-
随着环保意识的增强,天然气作为一种清洁能源被广泛使用,但天然气中含有的大量H2S,不仅会对设备和管线造成腐蚀,而且也是造成酸雨的污染源之一,严重危害环境和人类健康[1-2]。因此,脱除天然气中的H2S,对保护设备、管线和环境等具有重大意义。
目前,工业中应用较多的天然气脱硫工艺主要有湿法、干法和膜法脱硫。湿法脱硫技术主要有乙醇胺(MEA)法[3]、低温甲醇法[4]、DDS脱硫技术[5]和LO-CAT硫磺回收技术[6];干法脱硫技术主要有活性炭法、分子筛法和氧化铁法[7];膜法脱硫技术主要有膜基吸收法和膜蒸馏法[8]。尽管这些技术已经在工程中得到了较为广泛的应用,却不能忽视其在实际应用中存在的问题:湿法脱硫技术存在工艺复杂、投资费用高、能耗大和产生大量的脱硫废水等缺点[9];干法脱硫技术存在脱硫条件要求严格、不适用于高浓度H2S脱除和再生困难等缺点[10];膜法脱硫技术存在制膜工艺较为复杂、膜的使用寿命短和处理后浓缩液难处理等缺点[11-12]。因此,亟需研发一种工艺简单、成本低、安全高效的脱硫技术,探究内循环微电解技术应用于天然气中H2S处理的可行性及其对天然气中H2S的处理效果,旨在为内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理提供指导,同时为天然气中H2S处理提供一种简单高效的技术方法。
内循环微电解技术将铁作为阳极,将活性炭作为阴极,当混合浸入废水时,形成大量的微小原电池,其主要通过微电池、氧化还原、絮凝、吸附沉淀和微电场附集等作用去除废水中的污染物[13-14]。内循环微电解具有成本低、工艺简单、使用范围广、使用寿命长、处理效果好及操作维护简单等优点[15],在印染[16]、焦化[17-18]、石油[19]、制药[20]、造纸[21]等工业废水的处理中得到了广泛的应用,对COD和色度的去除具有很好的效果,但内循环微电解技术应用于天然气脱硫的研究却鲜有报道。
本研究采用内循环微电解技术处理天然气中的H2S,考察了反应时间、通气速率、铁炭比和pH等4个因素对H2S去除效果的影响,筛选出3个影响H2S去除效果的主控因子,采用Box-Behnken响应曲面法,对处理H2S的反应条件进行了优化,以得到内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理的最佳工艺条件。最终可以得出内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理是可行的,研究结果为内循环微电解应用于天然气中H2S的处理提供参考,同时,为天然气中H2S的处理提供了一种简单高效的技术方法。
全文HTML
-
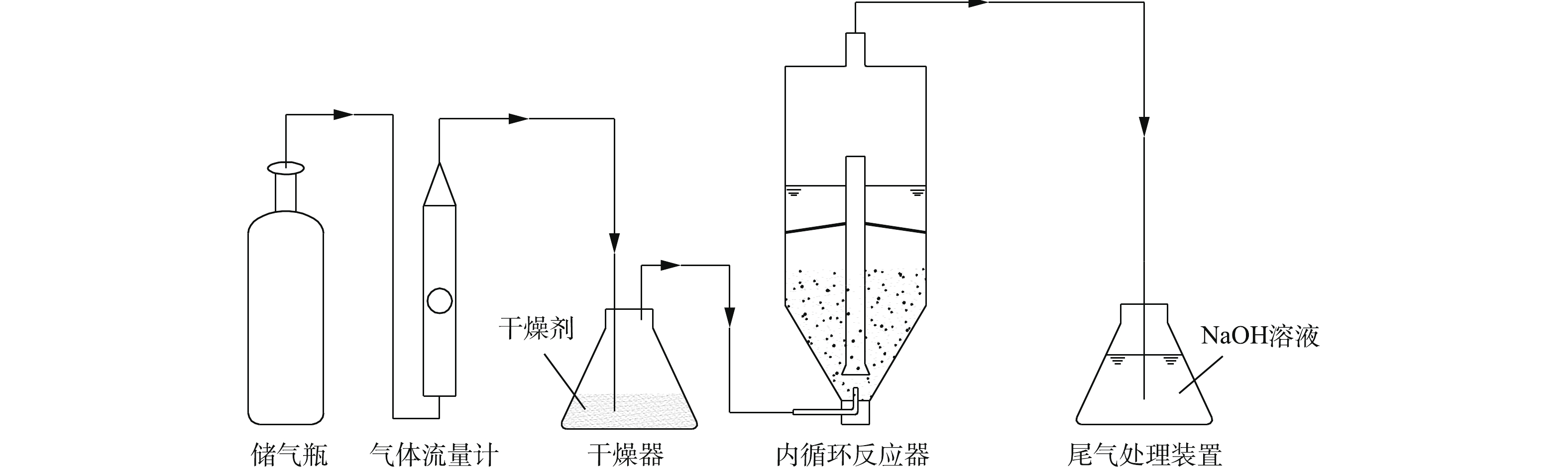
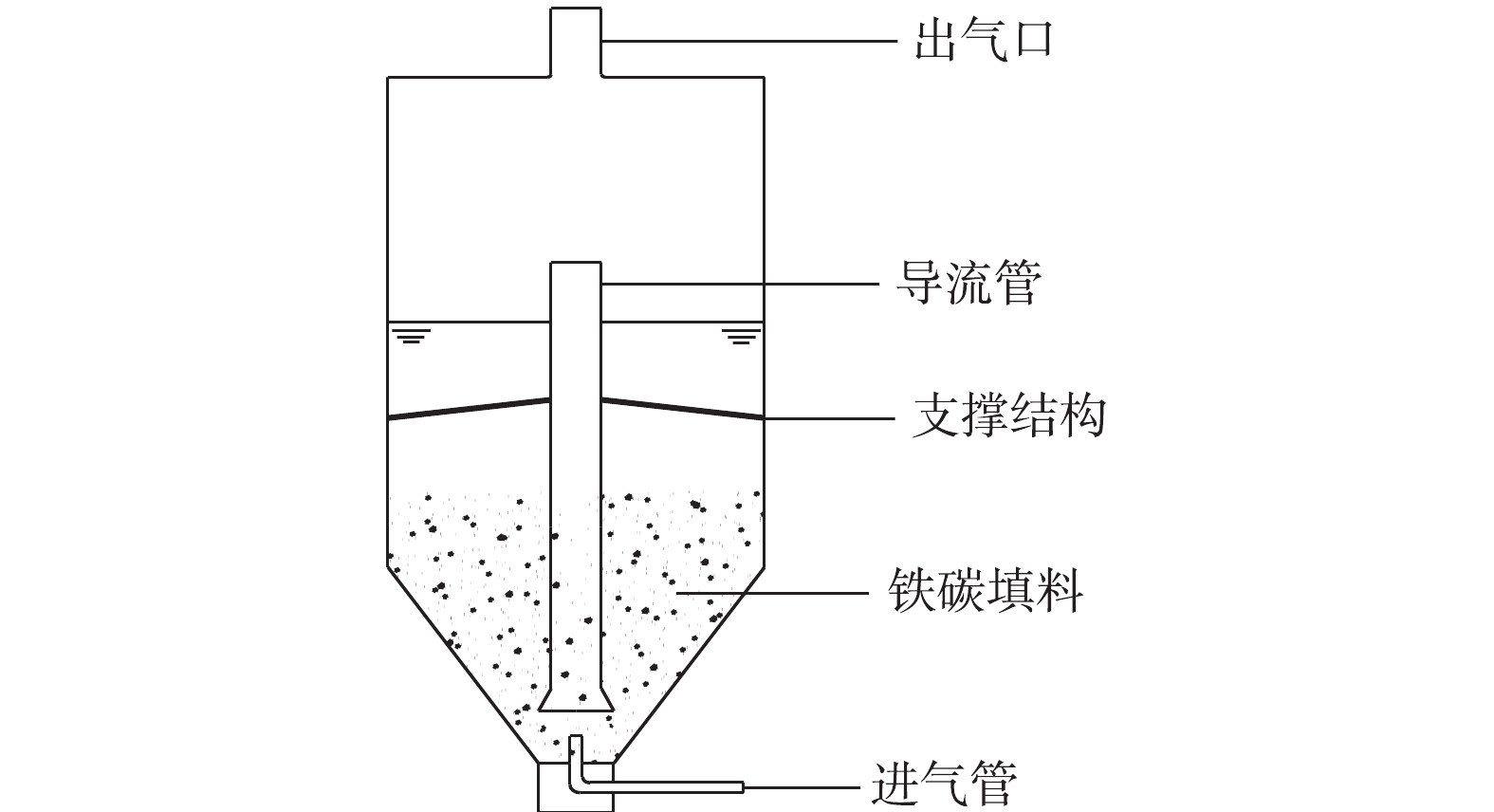
实验中使用的NaOH、Na2S、盐酸和丙酮等试剂,均为分析纯;实验室用水为去离子水。使用的主要仪器有Multi3420型pH计、TD5002C分析天平、YQY-12氧气减压阀、CHYS-241硫化物测量仪、A14 H2S气瓶、LZB型空气流量计和内循环式反应器,反应器为自制,结构如图1所示。
-
实验装置如图2所示。在进行铁屑预处理时,首先用去离子水反复清洗3~5遍,以去除表面的灰尘,然后将铁屑置于丙酮溶液中浸泡30 min,去除表面的油污及其他杂质,再用5%的盐酸浸泡30 min,去除铁屑表面的氧化膜,使铁屑活化,最后用去离子水清洗至中性[22]。
在进行活性炭预处理时,首先,用去离子水反复清洗3~5遍,以去除表面的灰尘和杂质,然后将活性炭浸泡在高浓度的Na2S溶液中3 d以上,以消除实验过程中活性炭吸附作用的影响[23]。
将预处理后的铁屑和活性炭按照一定的质量比(总质量为300 g)混合后,置于内循环式反应器中,并在反应器中加入适量的水,气瓶中含有H2S的天然气(为了防止甲烷引起爆炸,本研究采用N2和H2S的混合气体进行模拟),用空气流量计控制流量,经过干燥器(防止水蒸气进入气体流量计和储气瓶而发生腐蚀泄露)干燥后,通入反应器中进行反应,尾部通过NaOH溶液吸收尾气中的H2S,以测定处理后H2S的剩余含量,计算H2S的去除率。
-
使用Multi3420型pH计进行pH的测定;处理后,H2S的剩余含量使用CHYS-241硫化物测量仪进行测定,此方法具有简便快捷的优点,准确度和精密度均可达到检测要求[24]。
内循环微电解技术脱除天然气中H2S见反应式(1)和式(2),同时会有Fe(OH)3的生成(见式(3)),可以通过混凝沉淀作用加快FeS的沉淀。
-
1)单因素实验设计。通过控制变量,分别研究不同反应时间、通气速率、铁炭比和pH对H2S去除率的影响,筛选出影响H2S去除效果的3个主要因素。
2)响应曲面优化实验设计。在单因素实验的基础上,采用Design Expert软件中Box-Behnken法进行设计,以H2S去除率为响应值,确定3因素3水平的响应曲面分析实验,对实验结果进行ANOVA分析及二次回归拟合,确定模型的可行性。最终获得各因素间的交互作用对响应值的影响和最优反应条件。采用二阶模型[22]计算H2S去除率,计算方法如式(4)所示。
式中:Y为H2S去除率的预测值;
${ \propto _0}$ 为偏移项;${ \propto _i}$ 为线性偏移系数;${ \propto _{ii}}$ 为二阶偏移系数;∝ij为交互作用系数。3)验证实验设计。在模型预测的最佳反应条件下进行实验,测定H2S剩余含量,计算去除率,验证模型的可靠性。
1.1. 主要试剂与仪器
1.2. 实验方法
1.3. 分析方法
1.4. 实验设计
-
1)反应时间对处理效果的影响。在实验中,天然气中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1、铁炭比为1∶1和pH为7的条件下,研究了反应时间对H2S去除率的影响,实验结果如图3所示。由图3可见,随着反应时间的增加,H2S剩余含量逐渐减少,H2S去除率逐渐增大。反应30 min前,H2S剩余含量迅速减少,H2S去除率迅速增大,这是由于反应初期水中不断产生Fe2+,从而加速FeS的生成,同时氧化还原、絮凝沉淀等作用也起到很好的脱硫促进作用[25],进而可以迅速去除H2S;在30 min时,H2S剩余含量为377.5 mg·m−3,其去除率达到52.81%;而在反应30 min后,H2S剩余含量随着时间的延长缓慢减少,H2S去除率随着时间的延长缓慢升高,这主要是因为随着反应的进行,Fe被大量消耗,形成的原电池数量减少,从而使反应速率下降;在反应进行到120 min时,H2S剩余含量仅剩63.5 mg·m−3,去除率高达92.06%。由于在反应时间为30 min时,剩余H2S的浓度接近《天然气》(GB 17820-2012)中三类标准,综合因素优化和经济因素考虑,后续实验中的反应时间设为30 min。
2) 通气速率对处理效果的影响。控制天然气中H2S初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、反应时间为30 min、铁炭比为1∶1和pH为7的条件下,研究通气速率对H2S去除率的影响,实验结果如图4所示。由图4可知,随着通气速率的增大,H2S剩余含量先减少后增加,H2S去除率先升高后降低,当通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1时,H2S剩余含量达到最低值,为387.5 mg·m−3,其去除率为51.56%;当通气速率小于0.4 m3·h−1时,H2S去除率随着通气速率的增大而升高,这是因为在一定条件下,传质系数会随着通气速率的增大而增大[26],天然气中的H2S与铁炭的接触更加充分,从而使处理效果越来越好。当通气速率大于0.4 m3·h−1时,H2S去除率随着通气速率的增大而降低,分析其原因主要有以下2点:通气速率增大,气体对铁炭的作用力也相应增大,使得铁炭分离,形成的原电池数量大量减少而影响处理效果;随着通气速率增大,溶液中的气泡数量会随之增加,大量的气泡聚集导致气泡的体积增大,比表面积减少,使传质系数减少而影响处理效果。因此,最终确定反应的最佳通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1。
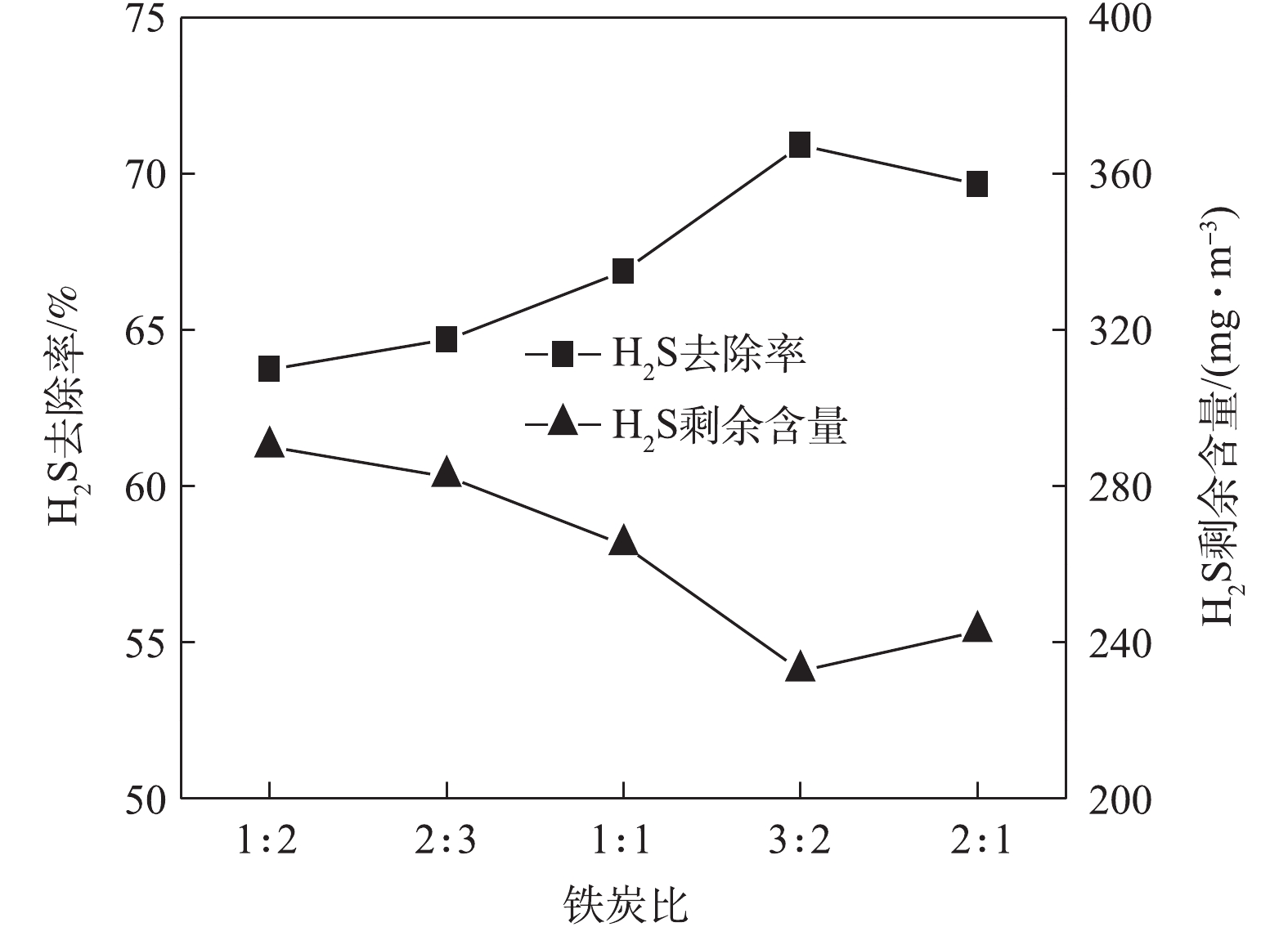
3) 铁炭比对处理效果的影响。控制天然气中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、反应时间为30 min、通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1和pH=7的条件下,研究了铁炭比(总质量不变)对H2S去除率的影响,实验结果如图5所示。由图5可见,随着铁炭比的增加,H2S剩余含量先减少后增加,H2S去除率先增大后降低,当铁炭比为3∶2时去除效果最好,H2S剩余含量达到最低值,为232.75 mg·m−3,H2S去除率达到70.91%。当铁炭比小于3∶2时,随着铁炭比的增加,反应体系中Fe的含量增加,使反应器中原电池的数量增加,有效地提高了H2S的去除效果,使得H2S去除率呈现逐渐升高的趋势;当铁炭比大于3∶2时,造成Fe大量剩余,当反应开始后,短时间内会形成过多的铁泥沉积在活性炭表面,使形成原电池数量减少,从而阻碍反应的进行[21],故导致H2S去除率呈现逐渐降低的趋势。因此,最终确定反应的最佳铁炭比为3∶2。
4) pH对处理效果的影响。控制天然气中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3,在室温、反应时间为30 min、通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1和铁炭比为3∶2的条件下,研究pH对H2S去除率的影响,结果如图6所示。由图6可知,随着pH的增加,H2S剩余含量逐渐减少,H2S去除率逐渐升高;当pH为6时,H2S剩余含量为14.5 mg·m−3,去除率高达98.19%;而当pH为12时,H2S剩余含量为377.5 mg·m−3,去除率仅为52.81%,可见pH对H2S的去除效果有着重要的影响。这是因为当pH较低时,反应体系酸性越强,微电池的电位差越大,原电池的电动势越大,微电解反应较快,处理效果较好;随着pH的增加,微电池的电位差降低,反应变慢,导致处理效果下降[27]。
-
1) Box-Behnken设计。从以上单因素实验结果可知,反应时间对H2S的去除效果有一定的影响,但当反应一段时间后,对H2S的去除效果的影响很小。因此,最终选择铁炭比、通气速率和pH 3个因素进行响应曲面分析,采用Design Expert软件中的Box-Behnken法进行设计,以铁炭比、通气速率和pH作为自变量,以H2S去除率作为因变量,进行3因素3水平的响应曲面分析,确定各个因素对H2S处理效果的影响。实验设计因素与水平如表1所示,响应曲面实验运行结果如表2所示。实验中H2S的初始含量为800 mg·m−3。
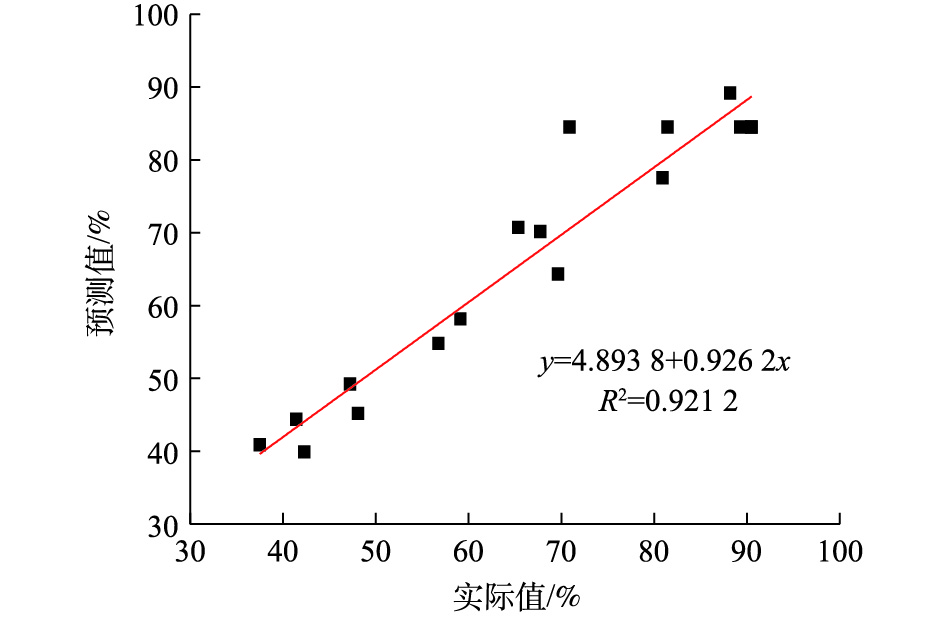
2) ANOVA分析及二次回归拟合。根据Design Expert软件设计的实验模型进行ANOVA分析和模型的显著性分析,结果如表3所示。分析结果显示,在H2S去除率的模型中P=0.003 3,P<0.05,说明回归模型显著;失拟项不显著(P=0.676 9>0.05),这说明模型的预测值和实际值的误差较小,能够较好地反映响应值变化;在95%置信区间内,模型与实际值拟合较好。因此,可以将此模型用于内循环微电解处理天然气中H2S效果的预测。由图7可知,模型的实际值与预测值差别较小,R2为0.921 2,这说明模型可以较好地反映各个因素对H2S去除效果的影响。通过统计学分析,估计出二次回归方程中的回归系数(表3),由实验结果拟合得到天然气中H2S去除率的二次响应曲面方程(如式(5)所示)。
3)交互作用的响应曲面分析。通过软件对实验数据进行回归分析,得到回归方程的响应曲面和等高线图,如图8~图10所示。在pH=7的情况下,考察了铁炭比和通气速率对H2S去除率的交互作用影响(见图8)。由图8可知,无论是铁炭比和通气速率如何改变,H2S去除率均随着通气速率和铁炭比的增加而呈现先增大后减小的趋势,因此,铁炭比和通气速率2个因素间的交互作用不明显。
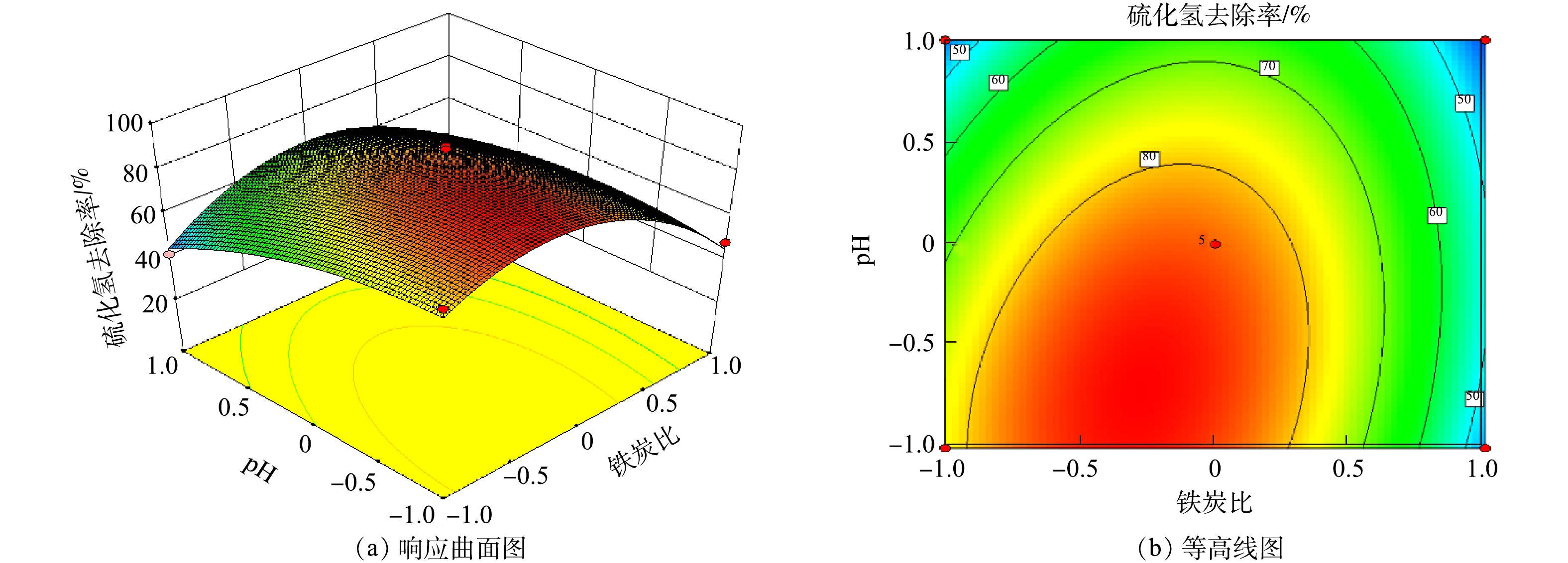
在通气速率为0.4 m3·h−1的情况下,考察了铁炭比和pH对H2S去除率的交互作用影响(见图9)。由图9可知,无论铁炭比如何改变,H2S去除率总是随着pH的增大而减小;无论pH如何变化,H2S去除率总是随着铁炭比的增大而呈现先增大后减小的趋势。因此,铁炭比和pH 2个因素间没有明显的交互作用。
在铁炭比为3∶2的情况下,考察了通气速率和pH对H2S去除率的交互作用影响(见图10)。由图10可知,无论通气速率如何改变,H2S去除率都随着pH的增大而减小;无论pH如何变化,H2S去除率总是随着通气速率的增大而呈现先增大后减小的趋势。因此,通气速率和pH 2个因素间没有明显的交互作用。
综合响应曲面图和ANOVA分析中各因素的F值(C(12.03)>B(11.05)>A(5.22))可知,影响天然气中H2S去除效果的因素依次为pH>通气速率>铁炭比。通过Design Expert软件优化获得的最佳反应条件:铁炭比为3∶2,通气速率为0.33 m3·h−1,pH为6.1。在最优的条件下,模型预测H2S去除率为92.66%,模型预测值的95%置信区间为80.17%~100%。
-
在上述最佳反应条件下进行实验,结果表明H2S去除率为84.6%,其落在模型预测值的95%置信区间(80.16%~100%)内。我国大部分气田的天然气中H2S含量小于800 mg·m−3,在最佳反应条件下,即使H2S的去除率取置信区间的下限80.16%,处理后H2S剩余含量小于158.72 mg·m−3,仍然可以达到《天然气》(GB 17820-2012)[28]中三类标准。通过验证实验证明,Design Expert响应曲面法具有较好的预测效果,可以利用响应曲面法对内循环微电解处理天然气中H2S的去除率进行预测。
2.1. 单因素实验
2.2. 响应曲面优化
2.3. 验证实验
-
1)采用内循环微电解对天然气中的H2S进行处理,单因素实验结果表明,采用内循环微电解技术处理天然气中H2S具有可行性。
2)通过Design Expert软件中Numercal优化功能,得到H2S去除效果最优时的反应条件:通气速率为0.33 m3·h−1、铁炭比为3∶2、pH为6.1。在此条件下,H2S的平均去除率为84.6%,处理后H2S剩余含量可从800 mg·m−3降至158.72 mg·m−3,可以达到《天然气》(GB 17820-2012)中三类标准。因此,内循环微电解技术可以有效地去除天然气中的H2S。



 下载:
下载: