-
苯扎氯铵(benzalkonium chlorides, BACs)主要由3种正烷烃基(n-C12H25、n-C14H29和n-C16H33)取代二甲基苄基氯化铵组成的同系物混合物[1],因其具有较强的杀菌作用,常被作为洗涤剂、纺织物软化剂、界面转化活性剂、矿物浮选剂、杀菌剂以及个人护理品中的防护和抗静电成分[2]。由于杀菌剂生产及使用量的逐年递增,BACs被美国和加拿大列为高产量化学品[3]。BACs的大量生产和消耗,将不可避免地随着时空迁移进入环境中。近年来,BACs陆续在多种环境介质中被检出,如污水处理厂进水[4-5]、医院废水[6]、洗衣店出水[6](表1)、天然水体[7-8]、污水厂污泥[9]、河口沉积物[10-11]以及土壤[12]中。其中,河水中BAC-12和BAC-14的含量分别达到2.7~5.8 μg·L−1和6.3~36.6 μg·L−1[7];地表水中BAC-12、BAC-14和BAC-16的总量达到(3.24±14)~(72.5±14) μg·L−1[8];RUAN等[9]在中国52个污水处理厂污泥中检测出BACs的含量为0.09~191 μg·g−1;LI等[10]在中国珠江口的沉积物中发现BACs的含量为49.3~1 050 ng·g−1;FERRER等[11]曾报道BAC同系物在美国的河水沉积物中的浓度为22~206 μg·kg−1。KANG等[12]在韩国土壤中检测到BACs的含量为0.001~8.5 mg·kg−1。
环境中BACs的存在对生物具有潜在的毒性风险。毒理学研究表明,BACs对哺乳动物和水生动物均有急性和慢性毒性。BACs对大鼠的半数致死量(LD50)为234~525 mg·kg−1[13-14]。MELIN等[15]发现,BACs能够干扰雌性小鼠的排卵系统和发情周期,并降低雄性小鼠的精子浓度和活动能力,从而降低小鼠的繁殖率。BACs对水生生物(如藻类、水蚤、轮虫和原生动物)均具有急性毒性,半数效应浓度(EC50)为21~2 940 μg·L−1[16-18]。在欧盟修订的(EC)No.1272/2008条例中,将BACs归类为“对水生生物毒性极大”的物质,并认为对与其共存污染物的迁移性和生物有效性具有显著影响[19]。
在水环境中发现的BACs主要来自城市污水处理厂[4]。季铵盐化合物的存在可能会引起活性污泥潜在的急性反应,影响污泥的微生物活性和生存能力,从而影响其去除污染物的能力[20-21]。迄今为止,有关BACs对活性污泥微生物活性影响的研究鲜有报道。本研究在序批式反应器(SBR)处理模拟废水的基础上,以BACs的主要成分十二烷基二甲基苄基氯化铵(dodecylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride, DDBAC)为研究对象,通过污泥的微生物活性指标、氧化还原酶活性以及DDBAC浓度变化的测定,探究在DDBAC暴露下活性污泥的急性反应及微生物活性变化,以期为评估BACs在污水处理厂中的行为及影响提供参考。
全文HTML
-
实验室所用的接种污泥取自某城市污水处理厂的回流污泥。母反应器SBR的工作体积为36 L,温度控制在(22±1)℃,污泥浓度(MLSS)控制在3 000~3 500 mg·L−1,每天包含2个周期的循环,每个周期运行方式为:进水阶段(15 min)、好氧曝气阶段(180 min)、缺氧搅拌阶段(300 min)、沉降阶段(90 min)、排水阶段(15 min)和闲置阶段(120 min)。好氧阶段使用曝气设备进行曝气,溶解氧控制在2 mg·L−1左右;搅拌阶段使用搅拌器进行搅拌,溶解氧控制在0.5 mg·L−1左右,使用1.0 mol·L−1 NaHCO3和1.0 mol·L−1HCl调节系统pH,使初始pH维持在7.0±0.2。运行3个月后,系统对氮的去除率达到99%左右,表明SBR运行状态稳定。
本研究采用模拟废水,水质特性为:化学需氧量(COD)为400 mg·L−1左右,氨氮(
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N)为40 mg·L−1左右,溶解性磷(SOP)为5 mg·L−1左右。模拟废水主要由葡萄糖、NH4Cl、KH2PO4、MgSO4、CaCl2和微量元素组成,其中微量元素包括0.03 g·L−1CuSO4·5H2O、0.06 g·L−1 Na2MoO4·2H2O、0.12 g·L−1 ZnSO4·7H2O、0.12 g·L−1 MnCl2·4H2O、0.15 g·L−1H3BO3、0.15 g·L−1 CoCl2·6H2O、0.18 g·L−1 KI、1.5 g·L−1 FeCl3·6H2O、10 g·L−1EDTA。微量元素投加量为0.5 mL·L−1。 -
在进行DDBAC在SBR系统中的短期暴露实验时,从稳定运行的母反应器里取出适量污泥混合均匀,平均分配在7个完全相同的SBR子反应器中,每个反应器有效容积为3 L,7个反应器运行方式和母反应器相同。污泥浓度(MLSS)控制在3 000~3 500 mg·L−1,污泥负荷(以COD计)大约为0.3 kg·(kg·d)−1(以MLSS计),污泥停留时间(SRT)大约为15 d,水力停留时间(HRT)为20 h。反应器中DDBAC浓度分别为0、0.1、1、2、5、10和20 mg·L−1,运行一个周期后,取上清液测定DDBAC在水相中的残余量,取底泥进行TCC-脱氢酶活性、CAT活性的测定,然后弃去上清液,重新换入模拟废水,然后进行污泥耗氧速率OUR的测定。
在进行DDBAC对硝化过程的影响实验时,取母反应器活性污泥静置倒掉上清液,用自来水重复清洗3遍,再用不含C、N、P的配水清洗3遍,以充分去除原水样中C、N、P的含量。污泥浓度控制在3 000~3 500 mg·L−1,平行操作2组实验,实验期间需要曝气,曝气量控制在2 mg·L−1。温度调整至(20±1) ℃,通过1.0 mol·L−1NaHCO3和1.0 mol·L−1HCl,调节pH至7.0±0.2。起始基质(
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N和$ {\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ -N)浓度均为30 mg·L−1,其中DDBAC投加浓度与SBR子反应器中一致,每隔10 min取样分析$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N和$ {\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ -N浓度变化,直到出水各指标稳定,实验结束。 -
本研究中的常规项目如混合液悬浮固体浓度(MLSS)、
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N、$ {\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ -N、$ {\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N指标参照文献中的方法[22]测定,溶解氧采用便携式溶氧仪监测。污泥耗氧速率(OUR)采用有氧厌氧呼吸仪(美国RSA公司)测定。比氨氧化率(SAOR)、亚硝酸盐氧化率(SNOR)和硝酸盐还原率(SNRR)的测定方法参照文献中的方法[23]。
TCC-脱氢酶采用常温萃取法[22-24]测定,过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性采用紫外分光光度法[25]测定。
低于0.2 mg·L−1的DDBAC浓度采用Agilent 1260 Infinity液相色谱/6410三重四极杆液质联用系统测定,色谱柱为ZORBAX RRHD Eclipse Plus C18 2.1 mm×50 mm, 1.8 μm,流动相为2种溶液的混合液,溶液A为20 mmol·L−1乙酸铵水溶液(含0.2%甲酸),溶液B为甲醇和乙腈的混合液(甲醇∶乙腈=3∶7),流动相为A∶B=20∶80(体积比),流速为0.3 mL·min−1,温度为25 ℃,进样体积为2 μL,雾化气压力为310 kPa,干燥器温度为350 ℃,干燥器流速为10 L·min−1,采用正离子扫描方式,根据峰面积计算出其含量。高于0.2 mg·L−1的DDBAC浓度采用改进的二硫蓝离子对提取方法[26]进行测定。
1.1. 接种污泥和进水水质
1.2. 实验方法
1.3. 分析方法
-
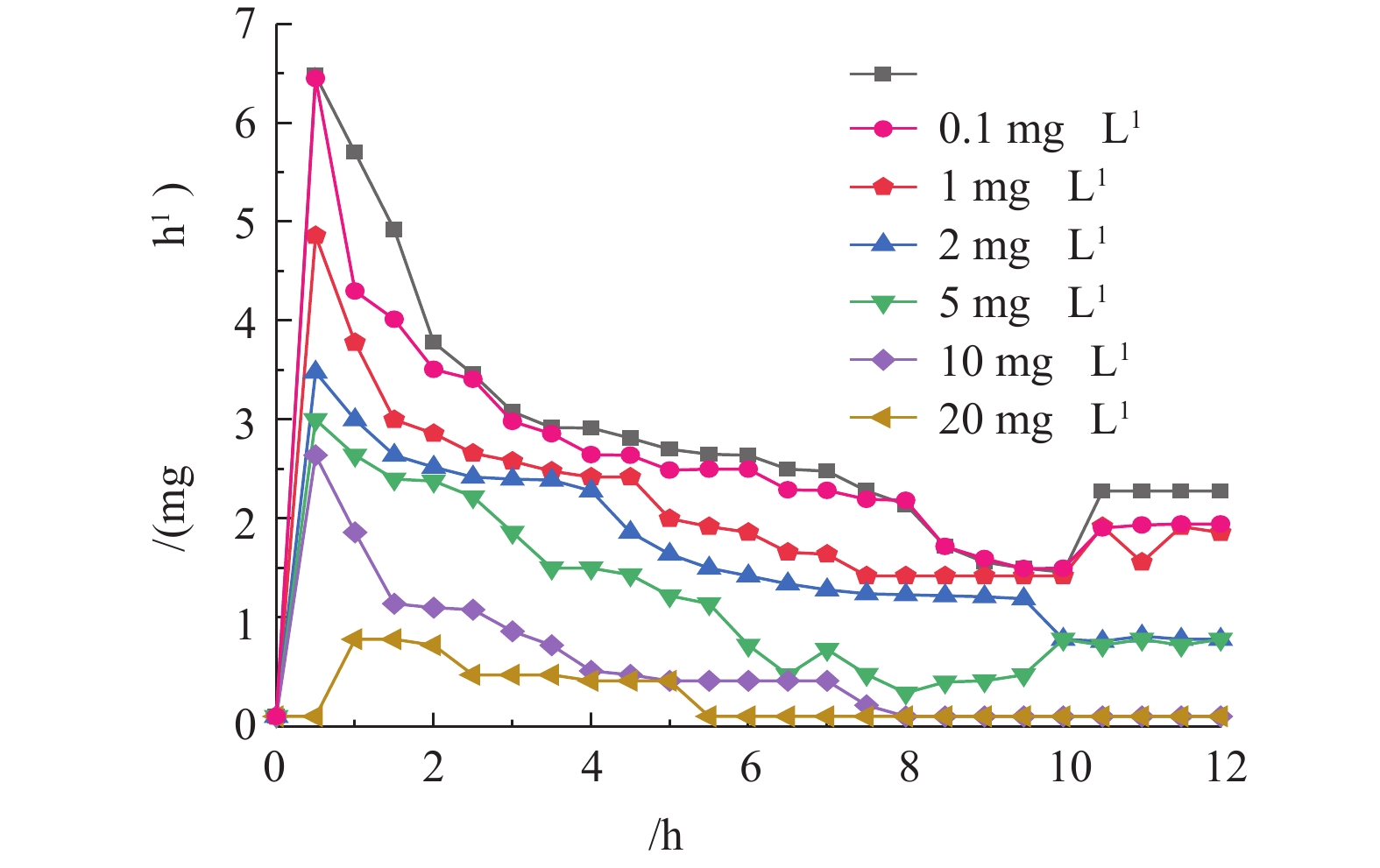
OUR是指活性污泥在单位时间内所利用氧的量,是评价污泥微生物代谢活性的一个重要指标。根据不同系统运行12 h后测定相同体积活性污泥OUR的变化,可以判断不同浓度DDBAC暴露下污泥性质的变化,结果如图1所示。前1 h,OUR呈明显的上升趋势,不含DDBAC的系统中污泥OUR最高达6.48 mg·h−1。随着DDBAC浓度的增加,最高OUR呈下降趋势。在1 mg·L−1 DDBAC的系统中,OUR最大为4.86 mg·h−1。当DDBAC浓度达到20 mg·h−1时,污泥OUR上升缓慢,1 h时最高OUR为0.78 mg·h−1;1 h后,7组反应器中污泥的OUR均逐渐降低,且DDBAC浓度越高,OUR的降低趋势越明显。当DDBAC浓度达到20 mg·L−1时,经过5.5 h后,污泥的呼吸速率降为0。结果表明,随着DDBAC浓度的增加,活性污泥中呼吸酶活性越低,氧的吸收和利用率越低。DDBAC作为有机抗菌剂,与细胞膜具有较好的相容性,可损伤细胞膜,造成细胞裂解;或与细胞膜融合,损坏细胞中的酶、蛋白质,使氧化磷酸化过程和电子传递系统受到影响,导致呼吸作用受到抑制。ZHANG等[27]和CROSS等[28]亦认为呼吸酶活性的下降是由DDBAC引起细胞裂解所致。
-
DDBAC对硝化反应中的氨氮的降解过程影响如图2(a)所示,对亚硝氮的降解过程影响如图2(b)所示。从图2(a)中可以看出,当DDBAC浓度为0.1 mg·L−1和1.0 mg·L−1时,氨氮的转化速率大于空白对照组,即DDBAC的存在能够促进氨氮的氧化过程。当DDBAC浓度为2、5、10和20 mg·L−1时,氨氮的氧化速率随着DDBAC浓度的升高而逐渐下降,氨氮去除率分别为94.28%、81.61%、67.59%和59.92%。这表明,DDBAC的过量存在(≥2.0 mg·L−1)抑制了氨氧化菌的活性,影响好氧条件下氨氮的转化过程,且浓度越高,抑制效果越明显。此结果与SÜTTERLIN等[29]研究结果一致。从图2(b)中可以看出,低浓度DDBAC对亚硝酸盐氧化菌几乎无影响,20 mg·L−1的DDBAC短期暴露在系统中,使得亚硝氮降解率从100%降到(62.98±0.02)%,亚硝酸盐氧化菌受到一定抑制。此现象可能与微生物群落中氨氧化菌AOB与亚硝酸盐氧化菌NOB的相对丰度有关。与亚硝酸盐氧化菌相比,氨氧化菌的产率低、比增长速率小,更容易受到外界环境的影响[30]。
-
图3展示了不同浓度DDBAC对系统内SAOR、SNOR和SNNR的影响。当DDBAC浓度为0.1 mg·L−1和1.0 mg·L−1时,对系统内SAOR、SNOR和SNNR基本无影响。当DDBAC浓度为2 mg·L−1时,SAOR(以
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N计)由(2.99±0.16) mg·(g·h)−1(以MLSS计)降至(2.82±0.15) mg·(g·h)−1,降低了5.72%;当DDBAC浓度为20 mg·L−1时,SAOR降至(1.79±0.09) mg·(g·h)−1,降低40.08%。DDBAC对SNOR的影响较小,当DDBAC浓度≤10 mg·L−1时,SNOR基本不受影响;当DDBAC浓度达到20 mg·L−1时,系统内SNOR受到较大影响,与对照组相比,下降了37.02%。当进水DDBAC浓度高于2 mg·L−1时,SAOR低于SNOR,此现象表明,氨氧化过程更易受到DDBAC的影响,与2.2节中的研究结果相呼应。由图3(b)可看出,当DDBAC浓度达到20 mg·L−1时,SNNR(以$ {\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N计)由(23.69±0.61) mg·(g·h)−1(以MLSS计)降到(18.64±0.62) mg·(g·h)−1,下降了(21.32±0.59)%。此研究结果表明,与硝酸盐还原过程相比,DDBAC对硝化过程,尤其是氨氧化菌主导的氨氧化过程的抑制作用更加显著。这是由于与异养型微生物相比,主导硝化过程的硝化细菌世代时间长,增长速率低,一般只占活性污泥微生物总量的5%左右,对环境条件要求较为苛刻。因此,DDBAC对硝化过程的抑制性更强。 -
在有机化合物的好氧生物降解过程中,TCA循环是主要的代谢过程[31]。TCC-脱氢酶参与了TCA循环,能较好地反映微生物异养代谢行为。因此,在本研究中,脱氢酶活性可以作为有机化合物生物降解能力的指标之一,来评价DDBAC造成的急性效应[32]。TCC-脱氢酶活性的抑制率5%~25%属轻度抑制,25%~60%属中度抑制,大于60%属重度抑制[33-34]。DDBAC对污泥样品中TCC-脱氢酶活性的影响如图4所示。当DDBAC浓度低于2 mg·L−1时,DDBAC对TCC-脱氢酶活性的影响几乎可以忽略不计。当DDBAC浓度为2、5和10 mg·L−1时,TCC-脱氢酶活性与空白组对比,分别降低了(10.50±1.70)%、(24.20±0.01)%和(24.31±0.68)%。此时为轻度抑制;当DDBAC浓度增加到20 mg·L−1时,抑制率增加到(31.42±0.29)%,为中度抑制。根据以往的研究,季铵盐类化合物在活性污泥中的行为一般为3个过程:吸附、抑制和生物转化[35]。也有报道[26]认为,95%的季铵盐都会吸附于颗粒物,季铵盐浓度越高,对微生物的吸附量越大,对活性污泥活性的抑制作用越强。脱氢是微生物氧化分解有机物过程中的关键步骤,TCC-脱氢酶活性降低,降低了微生物对有机物的氧化分解速率,也反映了DDBAC对微生物种群的毒害作用。
CAT是生物呼吸和代谢过程中的末端还原酶,它能将对细胞有毒害作用的H2O2分解为水和氧气[36]。图4显示了DDBAC对TCC-脱氢酶活性、过氧化氢酶活性的影响。当DDBAC浓度为1.0 mg·L−1和2.0 mg·L−1时,对CAT的影响几乎相同,抑制率在18%左右;DDBAC浓度达到5 mg·L−1时,抑制率为22.4%;DDBAC浓度为10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1时,抑制率均为47%左右。此研究结果表明,含DDBAC废水的输入对污泥中的微生物的呼吸和代谢过程产生了负面影响,破坏了污泥的抗氧化机制。腾跃等[37]曾观察过苯扎溴铵与过氧化氢酶之间的微观作用机理,发现苯扎溴铵能够通过改变部分的氨基酸残基和蛋白质的二级结构,使过氧化氢酶的骨架结构变松散,进而抑制了过氧化氢酶的活性。
-
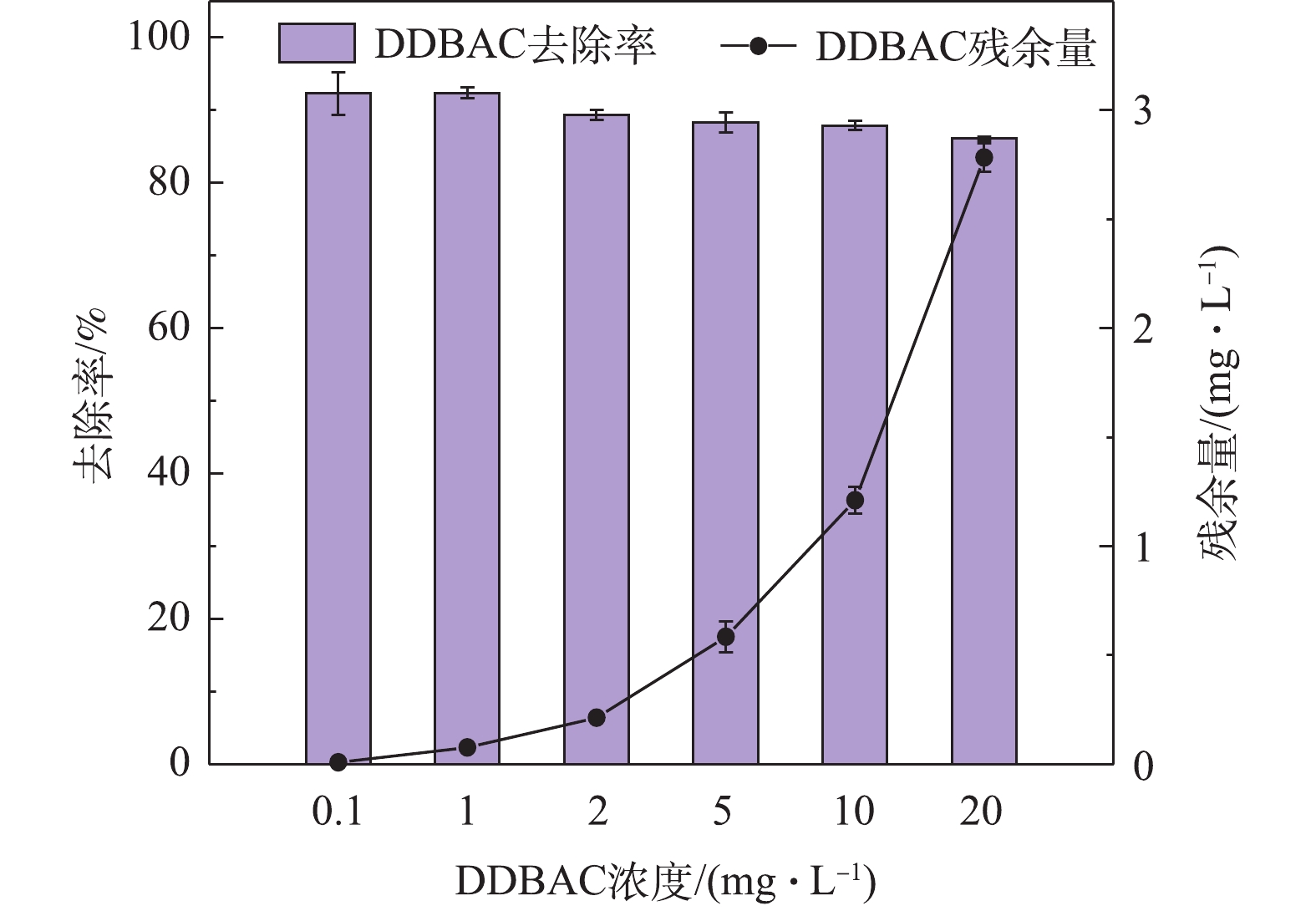
图5展示了微生物对不同浓度DDBAC的去除情况。当DDBAC的进水浓度为0.1 mg·L−1时,系统对DDBAC的去除率达到(92.30±2.97)%;当DDBAC初始浓度≥1 mg·L−1时,活性污泥微生物对DDBAC的去除潜力随着其浓度的增加而逐渐减弱,去除率由92.3%(初始浓度1 mg·L−1)降至(86.09±0.32)%(初始浓度20 mg·L−1),出水中的DDBAC浓度由(0.008±0.003) mg·L−1增加到(2.78±0.06) mg·L−1。造成此结果可能的原因是,活性污泥处理系统具有一定的容纳、消化和去除DDBAC的潜力,但是能力尚有限,当DDBAC浓度逐渐增大时,系统中的微生物不能够在有限的处理时间内将DDBAC完全去除,因此导致了出水中DDBAC的残留。当DDBAC浓度较大时,水相中残留的DDBAC将随着出水排至流域水环境中,造成河流、湖泊等地表水以及沉积物中DDBAC的积累,且DDBAC具有生物毒性,将增加水环境健康管理负担和安全用水的风险。
2.1. DDBAC浓度变化对污泥OUR的影响
2.2. DDBAC对硝化过程的影响
2.3. DDBAC对污泥SAOR、SNOR、SNNR的影响
2.4. DDBAC对氧化还原酶活性的影响
2.5. 微生物对DDBAC的去除潜力
-
1) DDBAC能够影响污泥的耗氧速率,对污泥的呼吸产生抑制作用,且其浓度越高,抑制作用越强。
2)相对于反硝化过程,DDBAC对硝化过程,尤其是氨氧化菌主导的氨氧化过程的抑制作用更加显著。当DDBAC浓度≥2.0 mg·L−1时,即能够抑制氨氮的转化过程,且浓度越高,抑制效果越明显。
3)当2 mg·L−1≤DDBAC≤10 mg·L−1时,DDBAC对脱氢酶活性为轻度抑制;DDBAC浓度为20 mg·L−1时,对脱氢酶活性为中度抑制,严重影响污泥代谢过程。
4) DDBAC对过氧化氢酶活性的抑制作用随其浓度的升高而加强,可影响微生物的呼吸和代谢过程,破坏污泥的抗氧化机制。
5)活性污泥微生物对DDBAC具有一定的去除潜力,但处理能力尚有限,出水中残留的DDBAC将增加水环境健康管理负担,提高安全用水的风险。





 下载:
下载: