-
全氟烷基酸(perfluoroalkyl acid,PFAAs)是指C—H键全部被C—F键所代替的烷基酸类人工合成化合物. 由于C—F键键能高达485 kJ·mol−1,PFAAs具有极强的化学稳定性、生物稳定性和热稳定性. 自20世纪50年代起,人们开始将其应用在消防、制造业等诸多行业中[1]. PFAAs相关产品在生产、使用、处置过程中,通过污水排放、地表径流、大气沉降等不可避免地被排放进入环境. 由于PFAAs的环境持久性、生物累积性、远距离迁移特性,已在全世界各种环境介质[2-5]、生物体[6]和人体内[7-8]陆续被检出. 研究表明[9-10],PFAAs具有致癌及神经、生殖毒性等,并具有内分泌干扰性. 由于PFAAs的高水溶性和难挥发性,水体成为其主要归趋之一[11]. 因此,了解PFAAs在水环境中的分布与含量具有重要意义,可为后续水中全氟烷基酸的控制与去除提供数据支撑.
有研究报道,长江下游干流水体中ΣPFAAs浓度为191 ng·L−1[12]、海河流域为174 ng·L−1[13]、太湖流域为229 ng·L−1[14],处于国内较高污染水平. 目前对黄河下游地区重要饮用水源地的引黄水库中PFAAs的污染水平鲜有报道. 黄河是我国的第二长河,流域及周边分布着众多水系,密集的工业群及频繁的农业活动,研究显示[15],黄河流域上游地表水水质较优,宁夏至山东沿线等中下游城市地表水水质较差. 黄河中游渭南—郑州段表层水样中ΣPFAAs含量为18.4—56.9 ng·L−1,PFAAs通量呈先降低后增加的趋势,表明上游及支流有污染源汇入[16]. 山东位于黄河下游,部分城市聚集着许多大型氟化工业园区和涉氟工业企业,与中上游相比,PFAAs的污染可能会更严重,并通过饮用水等暴露方式进入人体. 本研究采集了山东省19座引黄水库表层水,采用固相萃取-高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱联用法检测分析了17种PFAAs污染水平及其分布特征,并开展了相关性分析和环境风险评价,初步了解了其污染特征.
-
17种全氟烷基酸混合标准溶液系列(Wellington Laboratories,2000 ng·mL−1,PFCA-MXB),包含:全氟丁酸、全氟戊酸、全氟己酸、全氟庚酸、全氟辛酸、全氟壬酸、全氟癸酸、全氟十一烷酸、全氟十二烷酸、全氟十三烷酸、全氟十四烷酸、全氟十六烷酸、全氟十八烷酸、全氟丁烷磺酸、全氟己烷磺酸、全氟辛烷磺酸、全氟癸烷磺酸. 9种全氟烷基酸内标(Wellington Laboratories,2000 ng·mL−1,WEL-MPFAC-MXA),包含全氟丁酸内标、全氟己酸内标、全氟庚烷磺酸内标、全氟壬酸内标、全氟辛烷磺酸内标、全氟葵酸内标、全氟壬酸内标、全氟十一酸内标、全氟十二酸内标(表1).
甲醇(色谱纯,德国Merck公司),甲酸(色谱纯,美国热电公司),试验用水为超纯水.
-
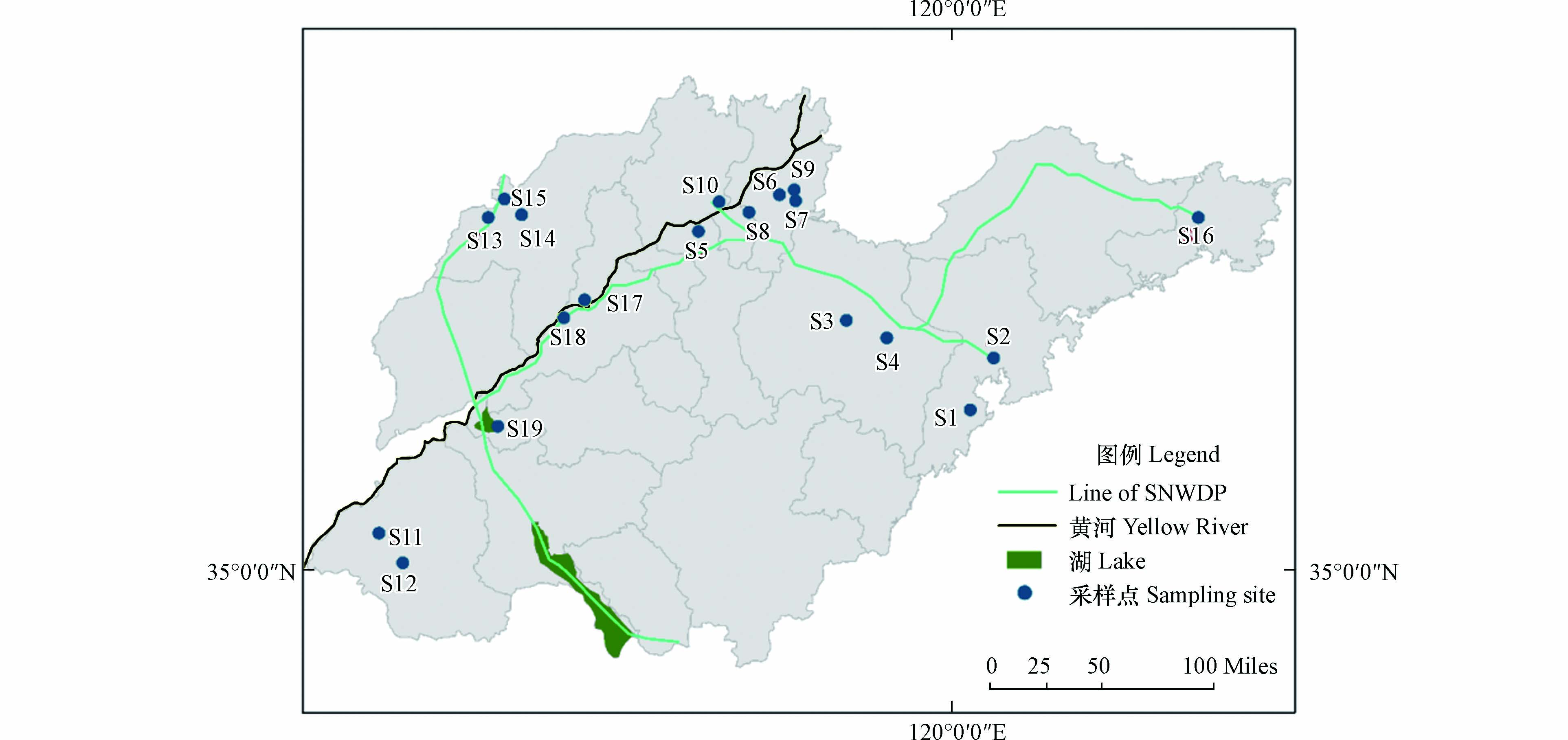
选取山东省十九座有代表性的引黄水库(图1),分别在丰水期(2021年8月)和枯水期(2022年1月)进行现场采样. 用玻璃采样器采集水库出水口水面以下0.5 m的表层水,体积不少于2 L,用聚丙烯广口瓶保存水样,于水库取水口进行取样,同时采集平行样1份.
采用固相萃取进行样品富集. 依次用5 mL甲醇,5 mL 1%氨水甲醇溶液,5 mL去离子水活化Waters WAX固相萃取柱. 样品经0.7 μm玻璃纤维滤膜去除颗粒物质后,取500 mL样品过活化后的固相萃取柱,然后用5 mL 20%甲醇淋洗,最后依次用4 mL 1%氨水甲醇溶液、4 mL 1%氨水洗脱. 洗脱液经氮吹浓缩至干,残留物用0.5 mL 50%甲醇-水溶液溶解,待UPLC-MS/MS分析.
-
采用超高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱法(Waters公司,Xevo TQS UPLC-MSMS)测定水样中17种PFAAs浓度[17]. 色谱管路全部更换为peek管路,且整个试验流程中避免使用聚四氟乙烯材质的容器,以避免产生超高背景值. 液相色谱柱为Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3柱(50 mm×2.1 mm,1.7 μm),柱温40 ℃;流速0.4 mL·min−1;样品室温度10 ℃;进样体积10.0 μL. 流动相A为20 mmol·L−1乙酸铵-水溶液,流动相B为甲醇-乙腈(8:2,V/V),梯度洗脱,洗脱程序及流速见表2.
采用电喷雾电离源负离子扫描,多反应监测(MRM)模式检测;毛细管电压为2.5 kV;离子源温度为120 ℃;脱溶剂温度500 ℃;脱溶剂气流量(氮气,纯度99.999%)和锥孔气流量(氮气,纯度99.999%)分别为800、50 L·h−1;碰撞气流量(氩气,纯度99.999%)为0.20 mL·min−1. 17种PFAAs的质谱条件参数详见表3. 在仪器检测过程中,每10个样品添加一个溶剂空白(1:1甲醇和水)和1个标准溶液. 为控制样品制备和测定过程可能带来的外源性污染,样品制备和测定的同时用超纯水进行空白试验,试验结果为扣除空白基质后的数值. 样品采用内标法进行测定,标准系列浓度范围为0.1—100 μg·L−1,相关性系数R2≥0.995. 样品富集 1000 倍后,PFOA、PFNA 和 PFDA 检测下限为 0.5 ng·L−1,其他均为 1 ng·L−1 ,方法回收率 为 68.1%—109.4%.
-
由于我国对PFAAs的环境风险评价还没有统一的标准,本研究采用较为广泛的风险熵值法(risk quotient,RQ). 计算公式[18]为:
式中,Cm:实际样品中目标物质的浓度;Cp:预测无效应浓度.
采用评估因子法和物种敏感度分布法得到各PFAAs的Cp,水中PFOA、PFNA、PFHxA、PFOS、PFHpA、PFDA的Cp分别为100、32、97、25、32、11 μg·L−1[19]. RQ大于1,则认为有风险[20].
-
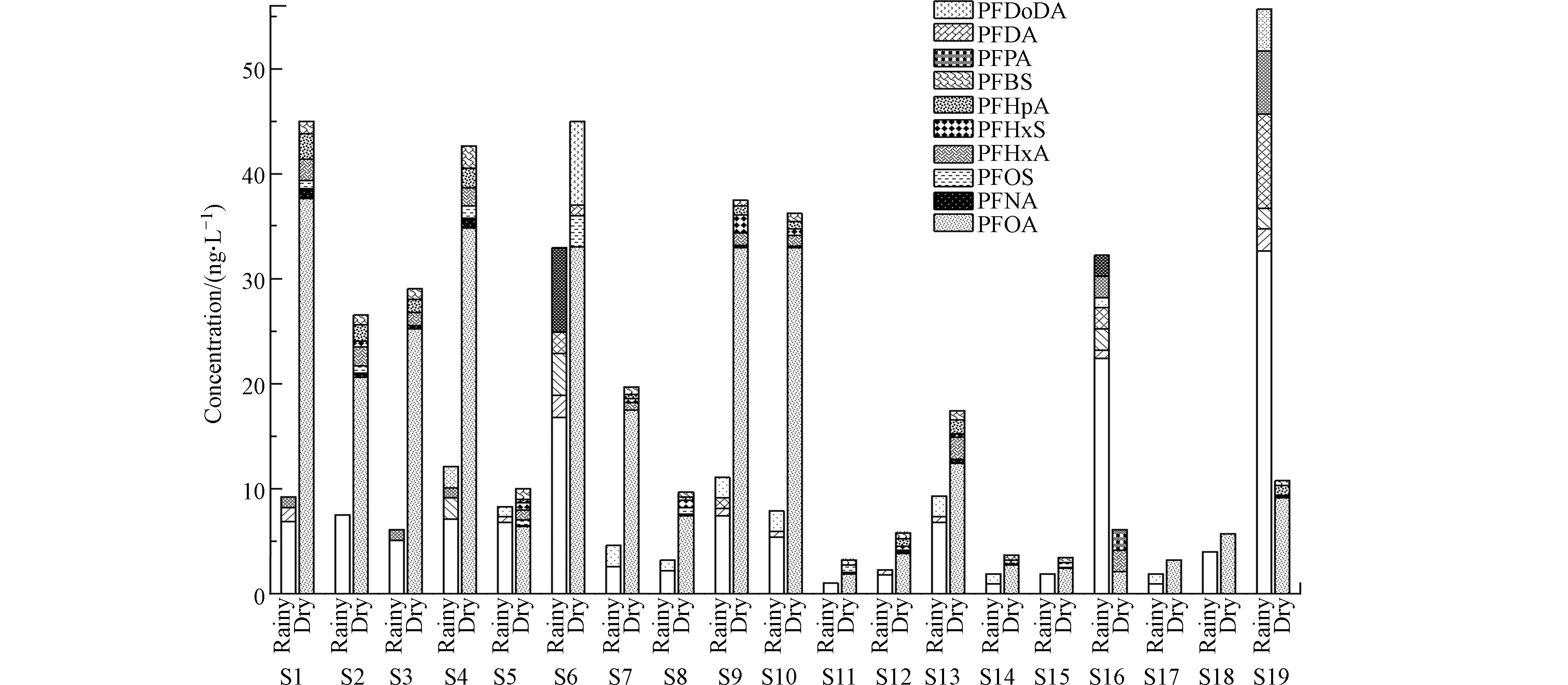
对19个黄河下游地区引黄水库丰水期、枯水期的表层水样品中17种PFAAs浓度进行分析,共检出10种PFAAs.
-
丰水期检出8种PFAAs,包括3种全氟烷基磺酸(PFSAs)、5种全氟烷基羧酸(PFCAs),检出率呈PFOA > PFNA = PFHxS > PFHpA > PFOS = PFHxA > PFBS= PFDoDA的顺序;枯水期共检出10种PFAAs,包括3种PFSAs以及7种PFCAs,检出率呈PFOA > PFNA = PFBS> PFHPA > PFHxA > PFHxS> PFOS > PFPeA = PFDA = PFDoDA的顺序,详细结果见图2. 综合枯水期、丰水期的数据来看,全部样品中检出率最高的为PFOA、PFNA和PFHxS,PFOA是所有样品中检出频率最高的PFAAs.
按照碳链长短把PFAAs分为短链(C≤6)、中链(7≤C≤10)和长链(C≥11)3类[21],本研究检出的PFAAs大部分为中短链全氟烷基酸,长链全氟烷基酸检出1项,分布呈现出中链>短链>长链的情况. 其原因可能有两方面:(1)随着近年来对长链产品的限制,短链产品是逐渐被广泛应用的;(2)长链PFAAs更倾向于分配到沉积物和悬浮颗粒物中[22].
-
结果显示(图2),丰水期样品中ΣPFAAs浓度范围为1—55.7 ng·L−1,平均值为8.3 ng·L−1;枯水期则为3.2—45.1 ng·L−1,平均值为19.0 ng·L−1. 对检出率最高的PFOA进行重点分析,其含量占比最高,丰水期浓度范围为0.9—32.6 ng·L−1,平均值为7.4 ng·L−1,占总量均值的89%;枯水期浓度范围为1.9—37.6 ng·L−1,平均值为15.3 ng·L−1,占总量均值的81%.
本研究中,黄河下游地区引黄水库丰水期各水样中PFOA占ΣPFAAs的47.4%—100%,枯水期占34.4%—100%. PFOA检出浓度整体高于其他检出PFAAs,说明PFOA为黄河下游地区山东引黄水库表层水中PFAAs的主要污染物.
-
除泰安东平湖水库外,其它水库ΣPFCs浓度丰水期低于枯水期,这可能与丰水期时水体被稀释有关. 泰安东平湖水库丰水期PFOA浓度为32.6 ng·L−1,明显高于枯水期浓度(9.1 ng·L−1),PFHxA、PFHpA、PFBS浓度也高于枯水期,可能丰水期时周围存在污染源汇入,也可能是由于南水北调水的掺入. 沿海城市青岛与威海PFOA浓度在丰水期和枯水期明显不同,丰水期青岛(两个水库平均值)、威海水库PFOA浓度分别为7.2、22.4 ng·L−1,枯水期则分别为29.1、2.1 ng·L−1,由于青岛和威海分别处于胶东半岛的西南、正东方向,这很可能是由于季风气候及湿沉降双重作用的结果[23]. 潍坊、东营、滨州水库表层水中枯水期PFOA浓度范围为7.4—34.8 ng·L−1,明显高于其它城市,这可能与当地纺织、石油化工等特色产业有关. 除以上特别说明的城市外,其他水库同一时期PFOA浓度差别并不显著. 特别是淄博市的氟化工、德州市的光伏产业并没有导致PFAAs的浓度明显升高,这可能与当地政府重视环保有关,也可能与多氟化合物的替代有关,还需要继续跟踪监测.
不同区域工业生产中使用的原材料不同,会导致各地地表水中PFAAs单体的浓度有所差异[24-25]. 通过各水库表层水中PFAAs组成发现(图3),丰水期17种全氟烷基酸含量占比(平均值)依次为PFOA(72.9%)> PFHxS(13.7%) > PFNA(3.8%) > PFHpA(2.7%) > PFOS(2.0%) = PFHxA(2.0%)> PFDoDA(1.8%) > PFBS(1.2%);枯水期为PFOA(77.3%)> PFBS(5.1%)> PFHxA(4.4%)> PFOS(3.2%)= PFHpA(3.2%)>PFHxS(2.2%)> PFNA(1.8%)> PFPeA(1.7%)> PFDoDA(0.9%)> PFDA(0.1%). 丰水期、枯水期两批次样品检出的PFAAs百分组成存在一定差距,通过T检验也发现丰水期和枯水期水样中 PFAAs 的组分浓度存在显著性差异 (P<0.05),这说明黄河下游地区山东段引黄水库中全氟烷基酸不同季节污染来源不同.
-
本研究样本中PFOA浓度范围为0.9—37.6 ng·L−1,均值11.4 ng·L−1,是本研究范围内最主要的全氟烷基酸. 我国目前尚未颁布关于PFAAs的地表水环境质量标准,《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB 5749—2022)附录A中规定了生活饮用水水质参考指标全氟辛酸的限值为0.00008 mg·L−1. 本研究所有样本中PFOA浓度均低于该限值.
从表4可以看出,黄河下游地区引黄湖库PFOA浓度与其他报道的黄河水中污染水平相当;与其他地区湖库,例如深圳水库群、千岛湖、洞庭湖、洪湖、意大利Lake Maggiore的污染水平相当,低于骆马湖、太湖、巢湖、长江流域、韩国Lake Shihwa. 由于本研究仅对表层水中PFAAs的质量浓度进行了测定分析,尚未开展PFAAs在水库垂直方向浓度差异、底泥及颗粒物的吸附与分配等方面的研究,尚无法全面说明引黄水库中全氟烷基酸的污染程度,仍需在今后深入开展相关研究工作.
-
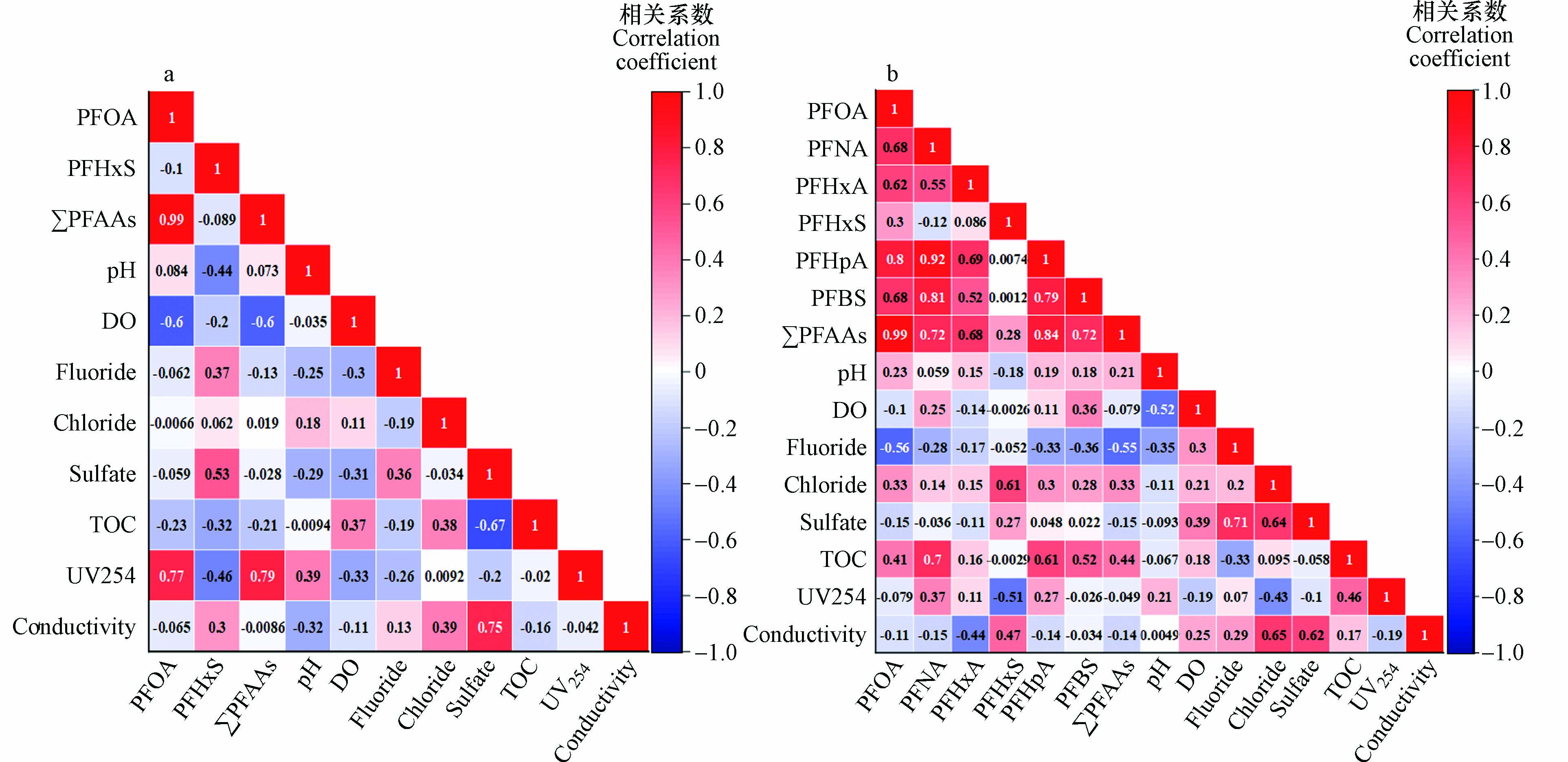
对丰、枯水期检出频率大于50%的PFAAs与pH、TOC、溶解氧等8种常规指标进行Spearman相关性分析. 分析发现,丰水期(图4a)PFOA和∑PFAAs与溶解氧(DO)呈负相关,可能是由于溶解氧的存在有利于微生物降解PFAAs[36];与UV254呈正相关,Zhang等[37]曾报道陆地类腐殖质成分是土壤中PFAAs的重要载体,它将污染物带入河流,并通过地表径流冲刷传播;与TOC呈弱的负相关,可能与丰水期水量被稀释有关;而与pH、氟化物、氯化物、硫酸盐、电导率相关性不大.
在枯水期(图4b),PFOA和∑PFAAs与溶解氧(DO)的相关性不大,但与氟化物呈负相关,可能是由于冬季水温低,微生物代谢活动差,无法把PFAAs矿化导致的. 除了PFHxS外,其它PFAAs与TOC呈正相关,这可能是由于枯水期PFAAs浓度水平增加导致的,而枯水期TOC的增加使PFHxS与其他有机物形成竞争吸附,PFHxS可能更倾向于分配在沉积物中. 在丰、枯水期PFHxS均与UV254呈负相关,这也可能是由于与腐殖酸等大分子有机物竞争吸附.
总之,引黄水库中PFAAs的含量是外源污染与水库其他水质指标综合作用的结果,因此,控制PFAAs的污染水平还需要采取多种手段.
-
根据本研究中样品的检出结果,结合已查询到的PFAAs的预测无效应浓度,计算了表层水中4种PFAAs(PFOA、PFNA、PFOS、PFHxA)的风险熵RQ值,结果如图5.可以看出,所有采样点位的样品中 PFAAs 的 RQ 值都远低于 1,最高 RQ 值为 0.000376(PFOA),说 明黄河下游地区各引黄水库 PFAAs 的生态风险较低.
-
通过研究分析黄河下游地区山东省19处引黄水库表层水中17种全氟烷基酸的浓度,并进行风险评估,得出以下结论:
(1)19个采样点表层水中均检出PFAAs,中链PFOA为主要组分. 表层水中17种全氟烷基酸总质量浓度范围为1—55.7 ng·L−1,在国内外属于低污染水平.
(2)相关性分析结果表明,引黄水库中PFAAs的含量是外源污染与水库其他水质指标综合作用的结果,因此,控制PFAAs的污染水平还需要采取多种手段.
(3)PFOA、PFNA、PFOS、PFHxA环境风险评价结果显示,总体风险熵值远低于1,黄河下游地区各引黄水库PFAAs环境风险较低.
由于大部分PFAAs缺乏预测无效应浓度参数,未能得到全部PFAAs的环境风险,也未考虑多种污染物可能带来的复合环境风险. 此外,本研究对象为水库表层水,由于条件限制,尚未开展水相及沉积相中PFAAs的污染分布、迁移转化等方面研究. 后续将持续关注PFAAs在引黄水库中的多介质赋存、空间分布迁移转化行为,进一步探明PFAAs在引黄水库中的污染特征与生态环境风险.
黄河下游地区引黄水库表层水中全氟烷基酸的分布特征与风险评估
Distribution and risk assessment of Perfluoroalkyl acid in surface water of diversion reservoirs from the lower Yellow River
-
摘要: 全氟烷基酸(perfluoroalkyl acid,PFAAs)具有环境持久性、生物富集性、潜在毒性等特点,其在水中的污染问题受到了全球各国普遍重视. 为探明黄河下游地区各地引黄水库水中全氟烷基酸的污染特征,先后于2021年丰水期和枯水期收集了十九座黄河下游地区山东段引黄水库的表层水,采用固相萃取-超高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱法测定了表层水中17种全氟羧酸和全氟磺酸的浓度,分析了全氟烷基酸的种类、含量及时空变化特征,开展了全氟烷基酸与水质参数的相关性分析并采用熵值法对典型全氟烷基酸进行了环境风险评价. 结果显示,所调查的十九座引黄水库表层水中可检出全氟辛酸、全氟壬酸、全氟辛烷磺酸、全氟己酸、全氟己烷磺酸和全氟庚酸,总质量浓度范围为1—55.7 ng·L−1;风险评估结果表明该流域内所调研的引黄水库表层水体中全氟辛酸等典型全氟烷基酸的风险熵值远低于1,污染水平尚未达到对生态环境造成风险的水平.Abstract: Perfluoroalkyl acid (PFAAs) have attracted widespread attention owing to their environmental persistence, bioaccumulation, and potential toxicity. To explore the pollution characteristics of PFAAs in diversion reservoirs from the lower Yellow River, the surface water of 19 Yellow River diversion reservoirs in Shandong Province was collected in rainy and dry periods in 2021, respectively. The 17 perfluorocarboxylic acids and perfluorosulfonic acids in the surface water were determined by solid-phase extraction enrichment and high-throughput detection with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Perfluoroalkyl acids were analyzed for their composition, types, and spatial and temporal variation characteristics. The correlation analysis between PFAAs and water quality parameters, as well as entropy-based assessments of typical PFAAs, have been conducted in this study. The results showed that perfluorooctanoic acid, perfluorononanoic acid, perfluorooctane sulfonates, perfluorohexanoic acid, perfluorohexanesulfonic acid and perfluoroheptane sulfonic acid were detected, and ∑PFAAs concentrations ranged from 1 ng·L−1 to 55.7 ng·L−1. Using environmental risk assessment, the results showed that the risk quotient was far lower than 1 for all samples. The PFAAs pollution level in the surface water of the Yellow River diversion reservoirs has not reached the level of risk to ecological environment.
-

-
表 1 PFAAs基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of PFAAs detected in this study
类别
Category全称
Full name缩写
Abbreviation分子式
Molecular formulaCAS 全氟烷基羧酸(PFCAs) 全氟丁酸 perfluorobutyric acid PFBA C4HF7O2 375-22-4 全氟烷基羧酸(PFCAs) 全氟戊酸 perfluoropentanoic acid PFPeA C5HF9O2 2706-90-3 全氟己酸 perfluorohexanoic acid PFHxA C6HF11O2 307-24-4 全氟庚酸 perfluoroheptanoic acid PFHpA C7HF13O2 375-85-9 全氟辛酸 perfluorooctanoic acid PFOA C8HF15O2 335-67-1 全氟壬酸 perfluorononanoic acid PFNA C9HF17O2 375-95-1 全氟癸酸 perfluorodecanoic acid PFDA C10HF19O2 335-76-2 全氟十一烷酸 perfluoroundecanoic acid PFUnDA C11HF21O2 2058-94-8 全氟十二烷酸 perfluorododecanoic acid PFDoDA C12HF23O2 307-55-1 全氟十三烷酸 perfluorotridecanoic acid PFTrDA C13HF25O2 72629-94-8 全氟十四烷酸 perfluorotetradecanoic acid PFTeDA C14HF27O2 376-06-7 全氟十六烷酸 perfluorohexadecanoic acid PFHxDA C16HF31O2 67905-19-5 全氟十八烷酸 perfluorooctadecanoic acid PFODA C18HF35O2 16517-11-6 全氟烷基磺酸 (PFSAs) 全氟癸烷磺酸 perfluorodecane sulfonic acid PFDS C4HF9SO3 2806-15-7 全氟辛烷磺酸 perfluorooctanesulfonic acid PFOS C6HF13SO3 1763-23-1 全氟己烷磺酸 perfluorohexanesulfonic acid PFHxS C8HF17SO3 355-46-4 全氟丁烷磺酸 Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid PFBS C10HF21SO3 375-73-5 表 2 流动相梯度
Table 2. Mobile phase gradient
时间/min
Time初始
Initial1 6 7 8.5 8.51 10 A/% 65 50 30 10 10 65 65 B/% 35 50 70 90 90 35 35 表 3 17种PFAAs的质谱条件参数
Table 3. Mass spectrum parameters of 17 PFAAs
序号
Number全氟烷基酸名称
Name电喷雾离子源
Electron spray ionization母离子
Parent Ion m/z锥孔电压/ V
Cone voltage子离子
Daughter ion m/z碰撞能/ eV
Collision energy1 全氟丁酸
PFBA— 213 14 169* 10 125 12 2 全氟丁酸内标
MPFBA— 217 14 172* 10 — — 3 全氟戊酸
PFPeA— 263 14 219* 10 141 10 4 全氟丁烷磺酸
PFBS— 299 45 80* 30 99 28 5 全氟己酸
PFHxA— 313 14 269* 10 119 20 6 全氟己酸内标
MPFHxA— 315 14 270* 10 119 20 7 全氟庚酸
PFHpA— 363 14 319* 10 169 18 8 全氟庚烷磺酸
PFHxS— 399 56 80* 32 99 30 9 全氟庚烷磺酸内标
MPFHxS— 403 56 84* 32 103 30 10 全氟辛酸
PFOA— 413 14 369* 10 169 18 11 全氟辛酸内标
MPFOA— 417 14 372* 10 169 18 12 全氟壬酸
PFNA— 463 16 419* 10 169 20 13 全氟壬酸内标
MPFNA— 468 16 423* 10 169 20 14 全氟辛烷磺酸
PFOS— 499 60 80* 30 99 28 15 全氟辛烷磺酸内标
MPFOS— 503 60 80* 30 99 28 16 全氟癸酸
PFDA— 513 16 469* 10 169 22 17 全氟癸酸内标
MPFDA— 515 16 470* 10 169 22 18 全氟十一酸
PFUdA— 563 16 519* 11 169 24 19 全氟十一酸内标
MPFUdA— 565 16 520* 11 169 24 20 全氟癸烷磺酸
PFDS— 599 70 80* 50 99 34 21 全氟十二酸
PFDoA— 613 16 569* 12 169 24 22 全氟十二酸内标
MPFDoA— 615 16 570* 12 169 24 23 全氟十三酸
PFTrDA— 663 16 619* 12 169 28 24 全氟十四酸
PFTeDA— 713 18 669* 12 169 30 25 全氟十六酸
PFHxDA— 813 20 769* 12 169 30 26 全氟十八酸
PFODA— 913 20 869* 15 169 30 注: * 表示定量离子. *Represent quantitative ion. 表 4 不同研究区湖库水中主要PFAAs比较
Table 4. Comparison of PFAAs in surface water of lake reservoira from different regions
采样水体
Sampling waterPFOA/(ng·L−1) 参考文献
References山东引黄水库水 0.9—37.6 本研究 东营黄河水 2.04—2.68 [26] 黄河河南段 0.459—12.7 [14] 深圳水库群 0.29—7.3 [27] 珠江三角洲同沙水库 2.15—26.70 [28] 千岛湖(新安江水库) 0.52—3.61 [29] 骆马湖 7.6—81.34 [30] 太湖 16.9—39.7 [31] 巢湖 17.1—33.3 [32] 洞庭湖 3.22—8.53 [33] 洪湖 6.25—12.39 [33] 长江流域重庆段 1.16—49.87 [21] Lake Shihwa (韩国) 50—62 [34] Lake Maggiore (意大利) 1.8—2.9 [35] -
[1] SUNDERLAND E M, HU X C, DASSUNCAO C, et al. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects [J]. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 2019, 29(2): 131-147. [2] 郑宇, 路国慧, 邵鹏威, 等. 青藏高原东部过渡区水环境中全氟化合物的分布特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(5): 1192-1201. doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019081506 ZHENG Y, LU G H, SHAO P W, et al. Level and distribution of perfluorinated compounds in snow and water samples from the transition zone in eastern Qinghai-Tibet [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(5): 1192-1201(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019081506
[3] 宋彦敏, 刘慧, ZAKARI Sissou, 等. 全氟磺酸类物质在沙质沉积物中的迁移规律 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(5): 850-857. doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.05.2015112706 SONG Y M, LIU H, SISSOU Z, et al. Transport behavior of perfluorinated sulfonic acids in sandy sediment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(5): 850-857(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.05.2015112706
[4] 薛欢欢, 丁光辉, 张楠楠, 等. 大连湾表层海水全氟烷基化合物污染水平及分布研究 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(2): 252-257. XUE H H, DING G H, ZHANG N N, et al. Study on pollution level and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances in surface seawater of Dalian Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(2): 252-257(in Chinese).
[5] 马梦宇, 赵兴茹, 申金山, 等. 洞庭湖鱼中全氟烷基化合物的污染特征及健康风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1011-1019. doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019112905 MA M Y, ZHAO X R, SHEN J S, et al. Pollution characteristics and health risk of perfluoroalkyl substances in fish from Dongting Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1011-1019(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019112905
[6] LORENZO M, CAMPO J, FARRÉ M, et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the Ebro and Guadalquivir River Basins (Spain) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 540: 191-199. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.045 [7] HAN W C, GAO Y, YAO Q, et al. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in matched parental and cord serum in Shandong, China [J]. Environment International, 2018, 116: 206-213. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.04.025 [8] ZHANG Y, MUSTIELES V, SUN Y, et al. Association between serum per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances concentrations and common cold among children and adolescents in the United States [J]. Environment International, 2022, 164: 107239. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107239 [9] LIU B L, ZHANG H, YU Y, et al. Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in soil of the Pearl River Delta, China: Spatial distribution, sources, and ecological risk assessment [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2020, 78(2): 182-189. doi: 10.1007/s00244-019-00674-1 [10] FANG C, WU X L, HUANG Q S, et al. PFOS elicits transcriptional responses of the ER, AHR and PPAR pathways in Oryzias melastigma in a stage-specific manner [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2012, 106/107: 9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.10.009 [11] ZHOU J, LI Z, GUO X T, et al. Evidences for replacing legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances with emerging ones in Fen and Wei River Basins in central and Western China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 377: 78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.050 [12] 张悦清, 张爱国, 曹莉, 等. 长江流域全氟化合物污染态势与生态效应 [J]. 环境监控与预警, 2020, 12(5): 58-67. ZHANG Y Q, ZHANG A G, CAO L, et al. Contamination status and ecological effects of perfluoroalkyl substances in the Yangtze Basin [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2020, 12(5): 58-67(in Chinese).
[13] LI F S, SUN H W, HAO Z N, et al. Perfluorinated compounds in Haihe River and Dagu drainage canal in Tianjin, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 84(2): 265-271. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.060 [14] CHEN M, WANG Q, SHAN G Q, et al. Occurrence, partitioning and bioaccumulation of emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Taihu Lake, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 634: 251-259. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.301 [15] 刘鸿志, 王光镇, 马军, 等. 黄河流域水质和工业污染源研究 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2021, 37(3): 18-27. LIU H Z, WANG G Z, MA J, et al. Water quality status and industrial pollution sources in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2021, 37(3): 18-27(in Chinese).
[16] 李琦路, 程相会, 赵祯, 等. 黄河中游(渭南—郑州段)全/多氟烷基化合物的分布及通量 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 228-238. LI Q L, CHENG X H, ZHAO Z, et al. Distribution and fluxes of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the middle reaches of the Yellow River(Weinan-Zhengzhou section) [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(1): 228-238(in Chinese).
[17] 温馨, 吕佳, 陈永艳, 等. 固相萃取-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定生活饮用水中11种全氟化合物 [J]. 卫生研究, 2020, 49(2): 272-279. WEN X, LYU J, CHEN Y Y, et al. Determination of 11 perfluorinated compounds in drinking water by solid phase extraction-ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2020, 49(2): 272-279(in Chinese).
[18] LIU J C, LU G H, XIE Z X, et al. Occurrence, bioaccumulation and risk assessment of lipophilic pharmaceutically active compounds in the downstream rivers of sewage treatment plants [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 511: 54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.033 [19] HOKE R A, BOUCHELLE L D, FERRELL B D, et al. Comparative acute freshwater hazard assessment and preliminary PNEC development for eight fluorinated acids [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 87(7): 725-733. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.066 [20] 金磊. 黄浦江上游太浦河水源水体中全氟化合物赋存特征及风险评价 [J]. 净水技术, 2021, 40(1): 54-59. JIN L. Risk assessment and occurrence characteristics of PFCs in water body of taipu water source in upstream of Huangpu River [J]. Water Purification Technology, 2021, 40(1): 54-59(in Chinese).
[21] 杜国勇, 蒋小萍, 卓丽, 等. 长江流域重庆段水体中全氟化合物的污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(11): 2266-2272. DU G Y, JIANG X P, ZHUO L, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of perfluorinated compounds in surface water from Chongqing section of the Yangtze River [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(11): 2266-2272(in Chinese).
[22] 曾士宜, 杨鸿波, 彭洁, 等. 贵州草海湖泊表层水与沉积物中全氟化合物的污染特征及风险评估 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1193-1205. doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072404 ZENG S Y, YANG H B, PENG J, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of perfluorinated compounds in surface water and sediments of Caohai Lake of Guizhou Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1193-1205(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020072404
[23] WANG S Q, LIN X P, LI Q, et al. Neutral and ionizable per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the urban atmosphere: Occurrence, sources and transport [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153794. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153794 [24] SO M K, MIYAKE Y, YEUNG W Y, et al. Perfluorinated compounds in the Pearl River and Yangtze River of China [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 68(11): 2085-2095. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.02.008 [25] 张明, 唐访良, 俞雅雲, 等. 钱塘江(杭州段)表层水中全氟化合物的残留水平及分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(12): 4471-4478. ZHANG M, TANG F L, YU Y Y, et al. Residue concentration and distribution characteristics of perfluorinated compounds in surface water from Qiantang River in Hangzhou section [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(12): 4471-4478(in Chinese).
[26] 路国慧, 沈亚婷, 何俊, 等. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定黄河河口段水中全氟化合物的初步研究 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2012, 31(1): 147-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.01.020 LU G H, SHEN Y T, HE J, et al. Preliminary study on perfluorinated compounds in waters from the Yellow River Estuary area by utilizing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(1): 147-153(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.01.020
[27] 王鑫璇, 张鸿, 何龙, 等. 深圳水库群表层水中全氟化合物的分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(6): 2085-2090. WANG X X, ZHANG H, HE L, et al. Distribution of perfluorinated compounds in surface water of Shenzhen Reservoir groups [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(6): 2085-2090(in Chinese).
[28] 张佳骥, 薛晓燕, 黄楚珊, 等. 珠江三角洲同沙水库全氟辛酸和全氟辛烷磺酸污染现状调查 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(12): 2600-2608. doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017031702 ZHANG J J, XUE X Y, HUANG C S, et al. Survey of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate in surface water from Tongsha Reservoir of Pearl River Delta, South China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(12): 2600-2608(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017031702
[29] 张明, 唐访良, 程新良, 等. 千岛湖(新安江水库)表层水中全氟化合物的残留水平及分布特征 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(2): 337-345. doi: 10.18307/2020.0204 ZHANG M, TANG F L, CHENG X L, et al. Occurrence and distribution of perfluorinated compounds in surface water of Lake Qiandao(Xin'anjiang Reservoir) [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(2): 337-345(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0204
[30] 黄家浩, 吴玮, 黄天寅, 等. 骆马湖表层水和沉积物中全氟化合物赋存特征、来源及健康风险评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(7): 3562-3574. HUANG J H, WU W, HUANG T Y, et al. Characteristics, sources, and risk assessment of perlyfluoroalkyl substances in surface water and sediment of Luoma Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(7): 3562-3574(in Chinese).
[31] MA X X, SHAN G Q, CHEN M, et al. Riverine inputs and source tracing of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Taihu Lake, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 612: 18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.235 [32] PAN X, YE J, ZHANG H, et al. Occurrence, removal and bioaccumulation of perfluoroalkyl substances in lake Chaohu, China [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(10): 1692. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16101692 [33] 李珍. 长江中游地区湖泊全氟化合物的污染特征及生态风险评估[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院武汉植物园), 2019. LI Z. Distribution and risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in lakes from the middle reach of Yangtze River, China[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019(in Chinese).
[34] ROSTKOWSKI P, YAMASHITA N, SO I M K, et al. Perfluorinated compounds in streams of the Shihwa Industrial Zone and Lake Shihwa, South Korea [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2006, 25(9): 2374-2380. doi: 10.1897/05-627R.1 [35] LOOS R, WOLLGAST J, HUBER T, et al. Polar herbicides, pharmaceutical products, perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), and nonylphenol and its carboxylates and ethoxylates in surface and tap waters around Lake Maggiore in Northern Italy [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, 387(4): 1469-1478. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-1036-7 [36] 薛学佳, 周钰明, 吴敏, 薛静, 徐飞高. 含氟有机化合物优势降解菌的筛选 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2004, 27(1): 11-12,110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2004.01.006 XUE X J, ZHOU Y M, WU M, et al. Screening of dominant strains of degrading organo-fluorine compounds [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2004, 27(1): 11-12,110(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2004.01.006
[37] ZHANG F S, WANG Y L, WEI Z, et al. Perfluorinated compounds in a river basin from QingHai-Tibet Plateau: Occurrence, sources and key factors [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 228: 113043. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113043 -



 下载:
下载: