新烟碱类杀虫剂(neonicotinoid insecticides)因高效、低毒和广谱的特点,已成为自拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂商品化之后销售量增长最快的一类杀虫剂。作为激动剂,新烟碱类杀虫剂作用于位于神经后突触的烟碱乙酰胆碱受体,可有效防治如半翅目害虫蚜虫、粉虱和飞虱及鞘翅目的甲虫类等靶标害虫[1]。近年来,新烟碱类杀虫剂因高检出率和对非靶标生物蜜蜂的影响备受争议[2],基于对环境友好生物(蜜蜂)的保护,美国、欧盟等国家和地区对部分新烟碱类杀虫剂实施了使用限制或禁用等措施。有研究表明该类杀虫剂对非靶标生物的影响不仅局限于蜜蜂,其他类昆虫例如欧洲蜻蜓目的减少与该类物质亦相关[3]。新烟碱类杀虫剂对哺乳动物、鸟类和鱼类具有低急性毒性,但存在慢性毒性。噻虫嗪亚慢性毒性暴露可引起雄性大鼠肝脏、肾脏和脑组织病理学改变[4]。随暴露时间延长,噻虫嗪可引起小鼠肝脏损伤加重并发生增生,进而形成肝脏肿瘤[5]。噻虫嗪90 d连续暴露可导致家兔肝脏细胞坏死、淋巴浸润和肝脏纤维化、癌胚抗原升高,这表明噻虫嗪不仅存在肝毒性同时存在致癌性[6]。新烟碱类杀虫剂对水生生物存在毒性效应,噻虫嗪和噻虫胺对双翅目和介形亚纲的水生昆虫种群数量有不利影响[7]。噻虫嗪暴露可诱导斑马鱼氧化应激及剂量相关的肝脏DNA损伤[8]。噻虫嗪慢性暴露可导致稀有鮈鲫肝脏损伤和性腺发育迟缓,同时伴随性腺和甲状腺作用轴相关基因转录组水平表达异常[9]。吡虫啉和呋虫胺慢性暴露可导致稀有鮈鲫免疫系统相关基因下调及部分处理组血清免疫球蛋白减少[10]。上述研究表明,新烟碱类杀虫剂对鱼类存在潜在的内分泌干扰、免疫系统干扰等特性,但是关于鱼类致癌效应相关报道较少。
鱼类作为重要的水生生物同时又是脊椎动物最大的种群,有着与哺育动物相似的生理系统,以及与其他脊椎动物类似的内分泌干扰系统。针对鱼类开展毒性效应研究将对其他脊椎动物的研究具有重要参考价值。同时,鱼类作为环境污染的生物指标体可以用作水环境污染风险,尤其是因农业生产造成的地表径流污染或间接的因食物链造成的风险[11]。我国特有水生鱼种稀有鮈鲫(Gobiocypris rarus)因体型小、易培养、生命周期短和繁殖率高等优势作为实验室模式鱼种已应用于多种内分泌干扰物的研究中[12-13]。本研究通过噻虫嗪暴露实验开展新烟碱类杀虫剂早期生命阶段毒性效应研究,为水环境中非靶标生物毒性风险评估提供依据。
1 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 试剂和仪器(Reagents and instruments)
噻虫嗪纯度>99%,购自Sigma-Aldrich Chemical公司。SYBR Green PCR master mix和M-MLV购自美国Promega公司,Trizol reagent等试剂为美国Invitrogen公司生产。定量PCR管和MxPro Multicolor Real-Time PCR Detection System购自美国Stratagene公司。
1.2 实验鱼(Fishes for test)
稀有鮈鲫养殖用水为经活性炭过滤并曝气的自来水,pH 7.2~7.6,硬度44.0~61.0 mg·L-1(以CaCO3质量计),水温控制在(25±1)℃,光周期为16 h∶8 h(昼∶夜),溶氧不低于7 mg·L-1。饲养期每日投喂3次,即小颗粒商品饵料(TetraMin)2次和刚孵化的丰年虫幼虫(Artemia nauplii)1次,并及时清除多余饵料和排泄物。
1.3 实验设计(Experimental design)
早期生命阶段暴露实验分别取同对稀有鮈鲫亲本所产受精4 h内胚胎和孵化后7 d幼鱼,以半静态实验方式暴露于浓度为0.5、5和50 μg·L-1噻虫嗪。胚胎暴露实验至孵化后4 d结束实验,每个处理组50粒胚胎,3个平行,统计孵化时间、胚胎死亡率;幼鱼暴露28 d,每个处理30尾幼鱼,统计死亡率和幼鱼体长,并于实验结束时收集幼鱼样品储存在-80 ℃待测。
1.4 基因定量(Gene quantification)
通过荧光定量PCR法测定幼鱼体内胆固醇合成及癌症信号通路相关功能基因(sc5d、ebp、sc4mol、mdm2、p53、p21、mycb、nsdhl、caspase3和ctsl1a)转录水平的表达情况,引物如表1所示。内参基因使用管家基因β-actin,确定每个引物的扩增效率,用含有目标片段的重组质粒进行扩增,以10倍稀释进行定量PCR扩增,检测引物的扩增效率。选取目标基因和内参基因的扩增效率差异在±5%的引物,建立其标准曲线。扩增体系总体积为25 μL,PCR反应液包括SYBR Green PCR master mix(Stratagene,美国)11.25 μL、25 μmol·L-1正义和反义引物各0.4 μL、cDNA和双蒸馏水。PCR反应程序为95 ℃, 7 min;40个循环:95 ℃ 15 s,58 ℃ 40 s;在最后一个循环结束后做熔解曲线,确定PCR反应质量。
表1 稀有鮈鲫胆固醇合成和癌症信号通路相关基因
Table 1 Genes related to cholesterol synthesis and cancer signaling pathways in rare minnow

基因Gene引物序列(5’→3’)Sequence (5’→3’)产物/bpProduct size/bp基因序列号Genbank accession numberβ-actinF: CAGGGCGTGATGGTGGGGATR: GGTTGGCTTTGGGGTTGAG226DQ539421p53F: GCAATAGCAGCTGCATGGR:CAGCATCTGACCTTCCTGAGT83KC477763p21F: GATAGATGGCGACATGATGCR: TGCACAGGCATCCTTCATAG140KJ411872mycbF: TTAAGGCCAACAGCAAATGGR:TTGAGGGTGTGGCAAGTAGTG151EE594509mdm2F: AACAGCGAGTCTTCGGACGR: GCGTCGGAGTTGATGGACT134KC477761nsdhl1F: CATGCGGTTACATCCTGGTGR: TACCCACATCTGCGGAAGG147EE393009sc5dF: CATGGCCTGAAGATGAGCCTR: TAGCTCAATGCACCCAGGC100EE393234ebpF: CTATTGGCCACGCAACCTGR: TGGCAAGCAGCAGTATCCC107EE396511ctsl1aF:GCAAGAACGCCATGATCTAGCR: TGGCTATTGACGCTGGACAC100EE394315sc4molF:TGGGAGAGACAGTGGAAGTGCR: GCCAATACATAAGGCCAGCG149EE399050caspase3F: TGTTGCTCAGTCATGGAGATGR: CCAGGATCCAGCTCTGTACC163JQ743659
1.5 数据处理与分析(Data processing and analysis)
所有数据分析均通过SPSS 13.0(SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA)。定量结果均表示为平均值±标准偏差,实验组与对照组间差异分析用one-way ANOVA,差异显著性用Bonferroni’s检验,显著性水平为P<0.05。作图软件使用Sigmaplot 10.0和R语言。
2 结果(Results)
2.1 噻虫嗪暴露对稀有鮈鲫胚胎孵化的影响(Effects of thiamethoxam exposure on embryo incubation of rare minnow)
噻虫嗪暴露导致稀有鮈鲫胚胎死亡率增加,50 μg·L-1处理组中胚胎死亡率较对照组显著增加(图1(a)),孵化后仔鱼畸形率较对照组显著增加(图1(b)),稀有鮈鲫仔鱼脊柱弯曲程度和畸形率随噻虫嗪浓度增加而增加,同时处理组呈现鱼鳔发育迟缓现象(图2)。
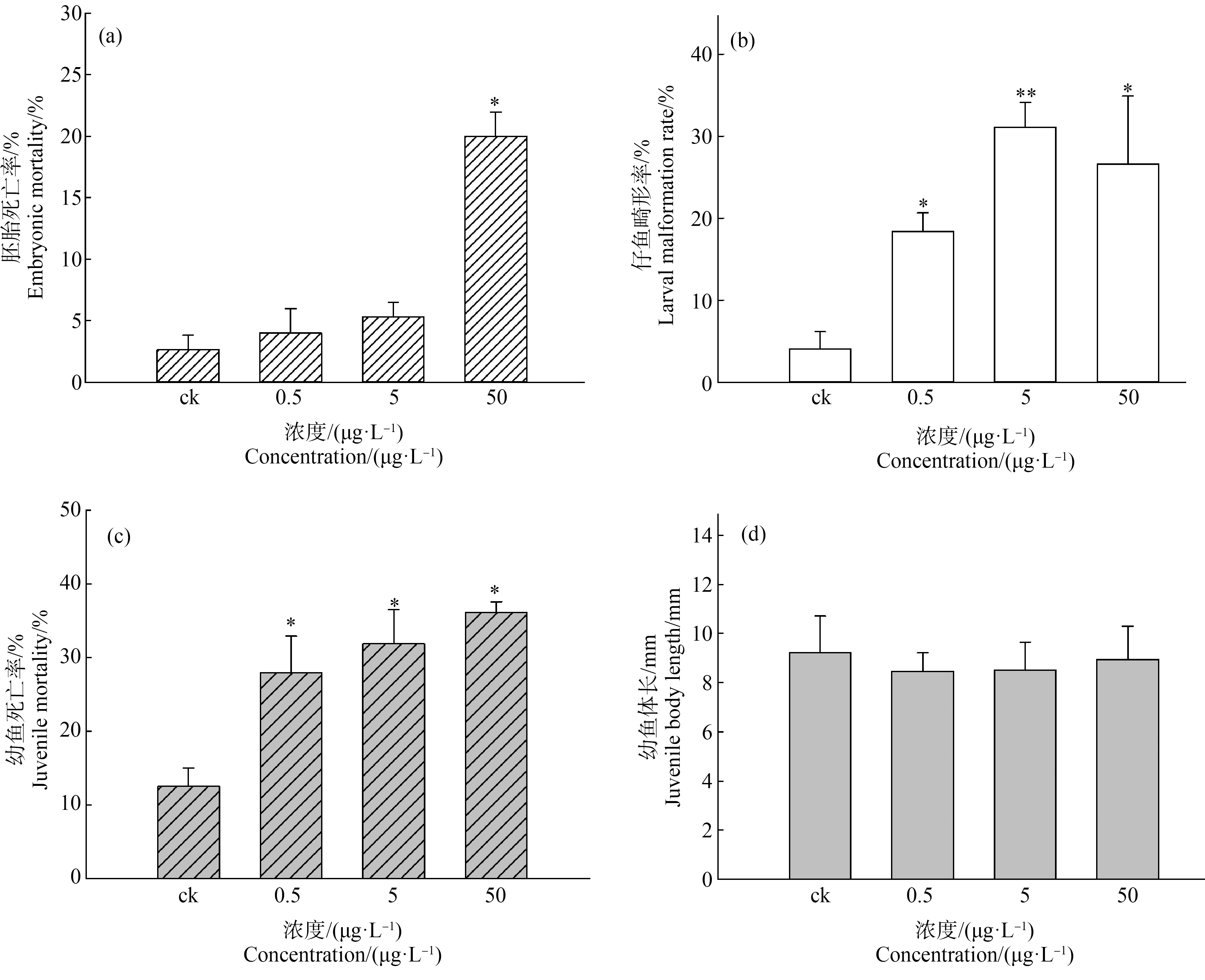
图1 噻虫嗪暴露对稀有鮈鲫早期生命阶段影响
注:*表示P<0.05;**表示P<0.01。
Fig.1 Effects of thiamethoxam exposure on early life stage of rare minnow
Note: *represents P<0.05; **represents P<0.01.

图2 噻虫嗪暴露对孵化后仔鱼影响
注:(a)对照组4 dpf仔鱼;(b)0.5 μg·L-1处理组4 dpf仔鱼;(c)5 μg·L-1处理组4 dpf仔鱼;(d)50 μg·L-1处理组4 dpf仔鱼;箭头指示脊柱弯曲。
Fig.2 Effects of thiamethoxam exposure on larvae after hatching
Note:(a)4 dpf larvae in control group;(b)4 dpf larvae in 0.5 μg·L-1treatment group;(c)4 dpf larvae in 5 μg·L-1treatment group;(d)4 dpf larvae in 50 μg·L-1treatment group; arrows indicate curvature of the spine.
2.2 噻虫嗪暴露对稀有鮈鲫幼鱼影响(Effects of thiamethoxam exposure on juvenile rare minnow)
噻虫嗪幼鱼28 d暴露实验表明,随着噻虫嗪暴露浓度增加幼鱼死亡率增加,且与对照组相比显著增高(图1(c));28 d暴露实验结束测量幼鱼体长,结果表明处理组幼鱼体长虽有下降但与对照组相比未见显著性差异(图1(d))。通过存活幼鱼形态学观察,发现随着暴露组浓度增高幼鱼体内出血点增多,存在颅面畸形(图3)。
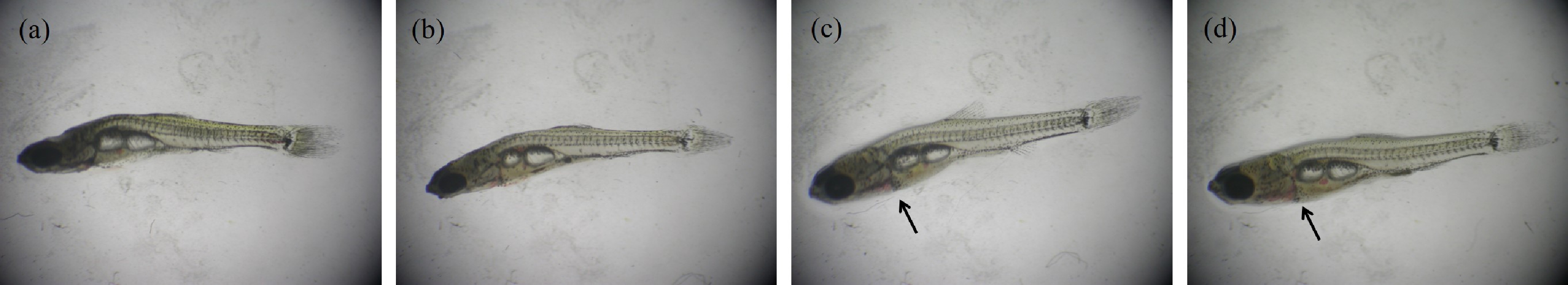

图3 噻虫嗪28 d暴露实验对稀有鮈鲫幼鱼影响
注:(a)对照组幼鱼;(b)0.5 μg·L-1处理组幼鱼;(c)5 μg·L-1处理组幼鱼;(d)50 μg·L-1处理组幼鱼;箭头指示幼鱼内脏出血点。
Fig.3 Effects of 28 d thiamethoxam exposure on juvenile rare minnow
Note:(a)Juvenile rare minnow in control;(b)Juvenile rare minnow in 0.5 μg·L-1treatment group;(c)Juvenile rare minnow in 5 μg·L-1 treatment group;(d)Juvenile rare minnow in 50 μg·L-1treatment group; arrows indicate visceral hemorrhages in juvenile fish.
2.3 稀有鮈鲫幼鱼功能基因表达情况(Expression of functional genes in juvenile rare minnow)
幼鱼功能基因定量结果显示,C5-固醇脱氢酶基因(sterol-C5-desaturase gene, sc5d)、3-β-羟基类固醇-8,7-异构酶基因(EBP cholestenol delta-isomerase gene, ebp)、甲基固醇单加氧酶基因(methylsterol monooxygenase gene, sc4mol)和原癌基因(MDM2 proto-oncogene, mdm2)在暴露组中均下调;p53肿瘤抑制基因(p53 tumor suppressor gene, p53)、p21肿瘤抑制基因(p21 tumor suppressor gene, p21)和MYC原癌基因Bhlh转录因子(MYC proto-oncogene Bhlh transcription factor, mycb)等在5 μg·L-1处理组中显著下调,在0.5 μg·L-1和50 μg·L-1处理组中上述基因表达与对照组相比无显著性差异;NAD(P)依赖的类固醇脱氢酶基因(NAD(P)dependent steroid dehydrogenase-like, nsdhl)、凋亡相关半胱氨酸肽酶基因(apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase, caspase3)和组织蛋白酶基因(cathepsin La, ctsl1a)与对照组相比无显著性差异(图4)。
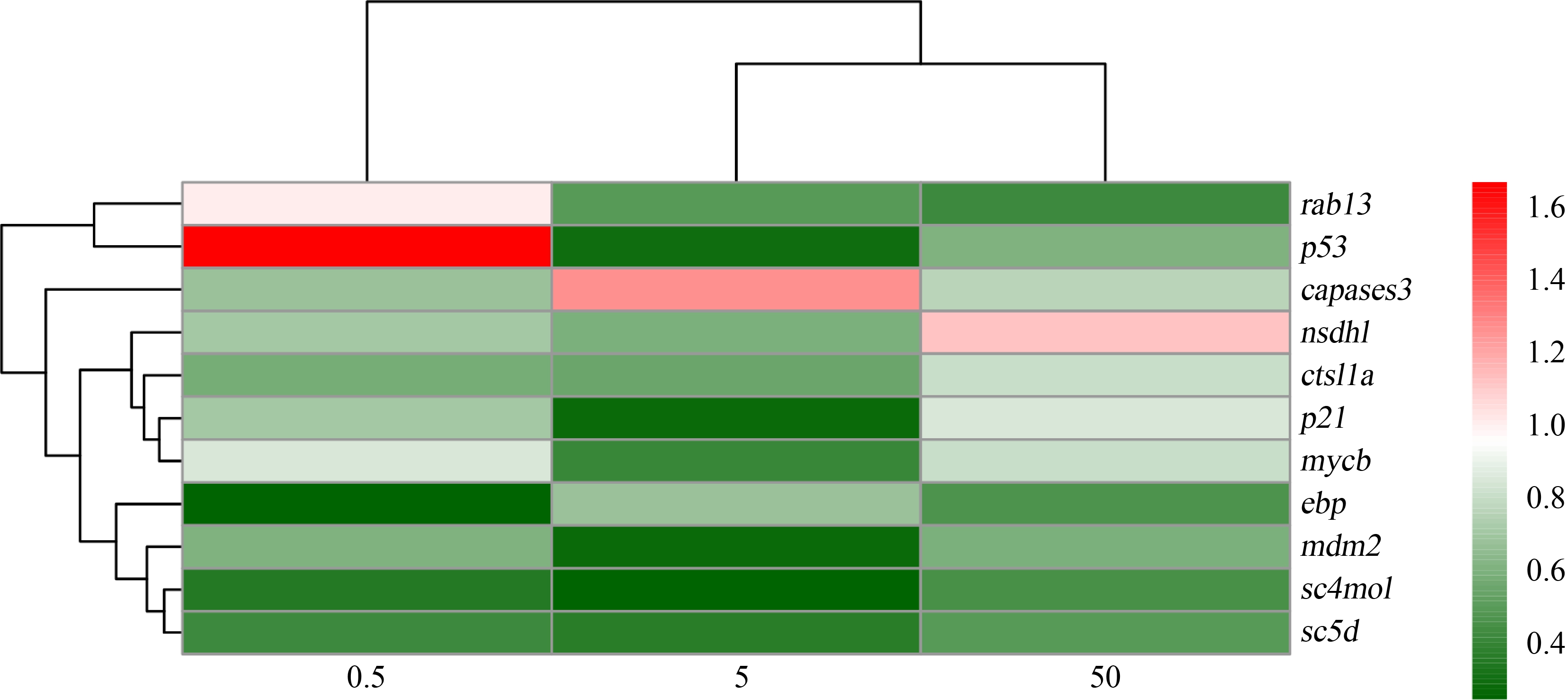
图4 噻虫嗪28 d暴露稀有鮈鲫幼鱼基因定量结果热图
Fig. 4 Heatmap of gene quantification in juvenile rare minnow after thiamethoxam 28 d exposure
3 讨论(Discussion)
早期生命阶段是鱼类生长发育的重要阶段,早期生命阶段毒性测试对化学品水生生物毒性评估具有重要意义[14]。噻虫嗪暴露导致稀有鮈鲫胚胎死亡率增加,但仅高浓度组胚胎死亡率与对照组存在显著差异;各处理组仔鱼死亡率较对照组均显著增加,仔鱼出现畸形,且随药物浓度增加脊柱弯曲程度加重。这一结果与文献报道的鱼类早期生命阶段药物暴露相关研究具有相似性。如氯氰菊酯暴露可以导致鲤鱼胚胎孵化率降低,孵化后仔鱼死亡率增加[15],环丙沙星可导致鲤鱼胚胎孵化后畸形率增加[16]。随诺氟沙星暴露浓度增加,斑马鱼胚胎呈现剂量依赖的发育迟缓,死亡率增加和脊柱弯曲[17]。暴露浓度50 ng·L-1的4种农药(腈苯唑、吡唑醚菌酯、恶霜灵和戊菌隆)均可导致斑马鱼心包囊和卵黄囊水肿比率及脊柱弯曲率显著增高[18]。早期生命阶段药物暴露,常导致胚胎、仔鱼发育损伤,甚至死亡,低浓度噻虫嗪暴露虽未引起胚胎死亡率显著增加,但低浓度处理组仔鱼死亡率显著增加,这表明胚胎阶段的暴露对鱼类存活存在风险。
噻虫嗪28 d暴露可引发幼鱼颅面畸形、体内出血点增加和死亡率增加,与胚胎、仔鱼阶段死亡率增加具有一致性,但与前期研究中成鱼暴露并未造成死亡的结果不一致[9]。鱼类不同生长发育阶段对毒性污染物敏感性存在差异,如酮基布洛芬暴露可导致斑马鱼胚胎出现剂量依赖的发育改变,如水肿、孵化延迟、脊柱弯曲和死亡率增加,但相同暴露浓度并未导致成鱼死亡[19]。双酚AF暴露可延缓斑马鱼胚胎发育和孵化,斑马鱼幼鱼出现心包水肿、背脊弯曲等,胚胎期和幼鱼期对药物暴露反应敏感度存在差异[20]。鱼类早期生命阶段对药物暴露具有较高的毒性敏感性,噻虫嗪早期生命阶段暴露结果预示着该类化学品可能对鱼类种群繁衍产生负面效应。
据报道多种农药存在内分泌干扰效应[21],同时亦存在致癌性[22-23]。噻虫嗪慢性膳食暴露可诱发小鼠肝脏肿瘤发生,这一过程最初表现为血浆胆固醇含量降低、肝脏细胞坏死[24]。有研究表明,哺乳动物体内ebp是烯胆甾烷醇合成的重要调控基因[25];sc5d调控胆固醇生物合成中催化脱氢反应,可将烯胆甾烷醇转化为7-脱氢胆固醇[26];sc4mol缺失可导致胆固醇生物合成障碍[27],上述基因也是鱼类重要的胆固醇合成调控基因[28-29]。噻虫嗪28 d暴露导致稀有鮈鲫幼鱼sc5d、ebp和sc4mol在转录水平表达下调,表明药物暴露干扰了鱼体胆固醇合成。微克级水平非甾类芳香酶抑制剂法曲唑(fadrozole)暴露斑马鱼48 hpf、96 hpf和28 dpf均导致其sc4mol转录水平表达下调[30]。胆固醇是细胞生物进程中必需脂质和激素合成的重要前体[31],胆固醇合成紊乱和疾病甚至癌症发生相关[32],肿瘤细胞形成和生长伴随着胆固醇合成通路表达变化。mdm2是鱼类早期生命阶段重要基因,斑马鱼胚胎mdm2基因敲除会引起p53依赖的凋亡活性增加[33]。据报道,p53基因可通过调节细胞周期和细胞分化进而抑制肿瘤发生,p53表达下调预示着细胞分化、再生甚至肿瘤发生[34]。p21基因是细胞周期调节重要基因,同时也在细胞凋亡和分化过程中有着重要作用[35],其表达下调与多种癌症发生相关。MYC基因编码的核磷酸化蛋白,具有多功能性,可调控细胞周期、细胞生长、凋亡、细胞代谢、生物合成和黏附核线粒体发生[36],myc表达下调可诱发细胞凋亡,限制肿瘤细胞分化[37]。在转录水平上,低浓度噻虫嗪(0.5 μg·L-1)暴露导致稀有鮈鲫仔鱼mdm2和p53表达相反,这表明在低浓度处理组中机体通过基因调控来降低外源物质带来的伤害;但在5 μg·L-1和50 μg·L-1处理组中二者较对照组均下降,表明药物处理进一步引发了功能基因表达紊乱。5 μg·L-1噻虫嗪处理组中稀有鮈鲫幼鱼p53、p21和mycb等基因表达显著下调,表明噻虫嗪暴露对稀有鮈鲫早期生命阶段细胞生长、凋亡均有负面效应,继而可能诱发鱼类肿瘤发生。前期研究发现,噻虫嗪慢性暴露可以导致稀有鮈鲫成鱼多个内分泌作用轴功能基因表达紊乱,并伴有肝脏细胞排列异常、组织坏死和肿瘤形成等现象[9]。噻虫嗪28 d暴露导致稀有鮈鲫幼鱼胆固醇合成通路和癌症信号通路关键基因的表达变化,幼鱼死亡率增加预示着该类化学品对非靶标生物鱼类存在复杂的毒性效应。
针对稀有鮈鲫早期生命阶段所开展新烟碱类杀虫剂噻虫嗪暴露实验,结果表明μg·L-1浓度水平的噻虫嗪对非靶标生物鱼类存在毒性效应,降低鱼类早期生命阶段存活率,对种群的繁衍可能存在负面效应。鉴于此,该类农药的管理和使用中应充分考虑非靶标生物(鱼类)的毒性效应,降低因大量使用造成的环境风险,以便更好地保护水生态系统完整性。
[1] 唐振华, 陶黎明, 李忠.害虫对新烟碱类杀虫剂的抗药性及其治理策略[J].农药学学报, 2006, 8(3): 195-202
Tang Z H, Tao L M, Li Z.Resistance of insect pests to neonicotinoid insecticides and management strategies[J].Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2006, 8(3): 195-202(in Chinese)
[2] Wang X R, Goulson D, Chen L Z, et al.Occurrence of neonicotinoids in Chinese apiculture and a corresponding risk exposure assessment[J].Environmental Science &Technology, 2020, 54(8): 5021-5030
[3] Barmentlo S H, Vriend L M, Grunsven R H A, et al.Environmental levels of neonicotinoids reduce prey consumption, mobility and emergence of the damselfly Ischnura elegans[J].Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 56(8): 2034-2044
[4] Khaldoun-Oularbi H, Bouzid N, Boukreta S, et al.Thiamethoxam Actara®induced alterations in kidney liver cerebellum and hippocampus of male rats[J].Journal of Xenobiotics, 2017, 7(1): 7149
[5] Pastoor T, Rose P, Lloyd S, et al.Case study: Weight of evidence evaluation of the human health relevance of thiamethoxam-related mouse liver tumors[J].Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, 2005, 86(1): 56-60
[6] El Okle O S, El Euony O I, Khafaga A F, et al.Thiamethoxam induced hepatotoxicity and pro-carcinogenicity in rabbits via motivation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and anti-apoptotic pathway[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(5): 4678-4689
[7] Basley K, Goulson D.Neonicotinoids thiamethoxam and clothianidin adversely affect the colonisation of invertebrate populations in aquatic microcosms[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(10): 9593-9599
[8] Yan S H, Wang J H, Zhu L S, et al.Thiamethoxam induces oxidative stress and antioxidant response in zebrafish(DanioRerio)livers[J].Environmental Toxicology, 2016, 31(12): 2006-2015
[9] Zhu L F, Li W, Zha J M, et al.Chronic thiamethoxam exposure impairs the HPG and HPT axes in adult Chinese rare minnow(Gobiocypris rarus): Docking study, hormone levels, histology, and transcriptional responses[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 185: 109683
[10] Hong X S, Zhao X, Tian X, et al.Changes of hematological and biochemical parameters revealed genotoxicity and immunotoxicity of neonicotinoids on Chinese rare minnows(Gobiocypris rarus)[J].Environmental Pollution, 2018, 233: 862-871
[11] Lakra W S, Nagpure N S.Genotoxicological studies in fishes: A review[J].The Indian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2009, 79(1): 93-97
[12] Zha J M, Sun L W, Zhou Y Q, et al.Assessment of 17α-ethinylestradiol effects and underlying mechanisms in a continuous, multigeneration exposure of the Chinese rare minnow(Gobiocypris rarus)[J].Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2008, 226(3): 298-308
[13] Zha J M, Wang Z J, Wang N, et al.Histological alternation and vitellogenin induction in adult rare minnow(Gobiocypris rarus)after exposure to ethynylestradiol and nonylphenol[J].Chemosphere, 2007, 66(3): 488-495
[14] Wheeler J R, Maynard S K, Crane M.An evaluation of fish early life stage tests for predicting reproductive and longer-term toxicity from plant protection product active substances[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2014, 33(8): 1874-1878
[15] Richterová Z, Máchová J, Stará A, et al.Effects of cyhalothrin-based pesticide on early life stages of common carp(Cyprinus carpioL.)[J].BioMed Research International, 2014, 2014: 107373
[16] Zivna D, Plhalova L, Chromcova L, et al.The effects of ciprofloxacin on early life stages of common carp(Cyprinus carpio)[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2016, 35(7): 1733-1740
[17] 王冬梅, 谷从友, 刘铜, 等.诺氟沙星对斑马鱼胚胎发育的毒性作用及对TGF-β1的影响[J].生物技术通报, 2016, 32(1): 169-173
Wang D M, Gu C Y, Liu T, et al.The deleterious effects of norfloxacin on zebrafish embryonic development and TGF-β1 expression[J].Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(1): 169-173(in Chinese)
[18] 吴玉琼, 陈莹, 胡永乐, 等.四种新型农药对斑马鱼胚胎发育的毒性效应[J].生物技术通报, 2017, 33(6): 155-161
Wu Y Q, Chen Y, Hu Y L, et al.Toxic effects of four currently-used pesticides on zebrafish embryonic development[J].Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(6): 155-161(in Chinese)
[19] Rangasamy B, Hemalatha D, Shobana C, et al.Developmental toxicity and biological responses of zebrafish(Danio rerio)exposed to anti-inflammatory drug ketoprofen[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 213: 423-433
[20] 杨洋, 陈亚文, 唐天乐, 等.双酚AF暴露对胚胎期和幼鱼期斑马鱼的毒性效应[J].环境科学研究, 2015, 28(8): 1219-1226
Yang Y, Chen Y W, Tang T L, et al.Toxic effects of bisphenol AF on zebrafish embryos and larvae[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(8): 1219-1226(in Chinese)
[21] 方琪, 马彦博, 张思远, 等.农药内分泌干扰效应研究进展[J].生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(1): 98-110
Fang Q, Ma Y B, Zhang S Y, et al.Research progress in endocrine disrupting effects of pesticides[J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(1): 98-110(in Chinese)
[22] Zárate L V, Pontillo C A, Espa ol A, et al.Angiogenesis signaling in breast cancer models is induced by hexachlorobenzene and chlorpyrifos, pesticide ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J].Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2020, 401: 115093
ol A, et al.Angiogenesis signaling in breast cancer models is induced by hexachlorobenzene and chlorpyrifos, pesticide ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J].Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2020, 401: 115093
[23] Yang G L, Lv L, Di S S, et al.Combined toxic impacts of thiamethoxam and four pesticides on the rare minnow(Gobiocypris rarus)[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(5): 5407-5416
[24] Green T, Toghill A, Lee R, et al.Thiamethoxam induced mouse liver tumors and their relevance to humans.Part 1: Mode of action studies in the mouse[J].Toxicological Sciences: An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, 2005, 86(1): 36-47
[25] Long T, Hassan A, Thompson B M, et al.Structural basis for human sterol isomerase in cholesterol biosynthesis and multidrug recognition[J].Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2452
[26] Sugawara T, Fujimoto Y, Ishibashi T.Molecular cloning and structural analysis of human sterol C5 desaturase[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2001, 1533(3): 277-284
[27] Kalay Yildizhan I, Gökp nar ⅰli E, Onoufriadis A, et al.New homozygous missense MSMO1 mutation in two siblings with SC4MOL deficiency presenting with psoriasiform dermatitis[J].Cytogenetic and Genome Research, 2020, 160(9): 523-530
nar ⅰli E, Onoufriadis A, et al.New homozygous missense MSMO1 mutation in two siblings with SC4MOL deficiency presenting with psoriasiform dermatitis[J].Cytogenetic and Genome Research, 2020, 160(9): 523-530
[28] Wang N, Gong Z H, Wang J L, et al.Characterization of Chinese tongue sole(Cynoglossus semilaevis)24-dehydrocholesterol reductase: Expression profile, epigenetic modification, and its knock-down effect[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2021, 312: 113870
[29] Wang N, Wang R K, Wang R Q, et al.Transcriptomics analysis revealing candidate networks and genes for the body size sexual dimorphism of Chinese tongue sole(Cynoglossus semilaevis)[J].Functional &Integrative Genomics, 2018, 18(3): 327-339
[30] Muth-Köhne E, Westphal-Settele K, Brückner J, et al.Linking the response of endocrine regulated genes to adverse effects on sex differentiation improves comprehension of aromatase inhibition in a Fish Sexual Development Test[J].Aquatic Toxicology, 2016, 176: 116-127
[31] Yang J, Wang L H, Jia R B.Role of de novocholesterol synthesis enzymes in cancer[J].Journal of Cancer, 2020, 11(7): 1761-1767
[32] Ershov P, Kaluzhskiy L, Mezentsev Y, et al.Enzymes in the cholesterol synthesis pathway: Interactomics in the cancer context[J].Biomedicines, 2021, 9(8): 895
[33] Langheinrich U, Hennen E, Stott G, et al.Zebrafish as a model organism for the identification and characterization of drugs and genes affecting p53 signaling[J].Current Biology, 2002, 12(23): 2023-2028
[34] Yun M H, Gates P B, Brockes J P.Regulation of p53 is critical for vertebrate limb regeneration[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(43): 17392-17397
[35] Ghanem L, Steinman R.A proapoptotic function of p21 in differentiating granulocytes[J].Leukemia Research, 2005, 29(11): 1315-1323
[36] Mohamed A N.MYC(MYC proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor)[J].Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology, 2018(6): 1
[37] Lan F F, Wang H, Chen Y C, et al.Hsa-let-7g inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulation of c-Myc and upregulation of p16(INK4A)[J].International Journal of Cancer, 2011, 128(2): 319-331