-
工业是我国国民经济中十分重要的物质生产部门之一。随着我国工业的飞速发展,工业生产规模不断扩大,由此产生了越来越多的环境问题。在工业生产过程中,各类行业的化工产品数量种类繁多,成分复杂多样,会产生大量的化工废水。这类废水通常含有许多复杂难降解的污染物,并且具有较强的生物毒性,排放到环境中可能会破坏生态环境,危害人类健康。因此,通过一定的处理手段使化工废水达到无毒排放是十分重要的。
-
化工废水是指在化学工业生产过程中所产生的废水和废液。由于化学工业过程中生产的产品复杂多样,使用到的许多原辅材料是有毒且不可生物降解的,因此这类废水成分复杂,甚至还有很大可能包含有毒有害污染物[1]。
-
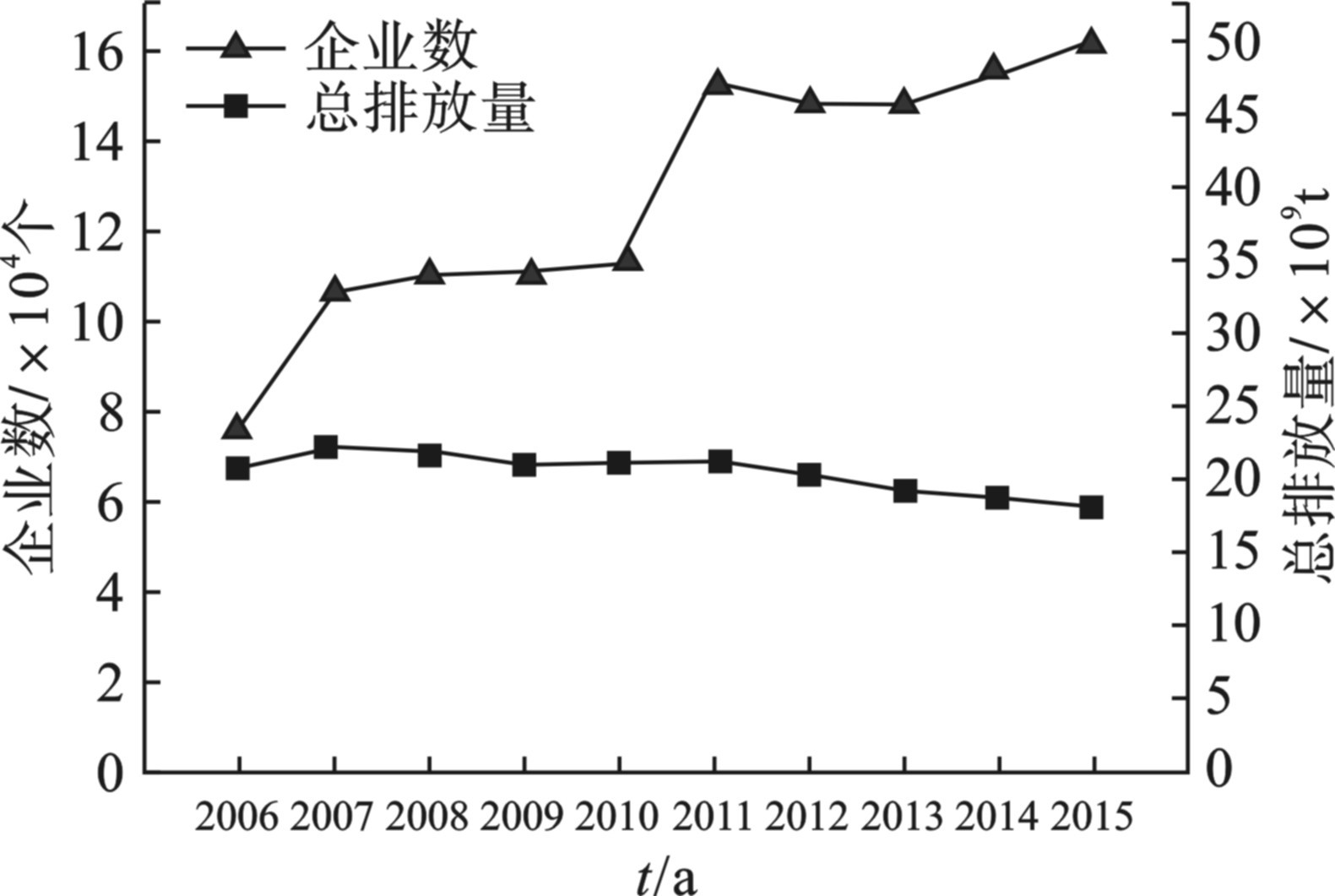
我国每年的工业废水排放量较大。根据中国环境统计年鉴提供的数据统计出2006 ~2015年10年间全国工业企业总数和工业废水排放总量,见图1[2-11]。国家统计局于2015年以后停止公布工业废水总排放量数据,因此图中数据截止到2015年。
图1可知,近10年间工业企业在数量上大体上呈现出逐年增加的趋势。根据雷平等[12]的研究,企业数量对经济增长有一定的促进作用,并且企业数量对产出的弹性随时间而表现出增长的趋势,经济越发达,这种影响的效果就会越明显。同时可以看出,工业废水的排放总量大体上呈现出降低的态势,这一结果是在政府和企业的共同努力下,采取生产技术创新、淘汰落后产能、降低产品的水资源消耗和废水的再生利用等一系列的措施所达到的。
-
工业废水的类型多种多样,我国工业废水的排放主要集中在煤化工、造纸、纺织、印染、电镀、农药、食品加工和冶金等行业[13]。
煤化工废水主要是以煤炭为原料,采用一定的化学技术进行加工处理,在这个过程中会产生成分复杂多样的废水,这类废水通常浓度较高、毒性较大[14]。煤化工废水的色度和浊度较高,综合废水的化学需氧量(chemical oxygen demand, COD)一般在5 000 mg/L左右,氨氮在200 mg/L~500 mg/L之间,含有大量氨氮、硫、酚类、氰类和多环芳香族化合物等有毒有害物质,并且含有吡啶、咔唑和三联苯等难降解有机物。
造纸废水是指制浆造纸工艺过程中产生的废水。由于产品需求量大,生产工序繁多,工艺复杂,所产生的废水排放量大、负荷高、色度高、泡沫多,通常有较重的气味,且废水中所含污染物种类多种多样,如纤维素、半纤维素、油墨和含氯化合物等[15]。此外,废水中也可能含有毒性较大的致癌物质二噁英,对生态环境和人体健康造成了一定的威胁。
纺织废水是指在纺织工业过程中产生的废水,主要是原料蒸煮、漂洗和上浆过程中含各种有机物的废水。印染废水是洗染、印花等工艺过程中产生的废水,含有大量染料、洗涤剂等有机物以及各种无机物,具有较强的污染性。纺织印染废水成分复杂多样,有机物浓度高,色度高,pH变化大,碱性大,水质水量有较大变化,具有一定的处理难度[16]。
电镀废水一般来源于生产工艺过程中的镀件清洗水、废电镀液和设备冷却水等。由于电镀工艺在生产过程中需要用到大量的水,因此电镀废水的产生量很大,包含铬、镉、镍、铜、锌、金和银等金属离子[17]以及氰化物、有机酸等,还含有致癌、致畸和致突变的有害物质,通常具有较大的毒性。
农药废水是指农药厂在农药生产过程中所产生的含有原药、生产主要原料和中间体的废水。我国是全球范围内最大的农药生产国和出口国[18],农药品种多种多样,可分为杀虫剂、杀菌剂、除草剂和植物生长调节剂,由此造成农药废水水量大、水质复杂和污染物浓度较高,COD可达每升数万毫克,并含有许多难以生物降解的物质,有对人体呼吸道和黏膜有害的恶臭。此外,废水中还含有酚、砷和汞等有害物质,使农药废水具有很大的毒性[19]。
食品加工废水是在食品工业中原料的处理、洗涤、脱水、过滤和蒸煮过程中所产生的废水[20]。由于食品工业种类丰富,包括酿造、制糖、乳品加工和肉类等,因此排放出的废水含有大量有机物、蛋白质、有机酸和碳水化合物,具有很强的耗氧性,可生化性好,毒性相对较小[21]。
冶金废水是在冶金工业中冷却、酸洗、除尘,烟气洗涤和冲渣等工艺过程中所产生的废水。具有水量大、种类多和水质复杂多样的特点[22]。此外,废水污染物浓度高,重金属含量高,偏酸性,色度和气味较大,容易产生泡沫,通常具有较大的毒性。
-
现有常见的废水排放标准主要关注于化学/生物需氧量、氨氮、总氮、总磷、色度、浊度及特定污染物(如有机卤素、重金属离子和新型污染物等)常规理化指标和污染物浓度,这些指标只能关注一种或多种污染物的污染水平,并不能反映废水的综合生物毒性效应。排出物中有毒物质十分复杂多样,仅靠化学分析来确定对生物体有毒的化学物质的方法是十分有限的。由于化工废水成分复杂多样,有些排放的废水虽达到了常规理化指标的排放标准,但实际上仍然可能存在对环境乃至人体健康存在危害的污染物,从而使水体存在一定的毒性。因此,有必要结合综合生物毒性测试进行水质评价[23]。
-
排水综合生物毒性测试采用一组标准模式生物,直接通过水生生物毒性测试的方法来评价排水综合毒性[24]。成组生物毒性涉及多种毒性测试方法,包括急性毒性、内分泌干扰毒性、遗传毒性、发育毒性和细胞毒性[25]等。其中,急性毒性测试包含发光细菌急性毒性测试、藻类急性毒性测试、大型溞急性毒性测试、斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性测试和鱼类急性毒性测试等;内分泌干扰毒性包括鱼类短期生殖试验(OECD 229)、生物标志物(如于卵黄蛋白原(Vitellogenin, VTG)、睾酮(Testosterone, T)和17α-雌二醇(Estradiol, E2)等)含量测试等;遗传毒性包括AMES实验、微核实验、单细胞凝胶电泳实验、SOS染色体实验和8-羟基脱氧鸟苷实验等;发育毒性包括爪蟾胚胎毒性、斑马鱼胚胎毒性等。急性毒性评价方法,见表1。
-
毒性测试的方法多种多样,需要一种统一的分类方法对废水的毒性大小进行划分,PERSOONE et al[26]提出了一种毒性单位分级评价法,它是在一系列标准生物急性毒性测试的基础上,结合测试结果的半数效应浓度(EC50)或者半数致死浓度(LC50)值,将其转化成毒性单元(toxic unit, TU),从而综合评价废水的毒性大小以及水质的安全性。TU值的计算方法为:如果样品对受试生物的毒性效应(抑制率或致死率)<50%时,则TU为毒性效应(抑制率或致死率)与50%的比值;如果样品对受试生物的毒性效应(抑制率或致死率)>50%时,则需先计算出其EC50或LC50,TU值的计算公式为:TU=[1/EC50或LC50]×100。如果同时应用多种生物进行毒性测试,则需先计算各个生物的TU值,综合后取平均值,再根据表2所划分的毒性等级,得出废水的毒性强弱,最后进行水质的安全评价。
-
20世纪90年代,美国环境保护局(U.S. Environmental Protection Agency,US EPA)提出了用于工业废水和生活污水中毒性物质鉴别与评价的一套完整方案——毒性鉴定评价(toxicity identification evaluation,TIE)方法。这种方法的核心是将生物测试与化学分析相结合,以生物作为毒性效应的检测器,通过生物测试检测毒性有无或大小,结合化学分析测定致毒污染物。总体来说,TIE包含3个阶段,第一阶段是毒性表征,主要是对废水进行各种物理化学处理,对比处理前后毒性的变化,推断致毒物质的大致类型;第二阶段是毒性鉴定,根据第一阶段的测试结果,针对某一类污染物做具体分析;第三阶段为毒性确认,经过前两阶段的测试,初步鉴别出废水中的主要毒性污染物,这一阶段的工作是对前两阶段的测试结果进行验证[27]。
欧盟还发展了另一种毒性鉴定评价方法——效果导向分析(effect-directed analysis, EDA),它是一套针对有机污染物的分析测试方法[28]。EDA综合运用生物测试和化学分析,以生物效应为导向,指导活性组分的分离,并对组分进行定性,实现效应物的鉴定,最终明确样品的生物效应和主要效应物。该方法克服了单一化学分析或单一生物测试在环境样品应用中的不足,不仅可测试样品的生物效应,并且能明确效应化合物,避免了化学分析中检测的盲目性和生物测试中效应物质的不确定性。EDA主要通过交替进行生物测试和化学分析筛查复杂环境样品中的效应化合物,其常规操作步骤为污染物提取、生物测试、色谱分离、效应化合物测定和效应确认[29-30]。
-
各个行业所产生的工业废水成分复杂,通常都具有很大的毒性,因此有必要确定有效的处理方法来降低工业废水的毒性[31]。采用先进技术升级污水处理厂是减少微污染物排放的一项关键战略。鉴于工业废水的复杂化学成分,去除毒性是评估污水处理厂性能的一个不可或缺的参数。JOHANNES et al[32]系统评估了臭氧和活性炭技术降低毒性的方法。各行业工业废水的毒性削减情况如下。
-
电镀废水中含有大量的重金属离子、氰化物和有机酸等有害物质,而且通常具有较大的毒性,为了防止它对环境甚至人体健康造成危害,有必要对其去除技术进行研究,寻求降低电镀废水毒性的方法。
电镀废水的传统处理方法有化学沉淀法、离子交换法、电解法、吸附法和膜分离法等。化学沉淀法主要是向废水中投加化学试剂,使水中的重金属离子生成沉淀物沉降下来而得以去除。离子交换法指利用离子交换树脂(或其他离子交换剂),将废水中的重金属离子置换出来,从而得以去除。电解法指废水在电场的作用下,溶液中的正负离子分别向阴阳两极迁移,使金属离子在阴极析出从而实现去除。吸附法主要是指用各种吸附剂将废水中的污染物质吸附去除。膜分离法是利用各种膜对不同物质选择透过性对废水中的污染物进行选择性去除,包括电渗析、反渗透、纳滤和超滤等[33-35]。
DURGO et al[36]利用废铁副产品硫酸亚铁和木飞灰来去除废水中的重金属,进行了细菌和人类细胞系的存活频率的测定和Ames试验,结果表明,处理后的出水仍存在一定的细胞毒性和轻微的诱变潜力,为了减少这种影响,在将粉煤灰用于中和/混凝/絮凝过程之前,必须对其进行预处理(部分去除高可溶性化合物)。BENVENUTI et al[37]在常规处理后,采用氧化工艺降解电镀废水中的有机添加剂,反应结束后,废水中总有机碳(total organic carbon, TOC)降低了38%;有机添加剂部分降解,降低了生物毒性。LI et al[38]制备和研究了一种新型磁性阳离子交换树脂(MCER)以高效去除电镀废水中的重金属离子,该树脂处理实际电镀废水时,目标污染物Ni2+、Cu2+的浓度急剧下降,满足电镀污染物排放标准要求,最终实现了电镀废水的无毒排放(TUa < 0.3)。KOBYA et al[39]在电混凝反应器中采用铁极板电极对碱性无氰、碱性氰化物和酸性锌电镀废水进行了处理研究,研究表明,铁电极对不同锌电镀废水中的锌离子和氰化物离子的去除效果显著。采用动态发光细菌法测定了废水的毒性水平,处理后的废水可达无毒排放。符丽纯等[40]开发了一种以树脂吸附为核心技术的“生物接触氧化+磁性树脂+螯合树脂”的深度处理技术对电镀废水进行处理,出水总Cu、总Ni的质量浓度﹤0.1 mg/L,出水COD<19.6 mg/L,基本达到《地表水环境质量标准:GB 3838—2002》地表Ⅲ类水质标准。选取发光菌对进出水进行了急性毒性测试,废水的TU值经过处理之后由最初的50降低为出水的1,毒性由高毒降为无毒。选取斑马鱼进行了慢性毒性测试,结果表明,经树脂处理过后的出水慢性毒性基本消除。KIM et al[41]开发了一种UV-LED/H2O2/Cu2+系统来去除金属电镀废水中典型的氰化物,利用这种方法,氰化物可以在30 min内被有效去除。使用发光菌作为受试生物进行急性毒性实验,最终,在处理1 h后,出水对发光菌的急性毒性降低了64.6%;在去除效率和毒性降低方面,UV-LED/H2O2/Cu2+系统可能是去除废水中氰化物的一种替代方法。
电镀废水中的主要污染物为重金属离子,其次为电镀过程中的各种添加剂,由此造成电镀废水具有很强的毒性。综上,采用生化法处理电镀废水可以显著降低电镀废水的毒性,说明生化系统具有“解毒”功效,电镀废水中的有毒物质在生化系统中进行降解转化,采用生物法联合其他工艺技术可以作为电镀废水深度处理技术方法。
-
合成有机染料的大规模生产和广泛应用使其渗透到水和土壤环境的不同空间,由此产生大量的印染废水。此类废水一般成分都非常复杂,色度高,碱性大,COD和TOC含量高,必须采用特定的技术进行处理才能使其达到排放标准。
印染废水的主要处理方法有物理法、化学法和生物法3大类,其中,物理法包括吸附法、膜分离法和磁分离法;化学法包括电化学法、超临界水氧化法、臭氧氧化法、Fenton氧化法和分子筛湿式催化氧化法;生物法包括厌氧法、好氧法和厌氧-好氧联合法[16, 42-45]。
根据FRIJTERS et al[46]的研究,荷兰的一家纺织厂所产生的印染废水采用顺序厌氧/好氧的方法得到了有效的处理,该处理方法可使印染废水的色度降低80%~95%。发光菌急性毒性结果表明,厌氧/好氧顺序处理后的出水对发光菌无毒性。周崟等[47]以Ti/RuO-IrO2为阳极、不锈钢板为阴极,采用电解法处理活性艳蓝印染废水,结果表明,在特定的电解条件下,电解15 min后印染废水的色度去除率可达100%,采用发光菌进行急性毒性实验结果表明,电解120 min后,与原水相比,出水发光菌的发光强度提高到60.88%,表明废水在该处理过程中毒性得到了有效削减。KALATHIL et al[48]设计了一种基于颗粒活性炭的单室微生物燃料电池对印染废水进行处理,经过48 h的处理后,与原水相比,出水COD降低了71%;毒性测试表明,与原始印染废水相比,处理过后的废水毒性得到了有效地降低。CHEN et al[49]采用间接电氧化法、电絮凝法和电Fenton法对某高矿化度、难生物降解有机物印染废水进行预处理对比研究,结果表明,采用电Fenton法对原色染料废水进行预处理,可去除大量难降解化合物,降低废水的毒性,提高废水的可生化性。生物方法也是去除印染废水的一种工业方法。HERNANDEZ et al [50]利用小球藻的活性和非活性生物质从水溶液中去除刚果红(CR)染料,通过生物吸附和生物降解过程,小球藻在5 mg/L和25 mg/L的浓度下可以对染料有83%和58%的去除率;对2种枝角纲动物(大型溞和模糊网纹溞)进行的48 h急性毒性实验表明,与原水相比,出水中染料的毒性显著降低。一色齿毛菌是分离自野外的一株能够降解木质素的白腐真菌,姚英等和于存[51]研究了一色齿毛菌对染料的脱色能力及脱色前后染料毒性的变化,结果表明,一色齿毛菌对刚果红的脱色效果最为明显,毒性也有一定程度的降低。LIANG et al[52]首次采用高锰酸盐和臭氧(KMnO4-O3)联合技术处理不同种类的纺织印染废水,结果表明,该方法能有效的处理印染废水,处理后废水的COD和TOC分别降低了80%和70%,生物降解率提高了0.33~0.68;选取发光菌作为受试生物对处理前后的废水进行了毒性评价,出水与原水相比,毒性降低了34.4%~95.5%,基本可以实现废水的无毒排放。
印染废水的主要制毒物质为各类染料,色度高,处理难度大,造成印染废水具有较大的毒性,总结可得,高级氧化法包括电化学氧化法、电Fenton法等对印染废水的毒性有较为明显的削减作用。
-
煤化工废水中通常含有氨、氮和硫等各项难降解的有机物,为了防止它们直接排放到环境中造成危害,必须采用有效的方法对煤化工废水进行处理。国内外学者提出了各种煤化工废水的处理方法:活性污泥工艺、A/O工艺、SBR工艺、生物膜法、物理吸附工艺、高级氧化工艺和膜分离技术[14, 53-54]。
ZHANG et al[55]采用溶胶浸渍两步法制备了负载型钙钛矿催化剂LaCoO3/X,研究了该催化剂在UV-催化湿式过氧化氢氧化(UV-CWPO)系统中净化煤化工废水浓液的可行性。研究结果表明,反应60 min后,COD、TOC和UV254的去除率分别为89.7%、84.6%和98.1%。在最佳操作条件下,氧化出水由高毒转为无毒,BOD5/COD 从0.02提高到0.412,氧化出水的可生化性大大提高。XU et al[56]将阴极电Fenton技术与阳极光催化技术相结合,构建了一种新型的Fe@Fe2O3/CF阴极双室光电化学氧化系统,用于煤化工废水的深度处理。研究结果表明,废水经上述处理后相应的COD、BOD5、TOC和总酚的出水浓度分别为31.5、3.9、8.4和13.8 mg/L,满足严格的污水排放标准,随后又采用大型溞固定化实验测定了废水的急性毒性。反应120 min后,出水急性毒性明显下降,从67%下降到18%。陆曦等[57]针对煤化工废水中多元酚难以处理的问题,采用O3耦合H2O2的方法处理煤化工废水。实验结果表明,在特定的实验条件下,对苯二酚的去除率可达100%,TOC 去除率为39%。利用发光细菌的相对发光强度对废水处理前后的急性毒性进行研究,反应60 min后,发光菌的相对发光强度提高到48%,废水的生物毒性大幅减弱。
煤化工废水中的酚类物质是造成煤化工废水高毒性的主要原因,采用高级氧化法如电Fenton法、O3耦合H2O2法可以提高废水的可生化性,显著降低煤化工废水的毒性。
-
近年来,石化工业发展迅速,伴随而来的问题是产生了大量的石化废水。石化废水主要含有苯类化合物、有机物、高盐废水和油污等,它们具有较强的破坏性和高度污染性[58]。石化废水的处理方法包括吸附法、膜分离法、电催化氧化法、曝气生物滤池法、芬顿/光芬顿法、湿空气氧化法和催化湿空气氧化法、生物处理技术等[59]。
GONG et al[60]采用电凝(EC)和Fered-Fenton(FF)法处理石化废水,该研究阐明了FF和EC处理过程中的减毒机理和污染物去除特性,为石化生产废水处理设施的减毒和运行提供了有价值的指导,结果表明,FF在降低毒性方面表现出更高的性能,处理30 min后,其发光抑制比EC低10.3%。该项研究表明,石化废水中的反渗透浓缩物中有机污染物和重金属的去除直接影响毒性降低,同时提示小分子有机污染物去除量的增加对毒性降低具有至关重要的影响。张瑛等[61]利用明亮发光杆菌、斜生栅藻和大型溞对石化废水进行毒性测试,分析急性毒性和水质指标之间的相关性,并利用TIE方法对石化废水进行关键致毒物质分析,结果表明石化废水中的主要致毒物质是非极性有机物和可滤型物质,为石化废水的毒性评价提供的一定的研究基础。
-
制药废水是新型污染废水,人类如果长期接触废水中的各种药物会严重危害人类健康。制药废水成分复杂,排放量很大,有机物含量高,可生化性差,生物毒性较大,属于较难处理的一类废水[62]。
制药废水的处理方法包括物理法、化学法、生物法和非常规处理技术。其中物理法包括吸附法、膜分离技术和气浮法等;化学法包括混凝法、臭氧氧化法、Fenton法、电化学氧化法、光催化氧化法和超声波氧化法等;生物法包括好氧厌氧技术、微生物燃料电池法和MBBR法等。这些处理技术均有各自的特点[63]。
高级氧化工艺在处理四环素 (TC) 和土霉素 (OTC) 方面引起了广泛关注,CHEE et al[64]采用光芬顿高级氧化技术,观察到在光芬顿过程开始时,四环素转化为对费氏弧菌毒性更大的转化产物,然后进一步氧化为无毒转化产物,所有的四环素转化产物对费氏弧菌的毒性均低于四环素,显著降低了四环素制药废水的毒性。由此可见,高级氧化法能够显著降低制药废水的毒性。
-
农药废水中含有大量的有毒物质,常具有高毒性、高盐分、高氨氮和高COD等特点,若得不到有效处理,排放到环境中的有毒物质有很大可能通过食物链进入人体,因此必须要对农药废水进行有效的处理。
当前农药废水的处理方法包括物理法、化学法和生物法。其中,物理法包括萃取法、吸附法和膜分离法;化学法包括湿式氧化、Fenton试剂氧化、臭氧氧化法、焚烧法、微电解法、电化学氧化法和光催化氧化法;生物法包括活性污泥法、生物膜法和厌氧生物处理法。近年来,一些新技术方法也被用于农药废水的处理中,如磁分离技术、超声波处理技术和超临界水氧化技术等[18-19, 65-67]。
毒死蜱是一种广泛应用于农业的有机磷农药。FEMIA et al [68]采用UV/H2O2降解农药废水中的毒死蜱,实验结果显示,该处理方法能有效去除废水中的毒死蜱,经过4 h的降解后,TOC的去除率可达70%。选取发光菌作为受试生物评价了处理前后废水的急性毒性,反应60 min后,废水对发光菌的抑制率由80%降低到了10%,废水的急性毒性得到了有效的削减。熊正龙等[69]采用超声/臭氧(US/O3)工艺处理农药废水,对农药废水的可生化性和生物毒性进行了研究。实验结果表明,US/O3工艺能显著改善农药废水可生化性和生物毒性,BOD5/COD 由0.03 提高至0.55。生物毒性采用发光细菌法测定,以EC50表示,农药废水经过处理,EC50从11%增至52%,生物毒性降低78.85%。
由于农药对特定生物(害虫、细菌等)有生长抑制和致死效应,农药废水相较于其他行业的工业废水来说含有更多的有毒物质,因此也会产生更高的生物毒性。有研究表明,臭氧氧化对农药废水有较好的处理效果,在较短时间内可使吡虫啉农药废水的去除率达到90%以上,虽然臭氧氧化能很好地去除废水中的吡虫啉,但是仍然存在出水矿化率低的问题。此外臭氧处理过程中可能会产生比其母体污染物毒性更高的有害中间产物,从而造成出水毒性升高。针对臭氧处理后毒性升高的问题,有研究表明,生物滤池能够显著降低由于臭氧氧化带来的急性毒性、发育毒性、内分泌干扰毒性和基因毒性。这可能是因为臭氧氧化产生的中间产物和小分子产物为生物滤池中的微生物提供了碳源,有利于生物滤池对其进行进一步的矿化。
-
化工废水排放量大,成分复杂,类型多样,主要集中在煤化工、造纸、纺织、印染、电镀、农药、食品加工和冶金等行业。化工废水一般生物毒性较大,需要经过特定的方法进行处理才能实现无毒排放。由于化工废水成分复杂多样,有些废水排放时虽然已经达到了常规理化指标的标准,但实际上依然存在一些有毒有害物质从而使废水具有一定的生物毒性,因此需要结合综合生物毒性测试来评价水质的安全性。为了对工业废水和生活污水中毒性物质进行鉴别与评价,美国环境保护局和欧盟分别提出了TIE和EDA模式。在处理工艺研发方面,目前已开发多种处理方法可以对化工废水的毒性进行有效削减。结果显示,高级氧化、臭氧联合生物滤池等处理方法能有效去除废水中的特征污染物,降低废水的毒性,使废水达到无毒排放。在环境监管方面,关于城市污水处理厂污染物排放标准,国家标准征求意见稿和部分地方标准都增加了急性毒性指标,包括鱼胚、水、藻类和发光细菌等。此外,有国内外学者采用基于好氧污泥呼吸速率(oxygen uptake rate, OUR)的化工废水水质评价方法对化工废水接管标准提出了建议,丰富了污染物排放标准中的毒性指标,为化工行业废水的毒性评价及差异化接管标准提供了依据,对化工废水的毒性削减有一定的借鉴意义,有望助力实现化工废水的无毒排放。总体而言,未来关于化工废水毒性评价及削减,一定会从突破处理技术和加强环境监管两方面齐头并进,有效实现化工废水的无毒排放。
化工废水毒性评价方法及毒性削减研究进展
Research progress of toxicity evaluation methods and toxicity reduction of chemical wastewater
-
摘要: 化工废水排放量大,成分复杂,包含多种有毒有害物质,如果不经过适当的处理将会对自然环境乃至人们的身体健康造成一定的危害。生物毒性测试可以在化学分析的基础上更加全面系统地评价水质的安全性,文章综述了不同化工行业废水的毒性削减情况,为化工废水的毒性减排提供借鉴。Abstract: Chemical wastewater has the features of large emissions, complex composition, and it contains a variety of toxic and harmful substances. It will cause certain harm to the natural environment and even people's health without the effective treatment. Biological toxicity testing can evaluate the safety of water quality more comprehensively and systematically base on the chemical analysis. This article summarized the toxicity reduction of wastewater in different chemical industries, and provided a reference for the reduction of toxicity of the chemical wastewater.
-
Key words:
- chemical wastewater /
- toxicity evaluation /
- biological toxicity test /
- toxicity reduction
-

-
表 1 急性毒性评价方法
测试项目 受试生物 测试指标 需要仪器/设备 藻类生长
抑制毒性斜生珊藻、羊角月牙藻、舟形
藻、水华鱼腥藻、集球藻72 h EC50
细胞计数
光密度
叶绿素照度计
光照培养箱
机械振荡器
检测细胞设备
(电子颗粒计数计,分光光度计)发光细菌
急性毒性发光细菌 IC50 Microtox M500 溞类急性毒性 大型溞 24 h EC50 溶解氧测定仪
硬度计
pH计
TOC;
COD鱼类急性毒性 稀有鮈鲫、斑马鱼、剑尾鱼 96 h LC50 溶解氧测定仪
硬度计
pH计
分析天平表 2 毒性单位分级标准
分级 TU值 毒性 Ⅰ TU<0.4 无毒 Ⅱ 0.4≤TU<1 微毒 Ⅲ 1≤TU<10 中毒 Ⅳ 10≤TU<100 高毒 Ⅴ TU≥100 剧毒 -
[1] NASR F A, DOMA H S, ABDEL Halim HS, et al. Chemical industry wastewater treatment[J]. The Environmentalist, 2007, 27(2): 275 − 286. doi: 10.1007/s10669-007-9004-0 [2] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2007[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2007. [3] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2008[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2008. [4] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2009[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2009. [5] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2010[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2010. [6] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2011[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2011. [7] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2012[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2012. [8] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2013[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2013. [9] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2014[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2014. [10] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2015[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2015. [11] 国家统计局、环境保护部. 中国环境统计年鉴—2016[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2016. [12] 雷平, 施祖麟. 企业数量、规模与经济增长——基于省级工业面板数据的研究[J]. 经济经纬, 2008(2): 101 − 104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1096.2008.02.028 [13] 张统, 李志颖, 董春宏, 等. 我国工业废水处理现状及污染防治对策[J]. 给水排水, 2020, 56(10): 1 − 3. [14] 郑彭生. 煤化工废水厌氧生物处理技术研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(6): 24 − 27. [15] 成琳. 造纸废水处理技术的研究进展[J]. 化学工程师, 2021, 35(5): 60 − 62. [16] 张彦. 纺织印染废水处理的自动化策略与系统设计[J]. 工业水处理, 2021, 41(3): 133 − 136. [17] 姜玉娟, 陈志强. 电镀废水处理技术的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2015, 40(3): 45 − 48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2015.03.011 [18] 周涛. 农药废水处理方法与工艺研究进展[J]. 绿色科技, 2020(24): 60 − 62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2020.24.019 [19] 赵经纬. 农药废水的资源化处理及减排技术展望[J]. 世界农药, 2010, 32(S1): 38 − 43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6485.2010.z1.010 [20] 翁新春, 方薇, 陈祎斐. 食品工业废水处理工艺及节能探究[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2015(2): 63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2015.02.055 [21] 王思巧. 食品工业废水处理技术概述[J]. 科技经济导刊, 2016(9): 141 − 142. [22] 蔡荣华, 高春娟, 张家凯, 等. 冶金废水资源及其利用[J]. 盐业与化工, 2013, 42(6): 1 − 3. [23] 江敏顾, 李咏梅. 废水综合毒性研究方法综述[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2007, 30(增1): 193 − 197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2007.增1.077 [24] 梁慧, 袁鹏, 宋永会, 等. 工业废水毒性评估方法与应用研究进展[J]. 中国环境监测, 2013, 29(6): 85 − 91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2013.06.017 [25] 赵风云, 孙根行. 工业废水生物毒性的研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2010, 30(4): 22 − 25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2010.04.006 [26] PERSOONE G, MARSALEK B, BLINOVA I, et al. A practical and user-friendly toxicity classification system with microbiotests for natural waters and wastewaters[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 2003, 18(6): 395 − 402. doi: 10.1002/tox.10141 [27] 赵建亮, 方怡向, 应光国. 工业废水毒性鉴定评价方法体系的建议及其应用示例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(3): 549 − 559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.03.028 [28] 陈玲, 翁景霞, 刘苏, 等. 工业废水毒性评估与致毒物质鉴别技术进展[J]. 环境监控与预警, 2018, 10(3): 1 − 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2018.03.001 [29] LI H, ZHANG J, YOU J. Diagnosis of complex mixture toxicity in sediments: Application of toxicity identification evaluation (TIE) and effect-directed analysis (EDA)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 944 − 954. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.005 [30] 高巍. 化工废水处理工艺技术的研究及应用进展[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2021(1): 85 − 86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2021.01.048 [31] 易小意. 毒性鉴别评价和效应导向分析的联用: 广州河涌沉积物中致毒物的筛查[D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所), 2017. [32] JOHANNES V, MICHAEL S, ULF M, et al. Systematic review of toxicity removal by advanced wastewater treatment technologies via ozonation and activated carbon[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53: 13,7215 − 7233. [33] 熊道毅, 王硕煜, 丁贵军, 等. 膜分离技术在电镀废水处理中的应用进展[J]. 科技展望, 2016, 26(20): 75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8289.2016.20.068 [34] 张厚, 施力匀, 杨春, 等. 电镀废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2018, 40(2): 36 − 41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3849.2018.02.009 [35] 巨润科. 电镀废水处理技术的研究进展[J]. 当代化工研究, 2016(3): 27 − 28. [36] DURGO K, ORESCANIN V, HORVAT T, et al. Cytotoxicity and mutagenicity study of waste and purified water samples from electroplating industries prepared by use of ferrous sulfate and wood fly ash[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A. 2005, 40(5): 949-957. [37] BENVENUTI T, RODRIGURS M, ARENZON A, et al. Toxicity effects of nickel electroplating effluents treated by photoelectrooxidation in the industries of the Sinos River Basin[J]. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 2015, 75: 17 − 24. [38] LI Q, FU L, WANG Z, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel magnetic cation exchange resin and its application for efficient removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 165: 801 − 810. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.150 [39] KOBYA M, DEMIRBAS E, OZYONAR F, et al. Treatments of alkaline non-cyanide, alkaline cyanide and acidic zinc electroplating wastewaters by electrocoagulation[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2017, 105: 373 − 385. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2016.11.020 [40] 符丽纯, 戴建军, 陈利芳, 等. 基于树脂吸附的电镀废水深度处理工程实例[J]. 水处理技术, 2018, 44(1): 128 − 131. [41] KIM T K, KIM T, JO A, et al. Degradation mechanism of cyanide in water using a UV-LED/H2O2/Cu2+ system[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 208: 441 − 449. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.198 [42] 刘俊逸, 黄青, 李杰, 等. 印染工业废水处理技术的研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(3): 1 − 6. [43] 任钢锋. 我国工业印染废水处理状况研究[J]. 节能与环保, 2021(4): 76 − 78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-539X.2021.04.028 [44] 丁振中, 张超, 朱萌. 活性染料印染废水处理工艺研究[J]. 皮革制作与环保科技, 2021, 2(6): 161 − 162. [45] TKACZYK A, MITROWSKA K, POSYNIAK A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 717: 137222. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137222 [46] FRIJTERS C, VOS R H, SCHEFFER G, et al. Decolorizing and detoxifying textile wastewater, containing both soluble and insoluble dyes, in a full scale combined anaerobic/aerobic system[J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(6): 1249 − 1257. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.01.013 [47] 周崟, 李平, 吴锦华, 等. 活性艳蓝KN-R染料废水的电解氧化及其毒性削减[J]. 化工环保, 2009, 29(1): 10 − 13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2009.01.003 [48] KALATHIL S, LEE J, CHO M H. Efficient decolorization of real dye wastewater and bioelectricity generation using a novel single chamber biocathode-microbial fuel cell[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 119: 22 − 27. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.059 [49] CHEN Z, HUANG X, SUN X, et al. Comparative study of the degradation of real dyestuff effluents by three kinds of electrolysis methods[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012, 253–255: 943–948. [50] HERNANDEZ M, CRISTIANI E, MARTINEZ F, et al. Bioremoval of the azo dye Congo red by the microalga Chlorella vulgaris[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(14): 10811 − 10823. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4277-1 [51] 姚英, 于存. 一色齿毛菌对刚果红的脱色优化及其毒性变化研究[J]. 菌物学报, 2019, 38(2): 272 − 280. [52] LIANG J, NING X A, SUN J, et al. An integrated permanganate and ozone process for the treatment of textile dyeing wastewater: Efficiency and mechanism[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 204: 12 − 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.112 [53] 张颖. 煤化工废水处理关键问题解析及技术发展趋势[J]. 石河子科技, 2021(3): 18 − 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0899.2021.03.010 [54] 费凡, 张培培. 煤化工废水处理技术进展及发展方向[J]. 化工管理, 2019(4): 35 − 36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4800.2019.04.019 [55] ZHANG W, LIU Z, CHEN P, et al. Preparation of supported perovskite catalyst to purify membrane concentrate of coal chemical wastewater in UV-catalytic wet hydrogen peroxide oxidation system[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(9): 4906. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094906 [56] XU P, XU H, ZHENG D, et al. The efficiency and mechanism in a novel electro—Fenton process assisted by anodic photocatalysis on advanced treatment of coal gasification wastewater[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 968 − 974. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.171 [57] 陆曦, 牟伟腾, 刘宁, 等. 臭氧耦合过氧化氢去除煤化工废水中对苯二酚研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(6): 225 − 230. [58] XIANG W. The research on the current situation and advances of petrochemical wastewater treatment[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 1914: 550–553. [59] 何娟. 石油化工废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 节能与环保, 2021(7): 54 − 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-539X.2021.07.020 [60] GONG C, REN X, HAN J, et al. Toxicity reduction of reverse osmosis concentrates from petrochemical wastewater by electrocoagulation and Fered-Fenton treatments[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 286: 131582. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131582 [61] 张瑛, 曹迪, 胡丽萍, 等. 某石化废水的综合毒性评价及其处理工艺对毒性的削减规律研究[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(5): 109 − 118. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170212001 [62] CHEN W, HE Z, HUANG G, et al. Direct Z-scheme 2D/2D MnIn2S4/g-C3N4 architectures with highly efficient photocatalytic activities towards treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater and hydrogen evolution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359: 244 − 253. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.141 [63] 吴巍, 刘玲, 赖晓晨. 弗罗里硅土处理低质量浓度氨氮废水研究[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 17 − 21. [64] CHEE H, HEE D, SONG B. Oxidation of tetracycline and oxytetracycline for the photo-Fenton process: Their transformation products and toxicity assessment[J]. Water Research, 2020, 172: 115514. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115514 [65] 姜城焰, 刘睿, 刘立恒. 农药废水处理研究进展[J]. 轻工科技, 2021, 37(1): 88 − 91. [66] TRELLU C, OLVERA VARGAS H, MOUSSET E, et al. Electrochemical technologies for the treatment of pesticides[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 26: 100677. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2020.100677 [67] JIANG J. Research on catalytic oxidation pretreatment of organic pesticide wastewater with high concentration[J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2016, 62: 05004. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/20166205004 [68] FEMIA J, MARIANI M, ZALAZAR C, et al. Photodegradation of chlorpyrifos in water by UV/H2O2 treatment: toxicity evaluation[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2013, 68(10): 2279 − 2286. doi: 10.2166/wst.2013.493 [69] 熊正龙, 刘爱翠, 刘国伟, 等. US/O3工艺改善农药废水可生化性和生物毒性的效能[J]. 工业水处理, 2014, 34(3): 65 − 67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2014.03.018 -



 下载:
下载:

