-
赤泥是氧化铝提取过程中产生的有害碱性固体废物[1],每生产1 t氧化铝约产生1~2 t赤泥[2]。世界范围内的赤泥堆存量大约为4.5×109 t,且每年按约1.2×108 t增加[3]。2020年,我国赤泥产生量超过1×108 t,累积堆存量已达到1.6×109 t[4],占用大量土地,造成土地污染、空气粉尘污染及地下水污染等环境问题[5-6]。赤泥具有高盐性、高碱性、颗粒细小、养分极度缺乏、植物难以生长、生态重建难等特点[7];脱水矿泥含水量高、粒度小,堆存时易形成“超架空结构”,存在溃坝风险等特点[8]。
目前,赤泥控碱的主要方法有酸浸法、盐类浸出法、生物调碱法等[9]。无机酸可以中和赤泥中的自由碱以及化学结合碱[10],但其存在酸用量大、易造成二次污染[4]。FeCl3对赤泥具有一定的控碱效果,同时,随着陈化时间的延长,降碱效果更好[11]。MgCl2对赤泥有良好的控碱效果[12],同时,能够补充赤泥、矿泥壤质化壤土的镁含量,以满足植物生长所需元素。石膏和有机物的添加降低了铝土矿残渣的碱度和盐度,利于生物定植[13]。植物生长对赤泥的 pH、有机质、水稳定聚集和结构稳定性等方面有积极影响[14]。目前,对赤泥进行控碱之后,与矿泥进行混合,并添加肥料和种植植物的壤质化处置方式暂未见报道。
生物有机肥含有大量有机质、植物生长必需元素以及大量功能微生物,同时能改善土壤理化性质、补充微生物[15-16]。鬼针草是1年生菊科草本植物,抗逆性强,自我繁殖能力极强,生长快,生物量大等特点[17],可作为赤泥矿泥壤质化生态修复的先锋植物。本研究将添加组合药剂后的改性赤泥 (DBR) ,与脱水矿泥 (MS) 按1∶4 (干重比) 进行混合,得到壤质化壤土,同时配施生物有机肥、种植鬼针草进行生态修复,探索赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复的可行性,拟为矿山采空区矿坑生态修复提供参考。
-
赤泥采自中国铝业股份有限公司广西分公司赤泥堆场新进堆存赤泥,矿泥采自该公司位于矿山三期的脱水矿泥。赤泥含水率19.26%、pH为10.78~10.82、电导率1 773~1 782 μS·cm−1;矿泥含水率52.48%、pH为6.68~6.81、电导率176.9~177.3 μS·cm−1。赤泥和脱水矿泥主要化学组分见表1。
无水氯化镁 (MgCl2) 为分析纯;无水氯化铁 (FeCl3) 为化学纯;石膏粉 (CaSO4, 97%) ;生物有机肥 (有效活菌数≥8×107·g−1、有机质≥40%、N+P2O5+K2O≥8%) ;鬼针草采自桂林理工大学校园内,平均株高约15 cm。
-
首先将1.7 g·kg−1 氯化镁、3.3 g·kg−1石膏粉和5.0 g·kg−1 氯化铁与赤泥 (干重比) 混合均匀,得到改性赤泥 (DBR) ,陈化2 d后,与脱水矿泥 (MS) 按1∶4 (干重比) 进行充分混合,得到壤质化壤土;称取0、1%、1.5%、2%、3%有机生物肥,与壤质化壤土 (干重比) 混合均匀,其中一组种植鬼针草 (S) ,另外一组未种植鬼针草作为对照组 (CK) ,组名称分别设为:S−0、S−1%、S−1.5%、S−2%、S−3%;CK−0、CK−1%、CK−1.5%、CK−2%、CK−3%。每组处理重复3次。在鬼针草生长0、30和60 d取各组0~20 cm处的壤质化壤土进行分析测试。
-
pH及OH−质量分数采用pH计 (pHS-3E,上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司) 测定;电导率 (EC) 采用电导率仪 (DDS-801,贵阳学通仪器仪表有限公司) 测定;CO32-和HCO3−质量分数采用双指示剂中和滴定法测定[18];K+、Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+和Al3+质量分数采用电感耦合光谱法 (Optima 7000DV, PerkinElmer) 测定,并将Al3+质量分数转化为AlO2−质量分数[19];有机质 (O.M) 采用重铬酸钾−外加热法 (NY/T 1121.6-2006) 测定[20];容重 (BD) 采用环刀法 (NY/T 1121.4-2006) 测定[21];采用台式X射线衍射仪 (X’Pert3 Power, Malvern Panalytical Limited) 、场发射扫描电镜 (JSM-7900F,日本电子株式会社) 进行矿相分析与表征。
-
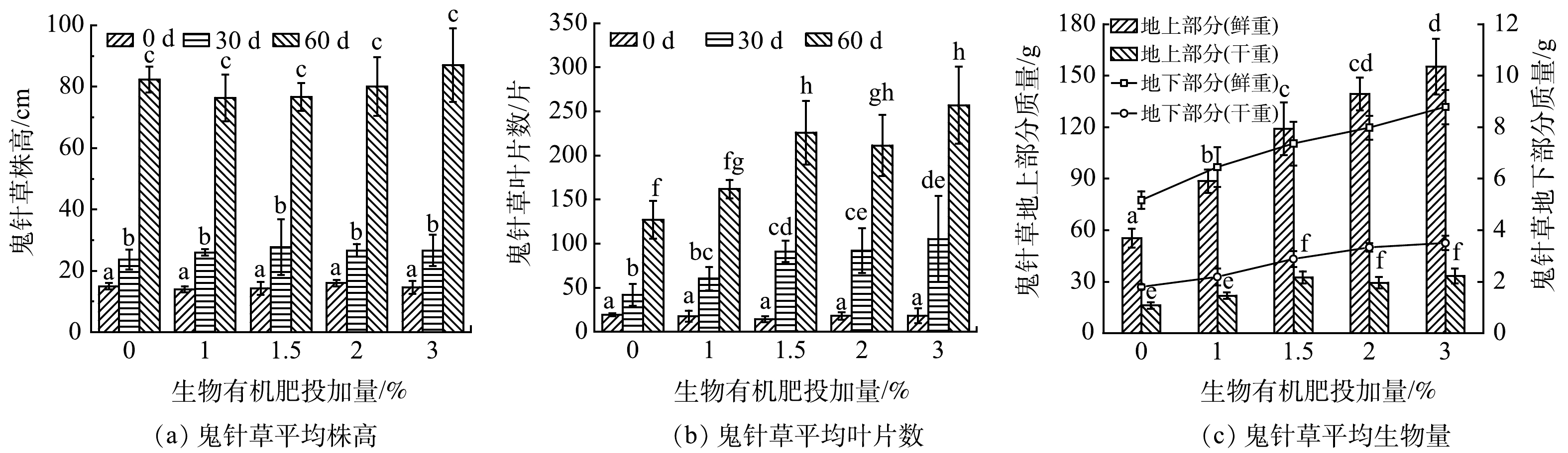
由图1(a)可知,配施生物有机肥与否对鬼针草的平均株高基本没有影响;由图1(b)~图1(c)可看出,鬼针草的平均叶片数、平均地上鲜重、平均地上干重、平均地下鲜重和平均地下干重随配施生物有机肥比例的增加而增加,但超过1.5%时,影响较小。图2为鬼针草不同生长时期的情况,可看出配施生物有机肥比例对鬼针草生长的影响。因此,考虑到生态修复成本,配施1.5%生物有机肥具有较好的工程技术性价比。
-
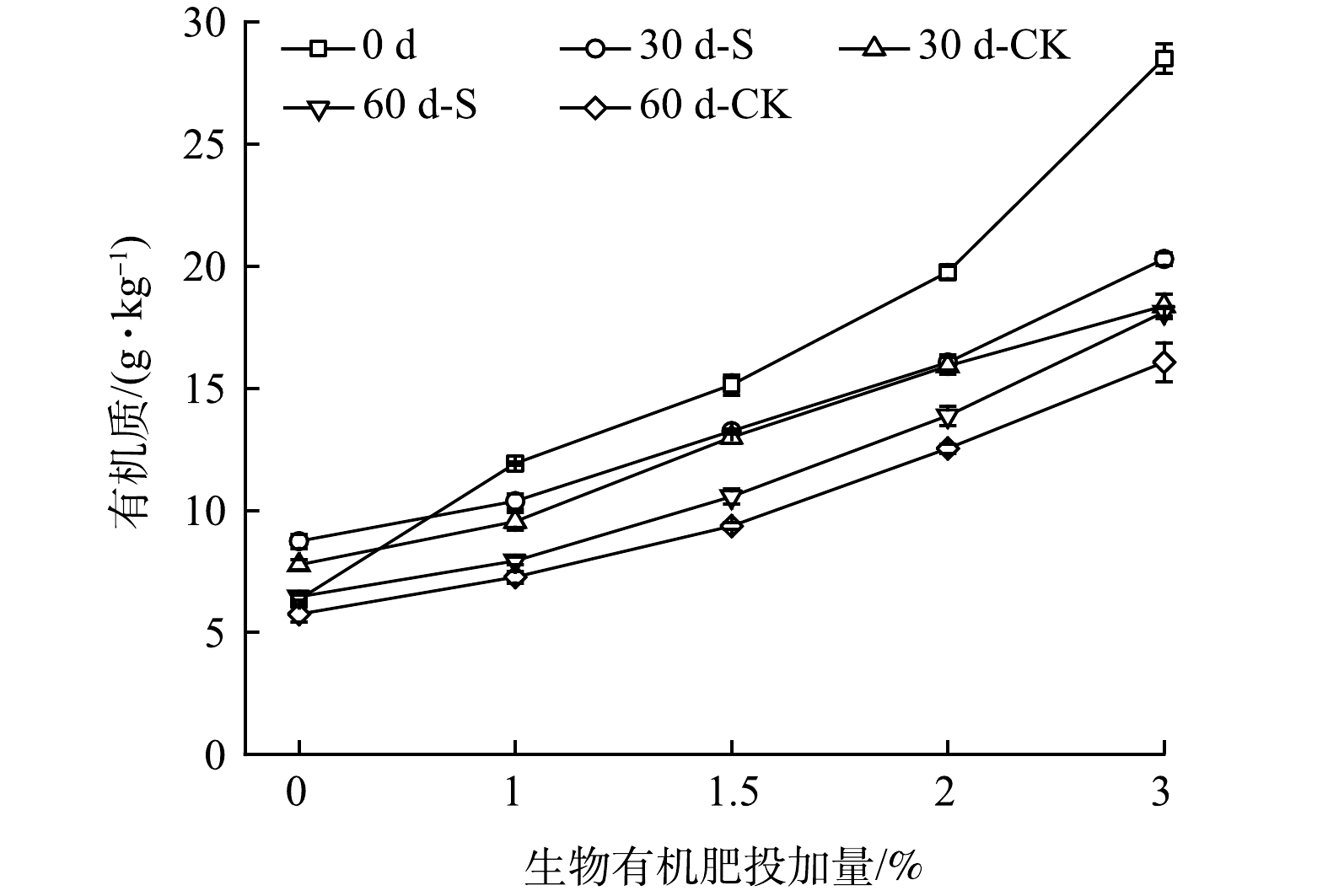
不同时间的有机质变化见图3,可看出,壤质化壤土有机质随配施生物有机肥比例的增加而增加;壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组壤质化壤土有机质为10.56 g·kg−1,与对照组 (9.35 g·kg−1) 相比,上升了11.49%。由此可看出,种植鬼针草可能有利于有机质的积累,降低有机质的消耗。
-
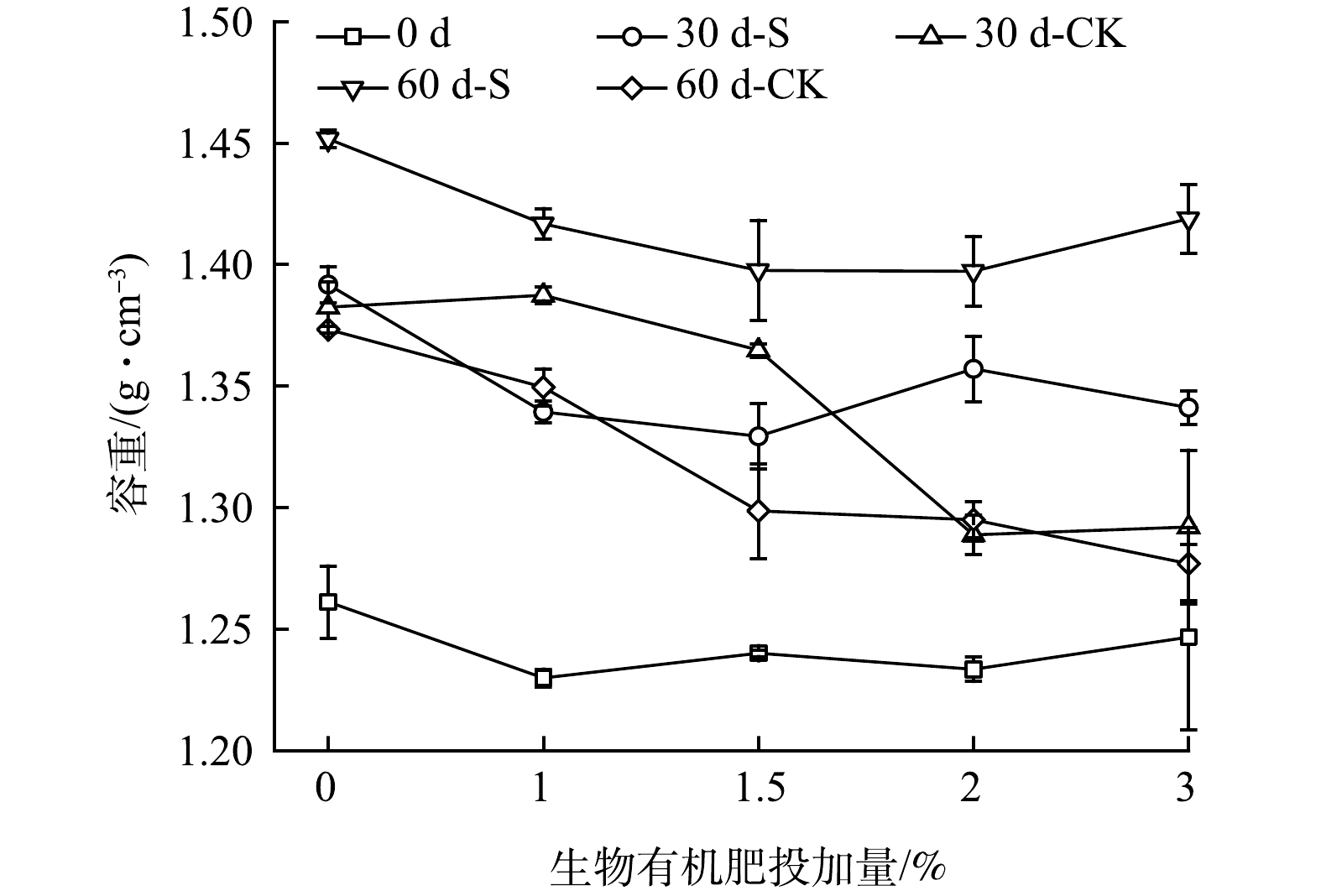
为评价配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土容重的影响,测定了不同时间的容重 (图4)。由图4可看出,配施一定比例的生物有机肥能减缓容重的上升趋势,改善物理性质,使其低于广西平果矿区采空区周边坡地和耕地容重[22];但随着鬼针草种植时间的延长,壤质化壤土容重有所上升。其原因可能是,鬼针草生长、微生物−植物协同作用导致有机质下降趋势较大[23-24],故引起容重上升 (图8) 。
-
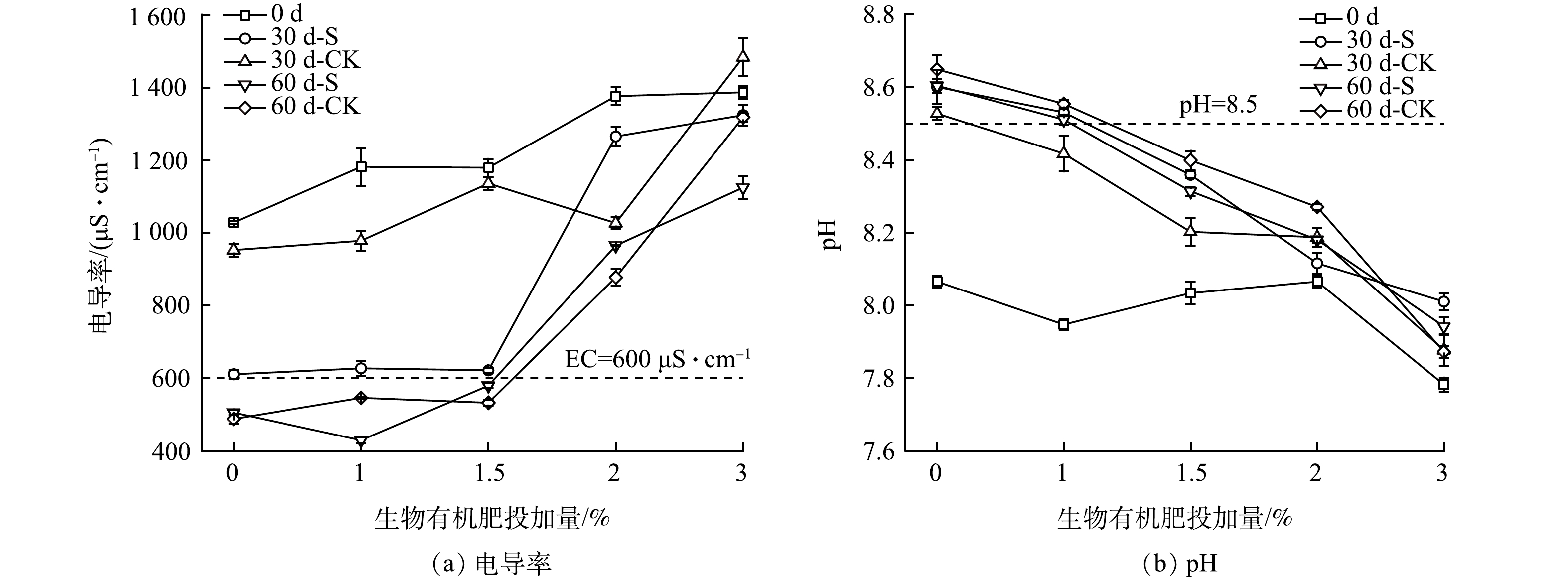
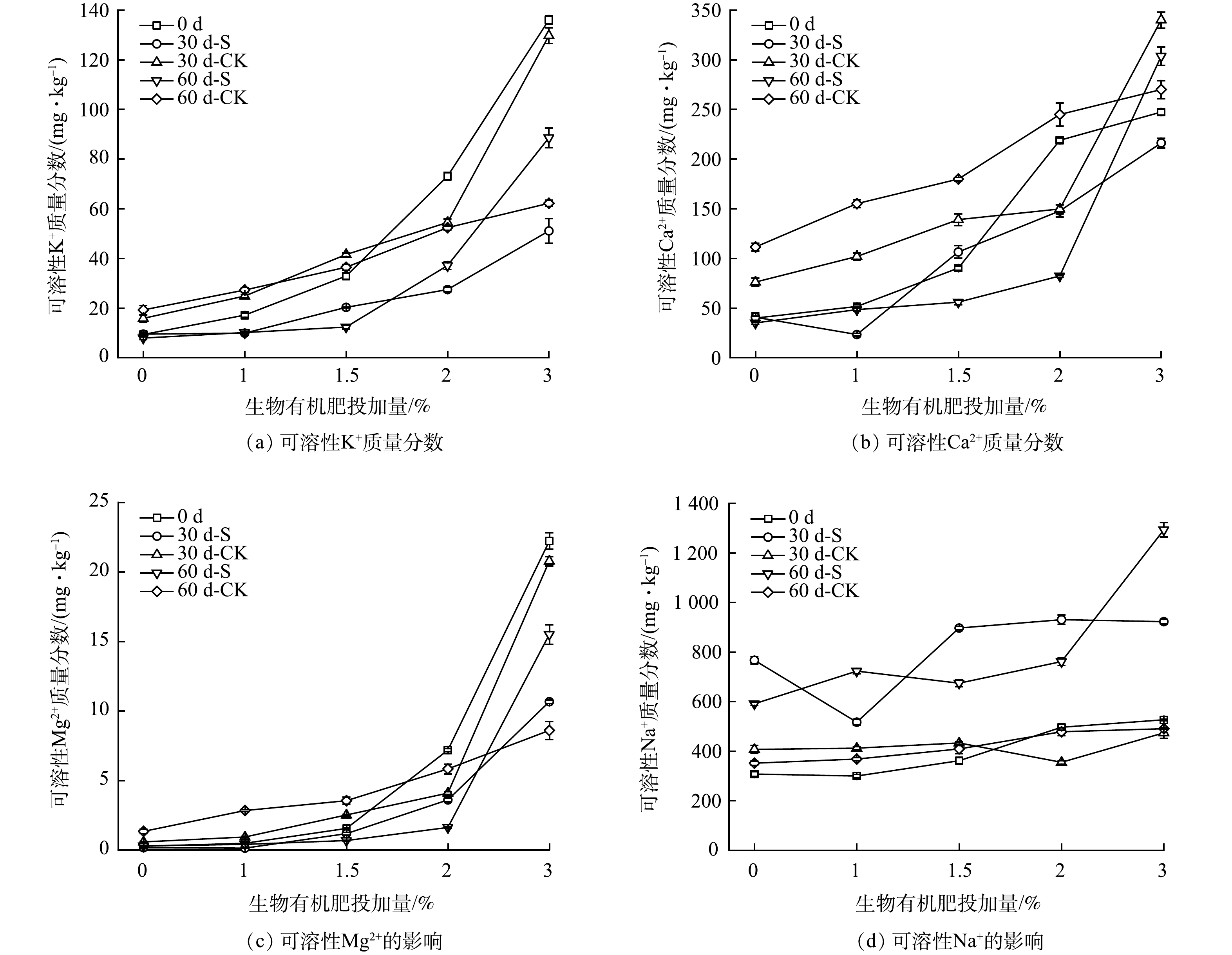
通过测定不同时间的电导率 (图5(a)) 和可溶性阳离子 (图6) ,以分析配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土的盐分变化过程。由图5(a)可知,随配施生物有机肥比例的增加,电导率逐渐上升;随着处置时间的增加,电导率逐渐下降,但仍高于广西平果矿区采空区周边坡地和耕地的电导率[22]。壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组电导率为579.4 μS·cm−1,与0 d相比 (1 179 μS·cm−1) ,下降了50.85%;配施1~1.5%生物有机肥的电导率对敏感作物生长有障碍 (250~600 μS·cm−1) ,多数作物能生长正常[25]。因此,从控盐技术经济性分析,生物有机肥施加量控制在1.5%及以下较为适宜。引起电导率变化的原因可能是:1) 生物有机肥中的有机质、鬼针草的根基高活性微生物群落的呼吸及生长过程中分泌含H+的化学物质能够与赤泥中的化学结合碱反应[26-28],使得可溶性阳离子增加 (图6) ,引起电导率上升,且配施生物有机肥比例越大,电导率越高;2) 石膏也会逐渐溶解产生Ca2+,与化学结合碱中的Na+发生置换反应,使得可溶性Na+增多[29],引起电导率上升 (图6(d)) ;3) 但随着可溶性阳离子与碱性阴离子反应生成难溶性固体[12],同时存在部分离子随浇水水流流出,且鬼针草为满足其生长吸收部分离子,在3者的共同作用下,可溶性阳离子逐渐减少 (图6) ,电导率逐渐下降,而配施更高比例的生物有机肥因盐离子总量高而下降速率较缓。
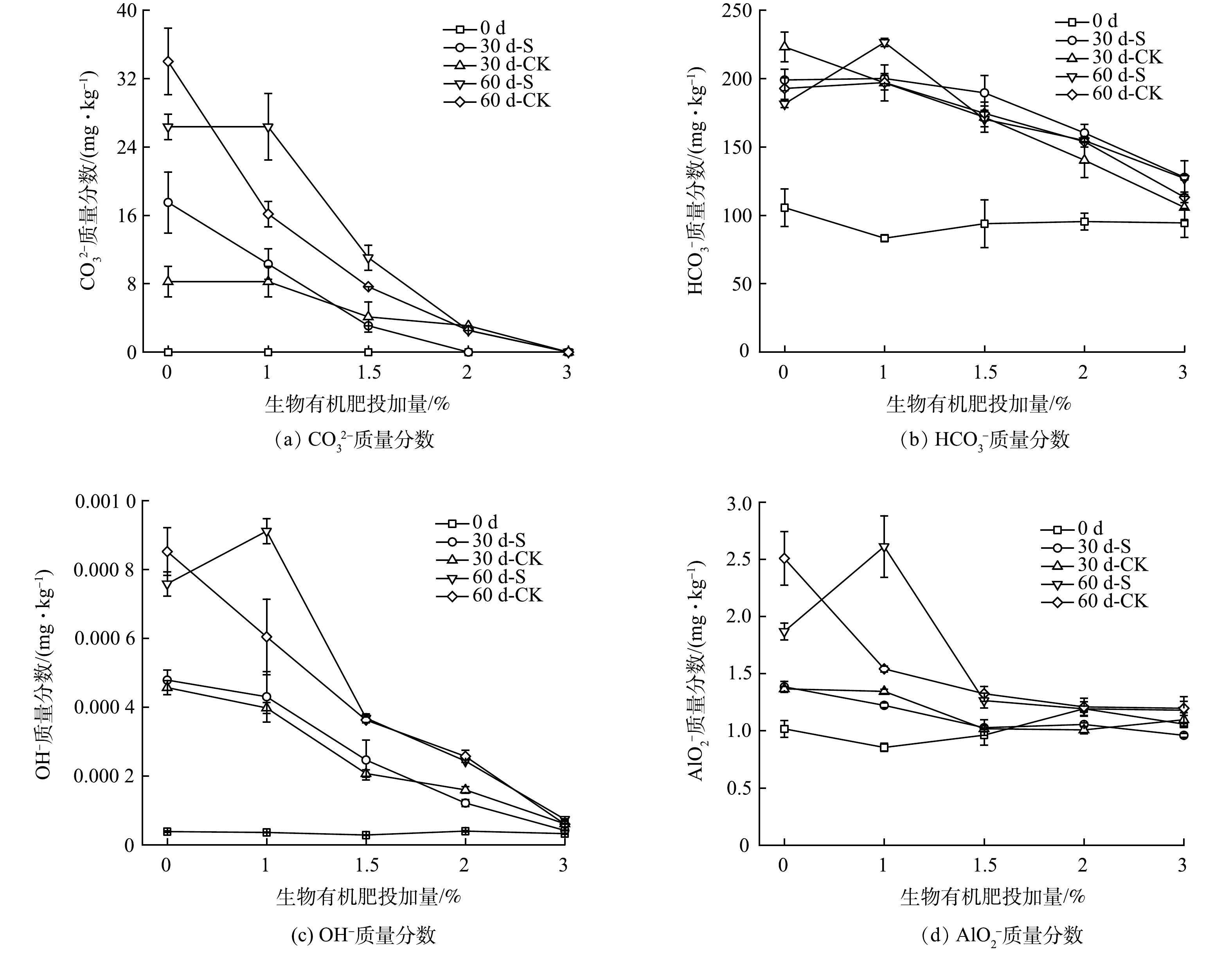
为评价配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土碱性调控的改良效果,测定了不同时间的pH (图5(b)) 和碱性阴离子 (图7) 。由图5(b)可看出,随配施生物有机肥比例和种植鬼针草时间的增加,pH逐渐下降。壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组pH为8.31,与0 d相比 (8.03) ,虽上升了3.49%,但仍低于CK−1.5%组 (8.40) ;配施1.5%生物有机肥及以上的壤质化壤土pH小于8.5,满足矿山回填的要求[30]。因此,基于控碱技术经济性考虑,生物有机肥配施比例控制在1.5%较为适宜。引起pH变化的原因可能是,生物有机肥中的有机酸能与可溶性碱发生反应,使得pH下降,逐渐打破化学结合碱的平衡状态并使之溶解,碱性阴离子质量浓度逐渐上升 (图7) [11],从而引起pH上升;鬼针草的根呼吸、根基高活性微生物群落的呼吸和生长过程中分泌含H+的化学物质逐渐增多[27-28],减缓pH的上升趋势。
-
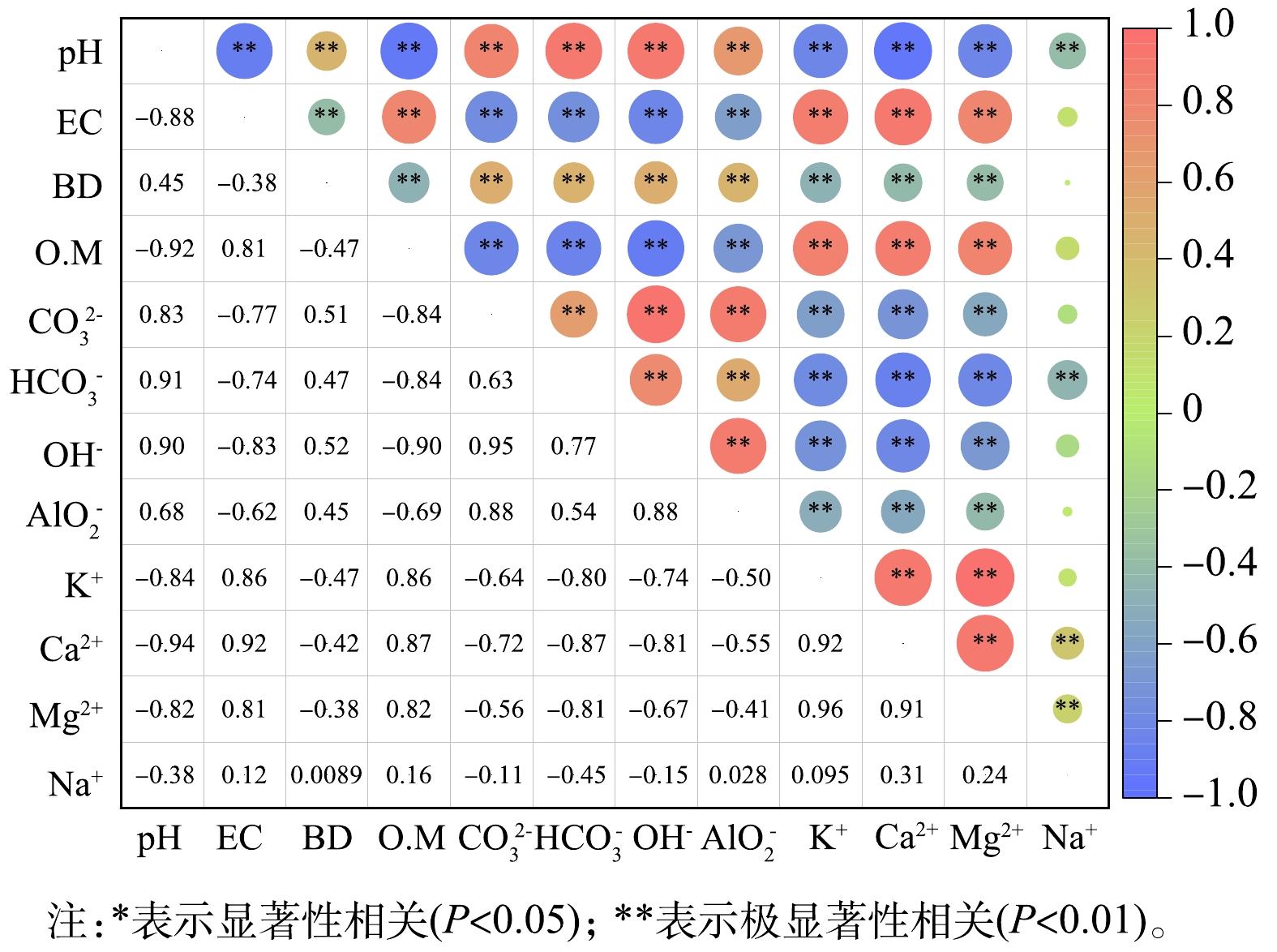
为了解生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土理化性质的影响,对壤质化壤土各指标之间的相关性进行Pearson分析 (见图8) 。由图8可知,碱性阴离子和盐分变化对pH有显著影响 (P<0.01) ;同时,有机质可能通过促进鬼针草生长分泌的酸性物质对碱性物质的中和作用对pH产生影响[27-28]。有机质与容重之间存在极显著负相关 (P<0.01) ,这说明增加有机质对壤质化壤土物理性质的改善起到积极作用。因此,添加有机质即配施生物有机肥利于壤质化壤土的盐碱调控[26],改善其理化性质,加快赤泥、矿泥壤质化壤土的成土过程,这可为后续大规模的赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复提供参考。
-
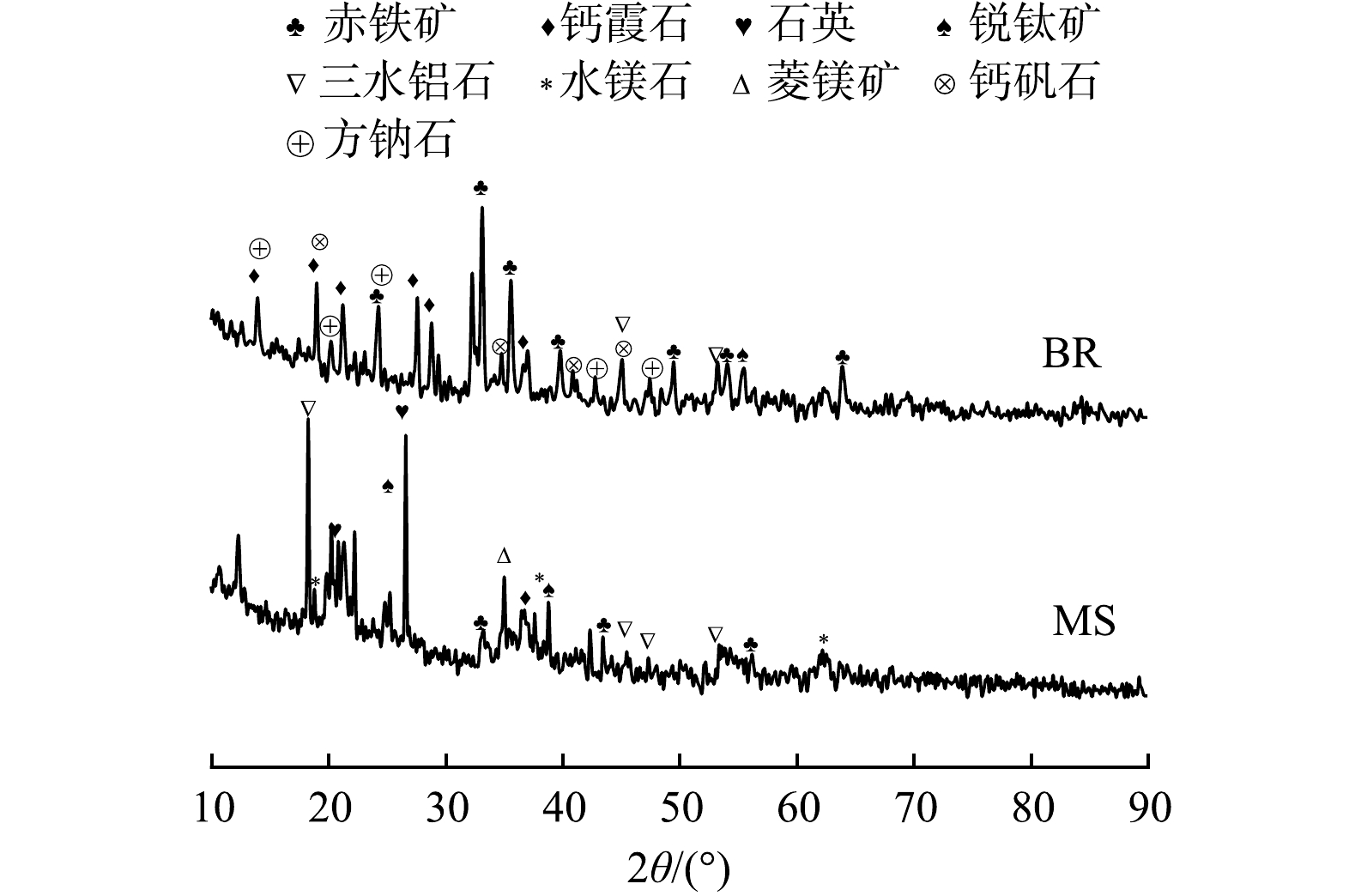
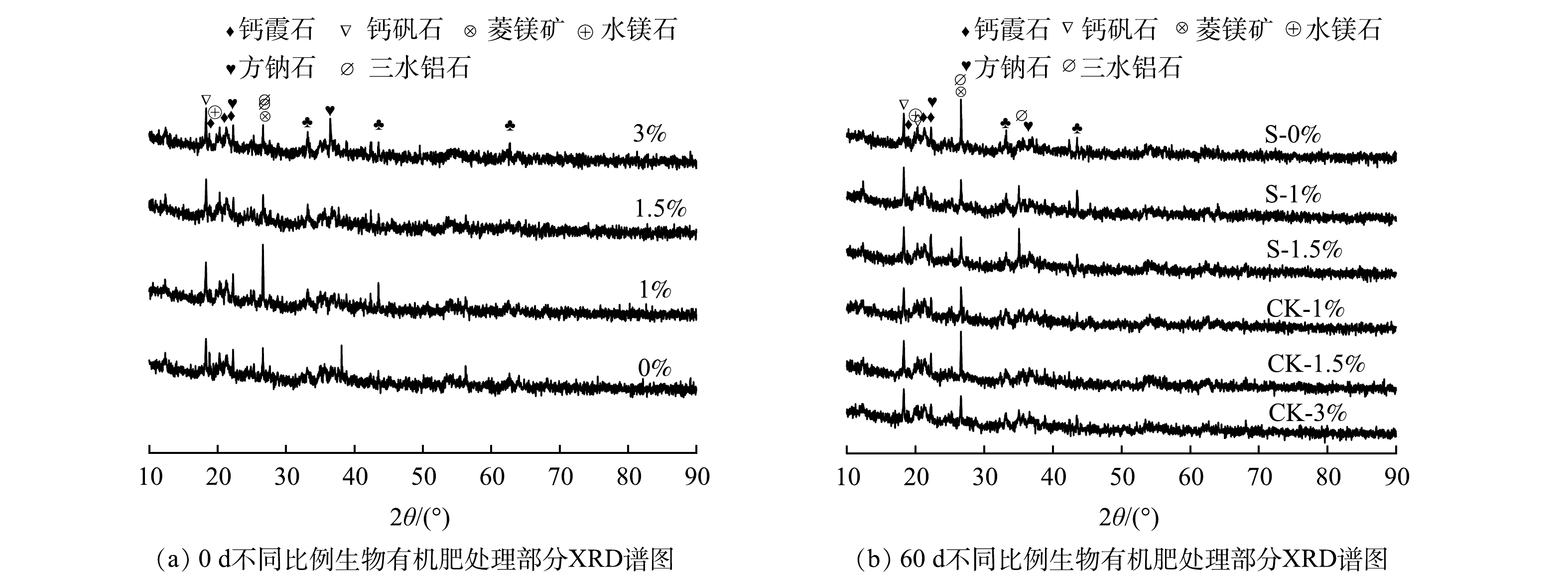
赤泥、脱水矿泥和部分壤质化壤土的XRD谱图见图9和图10,矿相组成见表2,SEM-EDS见图11。根据图9、图10和表2可看出:壤质化处置60 d时,较0 d相比,CK−1.5%组壤质化壤土钙霞石、钙矾石、方钠石、菱镁矿和三水铝石减少,而水镁石增加;CK−3%组的钙霞石、菱镁矿和三水铝石减少,钙矾石和水镁石增加,2者的矿相变化较为接近。因此,基于盐碱控制的技术经济性考虑,生物有机肥施加量控制在1.5%更为经济。S−1.5%组的钙霞石、钙矾石、方钠石和三水铝石减少,而水镁石和菱镁矿增加,这说明种植鬼针草能加速钙霞石、钙矾石和方钠石等化学结合碱的溶出,水镁石和菱镁矿等难溶物质的形成,利于壤质化壤土的盐碱调控。
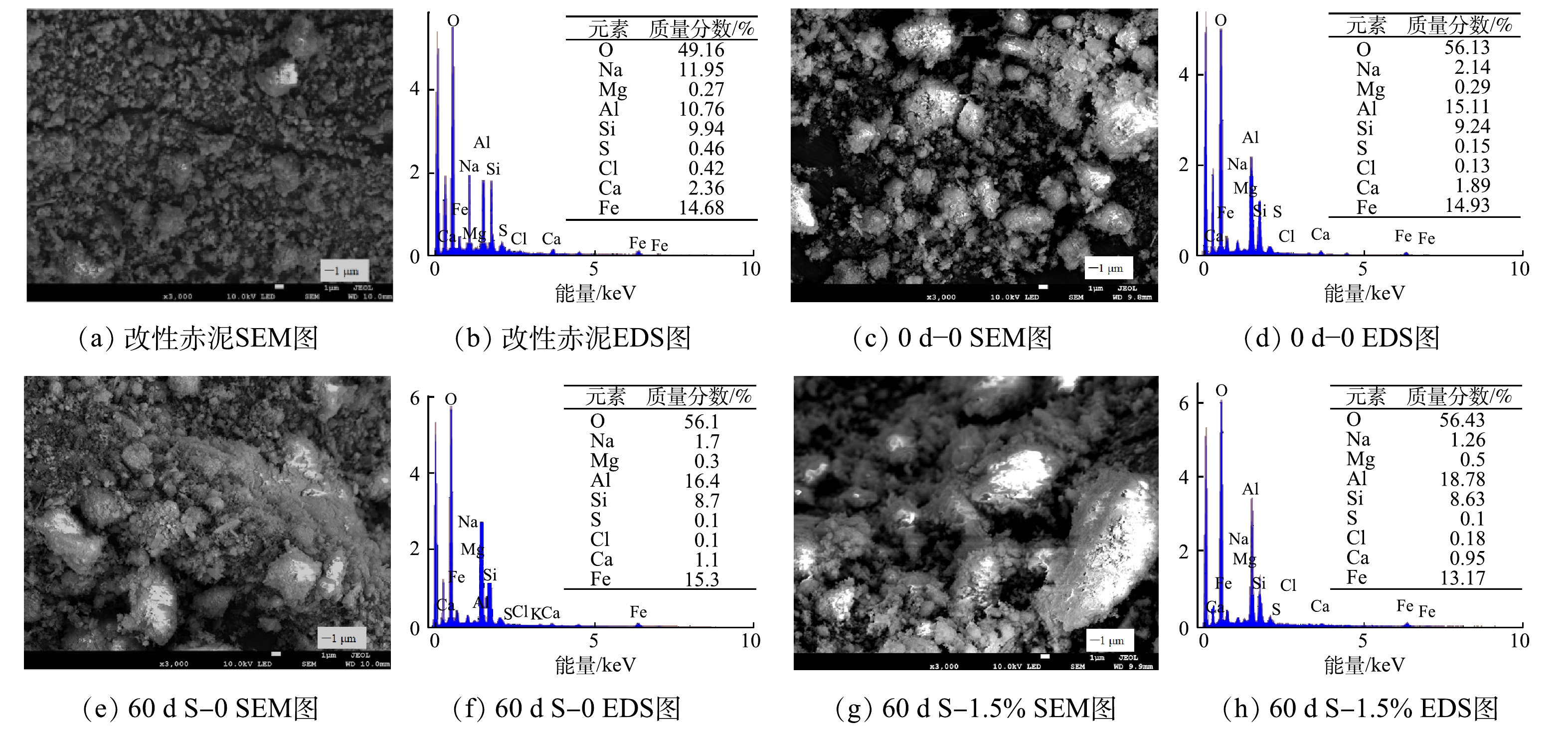
此外,从图11可看出,改性赤泥有较多的细小颗粒且各颗粒间孔隙较小,而经与脱水矿泥混合后(0 d−0组),颗粒尺寸和孔隙明显增大,Na质量分数减少9.81%;壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组的Na质量分数减少10.69%,颗粒变大。因此,配施生物有机肥和延长鬼针草种植时间,能降低Na质量分数,从而降低了其对颗粒团聚的阻碍作用[31];同时,在Ca2+、有机质和微生物的共同作用下,能形成较大的颗粒结构[32-34]。
-
1) 配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草降低了壤质化壤土的盐碱性胁迫,改善了物理性质,对赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复有着积极的作用。
2) 配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草能加速壤质化壤土钙霞石、钙矾石和方钠石等化学结合碱的溶出,水镁石和菱镁矿等难溶物质的形成。
3) 配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草能加快Na质量分数的下降,有利于形成较大的颗粒结构,有效改善壤质化壤土的土理性质。
4) 在生物有机肥的投加量方面,配施3%生物有机肥对赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复的效果最好,但考虑到修复成本,配施1.5%生物有机肥更适用于大规模的生态修复。
生物有机肥和鬼针草对赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复的影响
Effects of bio-organic fertilizer and sticktights on the ecological restoration of bauxite residue and dehydrated mineral slime loam disposal
-
摘要: 为解决赤泥、矿泥规模化安全处置问题,以拜耳法改性赤泥和脱水矿泥为研究对象,配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草,通过分析壤质化壤土的理化指标和矿相变化,探究生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复的影响。结果表明,壤质化壤土的理化性质随配施生物有机肥比例的增加而改善,鬼针草生长越旺盛。其中,鬼针草在配施3%生物有机肥的壤质化壤土中平均长至87.0 cm,叶片数平均257 片,pH和电导率分别降至7.87和429.01 μS·cm−1。Pearson相关性分析结果表明,增加有机质对壤质化生态修复起积极作用。壤质化处置60 d时,配施1.5%生物有机肥,碱性化学结合碱和Na质量分数减少,形成较大的团聚体。本研究结果可为赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复提供参考。Abstract: In order to solve the problem of large-scale safe disposal of bauxite residue and dehydrated mineral slime, the Bayer method dealkalized bauxite residue and dehydrated mineral slime were taken as the research object, and bio-organic fertilizer and planting of sticktights were applied. The physical and chemical indexes and mineral phase changes of loam soils were analyzed, and the effects of bio-organic fertilizer and planting sticktights on the loam ecological restoration of bauxite residue and dehydrated mineral slime were explored. The results showed that physicochemical properties of loam soils were improved with the increase of the proportion of bio-organic fertilizer application, and the growth of sticktights was more vigorous. Among them, the average length of sticktights was 87.0 cm and the average number of leaves was 257 in loam soils with 3% bio-organic fertilizer, the pH and electrical conductivity decreased to 7.87 and 429.01 μS·cm−1. The results of Pearson correlation analysis showed that increasing organic matter played a positive role in the restoration of loam ecology. After 60 days of treatments, 1.5% bio-organic fertilizer was applied, the mass fraction of alkaline chemical combination alkali and Na decreased, and large aggregates were formed. The results of this study can provide a reference for the ecological restoration of bauxite residue and dehydrated mineral slime.
-
赤泥是氧化铝提取过程中产生的有害碱性固体废物[1],每生产1 t氧化铝约产生1~2 t赤泥[2]。世界范围内的赤泥堆存量大约为4.5×109 t,且每年按约1.2×108 t增加[3]。2020年,我国赤泥产生量超过1×108 t,累积堆存量已达到1.6×109 t[4],占用大量土地,造成土地污染、空气粉尘污染及地下水污染等环境问题[5-6]。赤泥具有高盐性、高碱性、颗粒细小、养分极度缺乏、植物难以生长、生态重建难等特点[7];脱水矿泥含水量高、粒度小,堆存时易形成“超架空结构”,存在溃坝风险等特点[8]。
目前,赤泥控碱的主要方法有酸浸法、盐类浸出法、生物调碱法等[9]。无机酸可以中和赤泥中的自由碱以及化学结合碱[10],但其存在酸用量大、易造成二次污染[4]。FeCl3对赤泥具有一定的控碱效果,同时,随着陈化时间的延长,降碱效果更好[11]。MgCl2对赤泥有良好的控碱效果[12],同时,能够补充赤泥、矿泥壤质化壤土的镁含量,以满足植物生长所需元素。石膏和有机物的添加降低了铝土矿残渣的碱度和盐度,利于生物定植[13]。植物生长对赤泥的 pH、有机质、水稳定聚集和结构稳定性等方面有积极影响[14]。目前,对赤泥进行控碱之后,与矿泥进行混合,并添加肥料和种植植物的壤质化处置方式暂未见报道。
生物有机肥含有大量有机质、植物生长必需元素以及大量功能微生物,同时能改善土壤理化性质、补充微生物[15-16]。鬼针草是1年生菊科草本植物,抗逆性强,自我繁殖能力极强,生长快,生物量大等特点[17],可作为赤泥矿泥壤质化生态修复的先锋植物。本研究将添加组合药剂后的改性赤泥 (DBR) ,与脱水矿泥 (MS) 按1∶4 (干重比) 进行混合,得到壤质化壤土,同时配施生物有机肥、种植鬼针草进行生态修复,探索赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复的可行性,拟为矿山采空区矿坑生态修复提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
赤泥采自中国铝业股份有限公司广西分公司赤泥堆场新进堆存赤泥,矿泥采自该公司位于矿山三期的脱水矿泥。赤泥含水率19.26%、pH为10.78~10.82、电导率1 773~1 782 μS·cm−1;矿泥含水率52.48%、pH为6.68~6.81、电导率176.9~177.3 μS·cm−1。赤泥和脱水矿泥主要化学组分见表1。
表 1 赤泥、脱水矿泥的化学成分Table 1. Chemical composition of bauxite residue and dehydrated mineral slime %供试样品 Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 TiO2 CaO Na2O MgO 其他 赤泥 11.7 15.2 44.5 — 10.3 2.7 — 15.6 脱水矿泥 31.8 28.1 12.0 3.7 0.7 1.1 4.1 12.2 注: “—”表示未检出。 无水氯化镁 (MgCl2) 为分析纯;无水氯化铁 (FeCl3) 为化学纯;石膏粉 (CaSO4, 97%) ;生物有机肥 (有效活菌数≥8×107·g−1、有机质≥40%、N+P2O5+K2O≥8%) ;鬼针草采自桂林理工大学校园内,平均株高约15 cm。
1.2 实验方法
首先将1.7 g·kg−1 氯化镁、3.3 g·kg−1石膏粉和5.0 g·kg−1 氯化铁与赤泥 (干重比) 混合均匀,得到改性赤泥 (DBR) ,陈化2 d后,与脱水矿泥 (MS) 按1∶4 (干重比) 进行充分混合,得到壤质化壤土;称取0、1%、1.5%、2%、3%有机生物肥,与壤质化壤土 (干重比) 混合均匀,其中一组种植鬼针草 (S) ,另外一组未种植鬼针草作为对照组 (CK) ,组名称分别设为:S−0、S−1%、S−1.5%、S−2%、S−3%;CK−0、CK−1%、CK−1.5%、CK−2%、CK−3%。每组处理重复3次。在鬼针草生长0、30和60 d取各组0~20 cm处的壤质化壤土进行分析测试。
1.3 分析方法
pH及OH−质量分数采用pH计 (pHS-3E,上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司) 测定;电导率 (EC) 采用电导率仪 (DDS-801,贵阳学通仪器仪表有限公司) 测定;CO32-和HCO3−质量分数采用双指示剂中和滴定法测定[18];K+、Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+和Al3+质量分数采用电感耦合光谱法 (Optima 7000DV, PerkinElmer) 测定,并将Al3+质量分数转化为AlO2−质量分数[19];有机质 (O.M) 采用重铬酸钾−外加热法 (NY/T 1121.6-2006) 测定[20];容重 (BD) 采用环刀法 (NY/T 1121.4-2006) 测定[21];采用台式X射线衍射仪 (X’Pert3 Power, Malvern Panalytical Limited) 、场发射扫描电镜 (JSM-7900F,日本电子株式会社) 进行矿相分析与表征。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 生物有机肥对鬼针草生长的影响
由图1(a)可知,配施生物有机肥与否对鬼针草的平均株高基本没有影响;由图1(b)~图1(c)可看出,鬼针草的平均叶片数、平均地上鲜重、平均地上干重、平均地下鲜重和平均地下干重随配施生物有机肥比例的增加而增加,但超过1.5%时,影响较小。图2为鬼针草不同生长时期的情况,可看出配施生物有机肥比例对鬼针草生长的影响。因此,考虑到生态修复成本,配施1.5%生物有机肥具有较好的工程技术性价比。
2.2 生物有机肥对壤质化壤土有机质的影响
不同时间的有机质变化见图3,可看出,壤质化壤土有机质随配施生物有机肥比例的增加而增加;壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组壤质化壤土有机质为10.56 g·kg−1,与对照组 (9.35 g·kg−1) 相比,上升了11.49%。由此可看出,种植鬼针草可能有利于有机质的积累,降低有机质的消耗。
2.3 生物有机肥和鬼针草对壤质化壤土容重的影响
为评价配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土容重的影响,测定了不同时间的容重 (图4)。由图4可看出,配施一定比例的生物有机肥能减缓容重的上升趋势,改善物理性质,使其低于广西平果矿区采空区周边坡地和耕地容重[22];但随着鬼针草种植时间的延长,壤质化壤土容重有所上升。其原因可能是,鬼针草生长、微生物−植物协同作用导致有机质下降趋势较大[23-24],故引起容重上升 (图8) 。
2.4 生物有机肥和鬼针草对壤质化壤土盐碱性的影响
通过测定不同时间的电导率 (图5(a)) 和可溶性阳离子 (图6) ,以分析配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土的盐分变化过程。由图5(a)可知,随配施生物有机肥比例的增加,电导率逐渐上升;随着处置时间的增加,电导率逐渐下降,但仍高于广西平果矿区采空区周边坡地和耕地的电导率[22]。壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组电导率为579.4 μS·cm−1,与0 d相比 (1 179 μS·cm−1) ,下降了50.85%;配施1~1.5%生物有机肥的电导率对敏感作物生长有障碍 (250~600 μS·cm−1) ,多数作物能生长正常[25]。因此,从控盐技术经济性分析,生物有机肥施加量控制在1.5%及以下较为适宜。引起电导率变化的原因可能是:1) 生物有机肥中的有机质、鬼针草的根基高活性微生物群落的呼吸及生长过程中分泌含H+的化学物质能够与赤泥中的化学结合碱反应[26-28],使得可溶性阳离子增加 (图6) ,引起电导率上升,且配施生物有机肥比例越大,电导率越高;2) 石膏也会逐渐溶解产生Ca2+,与化学结合碱中的Na+发生置换反应,使得可溶性Na+增多[29],引起电导率上升 (图6(d)) ;3) 但随着可溶性阳离子与碱性阴离子反应生成难溶性固体[12],同时存在部分离子随浇水水流流出,且鬼针草为满足其生长吸收部分离子,在3者的共同作用下,可溶性阳离子逐渐减少 (图6) ,电导率逐渐下降,而配施更高比例的生物有机肥因盐离子总量高而下降速率较缓。
为评价配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土碱性调控的改良效果,测定了不同时间的pH (图5(b)) 和碱性阴离子 (图7) 。由图5(b)可看出,随配施生物有机肥比例和种植鬼针草时间的增加,pH逐渐下降。壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组pH为8.31,与0 d相比 (8.03) ,虽上升了3.49%,但仍低于CK−1.5%组 (8.40) ;配施1.5%生物有机肥及以上的壤质化壤土pH小于8.5,满足矿山回填的要求[30]。因此,基于控碱技术经济性考虑,生物有机肥配施比例控制在1.5%较为适宜。引起pH变化的原因可能是,生物有机肥中的有机酸能与可溶性碱发生反应,使得pH下降,逐渐打破化学结合碱的平衡状态并使之溶解,碱性阴离子质量浓度逐渐上升 (图7) [11],从而引起pH上升;鬼针草的根呼吸、根基高活性微生物群落的呼吸和生长过程中分泌含H+的化学物质逐渐增多[27-28],减缓pH的上升趋势。
2.5 壤质化壤土各指标之间的相关性
为了解生物有机肥和种植鬼针草对壤质化壤土理化性质的影响,对壤质化壤土各指标之间的相关性进行Pearson分析 (见图8) 。由图8可知,碱性阴离子和盐分变化对pH有显著影响 (P<0.01) ;同时,有机质可能通过促进鬼针草生长分泌的酸性物质对碱性物质的中和作用对pH产生影响[27-28]。有机质与容重之间存在极显著负相关 (P<0.01) ,这说明增加有机质对壤质化壤土物理性质的改善起到积极作用。因此,添加有机质即配施生物有机肥利于壤质化壤土的盐碱调控[26],改善其理化性质,加快赤泥、矿泥壤质化壤土的成土过程,这可为后续大规模的赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复提供参考。
2.6 生物有机肥和鬼针草对壤质化壤土矿物矿相和形态的影响
赤泥、脱水矿泥和部分壤质化壤土的XRD谱图见图9和图10,矿相组成见表2,SEM-EDS见图11。根据图9、图10和表2可看出:壤质化处置60 d时,较0 d相比,CK−1.5%组壤质化壤土钙霞石、钙矾石、方钠石、菱镁矿和三水铝石减少,而水镁石增加;CK−3%组的钙霞石、菱镁矿和三水铝石减少,钙矾石和水镁石增加,2者的矿相变化较为接近。因此,基于盐碱控制的技术经济性考虑,生物有机肥施加量控制在1.5%更为经济。S−1.5%组的钙霞石、钙矾石、方钠石和三水铝石减少,而水镁石和菱镁矿增加,这说明种植鬼针草能加速钙霞石、钙矾石和方钠石等化学结合碱的溶出,水镁石和菱镁矿等难溶物质的形成,利于壤质化壤土的盐碱调控。
表 2 赤泥、脱水矿泥和部分壤土矿相组成Table 2. Mineral phase contents of bauxite residue, dehydrated mineral slime and some loam soils% 供考察原料 BR MS 0 d 60 d 0 1% 1.5% 3% S−0 S−1% S−1.5% CK−1% CK−1.5% CK−3% 钙霞石 13.6 6.4 7.1 6.5 5.3 5.2 4.1 2.9 4 5.1 5.0 4.9 钙矾石 13.9 — 4.4 3.3 3.6 3.9 — — 3.9 4 4.2 4.6 方钠石 1.4 — 0.7 0.4 0.6 — 0.1 0.8 0.4 — — — 水镁石 — 2.8 3.9 3.5 3.9 4.1 1.2 5 5.3 4.4 4.9 5.3 菱镁矿 — 4.6 6.6 3.4 2.3 2.4 2.5 4.9 3.2 3.3 1.4 0.5 三水铝石 2.4 27.7 20 21.7 21.8 23.4 22.4 20.5 21.6 19.1 18.7 21.6 注: “—”表示未检出。 此外,从图11可看出,改性赤泥有较多的细小颗粒且各颗粒间孔隙较小,而经与脱水矿泥混合后(0 d−0组),颗粒尺寸和孔隙明显增大,Na质量分数减少9.81%;壤质化处置60 d时,S−1.5%组的Na质量分数减少10.69%,颗粒变大。因此,配施生物有机肥和延长鬼针草种植时间,能降低Na质量分数,从而降低了其对颗粒团聚的阻碍作用[31];同时,在Ca2+、有机质和微生物的共同作用下,能形成较大的颗粒结构[32-34]。
3. 结论
1) 配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草降低了壤质化壤土的盐碱性胁迫,改善了物理性质,对赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复有着积极的作用。
2) 配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草能加速壤质化壤土钙霞石、钙矾石和方钠石等化学结合碱的溶出,水镁石和菱镁矿等难溶物质的形成。
3) 配施生物有机肥和种植鬼针草能加快Na质量分数的下降,有利于形成较大的颗粒结构,有效改善壤质化壤土的土理性质。
4) 在生物有机肥的投加量方面,配施3%生物有机肥对赤泥、矿泥壤质化生态修复的效果最好,但考虑到修复成本,配施1.5%生物有机肥更适用于大规模的生态修复。
-
表 1 赤泥、脱水矿泥的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of bauxite residue and dehydrated mineral slime %
供试样品 Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 TiO2 CaO Na2O MgO 其他 赤泥 11.7 15.2 44.5 — 10.3 2.7 — 15.6 脱水矿泥 31.8 28.1 12.0 3.7 0.7 1.1 4.1 12.2 注: “—”表示未检出。 表 2 赤泥、脱水矿泥和部分壤土矿相组成
Table 2. Mineral phase contents of bauxite residue, dehydrated mineral slime and some loam soils
% 供考察原料 BR MS 0 d 60 d 0 1% 1.5% 3% S−0 S−1% S−1.5% CK−1% CK−1.5% CK−3% 钙霞石 13.6 6.4 7.1 6.5 5.3 5.2 4.1 2.9 4 5.1 5.0 4.9 钙矾石 13.9 — 4.4 3.3 3.6 3.9 — — 3.9 4 4.2 4.6 方钠石 1.4 — 0.7 0.4 0.6 — 0.1 0.8 0.4 — — — 水镁石 — 2.8 3.9 3.5 3.9 4.1 1.2 5 5.3 4.4 4.9 5.3 菱镁矿 — 4.6 6.6 3.4 2.3 2.4 2.5 4.9 3.2 3.3 1.4 0.5 三水铝石 2.4 27.7 20 21.7 21.8 23.4 22.4 20.5 21.6 19.1 18.7 21.6 注: “—”表示未检出。 -
[1] KUSRINI E, ZULYS A, YOGASWARA A, et al. Extraction and enrichment of lanthanide from Indonesian low grade bauxite using sulfuric acid heap leaching and phytic acid[J]. Engineering Journal, 2020, 24(4): 305-314. doi: 10.4186/ej.2020.24.4.305 [2] ZHU F, HUANG N, XUE S G, et al. Effects of binding materials on microaggregate size distribution in bauxite residues[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(23): 23867-23875. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7626-9 [3] ZHU F, XUE S G, HARTLEY W, et al. Novel predictors of soil genesis following natural weathering processes of bauxite residues[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(3): 2856-2863. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5537-9 [4] 陈珊, 陈允建, 谢鑫, 等. 赤泥脱碱方法及其机理研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2021, 40(10): 3414-3426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1625.2021.10.gsytb202110033 [5] PANDA I, JAIN S, DAS S K, et al. Characterization of red mud as a structural fill and embankment material using bioremediation[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 119: 368-376. [6] GELENCSÉR A, KOVÁTS N, TURÓCZI B, et al. The red mud accident in Ajka (Hungary): characterization and potential health effects of fugitive dust[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(4): 1608-1615. [7] 黄玲, 李义伟, 薛生国, 等. 氧化铝赤泥堆场盐分组成变化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(11): 2433-2439. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2016.11.021 [8] 陈斌, 翟文龙, 祝怡斌. 铝土矿矿泥脱水及固化研究进展[J]. 中国矿业, 2020, 29(S2): 368-370. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2020.S2.001 [9] 薛生国, 李晓飞, 孔祥峰, 等. 赤泥碱性调控研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(8): 2815-2828. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0144 [10] KONG X F, LI M, XUE S G, et al. Acid transformation of bauxite residue: conversion of its alkaline characteristics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 382-390. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.073 [11] 成官文, 张燎, 韦桥权, 等. FeCl3赤泥控碱及离子效应研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(2): 996-1005. [12] 张宇玲, 成官文, 韦桥权, 等. MgCl2和脱水矿泥对赤泥盐碱性的调控[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(3): 937-945. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202111076 [13] BRAY A W, STEWART D I, COURTNEY R, et al. Sustained bauxite residue rehabilitation with gypsum and organic matter 16 years after initial treatment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(1): 152-161. [14] ZHU F, LI X F, XUE S G, et al. Natural plant colonization improves the physical condition of bauxite residue over time[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(22): 22897-22905. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7508-1 [15] 常肖锐, 叶项宇, 王政, 等. 生物有机肥研究及应用进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021(22): 145-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2021.22.061 [16] 张俊峰, 颉建明, 张玉鑫, 等. 生物有机肥部分替代化肥对日光温室番茄生长与光合特性及肥料利用率的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2022(11): 44-50. [17] 杨霆, 黄美兰, 潘懿. 鬼针草和桑叶饲用原材料可行性分析[J]. 农业技术与装备, 2021(12): 17-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-887X.2021.12.006 [18] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 中国农业出版社, 2000: 193-195. [19] LI Y W, LUO X H, LI C X, et al. Variation of alkaline characteristics in bauxite residue under phosphogypsum amendment[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(2): 361-372. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4008-8 [20] 中华人民共和国农业部. 土壤检测第6部分土壤有机质的测定: NY/T 1121.6-2006 [S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [21] 中华人民共和国农业部. 土壤检测第4部分土壤容重的测定: NY/T 1121.4-2006 [S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [22] 段绍彦, 成官文, 解庆林, 等. 平果铝土矿矿区周边坡地、耕地土壤基础理化性质空间差异[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2021, 71(1): 201-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2021.01.025 [23] JONES B E H, HAYNES R J, PHILLIPS I R. Effect of amendment of bauxite processing sand with organic materials on its chemical, physical and microbial properties[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2010, 91(11): 2281-2288. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.06.013 [24] ANGIN I, ASLANTAS R, GUNES A, et al. Effects of sewage sludge amendment on some soil properties, growth, yield and nutrient content of raspberry (Rubus idaeus L. )[J]. Erwerbs-Obstbau, 2017, 59(2): 93-99. doi: 10.1007/s10341-016-0303-9 [25] 黄绍文, 王玉军, 金继运, 等. 我国主要菜区土壤盐分、酸碱性和肥力状况[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 906-918. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2011.1104 [26] SANTINI T C, KERR J L, WARREN L A. Microbially-driven strategies for bioremediation of bauxite residue[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 293: 131-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.024 [27] XUE S G, LI M, JIANG J, et al. Phosphogypsum stabilization of bauxite residue: conversion of its alkaline characteristics[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 77: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.016 [28] 莫思琪, 曹旖旎, 谭倩. 根系分泌物在重金属污染土壤生态修复中的作用机制研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(2): 382-392. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202201.008 [29] 喻阳华, 吴永贵, 喻理飞, 等. 磷石膏与碳酸钙对赤泥脱碱的效果及可能机理[J]. 无机盐工业, 2014, 46(10): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2014.10.015 [30] 环境保护部. 矿山生态环境保护与恢复治理技术规范(试行): HJ 651-2013[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2013. [31] BURKE I T, PEACOCK C L, LOCKWOOD C L, et al. Behavior of aluminum, arsenic, and vanadium during the neutralization of red mud leachate by HCl, gypsum, or seawater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(12): 6527-6535. [32] ZHU F, LIAO J X, XUE S G, et al. Evaluation of aggregate microstructures following natural regeneration in bauxite residue as characterized by synchrotron-based X-ray micro-computed tomography[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 573: 155-163. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.108 [33] 董远鹏, 刘喜娟, 董梦阳, 等. 腐殖质和硝酸钙对赤泥团聚体形成的促进作用[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(10): 1205-1210. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.10.004 [34] 胡树翔, 吕十全, 王新, 等. 生物质改良对赤泥土壤化修复的促进作用[EB/OL]. [2022-07-22]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5591.X.20220725.1737.008.html. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 杜诚豪,成官文,王云龙,曾玉辉,张正林,黄振艺. 黄豆/旱稻间作与肥料协同作用对矿泥、赤泥土壤化处置的影响. 金属矿山. 2024(06): 220-228 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: