多氯联苯(polychlorinated biphenyls, PCBs)具有优良的阻燃性、热稳定性、惰性和介电能力,而被广泛用作与人类生产生活紧密相关的阻燃剂、塑化剂油漆、复印纸和变压器油等。然而,1968年日本“米糠油事件”(即“油症”,20世纪世界八大公害事件之一)首次将人们的关注点从PCBs的商业应用转向对人类健康的影响上。因PCBs良好的化学稳定性,使其在自然环境中很难降解,而通过水、土、气和生物等载体转移,在人或动物体内富集,进而对生物体产生致癌、致畸、致突变,以及内分泌干扰等作用,对人类生存繁衍和可持续发展构成严重威胁[1-3]。近几十年来,对PCBs的修复一直是环境科学技术领域的研究热点。以微生物为核心的降解技术是公认的成本低、无二次污染、环境友好的修复技术,且特别适合土壤和河底底泥中低浓度持久性有机污染物的原位修复。不过,现已获得的PCBs降解菌却存在着降解高氯代PCBs能力差、抗毒能力低下、降解谱窄等缺陷。贾凌云[4]从变压器油污染物中筛选出一株降解PCBs的新菌株,经分子生物学鉴定和生理生化指标鉴定,确认该菌株为肠杆菌属(Enterobacter sp.),命名为LY402。实验证明该菌株不仅对PCBs具有良好的降解能力,而且呈现很强的抗污染物毒性的能力,她在无碳源液相中测定了LY402对PCBs生物降解的速率常数(K),单位为h-1。
由于进入环境中的有机污染物种类繁多,数量庞大,难以通过实验测定所有污染物的生物降解性,并且不同学者所采用的实验方法、条件也不尽相同,导致已公布的降解性数据之间的可比性较差。因此,最早用于药物的定量构效关系(quantitative structure activity relationships, QSAR)[5-15]研究方法便被移植来估算与预测有机污染物的生物降解性,由此形成物质的定量结构-生物降解性相关性(quantitative structure-biodegradability relationship, QSBR)分支学科[16-19]。已成为环境科学、医药和生物等学科的热门领域。因此,本文基于Hall与Kier等提出的原子类型电性拓扑指数(electrotopological state index of atom type,用“EA”表示)[20-22],建立PCBs生物降解速率常数(lnK)[4]的QSBR模型,以预测PCBs的lnK,并探讨影响lnK的主要结构因素。
PCBs的基本结构如图1所示,分子通式为“C12Hn+mCl10-n-m”,其中n≤5,m≤5。按照联苯环上氯原子取代数目和取代位置的不同,理论上有209种化合物,而在环境中出现频率较高的仅有90余种。
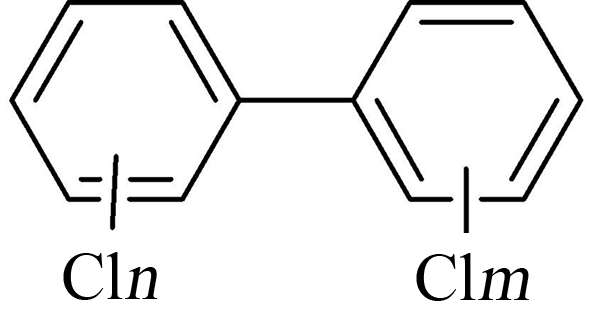
图1 多氯联苯(PCBs)的基本结构
Fig. 1 Basic structure of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
贾凌云[4]在无碳源液相中测定了LY402对66种PCBs生物降解的K,具体数值如表1所示。由于K值相差太大,取其对数用于建模,即lnK,其数值如表1所示。
表1 PCBs的分子结构与生物降解速率常数(lnK)
Table 1 The molecular structures and rate constants for biodegradation (lnK) of PCB congeners
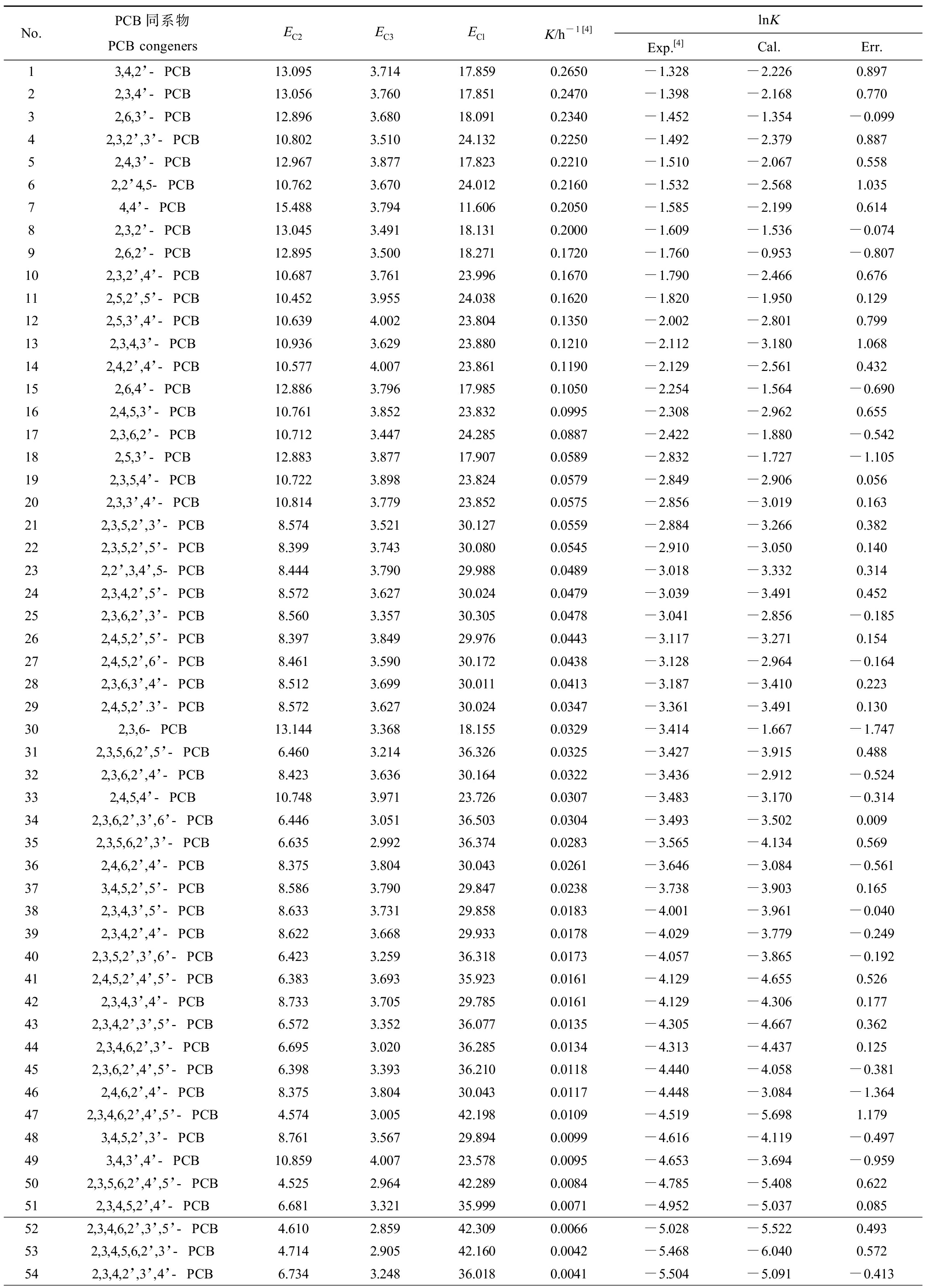
No.PCB同系物PCB congenersEC2EC3EClK/h-1[4]lnKExp.[4]Cal.Err.13,4,2’-PCB13.0953.71417.8590.2650-1.328-2.2260.89722,3,4’-PCB13.0563.76017.8510.2470-1.398-2.1680.77032,6,3’-PCB12.8963.68018.0910.2340-1.452-1.354-0.09942,3,2’,3’-PCB10.8023.51024.1320.2250-1.492-2.3790.88752,4,3’-PCB12.9673.87717.8230.2210-1.510-2.0670.55862,2’4,5-PCB10.7623.67024.0120.2160-1.532-2.5681.03574,4’-PCB15.4883.79411.6060.2050-1.585-2.1990.61482,3,2’-PCB13.0453.49118.1310.2000-1.609-1.536-0.07492,6,2’-PCB12.8953.50018.2710.1720-1.760-0.953-0.807102,3,2’,4’-PCB10.6873.76123.9960.1670-1.790-2.4660.676112,5,2’,5’-PCB10.4523.95524.0380.1620-1.820-1.9500.129122,5,3’,4’-PCB10.6394.00223.8040.1350-2.002-2.8010.799132,3,4,3’-PCB10.9363.62923.8800.1210-2.112-3.1801.068142,4,2’,4’-PCB10.5774.00723.8610.1190-2.129-2.5610.432152,6,4’-PCB12.8863.79617.9850.1050-2.254-1.564-0.690162,4,5,3’-PCB10.7613.85223.8320.0995-2.308-2.9620.655172,3,6,2’-PCB10.7123.44724.2850.0887-2.422-1.880-0.542182,5,3’-PCB12.8833.87717.9070.0589-2.832-1.727-1.105192,3,5,4’-PCB10.7223.89823.8240.0579-2.849-2.9060.056202,3,3’,4’-PCB10.8143.77923.8520.0575-2.856-3.0190.163212,3,5,2’,3’-PCB8.5743.52130.1270.0559-2.884-3.2660.382222,3,5,2’,5’-PCB8.3993.74330.0800.0545-2.910-3.0500.140232,2’,3,4’,5-PCB8.4443.79029.9880.0489-3.018-3.3320.314242,3,4,2’,5’-PCB8.5723.62730.0240.0479-3.039-3.4910.452252,3,6,2’,3’-PCB8.5603.35730.3050.0478-3.041-2.856-0.185262,4,5,2’,5’-PCB8.3973.84929.9760.0443-3.117-3.2710.154272,4,5,2’,6’-PCB8.4613.59030.1720.0438-3.128-2.964-0.164282,3,6,3’,4’-PCB8.5123.69930.0110.0413-3.187-3.4100.223292,4,5,2’.3’-PCB8.5723.62730.0240.0347-3.361-3.4910.130302,3,6-PCB13.1443.36818.1550.0329-3.414-1.667-1.747312,3,5,6,2’,5’-PCB6.4603.21436.3260.0325-3.427-3.9150.488322,3,6,2’,4’-PCB8.4233.63630.1640.0322-3.436-2.912-0.524332,4,5,4’-PCB10.7483.97123.7260.0307-3.483-3.170-0.314342,3,6,2’,3’,6’-PCB6.4463.05136.5030.0304-3.493-3.5020.009352,3,5,6,2’,3’-PCB6.6352.99236.3740.0283-3.565-4.1340.569362,4,6,2’,4’-PCB8.3753.80430.0430.0261-3.646-3.084-0.561373,4,5,2’,5’-PCB8.5863.79029.8470.0238-3.738-3.9030.165382,3,4,3’,5’-PCB8.6333.73129.8580.0183-4.001-3.961-0.040392,3,4,2’,4’-PCB8.6223.66829.9330.0178-4.029-3.779-0.249402,3,5,2’,3’,6’-PCB6.4233.25936.3180.0173-4.057-3.865-0.192412,4,5,2’,4’,5’-PCB6.3833.69335.9230.0161-4.129-4.6550.526422,3,4,3’,4’-PCB8.7333.70529.7850.0161-4.129-4.3060.177432,3,4,2’,3’,5’-PCB6.5723.35236.0770.0135-4.305-4.6670.362442,3,4,6,2’,3’-PCB6.6953.02036.2850.0134-4.313-4.4370.125452,3,6,2’,4’,5’-PCB6.3983.39336.2100.0118-4.440-4.058-0.381462,4,6,2’,4’-PCB8.3753.80430.0430.0117-4.448-3.084-1.364472,3,4,6,2’,4’,5’-PCB4.5743.00542.1980.0109-4.519-5.6981.179483,4,5,2’,3’-PCB8.7613.56729.8940.0099-4.616-4.119-0.497493,4,3’,4’-PCB10.8594.00723.5780.0095-4.653-3.694-0.959502,3,5,6,2’,4’,5’-PCB4.5252.96442.2890.0084-4.785-5.4080.622512,3,4,5,2’,4’-PCB6.6813.32135.9990.0071-4.952-5.0370.085522,3,4,6,2’,3’,5’-PCB4.6102.85942.3090.0066-5.028-5.5220.493532,3,4,5,6,2’,3’-PCB4.7142.90542.1600.0042-5.468-6.0400.572542,3,4,2’,3’,4’-PCB6.7343.24836.0180.0041-5.504-5.091-0.413
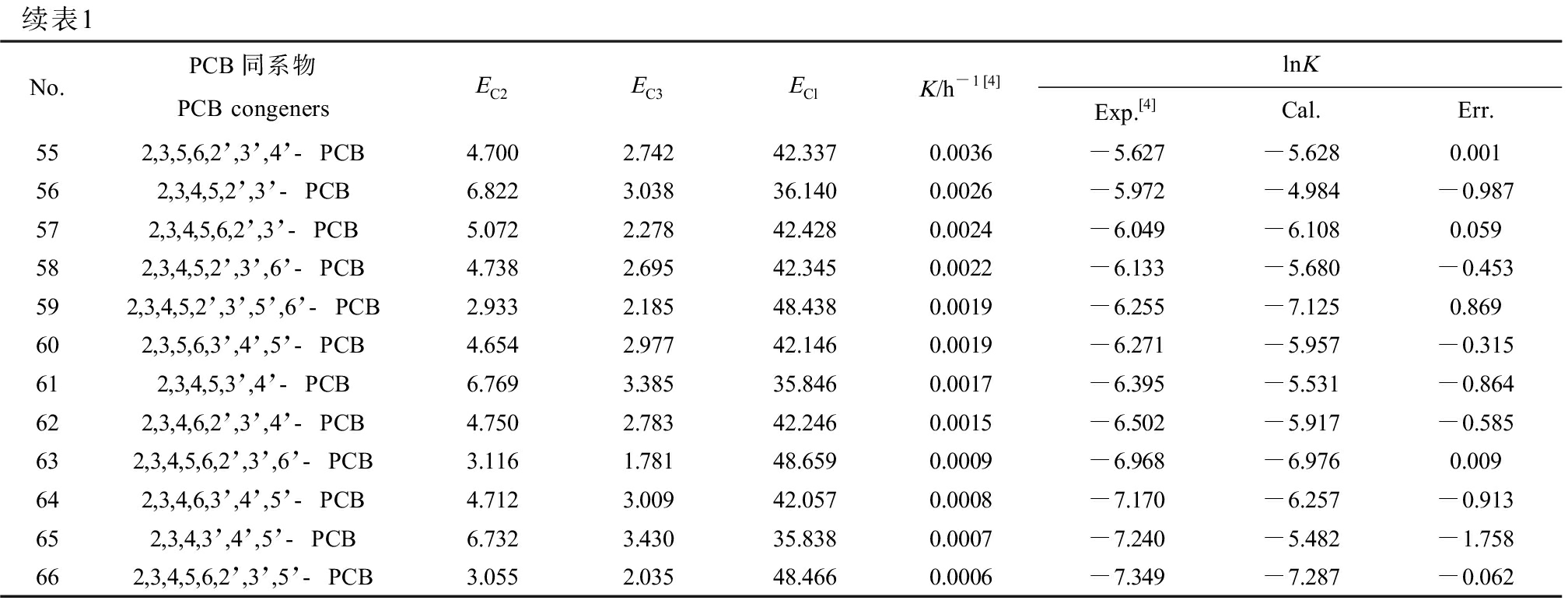
续表1No.PCB同系物PCB congenersEC2EC3EClK/h-1[4]lnKExp.[4]Cal.Err.552,3,5,6,2’,3’,4’-PCB4.7002.74242.3370.0036-5.627-5.6280.001562,3,4,5,2’,3’-PCB6.8223.03836.1400.0026-5.972-4.984-0.987572,3,4,5,6,2’,3’-PCB5.0722.27842.4280.0024-6.049-6.1080.059582,3,4,5,2’,3’,6’-PCB4.7382.69542.3450.0022-6.133-5.680-0.453592,3,4,5,2’,3’,5’,6’-PCB2.9332.18548.4380.0019-6.255-7.1250.869602,3,5,6,3’,4’,5’-PCB4.6542.97742.1460.0019-6.271-5.957-0.315612,3,4,5,3’,4’-PCB6.7693.38535.8460.0017-6.395-5.531-0.864622,3,4,6,2’,3’,4’-PCB4.7502.78342.2460.0015-6.502-5.917-0.585632,3,4,5,6,2’,3’,6’-PCB3.1161.78148.6590.0009-6.968-6.9760.009642,3,4,6,3’,4’,5’-PCB4.7123.00942.0570.0008-7.170-6.257-0.913652,3,4,3’,4’,5’-PCB6.7323.43035.8380.0007-7.240-5.482-1.758662,3,4,5,6,2’,3’,5’-PCB3.0552.03548.4660.0006-7.349-7.287-0.062
将化合物的抽象结构予以参数化是建立定量构效关系(QSAR/QSPR)模型的最重要步骤。拓扑指数为实现分子结构的数值化表征提供了简便方法。原子类型电性拓扑状态指数(E-state indices, En)是表征分子中每种非氢原子类型的结构参数,由两部分构成:其一是非氢原子类型本身的原子结构及局部拓扑环境,由此形成非氢原子的固有状态值(即本征值);其二是反映该原子受分子中其他非氢原子扰动程度的本征值增量。对于PCBs,只存在3种原子类型:![]() C—、
C—、![]() C⟨、—Cl,对应3种指数,依次为:EC2、EC3和ECl,具体计算过程参见文献[20-22]。
C⟨、—Cl,对应3种指数,依次为:EC2、EC3和ECl,具体计算过程参见文献[20-22]。
将PCBs分子的EC2、EC3和ECl作为自变量集,其生物降解速率常数(lnK)[4]作为因变量,采用最佳变量子集回归的方法(leaps-and-bounds regression)确定lnK模型的最佳变量组合。一般按照“三性原则”确定QSAR模型:一是统计性,样本容量(f)与自变量数(b)之比,称为容变比(SV),即SV=f/b>5的模型才具有统计意义[23],此是建立模型的基础。二是相关性,要求模型的可决系数(R2)>0.8,为高度相关[24]。三是预测性,要求模型的交叉验证相关系数![]() 显示良好的预测能力[25]。另外,Akaike信息判据(Akaike’s information criterion, AIC)、Kubinyi函数(Kubinyi function, FIT)[26-27]也用于衡量模型的质量,其计算公式如下:
显示良好的预测能力[25]。另外,Akaike信息判据(Akaike’s information criterion, AIC)、Kubinyi函数(Kubinyi function, FIT)[26-27]也用于衡量模型的质量,其计算公式如下:
(1)
(2)
导致AIC增大,FIT减小的自变量,不宜引入模型;式中,RSS表示估计标准误差(standard error of estimate)。
将66种PCBs的lnK[4]和上述3种拓扑指数输入MINITAB统计分析软件,运用其中的最佳子集回归方法选择最佳变量组合,建立的最佳QSAR模型如表2所示。其中![]() 和SD分别为削减误差比例、交叉验证判定系数、校正判定系数、Fisher统计值、容变比和估计标准误差。
和SD分别为削减误差比例、交叉验证判定系数、校正判定系数、Fisher统计值、容变比和估计标准误差。
由表2可知,![]() 和FIT等随自变量数增加而递增,AIC、SD均递降,都指向三元模型质量最优。故选定PCBs的lnK的QSBR模型:
和FIT等随自变量数增加而递增,AIC、SD均递降,都指向三元模型质量最优。故选定PCBs的lnK的QSBR模型:
lnK=148.522(±22.988)-2.597(±0.378)ECl-
6.614(±1.023)EC2-4.781(±0.826)EC3
(3)
115.076
表2 生物降解速率常数(lnK)和电性拓扑指数(EA)的最佳子集回归结果
Table 2 The results between electrotopological state index (EA) and rate constants for biodegradation (lnK) with leaps-and-bounds regression
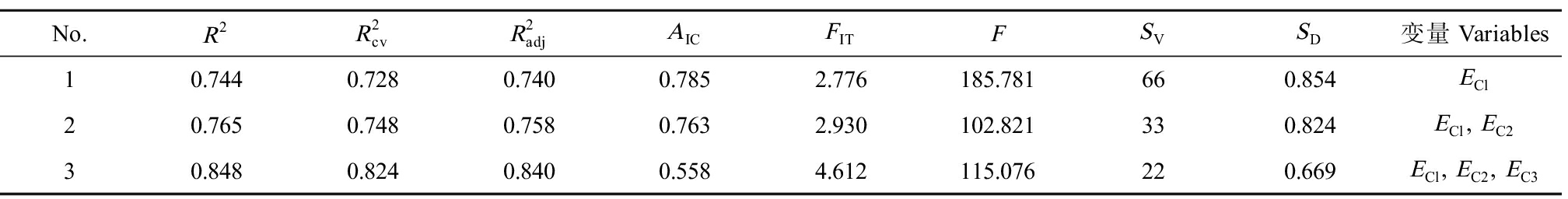
No.R2R2cvR2adjAICFITFSVSD变量Variables10.7440.7280.7400.7852.776185.781660.854ECl20.7650.7480.7580.7632.930102.821330.824ECl, EC230.8480.8240.8400.5584.612115.076220.669ECl, EC2, EC3
首先,模型(3)的SV=22,远大于5,显示模型具有很好的统计意义,随机性低,具备建模的基本要求。二是R2=0.848>0.8,呈现良好的拟合性。R2又称为削减误差比例,因此,模型(3)中隐含影响多氯联苯lnK的84.8%因素,仅有不足15.2%属于未知因素。三是![]() 远大于0.5,呈现良好的预测准确性。由表1可知,预测值(lnKcal.)与相应实验值(lnKexp.)较好吻合。为防止模型存在过拟合及离域点,要求
远大于0.5,呈现良好的预测准确性。由表1可知,预测值(lnKcal.)与相应实验值(lnKexp.)较好吻合。为防止模型存在过拟合及离域点,要求![]() 本模型
本模型![]() 远小于0.3,可见没有拟入噪音及奇异值。
远小于0.3,可见没有拟入噪音及奇异值。
EC2、EC3和ECl与氯原子的数目(d)的判定系数依次为0.995、0.653和1.000,显示高度相关。另外,这3种指数对66种PCBs的分子结构实现唯一性表征,不存在相同的数值。由此可见,模型(3)揭示了在生物降解环境相同情况下,PCBs生物lnK呈现的规律:一是与其分子内所含氯原子的数目(d)负相关;二是对于同分异构体,与氯原子所处位置有关。此与文献[4]给出的结论是一致的。
在模型(3)中,EC2、EC3和ECl前的系数均<0,说明PCBs分子中所含氯原子越多,其降解速率常数越小。其原因是联苯环上被氯取代的位点越多,其性质越稳定,降解菌破坏稳定的碳-氯键进而实现开环降解需要的能量也越高,因此,导致K降低。
综上所述:(1)由表1可知,EC2、EC3和ECl等指数对PCBs分子结构呈现良好的选择性,实现唯一性表征,即对不同的化合物,不存在相同的数值。(2) 经“三性”原则等检验,所建lnK线性模型不仅具有良好的相关性、稳定性,而且呈现良好的预测能力。(3) 根据进入模型的EC2、EC3和ECl可知,影响PCBslnK的主要因素是分子内所含氯原子的数目及其所处位置。
[1] 唐文雅, 竺美, 黄冬梅, 等. 危险废物鉴定中痕量多氯联苯的前处理优化分析[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2021, 33(3): 49-52
Tang W Y, Zhu M, Huang D M, et al. Study on optimization of sample preparation for trace PCBs in hazardous waste identification [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2021, 33(3): 49-52 (in Chinese)
[2] 王涛, 吴启美. 植物根际降解土壤多氯联苯机理研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(4): 36-44
Wang T, Wu Q M. Research progress on the mechanism of plant rhizosphere degradation of soil polychlorinated biphenyls [J]. Environmental Science& Technology, 2021, 44(4): 36-44 (in Chinese)
[3] 马丽莎, 谢文平, 田斐, 等. 广东沿海养殖牡蛎中多氯联苯残留水平及人体饮食暴露风险评估[J]. 南方水产科学, 2021, 17(2): 11-19
Ma L S, Xie W P, Tian F, et al. Bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in farmed oysters along Guangdong coast [J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2021, 17(2): 11-19 (in Chinese)
[4] 贾凌云. 多氯联苯降解菌的筛选及其降解性能研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2008: 65-70
Jia L Y. Isolation and characterization of a novel polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading bacterium [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2008: 65-70 (in Chinese)
[5] Feng H, Du X H, Chen Y, et al. 3D-QSAR models of anti-tumor activity for histone deacetylase inhibitors containing dihydropyridin-2-one [J]. Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry, 2020, 39(5): 855-860
[6] Zhu L L, Qin Z L, Feng C J. CoMFA Model and Molecular Design of Anti -excitatory Activity for Benzodiazepinooxazole Derivatives against Mice. Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2021, 40(8): 1075-1081
[7] Feng H, Feng C J. 3D-QSAR studies on the anti-tumor activity of N-aryl-salicylamide derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 1874-1880
[8] 廖立敏, 李建凤, 雷光东. 含氯苯酚类化合物结构表征与毒性预测[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(6): 266-272
Liao L M, Li J F, Lei G D. Structural characterization and toxicity prediction of chlorinated phenolic compounds [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(6): 266-272 (in Chinese)
[9] 张文灏, 陈景文, 徐童, 等. 外源化合物在鱼体内生物半减期的QSAR模型[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(3): 90-98
Zhang W H, Chen J W, Xu T, et al. QSAR models for predicting biological half-life of xenobiotics in fish [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(3): 90-98 (in Chinese)
[10] 冯长君. 基于CoMFA研究氟喹诺酮C-3噻唑酮衍生物抗胰腺癌活性[J]. 徐州工程学院学报:自然科学版, 2021, 36(3): 8-12
Feng C J. Study on anti-pancreatic cancer activity of fluoroquinolone C-3 thiazolone derivatives based on CoMFA [J]. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology: Natural Sciences Edition, 2021, 36(3): 8-12 (in Chinese)
[11] 郑玉婷, 乔显亮, 于洋, 等. 有机化学品生物富集因子定量结构-活性关系模型[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(2): 214-221
Zheng Y T, Qiao X L, Yu Y, et al. Quantitative structure-activity relationship model for bioconcentration factors of organic chemicals [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(2): 214-221 (in Chinese)
[12] 唐自强, 冯长君. 取代苯酚类化合物抑藻活性的CoMFA模型[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(4): 192-196
Tang Z Q, Feng C J. CoMFA model for inhibitory activity of chlorinated phenolic compounds to Dunaliella salina [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(4): 192-196 (in Chinese)
[13] 唐自强, 冯长君. 硝基芳烃对梨形四膜虫急性毒性的CoMFA模型[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(5): 327-332
Tang Z Q, Feng C J. CoMFA model for acute toxicity of nitroaromatic compounds to Tetrahymena pyriformis [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(5): 327-332 (in Chinese)
[14] 冯长君. 苯磺酰脲类化合物除草活性的CoFMA模型[J]. 徐州工程学院学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 34(2): 21-25
Feng C J. CoFMA model of herbicidal activity of phenyl-sulfonylurea derivatives [J]. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology: Natural Sciences Edition, 2019, 34(2): 21-25 (in Chinese)
[15] 冯长君. 硝基苯衍生物对发光菌抑制毒性的CoMFA模型[J]. 徐州工程学院学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 35(1): 28-31
Feng C J. CoMFA model of inhibitory activity for nitrobenzene derivatives to photobacteria [J]. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology: Natural Sciences Edition, 2020, 35(1): 28-31 (in Chinese)
[16] 贺美, 向廷生, 谢瑶, 等. 影响有机化学品快速生物降解性的分子结构参数研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2015, 34(3): 181-188
He M, Xiang T S, Xie Y, et al. A review on molecular structural descriptors affecting ready biodegradation of organic chemicals [J]. Ecological Science, 2015, 34(3): 181-188 (in Chinese)
[17] 樊健, 尚少鹏. 黄河包头段水体中取代酚的生物降解性研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2017, 36(1): 85-90
Fan J, Shang S P. Biodegradability of substituted benzenes in Baotou section of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2017, 36(1): 85-90 (in Chinese)
[18] Chen Y, Zeng Y X, Ji Z J, et al. Identification of stable quantitative trait loci for sheath blight resistance using recombinant inbred line [J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(5): 331-338
[19] 张丹, 晁聪, 李玉坤, 等. 定量构效关系应用于水中有机污染物降解过程的研究进展[J]. 化工环保, 2021, 41(4): 418-426
Zhang D, Chao C, Li Y K, et al. Research progresses on application of quantitative structure-activity relationship to degradation process of organic pollutants in water [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(4): 418-426 (in Chinese)
[20] 堵锡华, 王超. 碳纳米管吸附能力的神经网络理论模型[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(7): 1445-1451
Du X H, Wang C. Research on the adsorption of carbon nanotubes to aromatic compounds by neural network [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(7): 1445-1451 (in Chinese)
[21] Kier L B, Hall L H. An electrotopological-state index for atoms in molecules [J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 1990, 7(8): 801-807
[22] Hall L H, Kier L B. Electrotopological state indices for atom types: A novel combination of electronic, topological, and valence state information [J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1995, 35(6): 1039-1045
[23] 刘东, 章文军, 许禄. 手性羟酸和氨基酸类化合物的构效关系研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(2): 145-150
Liu D, Zhang W J, Xu L. Quantitative structure-activity/property relationships for chiral hydroxy acids and amino acids [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2009, 67(2): 145-150 (in Chinese)
[24] 张骥, 申鹏, 陆涛, 等. 黄酮类化合物抑制MMP-9的定量结构-活性关系和结构修饰的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(4): 383-392
Zhang J, Shen P, Lu T, et al. Theoretical studies on quantitative structure-activity relationship and structural modification for the inhibition of MMP-9 by flavonoids [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(4): 383-392 (in Chinese)
[25] 胡松青, 米思奇, 贾晓林, 等. 苯并咪唑类缓蚀剂的3D-QSAR研究及分子设计[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(10): 2402-2409
Hu S Q, Mi S Q, Jia X L, et al. 3D-QSAR study and molecular design of benzimidazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors [J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(10): 2402-2409 (in Chinese)
[26] Saíz-Urra L, Pérez González M, Teijeira M. 2D-autocorrelation descriptors for predicting cytotoxicity of naphthoquinone ester derivatives against oral human epidermoid carcinoma [J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2007, 15(10): 3565-3571
[27] Saíz-Urra L, González M P, Teijeira M. QSAR studies about cytotoxicity of benzophenazines with dual inhibition toward both topoisomerases Ⅰ and Ⅱ: 3D-MoRSE descriptors and statistical considerations about variable selection [J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2006, 14(21): 7347-7358
Corresponding author), E-mail: fengh@xzit.edu.cn
# 共同通讯作者(Co-corresponding author), E-mail: fengcj@xzit.edu.cn