-
我国养殖行业面临日益严峻的畜禽养殖废弃物利用率低、农业面源污染等问题[1]。农村能源结构仍以化石能源为主,能量利用率低,过程中伴随着温室气体和有害气体的排放,制约“碳达峰、碳中和”背景下的乡村能源转型[2]。党的二十大报告提出:“要全面推进乡村振兴,坚持农业农村优先展;要提升环境基础设施建设水平,推进城乡人居环境整治,推动绿色发展,促进人与自然和谐共生”。如何有效综合利用农业农村废弃物开展资源化,建设养殖场循环经济产业链,是目前养殖业粪污处理技术亟需解决的问题[3]。热电联供系统是一项非常有潜力的技术,具有高能源利用率、低碳效益和灵活的负荷调节能力[4]。基于沼气的热电联供系统是实现畜禽养殖废弃物资源化循环利用的重要技术手段。同时,分析沼气热电联供系统的工作原理和特性,建立仿真模型,对热电联供系统的优化调度、控制规划等方面具有重要意义。
近年来,国内外学者在农业废弃物热电联供系统建模与分析方面开展了相关研究工作。万鹏[5]利用TRNSYS平台建立了太阳能-发电余热加热沼气池系统的系统动态仿真模型,模拟分析了在北方地区系统的运行情况。黄显昆[6]利用Aspen plus流程模拟平台构建了沼气发电与好氧发酵余热联合驱动的分布式冷热电联供系统,并对系统性能进行了模拟分析与优化。苏博生[7]提出了沼气与太阳能热化学互补方法与系统,分析了能量转换规律与性能提升机理,并研制了热化学反应实验平台,并对能量转化机理进行了实验验证。HARALD等[8]分析并提出了一种用于在地中海条件下向热电联供系统供应生物质的优化模型,并评估了橄榄果渣、果核、葡萄园修剪残留物和其他木质纤维素生物质的优劣势。上述文献从多种能源结合、多种发酵方式结合、探索新型生物质发酵等角度,对热电联供系统开展了建模研究工作,而基于实际现场工艺流程,搭建仿真模型的研究较少。
在厌氧发酵产气过程中,沼气产量受多种因素的影响,如进料量、发酵温度、料液pH等。刘小川[9]设计了基于支持向量机 (support vector machine, SVM) 的厌氧消化系统的连续投料模型并对自制厌氧消化反应器的生物气产生量进行了分类预测。花亚梅等[10]采用改进BP(Back propagation)神经网络算法,根据厌氧发酵机理以及实际工程运行状况,建立以温度、pH作为输入层节点,沼气日产气量为输出层节点的预测模型。费凡等[11]分析沼气热电联供系统的进料量与产气量关系,得到拟合关系曲线和关系式,以此代表每个罐体进料量与产气量的关系。以上文献分析了不同温度、进料量、pH等因素对产气量的影响关系,然而未考虑外部环境因素 (如强降雨) 的多变性对沼气产量的影响。实际上,当夏季强降雨混入发酵料液中,会使料液的底物浓度与密度发生变化,使发酵罐有机负荷(organic loading rate,OLR)降低,进而引起沼气产量的变化[12]。因此,有必要考虑降雨量,建立更接近工程实际的养殖场沼气热电联供系统数学模型,以精确反映多变的外部环境下系统实际运行特性。
本研究以某奶牛养殖场沼气热电联供系统为研究对象,建立厌氧发酵罐、沼气净化装置、储气罐、内燃机发电机组、缸套水换热器、沼气锅炉、蓄热水箱的数学模型;并拟在甲烷容积产气率模型基础上考虑降雨量对沼气产量的影响,建立计及降雨量的日沼气产量模型使整个系统模型更贴合实际工程。在MATLAB/Simulink平台上进行仿真分析,结合实际运行数据,验证仿真模型的正确性与有效性;然后在验证仿真模型正确性基础上建立日净收益模型,利用仿真模型分别模拟计算不考虑降雨与考虑降雨时的系统日净收益并与实际日净收益对比分析分析;最后针对1月份发电机与沼气锅炉的沼气用量合理分配问题,利用日净收益模型计算分析不同进料量条件下发电机的最佳沼气用量以提高系统的经济效益,以期为实施热电联供系统的优化调度、控制规划等提供参考。
-
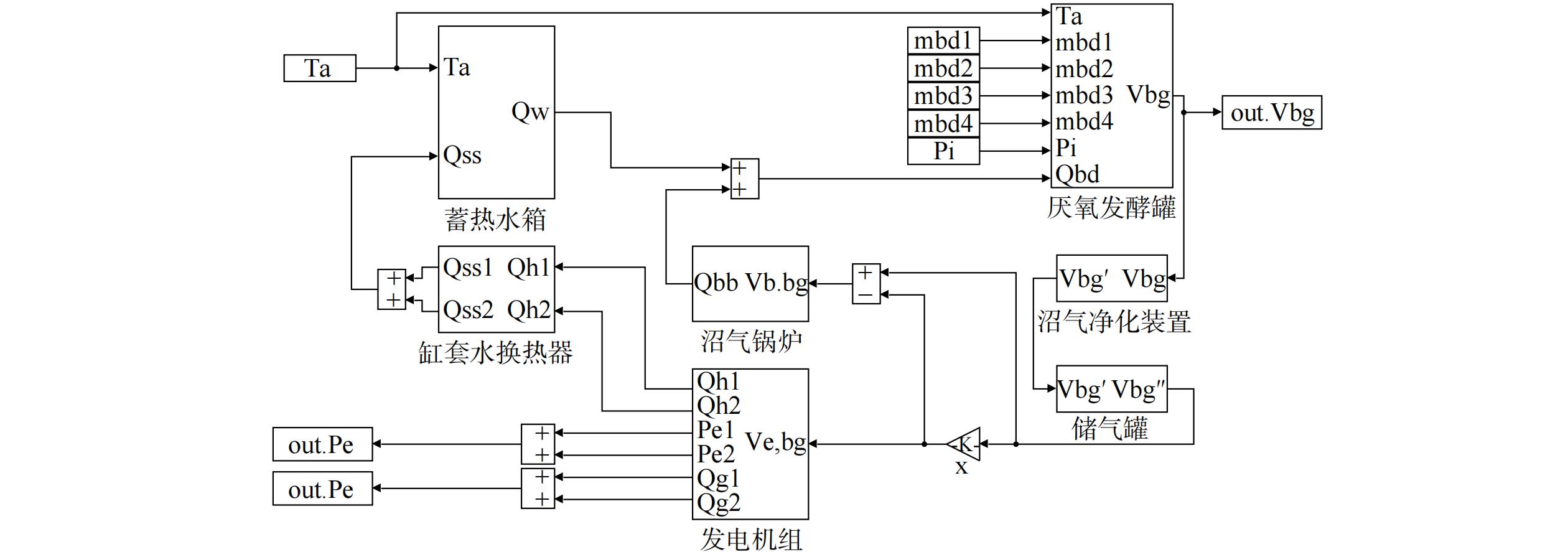
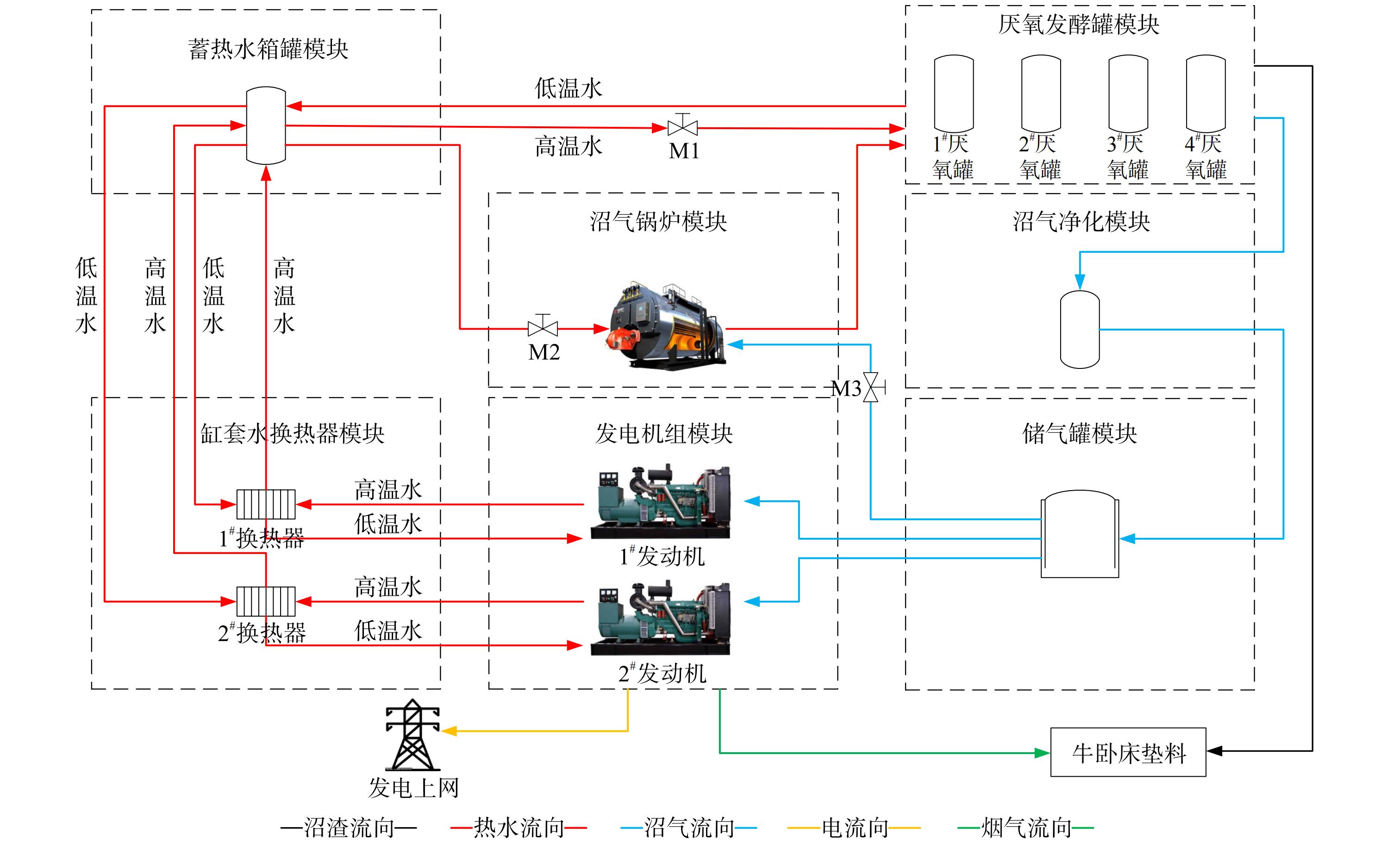
本研究以河北省衡水市某奶牛养殖场沼气热电联供系统为研究对象。系统主要由厌氧发酵罐模块、净化除硫模块、储气罐模块、沼气发电模块、缸套水换热器模块、蓄热水箱模块、沼气锅炉模块组成。系统结构及能流关系如图1所示。
养殖场牛粪尿经收集后于露天沉砂池储存。而后对沼气发酵料液进行预处理,主要是为了保证发酵料液处于厌氧发酵生产沼气的最佳状态[13]。经预处理池调节后进入厌氧发酵罐进行发酵。发酵后产生的沼气通过沼气净化装置、储气罐后作为内燃发动机燃料,通过燃烧膨胀做功产生原动力,带动发电机发电。发电机发电的同时产生约500 ℃的高温烟气和约80 ℃的缸套水。回收的缸套水热量进入蓄热水箱用于厌氧发酵罐保温;高温烟气用于烘干牛卧床垫料。发酵后的料液通过固液分离系统可将沼液和沼渣分开,沼液可用于有机饲料种植,沼渣用作生产牛卧床垫料的原料。图中M1~M3为流量阀门。实际调研结果表明,1月份为衡水市全年气温最低的月份,发电机余热不足以达到发酵罐厌氧发酵的热量需求,需开启沼气锅炉辅助加热。此时打开阀门M2与M3,关闭M1。其余月份发电机余热充足,完全可满足厌氧发酵的热需求量,打开M1阀门,关闭M2与M3阀。
-
厌氧发酵模块分为热平衡模型与日沼气产量模型两部分。现场厌氧发酵罐形状为圆柱形,数量为4。4个厌氧发酵罐目前全部投入使用且形状与构造完全相同。厌氧发酵类型为中温发酵。
1) 热平衡模型。为了便于模型的构建,引入以下5个假设条件。假设整个运行过程中只有下述5种热量交换,忽略添加新料液和去除旧料液混入混出的少量空气而引起的热量变化;假设发酵罐底部地面温度等于环境温度;假设厌氧罐各部分搭建物连接之间没有缝隙;假设实际场景中搅拌热扰不影响发酵池内的热环境;假设所测得的发酵罐的各个结构的厚度与面积完全准确。单个发酵罐的热平衡模型如式 (1) 所示。
式中:
$\Delta Q$ 为发酵罐内部变化热量,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{-1}}$ ;${Q_1}$ 为厌氧罐加热盘管加热量,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{ - 1}}$ ;${Q_2}$ 为加热新进料液耗热量,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{-1}}$ ;${Q_3}$ 为发酵罐散热量,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{-1}}$ ;${Q_4}$ 为沼气带走的显热损失,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{-1}}$ ;${Q_5}$ 为水蒸气蒸发耗热量,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{-1}}$ 。每个厌氧罐加热盘管加热量如式 (2) 所示。
式中:
$a$ 为该厌氧罐所需热量占蓄热水箱总加热量的比重;$ Q\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为蓄热水箱为全部厌氧罐加热的热量,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{{ - 1}}}}$ 。为保证厌氧发酵的高效运行,必须将发酵料液加热至适宜温度所需热量为
${Q_2}$ (式 (3))[14]。式中:
$ m\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为新进料液的流量,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{{ - 1}}}}$ ;$ c\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为发酵料液的比热,${\text{kJ}} \cdot {\left( {{\text{kg}} \cdot {\text{K}}} \right)^{ - 1}}$ ;$ T\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为发酵罐内发酵温度,${\text{K}}$ ;$ T_{\mathrm{m}} $ 为料液进入发酵罐之前的温度,${\text{K}}$ 。发酵罐加热的同时,发酵罐内也会有部分热量散发到空气和周围其他介质中去。发酵罐的热损失主要来自于发酵罐顶部、侧壁面、底部向周围环境中的散热[15]。散热量如式 (4) 所示。
式中:
${K_i}$ 为罐顶、罐壁和罐底各部分的综合传热系数,${\text{W}} \cdot {\left( {{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}} \cdot {\text{K}}} \right)^{ - 1}}$ ;$S{}_i$ 为各部分的传热面积,${{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ ;${T_i}$ 为各部分发酵罐外综合温度,${\text{K}}$ 。沼气在被及时排走的同时,也会带走一部分热量[16]。该热量如式 (5) 所示。
式中:
${f_{{{\mathrm{CH}}_4}}}$ 为甲烷体积占排出沼气体积的比例;$v$ 为发酵罐有效容积,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ ;${\gamma _v}$ 为甲烷的体积产率,${\text{kg}} \cdot {\left( {{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {\text{d}}} \right)^{ - 1}}$ ;$ T\mathrm{_a} $ 为外界空气温度,${\text{K}}$ 。水蒸气蒸发带走的热量损失是沼气排出带走的水蒸气导致的[16]。该热量如式 (6) 所示。
式中:
$ H\mathrm{_w} $ 为水蒸汽在发酵温度下的汽化潜热值,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {\text{k}}{{\text{g}}^{-1}}$ ;$ c_{\mathrm{g}} $ 为水蒸气的比热容,${\text{kJ}} \cdot {\left( {{\text{kg}} \cdot {\text{K}}} \right)^{ - 1}}$ ;$ W\mathrm{_w} $ 为沼气流携带的水蒸气的质量流量,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{-1}}$ ;$ X\mathrm{_w} $ 为沼气中所含的水分子份数。2) 计及降雨量的日沼气产量模型。为了便于模型的构建,假设发酵罐内各种物质的物理属性值为理想值。根据相应的甲烷体积产率和质量守恒可以求出日沼气产量。本研究所应用的甲烷动态产率计算依据为Chen和Hashimoto给出的粪便类的甲烷动态产率模型[17]。该模型如式 (7) 所示。
式中:
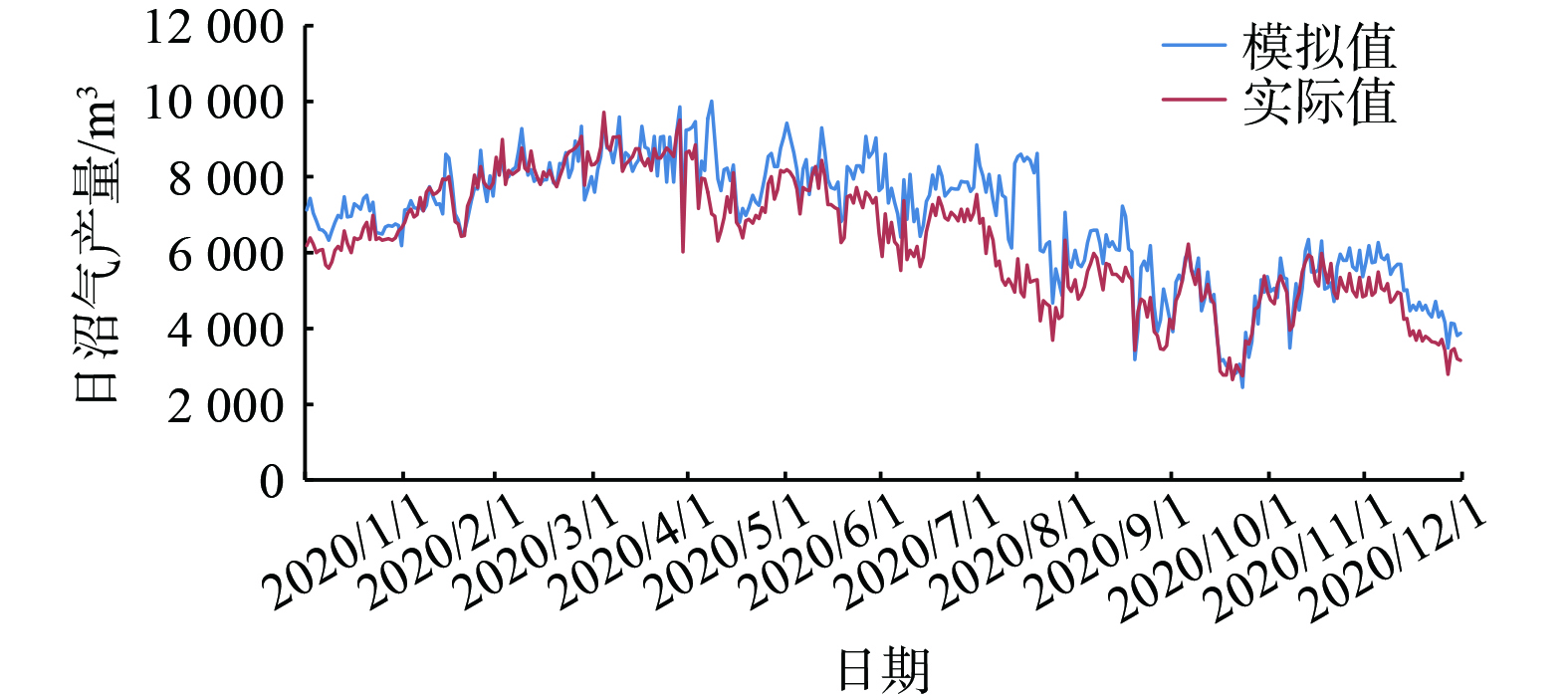
${\gamma _v}$ 为甲烷体积产气率,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {\left( {{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {\text{d}}} \right)^{ - 1}}$ ;${B_0}$ 为牛粪极限甲烷产率,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {\text{k}}{{\text{g}}^{-1}}$ ;${S_0}$ 为进料底物浓度,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}$ ;HRT为水力停留时间,${\text{d}}$ ;K为动力学参数;$ v\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为日进料量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ ;$ \mu\mathrm{_m} $ 为微生物最大生长比率,${{\text{d}}^{-1}}$ 。本研究首先尝试对不计及降雨量的养殖场沼气热电联供系统进行建模分析。该养殖场有4个形状与构造完全相同的沼气发酵罐,为节约研究成本与时间。本研究选用1号发酵罐进行验证。1号发酵罐全年日沼气产量模型仿真结果如图2所示。6、7、8、9月份日沼气产量模型模拟值与实际值的误差较大,且模拟值均高于实际值;其他月份时该模型的模拟值与实际值吻合性较好。
因误差较大的月份均为夏季,故认为误差较大原因与夏季有关。该养殖场地处河北省衡水市,其气候特点为冬季寒冷干燥,夏季高温多雨。经过现场调研,了解到该养殖场牛粪沉砂池为露天型,故推测造成6、7、8月份模型误差大与强降雨有关。夏季过多的降雨混入了露天粪池中的牛粪尿中,而预处理环节时仍按照无降雨天气时的固液比进行处理,进而使进入发酵罐的料液的底物浓度与密度与正常值产生了偏差,最终导致夏季时日沼气产量模拟值与实际值之间产生较大的偏差。故将发酵料液浓度与密度设为变量,建立降雨量模型,更接近工程实际。降雨量相关数据通过查询中国气象网获得。
经过调研发现,当出现强降雨时,降雨对料液浓度的影响会持续多天。设某天有强降雨,其降雨量值为
$p$ ,则$p$ 如式 (8) 所示。式中:
${p_i}$ 为混入强降雨后第n天料液中的降雨量值,${\text{mm}}$ ;${a_i}$ 为强降雨后第n天料液池中水的蒸发量,${\text{mm}}$ 。发酵料液的浓度如式 (9) 所示。
发酵料液的密度如式 (10) 所示。
式中:
${S_0}$ 为混入雨水后的进料底物浓度,$ \text{kg}\cdot\text{m}^{-3} $ ;${S_{00}}$ 为料液正常情况的进料底物浓度,$ \text{kg}\cdot\text{m}^{-3} $ ;$ v_{\mathrm{bd}0} $ 为不包含降雨的料液量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ ;$ v\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为包含降雨的料液量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ ;$ v_{\mathrm{w}} $ 为混入料液的雨水的体积,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ ;$ \rho\mathrm{_w} $ 为雨水的密度,取水的密度,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{- 3}}}}$ ;$p$ 为混入料液中的降雨量值,${\text{mm}}$ ;$ \rho\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为混入雨水后料液的密度,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{- 3}}}}$ ;$ v_{\mathrm{bd}0} $ 为不包含雨水的料液体积,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ ;$ \rho_{\mathrm{bd}0} $ 为正常料液密度,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{- 3}}}}$ ;$S$ 为沉砂池的面积,${{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ 。将式 (9) 代入到式 (7) 中可得计及降雨量的甲烷容积产气率模型,如式 (11) 所示。
根据质量守恒原理,计及降雨量的日沼气产量的数学模型如式 (12) 所示[14]。
式中:
$ V\mathrm{_{bg}} $ 为日产沼气体积,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{{- 1}}}}$ ;$ m\mathrm{_{bg}\mathrm{ }} $ 为日产沼气质量,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{{- 1}}}}$ ;$ f_{\mathrm{CH}_4} $ 为甲烷体积占排出沼气体积的比例;$ \rho_{\mathrm{bg}} $ 为沼气密度,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{- 3}}}}$ ;$ m\mathrm{_{bd}} $ 为罐内料液质量,${\text{kg}}$ ;$ \rho_{\mathrm{bd}} $ 为发酵料液密度,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{- 3}}}}$ ;${\rho _{{{\mathrm{CH}}_4}}}$ 为甲烷密度,${\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{- 3}}}}$ 。 -
沼气主要由甲烷、二氧化碳以及少量其它气体构成[18]。净化系统的作用主要为除去沼气中的硫化氢和水蒸气[19]。净化后的沼气流量如式 (13) 所示。
式中:
$ V'\mathrm{_{bg}} $ 为净化后的沼气流量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{ - }}}^1$ ;${x_{{{\mathrm{H}}_2}{\mathrm{O}}}}$ 为沼气中水的含量;${x_{{{\mathrm{H}}_2}{\mathrm{S}}}}$ 为沼气中硫化氢的含量。 -
储气罐的沼气进气流量与沼气输出流量相等,其流量如式 (14) 所示。
式中:
$ V_{\mathrm{bg}}^{''} $ 为经过储气罐后的沼气流量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{{ - 1}}}}$ 。 -
沼气锅炉主要作用为在1月份缸套水换热器提供的热量不足以为厌氧发酵供热时,沼气锅炉通过燃烧沼气为发酵罐供热。其产生的热量如式 (15) 所示[20]。
式中:
$ Q_{\mathrm{bb}} $ 为沼气锅炉所产生的热量,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{{ - 1}}}}$ ;$ V_{\mathrm{b,bg}} $ 为用于沼气锅炉的沼气流量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{{ - 1}}}}$ ;$ Q_{\mathrm{bg}} $ 为沼气的热值,${\text{MJ}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{ - 3}}}}$ ;$ \eta\mathrm{_b} $ 为锅炉的效率。 -
发电机组为内燃机发电机组,数量为2台。两台发电机型号完全一致,故只需对一台内燃机发电机进行分析。表1为发电机的相关能量参数表。在发电机负载率大于等于50%时,发电机的各种能量输出与能量输入基本上呈线性关系,故可求得电功率、缸套水热量、烟气热量与沼气输入流量之间的关系式。发电机能量公式如式 (16) 所示。
式中:
$ P\mathrm{_e} $ 为发电机的电功率,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ Q\mathrm{_h} $ 为发电机的缸套水的热量,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ Q\mathrm{_g} $ 为发电机的排出的烟气的热量,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ V\mathrm{_{e,bg}} $ 为用于发电的沼气流量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}} \cdot {{\text{d}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$ 。 -
缸套水换热器数量为2台,型号完全一致。缸套水换热器换出的热量如式 (17) 所示。
式中:
$ Q\mathrm{_{ss}} $ 为缸套水换热器换出的热量,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ \eta\mathrm{_{ss}} $ 为缸套水换热器的换热效率。 -
蓄热水箱的作用为收集缸套水的热量并为厌氧发酵罐供热。提供的热量如式 (18) 所示。
式中:
$ Q\mathrm{_l} $ 为蓄热水箱散失的热量,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ T_{\mathrm{w}} $ 为水箱内水温,${\text{K}}$ ;$ M\mathrm{_w} $ 为水箱内水的质量,${\text{kg}}$ ;$ c_{\mathrm{w}} $ 为水的比热,$ {\text{kJ}} \cdot {{\text{(kg}} \cdot {\text{K)}}^{{{ - 1}}}} $ ;$ U_{\mathrm{t,e_{ }}} $ 为水箱的散热系数,${\text{W}} \cdot {\left( {{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}} \cdot {\text{K}}} \right)^{ - 1}}$ ;$ A\mathrm{_{wt}} $ 为水箱的表面积,${{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$ 。 -
基于上述沼气热电联供系统的数学模型,在MATLAB/Simulink平台上搭建该系统的仿真模型进行仿真,模型中参数均由实际工程给出 (图3) 。
-
本研究利用2020年全年相关生产数据对模型进行正确性验证。因该热电联供系统结构复杂、设备繁多,本研究仅对日沼气产量模型与日发电量模型进行验证与分析。在分析模型的结果时,采用常用的统计方法线性回归决定系数R2 (R-Square) 、均方根误差RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) 和平均相对误差MRE (Mean Relative Error) 这三种数学方式来分析模型的准确性。一般认为,R2越接近于1,两者之间的相关性越好;0.8<R2<1,有较强相关性;0.6<R2<0.8,有强相关性;0<R2<0.2,相关较差或没有相关性[21]。RMSE与MRE越小,表示模型准确度越高。
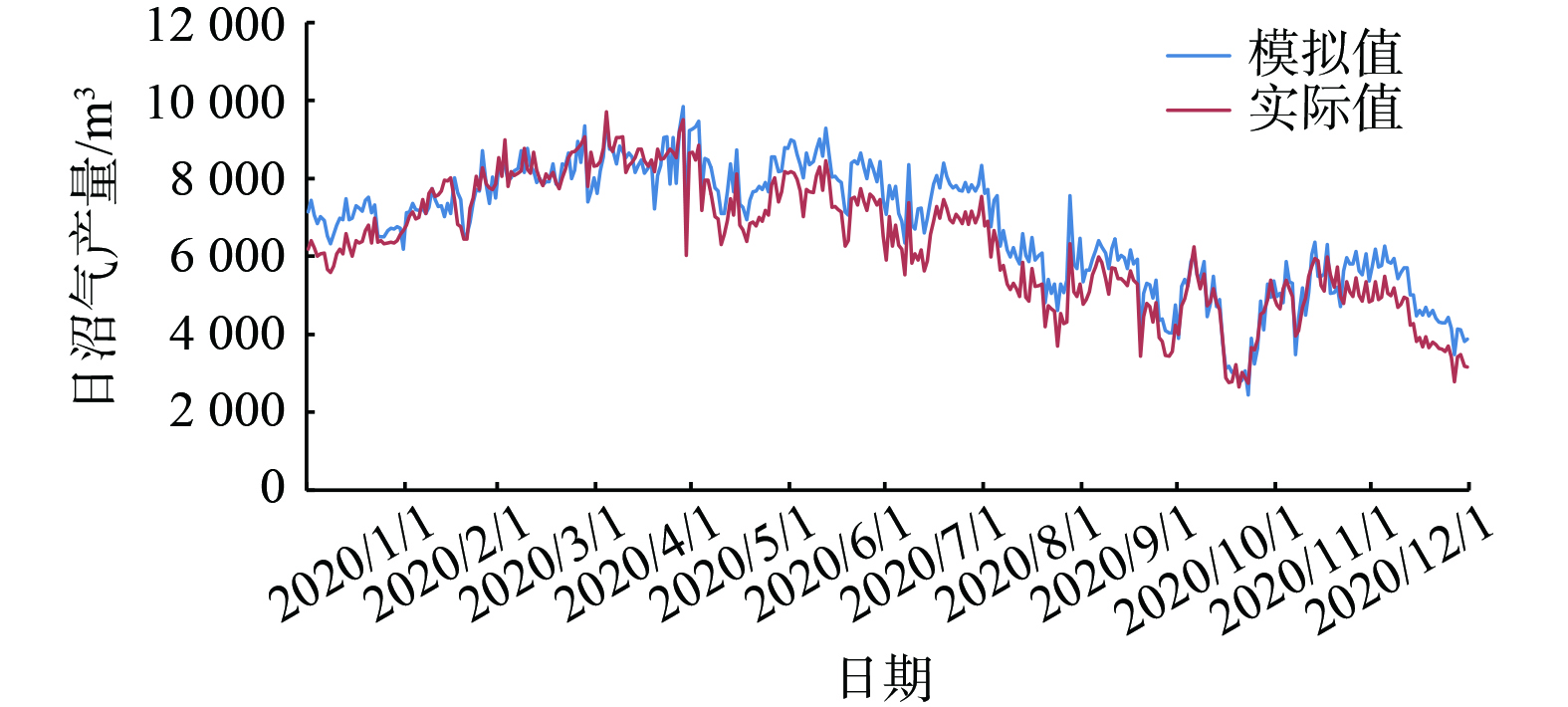
1) 厌氧发酵日沼气产量模型的验证。日沼气产量仿真结果如图4所示。夏季时模拟值与实际值的吻合性有了显著的提高,故确定日沼气产量模型夏季误差大的确与强降雨有关。有无降雨量模型时夏季日沼气产量的仿真精确性对比分析如表2所示。考虑降雨量的日沼气产量仿真模型,其各项指标的精确性有显著提升。
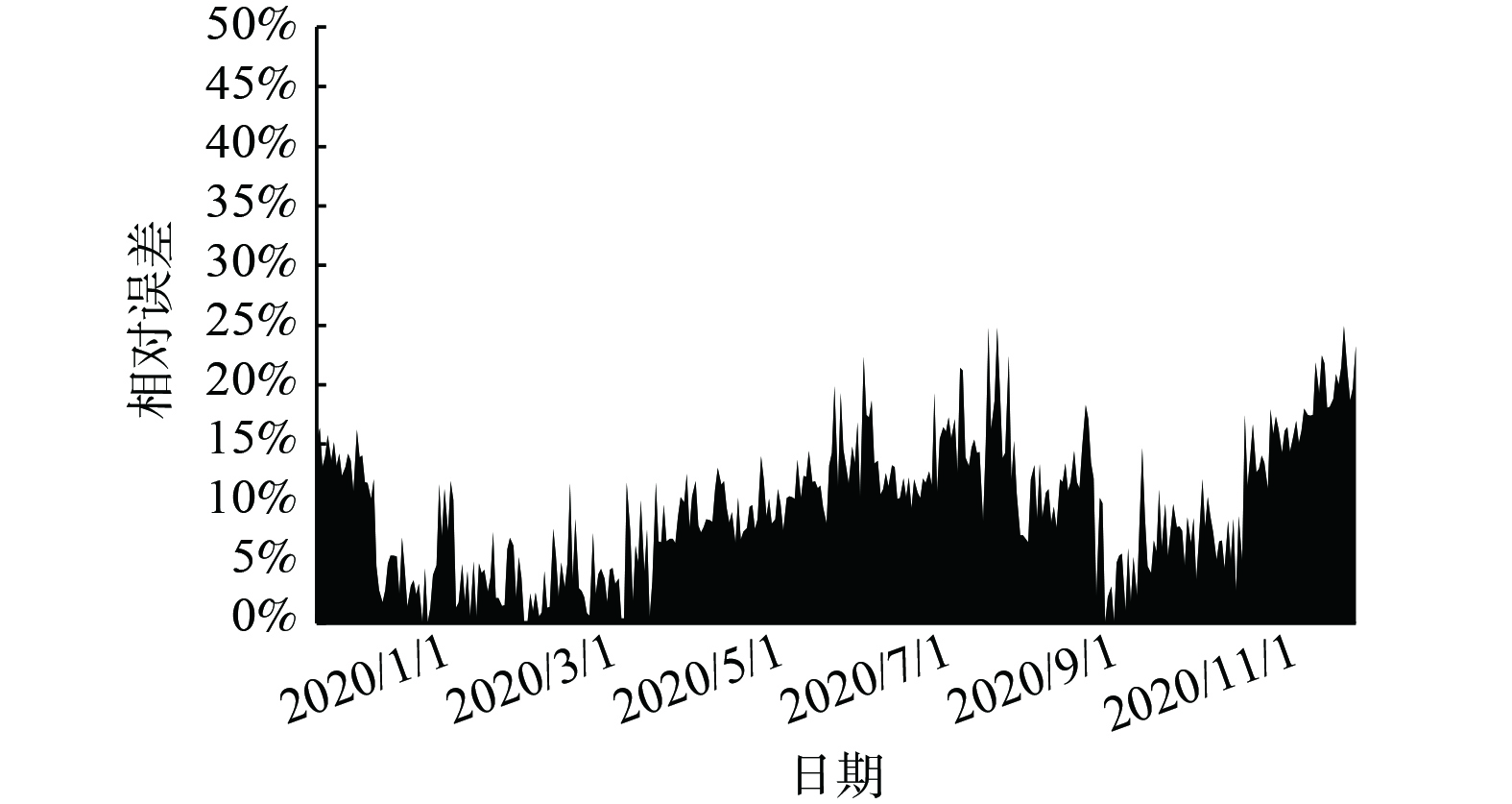
日沼气产量模型相对误差图如图5所示。虽然通过建立降雨量模型使仿真精度有了提高,但冬夏季误差与春秋季相比仍然较大。调研得知在夏季温度较高时,为确保奶牛的健康,养殖场会对奶牛进行喷淋降温,而喷淋水混入粪污中会造成料液浓度的偏差。其次,冬季的气温过低会导致料液结块,为了促进料液在粪道中流动而采用水流冲刷,此方法也会造成料液浓度的偏差。但该模型的模拟值与实际值之间R2达到0.73,RMSE为641.01 m3,MRE为9.73%。这表明模拟值与实际值之间有强相关性,且本模型具有有效性。
2) 发电机组日发电量模型的验证。发电机组模型的验证采用日发电量数据对模拟值与实际值进行对比验证。本研究利用2020年1月份日发电量数据对发电机组仿真模型进行精确性验证。发电机组模型的模拟值与实际值之间R2达到0.70,RMSE为698.86 kWh,MRE为12.43%。而由于R2达到0.70,故认为实际值与模拟值之间有强相关性,且本模型具有有效性。造成发电机组日发电量误差的原因可能有:建立发电机组仿真模型所依据的数学模型由发电机组设备参数近似拟合而来,故造成仿真模型结果与实际值的误差;发电机组仿真模型的输入值为沼气量,其由发酵罐仿真模型输出而得,沼气产量模拟与实际的误差也会造成发电机组模型的误差。仿真实验结果表明,本研究建立的养殖场沼气热电联供系统模型能较近似地反映发酵罐与发电机组模型相关参数的变化情况。仿真结果与实际所得数据之间会存在一定偏差,但仿真结果可近似地反映出养殖场沼气热电联供系统实际变化规律,可为实施热电联供系统的优化调度、控制规划提供理论参考。
-
本研究在计及降雨量的养殖场沼气热电联供系统仿真模型基础上建立系统日净收益模型,并对计及降雨量的日净收益、不计及降雨量的日净收益 (将降雨量输入为0 mm) 、实际日净收益 (通过调研获得) 三者进行对比分析。日净收益E如式 (19) 所示[22]。
式中:
$ \mathrm{Inc} $ 为日收入,元;$ \mathrm{Cos} $ 为平均到每日的运行成本,元。日收入
$ \mathrm{Inc} $ 如式 (20) 所示,包括发电机组发电产生的收益与牛卧床垫料产生的收入。式中:
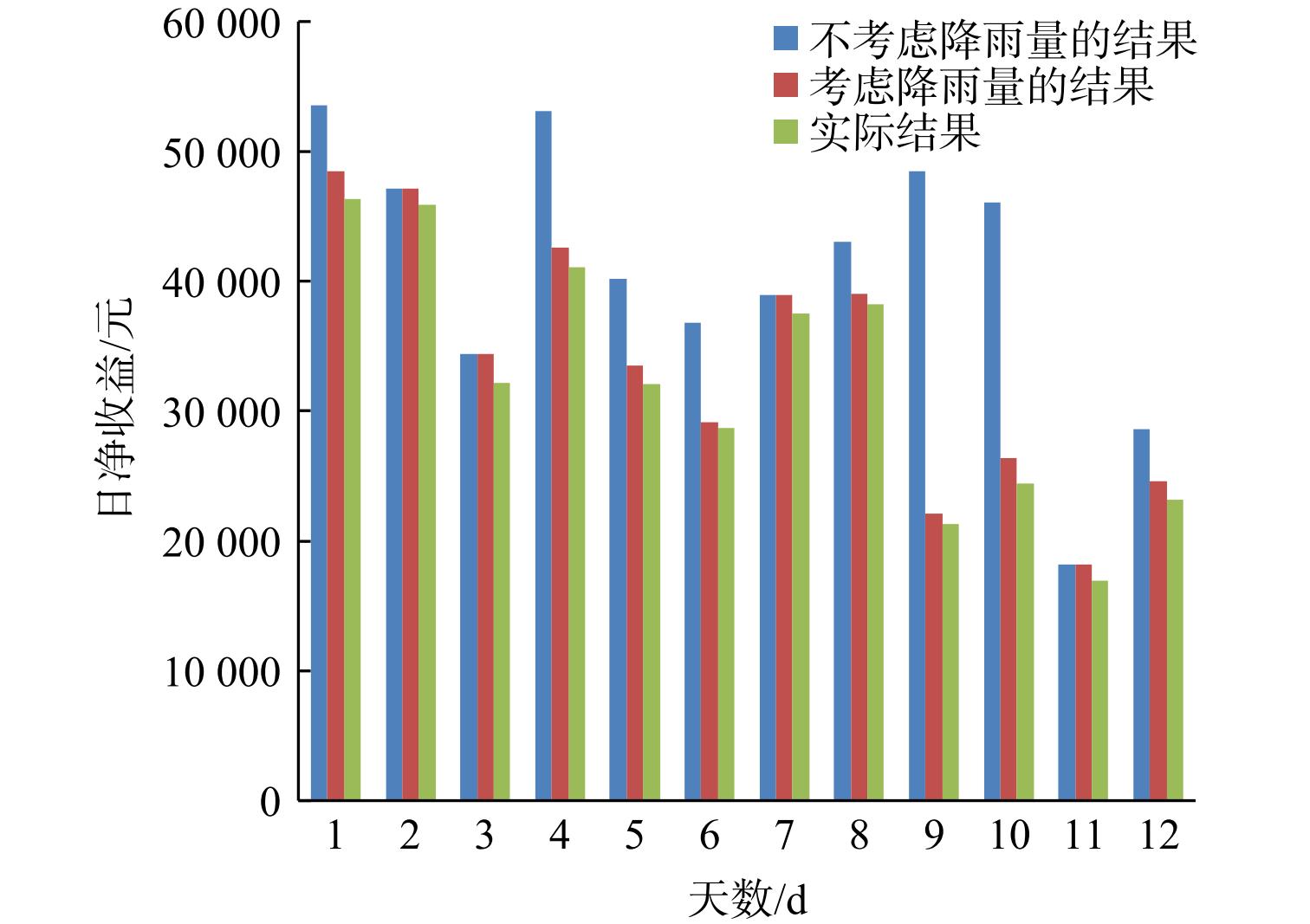
$ \mathrm{Inc_e} $ 为日发电收入,元;$ \mathrm{Inc_p} $ 为生产牛卧床垫料产生的收入,元;t为发电机运行时长,h;$ P\mathrm{_d} $ 为电价,$ 元\cdot {\text{kWh}}^{{-1}} $ ;$V$ 为每日产牛卧床垫料量,${{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ ;$ P\mathrm{_{cow}} $ 为牛卧床垫料单价,$ 元\cdot {\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ 。该养殖场所在地区6、7、8月份为雨季,本研究在该雨季每个月份中任选4 d (其中2 d为雨天,另外2 d为晴天) ,总计12 d。将每天相关数据输入仿真模型中,运行模型得到每天的净收益,结果如图6所示。不考虑降雨量的日净收益模拟值与实际日净收益值有着很大的偏差,且考虑降雨量的日净收益模拟值较不考虑降雨量的日净收益模拟值在准确性上有了很大提高。另外,无论有无降雨影响,日净收益模拟值均比实际值较高。原因是在某天系统不受降雨影响时,牛舍喷淋水 (因气温高通过喷淋对牛体表降温) 混入粪尿中会对发酵料液浓度和密度产生影响使模拟产气量偏高进而使日净收益模拟值偏高。目前尚缺少喷淋水相关数据,故无法对喷淋水对系统的影响进行分析研究。而在某雨天,系统受到降雨影响 (也受喷淋水影响) ,其产气量模拟值比实际值偏高;由产气量推算而出的日净收益模拟值自然比实际值较高。
-
前文分析的雨季经济效益表明,因雨季和除1月份其他月份外界温度较高,缸套水热量完全可满足发酵罐的热需求,此时不需要开启沼气锅炉加热,故不存在沼气分配问题。只有在1月份,由于外界环境温度低,仅依靠缸套水热量不足以维持发酵罐保温,需同时开启沼气锅炉提供热量。因此,如何对厌氧发酵产生的沼气进行合理分配使系统获得最佳经济效益是值得研究的问题。
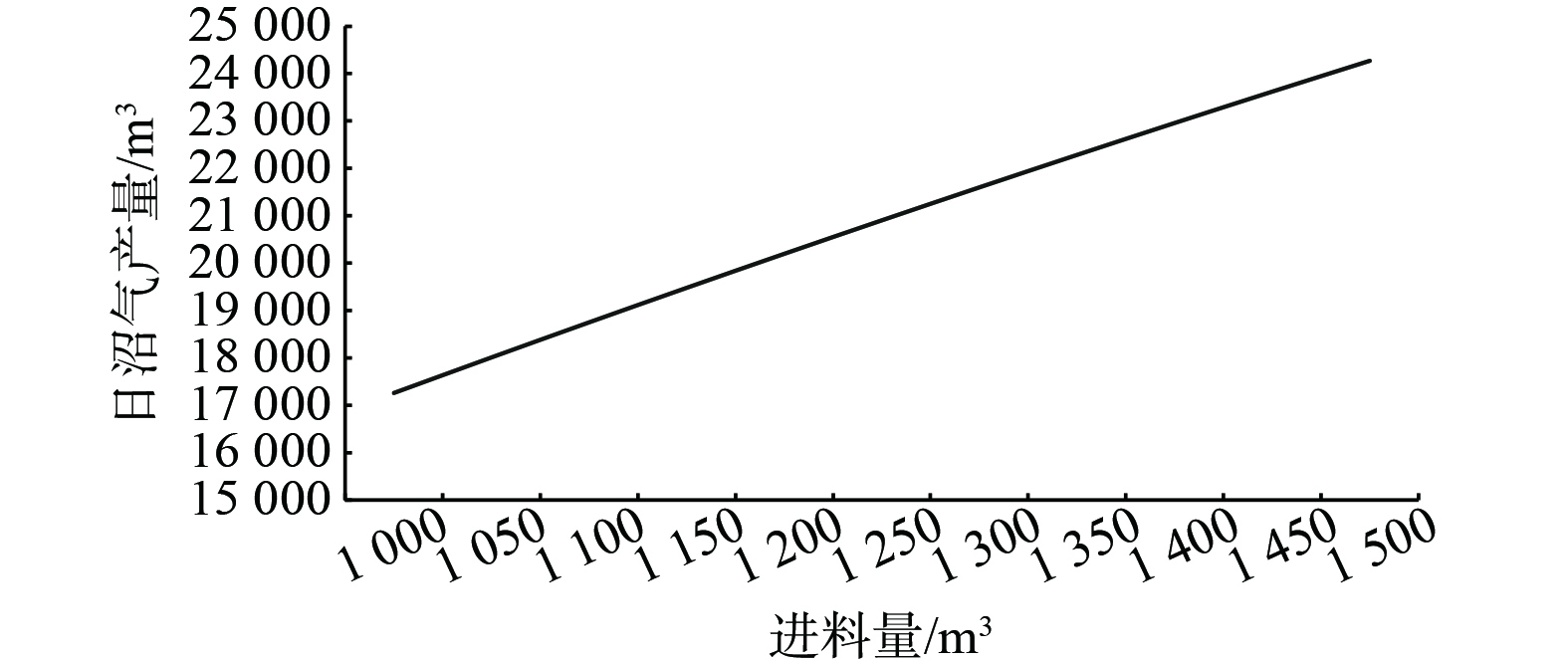
该地区冬季基本无降雨,故不考虑降雨影响。因此,本研究先利用仿真模型研究各种日进料量条件下的日沼气产量,并利用建立的日净收益模型研究1月份不同进料量条件下发电机不同沼气用量时系统的日净收益。该养殖场每天来料1 000~1 500 m3。故在仿真模型中,利用From Workforce模块,以50 m3为间隔分析日进料为1 000~1 500 m3时的产气状况。日沼气产量与日进料量的关系如图7所示。该仿真模型的约束条件如式 (21) 所示。
式中:
$ P\mathrm{_{e,\min}} $ 为发电机组最小功率,取额定功率的50%,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ P\mathrm{_{e,\max}} $ 为发电机组的额定功率,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ Q\mathrm{_{bb,\max}} $ 为沼气锅炉的额定功率,${\text{kW}}$ ;$ Q\mathrm{_N} $ 为厌氧发酵罐的热需求量,$ Q\mathrm{_N} $ 取值为进料量最多且环境温度最低时的热需求量,${\text{kW}}$ 。发电机负载率过大或过小都会对发电机本身造成不可逆转的伤害,故功率范围取50%~100%。蓄热水箱和沼气锅炉为厌氧发酵罐提供的热量必须满足任何时候发酵罐的热需求量,故另
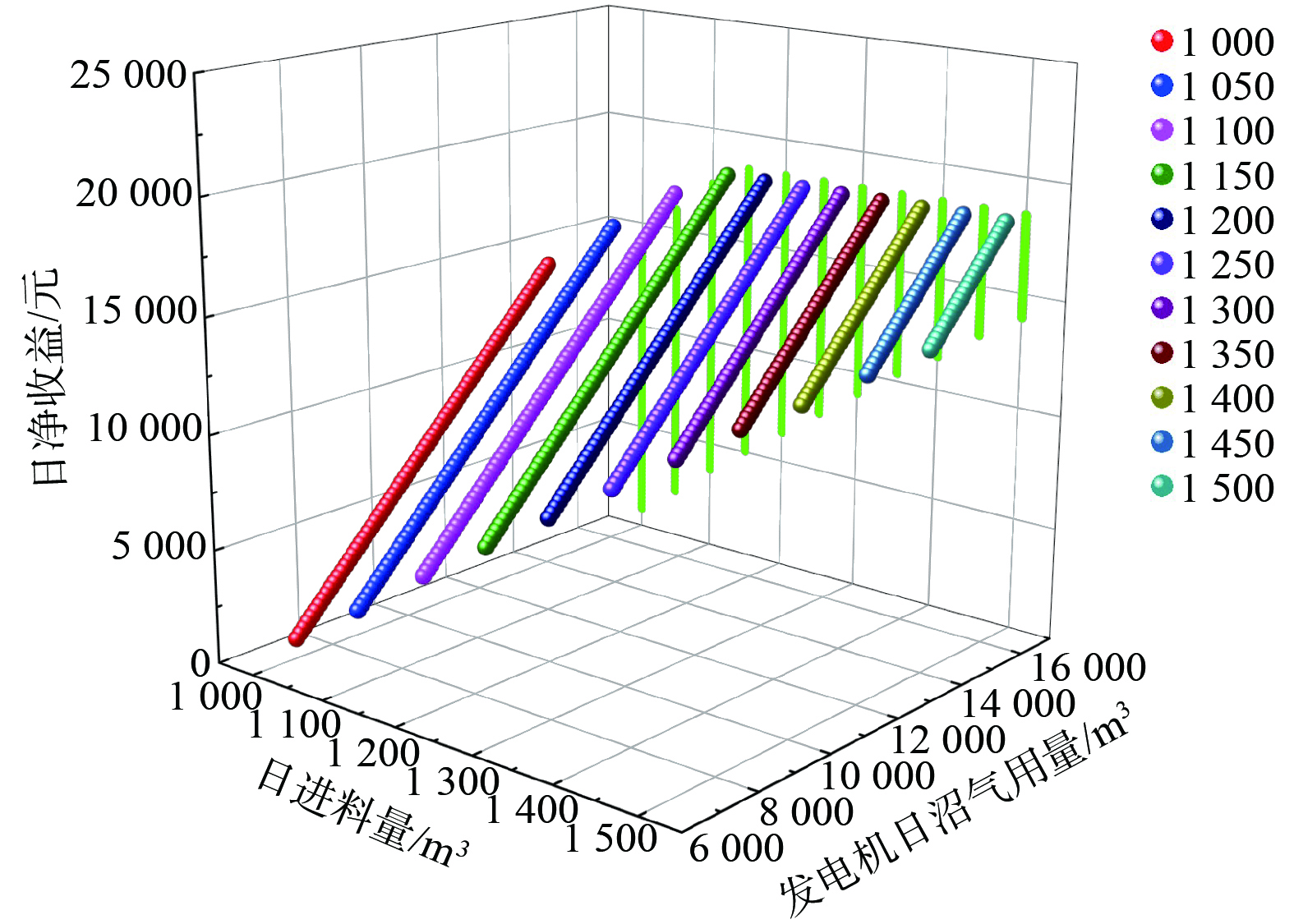
$ Q\mathrm{_{bd}}\geqslant Q\mathrm{_N} $ 。各种日进料量条件下发电机不同沼气用量所对应的日净收益如图8所示。对于一定的日进料量,日净收益总是随着发电机沼气用量的增加而增加。因日净收益主要源于发电上网和牛卧床垫料所得的收益,故日净收益与发电机沼气用量呈正相关关系。1) 当日进料量为1 000~1 150 m3时,每种日进料量的日净收益最大值随着日进料量的增加而增加。因为产气量随着进料量的增加而增加,在满足发酵罐热需求的同时可为发电机提供更多的沼气,故可产生更大的收益。2) 当日进料量为1 150~1 500 m3时,每种日进料量的日净收益最大值恒定不变,不会随沼气产量的增加而升高。因为此时发电机组已达满功率,再给发电机更多的沼气不会创造更多的收益,故日净收益最大值恒定不变。3) 在日进料量为1 150 m3且发电机日沼气用量为16 300 m3时,日净收益达到最大值。日进料量超过1 150 m3时,不仅没有使日净收益值有所提高,反而使多余的沼气无处利用。各种进料量条件下最佳发电机沼气量以及日净收益如表3所示。
-
1) 建立了养殖场沼气热电联供系统模型,可对实际场景进行有效仿真分析。模型模拟值与实测值波动趋势具有一致性。这表明仿真模型具有正确性和有效性,结果可为实施热电联供系统的优化调度、控制规划等提供理论参考。2) 考虑降雨量对沼气产量的影响,建立了更接近工程实际的计及降雨量的养殖场沼气热电联供系统模型,使雨季日沼气产量与实际产量更吻合、准确。3) 建立了以日净收益为指标的系统经济效益模型,利用已建立的仿真模型分析不考虑降雨量时、考虑降雨量时日净收益值与实际值的偏差。结果表明降雨对系统日净收益模拟结果造成了很大的偏差,并且计及降雨量后对日净收益模拟结果准确性有显著提高,再次验证了计及降雨量的养殖场沼气热电联供系统模型的有效性。4) 针对系统1月份沼气合理分配问题,利用MATLAB/Simulink平台分析1月份不同进料量条件下,发电机组不同沼气用量以及对应的系统日净收益。结果表明在1月份时,当日进料量等于1 150 m3且发电机沼气用量为16 300 m3时,系统的日净收益达到最大值。由于发电机满功率运行,即使再增加进料量,净收益值也不再增加。5) 本研究仅涉及降雨量的系统仿真模型,而由于缺乏喷淋水和冲刷水对料液浓度影响的现场数据,无法建立准确的数学模型,将在后续研究中做进一步分析。
计及降雨量的养殖场沼气热电联供系统建模与经济分析
Modeling and economic analysis of biogas cogeneration system for a dairy farm concerning rainfall
-
摘要: 针对夏季强降雨导致厌氧发酵沼气产量理论值偏离实际值的问题,构建计及降雨量的奶牛养殖场沼气热电联供系统仿真模型;然后利用仿真模型计算分析不考虑降雨时与考虑降雨时系统日净收益的偏差;最后探讨1月份发电机组与沼气锅炉的沼气合理分配问题以提高经济效益。首先基于实际现场能量流动关系,建立了厌氧发酵罐、沼气净化装置、储气罐、内燃机发电机组、缸套水换热器、沼气锅炉、蓄热水箱的数学模型。其次,考虑强降雨对料液浓度与料液密度的影响,建立降雨量模型,使雨季日沼气产量模拟值与实际值更吻合。然后在系统仿真模型基础上建立日净收益模型,分别模拟计算不考虑降雨与考虑降雨时的系统日净收益并与实际日净收益对比分析;最后利用日净收益模型求出不同日进料量条件下发电机组不同沼气用量所对应的日净收益,以确定各种进料量条件下的发电机组最佳沼气用量。利用养殖场2020年全年实际运行数据对沼气热电联供系统仿真模型进行正确性验证,建立降雨量模型后日沼气产量模拟值与实际值之间的线性回归决定系数由0.66提升至0.73;日发电量模拟值与实际值之间的线性回归决定系数为0.7;考虑降雨量后日净收益模拟值比不考虑降雨量的日净收益模拟值在准确性上有了很大提高。该研究结果表明,该模型对于该养殖场沼气热电联供系统的工艺流程模拟分析具有准确性和有效性,可为实施养殖场沼气热电联供系统的优化调度、控制规划等提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 奶牛养殖场沼气热电联供系统 /
- 仿真 /
- 厌氧发酵 /
- 降雨量 /
- 经济效益
Abstract: To address the issue of deviation between theoretical and actual values of anaerobic fermentation biogas production caused by heavy rainfall in summer, a simulation model of biogas cogeneration system in a dairy farm considering rainfall is constructed. The simulation model is then used to calculate and analyze the deviation between the daily net income of the system when rainfall is considered or not. The reasonable allocation of biogas between the power generation unit and biogas boiler in January is explored to improve economic benefits. Firstly, based on the actual on-site energy flow relationship, mathematical models of anaerobic fermentation tanks, biogas purification device, gas storage tank, internal combustion engine generator sets, cylinder liner water heat exchangers, biogas boiler, and heat storage water tank were established. Secondly, considering the impact of heavy rainfall on the concentration and density of feed liquid, a rainfall model is established to better match the simulated and actual values of daily biogas production during the rainy season. Then, based on the system simulation model, a daily net income model is established to simulate the daily net income of the system with and without considering rainfall, and compare the simulation results with the actual daily net income. Finally, the daily net income model is used to calculate the daily net income corresponding to different biogas consumption of the power generation unit under different daily feed conditions, in order to determine the optimal biogas usage rates of the power generation unit under various feed conditions. The simulation model of biogas cogeneration system was verified by using the actual operation data of the farm in 2020, and the linear regression coefficient of determination between the simulation value and the actual value of daily biogas production increased from 0.66 to 0.73 after incorporating the rainfall model. The linear regression coefficient of determination between the simulated value and the actual value of daily electricity generation was 0.7. The accuracy of the simulated daily net income after considering rainfall was greatly improved The simulation results demonstrated the effectiveness of the established model in simulating and analyzing the process flow of the biogas cogeneration system. The model can guide the implementation of optimal scheduling, control planning of the cogeneration system. -

-
表 1 发电机组能量参数
Table 1. Generator set energy parameters
沼气流量/ (m3·d−1) 负载率 电功率/kW 缸套水热量/kW 烟气热量/kW 1.63×104 100% 1560 897 710 1.28×104 75% 1170 680 595 8 800 50% 780 465 474 表 2 有无计及降雨量的日沼气产量仿真模型精确性对比分析
Table 2. Comparative analysis of accuracy of daily biogas production simulation models with and without considering rainfall
指标 无降雨量模型 有降雨量模型 R2 0.66 0.73 RMSE 889.80 m3 641.01. m3 MRE 11.93% 9.73% 表 3 各种日进料量条件下最佳发电机沼气用量及对应的最佳日净收益
Table 3. The optimal amount of biogas used in generators and the corresponding optimal daily net income under various daily feed conditions
日进料量/m3 发电机最佳沼气用量/m3 最佳日净收益/元 1 000 14 100 14 181.23 1 050 15 000 15 891.76 1 100 15 800 17 412.23 1 150 16 300 18 362.52 1 200 16 300 18 362.52 1 250 16 300 18 362.52 1 300 16 300 18 362.52 1 350 16 300 18 362.52 1 400 16 300 18 362.52 1 450 16 300 18 362.52 1 500 16 300 18 362.52 -
[1] 吴信, 万丹, 印遇龙. 畜禽养殖废弃物资源化利用与现代生态养殖模式[J]. 农学学报, 2018, 8(1): 163-166. [2] 曹岗林. 太阳能与发电余热复合增温沼气工程的热电联供系统性能研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2017. [3] 程勇富. 畜禽养殖废弃物资源化利用及标准化建设[J]. 农家参谋, 2022, 8(16): 114-116. [4] 解大, 陈爱康, 顾承红, 等. 并网式热电联供系统的时域建模与动态仿真[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(13): 3735-3747. [5] 万鹏. 基于TRNSYS的太阳能-发电余热加热沼气池系统研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2018. [6] 黄显昆. 现代生态农业园分布式冷热电联供系统模拟研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019. [7] 苏博生. 沼气与太阳能热化学互补机理及系统集成研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019. [8] FERNÁNDEZ-PURATICH H, REBOLLEDO-LEIVA R, DIÓGENES HERNÁNDEZ, et al. Bi-objective optimization of multiple agro-industrial wastes supply to a cogeneration system promoting local circular bioeconomy[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 300: 117333. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117333 [9] 刘小川. 基于支持向量机的厌氧消化连续投料模型的研究[D]. 桂林: 桂林电子科技大学, 2021. [10] 花亚梅, 赵贤林, 王效华, 等. 基于改进BP神经网络的厌氧发酵产气量预测模型[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(10): 5951-5956. [11] 费凡, 高立艾, 张瑞强, 等. 基于供需协调特性的养殖场沼气热电联供系统优化研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44(4): 231-237. [12] 武斌. 生物沼气生产利用系统建模分析及可持续性评价[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2016. [13] 陈一帆. 沼气工程的冷热电三联供系统的研究和分析[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2017. [14] 李娜. 太阳能辅助沼气生产和综合利用系统数值仿真[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2015. [15] 罗涛, 孟曦, 龙恩深, 等. 地上式沼气罐罐壁热负荷分析及工程运行[J]. 太阳能学报, 2017, 38(8): 2069-2076. [16] 张帅兵, 任绳凤, 王子伟. 沼气发酵罐热负荷特性研究与排料余热回收装置设计[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(6): 161-165. [17] CHEN Y R, HASHIMOTO A G. Substrate utilization kinetic model for biological treatment process[J]. Biotechnology And Bioengineering, 1980, 22(10): 2084-2086. [18] AWE O W, ZHAO Y Q, NZIHOU A, et al. A review of biogas utilisation, purification and upgrading technologies[J]. Waste And Biomass Valorization, 2017, 8(2): 267-283. doi: 10.1007/s12649-016-9826-4 [19] MISHRA A, KUMAR M, BOLAN N B, et al. Multidimensional approaches of biogas production and up-gradation: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 338(2): 125514. [20] 张亚鹏, 刘青荣, 吴家正, 等. 养殖场热电联产沼气综合利用模式研究[J]. 中国沼气, 2014, 32(3): 69-71. [21] 刘翌晨. 猪粪产甲烷潜力模型及厌氧消化过程研究[D]. 北京: 北京建筑大学, 2020. [22] 张亚鹏. 南方地区中型养殖场沼气热电联产系统设计及评价方法研究[D]. 上海: 上海电力学院, 2014. -



 下载:
下载: