-
塑料废弃物是高分子聚合物的混合物,其大小从几米到几纳米不等,包括塑料袋、农用塑料、食品包装、工业颗粒和化妆品微珠等物品,以及这些物品风化产生的碎片[1]。随着紫外线辐射、水力冲刷、物理磨损、生物栖息地以及冻融循环等外界因素的影响,大块的塑料废弃物被分解并降解成微小的塑料碎片或颗粒[2]。当粒径小于5 mm时,塑料碎片或颗粒被称为微塑料[3]。目前,微塑料已在世界范围内的海洋环境[3-4]、地表水系统[5-8]、陆地系统[9-11]和空气粉尘[12-13]中被广泛检出。微塑料体积小,比表面积大,老化后极易吸附环境中的有毒有害物质,如重金属[14]、抗生素[15]和细菌[16],可通过食物链[17]传播,对生物体生长发育、内分泌和繁殖产生不利影响[14-18]。微塑料的污染问题已成为当前研究热点。对于微塑料污染的研究长期以来一直集中在海洋环境,但是海洋中80%的微塑料源自于陆域[19],而河流是微塑料向海洋传输的重要途径[20]。因此,越来越多的学者和专家开始关注河流和湖泊等淡水环境中的微塑料[21-25]。河湖污染“表象在水里,根子在岸上”,大量的污染物均可通过排污口进入河湖。因此,应摸清入河排污口水体中微塑料的分布特征和主要来源,进而促进微塑料的有效管控。
沁河是黄河中下游重要的一级支流,素有“小黄河”之称。沁河下游主要位于河南省焦作市境内,其平面形态基本为平直型,河道断面较为规整,河床较宽,部分区域主槽宽度达20~30 m[26],已成为焦作市经济社会发展的重要水源地。因此,其水体微塑料污染情况对沁河流域和黄河下游的水体环境质量具有重要影响。2023年初河南省人民政府发布的《河南省新污染物治理工作方案》和《河南省加强入河排污口监督管理工作方案》均将微塑料列为重点关注的新污染物,并明确指出要建立新污染物排放源清单,开展环境健康风险评估,而沁河则是河南进行排污口排查的主要河流之一。目前,对于沁河的微塑料污染调查与评估,尤其是排污口水体的微塑料污染特征和行为的研究尚未见文献报道。因此,本研究拟通过对沁河 (焦作段) 入河排污口进行现场调查取样,重点探讨研究区域水体中微塑料的污染分布和特征,以及其可能带来的环境风险,以期对流域微塑料污染研究与防治工作提供参考。
-
焦作市位于河南省西北部,南临黄河,是一个以农业和旅游为主的城市,也是河南省中心城市群核心区之一。沁河源于山西省沁源县二郎神沟,由济源市五龙口入境焦作,流经沁阳、温县、博爱、武陟四县 (市) ,在武陟县嘉应观乡秦厂村东汇入黄河[26]。辖区内河道长度为80 km,滩区面积为46.1 km2;属于暖温带大陆性季风气候,年平均气温为10~14.4 ℃,多年平均径流量为8.27×108 m3[27];水力资源利用主要包括农业灌溉、工业生产和农村人畜,其中农业灌溉用水所占比例最大。
-
根据《污水监测技术规范》HJ 91.1-2019和《水质采样技术指导》HJ 494-2009规范和要求,2023年3月,围绕沁河 (焦作段) 流域采集排污口样品共计7个,对样点按照采样先后顺序进行编号,主要分布在四区涝河、安全河及北截排等沁河支流上 (图1) 。为避免采样环节中对水样带来微塑料污染,采用不锈钢水质采样器和玻璃瓶进行样品采集。样品采集前先用水样荡涤采样器和样品容器3次。每个样点采样设置2个平行样 (现场平行样品) ,将2次平行采集后的水样均匀混合装在棕色玻璃瓶中密封,每个排污口采集水样5 L。采集后的样品瓶置于冰袋上保存以保证样品的稳定性,样品瓶于12 h内带回实验室进行后续处理。在采样现场通过便携式多参数水质分析仪 (MANTA2225) 对水体进行常规水质指标 (包括水温、pH、溶解氧、电导率、氯化物、氨氮等) 的测定。
-
将采集水样先静置24 h,分离上层清液与底部沉积物;然后在底部沉积物中加入饱和NaCl溶液于高速离心机中进行离心浮选;随后转入装有上层清液的玻璃烧杯中,加入适量H2O2溶液(质量分数30%)进行消解处理;用玻璃棒轻微搅拌后,使用锡箔纸遮盖烧杯口,静置12 h(去除有机质)。待充分消解完后,使用真空抽滤装置对样品进行抽滤,滤膜采用孔径 0.45 μm、直径 50 mm 的玻璃纤维滤膜,得到滤膜放入带盖玻璃培养皿中,以备开展后续的鉴定与微观特性分析。
通过体视显微镜 (Stemi 508) 对滤膜上的物质进行观察拍照,观测时基于目前通用的微塑料鉴别标准来确定疑似微塑料,统计微塑料形貌特征。采用ImageJ 1.51软件测量微塑料的尺寸,被划分为20~100 μm、100~200 μm、200~500 μm、500~1 000 μm、1 000~2 000 μm和2 000~5 000 μm;微塑料的形状被划分为纤维、碎片、颗粒、薄膜、球形和絮状共6类;颜色依照微塑料真实颜色划分。
利用显微红外光谱仪 (Nicolet iN 10) 测定样品的红外光谱图,并将其与数据库中的谱图对比,判定微塑料的聚合物类型。其中,与标准谱图有65%以上的匹配度认定为相对应的物质。最后根据鉴定结果统计微塑料丰度。
-
为保证实验数据的准确性,避免环境因素的干扰,实验中所用到的超纯水及溶液均应经0.45 μm玻璃纤维滤膜过滤后方可使用。为避免滤膜本身杂质的干扰,所有滤膜在使用前均应在显微镜下检查一遍,以确保表面无杂质。实验过程中所用到的玻璃器皿均用过滤后的纯水反复冲洗3次以上方可使用,实验人员均着棉质实验服,佩戴丁腈手套,身处无尘环境中进行操作。实验全过程设置空白,对全部空白样品 (超纯水) 采用相同操作以消除全过程中外界带来的微塑料污染和干扰。检测发现空白样品中微塑料数量极少,表明实验过程对实验结果影响很小。
-
对于微塑料生态风险评价的研究还没有专门的评价体系,主要是通过借鉴其他污染物评价方法对微塑料进行风险评价。本研究采用污染负荷指数法、微塑料聚合物风险指数法和潜在生态风险评价法对排污口水体中微塑料进行生态风险评价。
1) 污染负荷指数法。TOMLINSON等[28]提出的污染负荷指数法是评价区域整体上承载污染物的负荷情况,能直接反映多种污染物对环境污染的贡献及其在时空上的变化趋势,具体计算式见 (1)~(3) 。
式中:
$ {\mathrm{C}\mathrm{F}}_{i} $ 为微塑料在样点i的污染系数;$ {C}_{i} $ 为微塑料在样点i的丰度;$ {C}_{oi} $ 为微塑料丰度的标准值,由于缺乏可用的微塑料丰度参考值,本研究采用所有样点中微塑料最低丰度作为参考值;$ {\mathrm{P}\mathrm{L}\mathrm{I}}_{i} $ 为微塑料在样点i的负荷指数;$ {\mathrm{P}\mathrm{L}\mathrm{I}}_{\mathrm{z}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{e}} $ 为研究区域整体风险负荷指数;n为研究区域内样点数量。2) 微塑料聚合物风险指数法。以微塑料聚合物种类和聚合物危害分数作为评估微塑料风险的指标,已被广泛用于评估微塑料对环境和生态的影响程度,即环境中微塑料风险环境评价。具体见公式 (4) [29]。
式中:
$ \mathrm{H}\mathrm{I} $ 为微塑料聚合物风险指数;$ {P}_{n} $ 为采样点不同微塑料聚合物类型的百分比;$ {S}_{n} $ 为组成微塑料聚合物的危害评分 (见表1) ;n为微塑料聚合物的种类。3) 潜在生态风险指数法。潜在生态风险指数法是瑞典科学家HAKANSON[30]根据重金属性质及环境行为特点提出的用于重金属污染评价的方法之一。PENG等[31]借鉴并改进该方法对微塑料污染风险进行评价,不仅考虑到微塑料浓度,而且综合考虑了多元素协同作用、毒性水平、污染程度等因素,计算公式见 (5)~(8) 。
式中:
$ {C}_{f}^{i} $ 为单一微塑料危害因子;$ {C}^{i} $ 为各点微塑料实测的丰度;$ {C}_{n}^{i} $ 为标准参考值。本研究采用Everaert等[32]利用数学模型估算出的地表水中微塑料的安全浓度6.65 n·L−1;$ {T}_{r}^{i} $ 为生态毒性响应因子;$ {P}_{i} $ 为某种微塑料实测的丰度;$ {S}_{n} $ 为各类微塑料危害评分;$ {E}_{r}^{i} $ 为单个微塑料的潜在生态风险指数;$ RI $ 为多种微塑料的潜在生态风险指数;n为样品中微塑料的种类数。根据不同微塑料聚合物组成成分和危害评分之间的差异,污染负荷指数法将环境风险分为4个等级,而风险指数法和潜在生态风险指数法分为5个等级,其等级划分见表2。
-
本研究水体中微塑料的丰度单位为“n·L−1”。采样点位图使用ArcGIS 10.2软件绘制。针对各样点之间的数据,进行了均值计算及其标准差核算,并用Origin2022绘制了相关结果图。
-
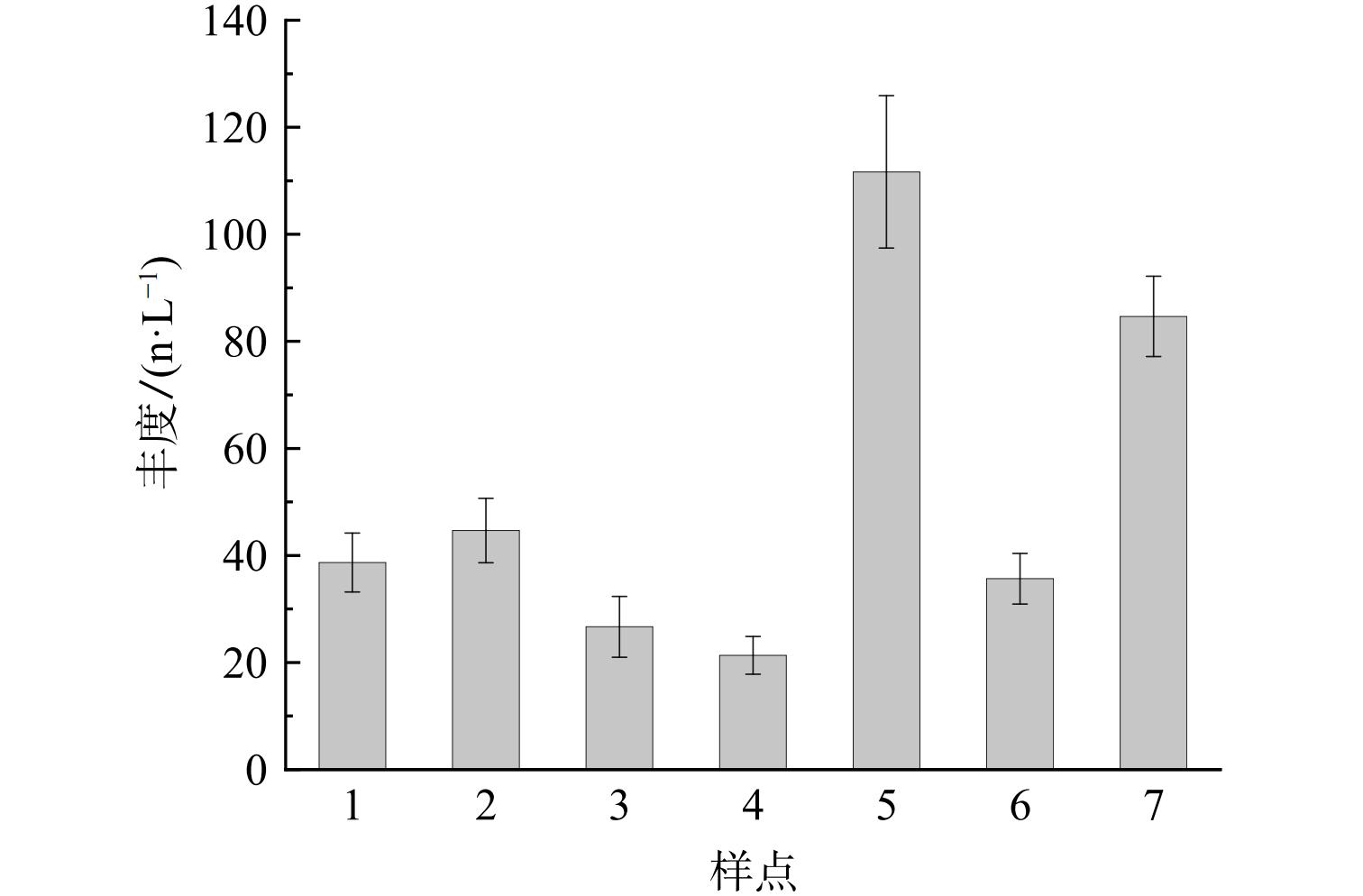
图2为沁河 (焦作段) 不同排污口水体中微塑料的丰度。7个排污口均有不同程度微塑料的检出,丰度为 (21.33±3.51)~(111.67±14.22) n·L−1,均值为 (51.90±32.22) n·L−1。这表明不同排污口微塑料丰度的差异性较大。7个排污口的丰度大小排序为:样点5 > 样点7 > 样点2 > 样点1 > 样点6 > 样点4 > 样点3。这与赵长民等[33]关于汜水河排污口水体微塑料的研究结果基本一致,主要是因为附近居民生活塑料垃圾制品的排放有较大影响,样点5微塑料丰度较高可能与排污管道采用塑料制品有一定关系。
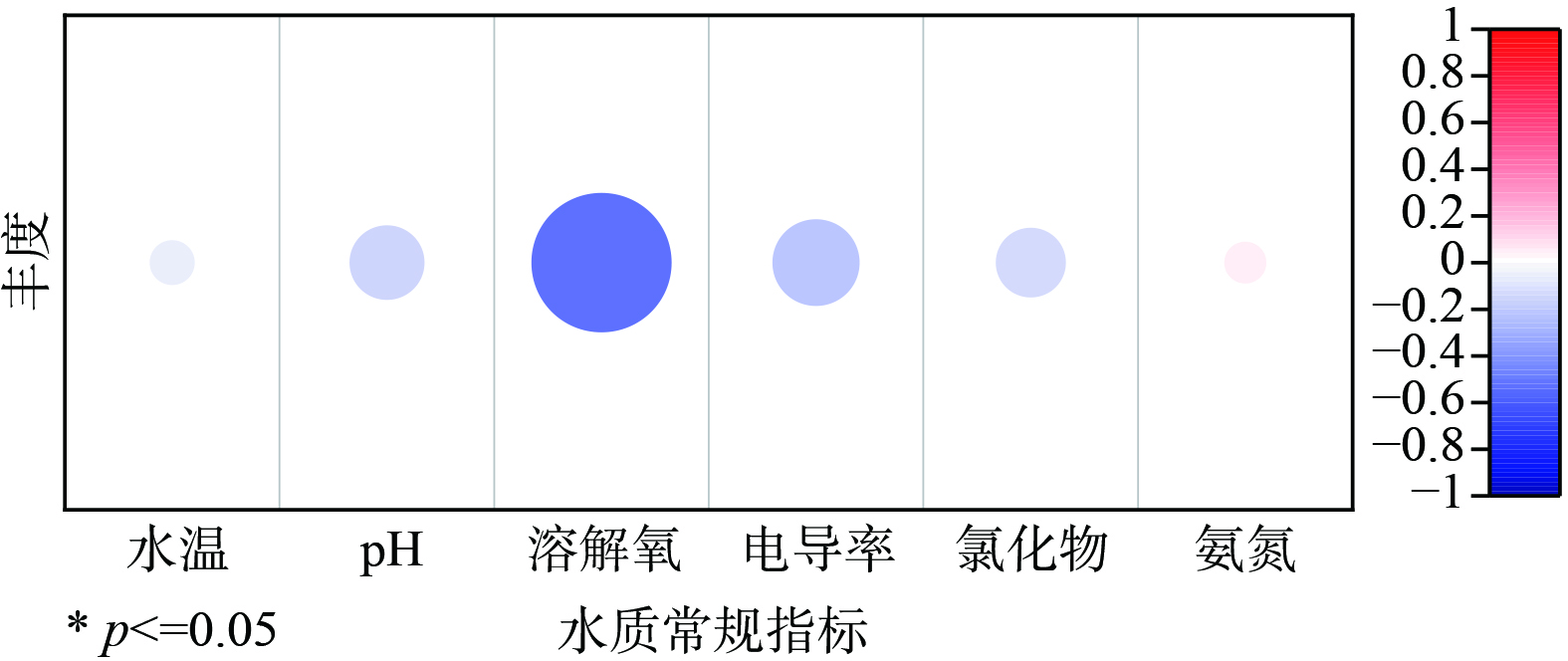
为弄清影响水体微塑料发生特征的影响因素,进一步采用Pearson相关分析法对丰度和水质常规指标 (水温、pH、溶解氧、电导率、氯化物和氨氮) 进行相关性分析 (图3) 。结果发现排污口水体中微塑料与水体6项常规指标均无显著相关性,这说明水体常规指标不是影响微塑料丰度的关键因素。DAI等[24]发现钱塘江微塑料的丰度与地区人均国内生产总值 (GDP) 呈正相关,且微塑料丰度和地方的产业发展及高强度的人类活动等方面关系密切,这说明城市和区域的经济发展和人类活动影响河流环境中微塑料的分布。
-
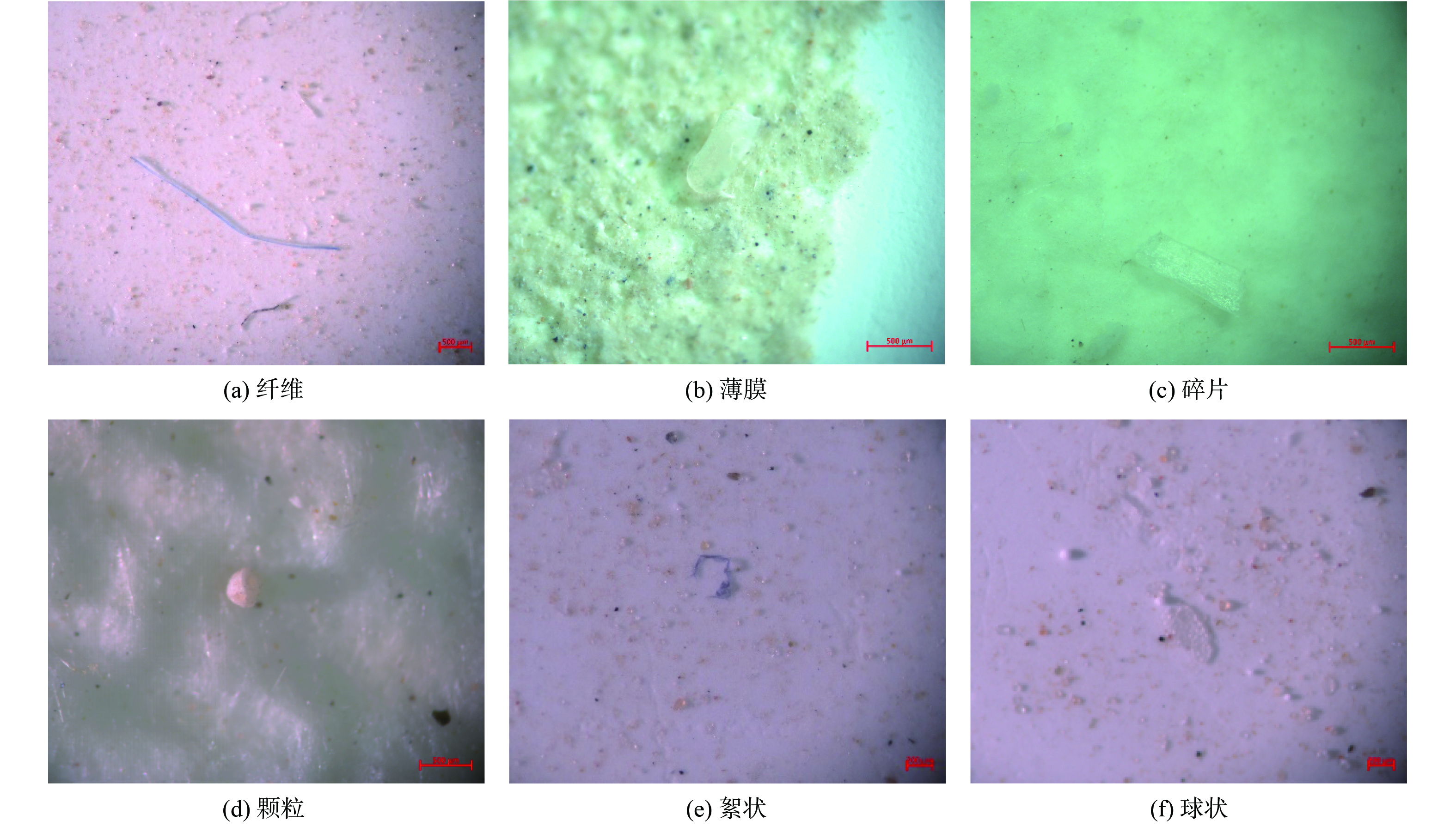
排污口水体中微塑料在体视显微镜下检测的形状有纤维、薄膜、碎片、颗粒、絮状和球状等,结果见图4。
不同形态在每个样点中的分配比例见图5。纤维状是研究区域排污口水体中微塑料的主要存在形态,占比64%~95%;其次是薄膜,占比为3%~24%,而且二者在所有排污口水体中均有检出。颗粒和絮状在部分排污口样点中检出,而球状仅在样点3中被检出。相关研究表明,环境中纤维状微塑料主要来自洗衣废水,洗涤过程中纺织品掉落纤维可以达到34.8%,而研究区域排污口水体主要以生活污水为主[34]。这是造成排污口水体中微塑料主要以纤维状形态存在的主要原因之一。另外,采样位置除样点7外,排污口均在农田边。因此,水体中的薄膜形态微塑料可能与农业生产活动有关。
-
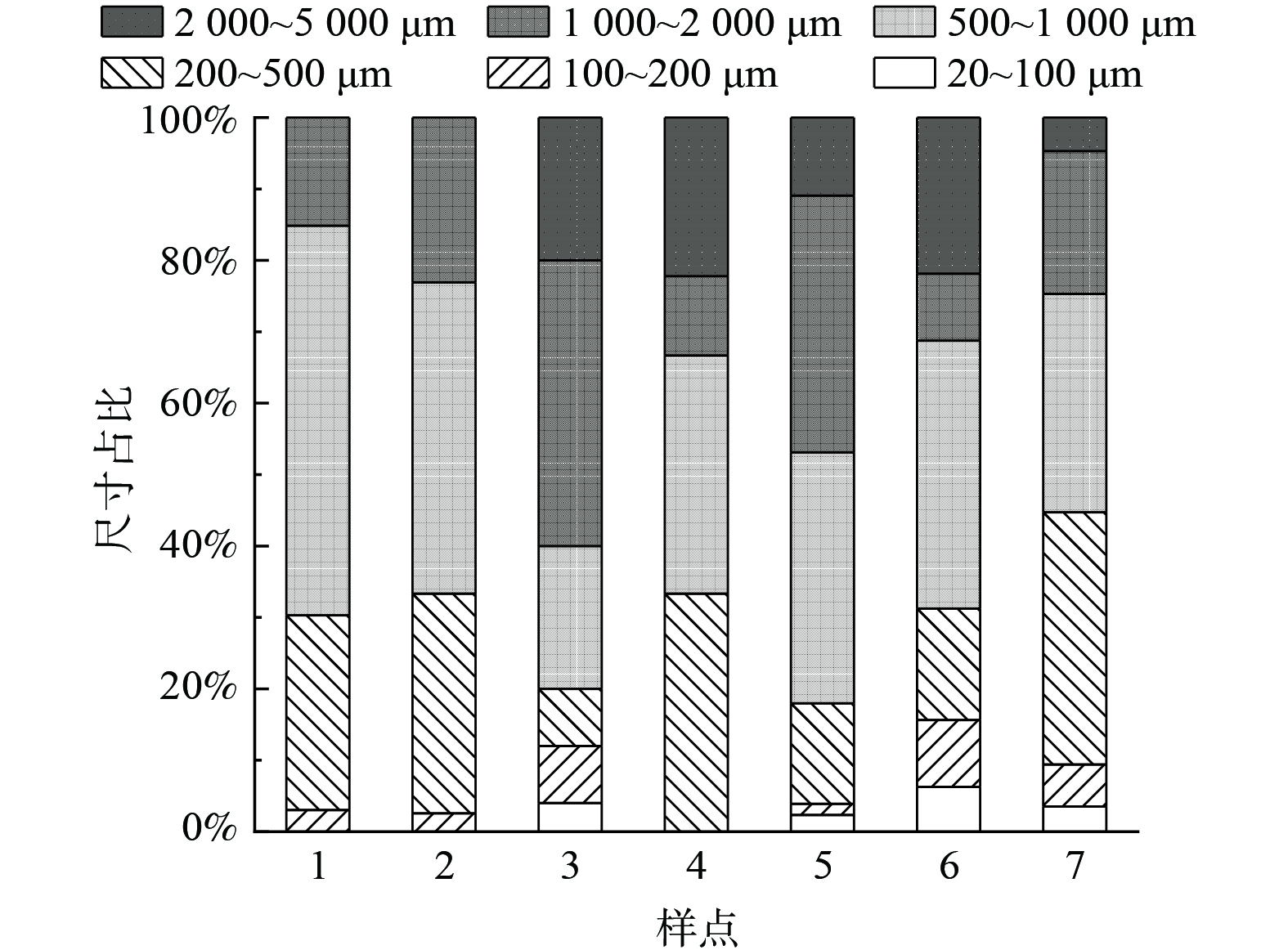
各排污口水体中微塑料尺寸分布见图6。从各排污口水体中微塑料的尺寸分布情况来看,研究区域排污口的微塑料尺寸主要集中在500~1 000 μm、200~500 μm及1 000~2 000 μm;尺寸<200 μm和>2 000 μm的微塑料相对较少。主要是因为较大粒径 (>2 000 μm) 的微塑料在风化、紫外线照射及水力冲击等外界作用下使得大尺寸的微塑料逐渐分解破碎形成更多抗冲击的小尺寸微塑料[35-36]。周泽妍等[37]发现,微塑料的尺寸可能与微塑料的各类形状有关,其中薄膜、纤维类微塑料的尺寸为500~2 000 μm。本研究中排污口水体中微塑料形状以纤维为主,而且占比高达60 %以上,故微塑料的尺寸分布也就集中在500~2 000 μm。另外,可能由于微塑料检测手段的限制,导致过小的微塑料无法检出,因此在本研究中尺寸<200 μm的微塑料比例不高。
-
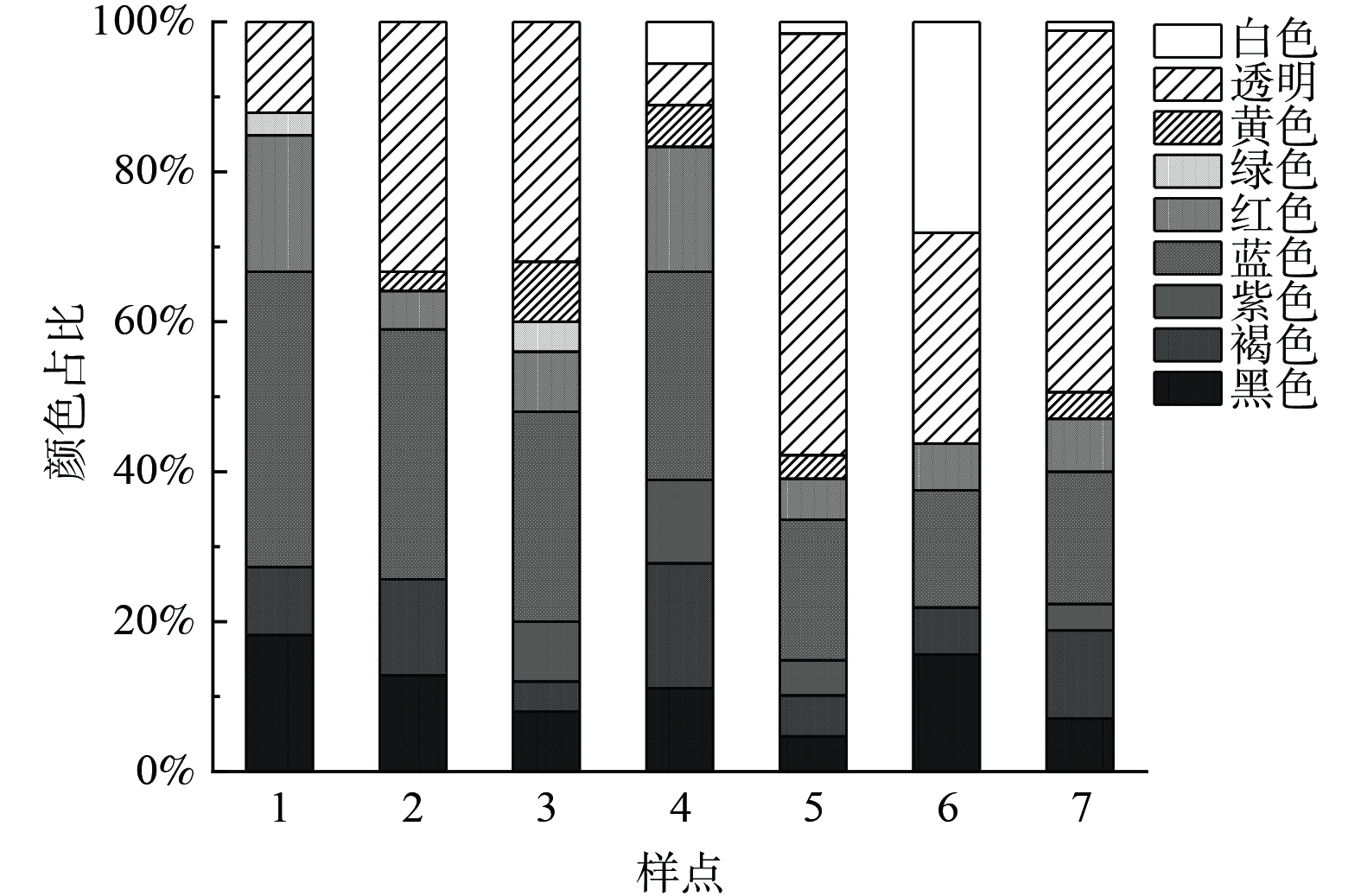
排污口水体中检出的微塑料有透明、白色、红色、黄色、绿色、蓝色、紫色、褐色和黑色等9种颜色,其分布结果见图7。其中,透明、红色、蓝色、褐色和黑色在所有样点均被检出;黄色、白色和紫色仅有部分样点被检出;而绿色仅在样点1和样点3中被检出。从微塑料颜色在各排污口的占比来看,大多数样点中透明微塑料占比最高,其中样点5和样点7中透明微塑料占比分别高达56%和48%。造成这一现象的主要原因是日常生活中人们常用的塑料制品如透明塑料袋、地膜、包装袋等均为透明材质,另一方面是因为彩色或浅色的微塑料经过长时间光老化、风化、紫外线照射等作用褪变为透明。其次为蓝色,各点位占比为15%~30%。这一现象和北京市通州区河流[38]、广州市区内珠江[39]中微塑料颜色方面的研究一样,均以透明色和蓝色为主。为提高塑料制品的吸引力,商家往往会在塑料成型前添加各种颜色母料,制成了各种颜色的塑料产品,所以导致各样点中不同颜色的微塑料都有一定的占比,而且不同的样点微塑料各类颜色占比差别较大。有相关研究表明有色微塑料多数来源于居民住宅区和污水厂排放的生活废水。
-
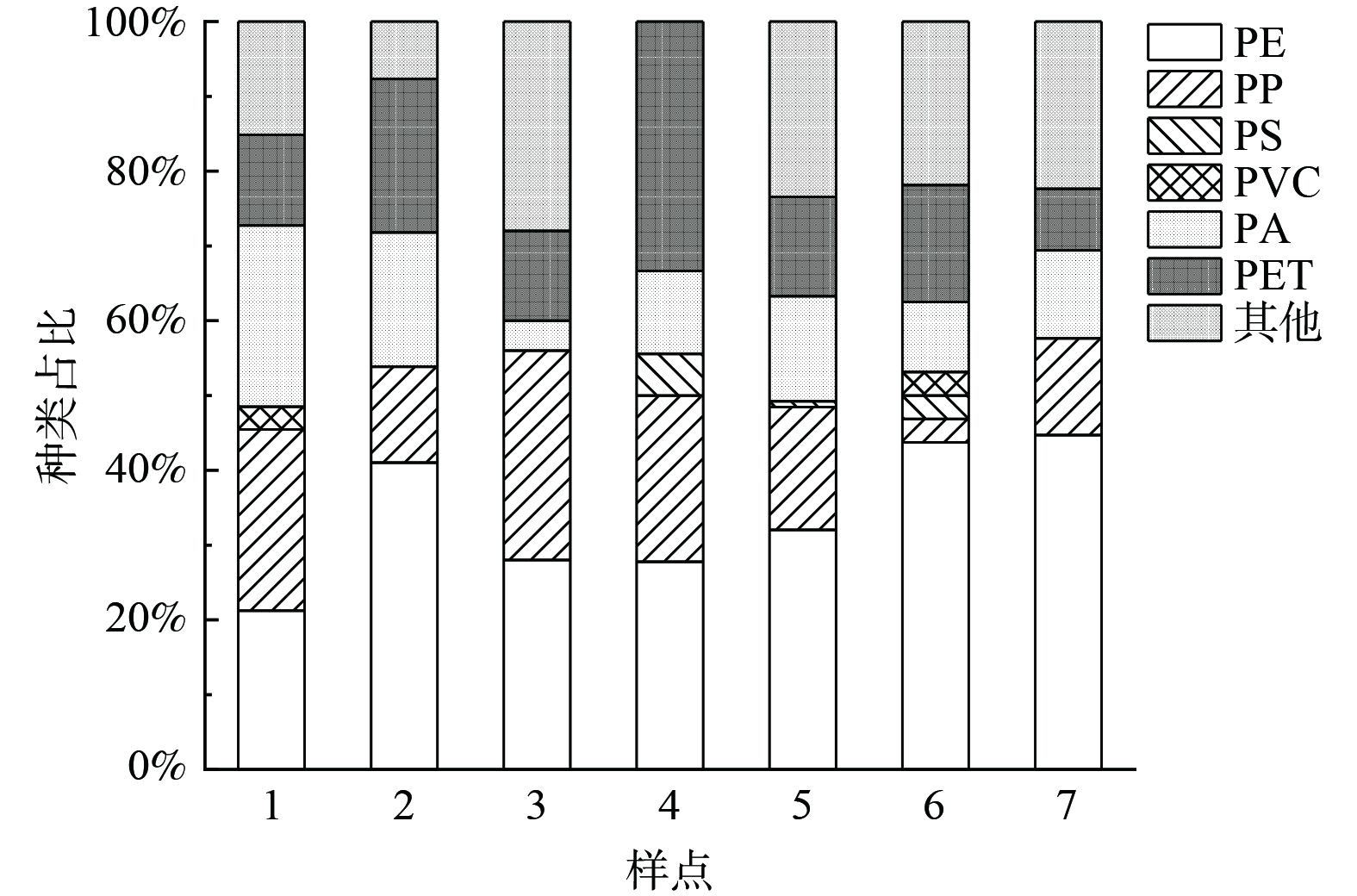
对提取到的微塑料进行进一步定性分析,发现7个排污口水体中可识别的微塑料种类有聚乙烯 (PE) 、聚丙烯 (PP) 、聚苯乙烯 (PS) 、聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 、聚酰胺 (PA) 和聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯 (PET) 等6种。图8表明,PE是排污口水体中主要的微塑料种类,除样点1和4外,其在样点的占比均较高,为21%~45%。另外,PP、PA和PET也在各样点均被检出;PS仅在样点4、5和6中被检出,而PVC则仅在样点1和样点6被检出。PE是农用覆盖薄膜、塑料包装材料、破塑料编织袋等的主要成分,排污口较高的PE可能来自农业生产和居民生活排放[40];PET主要来源可能是周围居民的日用品、包装膜、水瓶等[41];PP则作为工程塑料被应用于机械和电器行业[36]。另外,PP、PET和PE材质的纤维广泛应用于布料及编织袋、网的制作,与前面探讨的微塑料形状大多以纤维状为主基本一致。
-
1) 污染负荷指数法。为考察研究区域内排污口水体中微塑料总体污染状况,采用整体污染负荷法对研究区域微塑料生态风险进行评价,其环境风险情况见表3。该研究区域整体微塑料污染负荷为1.51 (<10) ,处于低风险。各样点对环境风险的贡献从大到小依次为样点5、样点7、样点2、样点1、样点6和样点3,差异不大。这是由于污染负荷指数法仅选用微塑料丰度作为参考指标,并未考虑微塑料聚合物的毒性大小,所以样点间的微塑料污染负荷指数分布与微塑料丰度分布规律相似,而且差别不大。另外,与国内相关湖泊河流的微塑料污染负荷指数相比,明显要高于淀山湖[35] (0.18~0.56) 、渭河[36] (0.43~0.79) 、珠江[39] (0.1~0.87) ,这说明排污口水体的微塑料可能是造成城市湖泊河流微塑料污染的主要来源之一。
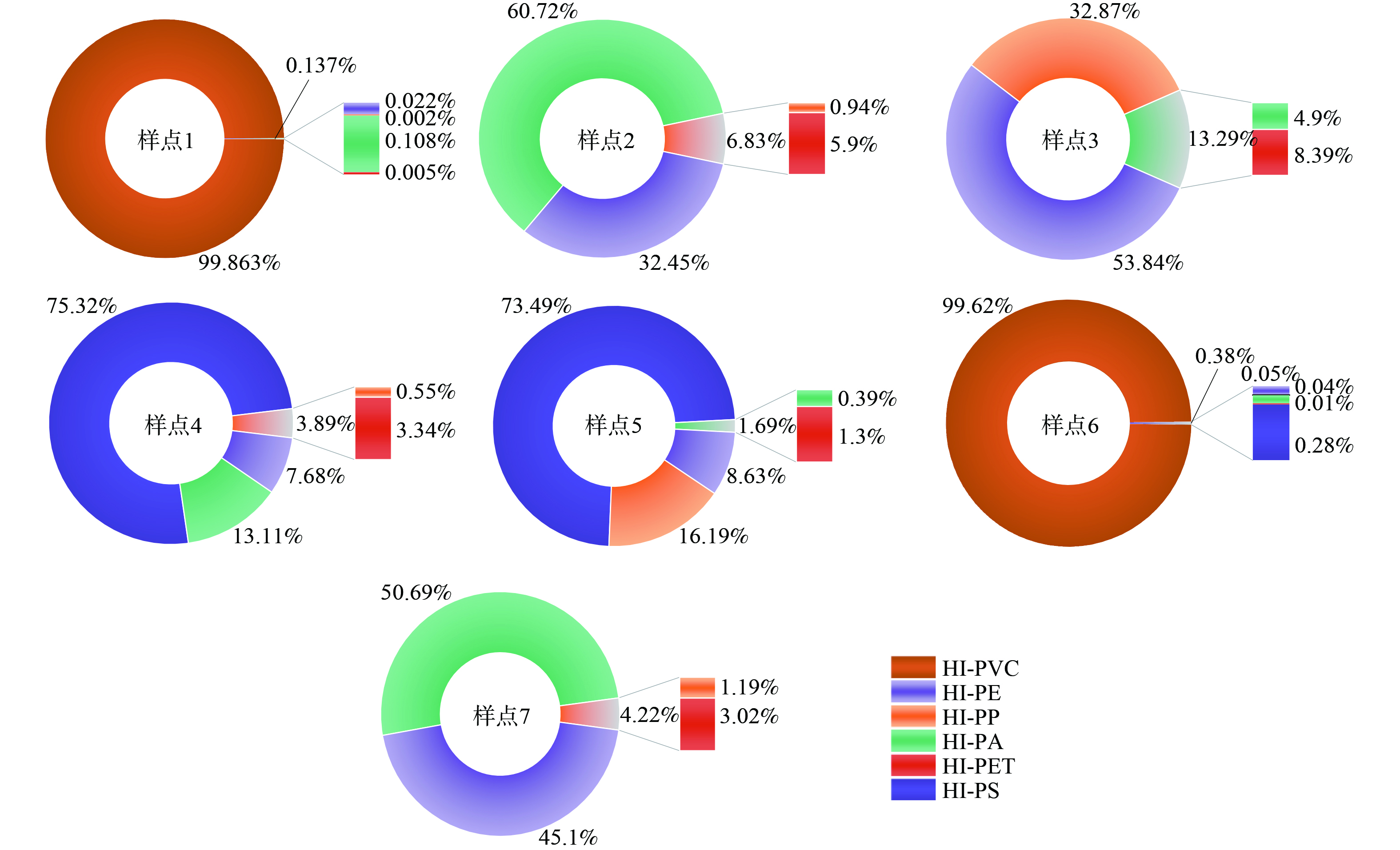
2) 微塑料聚合物风险指数法。由聚合物风险指数法计算的各排污口风险指数及其风险列于表4。样点1和样点6因检出有PVC,2个样点的HI分别高达10 565.45和10 590.88,风险等级已经为V (非常危险) 。这是由于PVC的危害评分很高,导致样点中一旦有PVC,会引起样点的风险水平骤然升高。另外,样点4、样点5和样点7的风险等级为III (高风险) ,这说明排污口水体中的微塑料引起的环境风险已比较严重。
为探讨不同类型污染物对样点环境风险的贡献,进一步对每个样点不同聚合物风险占比进行了分析统计,其结果见图9。样点1和6中PVC对样点HI的贡献均大于99%,因此,这2个样点排放的污水中微塑料风险主要是由PVC造成的。在样点2和7中,PA对HI的贡献最高,分别达60.72%和50.69%。样点3中,PE风险贡献率最高为53.85%。样点4和5中PS对样点HI的贡献则最高,分别为75.32%和73.49%。由此可见,各样点风险指数的高低与其赋存微塑料的种类分布差异密切相关。在我国可可西里特拉什湖[42]、湟水河流域[43]等地开展的微塑料风险指数评估结果也表明,高毒性聚合物会导致局部区域的高环境风险。
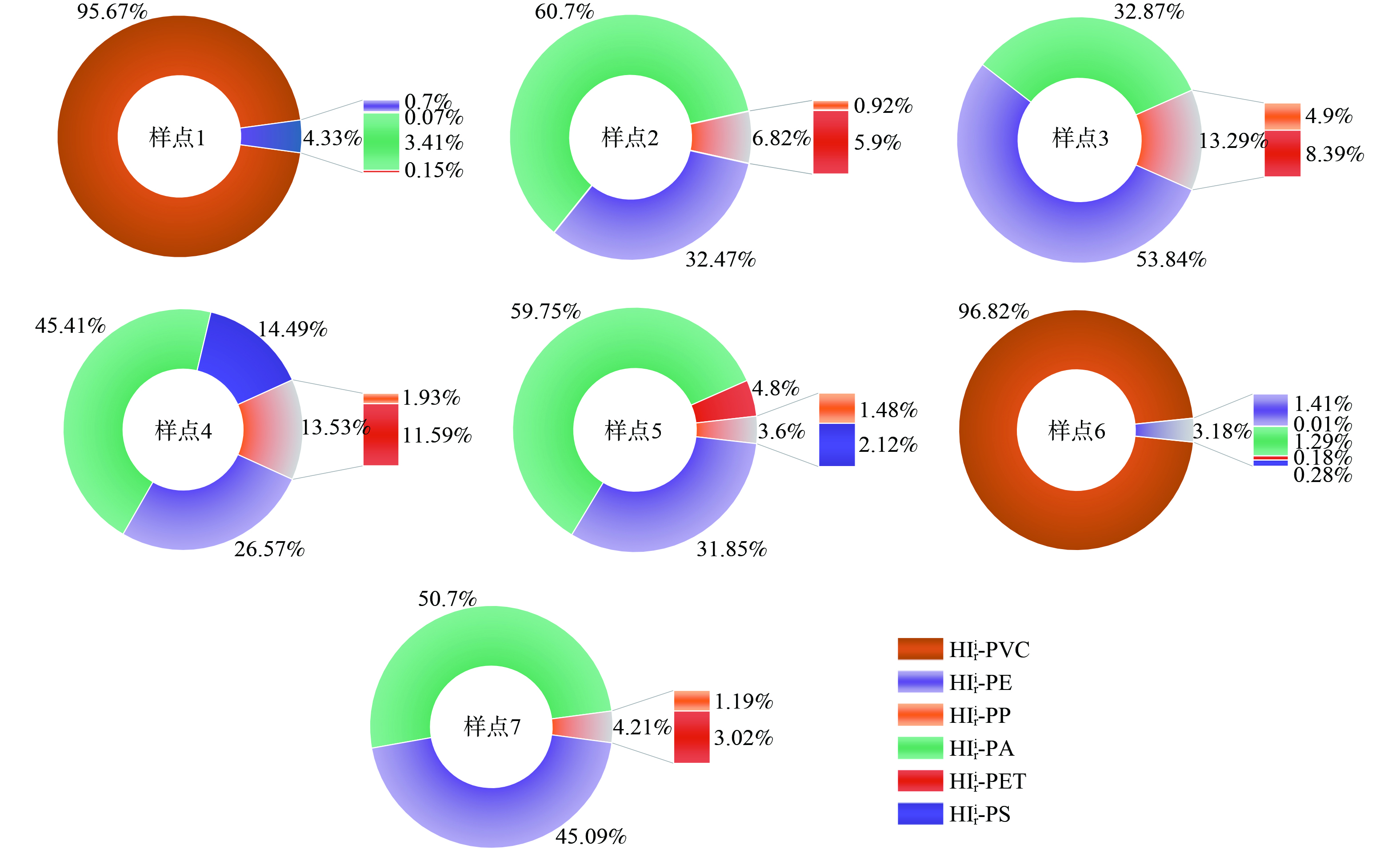
3) 潜在生态风险指数法。采用潜在生态风险指数法对排污口水体中微塑料进行风险评估,其结果见表5。样点1和样点6由于检出了PVC,所以RI值均在300以上,属于高风险等级,其他样点的风险指数值均低于15,属低风险等级。
不同类型微塑料潜在生态风险指数对各排污口水体环境风险的贡献率结果见图10。样点1和样点6中PVC风险占比最高,均大于95%;而在样点2、5和7中,PA形成的潜在生态风险最高,对RI的贡献分别为60.70%、59.75%和50.70%;样点4中PS对RI的贡献最高,为53.85%,其结果与聚合物组成危害指数法基本一致。这说明微塑料造成的环境风险大小不仅跟微塑料的丰度有一定关系,而且跟微塑料的种类密切相关,因为潜在生态风险很大程度上依赖于微塑料聚合物的危害评分。
-
1) 7个排污口水体中微塑料检出率为100 %,丰度为 (21.33±3.51) n·L−1~(111.67±14.22) n·L−1,平均丰度为 (51.90±32.22) n·L−1;通过Pearson相关分析分析,微塑料丰度与水质常规指标无显著相关性,说明水体常规指标不是影响微塑料丰度的关键因素。2) 排污口水体中微塑料大多以纤维状形态存在,占比高达64%~95%,其次是薄膜;尺寸分布集中在500~2 000 μm;颜色多以透明和蓝色为主;PE是各样点中主要的微塑料聚合物类型,可能来自周边区域的农业生产和居民生活排放。3) 采用污染负荷指数法评价该研究区域处于低风险,主要是因为仅选取微塑料丰度作为参考指标,未考虑聚合物的毒性影响;采用微塑料聚合物风险指数法和潜在生态风险指数法发现,有PVC检出的排污口环境风险较高,可能对局部区域的生态环境造成一定的潜在风险。4) 污染负荷指数法、微塑料聚合物风险指数法和潜在生态风险指数法用于微塑料环境风险评价具有一定的局限性,应该针对微塑料污染建立适合的环境风险评价方法和体系。
沁河 (焦作段) 入河排污水体微塑料污染特征及风险评价
Pollution characteristic and risk assessment of microplastics from sewage outlets in the Qin River(Jiaozuo section)
-
摘要: 河岸排污是引起河流水环境微塑料升高的主要途径。摸清沿河两岸排污水体中微塑料的赋存特征及其环境风险,是进行微塑料污染控制的前提。以黄河支流沁河 (焦作段) 为研究对象,采集7个入河排污口的污水样品,采用体视显微镜对微塑料丰度和形貌特征 (包括尺寸、形状及颜色等) 进行分析,发现微塑料在所有样点均有检出,尺寸为500~2 000 μm,颜色以透明和蓝色为主,纤维状是微塑料在各个样点的主要形状。进一步借助显微红外光谱仪对各样点污水中的聚合物类型进行了鉴定,结果显示排污口水体中微塑料种类以聚乙烯为主,其可能与周边区域的农业生产和居民生活排放有关。环境风险评价结果表明,研究区段整体处于低风险水平;排污口微塑料引起的环境风险不仅与其丰度有关,还依赖于微塑料的种类,有聚氯乙烯检出的样点1和6均呈现较高的环境风险。该研究结果可为黄河及其支流微塑料风险防控提供参考。Abstract: Wastewater discharge is the major source of microplastic pollution in river. Identification of the characteristics of microplastics and their environmental risks in the discharged waters along sides of river is a prerequisite for microplastic pollution control. The Qin River (Jiaozuo section), a tributary of the Yellow River, was selected as the research object and a total of 7 water samples were collected from sewage outlets. The abundance and morphological features of microplastics, including size, shape and color, were classified by using a stereomicroscope. Microplastics were found in all sample sites, and the sizes varied mainly between 500 and 2 000 μm. In addition, the colors were mainly transparent and blue, and fibrous was the main shape of microplastics at each sample point. Further, the types of polymers at all points were identified using microinfrared spectrometry. The results showed that the main type of microplastics in the sewage outlets was polyethylene, which mainly came from agricultural production and residential emissions in the surrounding areas. The results of the environmental risk assessment showed that the study area was at a low risk level overall. The environmental risk posed by microplastics at the outfalls was not only related to its abundance, but also depended on the type of microplastics. Sample sites 1 and 6 both presented higher environmental risks as polyvinyl chloride was detected. Research results could provide theoretical basis and data support for the prevention and control of microplastic risks in the Yellow River and its tributaries.
-
Key words:
- microplastics /
- sewage outlets /
- pollution characteristic /
- risk assessment /
- abundance
-

-
表 1 微塑料危害评分表
Table 1. Hazard score of microplastic polymers
聚合物种类 缩写 危害评分 聚丙烯 PP 1 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯 PET 4 聚乙烯 PE 11 聚苯乙烯 PS 30 聚酰胺 PA 47 聚氯乙烯 PVC 10 551 表 2 微塑料风险评价等级划分
Table 2. Criteria for microplastic pollution risk
风险等级 I II III IV V PLI <10 10~20 20~30 >30 HI 0~1 1~10 10~100 100~1 000 >1 000 RI <150 150~300 300~600 600~1 200 >1 200 表 3 研究区段整体微塑料排污环境风险
Table 3. The overall environmental risk of microplastics in the study area
样 点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ \mathrm{CF}_i $ 1.83 2.17 1.39 1.00 7.11 1.78 4.72 $ \mathrm{PLI}_i $ 1.35 1.47 1.18 1.00 2.67 1.33 2.17 $ {\mathrm{P}\mathrm{L}\mathrm{I}}_{\mathrm{z}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{e}} $ 1.51 表 4 各种类型微塑料在每个排污口中引起的风险指数
Table 4. Hazard score caused by microplastics to the risk of each outfall
样 点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 HI-PE 2.33 4.51 3.08 3.06 3.52 4.81 4.92 HI-PP 0.24 0.13 0.28 0.22 0.16 0.03 0.13 HI-PA 11.39 8.44 1.88 5.22 6.61 4.41 5.53 HI-PET 0.48 0.82 0.48 1.33 0.53 0.63 0.33 HI-PS — — — 30.00 30.00 30.00 — HI-PVC 10 551.00 — — — — 10 551.00 — HI 10 565.45 13.90 5.72 39.83 40.83 10 590.88 10.91 风险等级 V III II III III V III 注:“—”表示所在样点无对应聚合物检出。 表 5 各排污口微塑料聚合物潜在生态风险
Table 5. Potential ecological risks of different polymer in each outfall
样点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Ei r-PE 2.33 4.51 3.08 3.06 3.52 4.81 4.92 Ei r-PP 0.24 0.13 0.28 0.22 0.16 0.03 0.13 Ei r-PA 11.39 8.44 1.88 5.22 6.61 4.41 5.53 Ei r-PET 0.48 0.82 0.48 1.33 0.53 0.63 0.33 Ei r-PS — — — 1.67 0.23 0.94 — Ei r-PVC 319.73 — — — — 329.72 — RI 334.18 13.90 5.72 11.50 11.06 340.53 10.91 风险等级 III I I I I III I 注:“—”表示所在样点无对应聚合物检出。 -
[1] ZHANG Y, WANG Q, YALIKUN N, et al. A comprehensive review of separation technologies for waste plastics in urban mine[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 197: 107087. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2023.107087 [2] ANDRADY A L. Microplastics in the marine environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(8): 1596-1605. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030 [3] THOMPSON R C, OLSEN Y, MITCHELL R P, et al. Lost at sea: where is all the plastic?[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5672): 838-838. doi: 10.1126/science.1094559 [4] NAKANO H, ARAKAWA H. Oceanic microplastics in Japan: A brief review on research protocol and present pollution[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2022, 51: 102201. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2022.102201 [5] DING L, FAN M R, GUO X , et al. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Wei River, in the northwest of China [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 667: 427-434. [6] WANG W, YUAN W, CHEN Y, et al. Microplastics in surface waters of Dongting Lake and Hong Lake, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 633: 539-545. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.211 [7] HAN M, NIU X, TANG M, et al. Distribution of microplastics in surface water of the lower Yellow River near estuary[J]. Science of The total environment, 2020, 707: 135601. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135601 [8] ALAM F C, SEMBIRING E, MUNTALIF B S, et al. Microplastic distribution in surface water and sediment river around slum and industrial area (case study: Ciwalengke River, Majalaya district, Indonesia)[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 224: 637-645. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.188 [9] YA H, JIANG B, XING Y, et al. Recent advances on ecological effects of microplastics on soil environment[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 798: 149338. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149338 [10] HARLEY-NYANG D, MEMON F A, OSORIO BAQUERO A, et al. Variation in microplastic concentration, characteristics and distribution in sewage sludge & biosolids around the world[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 891: 164068. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164068 [11] CORRADINI F, MEZA P, EGUILUZ R, et al. Evidence of microplastic accumulation in agricultural soils from sewage sludge disposal[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 671: 411-420. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.368 [12] CHOUDHURY A, SIMNANI F Z, SINGH D, et al. Atmospheric microplastic and nanoplastic: The toxicological paradigm on the cellular system[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2023, 259: 115018. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115018 [13] JIA Q, DUAN Y, HAN X, et al. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the megalopolis (Shanghai) during rainy season: Characteristics, influence factors, and source[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 847: 157609. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157609 [14] WEN X, YIN L, ZHOU Z, et al. Microplastics can affect soil properties and chemical speciation of metals in yellow-brown soil[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 243: 113958. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113958 [15] WANG L, YANG H, GUO M H, et al. Adsorption of antibiotics on different microplastics (MPs): Behavior and mechanism[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 863: 161022. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161022 [16] SHEN M, ZENG Z, LI L, et al. Microplastics act as an important protective umbrella for bacteria during water/wastewater disinfection[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 315: 128188. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128188 [17] CASTRO-CASTELLON A T, HORTON A A, HUGHES J M R, et al. Ecotoxicity of microplastics to freshwater biota: Considering exposure and hazard across trophic levels[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 816: 151638. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151638 [18] SONG X, DU L, SIMA L, et al. Effects of micro(nano)plastics on the reproductive system: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 336: 139138. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139138 [19] ROCHMAN C M. Microplastics research—from sink to source[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6384): 28-29. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7734 [20] LEBRETON L C M, VAN DER ZWET J, DAMSTEEG J W, et al. River plastic emissions to the world's oceans[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 15611. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15611 [21] FAN Y, ZHENG K, ZHU Z, et al. Distribution, sedimentary record, and persistence of microplastics in the Pearl River catchment, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 251: 862-870. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.056 [22] YUAN W, LIU X, WANG W, et al. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in water, sediments, and wild fish from Poyang Lake, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 170: 180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.126 [23] LI J, OUYANG Z, LIU P, et al. Distribution and characteristics of microplastics in the basin of Chishui River in Renhuai, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 773: 145591. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145591 [24] DAI L, WANG Z, GUO T, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of microplastics in the Qiantang River in southeastern China[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 293: 133576. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133576 [25] MIN R, MA K, ZHANG H, et al. Distribution and risk assessment of microplastics in Liujiaxia Reservoir on the upper Yellow River[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 320: 138031. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138031 [26] 纪义虎, 左其亭, 马军霞. 基于Tapio和LMDI模型的沁河流域碳排放与水资源利用脱钩关系分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2023, 39(4): 94-101. [27] 刘强军, 牛晨煜, 赵珺. 黄河中游沁河流域汛期降水特征及突变分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(11): 19-22. [28] TOMLINSON D L, WILSON J G, HARRIS C R, et al. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index[J]. Helgolä nder Meeresuntersuchungen, 1980, 33(1): 566-575. [29] LITHNER D, LARSSON Å, DAVE G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2011, 409(18): 3309-3324. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.038 [30] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [31] PENG G, XU P, ZHU B, et al. Microplastics in freshwater river sediments in Shanghai, China: A case study of risk assessment in mega-cities[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 234: 448-456. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.034 [32] EVERAERT G, VAN CAUWENBERGHE L, DE RIJCKE M, et al. Risk assessment of microplastics in the ocean: Modelling approach and first conclusions[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 1930-1938. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.069 [33] 赵长民, 和兵, 李和通, 等. 汜水河(荥阳段)入河排污口水体微塑料赋存特征及风险评估 [J/OL]. 环境科学: 1-17. DOI:10.13227/j.hjkx.202304057. [34] BROWNE M A, CRUMP P, NIVEN S J, et al. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: sources and sinks[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(21): 9175-9179. [35] 周刚, 徐晨烨, 沈忱思, 等. 微塑料在淀山湖水环境的污染分布、组成特征和生态风险[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(4): 214-224. [36] 山泽萱, 张妍, 张成前, 等. 渭河微塑料污染现状与风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(1): 231-242. [37] 周泽妍, 王思琦, 张盼月, 等. 白洋淀-府河入淀口段沉积物中微塑料的丰度及分布特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(1): 360-367. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202003181 [38] 门聪, 李頔, 左剑恶, 等. 北京市通州区河流中微塑料组成的空间分布及潜在来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(7): 3656-3663. [39] YAN M, NIE H, XU K, et al. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in the Pearl River along Guangzhou city and Pearl River estuary, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 217: 879-886. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.093 [40] ZHANG Z, ZULPIYA M, WANG P. Occurrence and sources of microplastics in dust of the Ebinur lake Basin, northwest China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2023, 45(5): 1461-1474. doi: 10.1007/s10653-022-01279-9 [41] 郝若男, 史小红, 刘禹, 等. 乌梁素海水体微塑料空间分布规律及影响因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(7): 3316-3324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.07.035 [42] 孙雪纯, 侯书贵, 黄壬晖, 等. 可可西里特拉什湖中微塑料污染特征、来源和生态风险[J]. 环境科学学报, 2023, 43(2): 231-240. [43] 范梦苑, 黄懿梅, 张海鑫, 等. 湟水河流域地表水体微塑料分布、风险及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10): 4430-4439. -




 下载:
下载: