-
在联合国2015年提出了17个可持续发展目标的国际背景下,各国纷纷开始在循环经济、零废弃建设上展开积极探索。2018年23个C40城市签署《向零废物迈进的宣言》,2019年3月15日第四届联合国环境大会将固体废物列为重要议题。2021年欧盟委员会与欧洲多个城市签署为期2年 (2021—2023) 的《欧州绿色城市协议》,为城市管理部门分享最佳实践案例和制定指导方针。2022年12月14日,第77届联合国大会通过决议,宣布3月30日为“国际零废物日”。“无废”理念已成为国际共识,建立“无废城市”成为越来越多国家和城市的规划目标[1-8]。我国“无废城市”的概念是国际“无废”理念和实践的继承和发展。推进“无废城市”建设,不仅是推动固体废物污染环境防治的有力手段,也是推动减污降碳[9]的重要举措,有效缓解资源环境压力,发挥减污降碳协同效应,推动绿色低碳循环发展。2021年12月,生态环境部会同17个部门和单位联合印发《“十四五”时期“无废城市”建设工作方案》[10],明确“十四五”时期,国家将协同推进“无废城市”建设与深入打好污染防治攻坚战、碳达峰碳中和等国家重大战略,2022年4月,生态环境部发布了“十四五”时期“无废城市”建设名单[11],确定推进“113+8”个地级以上城市和地区开展“无废城市”建设。浙江省高度重视“无废城市”建设工作,将其作为实现经济社会高质量发展和碳达峰、碳中和目标重要抓手和高质量发展建设共同富裕示范区的重要内容。2020年初,省政府办公厅印发实施《浙江省全域“无废城市”建设工作方案》,在全国率先推进全省域“无废城市”建设。以浙江省数字化改革和全国首个“无废城市”数字化改革试点省为契机,自2021年下半年起,浙江省综合考虑覆盖“无废城市”建设涉及的各类固体废物,源头减量、综合利用、无害化处置全过程管理需求,以空气质量指数、水质指数建设方法为方法学框架,定量、直观反映和评价“无废城市”建设程度,筛选设计“无废城市”建设和固体废物污染防治的核心指标作为分指数,通过对分指数去量纲、等标化处理,将各项分指数值转化为百分制无量纲数据,用于开展不同维度的评价分析[12]。目前浙江省已发布多期“无废指数”,然而,“无废指数”建立发布之后该如何应用,如何将指数结果反馈给相关部门,管理部门如何通过“无废指数”结果反馈,及时识别短板,动态调整固废管理重点,优化“无废城市”建设任务是当前“无废指数”研究的空白。当前缺乏“无废指数”反馈机制,导致城市管理者无法在此基础上快速识别“无废城市”建设成效的优势和短板。因此,急需建立“无废指数”的反馈机制,提高“无废指数”对管理部门的决策指导作用和时效性,这将直接决定了“无废指数”能否为识别目标、发现短板、规划路径、动态优化、考核评估等提供指导和支撑。
针对上述问题,本研究聚焦“无废指数”与工业、农业、生活领域重点类别固体废物源头减量、资源化利用、贮存处置等关键环节对应的目标任务的关联关系,根据指数结果准确识别“无废城市”建设过程中各重点领域的比较优势和差距,构建“无废指数”反馈机制,直观地反映需综合施力的目标、任务,以及具备比较优势和示范效应的任务措施,通过多维度比较分析和研判,使地方管理部门及时优化“无废城市”整体推进策略,为政府相关部门提供决策指引。本研究具有3个创新点。1) 通过建立反馈机制可实现省级层面面数据调查、进展评估、结果反馈相互贯通,进一步强化省级各相关部门的固体废物管理目标衔接、责任分解和考核落实。2) 反馈机制可作为城市层面“无废城市”建设决策的支撑指引,准确识别城市的工业、农业、生活领域重点类别固体废物源头减量、资源化利用、贮存处置等关键环节的优势和短板,及时调整“无废城市”建设目标、任务措施。3) “无废指数”反馈机制创新了固体废物污染防治管理工作机制。“无废指数”基于时效数据结合指标拆解,实现了在工作考核之前的数据动态更新和及时反馈,可提升基层管理策略调整的精准性、时效性,确保年度等目标的实现。本研究进一步深化了“无废指数”的应用功能,可作为城市间整体情况、专项领域间发展趋势、相对优势和差距比较分析的参考,推动形成比学赶超工作局面。
-
1) 反馈机制要将指数拆解到可采集、可分解的统计调查数据,基于“无废城市”建设任务要求,分析城市在各重点领域和关键环节的进展情况,实现数据调查、进展评估、结果反馈相互贯通,进一步强化各相关部门的固体废物管理目标衔接、责任分解和考核落实。
2) 反馈机制要准确识别“无废城市”建设过程中各关键环节的比较优势和差距,进行多维度比较分析和研判,与其他城市横向对比,了解城市在全省的水平状态;与自身发展趋势纵向对比,了解城市进退步情况;各部门之间对比,了解管理部门整体推进进度差距。
3) 反馈机制要将“无废指数”与各领域各环节各类别固废目标任务进行有效关联,对照固体废物源头减量、资源化利用、贮存处置等关键环节工业、农业、生活领域重点类别的目标和任务进行分析,直观地反映需综合施力的目标、任务,以及具备比较优势和示范效应的任务措施,便于地方管理部门及时优化“无废城市”整体推进策略,为政府相关部门提供决策指引。
-
1) 城市无废办内部。市级无废办应组织召开“无废指数”专题会议,分管局领导参会研究部署,针对性地定位优势和短板、识别主体责任,研究改进方案,着力补短板、强弱项。
2) 城市无废办和相关部门。一是每期“无废指数”发布后,市级无废办针对排名靠后的分指标,通知或函告相关责任部门相应分指数情况和督促提升建议,要求责任部门提供书面反馈说明和下一步提升计划。二是在市级无废工作专班季度例会和年度工作推进会上,向全体专班成员单位通报指数情况和测算结果,督促相关责任部门自查提升。
3) 城市与省级交流反馈。市级无废办应不定期地将辖区内各类主体遇到的疑问、困难和建议等收集整理,通过电话或书面反馈给省无废办。省级无废办根据工作要求和实际情况,对相关建议进行研究采纳。
-
1) 形成目标引领和推动责任落实。“无废指数”测算结果可作为省级层面对各城市“无废城市”建设、固体废物治理成效和治理体系建设的目标设定、部门任务分解、成效评估考核等的参考依据,可作为落实《固废法》目标责任和考核评价制度、设区市固体废物污染防治信息发布的具体抓手。通过各项分指数的展示推动了省级层面各厅局数据质量的提高,为省级层面动态评估优化“无废城市”建设和固体废物治理管理决策提供及时反馈。
2) 开展多维度比较分析。“无废指数”及其分指数情况,可形成各城市“无废城市”画像,“无废指数”可作为区域间整体情况、专项领域间发展趋势、相对优势和差距比较分析的参考。识别影响各城市建设成效的优势和短板,督促指导各城市下一阶段重点工作任务,及时优化调整“无废城市”建设目标和工作任务。依托各地区分指数,展示不同地区“无废城市”建设成效,提高政府的认识程度和重视程度,推动形成比学赶超工作局面。
3) 提高公众感知。“无废指数”可作为省级层面宣传普及无废理念重要帮手。各项分指数与各层级工业生产、农业生产、城市生活等方面“无废城市”建设工作内容和对应的量化指标直接关联,可让工业企业、农业生产主体、城乡居民及相关管理部门直接感知其活动对“无废城市”建设成效的影响和成效。
-
1) 专项领域查漏补缺。“无废指数”测算结果可用于各城市科学制定“无废城市”建设目标任务,规划区域固体废物设施能力建设,对各管理部门设定针对性目标任务、考核要求。各分指数反映了各领域“无废城市”建设进展和成效情况,便于相关部门及时调整工作重点和管理策略。开展专项领域比较分析,精准识别影响城市“无废指数”核算结果的优势、短板及问题原因,在治理成效短板上及时调度和强化相关领域任务及相关指标统计制度建设情况,提出更有针对性的改进措施。通过城市在省内的整体排名和其他同类城市的对比情况,研究分析提升“无废指数”及其各项分指数水平的措施、任务和制度建设等,为地方“无废城市”建设相关管理决策和制定目标提供支撑。
2) 推动部分领域数据信息建设统计制度建设。“无废指数”指标拆解后可形成城市层面固体废物种类、产生、收运、利用、处置等情况的完整闭环信息,相关数据信息覆盖了《固废法》中关于设区市政府、各部门、企业固体废物信息发布的各项要求和统计指标,推动了各个口径上固体废物信息建设数据质量的提升。推动各城市完善相关数据的统计调查范围,倒逼各城市落实固体废物信息发布、相关部门和主体责任,促进了各个领域固体废物管理制度的完善、信息数据质量提升,提高自身固废管理数据的准确性和全面性,可有效支撑相关主体依法公开和发布固体废物信息。
3) 推动部门理清责任。“无废指数”可推动各部门工作任务衔接更清晰,实现对专项领域、重点任务、相关责任部门工作推进成效的快速分析评估和动态调整。推动各部门工作任务的优化调整,例如哪项最差,差距有多少,理清“无废指数”和“无废城市”建设任务的对应关系,分指数对应“无废城市”建设指标,建设指标对应的重点任务,与分指数相关的直接建设指标及任务有哪些、间接建设指标及任务有哪些。
-
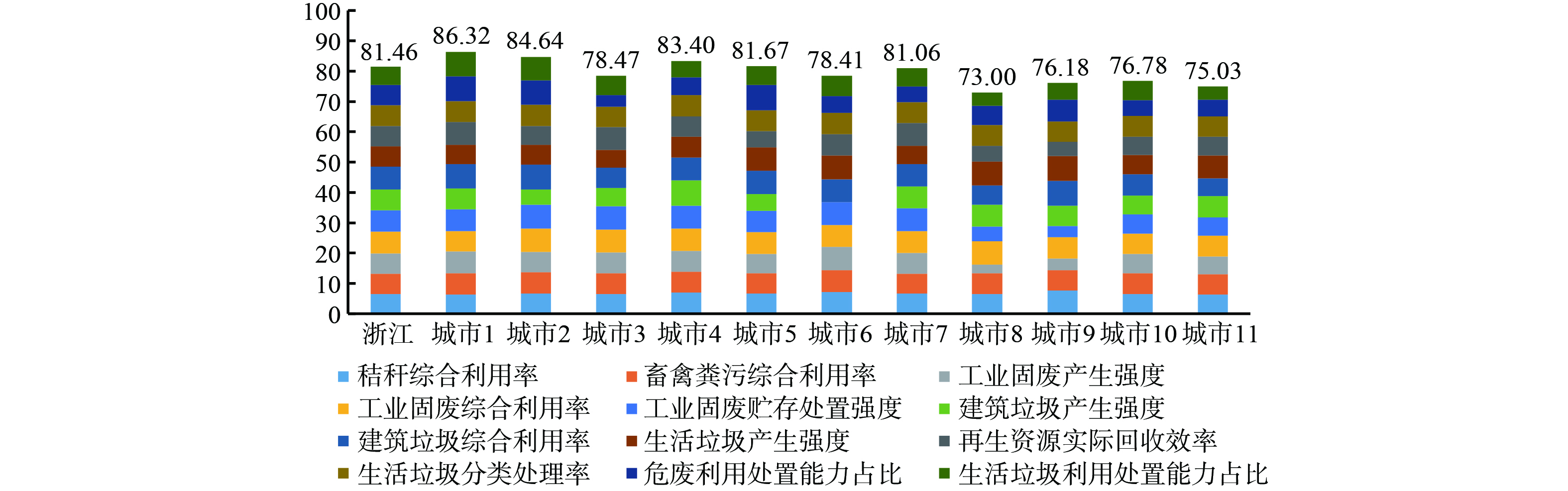
根据某年浙江省“无废指数”发布结果作图 (图1) 。浙江省各城市“无废指数”得分均在60分以上,处于良好水平。
-
浙江省“无废指数”为81.46分、较上期发布指数提高1.71分。11个市的指数依次为:城市1 (86.32) 、城市2 (84.64) 、城市3 (78.47) 、城市4 (83.40) 、城市5 (81.67) 、城市6 (78.41) 、城市7 (81.06) 、城市8 (73.00) 、城市9 (76.18) 、城市10 (76.78) 、城市11 (75.03) 。通过分析“无废指数”分指数 (图2) ,可以了解到各城市“无废指数”存在的短板:城市3的生活垃圾产生强度、危废填埋占比,城市5、7的畜禽粪污综合利用率,城市6的畜禽粪污综合利用率、生活垃圾分类处理率,城市8的工业固废产生强度,城市9的工业固废贮存处置强度和再生资源实际回收效率,城市11的秸秆综合利用率、建筑垃圾综合利用率、固废处置能力占比等,是各城市“无废城市”建设下阶段的重点工作任务。
-
以城市7为例分析“无废指数”测算结果及反馈建议。
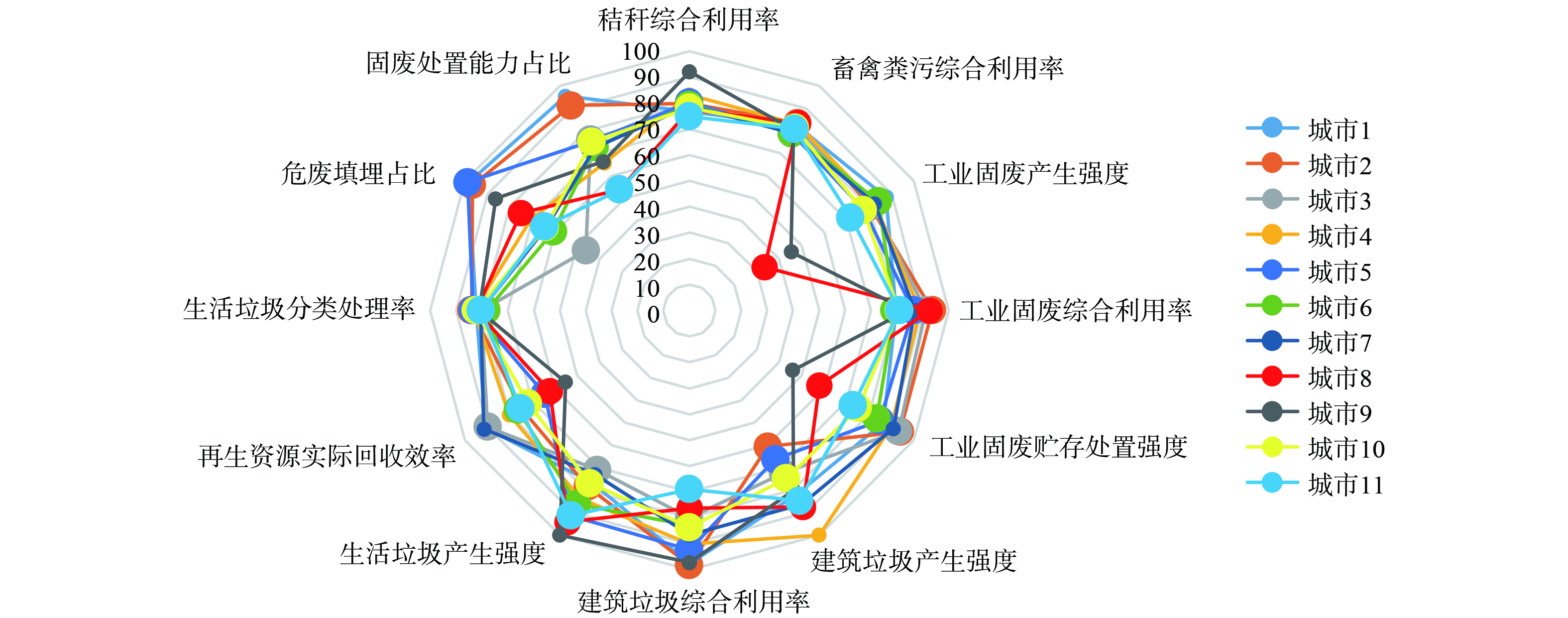
1) 指数整体表现。城市7“无废指数”81.06分,总排名第5位,接近全省平均分,处于中等水平。为分析城市7“无废指数”的优势项和短板项,选取城市7在全省排名中位列前三和后三的分指数为优势项和短板项。另外,低于全省平均的分指数也需重点注意。
城市7的优势。12项三级指标中,城市7有4项排入全省前三,分别是工业固废产生强度 (第3) 、工业固体废物贮存处置强度 (第3) 、建筑垃圾产生强度 (第3) 、再生资源实际回收效率 (第1) 。
城市7的短板。12项三级指标中,城市7有3项在全省后三位:分别是畜禽粪污综合利用率 (并列倒数第1) 、生活垃圾产生强度 (第10) 、危废填埋占比 (第9) 。此外,建筑垃圾综合利用率、生活垃圾分类处理率、固废处置能力占比也低于全省平均水平。
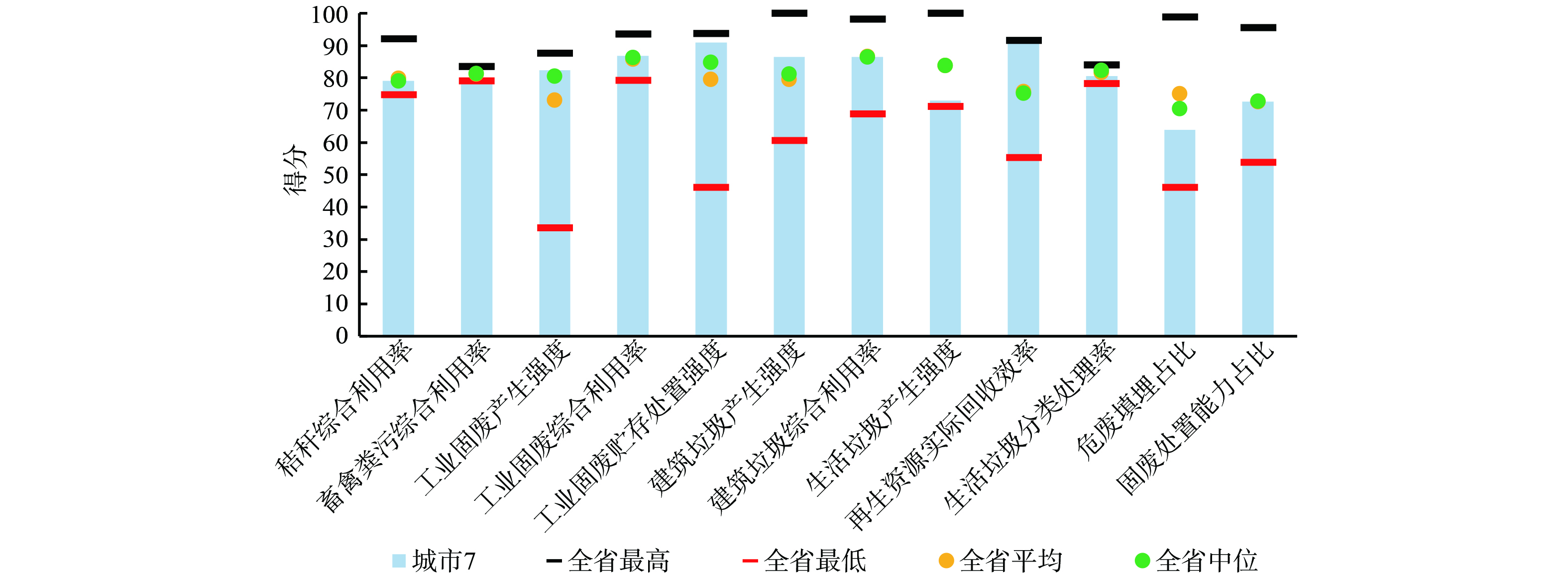
2) 全省排名情况。为了解城市7各项指数在全省的水平状态,根据数据分析各项分指数得分情况。城市7“无废指数”81.06分,总排名第五位,接近全省平均分,处于中等水平。 (见图3)
处于全省优秀水平:工业固废贮存处置强度、再生资源实际回收效率为全省最高分。处于全省中等水平:秸秆综合利用率、工业固废产生强度、工业固废综合利用率、建筑垃圾产生强度、建筑垃圾综合利用率、固废处置能力占比接近全省平均分。处于全省中等偏下水平:危废填埋占比、生活垃圾分类处理率低于全省平均和全省中位。处于全省最低水平:畜禽粪污综合利用率、生活垃圾产生强度接近全省最低分。
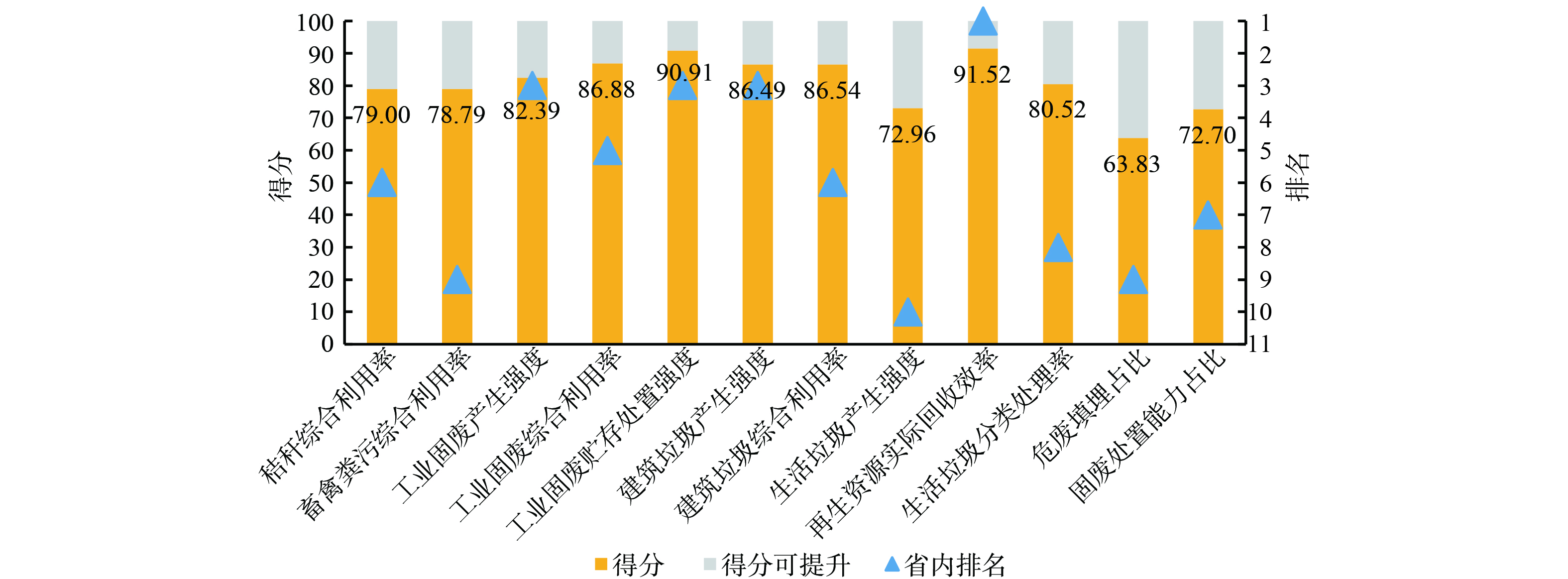
3) 分指数表现情况。为了解城市7各项分指数的表现情况,将城市7各项分指数得分及排名做对比分析。 (见图4) 80分以上表现优秀:再生资源实际回收效率得分及排名均为最高,工业固废产生强度、工业固废贮存处置强度得分及排名也较高,工业固废综合利用率、建筑垃圾产生强度、建筑垃圾综合利用率得分高排名不高;80分以下表现一般:生活垃圾分类处理率排名低,秸秆综合利用率、畜禽粪污综合利用率、固废处置能力占比得分排名均不高,危废填埋占比、生活垃圾产生强度分别为得分和排名最低。
4) 短板分析。针对排名全省后三位的分指数作为短板项,重点分析各短板项在全省处于的水平状态以及提升空间,通过“无废指数”分指数对标相关的“无废城市”建设指标的基数、目标值设置是否合理,对应的“无废城市”建设任务是否充足,并分析可能原因以及可以采取的措施。4点短板分析如下。
短板1 畜禽粪污综合利用率
当前畜禽粪污综合利用率91.00%在全省处于倒数第一水平,全省最高利用率92.90%;全省最低91.00%;全省平均91.96%;全省中位数92.00%。
原因有3点,首先,省级数据与市级数据存在差异。对比城市7发布的《城市7全域“无废城市”实施方案》中的2020年畜禽粪污综合利用率为97.61%,与省农业农村厅采集到的数据不符,数据衔接不畅,需考虑数据溯源问题和填报系统数据错误问题。
其次,建设指标目标值设定过低。城市7发布的《城市7全域“无废城市”实施方案》中畜禽粪污综合利用率目标值设定为90%以上 (省平均91.96%,省最高92.90%) 。可能导致畜禽粪污综合利用率低的原因有:规模养殖场布局不合理、种养规模不匹配、畜禽粪污利用配套设施不足、畜禽粪污综合利用补贴力度不足、有机肥沼肥施用装备不足等。全省其他相关支撑建设指标还有规模养殖场粪污处理设施装备配套率、畜禽粪污资源化利用率、病死动物无害化处理率、畜禽粪污收储运体系覆盖率、有机肥利用率等。
再次,工作任务设计不足。需考虑畜禽粪污利用设施能力是否不足,其次,对于综合利用率提升没有针对性任务设计,需强化畜禽粪污综合利用率相关任务的识别和设计,逐步提升综合利用率。
短板2 生活垃圾产生强度
当前生活垃圾产生强度39.49×104 t∙元−1在全省处于倒数第二水平,全省最高43.96×104 t∙元−1;全省最低2.99×104 t∙元−1;全省平均22.08×104 t∙元−1;全省中位数19.15×104 t∙元−1。
原因有2点,首先,相关支撑建设指标不足。与生活垃圾产生强度相关的支撑建设指标有3个:城乡生活垃圾增长率 (反向指标) 、生活垃圾回收利用率 (正向指标) 、生活垃圾分类覆盖面 (正向指标) 。根据城市7发布的《城市7全域“无废城市”实施方案》中的建设指标:城乡生活垃圾增长率为零增长,生活垃圾分类覆盖面100%,生活垃圾回收利用率目标值为60%, (当年浙江省目标值45%以上) 可分析,城市7对生活垃圾产生强度的控制可从源头减量入手。可能导致源头产生量大的原因有:1)全省其他相关支撑建设指标还有易腐垃圾分类收集清运量占比、城镇居民小区生活垃圾分类覆盖率、农村地区生活垃圾分类覆盖率等;2)生活垃圾增长率目标值可设为负增长;3)收运过程混入其他垃圾;4)垃圾末端处置设施的管理存在问题。
其次,工作任务设计不足。对于生活垃圾产生源的公民没有针对生活垃圾分类落实情况针对性设计任务,需强化对公民宣传教育,强化生活垃圾分类及源头减量相关任务的识别和设计。
短板3 危险废物填埋占比
当前危险废物填埋占比为21.89%,排名全省倒数第三,全省最高32.32%;全省最低2.66%;全省平均15.80%;全省中位数18.24%。
原因有2点。首先,无相关建设指标。与危险废物填埋占比相关的支撑建设指标有危废产生量 (反向指标) 、危废填埋量 (反向指标) ,而该城市发布的《城市7全域“无废城市”实施方案》中没有危废产生、填埋、处置相关指标,仅有危险废物运输转移联单和电子运单互联率、危险废物利用处置领跑企业数。建设指标支撑不足。城市7降低危废填埋占比可从源头减量和提高回收利用入手。可能导致危废源头产生量大的原因有:危险废物管理不规范、危废收集体系不完善、监管能力不足、收运过程混入一般工业固废、中小微企业危废分布散收运不及时等。可能导致危废利用率低的原因有:危废收集和处置能力结构性失衡和危废利用技术能力不足。应减少危废填埋量,提高综合利用能力。
其次,工作任务设计不足。需考虑危废利用处置能力是否不足,对于危废填埋没有针对性任务设计,需强化对危废填埋相关任务的识别和设计。例如从源头减少只能填埋处置的危废产生量,强化危险废物综合利用项目的设计,减少填埋量。
5) 相关建议。共性问题整体建议:相关建设指标设置不足或缺失,对应建设任务不足或缺失导致工作推进不利,进展缓慢,相关部门要加强工作落实。4点建议如下。
建议1 农业固废管理方面
提高畜禽粪污综合利用率建设指标目标值,提升畜禽粪污处理设施能力,强化畜禽粪污综合利用率相关任务的识别和设计。例如,加强粪污处理配套设施建设。加强技术指导服务,引导养殖场 (户) 建设废弃物贮存、处理、利用配套设施并确保正常运行。引导种植户使用以畜禽粪便为原料的农家有机肥,逐步提升综合利用率。
建议2 工业固废管理方面
增加危废产生、填埋、处置相关建设指标目标值。提升危废利用处置能力,强化对危废填埋相关任务的识别和设计。例如,加强垃圾焚烧飞灰的资源化利用技术研发,转变飞灰只能填埋处置的定位,减少危险废物填埋处置量。加大绿色低碳领域技术攻关,加强固体废物处置利用技术模式创新。建立固体废物分级分类管理,制定行业强化源头分拣和计量手段,提升固体废物分级分类管理水平,促进固体废物内部循环和外部资源化利用,减少固体废物处置量。
建议3 生活垃圾管理方面
提高生活垃圾回收利用率建设指标目标值,增加易腐垃圾处理量有效占比、有害垃圾处置量年增幅、人均生活垃圾量增幅等相关建设指标。提高餐厨垃圾、易腐垃圾、有害垃圾处理能力、生活垃圾分类收运能力;强化对公民宣传教育生活垃圾分类相关任务的识别和设计。例如,采用多种方式向公众普及生活垃圾分类知识,增强公众的分类意识。指导生活垃圾分类各项工作有序落实,提高公众垃圾分类知晓率、参与度和投放准确率。鼓励开展生活垃圾分类技术创新,实现生活垃圾分类管理智能化、专业化、信息化。
建议4 保障措施方面
市无废办应组织召开“无废指数”专题会议,分管局领导参会研究部署,针对性地定位优势和短板、识别主体责任,研究改进方案,着力补短板、强弱项。每期“无废指数”发布后,市无废办针对排名靠后的分指标,通知或函告相关责任部门相应分指数情况和督促提升建议,要求责任部门提供书面反馈说明和下一步提升计划。并在市无废工作专班季度例会和年度工作推进会上,向全体专班成员单位通报指数情况和测算结果,督促相关责任部门自查提升。另外,市无废办应不定期地将辖区内各类主体遇到的疑问、困难和建议等收集整理,通过电话或书面反馈给省无废办。省无废办根据工作要求和实际情况,对相关建议进行研究采纳。
-
1) 地方政府反响。“无废指数”首次发布后,各地党委政府高度重视,第一时间组织相关部门开展针对性研究,以“无废指数”及其分指数、指标体系为指引,查找差距短板、识别主体责任,研究改进方案,着力补短板、强弱项,为落实新固废法提出的固体废物污染环境防治目标责任和考核评价提供了创新经验。
2) 各部门反响。“无废指数”可推动各部门工作任务衔接更清晰,实现对专项领域、重点任务、相关责任部门工作推进成效的快速分析评估和动态调整。各部门着重关注数据衔接情况、数据对接机制、数据采集方法、调度频次等方面。
-
1) 督促激励各地补短争先。表征城市水平差异,识别优势和短板,精准发力,及时调整优化“无废城市”建设目标任务。
2) 推动各部门形成工作合力。以指数对点分析单为抓手,就各项分指数提升,促进相关部门落实自身主责任务,促进各部门数据与环保部门对接协同。
3) 推动固体废物信息数据归真。优化建筑垃圾、再生资源等数据统计调查范围、统一数据采集方式和渠道,提升数据准确性、全面性;也推动各层级相关部门数据上下贯通。
4) 创新固体废物污染防治管理工作机制。信息动态更新和及时反馈,提升基层管理精准性、时效性。
-
1) 固废信息化程度进展不一导致指数的数据质量参差不齐。需开展数字化分指数建设,推动数据报送的标准化规范化。并推动整体信息系统的优化升级和各部门数据的贯通。
2) 指标体系对规范化管理方面体现不足。目前指标体系都是硬性指标,在规范化管理方面,危废、生活垃圾、建筑垃圾都有规范化评估工作,将各领域规范化管理制度通过规范化分指数落地,体现不同地区规范化管理的水平成效。
3) 指标体系对治理体系建设方面体现不足。通过综合执法分指数建设推动基层不同层级固体废物治理体系和能力的完善和构建。
-
本研究分别建立了省级层面和市级层面“无废指数”反馈机制,针对性的给出了省级层面和市级层面在应用“无废指数”指导“无废城市”建设的分析和建议,强化省级各相关部门的固体废物管理目标衔接、责任分解和考核落实,准确识别城市工业、农业、生活领域重点类别固体废物源头减量、资源化利用、贮存处置等关键环节的优势和短板,提升基层管理策略调整的精准性、时效性。该“无废指数”反馈机制创新了固体废物污染防治管理工作机制,为“无废城市”建设中不同层级管理部门制定管理决策提供依据和支撑。
-
研究探讨建立数字化分指数。统筹“无废城市”成效评价和专项资金激励需求,推进各类固体废物信息化监管等分指数的建设研究。探索建立“无废城市”数字化分指数,依据新《固废法》关于固体废物信息发布、全过程监管和信息化追溯要求,从相关主体信息化终端、数据报送和共享、数据决策支持几个维度系统评估、直观反映跨层级、跨部门、跨领域、跨主体固体废物信息数据共享交换、回流反馈工作成效,推动形成以数据为驱动的协同监管机制。
研究探讨建立规范化分指数。研究探讨建立工业固体废物、城乡生活垃圾、建筑垃圾、产业废弃物等规范化分指数,完善危险废物规范化管理分指数,重点推动规范化考核评估要求任务拆解及标准化,建立量化表征形式。落实《固废法》部门责任要求,研究明确工业、农业、城市治理领域各类固体废物管理规范要求,建立对应规范化分指数,推动落实各部门固体废物管理法定责任。
研究探讨建立基层综合执法分指数。落实《固废法》执法检查提出的关于加强基层执法监管能力要求,基于基层综合执法清单、网格化监管执法清单等工作机制和技术规范,研究建立基层固体废物综合执法量化评估标准,推动将固体废物纳入基层综合执法事项。
研究探讨建立减污降碳协同增效分指数。推动“无废城市”建设与碳减排、碳达峰战略目标充分融合,全面落实《固体废物污染环境防治法》和推进“无废城市”建设的各项要求,在“无废指数”方法学框架下,构建定量、客观、科学、系统、简明反映减污降碳协同建设成效的减污降碳分指数,为地方政府、企业、公众准确理解各地方减污降碳建设成效提供依据,为协同推进“无废城市”与减污降碳提供科学决策工具。
“无废指数”反馈机制研究——以浙江省“无废城市”建设为例
Research on the feedback mechanism of “zero-waste index”: based on the “Zero-waste City” construction in Zhejiang Province
-
摘要: “无废指数”是定量、客观、科学、系统、简明的综合性指数,是为了反映“无废城市”建设和固体废物治理成效。“无废指数”建立发布之后如何将指数结果反馈给相关部门,提高指数对管理部门的决策指导作用和时效性是“无废指数”最重要的应用功能。基于我国“无废城市”建设指标体系和浙江省“无废城市”建设水平和任务安排,在前期“无废指数”研究基础上建立了“无废指数”反馈机制,通过拆解指标和分析时效数据,强化“无废指数”的实时反馈功能和 “无废城市”建设任务的指导作用。根据浙江省某年“无废指数”测算结果,分别针对性的给出了省级层面和市级层面的应用建议和实例分析,深化了“无废指数”多维度比较分析和研判的应用功能,实现了在工作考核之前的数据动态更新和及时反馈,将提升基层管理策略调整的精准性、时效性,确保年度等目标的实现。为“无废城市”建设中不同层级管理部门制定管理决策提供依据和支撑。“无废指数”反馈机制创新了固体废物污染防治管理工作机制,进一步形成比学赶超的赛马机制,充分发挥了“无废指数”对全域“无废城市”建设的导向引领作用。Abstract: “Zero-waste index” is a quantitative, objective, scientific, systematic and concise comprehensive index to reflect the construction of “Zero-waste city” and the effectiveness of solid waste management. The most important function of the “zero-waste index” is to provide feedback to relevant departments after the establishment and release of the index, and to improve the decision-making guidance and timeliness of the index to local management departments. Based on the construction index system of “Zero-waste city” in China and the construction level and task arrangement of “Zero-waste city” in Zhejiang Province, the “zero-waste index” was established on the basis of the previous “zero-waste index” research. The feedback mechanism of “zero-waste index” was established based on the previous research of “zero-waste index”, and the real-time feedback function of “zero-waste index” and the guiding role of “Zero-waste city” construction tasks were strengthened by dismantling the index and analyzing the time-efficient data. According to the calculation results of “zero-waste index” in Zhejiang Province in a certain year, the application suggestions and example analysis were given at provincial level and municipal level respectively, deepening the application function of multi-dimensional comparative analysis and judgment of “zero-waste index”, realizing the dynamic update and timely feedback of data before the work assessment. This would improve the accuracy and timeliness of the adjustment of management strategies at the grassroots level and ensure the achievement of annual targets. It provided the basis and support for the management departments at different levels to make management decisions in the construction of “Zero-waste city”. The feedback mechanism of “zero-waste index” innovated the management mechanism of solid waste pollution prevention and control, further formed the horse-racing mechanism of learning and catching up, and gived full play to the guiding role of “zero-waste index” on the construction of “Zero-waste city” in the whole region.
-

-
-
[1] KAZA S, YAO L C, BHADA-TATA P, et al. What a waste 2.0: A global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050[M]. Washington DC: The World Bank, 2018. [2] AWASTHI A, CHEELA V R S, D’ADAMO I, et al. Zero waste approach towards a sustainable waste management[J]. Resources, environment and sustainability, 2021, 3: 100014. doi: 10.1016/j.resenv.2021.100014 [3] ZAMAN A U, LEHMANN S. Urban growth and waste management optimization towards ‘zero waste city’[J]. City, culture and society, 2011, 2(4): 177-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ccs.2011.11.007 [4] ZAMAN A U. A comprehensive review of the development of zero waste management: lessons learned and guidelines[J]. Journal of cleaner production, 2015, 91: 12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.12.013 [5] CASTIGLIEGO J R, POLLACK A, CLEVELAND C J, et al. Evaluating emissions reductions from zero waste strategies under dynamic conditions: a case study from Boston[J]. Waste management, 2021, 126: 170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.02.026 [6] 李玉爽, 李金惠. 国际“无废”经验及对我国“无废城市”建设的启示[J]. 环境保护, 2021, 49(6): 67-73. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2021.06.016 [7] SAKCHAROEN T, RATANATAMSKUL C, CHANDRACHAI A. Factors affecting technology selection, techno-economic and environmental sustainability assessment of a novel zero-waste system for food waste and wastewater management[J]. Journal of cleaner production, 2021, 314: 128103. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128103 [8] SONG Q, LI J, ZENG X. Minimizing the increasing solid waste through zero waste strategy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015(104): 99-210. [9] 生态环境部. 减污降碳协同增效实施方案 [EB/OL]. [2023-10-01]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/202206/t20220617_985879.html. [10] 生态环境部. “十四五”时期“无废城市”建设工作方案[EB/OL]. [2023-10-01]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/202112/t20211215_964275.html. [11] 生态环境部. 关于发布“十四五”时期“无废城市”建设名单的通知[EB/OL]. [2023-10-01]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202204/t20220425_975920.html. [12] 滕婧杰, 祁诗月, 马嘉乐, 等. “无废指数”构建方法探究——以“浙江省无废指数”构建为例[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(3): 723-731. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202112102 -



 下载:
下载: