-
近年来,与传统的化学计量发动机相比,柴油和其他贫燃汽油车辆因其更好的燃油效率和低CO2排放量而拥有广阔的发展前景[1],但三效催化剂对NOx的催化还原效果较差[2]。随着氮氧化物排放造成的环境污染问题的日趋严重,在未来几年,交通运输部门对氮氧化物排放的监管也将更为严格。因此,有必要开发能够在柴油和其他贫燃汽油车辆的发动机处理系统之后还原NOx的催化系统[3]。为了解决这个问题,许多学者研究了NSR(NOx储存还原)技术及以NH3或烃为还原剂的NH3-SCR和HC-SCR催化体系[1]。HC-SCR因其不必通过外部加入还原剂而引起人们的广泛关注[2],并且已有研究证明HC-SCR是一种有效且经济的技术[4]。研究表明,TiO2不仅在光催化领域效果显著,在SCR应用中也是一种优良的催化剂载体[5]。TiO2具有强抗硫中毒能力、高比表面积[6]、低毒性和价格低廉的优势[7]。同时Ce基材料可以用作三效催化剂的重要组分,它们能够储存和释放氧气,进而起到促进CO和NO转化的作用[8]。王淑勤等[9]以TiO2为载体,负载Ce和Co元素,研究其脱硝性能,发现与纯TiO2相比,其效率提高了近50%。JIN等[10]将Mn-Ce活性组分负载在TiO2和Al2O3载体上,发现在80~150 ℃,Mn-Ce/TiO2的脱氮活性高于Mn-Ce/Al2O3。此外,杂多酸(HPAs)因具有假液相特性、强氧化还原能力、活泼的晶格氧、强质子酸性、无毒和非挥发性的特点而引起关注[11]。研究[12]表明,极性分子(如NO、NH3、吡啶)等可以进入HPAs内部,从而引发HPAs表面和内部反应。实验发现,NOx的去除率与杂多酸的酸度密切相关,杂多酸的酸性越强,去除率越高。其中HPW酸性最强,具有最高的NOx去除率。在HPW的各种结构中,已有研究探讨了Keggin型H3PW12O40的物理化学和催化性质,并且已经证明它是一种可以用于均相或非均相的有效超级酸[12]。但是在实际应用中,纯杂多酸也存在很多缺点,如比表面积小(<10 m2·g−1)、热稳定性低、机械强度差、在极性溶剂中溶解且难以回收,因此,应将其负载到载体上来克服这些缺点[13]。目前,负载磷钨酸的主要载体有活性炭、SiO2、TiO2、MCM-41、分子筛等中性载体[14]。
本研究采用浸渍法制备了TiO2、Ce-TiO2和Ce与H3PW12O40(HPW)共掺杂TiO2 3种催化剂,模拟烟气进行脱硝活性测试,使用X射线衍射(XRD)、傅里叶变换红外(FTIR)和扫描电镜(SEM)对制备的催化剂进行表征测试,同时进行了原位傅里叶变换红外光谱实验,阐明HPW和Ce在SCR反应中的作用,推测其可能的反应机理,为进一步深入研究烃类选择性催化还原NO反应机理提供参考。
-
通过浸渍法合成负载Ce和HPW的催化剂。首先,在剧烈搅拌下,将2份0.3 g HPW溶解在去离子水中;然后将2份HPW溶液(15%)逐滴分别加入到2 g TiO2中,剧烈搅拌2 h,将沉淀物静置12 h,100 ℃下干燥过夜,得到HPW-TiO2粉末;将其中1份HPW-TiO2样品在空气中400 ℃下煅烧4 h,得到HPW-TiO2(CM),另一个未煅烧的样品标记为HPW-TiO2(UCM)。
将3份0.186 g Ce(NO3)·6H2O(3%)溶解在去离子水中,完全溶解后,将硝酸铈溶液滴加到TiO2、HPW-TiO2(CM)和HPW-TiO2(UCM)中,剧烈搅拌2 h。然后将3个样品静置12 h,100 ℃下干燥过夜。最后,将2 g TiO2与其他3个样品一起在空气气氛中400 ℃煅烧4 h,以获得TiO2、3%Ce-TiO2、3%Ce-15%HPW-TiO2(CM)和3%Ce-15%HPW-TiO2(UCM)催化剂,简称为TiO2、Ce-TiO2、Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)。
-
采用具有Cu Kα(λ=0.154 06 nm)的BRUKER D8 ADVANCE衍射仪进行粉末X射线衍射(XRD)测试表征,管电压为40 kV,管电流为40 mA,扫描速率为11.8 (°)·min−1,扫描角度为5°~80°;采用S-4800场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察分析催化剂的微观形貌;通过BRUKER VERTEX 70光谱仪获得傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)的数据,扫描波数为400~4 000 cm−1。
-
以固定床装置评价各催化剂的C3H6-SCR反应活性。U型石英反应管内径为5 mm,外径为6 mm。催化剂用量为0.2 g,粒径为20~40目。标准C3H6-SCR反应的初始气体条件为:[NO]=[C3H6]=0.1%,[O2]=10%,以He作为平衡气,气体流量为100 mL·min−1,气体空速约为30 000 h−1。混合气体中NO浓度由化学传感器多组分气体分析仪进行监测,以NO脱除率
$ {\eta _{{\rm{NO}}}}$ 表示催化剂脱硝效率,计算方法见式(1)。式中:
$ {{C_{{\rm{NO,in}}}}}$ 为入口NO浓度,μg·L−1;$ {{C_{{\rm{NO,out}}}}}$ 为出口NO浓度,μg·L−1。 -
原位FT-IR测试在FT-IR光谱仪(BRUKER VERTEX 70)上进行,仪器分辨率为4 cm−1。在每次实验运行前,样品在400 ℃下,Ar气氛中以10 mL·min−1的总流速预处理20 min,除去吸附的杂质,然后冷却至目标反应温度。在C3H6(或NO+O2)吸附实验中,将样品在200 ℃下暴露于0.1% C3H6(或0.1% NO+10% O2)气流中60 min,然后Ar吹扫10 min。在瞬态研究中,首先将样品预先暴露于0.1% C3H6(或0.1% NO+5% O2)中,在200 ℃下吸附60 min,然后用Ar吹扫10 min,随后将气体转换为0.1% NO+5% O2(或0.1% C3H6),以获得FT-IR光谱的动态变化。
-
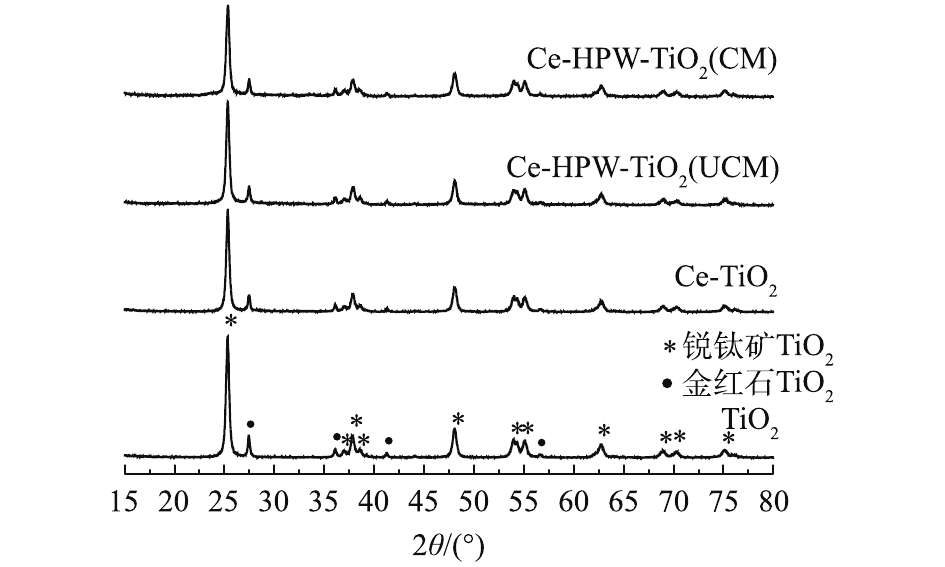
TiO2、Ce-TiO2、Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)催化剂的XRD结果如图1所示。据研究[7],在25.28°、36.84°、37.78°、38.42°、47.97°、53.79°、55.08°、62.70°、68.83°、70.32°和75.03°处出现的衍射峰对应于锐钛矿型TiO2的特征峰。在27.42°、36.06°、41.24°和56.64°处出现的衍射峰与金红石型TiO2的特征峰完全吻合。图1中未显示出Ce和H3PW12O40特征峰,仅出现了TiO2的特征峰。而且随着Ce和HPW的掺杂,TiO2衍射峰的强度逐渐减弱。这证明Ce和HPW的掺杂影响了TiO2的晶体结构,并且在载体表面上以非晶态高度分散。
图2是TiO2、Ce-TiO2、Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)的SEM图。图2(a)为纯TiO2的SEM图像,其表面表现为具有不光滑表面和不均匀颗粒的聚集体。掺杂Ce后,Ce-TiO2的形貌发生了明显的变化,催化剂表面变得更加光滑。HPW修饰的催化剂表现出与Ce-TiO2相似的形态和微观结构,如图2(c)和图2(d)所示。显然,Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)的颗粒形态更规则,分散性更好。这可能是由于各组分之间的强相互作用导致的,这种相互作用有利于催化活性的增强,可抑制TiO2颗粒的团聚过程、干扰晶体颗粒的生长以及增加催化剂表面积。
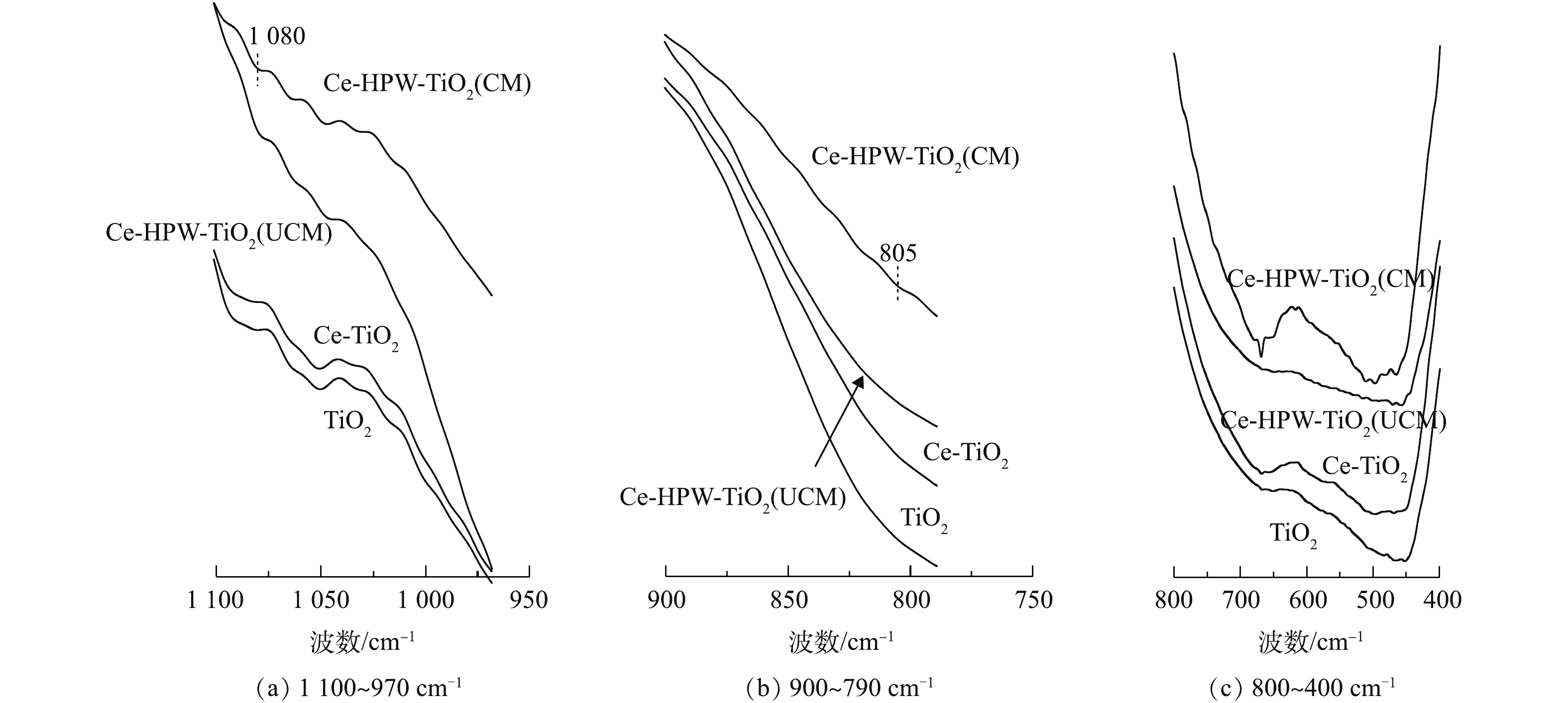
TiO2、Ce-TiO2、Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)的FT-IR谱图如图3所示。据研究[15-16],Ti―O、Ce―O、Ti―O―Ce键的伸缩振动峰值出现在800~400 cm−1。与TiO2的谱图相比,Ce-TiO2相应的透射带呈蓝移状态,这证明Ce成功掺入了TiO2骨架[17]。曲线Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)的趋势类似于曲线TiO2,峰值位置也存在蓝移现象,表明HPW、Ce和TiO2在催化剂表面存在相互作用。
与HPW相关的FT-IR研究[18]指出,P―Oa是指连接杂原子P和金属氧化物簇W3O13的一种氧原子,其伸缩振动峰出现在大约1 083 cm−1处,并且在802 cm−1处左右的峰可以归属于边缘共享W3O13八面体与W―Oc―W之间的拉伸。这几个特征峰可被用作证明HPW的Keggin结构存在的常用方法[19]。在图3中的800~1 100 cm−1处,HPW修饰的催化剂谱图存在Keggin结构典型振动带特征峰,表明Keggin型聚阴离子成功负载在催化剂表面。与Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)相比,Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)的HPW特征峰不明显,这可能是由于在负载HPW后没有进行煅烧导致的,使其没有很好地固定在催化剂表面上。
-
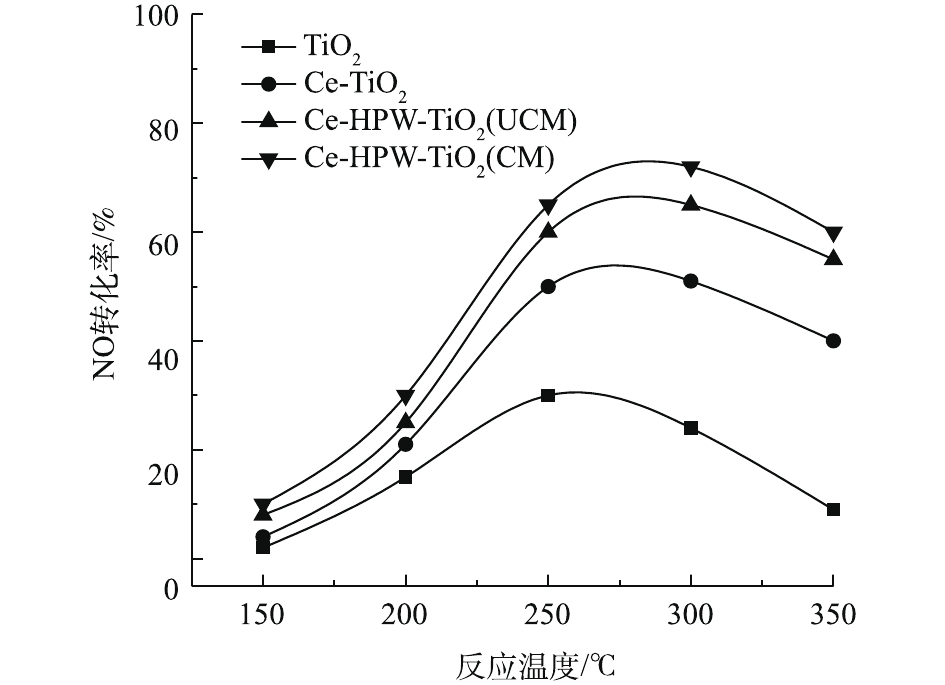
图4显示了纯TiO2以及掺杂Ce、HPW后的催化剂的C3H6-SCR活性随温度的变化情况。由图4可知,在中低温范围内(150~350 ℃),随着温度的升高,各催化剂对NO的转化率均呈先增大后减小的趋势。NO转化能力顺序为Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)>Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)>Ce-TiO2>TiO2。Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)催化剂显示最高的NO转化率,约为73%,这说明Ce和HPW的共掺杂显著促进了催化剂在中低温区的C3H6-SCR脱硝活性。由此还可看出,Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)虽然脱硝活性差距一直很小,但中间煅烧过的催化剂即Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)的活性还是优于Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)的活性。
-
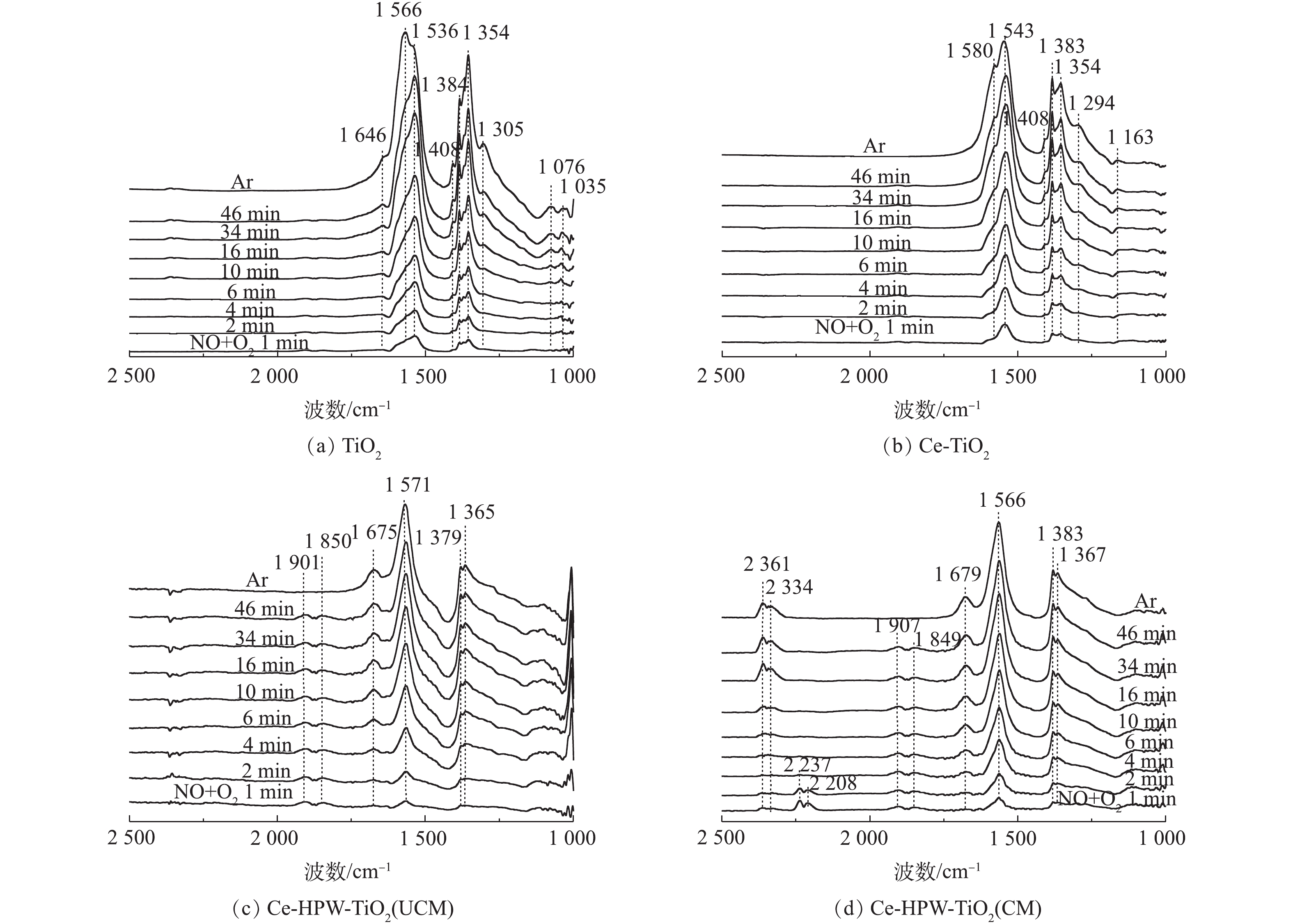
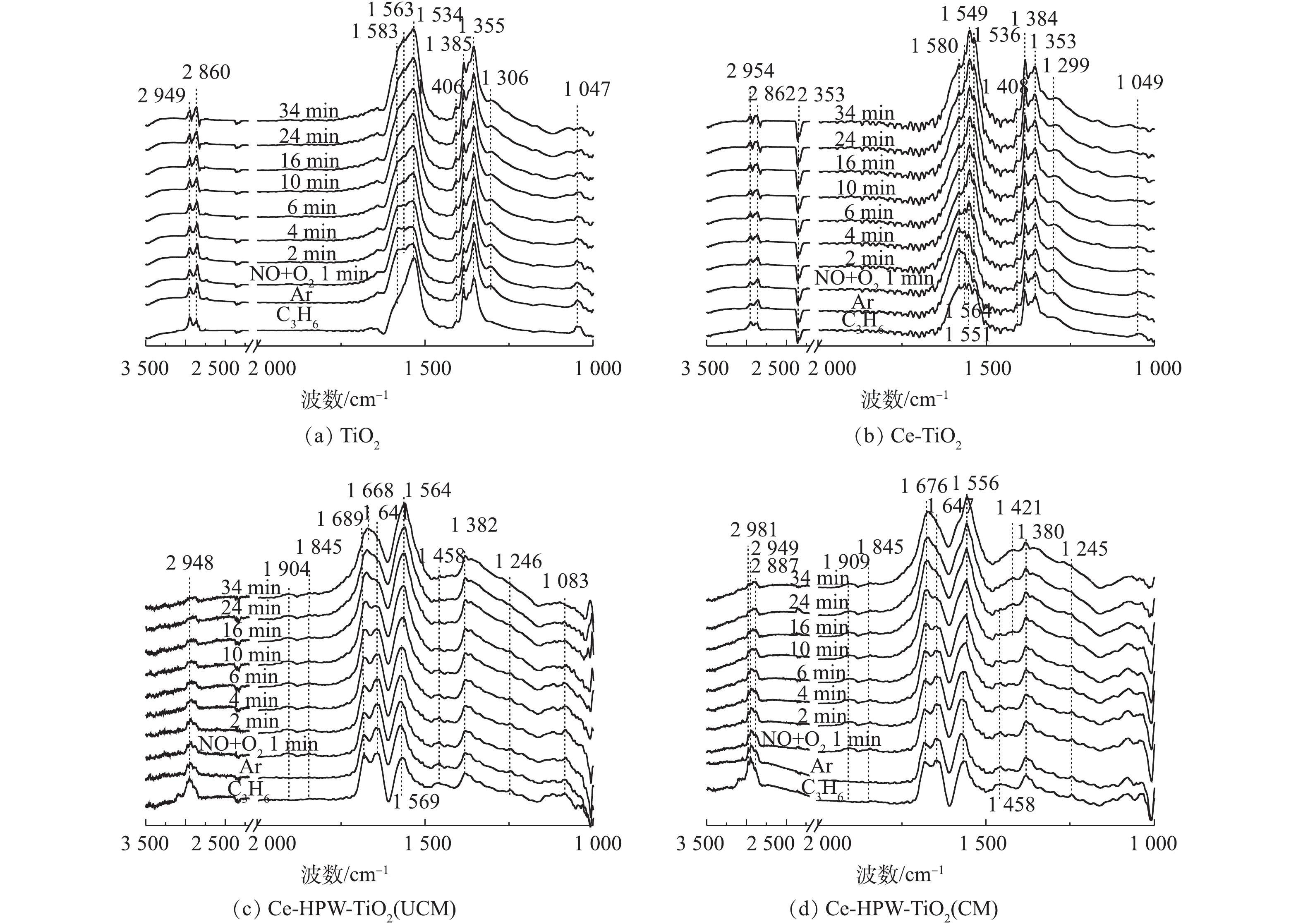
1) NO+O2共吸附。采用原位FT-IR技术测定了TiO2、Ce-TiO2、Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)上的NOx吸附物种,如图5所示。可以看出,图5中出现了归属于螯合双齿硝酸盐(1 035 cm−1)、单齿硝酸盐(1 076、1 294、1 354、1 367、1 383、1 536和1 679 cm−1)、双齿硝酸盐(1 163、1 305、1 543、1 566和1 580 cm−1)、桥联硝酸盐(1 646 cm−1)、单齿亚硝酸盐(1 408 cm−1)、气态吸附的NO(1 849 cm−1和1 907 cm−1)、亚硝鎓离子(NO+)(2 208 cm−1和2 237 cm−1)、亚硝酰阳离子(NO+)(2 334 cm−1)和[NO2]+物种(2 361 cm−1)[8, 20-27]的特征峰,这些特征峰的强度均随时间逐渐增强。TiO2(图5(a))催化剂在Ar吹扫10 min后,1 566 cm−1处吸收峰逐渐增强,而1 536 cm−1处的吸收峰强度逐渐降低。推测单齿硝酸盐不稳定,转化为双齿硝酸盐。Ce-TiO2的谱图与TiO2相似,但峰强度更高(图5(b)),这表明Ce的负载促进了TiO2对NOx的吸附能力。由图5(c)可以明显地看出,在将NO+O2引入反应池1 min后,立即出现了具有不同构型的硝酸盐物质。在Ar吹扫10 min后,1 850 cm−1和1 901 cm−1处的特征峰消失,这种现象归因于NO的气态吸附。图5(c)与图5(b)得到的硝酸盐的特征峰不同,表明HPW的添加改变了由Ce-TiO2吸附形成的硝酸盐物质。如图5(d)所示,Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)与Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)催化剂上NO+O2共吸附的原位FT-IR谱图基本相同。可以观察到,位于2 334 cm−1和2 361 cm−1处的峰随时间增强,2 208 cm−1和2 237 cm−1处的特征峰在2 min后消失,这种现象可能是由于吸附的NO+和O2之间的反应。此外,图5(d)中的特征峰强度比图5(c)中的特征峰强度增强,表明在二次浸渍之前,煅烧样品有利于增加结晶度并由此增强吸附NOx的能力。由此可知,Ce和HPW的掺杂可以增加吸附在催化剂表面上的硝酸盐物质的数量。
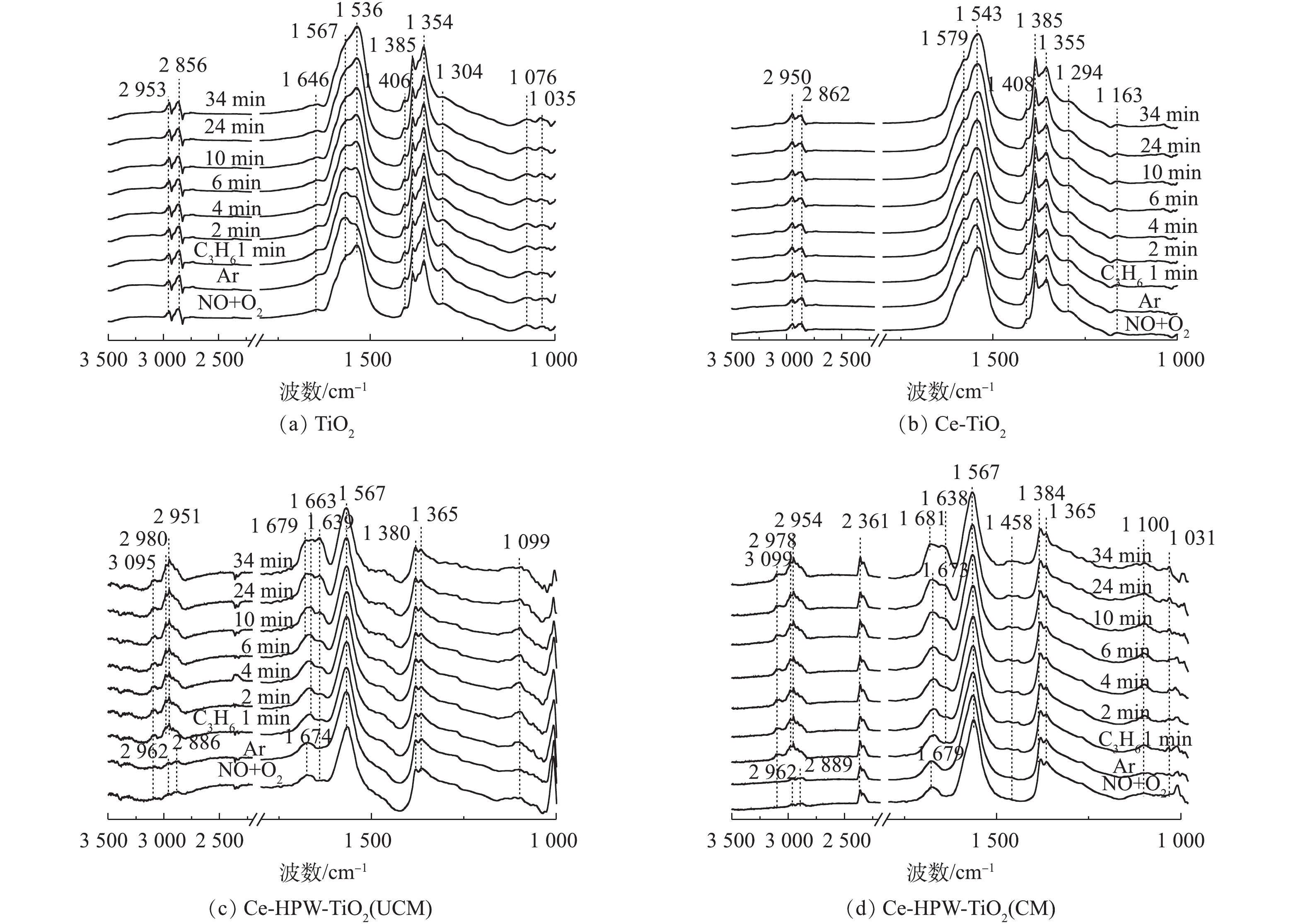
2) C3H6吸附。图6为通入C3H6的过程中TiO2、Ce-TiO2、Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)上吸附物种的动态变化情况。图6中的特征峰可归属于甲酸盐(1 368、1 382、1 598和2 885 cm−1)、乙酸盐(1 458、1 465、1 535、1 565、1 582和2 981 cm−1)、C―C振动(1 049、1 079、1 094、1 179、1 211和1 245 cm−1)、甲酸盐(COO−)振动特征峰(1 352 cm−1)、H2O(1 641 cm−1)、C3H6物种(1 658 cm−1)、碳酸盐(1 338、1 408、1 440、1 470和1 552 cm−1)、丙酮(1 670、1 682和1 723 cm−1)、CO2(2 357 cm−1)、烷烃的C―H伸缩振动峰(2 862、2 947和3 104 cm−1)、甲酸盐的COO−不对称伸缩振动和CH变形振动峰(2 954 cm−1)、碳氢化合物的C―C振动(1 299 cm−1)和未反应的丙烯(1 648 cm−1)[2, 8, 22, 28-32]。由图6可知,所有特征峰强度都随时间的增加而增强。如图6(a)所示,对于TiO2催化剂,Ar吹扫10 min后,1 368 cm−1和1 598 cm−1处的特征峰消失,同时出现1 582 cm−1处的新特征峰。这是由于甲酸盐稳定性较低,并转化成了乙酸盐。与TiO2相比,Ce-TiO2出现了更多的丙烯吸附物种(图6(a)),表明Ce的负载可促进TiO2对丙烯的吸附,从而产生更为丰富的C3H6吸附物种。Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)催化剂对于C3H6的吸附具有相同的趋势。由图6(c)可以看出,以1 440 cm−1和1 470 cm−1为中心的特征峰强度先增加,然后逐渐减小,直到完全消失。同时出现了位于1 458 cm−1的特征峰,这可能是由于碳酸盐不稳定,转化为乙酸盐。与Ce-TiO2相比,添加HPW的催化剂可增加丙烯的吸附种类,且主要吸附物种由乙酸盐转变为丙酮。
3)预吸附的NO+O2物种与C3H6之间的反应。预吸附的NOx物质与C3H6在200 ℃下的反应的原位FT-IR谱图如图7(a)~图7(d)所示。由图7(a)可知,在TiO2上1 567 cm−1处,峰强逐渐减弱,证明在反应过程中消耗了双齿硝酸盐,而双齿硝酸盐和C3H6吸附物种之间进行反应得到的COO−,与预吸附的单齿硝酸盐共吸附,使得1 536 cm−1处的峰强增加。将气体切换为C3H6后,Ce-TiO2催化剂未检测到表面物质的明显变化。由此可知,负载Ce对于优化C3H6与预吸附的NO+O2物质之间的反应过程是无效的。
Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)在预吸附NO+O2后,催化剂表面覆盖着各种NOx吸附物种,气体切换至C3H6后,归属于C―H弯曲振动的位于1 099 cm−1处的特征峰强度在前10 min内逐渐增加,随后减小。同时单齿硝酸盐的强度逐渐下降甚至消失,2 886 cm−1和2 962 cm−1处的O―H特征峰也消失,表明吸附的NOx物种在这一反应过程中被消耗了。另外部分出现了由于C3H6氧化产生的H2O(1 639 cm−1)、双齿碳酸盐(1 663 cm−1)、丙酮的C=O伸缩振动(1 679 cm−1)、甲酸盐的COO−不对称伸缩振动+CH变形振动(2 951 cm−1)和CH伸缩振动(2 980和3 095 cm−1)[8, 22, 32-33]等新峰,而且各特征峰的强度随时间的增加逐渐增强。但双齿硝酸盐物种相对稳定,因此,推断双齿硝酸盐在Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)催化剂上的反应是惰性的。Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)与Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)的红外谱图基本相似,通入C3H6后,归属于C―H弯曲振动(1 100 cm−1)的特征峰在前10 min逐渐增强,随后减弱。同时归属于C―C振动(1 031 cm−1)的特征峰在10 min后增强。表明C―H弯曲振动是在10 min内通入丙烯产生的,之后,该物质与吸附的NOx物种进行反应而被消耗,同时这一反应过程也伴随着C―C振动的形成和积累。此外,单齿硝酸盐和双齿硝酸盐强度逐渐减弱甚至消失,位于2 889 cm−1和2 962 cm−1处的O―H特征峰也逐渐消失,说明NOx吸附物种被消耗了。在这一过程中,出现了归属于乙酸盐、在C3H6氧化过程中产生的H2O(1 638 cm−1)、亚硝酸乙酯(1 673 cm−1)、甲酸盐的COO−不对称伸缩振动+CH的变形振动和C―H伸缩振动(2 978和3 099 cm−1)[8, 28, 29, 33]的新特征峰,而且它们的强度随时间的延长而增强。随后1 673 cm−1处的峰位移动到归属于丙酮C=O伸缩振动[32]的1 681 cm−1处,表明亚硝酸乙酯与吸附的C3H6物种进行了反应。观察到位于2 361 cm−1处的峰强略微增加,这要归因于[NO2]+和CO2的共吸附。可以看出,负载HPW后,催化剂吸附形成的硝酸盐物种基本都可以与丙烯物种反应,在催化剂上形成了丰富的活性物质,参与到C3H6-SCR反应中。
4)预吸附的C3H6物种与NO+O2之间的反应。NO+O2与预吸附的C3H6吸附物种在4种催化剂上反应的原位FTIR谱图如图8(a)~图8(d)所示。TiO2上发生的瞬态反应如图8(a)所示,归属于C―C振动的峰强度降低,同时归属于单齿硝酸盐(1 355和1 385 cm−1)、亚硝酸盐(1 406 cm−1)和双齿硝酸盐(1 534、1 563和1 583 cm−1)[8, 22, 30]的峰强在原峰的基础上增加,表明吸附的C3H6物种和相应的NOx吸附物种的共吸附。在1 299、2 860和2 949 cm−1处的峰保持相对稳定。Ce-TiO2与TiO2反应趋势相同,主要特征峰位置也相同。通入NO+O2后,归属于C―C振动和表面碳酸盐的峰强大大降低。同时单齿硝酸盐(1 353和1 384 cm−1)、亚硝酸盐(1 408 cm−1)、双齿硝酸盐(1 536、1 549、1 564和1 580 cm−1)和CO2(2 353 cm−1)[8, 22, 28, 30]的峰在原C3H6吸附物种峰的基础上逐渐增强,表明C3H6吸附物种和相应的NOx吸附物种存在共吸附现象。在反应过程中,1 299、1 408~1 536、1 641~1 723、2 862和2 954 cm−1处的其他特征峰保持相对稳定,这表明Ce-TiO2催化剂上吸附的大多数C3H6物种在SCR反应中是惰性的。CO2特征峰增强可能是由于在引入NO+O2后,气体吸附的C3H6被氧化成CO2。所以Ce的负载对催化剂上C3H6吸附物种的反应活性有轻微的促进作用。
通入NO+O2后,Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)上几乎所有C3H6吸附物种,如甲酸盐、乙酸盐、未反应的丙烯、烷烃的C―H伸缩(vCH)和C―H振动都减少,甚至消失,表明它们在与NOx吸附物种反应的过程中被消耗了。同时观察到在1 845和1 904 cm−1处,出现了归属于表面NO[8]的新特征峰。位于1 569 cm−1处的乙酸盐特征峰在4 min后向低波数移动,最终与逐渐增强的1 564 cm−1处的双齿硝酸盐重叠[8]。1 641 cm−1(未反应的丙烯)和1 689 cm−1(丙酮羧基C=O振动和单齿硝酸盐的共吸附[34])处的特征峰强度分别逐渐减小和增大,4 min后,这2个特征峰均与逐渐增强的1 668 cm−1处的
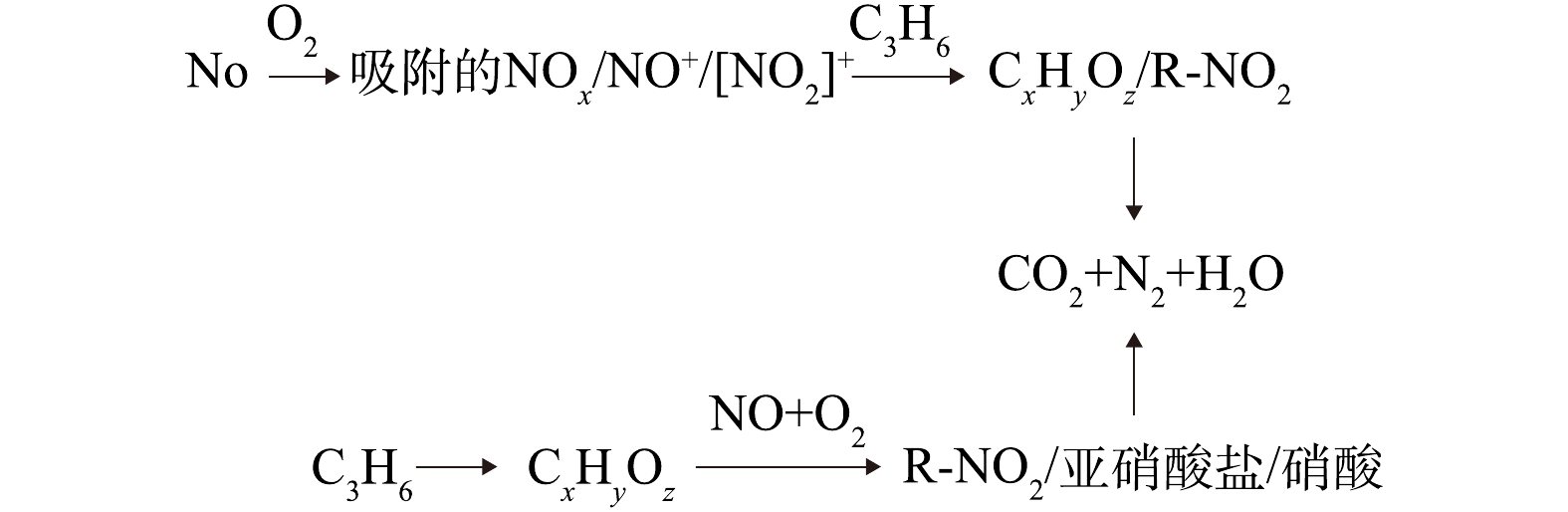
$ {\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ [35]物种重叠。在反应过程中,没有出现亚硝酸盐,但出现了$ {\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ 。与Ce-TiO2相比,HPW的负载丰富了参与C3H6-SCR反应的活性物质。Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)趋势与Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)基本相同,甲酸盐、乙酸盐、未反应的丙烯、烷烃的C―H不对称伸缩振动和C―H振动都减少甚至消失,且位于1 458 cm−1和1 565 cm−1处的乙酸盐分别在通入NO+O2 2 min和6 min后,逐渐向较低的波数移动,并逐渐与位于1 421 cm−1(亚硝酸盐)和1 556 cm−1(双齿硝酸盐)[8, 30]的特征峰重叠。归属于丙酮中羧基C=O振动的1 676 cm−1处特征峰一直在增强,推断这是由于通入NO+O2后丙酮和亚硝酸乙酯[29]共吸附造成的。上述结果表明Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)上几乎所有的C3H6吸附物种都参与了C3H6-SCR反应。基于上述实验结果,我们提出了可能存在的反应机理(如图9所示)。NO被O2氧化为NO2,并在催化剂活性位上以硝酸盐的形式储存,随后在C3H6-SCR反应中,与丙烯(通过产生甲酸盐,乙酸盐,亚硝酸乙酯和丙酮)产生相互作用,最终得到氧化产物(CO2,H2O)。同时还可能存在一条平行反应路径,即C3H6通过吸附在催化剂活性位上产生甲酸盐、丙酮和未反应的丙烯,这些吸附物种会进一步与NO和O2进行反应,最终得到CO2、H2O和N2。
-
1)用浸渍法制备了掺杂Ce、HPW的TiO2催化剂,在模拟烟气的情况下,考察了各催化剂在中低温区的脱硝活性,可以看出,Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)具有最佳的NO转化率,大约为73%。
2)催化剂吸附NO和C3H6的原位FT-IR分析表明,Ce和Keggin结构HPW的掺杂可以促进催化剂表面硝酸盐物质和丙烯吸附物种的形成。
3)在瞬态反应过程中发现,无论是在预吸附NO还是在预吸附C3H6的情况下,Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)催化剂表面发生的反应活性最高,基本上所有的NO或C3H6吸附物种都参与到了C3H6-SCR反应中。
4)基于瞬态反应,推出Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)催化剂的反应机理,发现该反应的中间体主要为无机硝酸盐、甲酸盐、乙酸盐和有机氮化合物。
5) Ce-HPW-TiO2(UCM)和Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)的活性测试、表征结果和FT-IR的研究表明,在浸渍负载HPW后、负载Ce之前对样品进行1次煅烧,有利于第2种活性物质的成功负载且有利于优化催化剂活性。
Ce-HPW-TiO2催化剂利用C3H6选择性催化还原NO反应的机理
Mechanism of C3H6 selective catalytic reduction reaction of NO by Ce-HPW-TiO2 catalyst
-
摘要: 为提高C3H6-SCR脱硝催化剂的低温脱硝性能,采用浸渍法合成了几种由铈和Keggin型磷钨酸改性的TiO2催化剂。在模拟烟气的实验条件下,考察了不同催化剂在150~350 ℃的脱硝活性,通过XRD、FT-IR和SEM对催化剂的理化性质进行了分析,并且通过原位FT-IR探究并对比了不同催化剂在吸附NO和C3H6时产生的吸附物种。结果表明:铈和磷钨酸的共掺杂大大提高了TiO2催化剂在中低温区的脱硝效率;Ce和H3PW12O40(HPW)成功负载于TiO2上,负载的HPW也保留了其Keggin结构,而且负载后的催化剂表面更加光滑,形态更加规则,分散性更好;原位FT-IR结果显示:Ce和HPW的掺杂可以促进催化剂表面硝酸盐物质和丙烯吸附物种的形成;同时发现无论是在预吸附NO还是在预吸附C3H6的情况下,Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)催化剂表面发生的反应活性最高。由此提出了Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM)催化剂的反应机理,发现其反应中间体主要为无机硝酸盐、甲酸盐、乙酸盐和有机氮化合物。Abstract: In order to improve the low-temperature denitration performance of C3H6-SCR denitration catalyst, several modified TiO2 catalysts with ceria and Keggin-type tungstophosphoric acid were synthesized by impregnation method. Under the experimental conditions of simulated flue gas, the denitrification activities of different catalysts at 150~350 ℃ was investigated. The physicochemical properties of these catalysts were analyzed by XRD, FT-IR and SEM. In situ FT-IR was used to investigate and compare the adsorbed species produced on different catalysts when they absorbed NO and C3H6. The results showed that the co-doping of cerium and phosphotungstic acid greatly improved the denitration efficiency of TiO2 catalyst in the middle and low temperature regions. Ce and H3PW12O40(HPW) were successfully supported on TiO2, and the supported HPW also retained its Keggin structure, and the catalysts after loading had more smooth surface, more regular shape, and better dispersion. The in situ FTIR spectra showed that the doping of Ce and HPW could promote the formation of nitrate and propylene adsorbed species on the surface of catalysts. At the same time, the surface of Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM) catalyst had the highest reactivity whether it was pre-adsorbed with NO or C3H6. Therefore, the reaction mechanism of Ce-HPW-TiO2(CM) catalyst was proposed, and the reaction intermediates were mainly inorganic nitrate, formate, acetate and organic nitrogen compounds.
-
Key words:
- phosphotungstic acid /
- NO reduction /
- C3H6-SCR /
- in situ FT-IR /
- mechanism
-

-
-
[1] MRAD R, COUSIN R, POUPIN C, et al. Propene oxidation and NO reduction over MgCu-Al(Fe) mixed oxides derived from hydrotalcite-like compounds[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 257: 98-103. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.02.020 [2] YUAN D L, LI X Y, ZHAO Q D, et al. A novel CuTi-containing catalyst derived from hydrotalcite-like compounds for selective catalytic reduction of NO with C3H6 under lean-burn conditions[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 309: 268-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.09.010 [3] AZIS M M, HÄRELIND H, CREASER D. On the role of H2 to modify surface NOx species over Ag-Al2O3 as lean NOx reduction catalyst: TPD and DRIFTS studies[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2014, 5: 296-309. [4] 刘欣, 苏亚欣, 董士林, 等. Co/Fe/Al2O3/cordierite催化C3H6选择性还原NO的实验研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2018, 46(6): 743-753. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.06.013 [5] KIM Y J, KWON H J, NAM I S, et al. High deNOx performance of Mn/TiO2 catalyst by NH3[J]. Catalysis Today, 2010, 151(3/4): 244-250. [6] PUTLURU S S R, MOSSIN S, RIISAGER A, et al. Heteropoly acid promoted Cu and Fe catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia[J]. Catalysis Today, 2011, 176(1): 292-297. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.11.087 [7] YAO S H, CHEN S, SHI Z L. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of Ce, H3PW12O40 co-doped TiO2 hollow fibers[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2014, 27: 343-349. doi: 10.1063/1674-0068/27/03/343-349 [8] LIU J, LI X Y, ZHAO Q D, et al. Combined spectroscopic and theoretical approach to sulfur-poisoning on Cu-supported Ti-Zr mixed oxide catalyst in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(8): 2426-2436. doi: 10.1021/cs5005739 [9] 王淑勤, 武金锦, 杜志辉. Co-Ce共掺杂对TiO2催化剂室温可见光催化脱硝性能的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(3): 361-369. [10] JIN R B, LIU Y, WU Z B, et al. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over Mn-Ce oxides supported on TiO2 and Al2O3: A comparative study[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(9): 1160-1166. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.11.049 [11] 宋忠贤. 固体酸改性CeO2催化剂的制备及其NH3-SCR机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2017. [12] WENG X L, DAI X X, ZENG Q S, et al. DRIFT studies on promotion mechanism of H3PW12O40 in selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 461: 9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.09.004 [13] 宋淑美, 王睿. 具有低温活性的高效脱硝催化体系研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2007, 27(s1): 108-112. [14] GÓMEZ-GARCÍA M A, PITCHON V, KIENNEMANN A, et al. Sorption-desorption of NOx from a lean gas mixture on H3PW12O40·6H2O supported on carbon nanotubes[J]. Topics in Catalysis, 2004, 30-31(1/2/3/4): 229-233. [15] PALACIO M, VILLABRILLE P I, ROMANELLI G P, et al. Ecofriendly liquid phase oxidation with hydrogen peroxide of 2,6-dimethylphenol to 2,6-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone catalyzed by TiO2-CeO2 mixed xerogels[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2009, 359(1/2): 62-68. [16] XUE W L, ZHANG G W, XU X F, et al. Preparation of titania nanotubes doped with cerium and their photocatalytic activity for glyphosate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 167(1): 397-402. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.007 [17] WANG Y J, CUI Y X, SUO Y H, et al. Influences of cerium on structure and catalytic performance of n-heptane hydroisomerization of Ni-HPW/MCM-48[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2015, 33(1): 46-55. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60382-3 [18] MICEK-ILNICKA A, BIELAŃSKA E, LITYŃSKA-DOBRZYŃSKA L, et al. Carbon nanotubes, silica and titania supported heteropolyacid H3PW12O40 as the catalyst for ethanol conversion[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2012, 421-422: 91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.001 [19] REN Z Y, TENG Y F, ZHAO L Y, et al. Keggin-tungstophosphoric acid decorated Fe2O3 nanoring as a new catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 297: 36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.06.036 [20] CHANSAI S, BURCH R, HARDACRE C, et al. The use of short time-on-stream in situ spectroscopic transient kinetic isotope techniques to investigate the mechanism of hydrocarbon selective catalytic reduction (HC-SCR) of NOx at low temperatures[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 281(1): 98-105. [21] GENG Y, XIONG S C, LI B, et al. H3PW12O40 grafted on CeO2: A high-performance catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(3): 856-866. [22] GUNNARSSON F, PIHL J A, TOOPS T J, et al. Lean NOx reduction over Ag/alumina catalysts via ethanol-SCR using ethanol/gasoline blends[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 202: 42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.009 [23] GUO R T, LI M Y, SUN P, et al. Mechanistic investigation of the promotion effect of Bi modification on the NH3-SCR performance of Ce/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(49): 27535-27545. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b10342 [24] JIANG H X, WANG Q Y, WANG H Q, et al. MOF-74 as an efficient catalyst for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(40): 26817-26826. [25] ZHA K W, CAI S X, HU H, et al. In situ DRIFTs investigation of promotional effects of tungsten on MnOx-CeO2/meso-TiO2 catalysts for NOx reduction[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(45): 25243-25254. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b08600 [26] ZHANG Q L, FAN J, NING P, et al. In situ DRIFTS investigation of NH3-SCR reaction over CeO2/zirconium phosphate catalyst[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 435: 1037-1045. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.180 [27] HADJIIVANOV K. Identification of neutral and charged NxOy surface species by IR spectroscopy[J]. Catalysis Reviews: Science and Engineering, 2000, 42(1/2): 71-144. [28] KRISTIANSEN T, MATHISEN K. On the promoting effect of water during NOx removal over single-site copper in hydrophobic silica APD-aerogels[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(5): 2439-2453. doi: 10.1021/jp406610v [29] SHIMIZU K, SATSUMA A. Selective catalytic reduction of NO over supported silver catalysts-practical and mechanistic aspects[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2006, 8(23): 2677-2695. doi: 10.1039/B601794K [30] SOBCZAK I, MUSIALSKA K, PAWLOWSKI H, et al. NO and C3H6 adsorption and coadsorption in oxygen excess: A comparative study of different type zeolites modified with gold[J]. Catalysis Today, 2011, 176(1): 393-398. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.11.028 [31] XU G Y, YU Y B, HE H. Silver valence state determines the water tolerance of Ag/Al2O3 for the H2-C3H6-SCR of NOx[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(1): 670-680. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b10860 [32] YU Y B, HE H, ZHANG X L, et al. A common feature of H2-assisted HC-SCR over Ag/Al2O3[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2014, 4(5): 1239-1245. [33] KAMEOKA S, KITA K, TANAKA S I, et al. Enhancement of C2H6 oxidation by O2 in the presence of N2O over Fe ion-exchanged BEA zeolite catalyst[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2002, 79(1/2/3/4): 63-67. [34] HAMADA S, HIBARINO S, IKEUE K, et al. Preparation of supported Pt-M catalysts (M=Mo and W) from anion-exchanged hydrotalcites and their catalytic activity for low temperature NO-H2-O2 reaction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2007, 74(3/4): 197-202. [35] LI Y H, DENG J L, SONG W Y, et al. Nature of Cu species in Cu-SAPO-18 catalyst for NH3-SCR: combination of experiments and DFT calculations[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(27): 14669-14680. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b03464 -



 下载:
下载: