-
重金属污染场地主要是由采矿、冶炼、电镀、化工、电子和制革染料等工业生产的“三废”等引起的. 随着我国工业化的快速发展,重金属污染场地环境安全问题形势严峻[1],土壤重金属污染具有隐蔽性好、潜伏周期长、毒性危害大和地域差异明显等特点[2 − 3]. 重金属在土壤环境中的累积和迁移会威胁到人类食品和饮用水安全、区域生态环境、人居环境健康和经济社会的可持续发展[4].
2014年4月发布的《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》[5]调查结果显示,耕地土壤环境质量堪忧,工矿业废弃地土壤环境问题突出. 从土地利用类型看,耕地、林地、草地土壤点位超标率分别为19.40%、10.00%、10.40%,同时指出工矿业、农业生产等人类活动和自然背景值高是造成土壤污染或超标的主要原因. 2022年《中国生态环境公报》[6]指出全国土壤环境污染加重的趋势得到了初步遏制. 目前影响农用地土壤环境质量的主要污染物是重金属,其中Cd为首要污染物,同时指出全国重点行业企业用地土壤污染的风险仍需进一步重视. 根据河南省生态环境厅发布《河南省2019年度土壤污染重点监管单位名录》[7],重金属污染企业占据名录中大部分企业,尤其以化工、冶炼、采矿等企业最为突出. 从地域上看,洛阳、济源和焦作所涉及的重金属污染企业众多,尤其以洛阳市栾川县和孟津县最为突出. 研究区域位于河南省洛阳市栾川县,主要以高山地形为主,该县拥有亚洲最大的钼矿开采企业(洛阳钼业),周边多有钼矿、铁矿、金矿等开采或冶炼厂. 该地区土壤污染特征主要以镉、铅、铜、锌、砷污染为主.
《河南省重金属污染防治工作指导意见》[8]明确提出“有序开展重金属污染地块治理与修复工作”的任务. 明确指出铅Pb、镉Cd、砷As、铜Cu、锌Zn等为重点污染物. 铅Pb、铜Cu、锌Zn等有色金属矿采选及冶炼为重金属污染防控重点行业,这些行业在研究区域内均有分布. 在开展土壤重金属污染治理之前对目标污染场地的重金属污染程度、累积效应、赋存形态、来源解析、迁移转化和生态风险评估工作十分关键,这对土壤污染修复技术的选择具有十分重要的指导意义. 如贾晗等[9]采用单因子污染指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法、地累积指数法等调查研究了安徽典型硫铁矿集中开采区土壤重金属污染特征和来源,发现研究区土壤中重金属元素主要来源为采矿活动综合源、大气沉降与农业综合源等. 余高等[10]通过单因子污染指数法、地积累指数法、潜在生态风险指数法和人体健康风险评价模型评价土壤Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Ni、Mn、As和Hg的生态环境风险,得到了研究区整体存在强潜在生态风险等结论. 王海洋等[11]利用内梅罗综合污染指数和潜在生态风险指数对矿区周边农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染水平开展评价. 万梦雪等[12]采用单因子指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法和地累积指数评价了上海市闵行区典型工业区的土壤污染状况,同时基于主成分分析-多元线性回归模型解析重金属的来源. 此外,Miao等[13]和Luo等[14]研究了由土壤重金属污染引起的健康风险,并开展量化分析评估.
可见,众多学者会采用多种指数评价方法对土壤重金属污染状况、生态风险和健康风险等进行评价,进一步借助主成分分析[15 − 18]、多元线性回归模型[9,12]、聚类分析[19 − 20]、正定矩阵因子分析模型[15](PMF)等方法模型识别污染源并进行定量解析,从而得到一个更具有参考性的结果. 然而,重金属的富集程度和生态风险也会受到重金属形态和土壤类型的影响. Tessier[21]提出的五步连续提取法将重金属的形态分为可交换态(F1)、碳酸盐结合态(F2)、铁锰氧化物结合态(F3)、有机结合态(F4)和残渣态(F5),不同形态重金属含量对迁移转化能力、生物可利用度和生态风险等有更深入的指示作用,这对于土壤修复技术的选择也很有意义. 洛阳栾川县区内矿产资源丰富,是我国著名的多金属矿集区,关于这一地区的重金属污染特征和生态风险的调查研究还比较匮乏. 此外,目前还缺乏关于矿区周边林地、农田和尾矿周边土壤类型对重金属富集和生态风险的影响研究. 更重要的是,几乎未见以重金属形态分析为部分依据开展源解析工作的研究报道.
基于此,本文以洛阳栾川县矿区周边为目标研究区域,采样点位主要布置在栾川县矿区周边,采用单因子指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法、地累积指数法来探究洛阳市栾川矿区周边7种重金属(As、Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr、Cd 和 Ni)污染特征,借助单因子和综合潜在生态风险指数分析重金属的潜在生态风险. 进一步探究土地利用类型和重金属形态对重金属富集和迁移转化生态风险的影响. 此外,采用Pearson相关性分析和主成分分析方法开展来源解析. 旨在为探索目标地区较适宜的土壤修复技术提供参考依据和理论指导.
-
研究区域为栾川县,隶属于洛阳市,位于河南西部,其地理坐标范围为东经111°11′—112°01′、北纬33°39′—34°11′之间. 总面积
2177 km2,东西长78.40 km,南北宽57.20 km. 栾川县区内土地利用类型包括耕地、园地、林地、草地、湿地、交通用地、城镇村与工矿用地、水域及水利设施用地. 县城处在狭长地带(图1中白色区域),主要以高山地形为主,位于豫西多金属成矿带的中心区域,区内矿产资源丰富,是我国著名的多金属矿集区,也是全国16个重要多金属成矿带的核心区域. 境内分布金属矿产、非金属矿产、能源矿产和水汽矿产4大类,共50余种,已探明储量的矿产19种,各类矿产地251处,其优势资源可归纳为钼、钨、铅、锌、金、银、铁、萤石等. 研究区域和采样点位主要布置在栾川县矿区周边,旨在探究矿区周边土壤重金属污染特征.采样过程主要参考《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166—2004)[22]的勘测、处理方法. 采样时通过经纬度定位并结合实际勘测对样点进行校准. 采样点位主要布置在矿区周边的农田、林地和尾矿范围内,共采集土壤样品47个,农田、林地和尾矿周边土壤样品的数量分别为20、12、15个. 采样深度为0—20 cm,采样重量不少于1 kg,采样过程中保证采集的每个样品来自相同的土壤类型,采样时去除落叶、砂石、动植物残体、有机残渣等杂物,以减少对土壤重金属元素含量测定的影响[23]. 经风干、磨碎、过筛后以备重金属元素(As、Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr、Cd和Ni)分析.
-
参考《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166—2004)[22]、《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB
15618 —2018)[24]的勘测和处理方法,并综合考虑研究区内3种土地利用类型. 样品总量测定的处理方法如下[25]:土壤样品消解后用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)检测Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr、Cd 和 Ni含量;用原子荧光光谱法(AFS)测定As含量. 重金属形态与潜在毒性分析主要采用Tessier等[21]提出的五步连续提取法. -
(1)单因子污染指数
单因子污染指数(Pi)法可以评价单个污染因子的污染程度,作为一种定量指标,可以应用于重金属污染程度的评价,一般以土壤背景值或标准限值作为评价标准. 表达式如式(1).
其中,Pi为土壤重金属i的单因子污染指数,Si为重金属i的评价标准,单位为mg·kg−1,主要参照土壤环境质量标准的风险筛选值作为标准,Ci为土壤重金属i的实测数据,单位为mg·kg−1. 根据单因子污染指数Pi的大小可将土壤重金属污染程度分为5类,分级标准如表1所示.
(2)内梅罗综合污染指数
内梅罗综合污染指数法[26]对单因子指数的平均值和最大值进行归纳处理,能够反映土壤环境中各项重金属的综合污染状况,突出污染最严重的重金属对环境的有害影响[27]. 为了综合评价洛阳栾川县矿区周边污染水平,采用内梅罗综合污染指数对土壤污染情况进行综合评价,计算公式如式(2)和式(3)所示:
式中,Pimax为单因子污染指数的最大值,Piave单因子污染指数的平均值,Pm为内梅罗综合污染指数,分级标准如表1所示.
(3)地累积指数
地累积指数(Igeo)法由德国科学家Muller提出,广泛应用于评价土壤重金属污染和累积程度,可以反映自然地质过程和人为活动对重金属污染产生的影响. 计算公式如下:
式中,Igeo 表示土壤重金属的地积累指数;Ci为土壤重金属i的实测数据,单位为mg·kg−1,Csi取自重金属i的土壤元素背景值,考虑到采样点位主要分布在土壤表层,因此元素背景值选择河南省土壤环境背景值[28](A层,0—20 cm),并将地累积指数分为7个等级,如表1所示.
(4)土壤重金属污染生态风险评价方法
瑞典学者Hakanson于1980年提出了潜在生态风险指数Eri,该方法综合考虑了各元素重金属浓度、联合环境效应和生态毒性差异性,定量评估重金属的潜在生态环境风险,如表2所示[29]. 计算公式如式(5)和式(6):
式中,Ci为重金属元素i的实测值,单位为mg·kg−1;Si为重金属i的评价标准,单位为mg·kg−1;Eri为土壤重金属i的单因子潜在生态风险指数;RI 为重金属综合潜在生态风险指数;Tri 表示重金属元素i的毒性系数,反映单元素污染影响的敏感性和生物学上的毒害性,Cr、Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、Ni、As的毒性系数依次为2、30、5、5、1、5、10[30 − 31].
-
主要采用Pearson相关性和主成分分析来开展源解析. Pearson相关性分析能够辨识不同重金属之间是否具有同源性. 主成分的概念由Karl Pearson在1901年提出,是考察多个变量间相关性一种多元统计方法. 其基本思想是通过原来变量的线性组合来解释原来变量的大部分信息,达到降维的目的,从而简化问题的复杂性. 本文主要运用主成分分析辨别土壤重金属污染源.
-
栾川县矿区周边表层土壤重金属Cr、Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、Ni、As检出率均为100%. 由表3可知,7种重金属的平均值均大于中位值,分别是背景值的1.05、52.46、20.96、9.68、12.72、1.45、82.90倍,这表明7种重金属在土壤表层均存在不同程度的累积和富集效应,Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、As等5种重金属污染尤为严重,这与该地区长期以来的矿业活动相关. 相对于风险筛选值的点位超标率来看,Cr、Ni的含量均低于风险筛选值,值得注意的是Cd的点位超标率达到了100.00%,相对于风险筛选值,As、Pb、Cu、Zn的点位超标率分别达到了61.10%、83.30%、61.10%、94.40%. 相对于风险管控值,土壤样品中Cd和Pb的点位超标率分别达到38.90%和22.20%. 此外,Cr 含量均低于风险管控值.
表3中的变异系数为标准差与平均值的比值,能够反映土壤重金属污染分布的空间变化程度,7种重金属元素的变异系数大小排序为As>Pb>Cu>Cd>Zn>Cr>Ni,其中Pb、Cu、As、Cd的变异系数均大于90%,为强变异,表明各采样点间重金属元素含量离散程度较高,空间分布不均匀,土壤受到外界干扰显著. Cr、Ni为中等变异,相对Pb、Cu、As空间异质性较弱,受矿区开采活动和人为活动的影响较小.
-
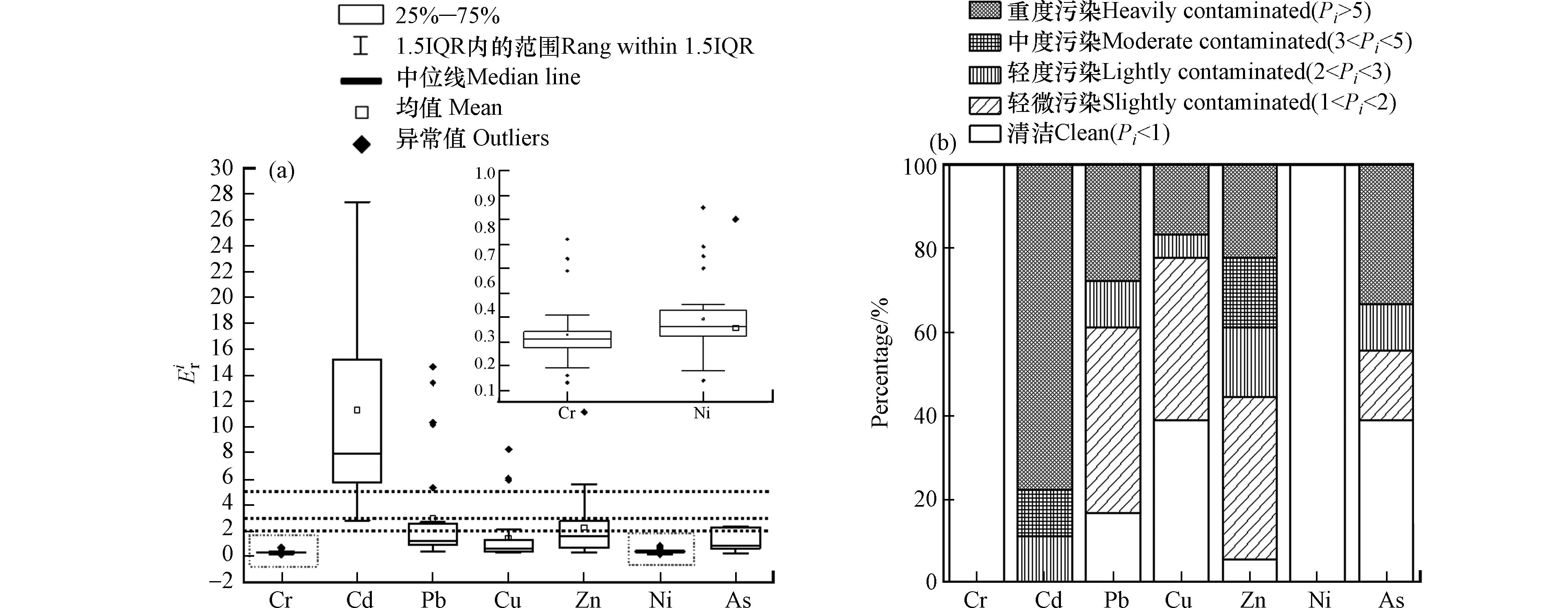
单因子污染指数可以反映出某个采样点单个元素的污染情况. 以土壤环境质量标准中重金属的风险筛选值作为评价标准进行单因子污染指数评价. 土壤重金属单因子污染指数箱线图如图2 (a)所示,所有样品中的Ni、Cr元素单因子污染指数值均小于1. 由图2 (b)可知,Ni和Cr的清洁水平占比达到100.00%,表明Ni和Cr元素几乎不存在土壤污染风险. Pb和Cu的单因子污染指数主要分布在3以下,不存在中度污染状况,重度污染水平的采样点位分别占27.78%和16.67%. Zn元素清洁点位仅占5.56%,其余点位均存在不同程度的污染. As元素在个别点位的单因子污染指数最高可达169.13. Cd元素的污染程度最为严重,轻度、中度和重度污染点位分别占11.11%、11.11%和77.78%. Cd、As、Zn、Pb和Cu污染程度分布较广,结合上文变异系数的相关分析,可能是本次采样点布置的区域主要是在矿区周边的农田、尾矿和林地中,重金属的富集程度可能受到矿区距离和土壤类型的影响.
-
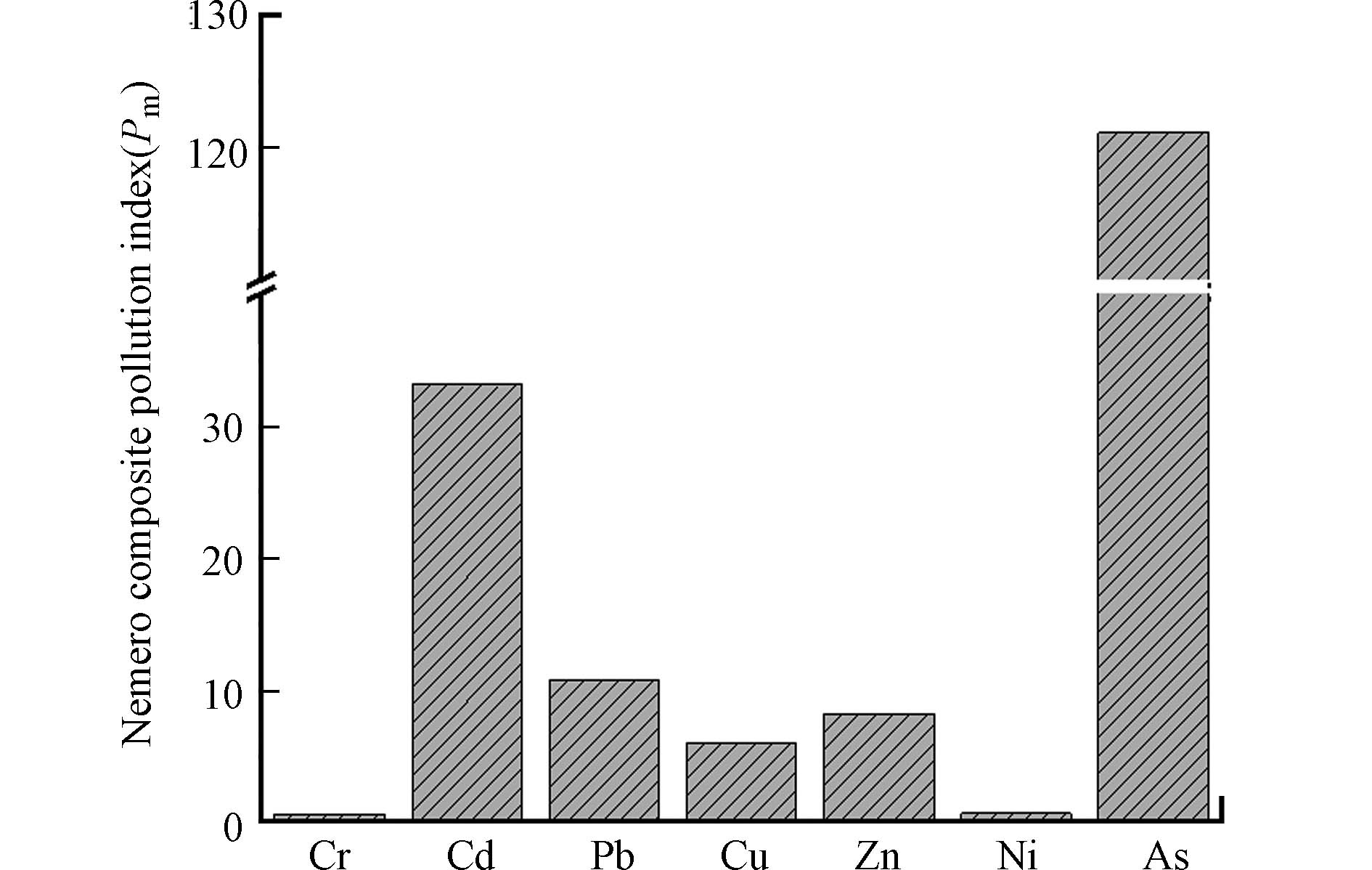
在单因子污染指数的基础上,利用公式(2)进行内梅罗综合污染指数计算与评价. 内梅罗综合污染指数可反映出区域范围内某重金属的综合污染情况,突出高浓度重金属对环境质量的影响. 由图3可知,重金属综合污染指数(Pm)变化范围处于0.5—120 之间,平均值为25.76. Cr和Ni的内梅罗综合污染指数分别为0.56和0.66处于清洁污染水平,除此之外,Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn和As均处于严重污染水平,尤其是Cd和As,这与单因子污染指数的结果一致.
-
应用地累积指数法进一步对栾川县矿区周边土壤重金属的污染程度进行评价,采用研究区的土壤元素背景值作为评价参比值[28],综合判别自然地质过程造成的背景值影响和人为活动的干扰.
由图4(a)可知,7种元素的地累积指数均值大小排序依次为:Cd(4.70)>Pb(2.87)>As(2.86)>Zn(2.77)>Cu(1.95)>Ni(−0.20)>Cr(−0.66). 其中Cr和Ni的地累积指数平均值均小于0,大部分点位处于无污染状态,16.67%的土壤样本为轻-中度污染(0≤Igeo<1). Pb和Zn地累积指数值的箱体主要位于中-强度和强度污染范围内(2≤Igeo<4),占比分别为33.3%和77.8%,如图4(b)所示. Cu的地累积指数值主要分布在轻中度污染—中强度污染之间(0≤Igeo<3),占比为77.8%. As的地累积指数箱体较长,污染程度分布较广,表明土壤中这6种元素受到地质背景和人为活动的影响较为明显. 此外采样点中As极强污染和轻中度污染均分别占33.33%,污染程度呈现两极分化现象,这说明As元素在采样点的某一特定区域内存在累积现象. Cd、Pb和As的极强度污染(Igeo>5)分别占38.89%、22.22%、33.33%,与单因子污染指数和内梅罗综合污染指数结果相似,Cd的地累积指数均处于强度污染以上(Igeo>3).
-
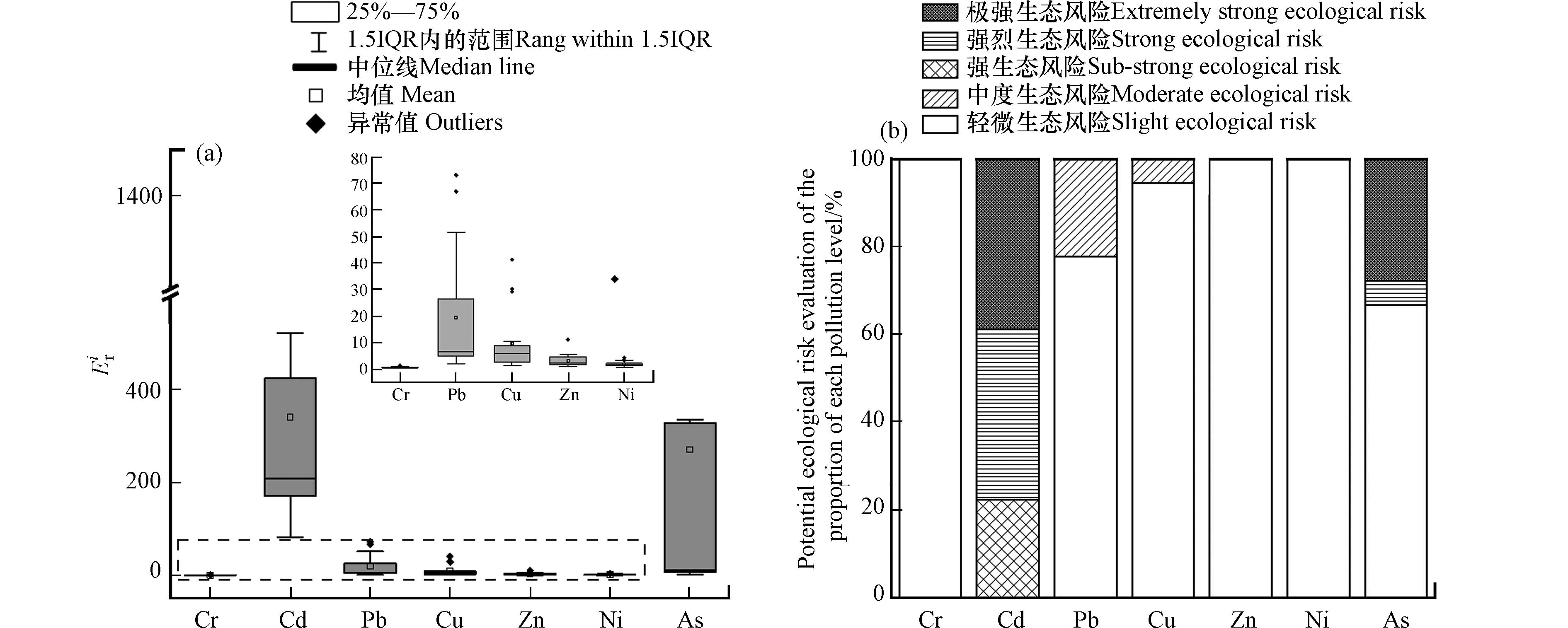
采用潜在生态风险指数法对洛阳栾川县土壤重金属生态风险进行评价. 由图5(a)和图5(b)可知,Cr、Ni、Zn的Eri均小于40,研究区全样点有轻微生态风险,其中Cr和Ni的Eri分别只有0.67、1.98. Pb的Eri处于1.90—73.24之间,平均值为19.50,个别点位存在中度生态风险,占比为22.20%. Cd的单因子潜在生态风险指数处于83.00—
1362.00 范围内,研究区全样点位处于强生态风险及以上,极强生态风险等级占38.89%. 此外,As产生极强生态风险的样品点位占27.78%. 结合单因子污染指数、内梅罗综合污染指数和地累积指数的结果,Cd和As的生态风险源于较强的污染程度和区域累积效应.洛阳栾川县周边表层土壤综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)平均值为647.01(表4),说明研究区土壤整体处于强烈生态风险水平,RI值的范围为95.30—
2670.35 ,变化范围大,部分采样点位的潜在生态风险较强,这可能归因于某一区域重金属的富集进而导致了局部污染和较强的生态风险. Cd和As的Eri对RI的贡献率较高,分别达到了52.74%和41.86%,从平均值来看,分别处于极强生态风险(Eri>320)和强烈生态风险(160<Eri≤320)范围内. 此外,相较于Cr、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni,Cd和As的标准差较大,Eri的数值分散程度较高,因此推测Cd和As在某一特定区域产生富集效应加大了此地区的生态风险. Cd和As作为引起土壤环境风险的主要因子,需引起关注.综上,洛阳栾川县矿区周边Cd和As的污染程度和生态风险最高,且在某一区域范围内存在明显的累积. 其次是Pb、Cu、Zn. 污染程度和生态风险最低的是Cr和Ni. 值得关注的是重金属的富集程度和生态风险可能受到重金属形态和土壤类型的影响. 基于此,对不同土地利用类型中重金属的形态和生态风险进行评价,以探究土地利用类型和重金属形态对重金属富集和生态风险的影响.
-
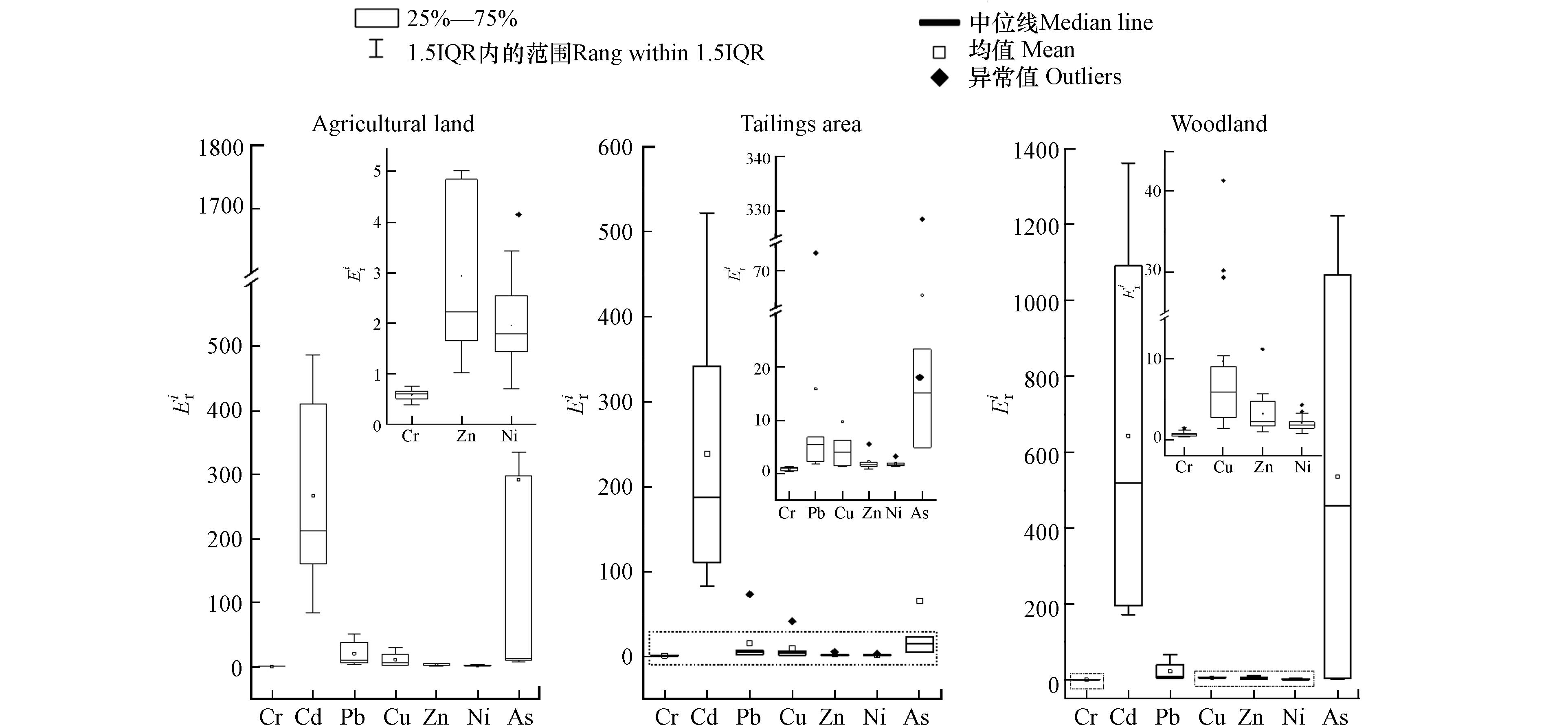
不同土地利用类型土壤重金属单因子潜在生态风险指数(Eri)如图6所示. 农田和林地的Cd和As的Eri明显高于尾矿周边土壤,农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤Cd的Eri均值分别达到267.05、238.65,为中度生态风险,林地土壤Cd的Eri均值为643.35,为强烈生态风险. 林地土壤Cd和As的Eri箱体较长,不同采样点位的生态风险程度较为分散. As在农田、尾矿周边和林地土壤中的Eri均值分别为292.30、65.30、536.10.
农田和林地As和 Cd 的潜在生态风险相对较高,尤其是林地土壤. 原矿经过选别作业处理后,其主要成分已在精矿中富集,剩余产物中有用目标组分含量相对较低,但从尾矿周边土壤采样区域的点位来看,仍需注意Cd以及个别点位Pb和As产生的潜在生态风险.
不同土地利用类型土壤重金属综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)如表5所示,从表5的均值来看,农田和林地的综合潜在生态风险分别达到了强生态风险和极强生态风险. 尾矿周边土壤的RI均值为334.73,为强生态风险,但从不同风险等级的样点占比情况来看,66.66%的点位处于中度生态风险及以下,强生态风险及以上占33.34%. 整体来看,林地的综合潜在生态风险最高,其次是农田和尾矿周边土壤.
-
土壤重金属的生态风险与重金属形态也存在很重要的联系. Tessier将土壤中的重金属形态分为5种:可交换态(F1)、碳酸盐结合态(F2)、铁锰氧化物结合态(F3)、有机结合态(F4)和残渣态(F5),5种重金属形态的生物利用度依次降低、迁移转化困难程度和生态风险强度依次增加. 其中可交换态的重金属吸附在黏土、腐殖质及土壤中某些成分上[32],易于迁移转化,生态风险较高;碳酸盐结合态受土壤环境pH值的变化较为敏感[33];铁锰氧化物结合态重金属一定程度上反映了人类活动对环境的污染,受到土壤pH和氧化还原环境条件变化的影响较大[34];有机结合态为重金属和土壤有机物的螯合;残渣态的重金属通常存在于矿物成分的晶格中,能长期稳定存在于土壤中,生态风险较低[35]. 前4种重金属形态常被称为有效态,为表征活性态重金属含量的指标. 残渣态又被称为非有效态,较为稳定[36 − 37].
不同土地利用类型土壤重金属形态如图7所示. 由图7(a)全样点中各重金属残渣态占比顺序依次为:Cr(90.52%)>Ni(72.88%)>As(71.85%)>Zn(44.50%)>Cu(34.55%)>Cd(27.87%)>Pb(13.16%),可见Cr、Ni和As的生物利用度和迁移转化风险较低,能够在土壤环境中稳定存在. As的存在形态主要为残渣态(71.85%),迁移能力和生物可利用度较差,但其污染强度较高,潜在生态风险较强,可交换态占比仅次于Cd(12.85%),这部分的As仍然值得关注.
重金属Cd的残渣态(非有效态)占比仅有27.87%,不足全量的1/3,可交换态占比也最高,占19.83%,有效态含量占比达到了72.13%,当土壤环境变化时易发生迁移转化. 由上文各污染指数评价得知土壤重金属Cd污染严重,叠加有效态占比较高,因此土壤重金属Cd污染值得关注. Pb的污染强度次于Cd和As,地累积指数介于Cd和As之间,值得注意的是Pb的有效态含量达86.84%,主要存在形态为碳酸盐结合态(30.32%)、铁锰氧化物结合态(35.70%)、有机结合态(20.67%),容易受到土壤环境pH、氧化还原电位的影响,在7种重金属中最不稳定.
因此,在全样点土壤重金属调研结果和进一步的靶向技术探索中,考虑到有效态含量占比和迁移转化生态风险,需要重点关注Cd和Pb重金属污染. 其次是Cu、Zn和可交换态的As.
根据图7中的(b)、(c)和(d),尾矿周边、林地、农田土壤类型中各重金属形态的占比分布规律与全样点结果相似,基本表现为Cr、As和Ni的重金属赋存形态主要为残渣态,在土壤中存在较为稳定且不易迁移. Pb的有效态含量最高,分别达到了88.48%(尾矿周边土壤)、94.34%(林地)和82.05%(农田),以铁锰氧化物结合态和碳酸盐结合态为主要存在形态. 林地土壤中Pb和Cd的有效态含量占比最高,其中Pb的碳酸盐结合态占比达到43.82%,明显高于农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤,因此当面临土壤pH降低的冲击时,林地土壤中的Pb迁移转化的生态风险较高. 林地中Cd的可交换态和有机结合态也明显高于农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤,分别占28.24%和33.31%,这表明林地土壤中的Cd对环境变化较为敏感,比农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤中的Cd更易迁移转化和被植物吸收;此外,33.31%有机结合态的Cd与土壤中的各种有机物如动植物残体、腐殖质等螯合. 相对于农田和林地土壤,尾矿周边土壤的As有效态占比最高(34.81%),其中的碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态和有机质结合态分别占10.14%、8.19%、6.63%. 尾矿周边土壤和农田土壤中Cu的有效态高于林地,分别达到了68.40%和68.20%,其中有机结合态Cu占比优势明显,分别为52.78%和48.86%,推测一定程度上归因于土壤中较高含量的有机物. 农田土壤中Zn的铁锰氧化物结合态含量相对较高,当土壤环境中的氧化还原电位和pH较低时,可能导致Zn的溶出,进而发生横向或纵向迁移,污染河流湖泊和地下水环境[38].
-
结合实地踏勘,采样区的潜在污染源可以分为固定源和移动源:其中固定源主要为分布在研究区域的涉重金属污染企业(采矿、冶炼、化工等). 移动源主要为运输矿产的卡车以及矿区工作人员车辆携带. 进一步还会受到自然源和人为源的干扰,使得土壤重金属由于自然淋溶、林业和农业活动而发生迁移. 各重金属污染的源识别和源解析仍需相关性和主成分分析来深入解释.
-
对不同重金属元素总量进行Pearson 相关性分析,来说明其同源性(图8). Pb与Cu、Zn之间在0.001水平上的相关系数分别达到了0.79和0.84,呈现极显著正相关(P<0.001,r>0.5);Zn和Cd的相关系数为0.83,同样呈现极显著正相关关系(P<0.001,r>0.5),这可以作为他们之间具备高度同源性的依据.
此外,Pb和Cd、Zn和As在0.01 水平上显著相关,相关系数分别为0.65、0.70,表明他们之间具有相同或相似的来源的可能较大. As和Pb、Cd的相关系数也达到了0.50以上,在0.05水平上显著相关,可能具有相同或相似来源,但仍需进一步的分析验证.
值得注意的是Cr与其他重金属之间均呈现负相关关系,Ni也表现出相似的规律,其相关系数均在−0.5—0之间,因此判断Cr和Ni的来源相对独立.
-
通过主成分分析对土壤重金属来源情况进行解析. 主成分分析提取到3个因子,且3个因子的特征值(3.64、1.27、1.19)均大于1,累积贡献率为 87.27%,能够解释土壤重金属元素所包含的信息. 分析结果见表6.
第一主成分(PC1)的解释方差为 52.07%,其中Cd、Pb、Zn在 PC1 上具有较高的正载荷,且相关性分析结果表明,这些元素两两之间呈极显著正相关,说明它们的来源相似. 其次是Cu和As载荷分别达到0.29和0.39,并且Cu与Pb,As与Pb、Cd、Zn的相关系数均大于0.5. 此外,Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu和As的变异系数分别达到了90.15%、118.83%、75.72%、115.88%、177.50%,除Zn以外均处于强分异水平,说明受到人为活动影响较大. 洛阳栾川县区内矿产资源丰富,分布着钼、钨、铅、锌、金、银、铁、萤石等矿产地251处. 研究区和采样点位附近拥有正在开采的矿场和开采遗址,根据当地的地形地貌,矿产开采过程中可能使地底深处的矿物暴露于地表,增加Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu、As重金属元素的释放通量,尤其是Zn、Cu、Cd、Pb,其有效态含量达到了50%—80%,当土壤环境发生变化(如雨水淋溶、农业浇灌等),容易产生迁移转化生态风险,增加土壤中的重金属含量[10]. 因此,推测PC1为矿业开采排放源.
第二主成分(PC2)解释方差为 18.20%,Cr在PC2上具有较高的正载荷(0.76),相关性分析表明Cr的来源相对独立,其总量均值水平(66.67 mg·L−1)与背景值(63.20 mg·L−1)相当,变异系数仅为48.14%,其来源受到人为活动的影响较小. 因此判断主成分PC2归因于自然源.
第三主成分(PC3)的解释方差为17.00%,Cu在PC3上具有较高的正载荷(0.71),其次是Ni和Pb,相关性结果表明Ni的来源独立,可以推断PC3为混合源,且其中包含自然源. Pb与Cu在0.001水平上呈现极显著正相关,具有同源性,且其变异系数仅相差2.95%,为强变异水平,推测受到矿产开采活动的影响较大.
值得注意的是Cd和As在主成分PC1中的载荷为正值,而在PC3中的载荷表现为负向影响,推测Cd和As在PC3中的亏损趋势并非由矿产开采活动引起. 结合重金属形态分析的结果,林地土壤中Cd的可交换态和有机结合态也明显高于农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤,分别占28.24%和33.31%,这表明林地中的Cd对环境变化较为敏感,其在PC3中的亏损可能归因于自然源(雨水淋溶导致的迁移转化或被被植物吸收)相对于农田和林地土壤,尾矿周边土壤中的As有效态占比最高(34.81%),而农田和林地土壤中As的可交换态占比较高,因此As在PC3中的亏损趋势在不同的土壤类型中原因有差异,尾矿周边土壤的As亏损可能归因于自然淋溶导致的迁移,农田和林地中As亏损归因于植物或农作物吸收.
综上所述,第一主成分PC1为矿业开采排放源;第二主成分PC2归因于自然源;第三主成分PC3归因于自然源(尾矿区域的自然淋溶)和人为源(林业和农业活动、采矿).
-
(1)洛阳栾川县矿区周边Cd和As的污染程度和生态风险最高,Eri分别达到341.21、270.81,且其空间分布不均匀,变异系数分别达到90.51%、177.50%. Igeo分别为4.70、2.86,在某一区域范围内存在明显的累积,为引起土壤环境风险的主要因子. 其次是Pb、Cu、Zn.
(2)污染程度和生态风险最低的是Cr和Ni,Eri分别只有0.67、1.98,且其空间异质性较弱(CV值均小于50%),受矿区开采活动和人为活动的影响较小. 此外Cr和Ni的生物利用度和迁移转化风险较低,残渣态占比90.52%和72.88%,能够在土壤环境中稳定存在.
(3)不同的重金属在林地、农田和尾矿中的富集程度和生态风险存在差异. 农田和林地As和Cd的潜在生态风险相对较高,尤其是林地土壤Eri分别达到536.10、643.35. 尾矿周边土壤Cd以及个别点位Pb和As潜在生态风险较高,值得进一步关注.
(4)Cd和Pb有效态含量占比较高,分别为72.13%和86.84%;其次是Cu、Zn和可交换态的As. 林地中Pb的碳酸盐结合态以及Cd可交换态和有机结合态明显高于农田和尾矿,对环境变化较为敏感. 尾矿周边土壤和农田土壤中Cu的有效态含量接近70%,明显高于林地土壤,迁移转化生态风险相对较高.
(5)第一主成分为矿业开采排放源;第二主成分归因于自然源;第三主成分归因于自然源(尾矿区域的自然淋溶)和人为源(林业和农业活动、采矿).
洛阳市栾川县矿区周边土壤重金属污染特征、来源与生态风险评价
Evaluation of heavy metal pollution characteristics, sources and ecological risks of soil around mining areas in Luanchuan County, Luoyang City
-
摘要: 为探究洛阳栾川县矿区周边土壤重金属污染特征与生态风险,采集并测定了研究区47个表层土壤(0—20 cm)样品 Zn、Cu、Cd、Pb、Cr、Ni和 As 重金属元素含量,运用单因子指数(Pi)、内梅罗综合指数法(Pm)、地累积指数(Igeo)、潜在生态风险指数(Eri和RI)、Tessier重金属五步提取法、主成分分析(PCA)等方法围绕重金属元素分布特征、污染程度、潜在生态风险、重金属形态和来源进行分析和讨论. 结果表明,Cd和As的污染程度和生态风险最高(Eri>160),空间分布不均匀(CV>90.00%),为引起土壤环境风险的主要因子;其次是Pb、Cu、Zn;最低的是Cr和Ni,且其空间异质性较弱,迁移转化风险较低. 不同的重金属在林地土壤、农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤中的富集程度和生态风险存在差异. 结合Eri和RI值来看,林地土壤As和Cd潜在生态风险较高,Eri分别达到了643.35和536.10. 从重金属形态分布来看,Cd和Pb有效态含量占比较高,分别为72.13%、86.84%;其次是Cu、Zn和As;林地土壤中Pb的碳酸盐结合态(43.82%)以及Cd可交换态(28.24%)和有机结合态(33.31%)明显高于农田和尾矿,发生迁移转化生态风险较高. 主成分分析结果表明主成分PC1、PC2和PC3分别归因于矿业开采排放源、自然源、和混合源(自然淋溶、林业和农业活动、采矿).Abstract: To investigate the characteristics and ecological risks of heavy metal pollution in soils around mining areas in Luanchuan County, Luoyang City, 47 surface soil (0—20 cm) samples in the study area were collected and measured for Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb, Cr, Ni and As, and single factor index (Pi), Nemero integrated index (Pm), ground accumulation index (Igeo), potential ecological risk index ( Eri and RI), Tessier's five-step extraction, and principal component analysis (PCA) were used to portray and delineate the distribution characteristics, pollution level, potential ecological risk, heavy metal fractionations and source apportionment. The results showed that Cd and As had the highest pollution degree and ecological risk (Eri>160), with heterogeneous spatial distribution (CV>90.00%), and were the main factors causing soil environmental risk; followed by Pb, Cu, and Zn; the lowest were Cr and Ni, and their spatial heterogeneity was weak and the migration transformation risk was low. The degree of enrichment and ecological risk of the different heavy metals in woodland soils, agricultural soils and soils around tailings differed. Based on the calculation results of the Eri and RI, the potential ecological risk of forest soil As and Cd was high, while the Eri were 643.35 and 536.10, respectively. The heavy metal fractionation analysis showed that Cd and Pb have a higher content in the effective state, 72.13% and 86.84%, respectively; followed by Cu, Zn and As; the carbonate bound state (43.82%) as well as the Cd exchangeable state (28.24%) and organic bound state (33.31%) of Pb in woodlands are significantly higher than the states in agricultural fields and tailing, with a higher ecological risk of migration transformation. The PCA results indicated that PC1, PC2 and PC3 were recognized as mining emission sources, natural sources, and mixed sources (natural leaching, forestry and agricultural activities, and mining), respectively.
-
重金属污染场地主要是由采矿、冶炼、电镀、化工、电子和制革染料等工业生产的“三废”等引起的. 随着我国工业化的快速发展,重金属污染场地环境安全问题形势严峻[1],土壤重金属污染具有隐蔽性好、潜伏周期长、毒性危害大和地域差异明显等特点[2 − 3]. 重金属在土壤环境中的累积和迁移会威胁到人类食品和饮用水安全、区域生态环境、人居环境健康和经济社会的可持续发展[4].
2014年4月发布的《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》[5]调查结果显示,耕地土壤环境质量堪忧,工矿业废弃地土壤环境问题突出. 从土地利用类型看,耕地、林地、草地土壤点位超标率分别为19.40%、10.00%、10.40%,同时指出工矿业、农业生产等人类活动和自然背景值高是造成土壤污染或超标的主要原因. 2022年《中国生态环境公报》[6]指出全国土壤环境污染加重的趋势得到了初步遏制. 目前影响农用地土壤环境质量的主要污染物是重金属,其中Cd为首要污染物,同时指出全国重点行业企业用地土壤污染的风险仍需进一步重视. 根据河南省生态环境厅发布《河南省2019年度土壤污染重点监管单位名录》[7],重金属污染企业占据名录中大部分企业,尤其以化工、冶炼、采矿等企业最为突出. 从地域上看,洛阳、济源和焦作所涉及的重金属污染企业众多,尤其以洛阳市栾川县和孟津县最为突出. 研究区域位于河南省洛阳市栾川县,主要以高山地形为主,该县拥有亚洲最大的钼矿开采企业(洛阳钼业),周边多有钼矿、铁矿、金矿等开采或冶炼厂. 该地区土壤污染特征主要以镉、铅、铜、锌、砷污染为主.
《河南省重金属污染防治工作指导意见》[8]明确提出“有序开展重金属污染地块治理与修复工作”的任务. 明确指出铅Pb、镉Cd、砷As、铜Cu、锌Zn等为重点污染物. 铅Pb、铜Cu、锌Zn等有色金属矿采选及冶炼为重金属污染防控重点行业,这些行业在研究区域内均有分布. 在开展土壤重金属污染治理之前对目标污染场地的重金属污染程度、累积效应、赋存形态、来源解析、迁移转化和生态风险评估工作十分关键,这对土壤污染修复技术的选择具有十分重要的指导意义. 如贾晗等[9]采用单因子污染指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法、地累积指数法等调查研究了安徽典型硫铁矿集中开采区土壤重金属污染特征和来源,发现研究区土壤中重金属元素主要来源为采矿活动综合源、大气沉降与农业综合源等. 余高等[10]通过单因子污染指数法、地积累指数法、潜在生态风险指数法和人体健康风险评价模型评价土壤Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Ni、Mn、As和Hg的生态环境风险,得到了研究区整体存在强潜在生态风险等结论. 王海洋等[11]利用内梅罗综合污染指数和潜在生态风险指数对矿区周边农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染水平开展评价. 万梦雪等[12]采用单因子指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法和地累积指数评价了上海市闵行区典型工业区的土壤污染状况,同时基于主成分分析-多元线性回归模型解析重金属的来源. 此外,Miao等[13]和Luo等[14]研究了由土壤重金属污染引起的健康风险,并开展量化分析评估.
可见,众多学者会采用多种指数评价方法对土壤重金属污染状况、生态风险和健康风险等进行评价,进一步借助主成分分析[15 − 18]、多元线性回归模型[9,12]、聚类分析[19 − 20]、正定矩阵因子分析模型[15](PMF)等方法模型识别污染源并进行定量解析,从而得到一个更具有参考性的结果. 然而,重金属的富集程度和生态风险也会受到重金属形态和土壤类型的影响. Tessier[21]提出的五步连续提取法将重金属的形态分为可交换态(F1)、碳酸盐结合态(F2)、铁锰氧化物结合态(F3)、有机结合态(F4)和残渣态(F5),不同形态重金属含量对迁移转化能力、生物可利用度和生态风险等有更深入的指示作用,这对于土壤修复技术的选择也很有意义. 洛阳栾川县区内矿产资源丰富,是我国著名的多金属矿集区,关于这一地区的重金属污染特征和生态风险的调查研究还比较匮乏. 此外,目前还缺乏关于矿区周边林地、农田和尾矿周边土壤类型对重金属富集和生态风险的影响研究. 更重要的是,几乎未见以重金属形态分析为部分依据开展源解析工作的研究报道.
基于此,本文以洛阳栾川县矿区周边为目标研究区域,采样点位主要布置在栾川县矿区周边,采用单因子指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法、地累积指数法来探究洛阳市栾川矿区周边7种重金属(As、Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr、Cd 和 Ni)污染特征,借助单因子和综合潜在生态风险指数分析重金属的潜在生态风险. 进一步探究土地利用类型和重金属形态对重金属富集和迁移转化生态风险的影响. 此外,采用Pearson相关性分析和主成分分析方法开展来源解析. 旨在为探索目标地区较适宜的土壤修复技术提供参考依据和理论指导.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区域概况及采样布点
研究区域为栾川县,隶属于洛阳市,位于河南西部,其地理坐标范围为东经111°11′—112°01′、北纬33°39′—34°11′之间. 总面积
2177 km2,东西长78.40 km,南北宽57.20 km. 栾川县区内土地利用类型包括耕地、园地、林地、草地、湿地、交通用地、城镇村与工矿用地、水域及水利设施用地. 县城处在狭长地带(图1中白色区域),主要以高山地形为主,位于豫西多金属成矿带的中心区域,区内矿产资源丰富,是我国著名的多金属矿集区,也是全国16个重要多金属成矿带的核心区域. 境内分布金属矿产、非金属矿产、能源矿产和水汽矿产4大类,共50余种,已探明储量的矿产19种,各类矿产地251处,其优势资源可归纳为钼、钨、铅、锌、金、银、铁、萤石等. 研究区域和采样点位主要布置在栾川县矿区周边,旨在探究矿区周边土壤重金属污染特征.采样过程主要参考《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166—2004)[22]的勘测、处理方法. 采样时通过经纬度定位并结合实际勘测对样点进行校准. 采样点位主要布置在矿区周边的农田、林地和尾矿范围内,共采集土壤样品47个,农田、林地和尾矿周边土壤样品的数量分别为20、12、15个. 采样深度为0—20 cm,采样重量不少于1 kg,采样过程中保证采集的每个样品来自相同的土壤类型,采样时去除落叶、砂石、动植物残体、有机残渣等杂物,以减少对土壤重金属元素含量测定的影响[23]. 经风干、磨碎、过筛后以备重金属元素(As、Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr、Cd和Ni)分析.
1.2 样品测定与分析方法
参考《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166—2004)[22]、《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB
15618 —2018)[24]的勘测和处理方法,并综合考虑研究区内3种土地利用类型. 样品总量测定的处理方法如下[25]:土壤样品消解后用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)检测Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr、Cd 和 Ni含量;用原子荧光光谱法(AFS)测定As含量. 重金属形态与潜在毒性分析主要采用Tessier等[21]提出的五步连续提取法.1.3 土壤重金属污染特征与生态风险评价方法
(1)单因子污染指数
单因子污染指数(Pi)法可以评价单个污染因子的污染程度,作为一种定量指标,可以应用于重金属污染程度的评价,一般以土壤背景值或标准限值作为评价标准. 表达式如式(1).
Pi=CiSi (1) 其中,Pi为土壤重金属i的单因子污染指数,Si为重金属i的评价标准,单位为mg·kg−1,主要参照土壤环境质量标准的风险筛选值作为标准,Ci为土壤重金属i的实测数据,单位为mg·kg−1. 根据单因子污染指数Pi的大小可将土壤重金属污染程度分为5类,分级标准如表1所示.
表 1 土壤重金属污染指数分级标准Table 1. Classification of heavy metal indexes单因子污染指数PiSingle factor pollution index 内梅罗综合污染指数PimaxNéméro composite pollution index 地累积指数IgeoGround accumulation index 范围 污染水平 范围 污染水平 范围 污染水平 Pi≤1 清洁 Pm≤0.7 清洁 Igeo≤0 无污染 1<Pi≤2 轻微污染 0.7<Pm≤1 尚清洁 0<Igeo≤1 轻-中度污染 2<Pi≤3 轻度污染 1<Pm≤2 轻度污染 1<Igeo≤2 中度污染 3<Pi≤5 中度污染 2<Pm≤3 中度污染 2<Igeo≤3 中-强度污染 Pi>5 重度污染 Pm>3 重度污染 3<Igeo≤4 强度污染 4<Igeo≤5 强-极强污染 Igeo>5 极强度污染 (2)内梅罗综合污染指数
内梅罗综合污染指数法[26]对单因子指数的平均值和最大值进行归纳处理,能够反映土壤环境中各项重金属的综合污染状况,突出污染最严重的重金属对环境的有害影响[27]. 为了综合评价洛阳栾川县矿区周边污染水平,采用内梅罗综合污染指数对土壤污染情况进行综合评价,计算公式如式(2)和式(3)所示:
Pm=(P2imax+P2iave)2 (2) Piave=1n∑Pi (3) 式中,Pimax为单因子污染指数的最大值,Piave单因子污染指数的平均值,Pm为内梅罗综合污染指数,分级标准如表1所示.
(3)地累积指数
地累积指数(Igeo)法由德国科学家Muller提出,广泛应用于评价土壤重金属污染和累积程度,可以反映自然地质过程和人为活动对重金属污染产生的影响. 计算公式如下:
Igeo=log2(Ci1.5×Cis) (4) 式中,Igeo 表示土壤重金属的地积累指数;Ci为土壤重金属i的实测数据,单位为mg·kg−1,Csi取自重金属i的土壤元素背景值,考虑到采样点位主要分布在土壤表层,因此元素背景值选择河南省土壤环境背景值[28](A层,0—20 cm),并将地累积指数分为7个等级,如表1所示.
(4)土壤重金属污染生态风险评价方法
瑞典学者Hakanson于1980年提出了潜在生态风险指数Eri,该方法综合考虑了各元素重金属浓度、联合环境效应和生态毒性差异性,定量评估重金属的潜在生态环境风险,如表2所示[29]. 计算公式如式(5)和式(6):
表 2 土壤重金属潜在生态风险指数分级标准Table 2. Grading criteria for the potential ecological risk index for heavy metals in soils单因子潜在生态风险指数Single factor potential ecological risk index 综合潜在生态风险指数Comprehensive potential ecological risk index 生态危害程度Degree of ecological hazard Eri<40 RI≤150 轻微生态风险 40<Eri≤80 151<RI≤300 中度生态风险 80<Eri≤160 301<RI≤600 强生态风险 160<Eri≤320 601<RI≤ 1200 强烈生态风险 Eri≥320 RI> 1200 极强生态风险 Eir=TirCiSi (5) RI=∑ni=1Eir (6) 式中,Ci为重金属元素i的实测值,单位为mg·kg−1;Si为重金属i的评价标准,单位为mg·kg−1;Eri为土壤重金属i的单因子潜在生态风险指数;RI 为重金属综合潜在生态风险指数;Tri 表示重金属元素i的毒性系数,反映单元素污染影响的敏感性和生物学上的毒害性,Cr、Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、Ni、As的毒性系数依次为2、30、5、5、1、5、10[30 − 31].
1.4 土壤重金属来源解析
主要采用Pearson相关性和主成分分析来开展源解析. Pearson相关性分析能够辨识不同重金属之间是否具有同源性. 主成分的概念由Karl Pearson在1901年提出,是考察多个变量间相关性一种多元统计方法. 其基本思想是通过原来变量的线性组合来解释原来变量的大部分信息,达到降维的目的,从而简化问题的复杂性. 本文主要运用主成分分析辨别土壤重金属污染源.
2. 结果与讨论(Results and Discussion)
2.1 土壤重金属含量的描述性统计
栾川县矿区周边表层土壤重金属Cr、Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、Ni、As检出率均为100%. 由表3可知,7种重金属的平均值均大于中位值,分别是背景值的1.05、52.46、20.96、9.68、12.72、1.45、82.90倍,这表明7种重金属在土壤表层均存在不同程度的累积和富集效应,Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、As等5种重金属污染尤为严重,这与该地区长期以来的矿业活动相关. 相对于风险筛选值的点位超标率来看,Cr、Ni的含量均低于风险筛选值,值得注意的是Cd的点位超标率达到了100.00%,相对于风险筛选值,As、Pb、Cu、Zn的点位超标率分别达到了61.10%、83.30%、61.10%、94.40%. 相对于风险管控值,土壤样品中Cd和Pb的点位超标率分别达到38.90%和22.20%. 此外,Cr 含量均低于风险管控值.
表 3 土壤重金属含量统计Table 3. Statistics of heavy metals in soil项目Item Cr Cd Pb Cu Zn Ni As 最小值/(mg·kg−1) 25.93 0.84 45.56 26.69 222.36 13.92 6.77 最大值/(mg·kg−1) 143.61 13.62 1757.85 603.92 2788.15 85.02 5073.75 中位数/(mg·kg−1) 59.97 2.095 158.68 116.16 550.86 35.55 36.82 平均值/(mg·kg−1) 66.67 3.41 467.49 193.60 795.03 39.62 812.44 标准差/(mg·kg−1) 32.09 3.09 555.52 224.33 601.97 18.23 1442.12 变异系数/% 48.14% 90.51% 118.83% 115.88% 75.72% 46.01% 177.50% 土壤背景值/(mg·kg−1) 63.20 0.065 22.30 20.00 62.50 27.40 9.80 点位超标率/% 39.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 72.00% 94.40% 风险筛选值/(mg·kg−1) 200.00 0.30 120.00 100.00 250.00 100.00 30.00 点位超标率/% 0.00% 100.00% 83.30% 61.10% 94.40% 0.00 61.10% 风险管控值/(mg·kg−1) 1000.00 3.00 700.00 — — — — 点位超标率/% 0.00% 38.90% 22.20% — — — — 偏度 1.20 2.29 1.43 1.93 2.14 1.04 2.07 峰度 0.81 5.92 0.57 2.79 5.69 0.68 3.56 表3中的变异系数为标准差与平均值的比值,能够反映土壤重金属污染分布的空间变化程度,7种重金属元素的变异系数大小排序为As>Pb>Cu>Cd>Zn>Cr>Ni,其中Pb、Cu、As、Cd的变异系数均大于90%,为强变异,表明各采样点间重金属元素含量离散程度较高,空间分布不均匀,土壤受到外界干扰显著. Cr、Ni为中等变异,相对Pb、Cu、As空间异质性较弱,受矿区开采活动和人为活动的影响较小.
2.2 土壤重金属污染与累积特征
2.2.1 单因子污染指数评价
单因子污染指数可以反映出某个采样点单个元素的污染情况. 以土壤环境质量标准中重金属的风险筛选值作为评价标准进行单因子污染指数评价. 土壤重金属单因子污染指数箱线图如图2 (a)所示,所有样品中的Ni、Cr元素单因子污染指数值均小于1. 由图2 (b)可知,Ni和Cr的清洁水平占比达到100.00%,表明Ni和Cr元素几乎不存在土壤污染风险. Pb和Cu的单因子污染指数主要分布在3以下,不存在中度污染状况,重度污染水平的采样点位分别占27.78%和16.67%. Zn元素清洁点位仅占5.56%,其余点位均存在不同程度的污染. As元素在个别点位的单因子污染指数最高可达169.13. Cd元素的污染程度最为严重,轻度、中度和重度污染点位分别占11.11%、11.11%和77.78%. Cd、As、Zn、Pb和Cu污染程度分布较广,结合上文变异系数的相关分析,可能是本次采样点布置的区域主要是在矿区周边的农田、尾矿和林地中,重金属的富集程度可能受到矿区距离和土壤类型的影响.
2.2.2 内梅罗综合污染指数评价
在单因子污染指数的基础上,利用公式(2)进行内梅罗综合污染指数计算与评价. 内梅罗综合污染指数可反映出区域范围内某重金属的综合污染情况,突出高浓度重金属对环境质量的影响. 由图3可知,重金属综合污染指数(Pm)变化范围处于0.5—120 之间,平均值为25.76. Cr和Ni的内梅罗综合污染指数分别为0.56和0.66处于清洁污染水平,除此之外,Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn和As均处于严重污染水平,尤其是Cd和As,这与单因子污染指数的结果一致.
2.2.3 地累积指数评价
应用地累积指数法进一步对栾川县矿区周边土壤重金属的污染程度进行评价,采用研究区的土壤元素背景值作为评价参比值[28],综合判别自然地质过程造成的背景值影响和人为活动的干扰.
由图4(a)可知,7种元素的地累积指数均值大小排序依次为:Cd(4.70)>Pb(2.87)>As(2.86)>Zn(2.77)>Cu(1.95)>Ni(−0.20)>Cr(−0.66). 其中Cr和Ni的地累积指数平均值均小于0,大部分点位处于无污染状态,16.67%的土壤样本为轻-中度污染(0≤Igeo<1). Pb和Zn地累积指数值的箱体主要位于中-强度和强度污染范围内(2≤Igeo<4),占比分别为33.3%和77.8%,如图4(b)所示. Cu的地累积指数值主要分布在轻中度污染—中强度污染之间(0≤Igeo<3),占比为77.8%. As的地累积指数箱体较长,污染程度分布较广,表明土壤中这6种元素受到地质背景和人为活动的影响较为明显. 此外采样点中As极强污染和轻中度污染均分别占33.33%,污染程度呈现两极分化现象,这说明As元素在采样点的某一特定区域内存在累积现象. Cd、Pb和As的极强度污染(Igeo>5)分别占38.89%、22.22%、33.33%,与单因子污染指数和内梅罗综合污染指数结果相似,Cd的地累积指数均处于强度污染以上(Igeo>3).
2.3 土壤重金属污染潜在生态风险评价
采用潜在生态风险指数法对洛阳栾川县土壤重金属生态风险进行评价. 由图5(a)和图5(b)可知,Cr、Ni、Zn的Eri均小于40,研究区全样点有轻微生态风险,其中Cr和Ni的Eri分别只有0.67、1.98. Pb的Eri处于1.90—73.24之间,平均值为19.50,个别点位存在中度生态风险,占比为22.20%. Cd的单因子潜在生态风险指数处于83.00—
1362.00 范围内,研究区全样点位处于强生态风险及以上,极强生态风险等级占38.89%. 此外,As产生极强生态风险的样品点位占27.78%. 结合单因子污染指数、内梅罗综合污染指数和地累积指数的结果,Cd和As的生态风险源于较强的污染程度和区域累积效应.洛阳栾川县周边表层土壤综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)平均值为647.01(表4),说明研究区土壤整体处于强烈生态风险水平,RI值的范围为95.30—
2670.35 ,变化范围大,部分采样点位的潜在生态风险较强,这可能归因于某一区域重金属的富集进而导致了局部污染和较强的生态风险. Cd和As的Eri对RI的贡献率较高,分别达到了52.74%和41.86%,从平均值来看,分别处于极强生态风险(Eri>320)和强烈生态风险(160<Eri≤320)范围内. 此外,相较于Cr、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni,Cd和As的标准差较大,Eri的数值分散程度较高,因此推测Cd和As在某一特定区域产生富集效应加大了此地区的生态风险. Cd和As作为引起土壤环境风险的主要因子,需引起关注.表 4 土壤重金属生态风险评价结果Table 4. Results of ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metalsEri RI Cr Cd Pb Cu Zn Ni As 最小值 0.26 83.00 1.90 1.33 0.89 0.70 2.26 95.30 最大值 1.44 1362.00 73.24 41.35 11.15 4.25 1691.25 2670.35 平均值 0.67 341.21 19.48 9.68 3.18 1.98 270.81 647.01 标准差 0.32 308.65 23.15 11.22 2.41 0.91 480.71 718.30 Eri对RI贡献率/% 0.10 52.74 3.01 1.50 0.49 0.31 41.86 综上,洛阳栾川县矿区周边Cd和As的污染程度和生态风险最高,且在某一区域范围内存在明显的累积. 其次是Pb、Cu、Zn. 污染程度和生态风险最低的是Cr和Ni. 值得关注的是重金属的富集程度和生态风险可能受到重金属形态和土壤类型的影响. 基于此,对不同土地利用类型中重金属的形态和生态风险进行评价,以探究土地利用类型和重金属形态对重金属富集和生态风险的影响.
2.4 不同土地利用类型中重金属形态分析与生态风险评价
2.4.1 不同土地利用类型重金属生态风险评价
不同土地利用类型土壤重金属单因子潜在生态风险指数(Eri)如图6所示. 农田和林地的Cd和As的Eri明显高于尾矿周边土壤,农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤Cd的Eri均值分别达到267.05、238.65,为中度生态风险,林地土壤Cd的Eri均值为643.35,为强烈生态风险. 林地土壤Cd和As的Eri箱体较长,不同采样点位的生态风险程度较为分散. As在农田、尾矿周边和林地土壤中的Eri均值分别为292.30、65.30、536.10.
农田和林地As和 Cd 的潜在生态风险相对较高,尤其是林地土壤. 原矿经过选别作业处理后,其主要成分已在精矿中富集,剩余产物中有用目标组分含量相对较低,但从尾矿周边土壤采样区域的点位来看,仍需注意Cd以及个别点位Pb和As产生的潜在生态风险.
不同土地利用类型土壤重金属综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)如表5所示,从表5的均值来看,农田和林地的综合潜在生态风险分别达到了强生态风险和极强生态风险. 尾矿周边土壤的RI均值为334.73,为强生态风险,但从不同风险等级的样点占比情况来看,66.66%的点位处于中度生态风险及以下,强生态风险及以上占33.34%. 整体来看,林地的综合潜在生态风险最高,其次是农田和尾矿周边土壤.
表 5 不同土地利用类型土壤重金属综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)Table 5. Comprehensive potential ecological risk index (RI) of soil heavy metals under different land use types项目Projects 综合潜在生态风险指数范围Comprehensive potential ecological risk index range 均值Average value 占比/% 轻微Minor 中度Moderate 强Strong 强烈Intense 极强Extremely strong 农田土壤 106.49— 2221.18 596.77 12.50 50.00 0.00 25.00 12.50 尾矿周边土壤 95.30—973.48 334.73 33.33 33.33 16.67 16.67 0.00 林地土壤 198.34— 2670.35 1215.89 0.00 25.00 0.00 50.00 25.00 2.4.2 不同土地利用类型中重金属形态分析
土壤重金属的生态风险与重金属形态也存在很重要的联系. Tessier将土壤中的重金属形态分为5种:可交换态(F1)、碳酸盐结合态(F2)、铁锰氧化物结合态(F3)、有机结合态(F4)和残渣态(F5),5种重金属形态的生物利用度依次降低、迁移转化困难程度和生态风险强度依次增加. 其中可交换态的重金属吸附在黏土、腐殖质及土壤中某些成分上[32],易于迁移转化,生态风险较高;碳酸盐结合态受土壤环境pH值的变化较为敏感[33];铁锰氧化物结合态重金属一定程度上反映了人类活动对环境的污染,受到土壤pH和氧化还原环境条件变化的影响较大[34];有机结合态为重金属和土壤有机物的螯合;残渣态的重金属通常存在于矿物成分的晶格中,能长期稳定存在于土壤中,生态风险较低[35]. 前4种重金属形态常被称为有效态,为表征活性态重金属含量的指标. 残渣态又被称为非有效态,较为稳定[36 − 37].
不同土地利用类型土壤重金属形态如图7所示. 由图7(a)全样点中各重金属残渣态占比顺序依次为:Cr(90.52%)>Ni(72.88%)>As(71.85%)>Zn(44.50%)>Cu(34.55%)>Cd(27.87%)>Pb(13.16%),可见Cr、Ni和As的生物利用度和迁移转化风险较低,能够在土壤环境中稳定存在. As的存在形态主要为残渣态(71.85%),迁移能力和生物可利用度较差,但其污染强度较高,潜在生态风险较强,可交换态占比仅次于Cd(12.85%),这部分的As仍然值得关注.
 图 7 不同土地利用类型土壤重金属形态分析Figure 7. Analysis of heavy metal patterns in soils of different land use types注:F1,F2,F3,F4,F5分别代表可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机结合态和残渣态(a)全样点重金属形态占比;(b)农田样点各重金属形态占比;(c)林地样点各重金属形态占比;(d)尾矿区域样点各重金属形态占比Note: F1, F2, F3, F4, F5 represent the exchangeable, carbonate bound, Fe-Mn oxide bound, organic bound and residue states respectively (a) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the whole sample; (b) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the farmland sample; (c) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the woodland sample; (d) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the tailings area sample
图 7 不同土地利用类型土壤重金属形态分析Figure 7. Analysis of heavy metal patterns in soils of different land use types注:F1,F2,F3,F4,F5分别代表可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机结合态和残渣态(a)全样点重金属形态占比;(b)农田样点各重金属形态占比;(c)林地样点各重金属形态占比;(d)尾矿区域样点各重金属形态占比Note: F1, F2, F3, F4, F5 represent the exchangeable, carbonate bound, Fe-Mn oxide bound, organic bound and residue states respectively (a) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the whole sample; (b) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the farmland sample; (c) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the woodland sample; (d) Proportion of heavy metal forms in the tailings area sample重金属Cd的残渣态(非有效态)占比仅有27.87%,不足全量的1/3,可交换态占比也最高,占19.83%,有效态含量占比达到了72.13%,当土壤环境变化时易发生迁移转化. 由上文各污染指数评价得知土壤重金属Cd污染严重,叠加有效态占比较高,因此土壤重金属Cd污染值得关注. Pb的污染强度次于Cd和As,地累积指数介于Cd和As之间,值得注意的是Pb的有效态含量达86.84%,主要存在形态为碳酸盐结合态(30.32%)、铁锰氧化物结合态(35.70%)、有机结合态(20.67%),容易受到土壤环境pH、氧化还原电位的影响,在7种重金属中最不稳定.
因此,在全样点土壤重金属调研结果和进一步的靶向技术探索中,考虑到有效态含量占比和迁移转化生态风险,需要重点关注Cd和Pb重金属污染. 其次是Cu、Zn和可交换态的As.
根据图7中的(b)、(c)和(d),尾矿周边、林地、农田土壤类型中各重金属形态的占比分布规律与全样点结果相似,基本表现为Cr、As和Ni的重金属赋存形态主要为残渣态,在土壤中存在较为稳定且不易迁移. Pb的有效态含量最高,分别达到了88.48%(尾矿周边土壤)、94.34%(林地)和82.05%(农田),以铁锰氧化物结合态和碳酸盐结合态为主要存在形态. 林地土壤中Pb和Cd的有效态含量占比最高,其中Pb的碳酸盐结合态占比达到43.82%,明显高于农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤,因此当面临土壤pH降低的冲击时,林地土壤中的Pb迁移转化的生态风险较高. 林地中Cd的可交换态和有机结合态也明显高于农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤,分别占28.24%和33.31%,这表明林地土壤中的Cd对环境变化较为敏感,比农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤中的Cd更易迁移转化和被植物吸收;此外,33.31%有机结合态的Cd与土壤中的各种有机物如动植物残体、腐殖质等螯合. 相对于农田和林地土壤,尾矿周边土壤的As有效态占比最高(34.81%),其中的碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态和有机质结合态分别占10.14%、8.19%、6.63%. 尾矿周边土壤和农田土壤中Cu的有效态高于林地,分别达到了68.40%和68.20%,其中有机结合态Cu占比优势明显,分别为52.78%和48.86%,推测一定程度上归因于土壤中较高含量的有机物. 农田土壤中Zn的铁锰氧化物结合态含量相对较高,当土壤环境中的氧化还原电位和pH较低时,可能导致Zn的溶出,进而发生横向或纵向迁移,污染河流湖泊和地下水环境[38].
2.5 土壤重金属污染来源解析
结合实地踏勘,采样区的潜在污染源可以分为固定源和移动源:其中固定源主要为分布在研究区域的涉重金属污染企业(采矿、冶炼、化工等). 移动源主要为运输矿产的卡车以及矿区工作人员车辆携带. 进一步还会受到自然源和人为源的干扰,使得土壤重金属由于自然淋溶、林业和农业活动而发生迁移. 各重金属污染的源识别和源解析仍需相关性和主成分分析来深入解释.
2.5.1 Pearson 相关性分析
对不同重金属元素总量进行Pearson 相关性分析,来说明其同源性(图8). Pb与Cu、Zn之间在0.001水平上的相关系数分别达到了0.79和0.84,呈现极显著正相关(P<0.001,r>0.5);Zn和Cd的相关系数为0.83,同样呈现极显著正相关关系(P<0.001,r>0.5),这可以作为他们之间具备高度同源性的依据.
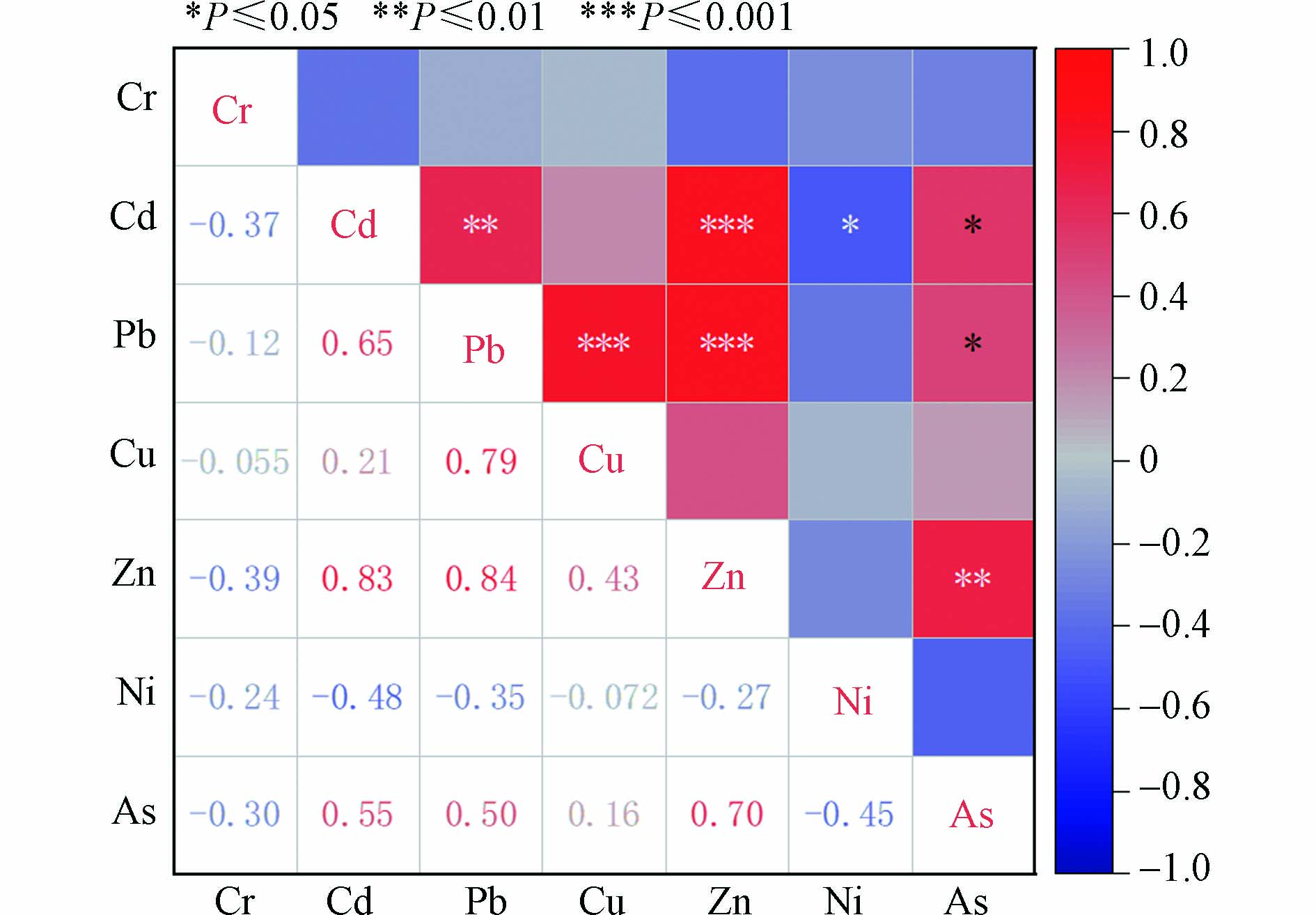 图 8 土壤重金属相关性热图Figure 8. Correlative heat map of soil heavy metal content注:P值表示相关系数的统计学意义. P值越小,越显著:P<0.05为有统计学差异,P<0.01为有显著统计学差异,P<0.001为有极其显著的统计学差异.Note: P-values indicate the statistical significance of the correlation coefficients. the smaller the P-value, the more significant it is: P<0.05 is a statistically significant difference, P<0.01 means a statistically significant difference, P<0.001 means an extremely significant statistical difference
图 8 土壤重金属相关性热图Figure 8. Correlative heat map of soil heavy metal content注:P值表示相关系数的统计学意义. P值越小,越显著:P<0.05为有统计学差异,P<0.01为有显著统计学差异,P<0.001为有极其显著的统计学差异.Note: P-values indicate the statistical significance of the correlation coefficients. the smaller the P-value, the more significant it is: P<0.05 is a statistically significant difference, P<0.01 means a statistically significant difference, P<0.001 means an extremely significant statistical difference此外,Pb和Cd、Zn和As在0.01 水平上显著相关,相关系数分别为0.65、0.70,表明他们之间具有相同或相似的来源的可能较大. As和Pb、Cd的相关系数也达到了0.50以上,在0.05水平上显著相关,可能具有相同或相似来源,但仍需进一步的分析验证.
值得注意的是Cr与其他重金属之间均呈现负相关关系,Ni也表现出相似的规律,其相关系数均在−0.5—0之间,因此判断Cr和Ni的来源相对独立.
2.5.2 基于PCA的土壤重金属来源解析
通过主成分分析对土壤重金属来源情况进行解析. 主成分分析提取到3个因子,且3个因子的特征值(3.64、1.27、1.19)均大于1,累积贡献率为 87.27%,能够解释土壤重金属元素所包含的信息. 分析结果见表6.
表 6 土壤重金属主成分Table 6. Principal component of soil heavy metals重金属Heavy metal 因子载荷Factor loading PC1 PC2 PC3 Cr −0.18 0.76 0.12 Cd 0.45 −0.06 −0.25 Pb 0.47 0.14 0.36 Cu 0.29 0.11 0.71 Zn 0.49 −0.15 − 0.0037 Ni −0.25 −0.60 0.40 As 0.39 −0.02 −0.35 特征值 3.64 1.27 1.19 方差贡献率/% 52.06 18.20 17.00 累积方差贡献率/% 52.06 70.27 87.27 第一主成分(PC1)的解释方差为 52.07%,其中Cd、Pb、Zn在 PC1 上具有较高的正载荷,且相关性分析结果表明,这些元素两两之间呈极显著正相关,说明它们的来源相似. 其次是Cu和As载荷分别达到0.29和0.39,并且Cu与Pb,As与Pb、Cd、Zn的相关系数均大于0.5. 此外,Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu和As的变异系数分别达到了90.15%、118.83%、75.72%、115.88%、177.50%,除Zn以外均处于强分异水平,说明受到人为活动影响较大. 洛阳栾川县区内矿产资源丰富,分布着钼、钨、铅、锌、金、银、铁、萤石等矿产地251处. 研究区和采样点位附近拥有正在开采的矿场和开采遗址,根据当地的地形地貌,矿产开采过程中可能使地底深处的矿物暴露于地表,增加Cd、Pb、Zn、Cu、As重金属元素的释放通量,尤其是Zn、Cu、Cd、Pb,其有效态含量达到了50%—80%,当土壤环境发生变化(如雨水淋溶、农业浇灌等),容易产生迁移转化生态风险,增加土壤中的重金属含量[10]. 因此,推测PC1为矿业开采排放源.
第二主成分(PC2)解释方差为 18.20%,Cr在PC2上具有较高的正载荷(0.76),相关性分析表明Cr的来源相对独立,其总量均值水平(66.67 mg·L−1)与背景值(63.20 mg·L−1)相当,变异系数仅为48.14%,其来源受到人为活动的影响较小. 因此判断主成分PC2归因于自然源.
第三主成分(PC3)的解释方差为17.00%,Cu在PC3上具有较高的正载荷(0.71),其次是Ni和Pb,相关性结果表明Ni的来源独立,可以推断PC3为混合源,且其中包含自然源. Pb与Cu在0.001水平上呈现极显著正相关,具有同源性,且其变异系数仅相差2.95%,为强变异水平,推测受到矿产开采活动的影响较大.
值得注意的是Cd和As在主成分PC1中的载荷为正值,而在PC3中的载荷表现为负向影响,推测Cd和As在PC3中的亏损趋势并非由矿产开采活动引起. 结合重金属形态分析的结果,林地土壤中Cd的可交换态和有机结合态也明显高于农田土壤和尾矿周边土壤,分别占28.24%和33.31%,这表明林地中的Cd对环境变化较为敏感,其在PC3中的亏损可能归因于自然源(雨水淋溶导致的迁移转化或被被植物吸收)相对于农田和林地土壤,尾矿周边土壤中的As有效态占比最高(34.81%),而农田和林地土壤中As的可交换态占比较高,因此As在PC3中的亏损趋势在不同的土壤类型中原因有差异,尾矿周边土壤的As亏损可能归因于自然淋溶导致的迁移,农田和林地中As亏损归因于植物或农作物吸收.
综上所述,第一主成分PC1为矿业开采排放源;第二主成分PC2归因于自然源;第三主成分PC3归因于自然源(尾矿区域的自然淋溶)和人为源(林业和农业活动、采矿).
3. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)洛阳栾川县矿区周边Cd和As的污染程度和生态风险最高,Eri分别达到341.21、270.81,且其空间分布不均匀,变异系数分别达到90.51%、177.50%. Igeo分别为4.70、2.86,在某一区域范围内存在明显的累积,为引起土壤环境风险的主要因子. 其次是Pb、Cu、Zn.
(2)污染程度和生态风险最低的是Cr和Ni,Eri分别只有0.67、1.98,且其空间异质性较弱(CV值均小于50%),受矿区开采活动和人为活动的影响较小. 此外Cr和Ni的生物利用度和迁移转化风险较低,残渣态占比90.52%和72.88%,能够在土壤环境中稳定存在.
(3)不同的重金属在林地、农田和尾矿中的富集程度和生态风险存在差异. 农田和林地As和Cd的潜在生态风险相对较高,尤其是林地土壤Eri分别达到536.10、643.35. 尾矿周边土壤Cd以及个别点位Pb和As潜在生态风险较高,值得进一步关注.
(4)Cd和Pb有效态含量占比较高,分别为72.13%和86.84%;其次是Cu、Zn和可交换态的As. 林地中Pb的碳酸盐结合态以及Cd可交换态和有机结合态明显高于农田和尾矿,对环境变化较为敏感. 尾矿周边土壤和农田土壤中Cu的有效态含量接近70%,明显高于林地土壤,迁移转化生态风险相对较高.
(5)第一主成分为矿业开采排放源;第二主成分归因于自然源;第三主成分归因于自然源(尾矿区域的自然淋溶)和人为源(林业和农业活动、采矿).
-
表 1 土壤重金属污染指数分级标准
Table 1. Classification of heavy metal indexes
单因子污染指数PiSingle factor pollution index 内梅罗综合污染指数PimaxNéméro composite pollution index 地累积指数IgeoGround accumulation index 范围 污染水平 范围 污染水平 范围 污染水平 Pi≤1 清洁 Pm≤0.7 清洁 Igeo≤0 无污染 1<Pi≤2 轻微污染 0.7<Pm≤1 尚清洁 0<Igeo≤1 轻-中度污染 2<Pi≤3 轻度污染 1<Pm≤2 轻度污染 1<Igeo≤2 中度污染 3<Pi≤5 中度污染 2<Pm≤3 中度污染 2<Igeo≤3 中-强度污染 Pi>5 重度污染 Pm>3 重度污染 3<Igeo≤4 强度污染 4<Igeo≤5 强-极强污染 Igeo>5 极强度污染 表 2 土壤重金属潜在生态风险指数分级标准
Table 2. Grading criteria for the potential ecological risk index for heavy metals in soils
单因子潜在生态风险指数Single factor potential ecological risk index 综合潜在生态风险指数Comprehensive potential ecological risk index 生态危害程度Degree of ecological hazard Eri<40 RI≤150 轻微生态风险 40<Eri≤80 151<RI≤300 中度生态风险 80<Eri≤160 301<RI≤600 强生态风险 160<Eri≤320 601<RI≤ 1200 强烈生态风险 Eri≥320 RI> 1200 极强生态风险 表 3 土壤重金属含量统计
Table 3. Statistics of heavy metals in soil
项目Item Cr Cd Pb Cu Zn Ni As 最小值/(mg·kg−1) 25.93 0.84 45.56 26.69 222.36 13.92 6.77 最大值/(mg·kg−1) 143.61 13.62 1757.85 603.92 2788.15 85.02 5073.75 中位数/(mg·kg−1) 59.97 2.095 158.68 116.16 550.86 35.55 36.82 平均值/(mg·kg−1) 66.67 3.41 467.49 193.60 795.03 39.62 812.44 标准差/(mg·kg−1) 32.09 3.09 555.52 224.33 601.97 18.23 1442.12 变异系数/% 48.14% 90.51% 118.83% 115.88% 75.72% 46.01% 177.50% 土壤背景值/(mg·kg−1) 63.20 0.065 22.30 20.00 62.50 27.40 9.80 点位超标率/% 39.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 72.00% 94.40% 风险筛选值/(mg·kg−1) 200.00 0.30 120.00 100.00 250.00 100.00 30.00 点位超标率/% 0.00% 100.00% 83.30% 61.10% 94.40% 0.00 61.10% 风险管控值/(mg·kg−1) 1000.00 3.00 700.00 — — — — 点位超标率/% 0.00% 38.90% 22.20% — — — — 偏度 1.20 2.29 1.43 1.93 2.14 1.04 2.07 峰度 0.81 5.92 0.57 2.79 5.69 0.68 3.56 表 4 土壤重金属生态风险评价结果
Table 4. Results of ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals
Eri RI Cr Cd Pb Cu Zn Ni As 最小值 0.26 83.00 1.90 1.33 0.89 0.70 2.26 95.30 最大值 1.44 1362.00 73.24 41.35 11.15 4.25 1691.25 2670.35 平均值 0.67 341.21 19.48 9.68 3.18 1.98 270.81 647.01 标准差 0.32 308.65 23.15 11.22 2.41 0.91 480.71 718.30 Eri对RI贡献率/% 0.10 52.74 3.01 1.50 0.49 0.31 41.86 表 5 不同土地利用类型土壤重金属综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)
Table 5. Comprehensive potential ecological risk index (RI) of soil heavy metals under different land use types
项目Projects 综合潜在生态风险指数范围Comprehensive potential ecological risk index range 均值Average value 占比/% 轻微Minor 中度Moderate 强Strong 强烈Intense 极强Extremely strong 农田土壤 106.49— 2221.18 596.77 12.50 50.00 0.00 25.00 12.50 尾矿周边土壤 95.30—973.48 334.73 33.33 33.33 16.67 16.67 0.00 林地土壤 198.34— 2670.35 1215.89 0.00 25.00 0.00 50.00 25.00 表 6 土壤重金属主成分
Table 6. Principal component of soil heavy metals
重金属Heavy metal 因子载荷Factor loading PC1 PC2 PC3 Cr −0.18 0.76 0.12 Cd 0.45 −0.06 −0.25 Pb 0.47 0.14 0.36 Cu 0.29 0.11 0.71 Zn 0.49 −0.15 − 0.0037 Ni −0.25 −0.60 0.40 As 0.39 −0.02 −0.35 特征值 3.64 1.27 1.19 方差贡献率/% 52.06 18.20 17.00 累积方差贡献率/% 52.06 70.27 87.27 -
[1] ZHOU X Y, WANG X R. Impact of industrial activities on heavy metal contamination in soils in three major urban agglomerations of China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 230: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.098 [2] 张浙, 卢然, 伍思扬, 等. 长江经济带矿山土壤重金属污染及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(7): 3763-3772. ZHANG Z, LU R, WU S Y, et al. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of mine soil in Yangtze River economic belt[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(7): 3763-3772 (in Chinese).
[3] 张义, 周心劝, 曾晓敏, 等. 长江经济带工业区土壤重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 2062-2070. ZHANG Y, ZHOU X Q, ZENG X M, et al. Characteristics and assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils of industrial regions in the Yangtze River economic belt[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 2062-2070 (in Chinese).
[4] LI C F, ZHOU K H, QIN W Q, et al. A review on heavy metals contamination in soil: Effects, sources, and remediation techniques[J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal, 2019, 28(4): 380-394. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2019.1592108 [5] 环境保护部, 国土资源部. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》[EB/OL]. http://www.gov.cn/govweb/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm, 2014-04-17. [6] 生态环境部. 《2021 中国生态环境状况公报》[EB/OL]. http://www.gov.cn/govweb/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm, 2014-04-17. [7] 河南省生态环境厅. 河南省2019年度土壤污染重点监管单位名录[EB/OL]. https://sthjt.henan.gov.cn/2019/09-05/1050558.html. [8] 河南省环境保护厅. 河南省重金属污染防治工作指导意见[EB/OL]. https://sthjt.henan.gov.cn/2017/09-22/1029524.html. [9] 贾晗, 刘军省, 王晓光, 等. 安徽典型硫铁矿集中开采区土壤重金属污染特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(9): 5275-5287. JIA H, LIU J X, WANG X G, et al. Pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in soil of a typical pyrite concentrated mining area in Anhui Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(9): 5275-5287(in Chinese).
[10] 余高, 陈芬, 张晓东, 等. 锰矿区周边农田土壤重金属污染特征、来源解析及风险评价[J]. 环境科学,2023, 44(8): 4416-4428, YU G, CHEN F, ZHANG X D, et al. Pollution characteristics, source analysis, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the surrounding farmlands of manganese mining area. [J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(8): 4416-4428(in Chinese).
[11] 王海洋, 韩玲, 谢丹妮, 等. 矿区周边农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 2104-2114. WANG H Y, HAN L, XIE D N, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in farmland soils around mining areas and pollution assessment[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 2104-2114 (in Chinese).
[12] 万梦雪, 焦文涛, 胡文友, 等. 城市工业区土壤重金属累积特征与来源解析——以上海市闵行区典型工业区为例[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 42(6): 1886-1898. WAN M X, JIAO W T, HU W Y, et al. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metals in urban-industrial soils – A case study in Minhang District of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(6): 1886-1898(in Chinese).
[13] MIAO X Y, MIAO D, HAO Y P, et al. Potential health risks associated to heavy metal contamination of soils in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Coastal Conservation, 2019, 23(3): 643-655. doi: 10.1007/s11852-019-00695-x [14] LUO C L, LIU C P, WANG Y, et al. Heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables near an e-waste processing site, South China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 481-490. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.024 [15] 杨振宇, 廖超林, 邹炎, 等. 湘东北典型河源区土壤重金属分布特征、来源解析及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(9): 5288-5298. YANG Z Y, LIAO C L, ZOU Y, et al. Distribution characteristics, source analysis, and potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Typical River Source Areas of Northeastern Hunan Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(9): 5288-5298(in Chinese).
[16] 赵长坡. 贾鲁河沉积物中重金属形态分析及潜在生态风险评价[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2014. ZHAO C P. Potential ecological risk and speciation analysis of heavy metals in sediments from Jialu river[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2014(in Chinese).
[17] 黄波涛. 典型危废处置利用企业周边土壤重金属分布特征、来源及风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(2): 435-445. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022062403 HUANG B T. Distribution characteristics, sources analysis and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils surrounding typical hazardous waste disposal and utilization plants[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(2): 435-445 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022062403
[18] 韦炳干, 虞江萍, 曹志强, 等. 唐山市设施菜地土壤重金属累积与有效态含量的影响特征[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(9): 2649-2657. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020043001 WEI B G, YU J P, CAO Z Q, et al. Factors impact on accumulation and availability of heavy metals in greenhouse vegetable soil from Tangshan City[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(9): 2649-2657 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020043001
[19] 胡杰, 赵心语, 王婷婷, 等. 太原市汾河河岸带土壤重金属分布特征、评价与来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2500-2509. HU J, ZHAO X Y, WANG T T, et al. Distribution characteristics, evaluation, and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of Fenhe riparian zone in Taiyuan city[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(5): 2500-2509 (in Chinese).
[20] 张淑珂, 孙国新, 姜杰. 白城市黑土区农田土壤重金属来源解析及积累评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2023,43(5):409-420. ZHANG S K, SUN G X, JIANG J. Analysis of heavy metal sources and evaluation of accumulation in agricultural soils in the black soil area of Baicheng City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2023,43(5):409-420(in Chinese).
[21] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [22] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166—2004)[S]. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. The Technical Specification for soil Environmental monitoring (HJ/T 166—2004) [S](in Chinese).
[23] ZHANG H, YU M, XU H J, et al. Geochemical baseline determination and contamination of heavy metals in the urban topsoil of Fuxin City, China[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2020, 12(6): 1001-1017. doi: 10.1007/s40333-020-0029-2 [24] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准: GB 15618—2018[S] Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land: GB 15618—2018[S] (in Chinese).
[25] 张甘霖, 龚子同. 土壤调查实验室分析方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. ZHANG G L, GONG Z T. Soil survey laboratory methods[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012(in Chinese).
[26] NEMEROW N L. Scientific stream pollution analysis[M]. Washington, Scripta Book Co. , 1974 [27] 赖书雅, 董秋瑶, 宋超, 等. 南阳盆地东部山区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11): 5500-5509. LAI S Y, DONG Q Y, SONG C, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the eastern mountainous area of the Nanyang Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5500-5509 (in Chinese).
[28] 邵丰收, 周皓韵. 河南省主要元素的土壤环境背景值[J]. 河南农业, 1998(10): 29. SHAO F S, ZHOU H Y. Soil environmental background values for major elements in Henan Province[J]. Henan Agriculture, 1998(10): 29(in Chinese)
[29] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [30] 张雅然, 车霏霏, 付正辉, 等. 青海湖沉积物重金属分布及其潜在生态风险分析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(6): 3037-3047. ZHANG Y R, CHE F F, FU Z H, et al. Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Lake Qinghai[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(6): 3037-3047 (in Chinese).
[31] 陈芬, 余高, 侯建伟, 等. 矿渣运输道路两侧农田土壤重金属风险评价[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(11): 9-21. CHEN F, YU G, HOU J W, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils on both sides of the slag transportation road[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science), 2020, 42(11): 9-21 (in Chinese).
[32] 李宇庆, 陈玲, 仇雁翎, 等. 上海化学工业区土壤重金属元素形态分析[J]. 生态环境, 2004(2): 154-155. LI Y Q, CHEN L, QIU Y L, et al. Speciation of heavy metals in soil from Shanghai Chemical Industry Park[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2004(2): 154-155 (in Chinese).
[33] SINGH A K, HASNAIN S I, BANERJEE D K. Grain size and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Damodar River–a tributary of the lower Ganga, India[J]. Environmental Geology, 1999, 39(1): 90-98. doi: 10.1007/s002540050439 [34] O’REILLY WIESE S B, MACLEOD C L, LESTER J N. A recent history of metal accumulation in the sediments of the Thames Estuary, United Kingdom[J]. Estuaries, 1997, 20(3): 483-493. doi: 10.2307/1352608 [35] PRESLEY B J, TREFRY J H, SHOKES R F. Heavy metal inputs to Mississippi Delta sediments[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 1980, 13(4): 481-494. doi: 10.1007/BF02191849 [36] 国家环境保护总局. 土壤环境监测技术规范[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2005. State Environmental Protection Administration. The Technical Specification for soil Environmental monitoring [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2005(in Chinese).
[37] 曾清如, 周细红, 杨仁斌, 等. 不同来源重金属在土壤中的形态分布差异[J]. 农村生态环境, 1994(3): 48-51. ZENG Q R, ZHOU X H, YANG R B, et al. Fractionation of Pb. Zn and Cd in three polluted soils and their residues in soybean[J]. Rural Eco-Environment, 1994(3): 48-51 (in Chinese).
[38] 李昊哲. 不同地膜条件下重金属在农田土壤的垂向分布特性研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2018. LI Z H. Study on the distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soil profile under different plastic film mulching[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018 (in Chinese).
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 卢慧,余涛,赵万伏,温晴,汤奇峰,李畅,张力月,侯青叶,杨忠芳. 土壤-葡萄体系中重金属的迁移富集与风险评估研究进展. 岩矿测试. 2024(06): 982-996 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)
-







 下载:
下载: