-
纳滤技术作为近年来国内外研究和应用热点的膜分离技术,可有效去除污染水体中化学需氧量(COD)、总磷(TP)、重金属和部分盐分,使出水指标达到《地表水环境质量标准》中Ⅲ类水标准,因而在污水深度处理、饮用水软化等领域得到了广泛应用,如纳滤对大部分微量有机污染物的截留率达到70%以上[1],大部分再生水中的微量新污染物在经过纳滤处理之后未检出[2]。然而,纳滤浓水处理问题一直是影响其推广应用的关键限制因素之一[3]。面对纳滤膜浓水COD值高、盐分浓度大、BOD5/COD较低、可生化性差等特点,膜浓水常用的处理方式包括超滤反渗透、蒸发浓缩处理等,但这些处理技术仍面临着污染物无法根本去除、能耗高、二次污染严重等缺点,因此,寻找高效水处理技术成为膜浓水深度处理的关键[4-5]。
臭氧氧化技术是一种广泛应用于饮用水消毒和污水处理的氧化技术,具有氧化活性高、应用范围广、生产操作简单等优点[6-8]。针对纳滤膜浓水的高污染特征,单独臭氧氧化技术仍存在臭氧利用率较低、氧化能力不足等限制。近年来发展的电催化臭氧氧化技术通过在传统臭氧氧化体系内引入电催化剂,利用电场作用促进臭氧分解过程中活性氧物种的生成,可显著提高氧化效率和反应速度,成为臭氧氧化技术关注的重点[9-10]。利用电催化臭氧氧化技术实现纳滤膜浓水高效处理表现出良好的潜力,然而,基于电催化臭氧氧化技术处理膜浓水的研究仍鲜见报道。
基于此,本研究以实际纳滤膜浓水为目标水体,通过构建电催化臭氧氧化体系探究其对纳滤膜浓水的深度净化性能,评估其对实际纳滤膜浓水中有机质和毒性的削减效果,为进一步完善膜法污水深度处理技术提供支撑。
-
磷酸、浓硫酸、硝酸、无水乙醇、硝酸钠、磷酸氢二钾、碳酸钠、二水氯化钙、硼酸、柠檬酸、钼酸钠、硫酸铜等均为分析纯。
GPC-6030D直流稳压电源;CF-VG10臭氧发生器;LZB-3WB气体转子流量计;ESNA1-4040纳滤膜组件;LRH-800-G光照培养箱;LDZX-75KBS压力蒸汽灭菌锅;T9S紫外可见分光光度计;F-7000荧光分光光度计;vario TOC cube总有机碳分析仪;DR 3900多参数水质检测仪。
-
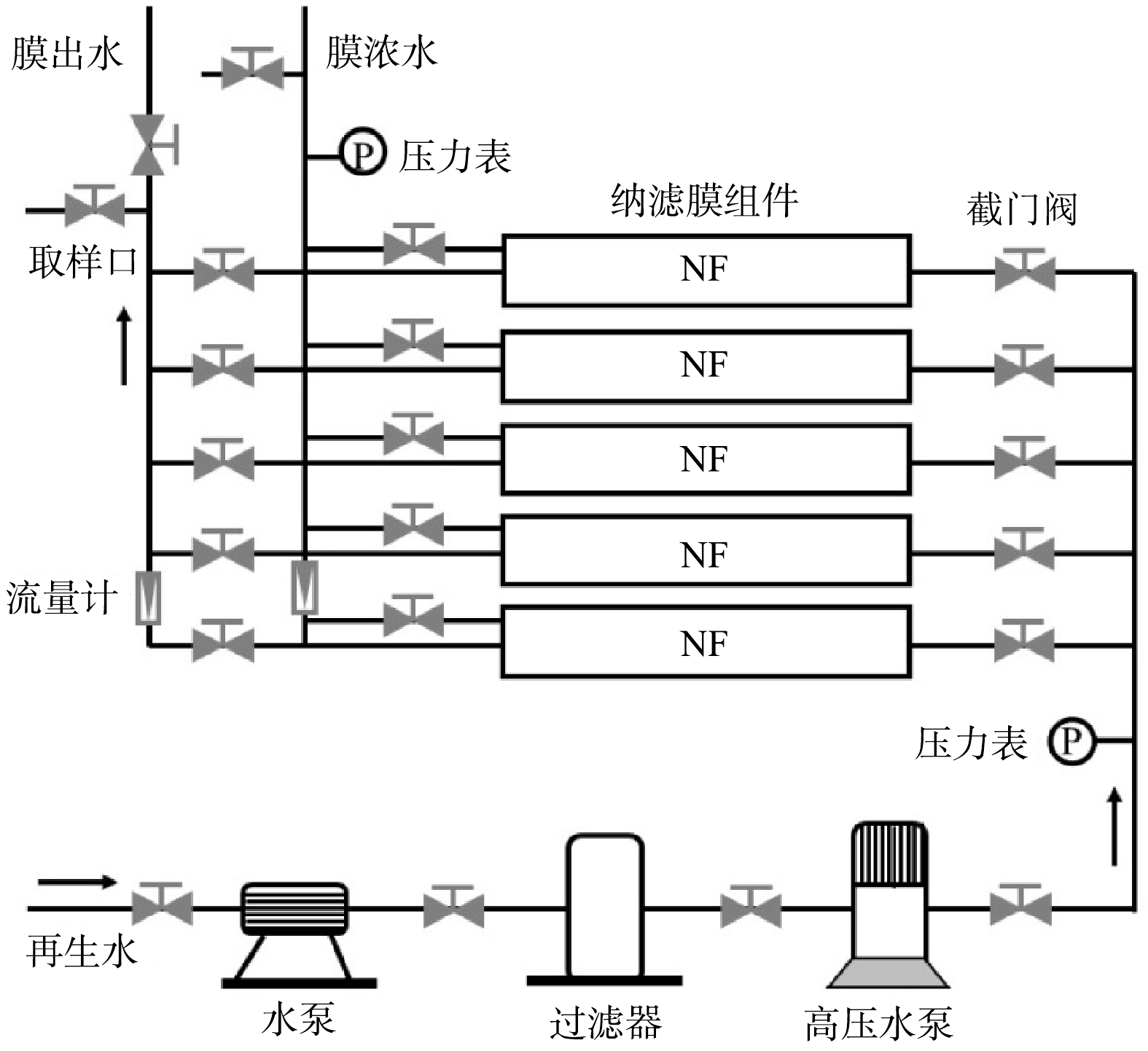
纳滤装置主要由过滤器、高压水泵、膜组件、流量计、压力表、配电箱等元件组成,其结构如图1所示。纳滤膜组件为美国海德能公司生产的ESNA1-4040系列高性能低压纳滤膜。再生水均取自北京市某再生水厂,其进水为周边的居民生活污水和工业废水。取得的实际再生水在进入膜组件之前,首先经过过滤器初步分离,以截留较大的颗粒污染物。再生水通过纳滤膜后分别形成富集较多污染物的膜浓水和较为清洁的膜出水。在实验过程中,通过调节流量计的截止阀控制产水率,即膜浓水和膜出水的比例。
-
电催化臭氧氧化处理膜浓水的反应装置如图2所示。反应器为圆柱形玻璃容器,高40 cm,直径20 cm,取10 L纳滤膜浓水置于反应玻璃容器中开展电催化臭氧氧化实验。电极为平板电极,阳极为负载二氧化锡的钛电极(Ti/SnO2),阴极为钛网电极,电极规格5×10 cm,电极间距设置为10 cm。以稳压直流电源为反应装置供电,设置电流密度10 mA·cm−2。空气通入臭氧发生器制得O3与O2混合气体,经曝气头均匀曝气后通入到反应器中,通过调节流量计设定通气流量为0.2 L·min−1,气态臭氧质量浓度8.3 mg·L−1。催化臭氧反应器顶部安装尾气排放管,通入到装有一定体积KI溶液(质量百分比为2%)的吸收瓶中,以吸收尾气中未反应的臭氧。
在单独臭氧氧化实验时,反应器中不放置电极;在单独电催化实验时,反应装置中不通入臭氧。在实验开始后的固定时刻进行取样分析。
-
电催化臭氧氧化处理膜浓水过程中毒性削减特性采用藻类生长抑制实验进行评价。实验按照《化学品-藻类生长抑制试验》标准方法(GB-T 21805-2008)进行[11],培养基为常用淡水蓝藻及绿藻培养基BG 11培养基,在正式实验之前首先对斜生栅藻母液按照标准方法进行接种培养。按照1:9的比例将斜生栅藻母液与灭菌后的培养基混合,光照培养箱的培养条件为:温度22 ℃,白色日光灯,光暗比12 h:12 h,光强3 000 lux左右。当藻类处于对数生长期(细胞浓度为1×104~2×104个·mL−1,一般培养3~5 d左右)时,按照相同的方法继续转接培养,培养至第3代时用于实验。毒性评价时,以吸光度代替藻密度进行生态毒理分析,分别取90 mL受试水样或纯水置于锥形瓶中,加入处于对数生长期的斜生栅藻培养液10 mL,分别记为实验组和空白对照组,而后将锥形瓶放入光照培养箱中,在设定好的条件下进行培养。在给定时刻测定680 nm波长下斜生栅藻的吸光度表示藻类的生长情况。
通过测定的吸光度数据计算斜生栅藻在实验期间的比生长率,以斜生栅藻的比生长率为基础,计算水样中的污染物对斜生栅藻生长的抑制率,斜生栅藻比生长率和抑制率计算公式分别如式(1)和式(2)所示。
式中:μi代表从开始到时间i时的斜生栅藻比生长率,%;Xi代表时间i时的生物量(以吸光度计);X0代表开始时的生物量(以吸光度计);Ij代表以比生长率为基础的斜生栅藻生长抑制率,%;μc代表空白组的比生长率,%;μj代表实验组的比生长率,%。
-
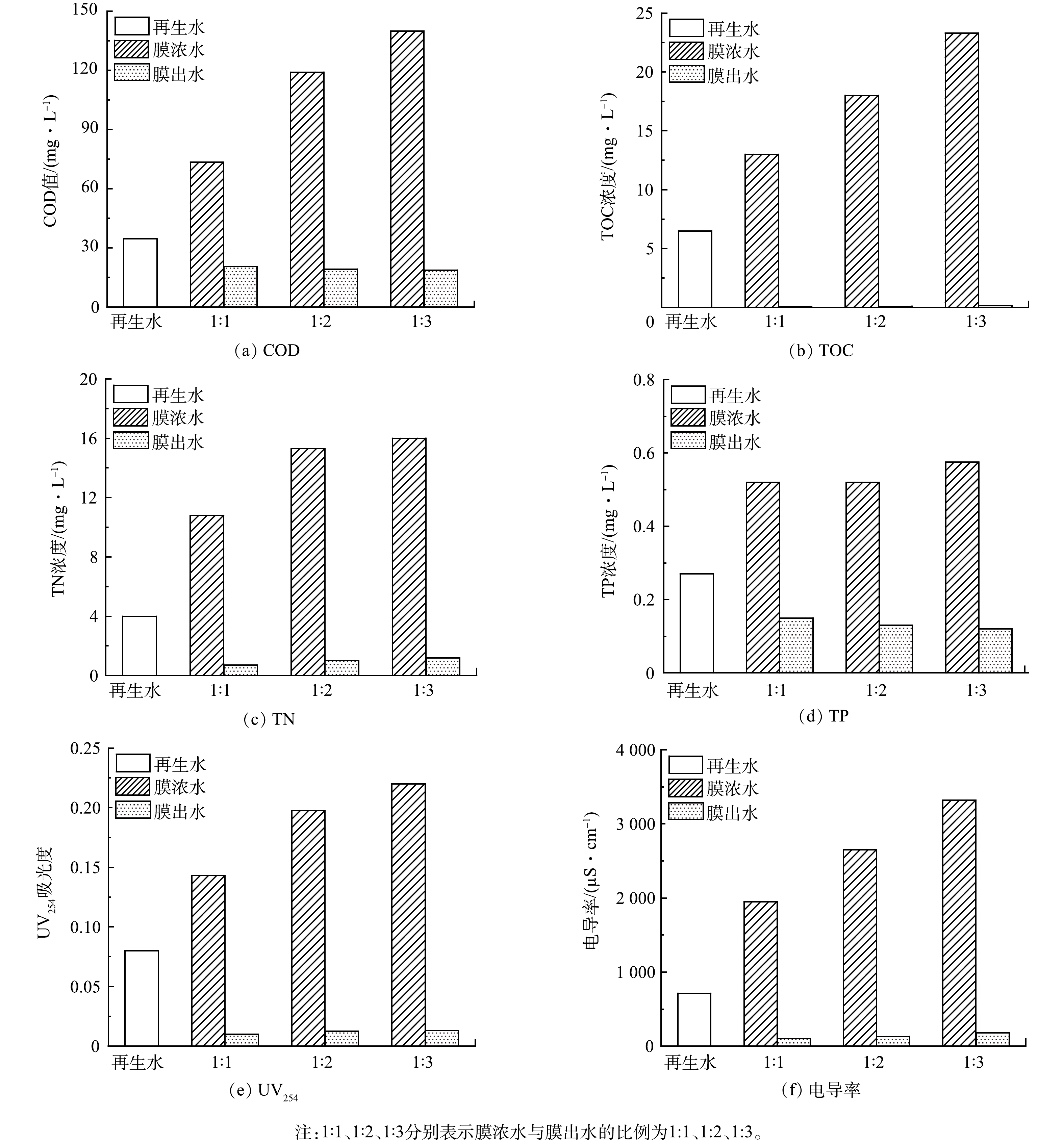
通过调节纳滤装置的流量计截止阀,将纳滤膜出水的产水率调节为50%、67%、75%,对应的膜浓水与膜出水比例分别为1:1、1:2、1:3,在装置稳定运行后取水样分析。图3所示为再生水及不同产水比例下膜出水与膜浓水的相关水质指标变化情况。可以看出,纳滤膜可以截留再生水中大部分溶解性盐类、有机污染物和无机污染物,提高再生水的品质。膜出水中相关水质指标可达到地表水环境质量标准Ⅲ类水的要求。而对应产生的膜浓水中各种水质指标明显升高,说明其富集了更多的污染物。综合考虑产水效率、出水水质和膜污染情况,以67%的产水率即膜浓水与膜出水的产水比例为1:2条件下获得的膜浓水为研究对象,进行电催化臭氧氧化处理纳滤膜浓水实验研究。
-
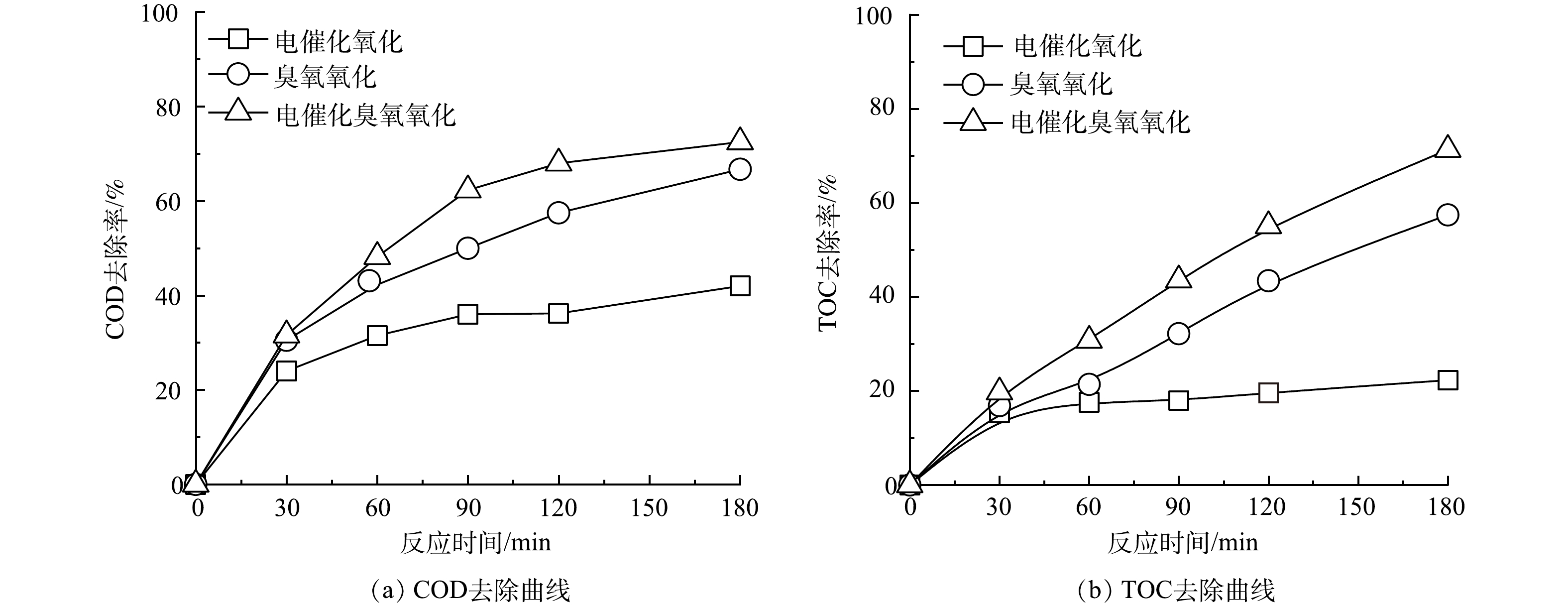
图4所示为电催化氧化、臭氧氧化和电催化臭氧氧化技术处理纳滤膜浓水过程中COD和TOC去除率变化曲线。可见,单独臭氧氧化体系反应180 min时,TOC和COD的去除率分别为67%和59%,说明臭氧氧化技术可实现膜浓水中有机污染物的有效降解,而单独的电催化氧化技术对膜浓水中的有机类污染物处理效果较差,经180 min持续氧化降解后,TOC和COD的去除率分别只有22%和42%。这可能是在设置电流密度(10 mA·cm−2)下,电催化过程中产生羟基自由基的能力较弱,因而对有机污染物的矿化降解能力有限所致。当在臭氧氧化体系中引入电催化反应后,COD和TOC的降解率大幅提高,反应180 min时可去除膜浓水中72%的COD和71%的TOC,说明电催化作用可显著提高臭氧氧化效率。
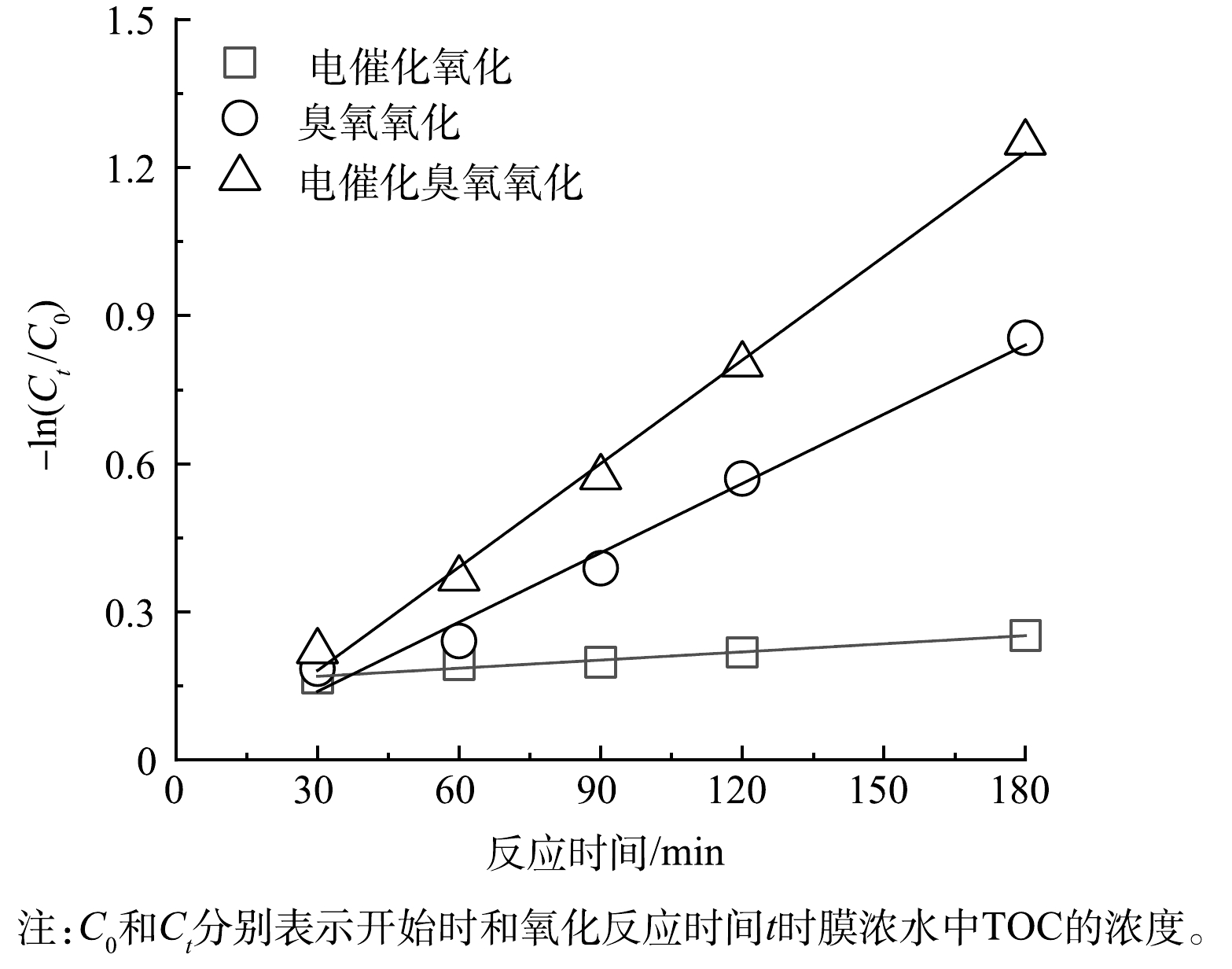
对不同氧化工艺下膜浓水TOC降解曲线进行动力学拟合(图5),发现3种工艺下膜浓水中TOC氧化降解均符合准一级动力学方程。单独电催化氧化技术的反应速率常数最低,仅0.05×10−2 min−1,单独臭氧氧化技术的反应速率达到0.47×10−2 min−1,而电催化臭氧氧化技术降解TOC的速率显著高于单独的电催化氧化技术和单独臭氧氧化技术,达到0.7×10−2 min−1,其催化降解TOC速率分别是单独电催化氧化的14倍,单独臭氧氧化的1.5倍,说明电催化臭氧氧化技术具有显著增强的膜浓水净化能力。
-
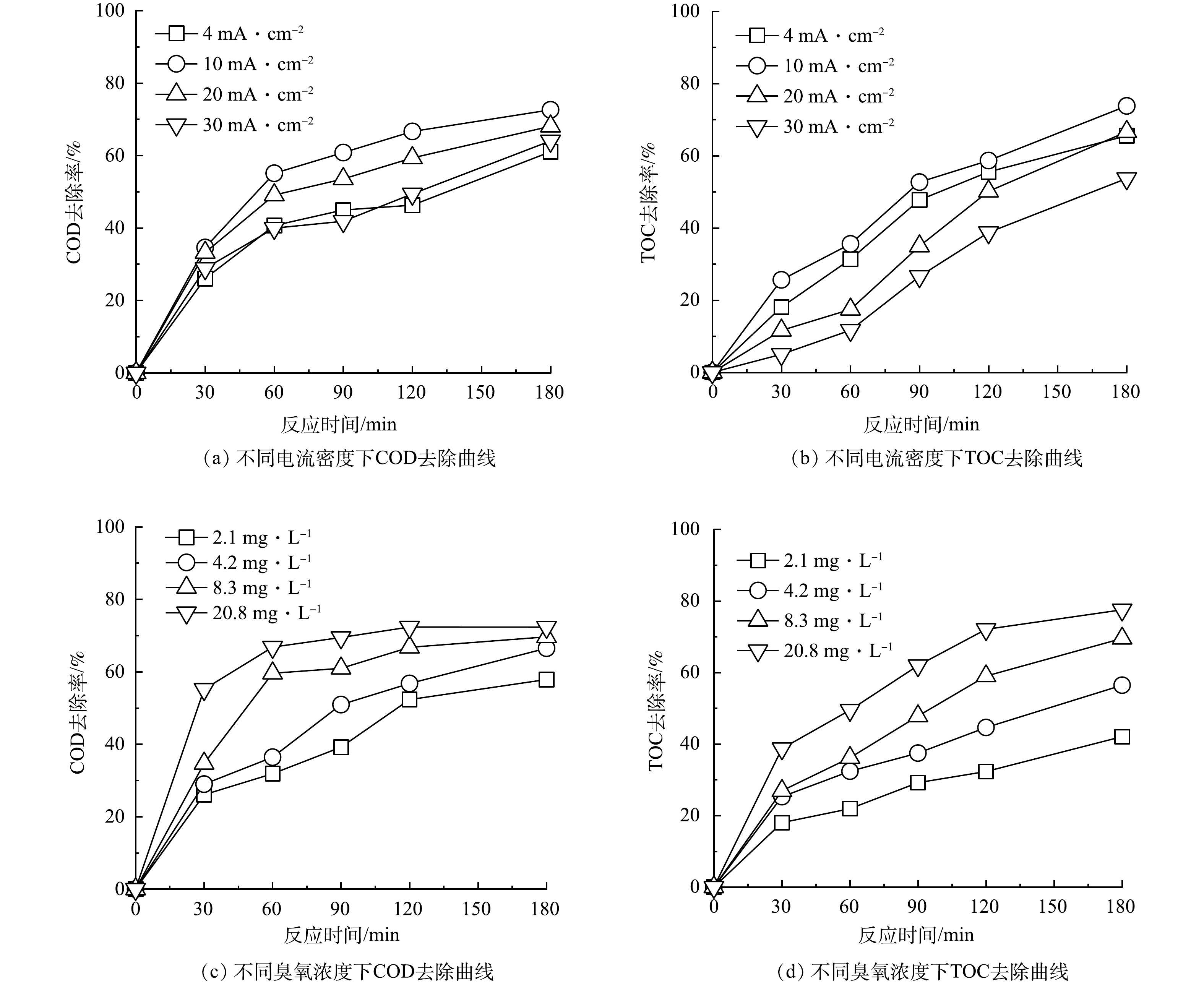
为优化电化学催化臭氧氧化工艺处理纳滤膜浓水的性能,首先考察了电流密度对膜浓水中COD、TOC去除效果的影响。分别设置了4.0、10.0、20.0、30.0 mA·cm−2电流密度,保持气相臭氧质量浓度为8.3 mg·L−1。不同电流密度下电催化臭氧氧化过程中COD、TOC的去除率变化曲线如图6(a)~(b)所示。当电流密度由4.0 mA·cm−2提升到10.0 mA·cm−2时,反应体系在180 min时的COD去除率从61%提升到了72%,TOC的去除率由65%提升到了73%。但当电流密度进一步增大到20.0 mA·cm−2和30.0 mA·cm−2时,对应的COD和TOC的去除率却出现降低,造成这种现象的原因可能是伴随着电流密度增加,施加的高偏压导致反应体系中水发生分解反应,进而降低了参与催化臭氧分解反应的电子数量,极大地影响了臭氧分解产生活性氧物种的效率[12]。
进一步通过调节臭氧发生器功率调整反应体系中气相臭氧浓度,图6(c)~(d)显示了不同臭氧浓度下电催化臭氧氧化过程中COD、TOC的去除率变化情况。随着气相臭氧浓度由2.1 mg·L−1增加至20.8 mg·L−1时,当反应结束时(180 min),电化学催化臭氧氧化反应体系对膜浓水COD的去除率由58%提升至72%,TOC的去除率从42%提升至77%,可以发现膜浓水中COD、TOC的去除率随臭氧含量的升高而逐渐升高,但其增加幅度随着臭氧浓度的升高而呈降低趋势。这是由于过高的臭氧浓度虽然可以提高活性氧物种生成数量,但反应体系内臭氧分子间发生无效碰撞的概率也明显升高,综合考虑电催化臭氧氧化工艺运行成本和效能,臭氧浓度选择为8.3 mg·L−1。
-
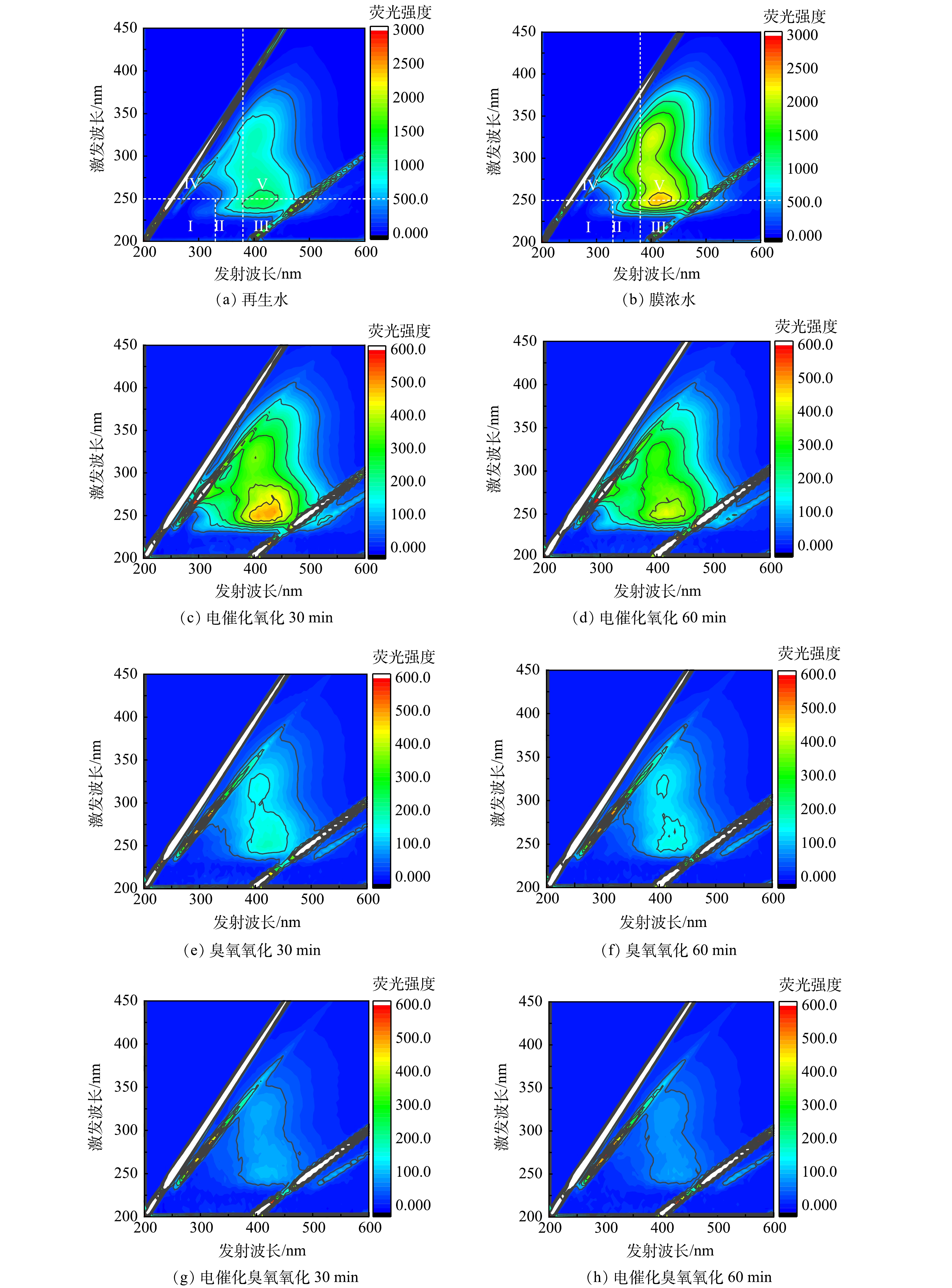
污水中代表性荧光有机污染物的最大荧光强度以及变化趋势能够表征可溶性有机污染物的含量和变化情况。图7显示了电催化氧化、臭氧氧化和电催化臭氧氧化处理纳滤膜浓水时三维荧光谱图变化情况。膜浓水中有机污染物在三维荧光谱图上主要表现为2个荧光峰,分别落在了区域III(Ex<250 nm/Em>380 nm)和区域V(Ex>250 nm/ Em>380 nm),表示主要的可溶性有机污染物为腐殖酸和富里酸类物质[13-14]。对比分析三维荧光谱图的变化趋势可以看出,臭氧氧化和电催化臭氧氧化对有机物的去除效果明显优于电催化氧化。根据膜浓水氧化处理前后荧光峰强度变化情况,经60 min降解后,臭氧氧化和电催化臭氧氧化均可去除95%以上的荧光有机污染物。
-
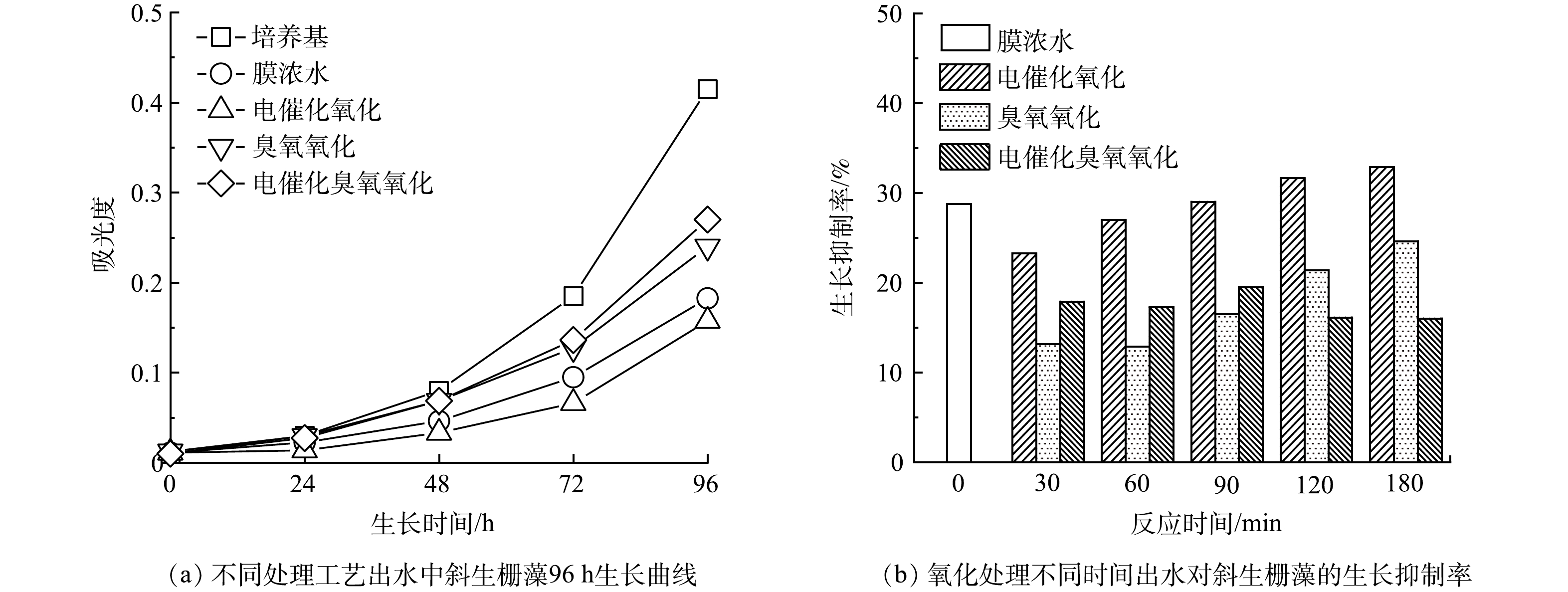
图8(a)所示是斜生栅藻在培养基中、未处理的膜浓水中以及不同氧化工艺处理180 min后的膜浓水中的生长曲线。可以看出,斜生栅藻经电催化臭氧氧化处理180 min后膜浓水中的生长繁殖状况优于单独的电催化氧化和臭氧氧化处理。与未处理的膜浓水相比,电催化氧化180 min后的膜浓水更不利于斜生栅藻的生长繁殖,造成这种状况的原因可能是有机污染物电化学氧化不彻底而产生的副产物影响了藻类的生长繁殖[15-16]。图8(b)所示为经氧化处理不同时间的膜浓水培养斜生栅藻96 h后斜生栅藻的生长抑制情况。电催化臭氧氧化技术处理后的膜浓水对斜生栅藻的生长抑制率从28.75%逐渐下降到16.0%,说明电催化臭氧氧化处理可有效降低膜浓水生态毒性。但单独的电催化氧化技术和臭氧氧化技术随着处理时间的增加,表现为对斜生栅藻的生长抑制率逐渐增大,当反应180 min时,二者对斜生栅藻的生长抑制率仍分别达32.8%和24.6%。表明电催化臭氧氧化技术不仅在处理效率上高于单独的电催化氧化和臭氧氧化,在膜浓水毒性削减效果上也更具优势。
-
1)电催化臭氧氧化可实现纳滤膜浓水的高效处理,反应180 min时可去除膜浓水中72%的COD和71%的TOC,其氧化降解TOC速率达到0.7×10−2 min−1,分别是单独电催化氧化和单独臭氧氧化的14倍和1.5倍。
2)以斜生栅藻生长抑制率评价不同氧化处理工艺对膜浓水的毒性削减效果,单独臭氧氧化对膜浓水处理后的斜生栅藻生长抑制率达24.6%,而电催化臭氧氧化深度处理后斜生栅藻生长抑制率仅16.0%,电催化臭氧氧化处理显著降低了膜浓水的生物毒性。
电催化臭氧氧化技术深度净化纳滤膜浓水
Advanced purification of nanofiltration membrane concentrated water by electrocatalytic ozonation technology
-
摘要: 纳滤膜浓水高效无害化处置是膜法污水深度处理值得关注的问题,传统臭氧氧化技术对膜浓水处置存在处理效率较低、氧化能力有限等问题。针对实际再生水深度净化工艺,构建并评估了电催化臭氧氧化技术对纳滤膜浓水净化效果。电催化臭氧氧化处理180 min可以去除膜浓水中72%的COD和71%的TOC,其一级反应速率常数是单独电催化氧化的14倍、单独臭氧氧化的1.5倍。进一步利用斜生栅藻生长抑制率指标评价了3种氧化过程对膜浓水处理时的毒性削减效果,单独臭氧氧化对膜浓水处理后的斜生栅藻生长抑制率达24.6%,而电催化臭氧氧化深度处理后斜生栅藻生长抑制率仅16.0%,电催化臭氧氧化技术处理后膜浓水的残存生物毒性显著降低。Abstract: The efficient treatment of nanofiltration membrane concentrated water is a noteworthy issue in the membrane-based wastewater treatment technologies. The traditional ozonation technology has the disadvantages such as low treatment efficiency and insufficient oxidation capacity for the treatment and disposal of membrane concentrated water. In this study, for the real process for advanced purification of the reclaimed water, the electrocatalytic ozonation technology was constructed to evaluate its performance on treating nanofiltration membrane concentrated water. Electrocatalytic ozonation could remove 72 % of COD and 71 % of TOC from membrane concentrated water after 180 min treatment. The first-order reaction rate constant was 14 times that of electrochemical oxidation alone and 1.5 times that of ozonation alone. Furthermore, the toxicity reduction performance of the three oxidation processes on membrane concentrated water treatment was evaluated by using the growth inhibition rate of Scenedesmus obliquus. The growth inhibition rate of Scenedesmus obliquus in membrane concentrated water treated by ozonation alone reached 24.6%, while the growth inhibition rate of Scenedesmus obliquus after electrocatalytic ozonation treatment was only 16.0%. The biological toxicity of membrane concentrated water treated by electrocatalytic ozonation system decreased significantly.
-
Key words:
- electrocatalytic /
- ozonation /
- reclaimed water /
- ecological risk /
- membrane concentrated water
-

-
-
[1] 张攀, 文湘华, 王波, 等. 纳滤生产再生水示范工程运行效果分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(9): 4985-4992. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201701044 [2] AGENSON K O, OH J-I, URASE T. Retention of a wide variety of organic pollutants by different nanofiltration/reverse osmosis membranes: controlling parameters of process[J]. Journal of Membrane Science. 2003, 225: 91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2003.08.006 [3] FADIL A E, VERBEK R, KYBURZ M, et al. From academia to industry: Success criteria for upscaling nanofiltration membranes for water and solvent applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science. 2023, 675: 121393. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2023.121393 [4] ZHANG X, KOIRALA R, PRAMANIK B, et al. Challenges and advancements in membrane distillation crystallization for industrial applications[J]. Environmental Research. 2023, 234: 116577. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116577 [5] 赵春霞, 顾平, 张光辉. 反渗透浓水处理现状与研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2009, 25(18): 2-5. [6] GERRITY D, GAMAGE S, HOLADY J C, et al. Pilot-scale evaluation of ozone and biological activated carbon for trace organic contaminant mitigation and disinfection[J]. Water Research. 2011, 45: 2155-2165. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.12.031 [7] WANG Y, YU G. Challenges and pitfalls in the investigation of the catalytic ozonation mechanism: A critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2022, 436: 129157. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129157 [8] YU Y H, YU C, WU Z, et al. Switching the primary mechanism from a radical to a nonradical pathway in electrocatalytic ozonation by onsite alternating anode and cathode[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2023, 457: 141340. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.141340 [9] LI Z, LI S, TANG Y, et al. Highly efficient degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid: An integrated photo-electrocatalytic ozonation and mechanism study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2020, 391: 123533. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123533 [10] 李默. 氧化-超滤工艺对污水厂二级出水有机物及生物毒性削减效能的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. [11] 潘雪梅, 邱芳芳, 王亲媛, 等. 有机改性层状双金属氢氧化物与甲基橙联合暴露对小球藻的毒性影响[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(1): 26-34. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202301004 [12] 周宇. 电增强活性炭纤维—臭氧体系去除水中硝基苯的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2016. [13] 郝瑞霞, 曹可心, 邓亦文. 城市污水处理过程中有机污染物三维荧光特性的变化规律[J]. 分析测试学报, 2007, 26(6): 789-792. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2007.06.005 [14] HALIM M, SPACCINI R, PARLANTI L, et al. Differences in fluorescence properties between humic acid and its size fractions separated by preparative HPSEC[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration. 2013, 129: 23-27. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.11.006 [15] MORADI N, VAZQUEZ C L, HERNANDEZ H G, et al. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern from the supernatant of anaerobically digested sludge by O3 and O3/H2O2: Ozone requirements, effects of the matrix, and toxicity[J]. Environmental Research. 2023, 235: 116597. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116597 [16] CUI B, FU S, HAO X, et al. Synergistic effects of simultaneous coupling ozonation and biodegradation for coking wastewater treatment: Advances in COD removal, toxic elimination, and microbial regulation[J]. Chemosphere. 2023, 318: 137956. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137956 -



 下载:
下载: