-
挥发性有机化合物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)是一类有机化合物的统称,是指饱和蒸气压大于70 Pa(常温下)、沸点为50~260 ℃(常压下)的有机化合物,主要包括酮类、烃类、芳烃类、醛类、醇类、脂类、胺类等物质[1]。许多VOCs类物质对人体及各个感官有刺激作用,且具有一定的毒性。因此,VOCs的治理迫在眉睫[2]。
VOCs的人为排放主要来自使用有机溶剂的工业活动、燃料燃烧和交通运输工程。据统计,我国VOCs的排放量非常大,已经远远高于粉尘和二氧化硫等污染物的排放量[3]。目前,处理VOCs的方法主要有2类:一是以工艺和设备改善为主的预防措施;二是以末端治理为主的控制措施。国内外VOCs处理技术主要是末端处理技术,包括吸附技术、化学吸收技术、催化燃烧技术、光催化技术和生物降解技术等[4-7]。其中,吸附处理技术具有效率高、能耗低、吸附剂再生效果好、实用且易于推广的特点,因而在VOCs处理和回收工艺中得到较为广泛的应用[8-9]。常用的活性炭吸附剂因具有再生困难、疏水性差、易燃烧等缺点,在工业应用中仍存在一定的局限性。与活性炭相比,分子筛具有不易燃烧、吸附选择性强等优点,并且其物理性质稳定、容易脱附,这些特点使其成为潜在的吸附剂[10-11]。
NaY分子筛比表面积大,微孔结构发达,对不同VOCs均具有良好的吸附性能,是优良的吸附材料。NaY分子筛对VOCs分子的吸附性能主要取决于内部孔道结构,不同沸石分子筛内部孔道结构不同,其吸附特性存在显著差异。ZHANG等[12]研究了不同多孔材料NaY、SBA-15、MCM-41和SiO2对甲苯的吸附性能,发现微孔含量最多的NaY沸石对甲苯吸附容量最大。在甲苯浓度较低时,NaY分子筛平衡吸附容量与活性炭接近,而ZSM-5、MCM-41等分子筛的平衡吸附容量均小于NaY分子筛[12]。张媛媛[13]采用硅烷化改性的方法对NaY分子筛进行改性,在高湿条件下,对甲苯和乙酸乙酯吸附性能进行了测定,发现改性后NaY抗湿性能明显提高。周瑛等[14]、王稚真[15]考察了NaY分子筛对含水蒸气VOCs的吸附性能,并通过改性制备出疏水性能优良的Y型分子筛。LIU等[16]研究了Pt对NaY沸石吸附乙醇的影响,发现Pt团簇可与乙醇分子形成化学键,增强了对乙醇的选择性吸附。NIGAR等[17]考察了干空气情况下不同硅铝比Y沸石对己烷的吸附特性,证明低硅铝比NaY、HY对己烷吸附容量高。这些研究探讨了分子筛疏水性能、硅铝比、化学键等因素对吸附剂吸附性能的影响,但吸附质种类单一,缺乏对多种典型VOCs吸附性能的系统研究。而实际工业废气种类繁多且含有水分,因此,本研究以NaY型分子筛作为吸附剂,从温度、湿度、进气浓度、循环使用性及吸附质物理性质等方面,较全面地探究了工业过程中排放的3种典型单组分VOCs丙酮、邻二甲苯、乙酸乙酯与含湿VOCs在NaY分子筛上的吸附性能,最终通过动力学方程进行拟合,得到吸附性能参数,绘制理论穿透曲线,为研究工业应用中分子筛的吸附行为提供参考。
-
试剂:丙酮、邻二甲苯、乙酸乙酯(均为分析纯)。沸石分子筛:NaY型(南开大学),Si/Al=5.2。仪器:质量流量计(北京七星华创电子股份有限公司,中国);N2吸附仪(Quantachrome Instruments NOVA2000型自动吸附仪,美国Quantachrome公司);VOC便携式检测仪(MiniRAE3000,美国华瑞);X射线衍射仪(D/MAX-2500PC,日本理学Rigaku);场发射扫描电子显微镜(S-4800-Ι,日本HITACHI)。
-
样品比表面积、孔体积、孔径和吸脱附曲线在Quantachrome Instruments NOVA2000型吸附仪上测定并绘制,以氮气为吸附质。测定前,样品于200 ℃下脱气2 h。样品的比表面积采用BET法计算。邻二甲苯、丙酮、乙酸乙酯的初始浓度和尾气浓度均由VOC便携式检测仪(RAE3000)测定。
在吸附实验中,NaY分子筛装填量均为800 mg,置于内径为8 mm的U型管内进行吸附实验,平衡吸附容量计算方法[18]见式(1)。
式中:q为平衡吸附容量,mg·g−1;F为气体流速,mL·min−1;t为吸附时间,min;C0、Ci分别为进气、吸附t时间后尾气中VOCs质量浓度,mg·m−3;W为吸附剂装填量,mg;ts为吸附平衡时间,min。
-
VOCs吸附实验装置见图1。可以看出,以高纯氮为载气,四通阀分为3路:一路稀释N2,一路通过鼓泡带出VOCs,一路通过鼓泡带出水蒸气。通过质量流量计控制气速,可配制出一定湿度、一定浓度的气体。3路气体混合后,进入吸附管吸附,通过VOCs便携式检测仪检测尾气浓度的变化,探究分子筛的吸附性能。
-
使用氮气吸脱附仪对NaY分子筛比表面积与孔径进行了测试,结果见图2。可以看出,分子筛对氮气的吸附等温线属于典型的Ι型等温线,即等温线的形状是微孔填充的特征[19]。在较低的相对压力p/p0时,吸附容量迅速增加;达到一定p/p0后,吸附容量趋于恒定数值,即达到极限吸附[20]。在低压段,吸附容量平缓增加,在孔壁形成单分子层吸附,随着压力的上升,在最细孔内开始出现毛细凝结现象;当压力持续增加时,较大的孔也被凝聚液填充直至完全,在多孔介质脱附过程中,毛细凝聚现象的解除从大孔再到小孔依次进行,吸脱附过程不完全可逆,出现吸脱附等温线不完全重合;在p/p0趋于1时,略出现迟滞现象,说明材料的孔形状与尺寸较均匀[21]。孔径分布曲线表明,NaY分子筛微孔尺寸主要分布在1.5~2.0 nm,峰值为1.92 nm,主要是NaY分子筛颗粒堆积孔的孔径,而其实际孔径为0.6~0.7 nm。根据测得数据分析,分子筛的比表面积和总孔隙体积分别为568.6 m2·g−1和0.277 9 mL·g−1;微孔表面积与微孔体积分别为339.4 m2·g−1和0.194 3 mL·g−1。由图3可见,分子筛晶体结构完整,其相对结晶度为90%,呈现典型的八面沸石型立方晶体。
-
采用导电胶黏结法对处理后样品进行扫描电镜分析,从而观察样品的表面形貌。图4是将NaY分子筛的图像放大10 000倍后所得到的SEM谱图。经过扫描电镜分析可知,NaY分子筛粒度分布致密,棱角分明,大小均匀,洁净度和纯度较高,分散度较好,是一种具有连续网络结构的纳米多孔材料。
-
1)温度对吸附性能的影响。综合典型工业生产行业的污染气体排放种类发现,乙酸乙酯、二甲苯、丙酮3种典型VOCs涵盖了汽车、造船、印刷、制药和家具制造等行业,其温度在23~40 ℃。因此,本实验在质量浓度为660 mg·m−3,空速为30 000 mL·(g·h)−1的条件下,选取温度303、318、328 K,对NaY分子筛吸附性能进行测试,实验结果如图5所示。可以看出:温度为303~328 K时,NaY分子筛对3种VOCs均能保持较大的吸附容量;温度由303 K升至328 K时,邻二甲苯吸附容量下降了3.66%,乙酸乙酯吸附容量下降了2.87%,丙酮吸附容量下降了10.0%。可见,NaY分子筛吸附时受温度的影响较大,适当降低温度有利于吸附。王稚真[15]测定了沸石分子筛对几种VOCs的吸附热焓,结果均小于0,随着温度的升高,分子筛对有机物的亨利常数值下降。这与分子筛吸附是放热过程,而且高温不利于吸附的观点吻合。通过实验数据可以发现,NaY对丙酮的吸附容量受温度的影响最大,而邻二甲苯、乙酸乙酯在NaY上的吸附容量受温度的影响较小。
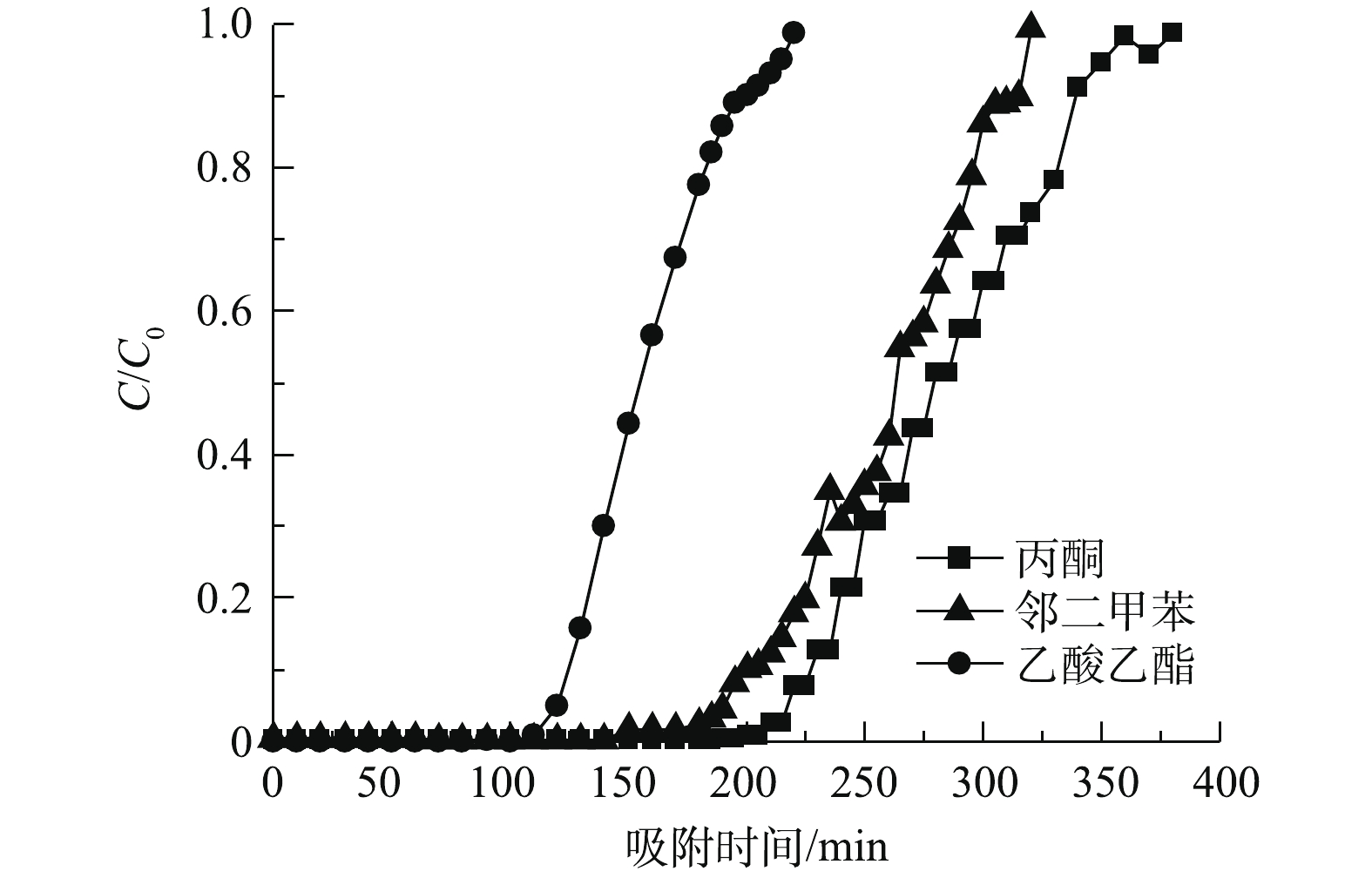
2)穿透时间与吸附容量。分子筛的穿透时间是工业应用中选择吸附剂的一项重要参数。在整个吸附过程中,进气浓度恒定,当尾气浓度达到进气浓度的5%时,即为吸附剂已穿透;当尾气浓度达到进气浓度的95%时,即为吸附饱和[15]。从开始吸附到穿透所用的时间为穿透时间[22],吸附至分子筛饱和的时间为吸附饱和时间,吸附饱和时间愈长,则吸附效果愈好。NaY分子筛对不同VOCs的吸附时间对比情况如图6所示,穿透时间、饱和时间和吸附容量的对比情况见表1。
图6反映了质量浓度为660 mg·m−3时3种VOCs穿透曲线的对比结果。可以看出,NaY分子筛对3种VOCs均有较高的吸附能力,对邻二甲苯的吸附容量最大,为185 mg·g−1,对丙酮和乙酸乙酯分别为176 mg·g−1和168 mg·g−1;对丙酮的穿透时间最长,为220 min,对邻二甲苯和乙酸乙酯分别为190 min和120 min。与NaY分子筛吸附性能相近的吸附材料为13X分子筛[23],测得其对丙酮吸附容量为170 mg·g−1。负载型分子筛对丙酮的吸附性能也存在一定局限性:Cu-Mn-Ce/5A负载型吸附剂[24]对丙酮的吸附容量为86.4 mg·g−1,Na-ZSM-5负载型吸附剂[25]吸附丙酮的容量为94 mg·g−1,均低于NaY分子筛的吸附性能。在吸附穿透时间上,Na-ZSM-5负载型吸附剂[25]对丙酮、乙酸乙酯的吸附穿透时间分别为50 min和35 min,远低于NaY分子筛。通过对比可以明显地看出,NaY分子筛具有吸附容量大、吸附时间长等优良吸附性能。
3)进气浓度对吸附的影响。由图7可知,在进气质量浓度较低时,质量浓度微小的变化即可导致平衡吸附容量迅速增大,这是典型的微孔吸附现象;当进气质量浓度达到一定时,吸附容量趋于稳定,说明分子筛吸附能力达到饱和[26]。从3种VOCs的吸附等温线可看出:在质量浓度低于660 mg·m−3时,NaY分子筛对3种气体吸附能力相当,对丙酮吸附容量略高于乙酸乙酯;随着进气质量浓度的增高,分子筛对丙酮与乙酸乙酯的平衡吸附容量发生交叉,即在高于660 mg·m−3后,乙酸乙酯平衡吸附容量高于丙酮;随着质量浓度的持续增高,分子筛对3种气体吸附容量趋于饱和,邻二甲苯、乙酸乙酯、丙酮最终平衡吸附容量分别为196、185和176 mg·g−1。
4)含湿VOCs对吸附性能的影响。工业上含VOCs的气体温度一般为23~40 ℃,湿度为30%~80%[27]。本研究在相对湿度为30%条件下(RH=30%),测定了3种典型VOCs的吸附穿透曲线与吸附容量。如图8所示,NaY分子筛吸附3种含湿VOCs,出现C/C0明显大于1.0的现象。这表明,3种VOCs和水蒸气存在显著的竞争吸附,并且随着吸附过程的进行,部分吸附质被极性更强的水分子置换出来,使得出口浓度高于入口浓度,即C/C0>1[13]。由表2可知,NaY分子筛对3种含湿VOCs的吸附容量远低于干燥环境时的吸附容量。
5) NaY分子筛与HY分子筛吸附对比。将NaY分子筛交换为HY分子筛,在25 ℃,空速30 000 mL·(h·g)−1,邻二甲苯质量浓度660 mg·m−3的条件下,进行了对比吸附实验,其吸附穿透曲线如图9所示,吸附容量与穿透时间见表3。有研究[28]表明,位于孔口附近的阳离子数目和种类会影响分子筛的孔径,通过阳离子交换可在一定程度上改变分子筛孔径与比表面积的大小。与上述结果相吻合,本实验中经交换后的HY型分子筛比表面积亦有所降低,这导致其吸附容量低于NaY,且较NaY先达到吸附饱和。
6)NaY分子筛的循环使用性能。利用吸附法吸附处理VOCs污染物时,须考虑吸附剂的再生问题。工业上常用的再生方法主要有高温水蒸气脱附、氮气吹扫、降压或真空脱附等。沸石分子筛具有良好的热稳定性,通过高温热处理可以进行有效再生[29]。本实验采用抽真空,200 ℃条件下脱附再生,其循环使用性能如图10所示。分子筛经真空高温脱附后,第1次脱附率达到了100%。再生后进行新一轮的吸附,随循环次数的增多,吸附容量出现了下降的趋势。循环多次后,仍能保持较高的吸附容量,吸附容量减少量均在20%以内,说明NaY分子筛有较好的循环使用性能,可重复多次进行吸附。
7)吸附质物性与吸附容量的关系。有研究[21]发现,分子筛对吸附质的吸附容量受分子动力学直径、沸点、密度、饱和蒸汽压等多种因素综合影响,造成吸附质与吸附剂亲和力不同,从而影响吸附行为。表4列出了3种典型VOCs的物性参数[30],将其与吸附容量进行关联,结果如图11~图13所示。
理论上,大于吸附质分子的孔径即可成为有效吸附孔径。但在本实验中,分子筛的有效吸附孔径为1.9 nm,远大于VOCs分子动力学直径,这时的孔径只起到通道作用[31-32]。从物性与吸附容量的关系可以看出,沸点、相对分子质量与吸附容量呈正相关关系,蒸汽压与吸附容量呈负相关关系。本研究中决定吸附性能的主要因素可能是VOCs的沸点与相对分子质量,随着沸点的增大,邻二甲苯、乙酸乙酯、丙酮在NaY分子筛上的吸附容量逐渐增高。分子筛对VOCs的物理吸附类似于气体液化和蒸汽凝结,沸点的大小与物质液化或凝结存在关联[33]。邻二甲苯的沸点远高于丙酮和乙酸乙酯,这意味着邻二甲苯分子更容易在分子筛孔隙间发生凝结或液化[34],因此,其物理吸附容量为最大。3种VOCs吸附容量大小为邻二甲苯>乙酸乙酯>丙酮,其原因可能是:分子筛自身有效吸附点位数量有限,当点位上每种VOC吸附数量相近时,分子质量大的邻二甲苯和乙酸乙酯因其单分子质量大于丙酮而表现出分子筛对其饱和吸附容量大。
-
在恒温下,不同浓度单组分气体和吸附剂长期接触达到平衡时,最大吸附容量和该组分的分压关系可以用吸附等温线方程[11]来描述,其计算方法见式(2)。对NaY分子筛吸附VOCs的行为,采用Langmuir吸附等温方程和Freundlich吸附等温方程来进行拟合,结果见图14和图15。
式中:qm为最大吸附容量,mg·g−1;K为Langmuir平衡常数,Pa−1;p为分压,Pa;因为吸附是放热过程,常数K随温度的升高而减少。如果在表面同一吸附位上的吸附分子之间互不作用,即吸附热与覆盖率无关,可以将式(2)重新整理得式(3)。
将1/q对1/p作图,校正实验数据与Langmuir模型的拟合程度,结果见图14。从该直线斜率与截距求得Langmuir常数K和饱和吸附极限值qm。
Freundlich方程拟合结果表明,在等温条件下,吸附热随覆盖率的增加呈对数下降时,吸附容量与压力的指数成正比。压力增加,吸附容量随之增大,但压力增大到一定程度以后,吸附剂吸附饱和,其饱和吸附容量维持恒定值。当中等程度覆盖时,Freundlich方程和Langmuir方程接近。式(4)为Freundlich吸附等温方程。
式中:Kf为与吸附剂和吸附质特性及温度有关的Freundlich常数;n为与温度有关常数。将式(4)两边取对数,得式(5)。将lnq对lnp作图,校正实验数据与Freundlich模型拟合程度见图15,从该直线斜率与截距求得Freundlich常数Kf和n。
分子筛采用Langmuir方程拟合度更高,说明Langmuir等温线能更好地描述NaY沸石吸附3种VOCs的等温过程。
-
YOON等[35-36]提出了吸附概率的半经验气体吸附模型(见式(6)),该模型可以很好地拟合S型穿透曲线,与本实验穿透曲线相适合。利用Yoon-Nelson模型对实验数据进行拟合,求出τ和
$k'$ ,对吸附实验进行评价。式中:C为吸附时间t的出口VOCs浓度,mg·m−3;C0为进口VOCs浓度,mg·m−3;
$k'$ 为速率参数,min−1;τ为半穿透时间(出口浓度达到进口浓度50%所对应的时间),min。将理论模型和实验数据进行拟合,ln[C/(C0−C)]与t的对应关系是一条直线,根据斜率和截距得到
$k'$ 和τ。拟合结果如图16所示,所得参数见表5。由表5可知,速率参数
$k'$ 顺序为丙酮<邻二甲苯<乙酸乙酯,表明吸附床层吸附丙酮速率最小,穿透时间最长,达到饱和吸附时间最慢,可实现长时间的吸附行为。乙酸乙酯τ值最小,表明达到穿透时间最快,这与实验测得数据一致,说明回归方程与实验数据相关度良好,模型拟合效果好。将得到的参数值
$k'$ 与τ代回式(6),得到式(7)。根据式(7)作图,可以得到各种VOCs的理论穿透曲线(如图17所示)。将实验曲线与拟合的理论曲线进行对比,可以看出拟合度较优。因此,用该模型来拟合气体吸附是合适的。在工业应用中,可选择该模型对固定床吸附VOCs过程中气体出口浓度与时间的关系进行预测,可为实际工业应用提供指导。
吸附概率的半经验气体吸附Yoon-Nelson模型,总结出ln[C/(C0−C)]与时间t之间的线性关系,可直观反映这2个变量的关系。本实验中,Yoon-Nelson模型最终拟合度在0.99以上,表明其可以较好地应用于模拟VOCs气体的吸附行为,这对工业应用具有实际的指导意义。
-
1)从温度、湿度、穿透时间、进气浓度和循环使用性等几个方面对NaY型沸石分子筛进行深入探究,当温度由303 K升至328 K时,分子筛对丙酮饱和吸附容量受温度的影响最大,下降了10.0%;相对湿度为30%条件下,分子筛吸附性能降低,疏水性较差;NaY分子筛表现出对3种VOCs均有较好的吸附特性,对丙酮吸附饱和时间达到355 min;在一定浓度范围内,NaY分子筛对丙酮与乙酸乙酯平衡吸附容量出现交叉;NaY分子筛循环性较优,对3种VOCs均可脱附再生,可进行下一轮吸附。
2)将NaY分子筛对VOCs吸附容量大小与VOCs的物性进行关联,可以看出,决定分子筛吸附的主要因素是VOCs分子的沸点。由于沸点过高,产生液化与凝结现象,从而导致吸附容量增大。
3)通过吸附热力学和动力学方程研究NaY分子筛吸附床层吸附不同VOCs的机理,发现Langmuir等温线能更好地描述NaY沸石吸附3种VOCs等温过程;Yoon-Nelson模型能够较好地模拟吸附过程,验证了吸附床对不同VOCs出口浓度与吸附时间存在线性关系,通过该模型可以得出半穿透时间与吸附速率常数,这对今后生产应用及工业放大具有实际指导意义。
NaY沸石分子筛在VOCs处理中的应用
Application of NaY zeolite molecular sieve in VOCs treatment
-
摘要: 为深入研究分子筛吸附VOCs的性能,采用固定床动态吸附法,对NaY分子筛吸附3种典型VOCs的性能进行了探究,考察了吸附温度、湿度、进气浓度和吸附质物理性质对吸附容量的影响,并探讨了NaY分子筛的循环使用性能;通过Yoon-Nelson模型,从吸附动力学角度,对单组分VOCs吸附穿透曲线进行了拟合。结果表明:NaY分子筛对3种VOCs的吸附饱和时间分别为丙酮355 min,邻二甲苯320 min,乙酸乙酯220 min;相对应的平衡吸附容量分别为丙酮176 mg·g−1,邻二甲苯196 mg·g−1,乙酸乙酯185 mg·g−1。NaY分子筛对VOCs吸附能力排序为邻二甲苯>乙酸乙酯>丙酮。温度由303 K升至328 K时,3种VOCs吸附容量均分别下降,邻二甲苯下降3.66%,乙酸乙酯下降2.87%,丙酮下降10.0%;VOCs相对湿度为30%时,吸附容量显著降低;进气浓度为660 mg·m−3时,出现吸附交叉的现象;NaY分子筛具有较好的循环使用性;吸附容量与沸点、分子质量存在正相关关系;3种VOCs在NaY分子筛固定床的吸附速率排序为乙酸乙酯>邻二甲苯>丙酮。Yoon-Nelson模型能够较好地模拟NaY分子筛吸附不同VOCs的过程,为分子筛的工业应用提供了参考。Abstract: In order to further study the VOCs adsorption performance on zeolite, the adsorption performance of three typical VOCs on NaY molecular sieve was studied by fixed bed dynamic adsorption method. The effects of adsorption temperature, humidity, concentration of inlet and physical properties of adsorbent on adsorption capacity were investigated, as well as the recycling property of NaY molecular sieve. The adsorption penetration curve of single-component VOCs was fitted with the Yoon-Nelson model from the perspective of adsorption kinetics. The results showed that the saturated adsorption times of acetone, o-xylene, and ethyl acetate on NaY molecular sieve were 355, 320 and 220 min, respectively, and their corresponding equilibrium adsorption capacities were 176, 196 and 185 mg·g−1, respectively. The adsorption capacity of VOCs on NaY was in the order of o-xylene>ethyl acetate>acetone. When the temperature increased from 303 K to 328 K, the adsorption capacities of three VOCs decreased by 3.66%, 2.87% and 10.0% for o-xylene, ethyl acetate, and acetone, respectively. At VOCs relative humidity of 30%, its adsorption capacity decreased significantly. Adsorption curve intersection occurred when inlet concentration was 660 mg·m−3. NaY molecular sieve had a good recycling performance. A positive correlations were obseved between the adsorption capacity and the physical properties of VOCs such as boiling point, molecular weight. The order of adsorption rate of three VOCs on NaY was as follows: ethyl acetate>o-xylene>acetone. The Yoon-Nelson model parameters could accurately predict VOCs adsorption behavior of NaY molecular sieve in a fixed bed reactor. It can provide basic data for industrial application of molecular sieve.
-
Key words:
- eolite molecular sieve /
- VOCs /
- adsorbents /
- fixed-bed
-

-
表 1 穿透时间与吸附容量
Table 1. Penetration time and adsorption capacity
VOCs 穿透时间/min 饱和时间/min 平衡吸附容量/(mg·g−1) 邻二甲苯 190 320 185 丙酮 220 355 176 乙酸乙酯 120 220 168 注:T=25 ℃,C0=660 mg·m−3,空速30 000 mL·(h·g)−1。 表 2 在湿度为30%条件下NaY对3种含湿VOCs穿透时间与吸附容量
Table 2. Penetration time and adsorption amount of three kinds of wet VOCs on NaY at 30% relative humidity
VOCs 穿透时间/min 饱和吸附容量/(mg·g−1) 邻二甲苯 20 5.21 丙酮 35 31.66 乙酸乙酯 25 24.99 注:T=25 ℃,C0=660 mg·m−3,空速30 000 mL·(h·g)−1。 表 3 NaY与HY吸附邻二甲苯穿透时间与吸附容量
Table 3. Penetration time and adsorption capacity of NaY and HY toward o-xylene adsorption
样品 穿透时间/
min饱和吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)饱和时间/
minSBET/
(m2·g−1)HY 185 157 270 448.1 NaY 190 185 320 568.6 注:T=25 ℃,C0=660 mg·m−3,空速30 000 mL·(h·g)−1。 表 4 吸附质的物性参数
Table 4. Physical properties of adsorbents
VOCs 相对分
子质量动力学
直径/nm沸点/
K20 ℃密度/
(g·cm−3)20 ℃蒸
汽压/kPa邻二甲苯 106.16 0.65 417.6 0.885 0.652 乙酸乙酯 88.11 0.48 350.2 0.901 10.10 丙酮 58.08 0.482 329.44 0.791 24.65 表 5 Yoon-Nelson方程拟合模型参数
Table 5. Yoon-nelson equation fitting parameters
VOCs $k'$ 
τ 丙酮 0.033 9 282.18 邻二甲苯 0.041 5 261.92 乙酸乙酯 0.055 1 162.57 -
[1] 赵琳. VOC的危害及回收与处理技术[J]. 化学教育, 2015, 36(16): 1-6. [2] 郭森, 童莉, 周学双. 石化行业的VOCs排放控制管理[J]. 化工环保, 2014, 34(4): 356-360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2014.04.012 [3] 魏巍. 中国人为源挥发性有机化合物的排放现状及未来趋势[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2009. [4] KIM H, JAFFE P R. Spatial distribution and physiological state of bacteria in a sand column experiment during the biodegradation of toluene[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(10): 2089-2100. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.018 [5] SAQER S M, KONDARIDES D I, VERYKIOS X E. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over binary mixtures of copper, manganese and cerium oxides supported on γ-Al2O3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2011, 103(3/4): 275-286. [6] HUANG H B, XU Y F, LEUNG Q Y. Low temperature catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: A review[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2015, 5: 2649-2669. [7] KAMAL M S, RAZZAK S A, HOSSAIN M M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs): A review[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 140: 117-134. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.05.031 [8] 卢晗锋, 殷操, 黄海凤, 等. 高分子吸附树脂对VOCs的动态吸附及其穿透模型[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2012, 40(4): 423-427. [9] LILLO-RODENAS M A, FLETCHER A J, THOMAS K M, et al. Competitive adsorption of a benzene-toluene mixture on activated carbons at low concentration[J]. Carbon, 2006, 44(8): 1455-1463. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.12.001 [10] 刘鹏, 龙超. 超高交联吸附树脂对气体中三氯乙烯的吸附研究[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2009, 25(5): 411-418. [11] 郭坤敏. 活性炭吸附技术及其在环境工程中的应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2016. [12] ZHANG W, QU Z, LI X. Comparison of dynamic adsorption/desorption characteristics of toluene on different porous materials[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2012, 24: 52-54. [13] 张媛媛. 疏水性硅基吸附剂的制备及VOCs吸附性能研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. [14] 周瑛, 卢晗锋, 王稚真, 等. VOCs和水在Y型分子筛表面的竞争吸附[J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(5): 1653-1657. [15] 王稚真. Y型分子筛吸附VOCs性能的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2010. [16] LIU M C, HSIEH C C, LEE J F. Impact of Pt and V2O5 on ethanol removal from moist air using pellet silica-bound NaY[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 54: 8678-8680. [17] NIGAR H, NAVASCUES N, DELALGLESIA O. Removal of VOCs at trace concentration levels from humid air by microwave swing adsorption, kinetics and proper sorbent selection[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 9(4): 193-200. [18] TAO W H, YANG T C, CHANG Y N, et al. Effect of moisture on the adsorption of volatile organic compounds by zeolite 13X[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2004, 130(10): 1210-1216. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2004)130:10(1210) [19] BARTHOMEUF D, DE MALLMANN A. Adsorption of aromatics in NaY and A1P04-5. Correlation with the sorbent properties in separations[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1990, 29(7): 1435-1438. [20] 赵振国. 吸附作用应用原理[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005. [21] HISASHI Y, AKIO K, TSUTOMU H, et al. Performance of VOC abatement by thermal swing honeycomb rotor adsorbers[J]. American Chemical Society, 2007, 46: 4316-4322. [22] 黄海凤, 褚翔, 卢晗锋, 等. MCM-41和SBA-15动态吸附VOCs特性和穿透模型[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2011, 25(2): 219-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2011.02.007 [23] OUMAIMA D, HADJ H. Use of silica particles made by nonionic surfactant for VOCs sorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2016, 7(9): 3371-3380. [24] 梁欣欣. 负载型分子筛对挥发性有机气体的吸附特性研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2015. [25] 顾勇义. ZSM-5沸石分子筛吸附脱附VOCs性能的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2012. [26] GUILLEMOT M, MIJOIN J, MIGNARD S, et al. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) removal over dual functional adsorbent/catalyst system[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2007, 75(3/4): 249-255. [27] 金伟力. 用于工业有机废气治理的分子筛吸附转轮高性能化研究[C]//中国环境科学学会. 2017中国环境科学学会科学与技术年会论文集(第四卷), 2017: 539-544. [28] 洪新, 李云赫, 高畅, 等. 改性NaY分子筛吸附脱除模拟燃料油中碱性氮化物[J]. 精细石油化工, 2018, 35(3): 20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9384.2018.03.005 [29] LEE D G, HAN Y J, LEE C H. Steam regeneration of acetone and toluene in activated carbon and dealuminated Y-zeolite beds[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 29: 1246-1252. doi: 10.1007/s11814-012-0044-x [30] 刘光启, 马连湘, 项曙光. 化学化工物性数据手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2012. [31] 陈金妹, 张健. ASAP2020比表面积及孔隙分析仪的应用[J]. 分析仪器, 2009(3): 61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-232X.2009.03.013 [32] COSNIER F, CELZARD A, FURDIN G, et al. Hydrophobi-sation of active carbon surface and effect on the adsorption of water[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(12): 2554-2563. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.05.007 [33] LEE S W, CHEON J K, PARK H J, et al. Adsorption characteristics of binary vapors among acetone, MEK, benzene, and toluene[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2008, 25(5): 1154-1159. doi: 10.1007/s11814-008-0190-3 [34] 梁大明. 中国煤质活性炭[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. [35] YOON Y H, NELSON J H. Application of gas adsorption kinetics: II. A theoretical model for respirator cartridge service life and its practical applications[J]. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 1984, 45(8): 517-524. doi: 10.1080/15298668491400205 [36] YOON Y H, NELSON J H. Application of gas adsorption kinetics: I. A theoretical model for respirator cartridge service life[J]. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 1984, 45(8): 509-551. doi: 10.1080/15298668491400197 -




 下载:
下载: