-
随着城市内河中氮和磷超标趋于严重,导致水体富营养化风险加大[1-3]。当城市内河外源污染得到有效控制时,其内源(底泥)释放的氮磷就成为导致水体富营养化的主要因素,并延缓生态系统的恢复[4-5]。因此,削减污染底泥氮磷释放是控制水体富营养化的主要措施之一[6]。
目前,削减底泥氮磷释放主要措施有疏浚技术和覆盖技术[7-8]。覆盖技术具有对底泥干扰小、工程造价低、可有效控制底泥氮磷向上层水迁移等优点,从而倍受国内外学者的关注[9-11]。覆盖技术的原理是:通过在底泥表面铺放覆盖材料使底泥与上层水体隔离,达到阻止底泥污染物向水体迁移的目的[12]。其中,覆盖材料是覆盖技术的核心,从早期惰性材料如砂砾、土壤等,发展到现在的各种活性材料如镧改性膨润土[13]、铁改性方解石[14]、改性氧化钙材料[11]等,活性薄层覆盖技术研究也愈加广泛与深入。但是,目前活性薄层覆盖技术在控制城市内河底泥氮磷释放实际工程中存在的问题有:覆盖材料施工时不易均匀铺设;城市内河雨季行洪排涝时,由于河水流速大、冲刷强度大,容易造成覆盖材料悬浮、流失,致使覆盖层变薄并逐渐失效[15-16]。因此,笔者所在课题组自主研发了一种城市河道污染底泥活性覆盖板的制作方法,进而提出一种基于产量高、成本适中的活性覆盖材料制备而成的具有抗冲刷性能好、透水性能高、均匀且形状多样、能够控制底泥氮磷释放的活性覆盖板以解决上述问题。
本研究中,以课题组自主研发的铝基锁磷剂[17-18]为主体材料,以水泥和粉煤灰为胶凝材料来制备活性覆盖板,分别研究了材料配比、水料比、成型压力和铝基锁磷剂颗粒粒径等4个因素对活性覆盖板抗冲刷性能和透水性能的影响,优选出较佳制备方式;并以污染底泥为研究对象,通过室内静态模拟实验探究了活性覆盖板覆盖控制氮磷释放效果。相关研究结果可为城市内河污染底泥活性覆盖板的实际应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
1)制板材料。实验所用铝基锁磷剂制备步骤为:将取自厦门某净水厂的脱水后污泥自然风干,待含水率降至为10%~13%时放入马弗炉中,在400 ℃下恒温煅烧2.5 h制得铝基锁磷剂,通过粉碎和筛分获得1~9 mm不等实验材料。该净水厂采用聚合双酸铝铁作为混凝剂,故此铝基锁磷剂中主要含有Si、Al、Fe等元素,其他参数详见文献[17],煅烧改性前后污泥理化性质变化详见文献[18]。实验采用水泥和粉煤灰作为胶凝材料,其中,水泥为普通硅酸盐水泥42.5级,粉煤灰为F类Ⅱ级粉煤灰。
2)底泥与上覆水。实验所用底泥为某城市景观湖中表层底泥。采用抓斗式采泥器(DXCN1/16型)取得的底泥通过16目(孔径1 mm)的钢筛,混合均匀作为实验所用底泥。实验所用上覆水为实验室自来水。
-
底泥活性覆盖板制备工艺流程如下:首先将铝基锁磷剂、水泥、粉煤灰按一定比例搅拌混匀,加一定量自来水搅拌2~3 min,静置5 min使原料充分混合;然后将搅拌好的底料先加入模框中,在一定的压力下进行压制,待压制成型后12~16 h可进行脱模;最后将成品在自然条件下进行养护14 d,即可得到实验所用的活性覆盖板。表1为该活性覆盖板的实验设计参数。
-
实验在透明方形有机玻璃槽中进行,尺寸为16.0 cm×16.0 cm×18.0 cm。实验中共有6个有机玻璃槽,分为2组,每组3个平行样,1#为对照系统(未覆盖),2#为覆盖系统。其中,覆盖系统所用活性覆盖板工况条件为:铝基锁磷剂(粒径1~3 mm)、水泥和粉煤灰占比分别为70%、15%和15%、水料比0.25、成型压力1.00 MPa。制备成型的活性覆盖板尺寸15 cm×15 cm×0.5 cm,覆盖板对底泥覆盖率约为90%(由于活性覆盖板模具制作时与实验装置大小有些误差,导致覆盖率不是100%)。每个有机玻璃槽中底泥为1.15 kg(厚度约为5.0 cm);上覆水体积为2.4 L(高约10 cm),利用虹吸原理通过塑料软管将自来水缓缓沿槽壁加入槽中。
实验在室内进行,历时36 d。在实验期间,有机玻璃槽口敞开(不控制上覆水溶解氧浓度)。定期测定各系统中水深5 cm处pH、溶解氧(DO)、氧化还原电位和水温;定期取水样测定其中的TP和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的质量浓度,取水样后用原水补充至原刻度线。 -
先将活性覆盖板在高压蒸汽灭菌锅中灭菌20 min以消除微生物干扰,自然冷却后备用。用去离子水配制氨氮质量浓度为10 mg·L−1的NH4Cl溶液,用0.1 mg·L−1的HCl和0.1 mg·L−1的NaOH溶液调节pH为中性,量取定量溶液倒入一系列容器中,再加入灭菌后的活性覆盖板,容器密封后在25 ℃、150 r·min−1条件下振荡,在反应开始后每隔一段时间取出部分容器,检测溶液的氨氮质量浓度。实验设置3组平行样,取3组实验结果的平均值分析。
-
1)活性覆盖板抗冲刷性能测试方法。活性覆盖板示意图如图1(a)所示。覆盖板抗冲刷性能以自定义的抗冲刷系数来具体反映,即在一定时间内,抗冲刷系数越大,证明覆盖板被冲击损失部分越小,反映其抗冲刷能力越强。实验冲损控制在2.0%以内,即抗冲刷系数大于98.0%。抗冲刷系数测试方法是将已吸水饱和的活性覆盖板放入水流流速为1.53 cm·s−1的有机玻璃水槽中冲刷120 h,再根据冲刷前后的质量计算其抗冲刷系数。其中,有机玻璃水槽尺寸为60 cm×30 cm×20 cm,控制水面高度为15 cm,采用潜水泵控制水体循环流动(装置见图1(b))。
2)活性覆盖板透水性能测试方法。透水性能是体现水在覆盖板中流动难易程度的指标,其大小用透水系数来评价。GB/T 25993-2010《透水路面砖和透水路面板》中透水块材透水等级A级和B级的要求是,透水系数分别大于等于0.02 cm·s−1和0.01 cm·s−1,因考虑活性覆盖板是用于河湖底泥覆盖,故本实验对活性覆盖板的透水能力要求更高,因而将其透水系数按10倍来定义,取值为0.10~0.20 cm·s−1。透水实验操作方式参照GB/T 25993-2010《透水路面砖和透水路面板》中的“附录C 透水系数测试方法”上相应内容实施,实验装置也根据相应规范自制(装置见图1(c))。
3)水体相关指标测定方法。水温和DO质量浓度采用便携式溶解氧测定仪测定(HACH,HQ30d型);pH采用便携式pH计测定(上海奥豪斯仪器有限公司,STARTER3100型);氧化还原电位采用便携式单参数ORP计测定(上海三信仪器有限公司,SX712型);TP质量浓度采用钼锑抗分光光度法[19];
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N质量浓度采用纳氏试剂光度法[19]。 -
活性覆盖板的抗冲刷系数Pm按照式(1)进行计算;在上覆水中,TP和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N质量浓度的削减率按照式(2)进行计算;活性覆盖板的氨氮吸附量按式(3)进行计算。式中:mb和ma分别为活性覆盖板冲刷后和冲刷前的质量,g。
式中:Pc为削减率;CNCi为取样时对照系统上覆水中TP或
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N质量浓度,mg·L−1;CCi为取样时覆盖系统上覆水中TP或${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N质量浓度,mg·L−1;i为取样次数。式中:X1为活性覆盖板的氨氮吸附量,mg·g−1;C0为溶液的氨氮初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ce为吸附反应后溶液氨氮质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为反应溶液的体积,L;m为活性覆盖板的质量,g。
活性覆盖板的透水系数kT按照GB/T 25993-2010《透水路面砖和透水路面板》中的“附录C 透水系数测试方法”中上相应公式进行计算,其中所得透水系数皆转换为标准温度时的透水系数k15,,单位为cm·s−1。采用Origin8.5软件分析对照系统和覆盖系统之间削减氮和磷污染物效果的差异。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 制备流程
1.3. 控制氮磷释放实验
1.4. 氨氮吸附实验
1.5. 测试方法
1.6. 数据处理
-
1)材料配比的影响。在铝基锁磷剂占比70%条件下,粉煤灰占比分别为5%、10%、15%和20%时,所制得的活性覆盖板的抗冲刷系数和透水系数变化如图2所示。由图2可见,粉煤灰的掺加量对于抗冲刷系数和透水系数均有影响,且对两者之间的影响存在着此消彼长的关系。其原因可能为,制备成型后的覆盖板在水泥粉煤灰等胶凝材料的粘结作用下,整体具有一定的紧密性,内部不易被冲损[20]。然而,表面铝基锁磷剂颗粒虽在粘结作用下与覆盖板主体接连,但接触面积较小,也较易脱落。随着粉煤灰掺加比例的增加,水泥的掺加比例相应减少,会使得粘结作用效果变差[21],从而导致所制备的覆盖板表面颗粒与主体间黏性降低。因而在较大流速情况下,可能出现被水流冲刷而脱落现象,使得抗冲刷系数降低,且该情况在粉煤灰掺比15%~20%时尤为明显,因此,适宜的粉煤灰掺加比例为15%。当粉煤灰占比增加,透水系数相应增加。其原因可能为,使用粉煤灰部分替代水泥后,会增大贯通孔隙比率[20]。当铝基锁磷剂、水泥和粉煤灰分别占比为70%、15%和15%时,抗冲刷系数为98.22%,透水系数为0.111 cm·s−1,具有强抗冲刷、高透水能力。综合考虑实验结果,选择此配比为较适材料配比,并以此配比进行后续的实验。
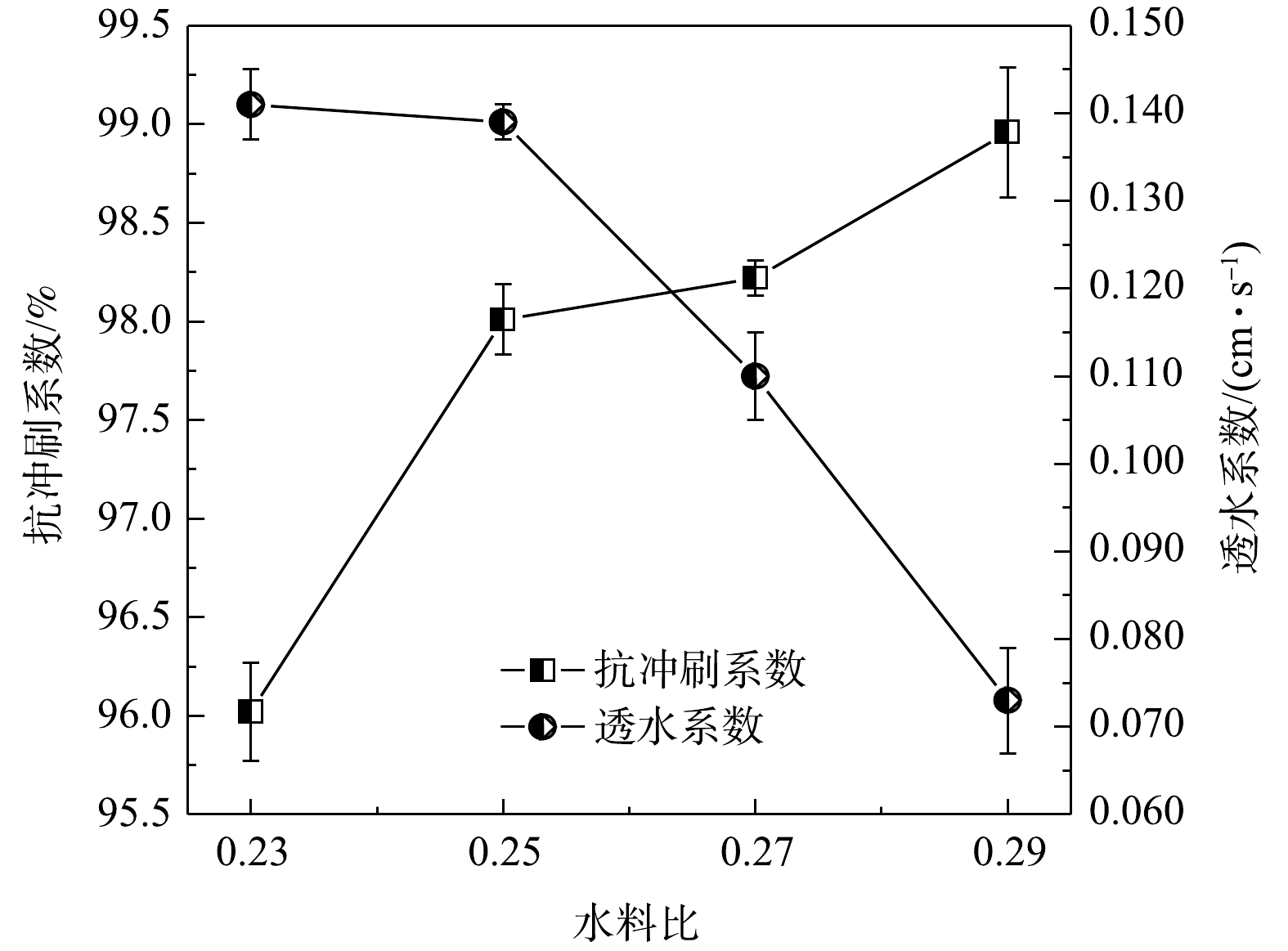
2)水料比的影响。不同水料比对活性覆盖板的性能影响如图3所示。由图3可见,随着水料比的增加,抗冲刷系数增加。其原因可能为,增加掺水量使得水泥的流动性增加,可以更好地将活性覆盖板表面的污泥颗粒包裹胶结,使得表面颗粒不易被水流冲刷而流失。而随着掺水量的增加,会使水泥浆的和易性逐渐加强,更多流动的浆体在流动过程中部分留在活性覆盖板孔隙中,使原有的孔隙变小或者堵塞[20],从而降低活性覆盖板透水系数。在水料比由0.27增加至0.29过程中,由于有部分浆体流至底部,并以胶凝形成封底[20],从而大幅度降低覆盖板的透水性能。综合上述结果可知,当水料比为0.25~0.27时,活性覆盖板的抗冲刷性能和透水性能均较好。综合考量,选定的水料比为0.25,此时活性覆盖板的抗冲刷系数为98.01%,透水系数为0.139 cm·s−1。
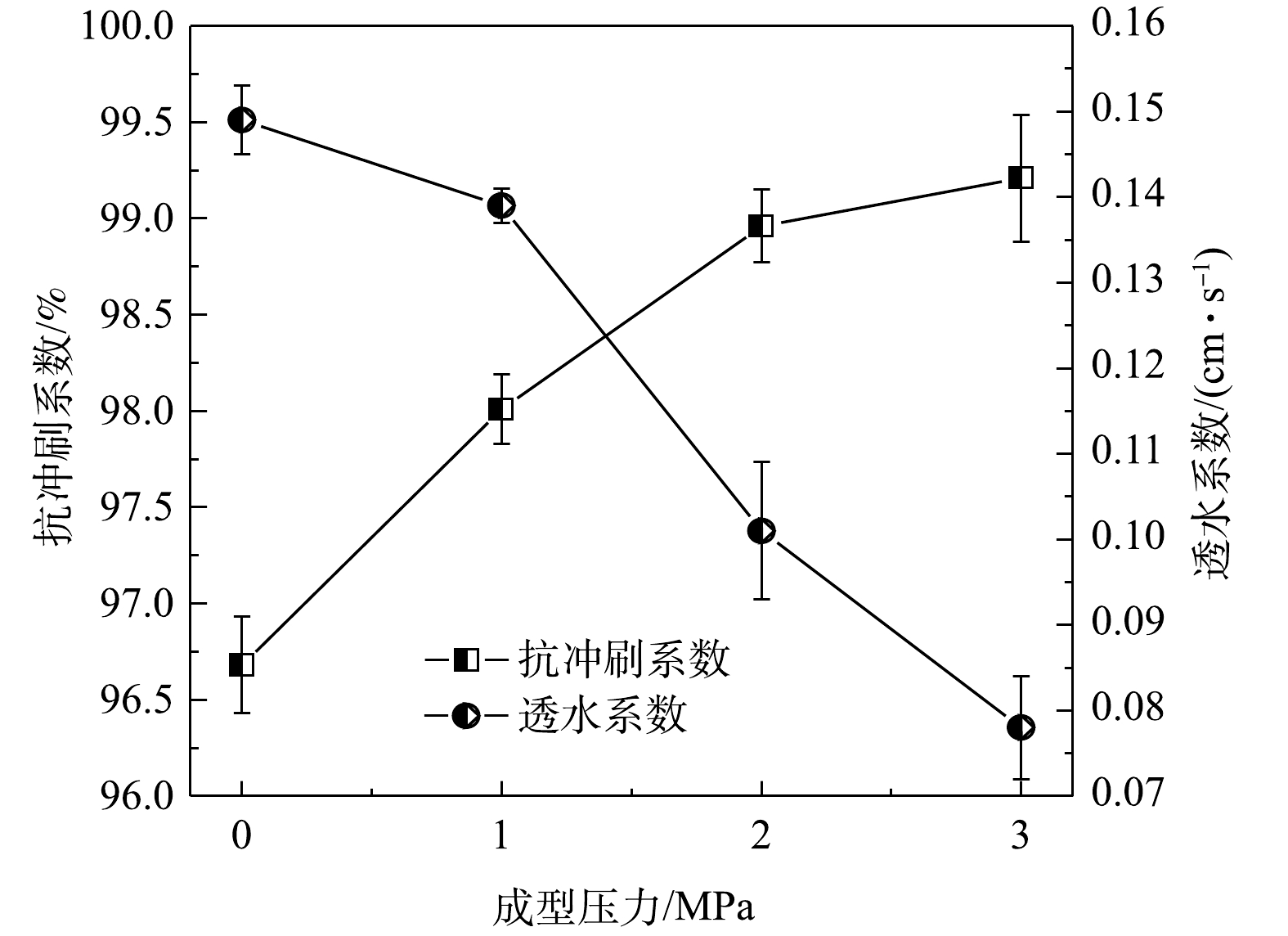
3)成型压力的影响。当成型压力分别为0.00、1.00、2.00和3.00 MPa,材料配比参数不变,水料比为0.25,不同成型压力的抗冲刷系数和透水系数变化如图4所示。由图4可见,当成型压力由0.00 MPa升至3.00 MPa时,抗冲刷系数由96.68%升至99.21%,透水系数由0.149 cm·s−1降至0.078 cm·s−1。这是因为,在压力机的作用下,覆盖板内部固体颗粒受到压力作用而重新排列堆积,从而使得已经形成的空隙不断被挤压和收缩,内部的水分和空气被排出,而同时在此过程中,粒径较小的水泥和粉煤灰在压力作用下填入这些狭小空隙,从而使得整个覆盖板更加密实稳固[22]。因此,随着成型压力的增加,覆盖板的抗冲刷系数增加,而透水系数减少。而制备过程中若不进行压制,虽然覆盖板内部留有的孔隙增多,但覆盖板表面被水泥包裹的颗粒松散且粘接性能差,容易被水流冲刷脱落,从而使得抗冲刷能力差。因此,覆盖板制备应给予适当的压力,确定的成型压力为1.00 MPa。
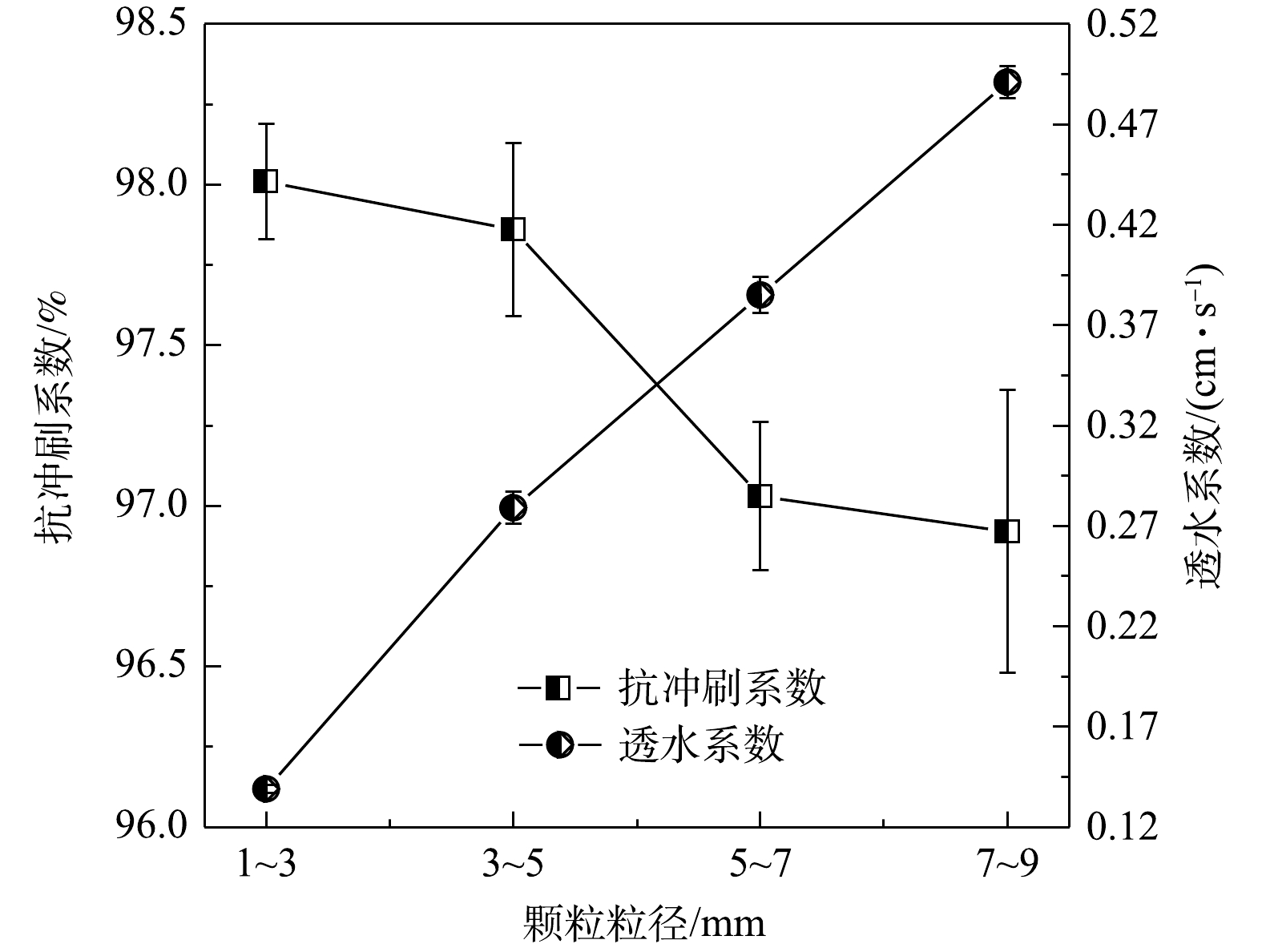
4)颗粒粒径的影响。当铝基锁磷剂粒径分别为1~3、3~5、5~7和7~9 mm时,材料配比参数不变,水料比为0.25,成型压力1.00 MPa,不同铝基锁磷剂粒径的抗冲刷性能和透水性能变化如图5所示。由图5可见,铝基锁磷剂粒径越大,其颗粒之间的空隙及覆盖板结构内部的孔隙也越大,这些孔隙可以增加覆盖板的透水性能。因此,透水系数随着颗粒粒径的增加而增大,且呈近似线性增长。然而当颗粒粒径越大时,抗冲刷系数下降。其原因可能为,在同等比例情况下的胶凝材料无法对于表面的较大颗粒有很好的粘接性,使得表面污泥颗粒较易脱落,且又有压制过程中较大颗粒粒径可能被压碎破裂,该部分破裂的污泥颗粒与胶凝材料没有充分接触,也较易脱落。综合考虑,在其他条件相同的情况下,选定的颗粒粒径为1~3 mm。
综合上述结果可知,铝基锁磷剂、水泥和粉煤灰分别占比70%、15%和15%、水料比为0.25、成型压力为1.00 MPa、污泥颗粒粒径为1~3 mm时,即为较佳的活性覆盖板制备条件,此时覆盖板的抗冲刷系数为98.01%,透水系数为0.139 cm·s−1。
以上述工况条件下制备的活性覆盖板通过XRF测试,发现其主要元素成分及占比分别为Si(28.99%)、Al(26.99%)、Ca(22.78%)、Fe(14.50%)、K(1.39%)、Mg(1.30%)、S(1.10%)、Ti(0.87%)、Na(0.29%)、P(0.29%)和Zn(0.20%)。铝基锁磷剂是以净水厂污泥改性而成[17-18],而净水厂污泥是净水厂在饮用水处理过程中加入铁盐、铝盐或铁铝盐絮凝沉淀水中悬浮物产生的安全副产物[23],其中含有较多的Si、Al、Fe等元素。水泥和粉煤灰中Ca、Si等元素较多,故制备出的活性覆盖板整体元素以Si、Al、Ca和Fe元素居多,其余元素含量相对较少。
-
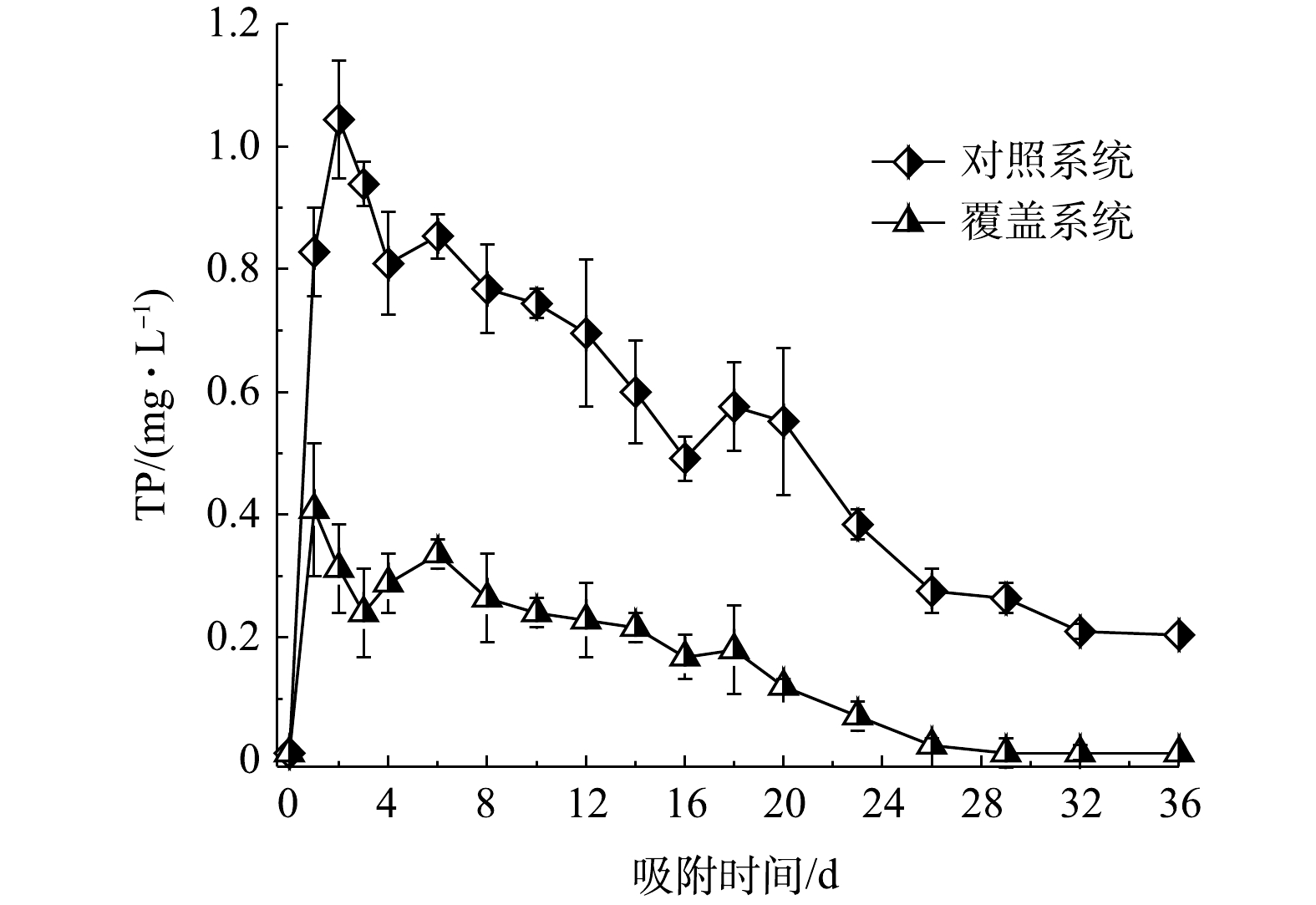
1)控制底泥磷释放效果。在实验历时36 d内,各系统上覆水的水温为28.7~33.7 ℃、pH为7.13~8.42、DO为1.25~7.17 mg·L−1、氧化还原电位为142~254 mV。各系统上覆水中的TP质量浓度的变化如图6所示。由图6可见,对照系统上覆水中TP质量浓度整体趋势先上升后下降,再呈现波动下降状态。分析原因可能为,在实验开始时,底泥与上覆水中磷含量差别较大,进而促使底泥中的磷大量向上覆水释放,后续实验过程中底泥磷的释放作用与上覆水磷向底泥的迁移作用呈现动态关系。与对照系统相比,覆盖系统对上覆水TP的平均削减率为73.78%。方差分析结果表明,覆盖系统上覆水磷质量浓度与对照系统存在显著性差异(P<0.05),可见,活性覆盖板能够有效控制底泥磷的释放,其控制磷释放途径可分以下3个部分:首先,活性覆盖板通过物理拦截作用减缓了底泥与上覆水的物质交换[24-25];其次,活性覆盖板材料中的铝基锁磷剂含有丰富的无定型铁铝盐,其比表面积较大且一般带正电荷[18, 23],因此,铝基锁磷剂颗粒中的铁铝氧化物、铁铝氢氧化物、铁铝络合物和某些金属离子(铁、铝、钙和镁离子等)容易通过配体(离子)交换、表面沉淀或络合等[23, 26]方式将磷固定在颗粒中;最后,水泥水化后主要生成水化硅酸钙、水化铝酸钙和Ca(OH)2等产物,同时铝基锁磷剂和粉煤灰中含有大量的SiO2以及Al3O2等活性组分,这些组分能够与水泥水化产物中的Ca(OH)2发生二次水化反应,即火山灰反应,再生成水化硅酸钙、水化铝酸钙等反应产物[27-28],即活性覆盖板含有丰富的水化硅酸钙、水化铝酸钙。水化硅酸钙能够解离出钙离子,同时诱导水中处于不稳态的磷酸根离子与其结合而生成磷酸铵镁和羟基磷酸钙[29-31],并附着在硅酸钙表面进而被去除。
2)控制底泥氨氮释放效果。各系统上覆水中的
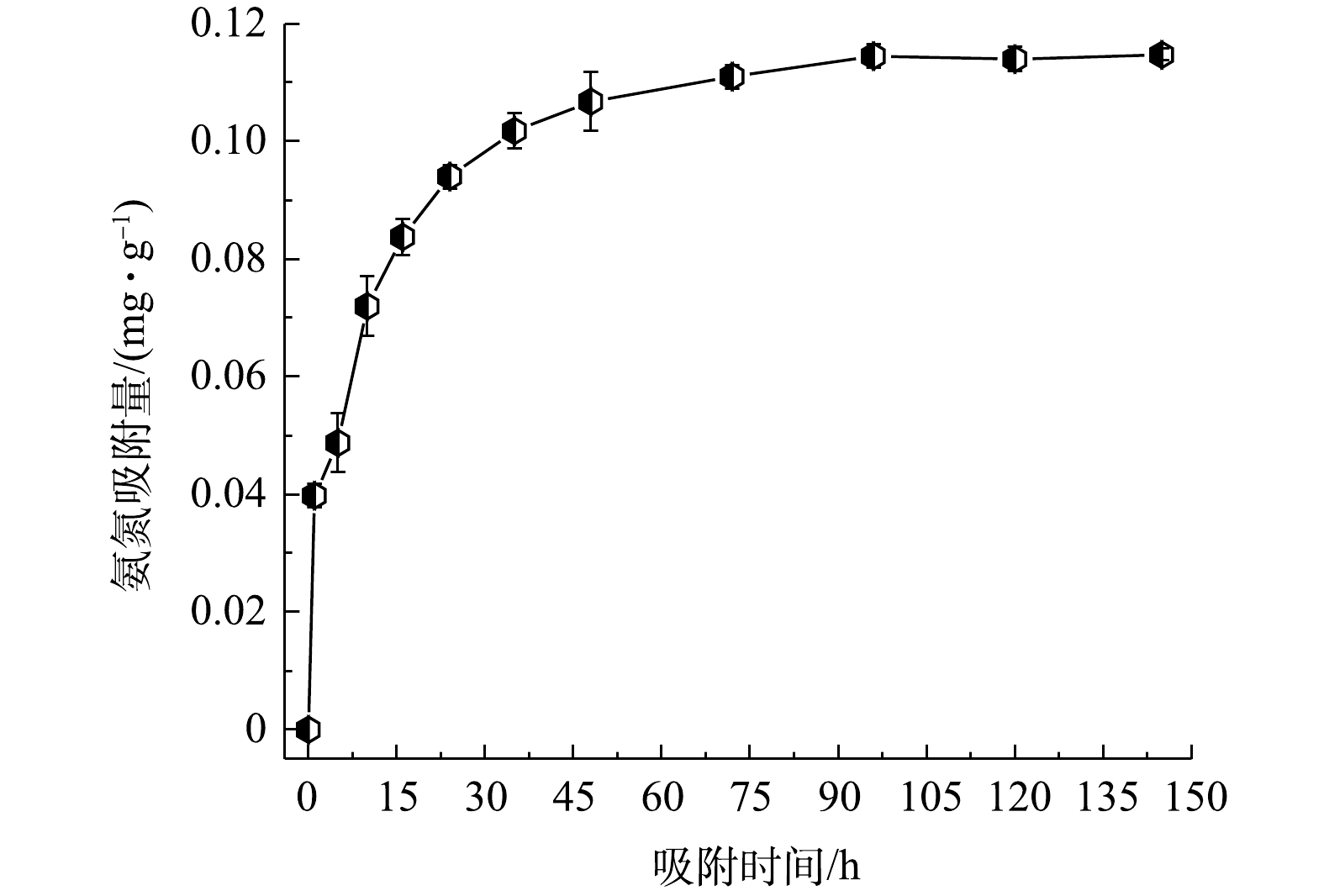
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N质量浓度的变化如图7所示。由图7可见,对照系统上覆水中氨氮质量浓度整体呈先迅速上升后下降的趋势,再上升后又缓慢下降,直至趋于初始浓度。其主要原因可能为,实验开始时上覆水和底泥间氨氮质量浓度相差较大,待底泥氨氮的释放占据主导地位,后续实验过程中底泥氨氮的释放作用和水体的自净作用之间呈动态关系,最后净化作用占主导地位。与对照系统相比,覆盖系统对上覆水${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的平均削减率为53.93%。方差分析结果表明,覆盖系统上覆水氮质量浓度与对照系统存在显著性差异(P<0.05),可见,活性覆盖板能够有效控制底泥氮的释放。铝基锁磷剂是活性覆盖板的主体原料,其对磷的吸附效果较佳,但其对于氨氮却没有吸附效果[17-18]。因此,为进一步说明活性覆盖板对氨氮具有吸附能力,考察了初始氨氮质量浓度为10 mg·L−1时,活性覆盖板在不同吸附时间下对氨氮的吸附量变化,结果如图8所示。由图8可知,活性覆盖板对于氨氮具有一定的吸附能力,但效果一般。由此推测,活性覆盖板控制氨氮释放途径主要可分以下2个方面:一方面,活性覆盖板通过物理遮掩等作用,将上覆水与污染底泥隔开,从而抑制了污染底泥中的
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N向上覆水中的迁移[24-25];另一方面,氨氮的吸附包括离子交换作用和物理吸附作用[32-33]。其中,活性覆盖板制备过程中水化生成的水化硅酸钙[27-28],其具有较大的比表面积、内部微孔发达,能够对向上覆水迁移的${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N起到物理吸附作用[34];同时,活性覆盖板中含有的金属离子(Ca2+、K+、Mg2+和Na+等),在一定情况下与${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ 发生离子交换作用[35],进而减少了水中${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N质量浓度。应当指出的是,覆盖板中的金属元素主要存在于晶体物质和玻璃相中,解吸参与离子交换作用的较少[36],因此,覆盖板对氨氮的吸附主要为物理吸附。
2.1. 制备实验
2.2. 控制氮磷释放的效果
-
1)在铝基锁磷剂(粒径1~3 mm)、水泥和粉煤灰占比分别为70%、15%和15%、水料比0.25、成型压力1.00 MPa的工况条件下,所制备的活性覆盖板抗冲刷性能和透水性能皆较佳,对应的抗冲刷系数和透水系数分别为98.01%和0.139 cm·s−1。
2)水泥占比、成型压力、水料比的增加有利于增加活性覆盖板的抗冲刷性能,不利于透水性能;粉煤灰占比、颗粒粒径的增加对于活性覆盖板的抗冲刷性能和透水性能的变化效果则与之相反。
3)与对照系统相比,覆盖系统对TP和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的平均削减率分别为73.78%和53.93%,可见,活性覆盖板能够有效控制污染底泥氮磷的释放。






 下载:
下载: