速[49–51],显著增强河流水动力过程,进而引起沉积物中的微塑料再悬浮至水体中.
微塑料进入河流后的归趋大体上有3个去向,一部分随水流继续向下游运移,一部分则由于自身重力或吸附污染物后增大密度而沉降至沉积物中,还有一部分被水生生物误食直接进入食物链[52]. 显然,微塑料在河流中的归趋受其迁移行为影响,而微塑料的环境迁移则取决于微塑料的理化性质、水环境条件、水动力变化及其他因素[53],尤其是河流水动力的变化影响着微塑料的水平运移、沉降和再悬浮等环境行为. 强水动力条件可促使沉积物发生再悬浮释放出微塑料,并加速其在河流中的水平运移过程;而弱水动力条件则使密度较大的微塑料沉降至沉积物中并减缓微塑料向下游的运移过程,进而影响微塑料在河流中的赋存与环境迁移过程. 因此,河流水动力变化显著影响微塑料在河流系统中的归趋.
-
水流流速会影响微塑料在河流中的空间分布. 微塑料在低流速的河道横断面上呈现出河流表层高而河床底部低的不均匀下降分布趋势,而在高流速的河道横断面上的分布则相对均匀[54]. 河流流速还可影响微塑料在河流纵向上的分布,如Tibbetts等[55]对英国Tame河城市段的3个监测点的微塑料分布进行了研究,发现流速越高的点位,其微塑料丰度也越低,而在洪泛区等低流速环境中微塑料则更容易发生积累,且河流水动力对微塑料纵向分布的影响较人口密度更明显[55]. 强降雨、洪水事件、飓风和支流汇入等自然环境因素均会引起河流发生湍流扰动. 如Haberstroh等[54]对美国佛罗里达州Hillsborough河的微塑料空间分布进行了监测,发现6月的河流水动力条件平稳,水体扰动少且存在垂向速度梯度,使得大部分微塑料集中于河流表面,平均浓度通量高达2321—4479 n·m−2·h−1,为水体中平均赋存浓度通量的10倍以上;而在7—8月的雨季,降雨事件的频发增强了水体湍流扰动,造成水体在垂向上发生均匀混合,并引发了水体与河床沉积物的介质交换作用,从而显著提高了水体中的微塑料分布通量.
可见,河流水动力变化是影响微塑料在河流环境中空间分布的关键因素,并使得河流表层中的微塑料丰度与水流流速呈现显著的负相关[52]. 总体而言,河流水流流速较大时,微塑料在横断面上的分布差异较小,疏水性较低和密度较小的微塑料更倾向于迁移至河流表层水体中[54]. 而水流流速较小的河流,密度较大的微塑料普遍沉降至河床底部,使其在横断面上分布差异较大. 此外,河流流态平稳时,微塑料主要集中在表层水体,而当水流发生湍流扰动,微塑料在横断面上的分布则更加均匀.
-
水流流速变化会影响微塑料的沉积分布. 如三峡水库水动力条件的季节性变化使微塑料在水体中的垂向分布呈现出明显的季节差异性,冬季微塑料垂向分布的荧光强度差异较为明显,荧光强度中位数>20的有8个采样点;而夏季垂向分布的荧光强度差异则不明显,荧光强度中位数>20的仅2个采样点[56]. 这主要是由于冬季蓄水期的流速缓慢,水体中绝大部分微塑料向上悬浮至表层水体或是向下沉积至河床底部沉积物;而夏季泄水期流速增大,导致沉积物中的微塑料发生再悬浮并转移至水体中. 水流流速的周期性变化使微塑料在河流中不断发生沉积和再悬浮,进而调节河流中微塑料的运移[54],并使其不断在消落带岸坡土壤、水体和沉积物间发生环境介质的迁移[56]. 微塑料在沉积物中的空间分布还受水动力扰动的影响.Niu等[57]研究发现,秦淮河(城市段)沉积物中的微塑料尺寸和数量沿沉积物深度呈规律性变化,尤其是微塑料平均数量沿沉积物深度而逐渐增加. 这可能是由于风力[58]、季节性降雨[59]和水生生物活动[60]引起的水动力扰动导致表层沉积物发生重新悬浮,造成微塑料在沉积物中发生垂向迁移,从而呈现出微塑料平均数量随沉积物深度增加而上升的趋势. 受沉积物中微生物降解作用的影响[57],离上覆水越远,沉积物中微生物群落受水动力扰动越小,使得沉积物中小尺寸微塑料(<2.0 mm)平均数量沿沉积物深度方向逐渐增加,而大尺寸微塑料(4.0—5.0 mm)则逐渐减少. 综上,河流流速减缓会导致大多数微塑料发生沉积,而流速升高和水动力扰动会引起沉积物再悬浮,造成微塑料重新发生释放并迁移至水体中.
-
相较于湖泊和海洋,河流生态系统中的水动力条件较为复杂. 即使是大密度微塑料,在水流湍急处也不易沉积在河床底部,反而可能会造成沉积物中的微塑料释放至水体中并随水流向下迁移[61]. 微塑料在河流中的迁移行为是纵向迁移、横向迁移和垂向迁移共同作用的结果. 在低流速条件下,微塑料运移以纵向迁移为主,密度小的微塑料更倾向分布于河流表面而不易在河道横断面内发生混合. 在高流速条件下,微塑料运移受横向和垂向迁移共同控制,这一迁移行为加速了微塑料与河床沉积物的交换进而加剧了沉积物中微塑料的释放[54]. 微塑料随水流方向的纵向迁移过程,则主要受水平流速的影响. 如乌江梯级筑坝显著减缓了水平流速,甚至造成水流的停滞,有效削弱了河流对微塑料的输移能力,尤其是当输移效应弱于沉降效应时,微塑料会随时间的推移而最终沉降至河流或水库的沉积物中[16]. 微塑料的垂向迁移过程,主要表现为水体与消落带、水体与沉积物间的迁移[52]. 由于微塑料在静水中的垂向迁移非常缓慢(速度量级mm·s−1)[56],使得微塑料垂向迁移过程受湍流扰动影响较大. 如长江支流香溪河,微塑料在水体与消落带之间的垂向迁移作用主要是由于地表径流的汇入和降雨导致湍流扰动和水位升高所引起,而在水体与沉积物之间的迁移则主要是通过微塑料重力沉降和水动力扰动来实现交换[52]. 湍流扰动会以不同方式影响微塑料的迁移行为,其中粒径大、表面不均匀且密度大的微塑料更容易被湍流所携带,从而使其更多地赋存于水体中下层和沉积物中;而粒径小、表面更光滑和圆形的颗粒则受扰动影响较小,则更多地分布于河流表面并随水流继续向下游进行运移.
总体而言,微塑料在河流横断面上的运移行为是不均匀的,且高度依赖于河流的水动力分布曲线[54]. 水平流速的快慢控制着微塑料向下游运移的纵向迁移过程,而湍流扰动的强弱则决定了微塑料在河流中的垂向迁移过程.
-
与微塑料相关的污染物主要包括两类,一种是来自塑料添加剂和聚合物原料的释放,另一种则来自对周围介质化学污染物质的吸附[62]. 塑料制品会通过添加一些化合物来提高性能并延长使用寿命. 如PE通常添加抗氧化剂(酚类化合物)和阻燃剂(多溴联苯醚),PVC则添加增塑剂(邻苯二甲酸酯类)和稳定剂(苯并三唑类)[63]. 这些添加剂的释放主要受风化条件(如紫外线辐射、生物降解、化学氧化和物理磨损等)、塑料种类和添加剂特性所控制[64-65]. 如Cheng等[66]发现微塑料的风化会减小粒径并可能破坏聚合物结构,从而加速了微塑料中阻燃剂的释放. 河流不同水动力条件形成的波浪、潮汐和泥沙运移等均可能会对微塑料产生物理性机械磨损,且研究发现机械磨损程度与微塑料类型有关[67],进而影响添加剂和聚合物的释放过程. 而对于沉积物中的微塑料,当水流流速较小时,微塑料在沉积物中静止或推移质运移,可与河床砂石形成机械摩擦作用而加速微塑料的裂解与老化[68],进而加剧添加剂的释放[65]. 当水流流速较大或发生湍流扰动时,沉积于河床底部的大部分微塑料会发生再悬浮过程,可有效减少微塑料颗粒与沉积物的接触和机械磨损作用[69],从而减弱微塑料的物理风化过程,降低污染物的释放.
同时,微塑料因其具有疏水表面和大比表面积等特性,可吸附环境介质中的多种污染物,甚至可成为有毒化学物质的载体. 尤其是河流中广泛存在的抗生素、止痛剂、抗炎、抗癫痫和抗抑郁等药品及个人护理品(PPCPs)新兴污染物[70],对水生生物、生态环境和人类健康均造成负面影响. 河流中频繁检出的抗生素(如环丙沙星、氧氟沙星、红霉素、四环素等[71–73])会在水生生物之间发生抗性基因的种间(内)传播[74]. 近年来,研究学者不断在河流微塑料表面检测到抗生素[75],并发现微塑料的表面吸附作用以及迁移过程会显著影响抗生素在河流中的环境行为和空间分布[76]. 一旦抗生素被微塑料所吸附,形成的复合污染对水生生物的危害更大[75]. 同时,淡水中的微塑料对抗生素的吸附能力较海水更高[77]. 显然,河流水动力变化不仅会影响微塑料的环境迁移行为,还可能会改变微塑料对抗生素的吸附特性,进而影响河流中新兴污染物的空间分布与归趋.
常见的抗生素密度(如环丙沙星1.46 g·cm−3和四环素1.38 g·cm−3)一般比PP、PE和PS等微塑料的密度大,微塑料吸附污染物后,更易沉降至河床底部,致使沉积物中的微塑料丰度也随之增加,进一步加剧了污染物对底栖动物的毒理效应. 而不同类型微塑料的比表面积、孔隙率、老化程度、极性和结晶度等物化性质存在较大差异[78–81],可能会导致微塑料对抗生素的吸附能力不同. 相关室内静态实验研究认为,PA主要通过氢键作用来增强微塑料对阿莫西林、四环素和环丙沙星等抗生素的吸附能力[77],具有芳香族表面结构的PE则通过静电和疏水作用,甚至发生特异性范德华力来实现微塑料对环丙沙星的吸附[82],而同样属于非极性的PS,则还可通过π-π作用来吸附污染物[78]. 由于室内实验条件与天然河流环境存在较大差异,尤其是静态实验下微塑料对污染物的吸附容量和速率均远大于河流[83],难以直接将实验结论外延至天然河流. 同时,目前针对水动力对微塑料吸附污染物的影响研究较少,尚未掌握不同水动力条件下微塑料对污染物的吸附与解吸规律,这在一定程度上阻碍了我们对抗生素等新兴污染物在河流中环境行为的认识.
天然河流一般为紊流流态,水流流速和湍流扰动均会影响微塑料的环境迁移行为,进而改变其对污染物的吸附特性[84]. 当水流流速较低时,微塑料可与水体中的污染物较为充分接触,从而增加了微塑料对污染物的吸附,并以异质聚集体形式沉降至河床底部中并发生累积. 当水流流速较高时,微塑料与水体中的污染物接触不够充分,减少了微塑料对污染物的吸附量,并增强了微塑料携带污染物向下游运移的能力. 然而当水体发生湍流扰动时,河流横断面内不同空间的水体均匀混合,并引发上覆水与沉积物介质发生物质交换,有效增大了污染物与微塑料的接触,进而显著增强微塑料对污染物的吸附能力,提升微塑料对污染物的吸附速率. 由于微塑料对抗生素等新兴污染物的吸附主要通过氢键、静电作用、疏水作用、范德华力和π-π作用等物理途径来实现,显然当河流发生水动力变化时,这种物理吸附极有可能因环境条件的改变而导致微塑料表面吸附的新兴污染物又重新释放至水环境中[82],进一步扩大新兴污染物对河流生态系统中微生物群落和底栖动物产生抗性基因等生态风险[74].
-
微塑料污染物广泛存在于河流生态系统中,常以纤维、碎片形状存在,PE和PP为主,颜色多呈黑白和透明,粒径小于1.0 mm.微塑料河流水体中的赋存丰度为0.1—105 n·m−3,而在沉积物中的丰度为10—104 n·kg−1. 河流流速和水流流态是造成微塑料时空分布高度变异的主要原因. 微塑料在河流中可发生同质/异质聚集、水平运移、沉降和再悬浮等环境迁移行为,而水流流速和湍流扰动等水动力变化决定着微塑料在河流系统中的迁移行为和归趋. 由于河流环境的复杂性,目前对于不同水动力条件下微塑料的环境迁移行为与污染物吸附/释放行为的相关研究仍存在一定的局限性和不足,未来可重点开展如下研究内容:
(1)基于河流中微塑料的监测数据,借助于数值模拟手段开展微塑料在河流系统中的迁移过程与归趋模拟和分析,探明河流水动力对微塑料环境迁移行为的影响规律,建立河流水动力和水环境变化多因素耦合下微塑料环境迁移模型与污染物输移通量的评价工具.
(2)开展微塑料及其吸附/释放污染物对河流生态系统的联合毒理效应研究,阐明不同微塑料与新兴污染物的相互作用机理,探明河流水动力条件对微塑料吸附/释放污染物的影响机制.
河流水动力对微塑料赋存与环境行为的影响研究进展
Advances in impact of river hydrodynamics on occurrence and environmental behaviour of microplastics
-
摘要: 对近年来国内外河流中微塑料的赋存特性和丰度情况进行了总结分析,围绕微塑料在河流中的典型迁移过程探究了水动力变化对微塑料分布、沉积、迁移和吸附/释放污染物等环境行为的影响规律,并提出了未来研究方向. 微塑料在河流中主要以纤维和碎片形状存在,聚乙烯(PE)、聚丙烯(PP)为主,颜色多呈黑白和透明,粒径小于1.0 mm;微塑料在水体和沉积物中的赋存丰度呈现出高度变异性,且迁移沉降过程、吸附/释放污染物等环境行为受水流流速和湍流扰动等水动力变化的显著影响. 未来应重视水动力和多因素耦合作用下微塑料分布与环境行为的影响研究,探明微塑料与其他污染物的联合毒理效应.Abstract: The occurrence characteristics and abundance of microplastics in rivers at home and abroad in recent years are summarized and analyzed. Based on the typical migration process of microplastics in rivers, the effects of hydrodynamic changes on the distribution, deposition, migration, adsorption/release of pollutants and other environmental behaviors of microplastics were explored, and the future research directions were proposed. The microplastics in rivers are mainly in the form of fibers and fragments. Polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) account for the majority. The colors are mostly black, white and transparent, and the particle size is less than 1.0 mm. The abundance of microplastics in water and sediment is highly variable, and environmental behaviors of microplastics such as migration and deposition, adsorption/release of pollutants are significantly affected by hydrodynamic changes such as flow velocity and turbulence disturbance. In the future, more attention should be paid to the study on the effects of the distribution and environmental behavior of microplastics under the coupling of hydrodynamic and multi-factors, and the joint toxicity of microplastics and other pollutants should be explored.
-
Key words:
- microplastics /
- river /
- hydrodynamics /
- migration /
- pollutant adsorption.
-

-
表 1 典型河流中微塑料的赋存特性
Table 1. Occurrence characteristics of microplastics in typical rivers
河流
River采样类型
Sampling type采样时间
Sampling time采样地点
Sampling location微塑料赋存*
Microplastic Occurrence经度
Longitude纬度
Latitude类型
Type形状
Shape颜色
Color粒径
Particle size丰度#
Abundance长江[12] 上覆水 2019年
10—11月95°45'—
121°46'E26°14'—
4° 5'NPP(>20%)
PE(>20%)纤维(>50%) 黑/灰色(26.4%—28.9%)
白/透明(25.3%—28.8%)<1.0 mm
(87.5%)20—2580
(avg.& 1270±830)沉积物 PS
(6.5%—10.5%)
PVC
(6.5%—10.5%)
PET
(6.5%—10.5%)蓝/红/黄(10.6%—12.8%)
绿色(4.6%—5.2%)
紫色(0.9%—1.9%)<1.0 mm
(91.3%)7—788
(avg. 286.20±208.62)海河天
津段[13]上覆水 2019年4月 117°10'—
117°42'E38°59'—
40° 0'NPE(44.1%)
PP(36.4%)纤维(46.9%)
碎片(27.2%)
薄膜(22.7%)
颗粒(2.3%)黑色(36.4%)
透明(26.4%)
蓝/绿色(14.9%)<1.0 mm
(85.2%)5600—31400
(avg. 11100±4400)沉积物 PE(42.6%)
PP(22.2%)纤维(74.2%)
碎片(15.7%)
薄膜(6.1%)
颗粒(4.0%)黑色(49.9%)
透明(11.4%)
蓝/绿色(21.7%)<1.0 mm
(64.2%)2141—10035
(avg. 4328±2037)珠江广
州段[14]上覆水 2017年7月 113°10'—
113°30'E23° 0'—
23°15'NPP(35.7%)
PE(28.6%)
PET(28.6%)纤维(80.9%)
碎片(18.9%)
薄膜(2.2%)白色(65.6%) 0.02—1.0 mm
(44.8%)
1.0—2.0 mm
(36.5%)379—7924
(avg. 2724)沉积物 PE(47.6%)
PP(26.2%)纤维(54.7%)
碎片(43.3%)
薄膜(1.9%)黄色(36.2%)
白色(26.8%)
黑色(11.7%)0.02—1.0 mm
(65.3%)
1.0—2.0 mm
(29.5%)80—9597
(avg. 1669)渭河平
原段[15]上覆水 2020年8月 108° 0'—
109°40'E33°45'—
34°30'NPE(41.3%)
PP(14.9%)
PS(13.8%)
PA(12.5%)
PVC(9.6%)
PET(4.8%)碎片(41.24%)
薄膜(41.19%)
纤维(17.58%)白色(43.2%)
黑色(20.7%)
蓝色(11.7%)
其他(10.1%)< 1.0 mm(83.13%)
1.0—2.0 mm
(9.95%)
2.0—5.0 mm
(6.92%)2300—21050
(avg. 9810)乌江[16] 沉积物 2019年9月 105° 0'—
109°30'E26°15'—
30° 0'NPE(42.1%)
PP(32.1%)
PET(17.0%)
PVC(2.5%)碎片(49.1%)
纤维(28.3%)
颗粒(22.6%)白色(48.4%)
黑色(12.6%)
红色(8.8%)< 1.0 mm
(87.4%)
1.0—5.0 mm
(12.6%)75.6—1036.2
(上游avg. 284.6
中游avg. 823.6
下游avg. 101.6)韩国
Nakdong
河[17]上覆水 2017年
2—10月128° 0'—
129° 0'E35° 0'—
37° 0'NPP(41.8%)
PES(23.1%)
PE(9.4%)
PA(5.8%)
PS(2.1%)n.g.$ n.g. <0.3 mm
(74%)avg. 293±83
(上游)
avg. 4760±5242
(下游)沉积物 PP(24.8%)
PE(24.5%)
PES(5.5%)
PVC(5.4%)
PS(5.3%)n.g. n.g. <0.3 mm
(81%)avg. 1970 ± 62 印尼
Cisadane
河[18]上覆水 n.g. 106°35'—
106°40'E6°0—
6°25'SPE(25.41%)
PS(22.95%)
PP(22.13%)碎片(64.15%)
泡沫(20.40%)
纤维(13.43%)
颗粒(1.99%)n.g. 0.5—1.0 mm
(61.69%)
1.0—5.0 mm
(22.64%)
<0.5 mm
(15.67%)13—113
(avg. 45±24)意大利
Ofanto
河[19]上覆水 2017年
2—12月
2018年5月n.g. n.g. PE(76%)
PS(12%)
PP(10%)
PVC(0.7%)碎片(56%)
薄膜(26%)
线状(7.6%)
纤维(6.8%)
颗粒(1%)透明(56%)
黑色(35%)
彩色(11%)n.g. (0.9±0.4)—
(13.0±5.0)注:*括号内数值代表占比;#上覆水的丰度单位n·m−3,沉积物的丰度单位n·kg−1;& avg.代表均值;$ n.g.代表文献数据缺失.
Note: * values in brackets represent proportion; # abundance unit of overlying water n·m−3, and abundance unit of sediment n·kg−1; & avg. represents the mean value; $ n.g. represents missing literature data. -
[1] WERBOWSKI L M, GILBREATH A N, MUNNO K, et al. Urban stormwater runoff: A major pathway for anthropogenic particles, black rubbery fragments, and other types of microplastics to urban receiving waters [J]. ACS ES& T Water, 2021, 1(6): 1420-1428. [2] de CARVALHO A R, GARCIA F, RIEM-GALLIANO L, et al. Urbanization and hydrological conditions drive the spatial and temporal variability of microplastic pollution in the Garonne River [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 769: 144479. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144479 [3] ALIMI O S, FARNER BUDARZ J, HERNANDEZ L M, et al. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(4): 1704-1724. [4] SMYTH K, DRAKE J, LI Y R, et al. Bioretention cells remove microplastics from urban stormwater [J]. Water Research, 2021, 191: 116785. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116785 [5] SANG W J, CHEN Z Y, MEI L J, et al. The abundance and characteristics of microplastics in rainwater pipelines in Wuhan, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 755: 142606. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142606 [6] WRIGHT S L, ULKE J, FONT A, et al. Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport [J]. Environment International, 2020, 136: 105411. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105411 [7] HORTON A A, WALTON A, SPURGEON D J, et al. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 586: 127-141. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.190 [8] TOURINHO P S, KOČÍ V, LOUREIRO S, et al. Partitioning of chemical contaminants to microplastics: Sorption mechanisms, environmental distribution and effects on toxicity and bioaccumulation [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 1246-1256. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.030 [9] LONG M, PAUL-PONT I, HÉGARET H, et al. Interactions between polystyrene microplastics and marine phytoplankton lead to species-specific hetero-aggregation [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 228: 454-463. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.047 [10] CAI Y M, LI C, ZHAO Y Q. A review of the migration and transformation of microplastics in inland water systems [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 19(1): 148. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010148 [11] ROCHMAN C M, HOH E, HENTSCHEL B T, et al. Long-term field measurement of sorption of organic contaminants to five types of plastic pellets: Implications for plastic marine debris [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(3): 1646-1654. [12] YUAN W K, CHRISTIE-OLEZA J A, XU E G, et al. Environmental fate of microplastics in the world's third-largest river: Basin-wide investigation and microplastic community analysis [J]. Water Research, 2022, 210: 118002. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.118002 [13] LIU Y, YOU J N, LI Y J, et al. Insights into the horizontal and vertical profiles of microplastics in a river emptying into the sea affected by intensive anthropogenic activities in Northern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 779: 146589. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146589 [14] LIN L, ZUO L Z, PENG J P, et al. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: A case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou City, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 644: 375-381. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.327 [15] BIAN P Y, LIU Y X, ZHAO K H, et al. Spatial variability of microplastic pollution on surface of rivers in a mountain-plain transitional area: A case study in the Chin Ling-Wei River Plain, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 232: 113298. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113298 [16] WU F X, WANG J F, JIANG S H, et al. Effect of cascade damming on microplastics transport in rivers: A large-scale investigation in Wujiang River, Southwest China [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 299: 134455. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134455 [17] EO S, HONG S H, SONG Y K, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and annual load of microplastics in the Nakdong River, South Korea [J]. Water Research, 2019, 160: 228-237. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.053 [18] SULISTYOWATI L, NURHASANAH, RIANI E, et al. The occurrence and abundance of microplastics in surface water of the midstream and downstream of the Cisadane River, Indonesia [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 291: 133071. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133071 [19] CAMPANALE C, STOCK F, MASSARELLI C, et al. Microplastics and their possible sources: The example of Ofanto River in southeast Italy [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 258: 113284. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113284 [20] KOUTNIK V S, LEONARD J, ALKIDIM S, et al. Distribution of microplastics in soil and freshwater environments: Global analysis and framework for transport modeling [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 274: 116552. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116552 [21] BELZAGUI F, CRESPI M, ÁLVAREZ A, et al. Microplastics' emissions: Microfibers’ detachment from textile garments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 248: 1028-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.059 [22] 吴香香, 李大鹏, 贾海峰, 等. 江南地区缓流水体中微塑料的表现规律 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(3): 62-66. WU X X, LI D P, JIA H F, et al. Microplastic pollution characteristic in slow-flowing water in the south region of the Yangtze River [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2022, 38(3): 62-66(in Chinese).
[23] ZHAO S Y, ZHU L X, WANG T, et al. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System, China: First observations on occurrence, distribution [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 86(1/2): 562-568. [24] ZHANG D D, FRASER M A, HUANG W, et al. Microplastic pollution in water, sediment, and specific tissues of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) within two different breeding modes in Jianli, Hubei Province, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 272: 115939. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115939 [25] COLE M, LINDEQUE P, FILEMAN E, et al. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(12): 6646-6655. [26] LIU P, ZHAN X, WU X W, et al. Effect of weathering on environmental behavior of microplastics: Properties, sorption and potential risks [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 242: 125193. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125193 [27] CHOI J S, HONG S H, PARK J W. Evaluation of microplastic toxicity in accordance with different sizes and exposure times in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus [J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2020, 153: 104838. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.104838 [28] CARBERY M, O'CONNOR W, PALANISAMI T. Trophic transfer of microplastics and mixed contaminants in the marine food web and implications for human health [J]. Environment International, 2018, 115: 400-409. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.03.007 [29] MAES T, JESSOP R, WELLNER N, et al. A rapid-screening approach to detect and quantify microplastics based on fluorescent tagging with Nile Red [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 44501. doi: 10.1038/srep44501 [30] LIU S D, SHANG E X, LIU J N, et al. What have we known so far for fluorescence staining and quantification of microplastics: A tutorial review [J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2022, 16(1): 8. [31] SIMMERMAN C B, COLEMAN WASIK J K. The effect of urban point source contamination on microplastic levels in water and organisms in a cold-water stream [J]. Limnology and Oceanography Letters, 2020, 5(1): 137-146. doi: 10.1002/lol2.10138 [32] COOK S, CHAN H L, ABOLFATHI S, et al. Longitudinal dispersion of microplastics in aquatic flows using fluorometric techniques [J]. Water Research, 2020, 170: 115337. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115337 [33] ZHOU Y F, HE G, JIANG X L, et al. Microplastic contamination is ubiquitous in riparian soils and strongly related to elevation, precipitation and population density [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 411: 125178. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125178 [34] RAKESH K, PRABHAKAR S, ANURAG V, et al. Effect of physical characteristics and hydrodynamic conditions on transport and deposition of microplastics in riverine ecosystem [J]. Water, 2021, 13(19): 2710. doi: 10.3390/w13192710 [35] BALLENT A, CORCORAN P L, MADDEN O, et al. Sources and sinks of microplastics in Canadian Lake Ontario nearshore, tributary and beach sediments [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 110(1): 383-395. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.037 [36] 王薪杰, 王一宁, 赵俭, 等. 河流水沙运动对微塑料运移过程影响研究进展 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2): 863-877. doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20210825.009 WANG X J, WANG Y N, ZHAO J, et al. Recent progress of the effect of suspended sediment movement on the transport of microplastics in rivers [J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(2): 863-877(in Chinese). doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20210825.009
[37] BHATTACHARYA P, LIN S J, TURNER J P, et al. Physical adsorption of charged plastic nanoparticles affects algal photosynthesis [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(39): 16556-16561. doi: 10.1021/jp1054759 [38] WANG X J, BOLAN N, TSANG D C W, et al. A review of microplastics aggregation in aquatic environment: Influence factors, analytical methods, and environmental implications [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 402: 123496. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123496 [39] ORIEKHOVA O, STOLL S. Heteroaggregation of nanoplastic particles in the presence of inorganic colloids and natural organic matter [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2018, 5(3): 792-799. doi: 10.1039/C7EN01119A [40] WANG X J, LI Y, ZHAO J, et al. UV-induced aggregation of polystyrene nanoplastics: Effects of radicals, surface functional groups and electrolyte [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2020, 7(12): 3914-3926. doi: 10.1039/D0EN00518E [41] ZHAO S Y, WARD J E, DANLEY M, et al. Field-based evidence for microplastic in marine aggregates and mussels: Implications for trophic transfer [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(19): 11038-11048. [42] CHEN C Z, CHEN L, YAO Y, et al. Organotin release from polyvinyl chloride microplastics and concurrent photodegradation in water: Impacts from salinity, dissolved organic matter, and light exposure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(18): 10741-10752. [43] UZUN P, FARAZANDE S, GUVEN B. Mathematical modeling of microplastic abundance, distribution, and transport in water environments: A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 288: 132517. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132517 [44] MAI L, SUN X F, XIA L L, et al. Global riverine plastic outflows [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(16): 10049-10056. [45] WONG J K H, LEE K K, TANG K H D, et al. Microplastics in the freshwater and terrestrial environments: Prevalence, fates, impacts and sustainable solutions [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719: 137512. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137512 [46] XIA F Y, YAO Q W, ZHANG J, et al. Effects of seasonal variation and resuspension on microplastics in river sediments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 286: 117403. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117403 [47] DRUMMOND J D, NEL H A, PACKMAN A I, et al. Significance of hyporheic exchange for predicting microplastic fate in rivers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2020, 7(10): 727-732. [48] BONDELIND M, SOKOLOVA E, NGUYEN A, et al. Hydrodynamic modelling of traffic-related microplastics discharged with stormwater into the Göta River in Sweden [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(19): 24218-24230. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08637-z [49] OCKELFORD A, CUNDY A, EBDON J E. Storm response of fluvial sedimentary microplastics [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 1865. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58765-2 [50] IMHOF H K, IVLEVA N P, SCHMID J, et al. Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles [J]. Current Biology, 2013, 23(19): R867-R868. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.09.001 [51] FISCHER E K, PAGLIALONGA L, CZECH E, et al. Microplastic pollution in lakes and lake shoreline sediments - A case study on Lake Bolsena and Lake Chiusi (central Italy) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 213: 648-657. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.012 [52] 陈圣盛, 李卫明, 张坤, 等. 香溪河流域微塑料的分布特征及其迁移规律分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(6): 3077-3087. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202109268 CHEN S S, LI W M, ZHANG K, et al. Distribution characteristics of microplastics and their migration patterns in Xiangxi River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(6): 3077-3087(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202109268
[53] YAN M Q, WANG L, DAI Y Y, et al. Behavior of microplastics in inland waters: Aggregation, settlement, and transport [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2021, 107(4): 700-709. doi: 10.1007/s00128-020-03087-2 [54] HABERSTROH C, ARIAS M, YIN Z W, et al. Effects of hydrodynamics on the cross-sectional distribution and transport of plastic in an urban coastal river [J]. Water Environment Research, 2020, 93(6): 186-200. [55] TIBBETTS J, KRAUSE S, LYNCH I, et al. Abundance, distribution, and drivers of microplastic contamination in urban river environments [J]. Water, 2018, 10(11): 1597. doi: 10.3390/w10111597 [56] 顾伟康. 水动力变化条件下三峡库区典型支流微塑料的分布及归趋[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019. GU W K. The distribution & fate of microplastic in the typical tributary of Three Gorges Reservoir(TGR): The influence of hydrodynamic properties[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019(in Chinese).
[57] NIU L H, LI Y Y, LI Y, et al. New insights into the vertical distribution and microbial degradation of microplastics in urban river sediments [J]. Water Research, 2021, 188: 116449. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116449 [58] REARDON K E, BOMBARDELLI F A, MORENO-CASAS P A, et al. Wind-driven nearshore sediment resuspension in a deep lake during winter [J]. Water Resources Research, 2014, 50(11): 8826-8844. doi: 10.1002/2014WR015396 [59] 徐沛, 彭谷雨, 朱礼鑫, 等. 长江口微塑料时空分布及风险评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(5): 2071-2077. doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2019.0248 XU P, PENG G Y, ZHU L X, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution and pollution load of microplastics in the Changjiang Estuary [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(5): 2071-2077(in Chinese). doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2019.0248
[60] XUE B M, ZHANG L L, LI R L, et al. Underestimated microplastic pollution derived from fishery activities and hidden in deep sediment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(4): 2210-2217. [61] 刘治君, 杨凌肖, 王琼, 等. 微塑料在陆地水环境中的迁移转化与环境效应 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(4): 59-65,90. LIU Z J, YANG L X, WANG Q, et al. Migration and transformation of microplastics in terrestrial waters and effects on eco-environment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(4): 59-65,90(in Chinese).
[62] SANTANA-VIERA S, MONTESDEOCA-ESPONDA S, GUEDES-ALONSO R, et al. Organic pollutants adsorbed on microplastics: Analytical methodologies and occurrence in oceans [J]. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 29: e00114. doi: 10.1016/j.teac.2021.e00114 [63] 陈蕾, 高山雪, 徐一卢. 塑料添加剂向生态环境中的释放与迁移研究进展 [J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(8): 3315-3324. CHEN L, GAO S X, XU Y L. Progress on release and migration of plastic additives to ecological environment [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 3315-3324(in Chinese).
[64] 张楠, 徐一卢, 陈蕾. 风化作用对微塑料影响的研究 [J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49(12): 3191-3194. ZHANG N, XU Y L, CHEN L. Study on the influence of weathering on microplastics [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(12): 3191-3194(in Chinese).
[65] PALUSELLI A, FAUVELLE V, GALGANI F, et al. Phthalate release from plastic fragments and degradation in seawater [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(1): 166-175. [66] CHENG H F, LUO H, HU Y A, et al. Release kinetics as a key linkage between the occurrence of flame retardants in microplastics and their risk to the environment and ecosystem: A critical review [J]. Water Research, 2020, 185: 116253. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116253 [67] SONG Y K, HONG S H, JANG M, et al. Combined effects of UV exposure duration and mechanical abrasion on microplastic fragmentation by polymer type [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(8): 4368-4376. [68] SUN Y R, YUAN J H, ZHOU T, et al. Laboratory simulation of microplastics weathering and its adsorption behaviors in an aqueous environment: A systematic review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 114864. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114864 [69] da COSTA J P, NUNES A R, SANTOS P S M, et al. Degradation of polyethylene microplastics in seawater: Insights into the environmental degradation of polymers [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 2018, 53(9): 866-875. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2018.1455381 [70] MASUD A, CHAVEZ SORIA N G, AGA D S, et al. Adsorption and advanced oxidation of diverse pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from water using highly efficient rGO-nZVI nanohybrids [J]. Environmental Science:Water Research & Technology, 2020, 6(8): 2223-2238. [71] ZHOU L J, YING G G, ZHAO J L, et al. Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in Northern China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(7): 1877-1885. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.03.034 [72] ZHANG Q Q, YING G G, PAN C G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6772-6782. [73] ZHANG G D, LU S Y, WANG Y Q, et al. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes and their correlations in Lower Yangtze River, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 257: 113365. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113365 [74] XU W H, YAN W, LI X D, et al. Antibiotics in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta and Pearl River Estuary, China: Concentrations, mass loading and ecological risks [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 182: 402-407. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.004 [75] FAN X L, ZOU Y F, GENG N, et al. Investigation on the adsorption and desorption behaviors of antibiotics by degradable MPs with or without UV ageing process [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: 123363. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123363 [76] 邵博群, 庞蕊蕊, 李烨, 等. 微塑料和其他新兴污染物相互作用研究进展 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(7): 214-222. SHAO B Q, PANG R R, LI Y, et al. Research progress on interaction between microplastics and other emerging contaminants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(7): 214-222(in Chinese).
[77] LI J, ZHANG K N, ZHANG H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 460-467. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.050 [78] HÜFFER T, HOFMANN T. Sorption of non-polar organic compounds by micro-sized plastic particles in aqueous solution [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 214: 194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.018 [79] BHAGAT K, BARRIOS A C, RAJWADE K, et al. Aging of microplastics increases their adsorption affinity towards organic contaminants [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 298: 134238. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134238 [80] WANG F, SHIH K M, LI X Y. The partition behavior of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanesulfonamide (FOSA) on microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 841-847. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.047 [81] GUO X Y, WANG X L, ZHOU X Z, et al. Sorption of four hydrophobic organic compounds by three chemically distinct polymers: Role of chemical and physical composition [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(13): 7252-7259. [82] ATUGODA T, WIJESEKARA H, WERELLAGAMA D R I B, et al. Adsorptive interaction of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on polyethylene microplastics: Implications for vector transport in water [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2020, 19: 100971. [83] HUANG S L, NG C O, GUO Q Z. Experimental investigation of the effect of flow turbulence and sediment transport patterns on the adsorption of cadmium ions onto sediment particles [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2007, 19(6): 696-703. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60116-8 [84] 肖洋, 成浩科, 唐洪武, 等. 水动力作用对污染物在河流水沙两相中分配的影响研究进展 [J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(5): 480-488. XIAO Y, CHENG H K, TANG H W, et al. Review of influence of hydrodynamic action on distribution of pollutants in water and sediment in river [J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2015, 43(5): 480-488(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载:

