-
超磁分离技术在电镀污水、含酚污水、含油污水及铜铁污水的处理中已取得了良好效果[1-4]。该技术利用磁场作用将污染物质进行去除,在处理非磁性污染物时还需额外添加磁种,具有反应迅速、去除率高的特点[5]。此外,超磁分离技术也被尝试用于处理其他污水,如城市生活污水。在生活污水处理预处理阶段中,超磁分离技术可将大部分颗粒态基质和磷污染物去除,以降低后续生化处理段出水的水质指标(COD和磷负荷)[6]。然而,该技术也会导致后续生化池进水的C/N大大降低,不利于生物脱氮。因此,有必要对超磁分离技术的实际应用工程进行系统评估,分析其技术影响,计算建设费用和运行费用,为工艺选择、设计和投资测算提供依据。
污水生物处理工艺模拟软件BioWin(以生物模型模拟活性污泥工艺,后简称“生物模型”)经过40多年的发展,被广泛应用于实际污水处理厂的运营优化及设计优化中[7],亦是一种有效的技术评估手段。特别是在污水处理厂脱氮除磷要求提高之后,该模型开始被用于工艺最优化设计、池体尺寸设计、运行参数优化设计及制定负荷冲击应对策略中[8]。
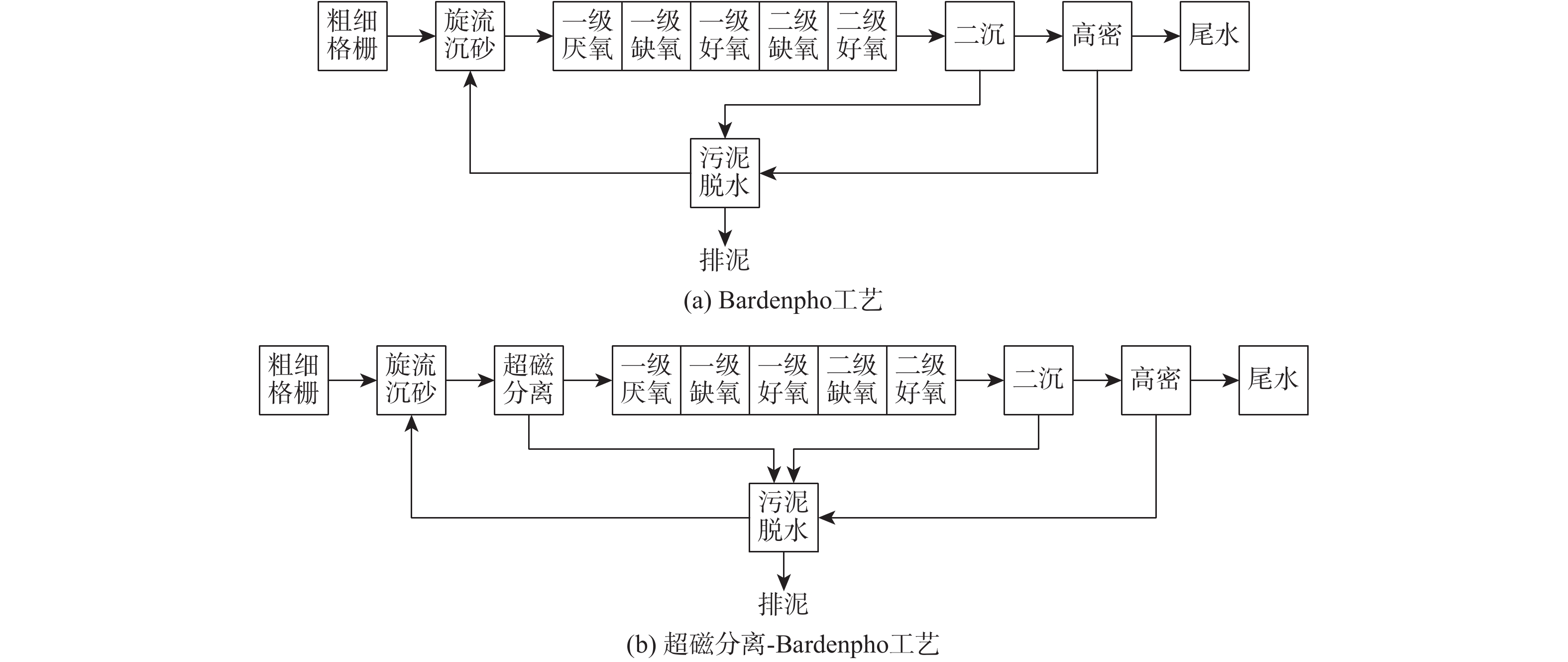
在北京某污水处理厂升级改造过程中,考虑应用超磁预处理技术。因此,本研究基于生物建模技术,评估2种工艺路线(五段Bardenpho工艺和超磁分离技术-五段Bardenpho工艺)的技术和经济有效性,以期为该厂应用超磁分离技术提供参考。
-
北京某污水处理厂出水原来执行一级A标准。现进行升级改造,改造后须执行《城镇污水处理厂水污染物排放标准》(DB11/890-2012)A标准。该污水处理厂的设计处理水量为20 000 m3·d−1。在进行工艺选择时,考虑加入超磁预处理单元以提高SS的去除,后续主体生化处理工艺采用五段Bardenpho工艺,并需定量化分析上述技术的有效性和经济性。因此,采用生物模型评估该厂是否可应用超磁分离为预处理技术。
-
超磁分离技术应用于污水处理的过程中,通常会加入磁种、混凝剂、助凝剂等。在混凝剂(如PAC)和助凝剂的作用下,小颗粒、胶体物质会脱稳形成絮体。此外,磷酸根也会与混凝剂结合形成絮体。磁粉的加入会使普通絮体变为磁絮体,并进一步实现磁絮体结合,形成磁性大颗粒,以便在磁场引力作用下,增强分离沉降作用。因此,超磁分离技术主要去除的污染物应为颗粒性物质,而磷酸根的去除则依赖于添加的混凝剂和助凝剂。
为获取生物模型构建所需进水水质参数,以该厂运行的一台超磁分离设备为研究对象,分析其进水和出水水质特征。该设备的处理规模为1 000 m3·d−1,投加药剂质量浓度为PAC 20 mg·L−1、PAM 2 mg·L−1、磁粉 100 mg·L−1、活性碳30~40 mg·L−1。实际测定超磁设备的进水和出水,并累计取样3 d,且避开雨天,均采用24 h混合取样方法进行取样。水质分析和划分方法参照荷兰STOWA准则[9-10]。水样呈弱碱性,进厂污水pH为7.7,出水7.2。进水和出水水质指标的平均值如表1所示。其中,COD和TP分别降低40%和61.7%,远高于TN和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的降低比例。设备COD/TN(C/N)由进水的3.4降低为出水的2.5,而COD/TP由28.0升高为43.9,故超磁处理不利于后续脱氮反应进行,会导致碳源更加不足。溶解性COD(CODmf)经超磁分离后,降低了25.2%。何秋杭[11]运用超磁分离技术处理生活污水时发现,CODmf降低了20%~50%。蒋长志[6]的研究表明,超磁分离技术对于COD表征的溶解性污染物的去除率达到34%。CODmf包含难降解溶解性COD和可降解溶解性COD。本研究的模型中假设超磁技术对于难降解和可降解CODmf的降低没有差异性。蒋长志[6]的研究结果表明,应用超磁分离技术处理市政污水时COD和SS分别可降低40%~70%和60%~90%。王哲晓等[12]在多个污水处理厂应用超磁分离技术的实践表明:当进水COD为203~220 mg·L−1,出水COD可降低48%~68%;当SS为156~230 mg·L−1时,出水SS可降低90%~93%。周建忠等[13]在北京朝阳某污水处理厂应用超磁技术时发现,装置进水COD、SS和TP分别为652、270和6.75 mg·L−1,出水分别降低63%、91%和92%。何秋杭[11]的研究中,超磁分离工艺出水COD降低了55%~75%。根据表1及文献数据,确定本案例中超磁分离设备的设定运行数据如表2所示。
-
运用BioWin 5.3软件(见图1)对2条工艺路线进行建模:一是Bardenpho工艺路线;二是超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺路线。由于2条工艺路线的主体生化工艺相似,故其构筑物的初始设计相同(见表3),然后对2条路线进行单独设计及运行优化。初始设计及运行条件为:构筑物总有效池容(不含二沉池)为13 744 m3,混合液回流比400%,污泥回流比100%,二沉池污泥排放量83 m3·d−1,曝气盘个数1 710,单个工作气量2.7 Nm3·h−1,PAC投加量为0,碳源投加量为0。
-
通过初始设计和运行参数进行初步模型模拟,比较2种工艺处理效果,同时探究温度对处理效果的影响(见表4)。模拟结果表明,温度几乎不影响COD、BOD5、SS等指标,而对TN、
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N略有影响,但仍可满足出水达标的要求。Bardenpho工艺出水COD为26~27 mg·L−1,不能满足京标A的要求,而超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺出水COD降为14 mg·L−1,可满足京标A(见表4)。这是由于超磁分离对CODmf有一定去除作用,在进水端即去除了部分难降解CODmf,使尾水留存的COD表征污染物的含量大大降低。然而,Bardenpho工艺和超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺出水的TN均无法达标,且超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺出水的TN高达36.2 mg·L−1。因此,超磁分离技术并不利于系统中TN,为满足达标要求,可能还需要投加昂贵的商业碳源。值得注意的是,2条工艺出水的TP均很高,Bardenpho工艺和超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺出水的TP分别为3.9~5.2 mg·L−1和2.4~2.5 mg·L−1,这可能是由于初始设计和运行参数(DO设定、剩余污泥量等)不合理所致。因此,需要优化初始参数以解决Bardenpho工艺出水COD、TP和TN的超标问题,及超磁分离-Bardenpho路线出水TP和TN的超标问题。 -
对Bardenpho工艺进行参数优化,设定温度为12 ℃。须优化的参数有曝气量、二沉池剩余污泥排放量(83、166、249和332 m3·d−1)、PAC投加量(0、676、876和 976 kg·d−1)、碳源投加量(0、4.2、4.5、9.0 t·d−1)、碳源投加位置(前缺氧池、后缺氧池、前后缺氧池均投加)、混合液回流比(200%、400%)、污泥回流比(50%、100%)等,部分情景模拟结果见表5。情景1~3为逐渐增大曝气量的情况,出水COD依然超标且脱氮除磷效果更差。由此可见,由于难降解CODmf的存在,Bardenpho工艺出水中COD表征的污染物仅靠生物降解无法实现达标排放,仍需添加三级深度处理设备。情景4~6为逐渐增大剩余污泥量,出水TP由4.2 降低至1.60 mg·L−1。尽管情景8的结果表明,降低曝气量有利于进一步提高TP去除率,但氨氮将会超标。因此,需投加一定量PAC和碳源以实现出水TP和TN达标。情景9的结果表明,PAC投加量为676 L·d−1时,可实现TP达标。情景10~19分别对碳源投加量、投加位置、内回流比、外回流比等参数进行优化,以期实现TN的达标[14]。情景10、11和14的模拟评估结果表明,碳源投加在后缺氧池更利于提升脱氮效果。崔洪升等[15]通过修正的TN模型得出,碳源投加在后缺氧池,其动力消耗低且碳源利用率高。最终结果为:当内回流比为200%、外回流比为50%、碳源投加量为4.2 t·d−1、PAC投加量为876 L·d−1时,可实现出水TN为9.2 mg·L−1、TP为0.19 mg·L−1,然而此时COD为26 mg·L−1,无法满足达标要求。
-
超磁设备的应用可大大降低进水COD,可能有利于削减好氧池的池容。为优化该参数,基于模型优化设计,其他运行参数使用初始值,设置好氧池池容削减梯度为0~80%,模拟结果见表6。结果表明,池容削减60%依然可满足降低COD和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的要求,但当池容削减量继续增加至70%和80%时,系统出水${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N出现无法达标的现象。池容削减可降低土建成本,从而降低投资成本,故建议好氧池池容削减50%。 -
在好氧池池容削减50%的基础上,进行了参数优化。优化参数包括曝气量设定、二沉池剩余污泥排放量(分别为83和166 m3·d−1)、PAC投加量(分别为0、276、376和476 kg·d−1)、碳源投加量(分别为0、5.8、6.3和 6.5 t·d−1)、混合液回流比(分别为100%、200%和400%)、污泥回流比(分别为50%和100%)等。部分情景模拟结果见表7。
情景1~2研究了曝气量对生化降解过程的影响,出水COD均小于15 mg·L−1,可满足出水水质指标要求。这是由于应用超磁分离预处理可去除难降解CODmf,有效降低出水COD。情景2~3中,逐渐增大污泥排放量,出水TP由2.38 mg·L−1降至1.64 mg·L−1,而氮的去除效果变差。因此,需投加一定的PAC和碳源以实现出水的TP和TN达标。情景4中,PAC投加量为876 L·d−1时,可实现TP达标。情景5~14为TN和TP协同达标的模拟优化,优化参数包括碳源投加量、PAC投加量、内回流比以及外回流比。根据前述的碳源投加位置优化结果,可将碳源投加在后缺氧池。
模拟结果表明,当内回流比为200%、外回流比为50%、碳源投加量为5.8 t·d−1、PAC投加量为476 L·d−1时,可实现出水TN为9.2 mg·L−1、TP为0.11 mg·L−1、COD为17 mg·L−1。运用模型的同时,对微生物群落构成进行模拟发现,与初始默认值相比,稳态时的微生物群落(普通异养菌+自养菌+除磷菌)中,普通异养菌减少了3%,占比77%,自养菌减少了11%,除磷菌增加了14%。
-
2条工艺路线的技术有效性比较结果见表8。其中,Bardenpho工艺存在出水COD超标风险,故宜增加深度处理的臭氧氧化技术单元。在实现COD和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N均达标的前提下,超磁预处理-Bardenpho工艺可削减好氧池池容50%。2条工艺的最佳内回流比和外回流比均为200%和50%。Bardenpho工艺的碳源投加量低于超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺,PAC投加量则相反。 -
分别进行了投资测算和运营测算2个方面的评估。在投资方面,2条工艺路线的差别包括超磁单元、生化池单元土建费用、用地投资、深度处理单元投资,其余构筑物认定为相同。运行方面,2条工艺路线的差别包括超磁药剂投加量、商业碳源投加量、超磁污泥处理费用、深度处理成本、污泥处理成本(含运输)及曝气和回流等工艺消耗的电费。其中,经济性评估模型中的部分参数参考生物模型优化后池容数据及确定的碳源、PAC药剂量等。
经济性评估模型的计算定额为:超磁分离单元设备费470万元、单方池容造价(含建筑材料)为941元·m3、地费为450元·m3、三级处理臭氧设备投资为183万元[16],三级处理臭氧氧化为每吨水0.21元[17]、商业碳源每吨水2 000元、PAC为每吨水1 600元、超磁投加的PAM为每吨水28 000元、超磁投加磁粉为每吨水4 000元、超磁投加活性炭为每吨水4 600元、污泥(以绝干量计)处理费为每吨水1 500元。电费计算方法为:电费0.722元·(kWh)−1,设计超磁单元功率70.53 kW,设计曝气功率180 kW。假设曝气流量和功率是线性关系,则Bardenpho工艺的曝气功率为180 kW,超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺曝气功率为144 kW,设计内回流功率30 kW,设计外回流功率44 kW。
-
基于设计水质的情景模拟结果,进行2条工艺路线的投资成本计算(见表9)。从投资成本来说,引入超磁预处理技术后,增加了超磁设备的投资,但生化池土建费用和用地成本均有所降低,且无需尾水深度处理单元。因此,粗略计算整体投资成本降低了60.1万元。
-
基于设计水质的情景模拟结果,进行2条工艺路线的运营成本计算(见表10)。从运营成本来说,引入超磁预处理技术后,虽然三级处理的PAC投加、污泥处理和尾水深度处理费用降低,但其他分项成本增加,电费差异体现在曝气和超磁耗费。引入超磁预处理技术后,运行费用每天增加0.739万元,折合每吨水成本增加0.37元。其中,商业碳源费用和超磁设备运行费用是主要增加点。故引入超磁预处理技术后,每年成本会增加270万元,远远大于投资成本降低的数额。综上所述,该厂选择五段Bardenpho工艺优于超磁分离-五段Bardenpho工艺。
-
1)生物模型可定量化比较2种工艺的技术有效性和经济性,为工艺选择提供决策支持。应用超磁预处理技术对于出水COD达标具有明显优势,但不利于生物脱氮。应用超磁预处理技术可降低投资成本,但运行成本增加,吨水增加0.37元。该厂选择五段Bardenpho工艺优于超磁分离-五段Bardenpho工艺。
2)应用生物模型可优化设计参数。基于模型模拟不同情景,可优化内外回流比、优化生物池池容、优化曝气设计、优化投加投加位点等,为设计提供技术支持。在应用超磁预处理技术后,好氧池池容较传统设计可降低50%,优化后的设计有利于降低投资成本。
3)应用生物模型可量化碳源投加量、PAC药剂投加量、曝气量、排泥量等参数,为经济型评估模型的确定提供参数支持。
基于生物模型评估超磁分离在生活污水处理厂预处理中的技术有效性及经济性
Evaluation of magnetic separation technology used in pretreatment of sewage treatment plant based on modelling
-
摘要: 在污水处理厂设计阶段,工艺的选择直接影响建设成本和运行成本。基于某污水处理厂升级改造的需求,在其方案比选阶段,采用污水生物处理工艺模拟软件(Biowin 5.3软件)比较了2种工艺(五段Bardenpho工艺与超磁预处理-五段Bardenpho工艺)的技术有效性,并通过建立经济性模型比较了2种工艺的经济性。结果表明:生物模拟软件可定量化评估待选技术的有效性和经济性,为工艺选择提供支撑;五段Bardenpho工艺在碳源用量方面占优,但尾水COD有超标风险;超磁分离-五段Bardenpho工艺在池容、曝气量方面更具优势;五段Bardenpho工艺投资成本高于超磁分离-五段Bardenpho工艺,但运行成本则相反。模拟软件评估结果表明,在污水处理厂的预处理阶段应用超磁分离技术可实现尾水COD的达标排放,有利于削减池容、降低投资成本,但不利于生物脱氮和节支降耗,每吨水的运行成本会增加0.37元,故该厂选择五段Bardenpho工艺更优。Abstract: During the design of a wastewater treatment plant, the selection of bio- process has a direct influence on the capital and operational cost s . As suc h , activated sludge modeling platform Biowin 5.3 software was employed to evaluate and compare the technical performances of the Bardenpho and magnetic separation-Bardenpho processes during the upgrade of a sewage treatment plant (STP). The economic performance of the two options is also evaluated for the comparison by an economic model. Results show that activated sludge model could quantitative compare two technologies and help decision-making. The Bardenpho process has lower carbon source consumption, but has the risk of violating the effluent discharge limit on COD. The magnetic-Bardenpho is superior in reducing tank capacity and aeration rate. The capital cost of the Bardenpho process is higher than that of the magnetic-Bardenpho process, while the operation cost is lower. The application of magnetic separation technology in pretreatment has advantages in reaching the effluent discharge standard on COD, and reducing the tank capacity and the capital cost, but it is not favorable in biological nitrogen removal and the operation cost is increased by 0.13 RMB/ton. Therefore, the Bardenpho process is selected for the case study STP.
-

-
表 1 超磁分离设备的进出水水质指标
Table 1. The characteristics of influent and effluent of the magnetic separation unit
水质指标 进厂污水/
(mg·L−1)超磁分离出水/
(mg·L−1)去除率 TCOD 131.7 79 40.0% CODmf 50.8 38 25.2% BOD5 72.5 35.2 51.4% 挥发性脂肪酸
(VFA,以COD计)7.9 6.6 16.5% TN 38.6 31.1 19.4% ${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ 29.8 29.4 1.3% DO 0.1 0.1 0.0% ${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ 1.6 1.8 6.3% ${\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ 0.3 0 100.0% TP 4.7 1.8 61.7% ${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ 1.9 0.8 57.9% TSS 54.5 28.8 47.2% VSS 47 15.5 67.0% 表 2 超磁设备的设计运行数据
Table 2. The operational results of the magnetic separation unit
水质指标 设计进水/
(mg·L−1)超磁处理后进水/
(mg·L−1)去除率/% TCOD 410 164 60 BOD5 203 112~122 40 ~ 61 SS 241 36~74 70 ~ 85 TN 72 56.7 8 ${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ 58 57.42 1 TP 8 3.12 61 ${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ 3.2 1.3 58 CODmf 158.3 110.81 30 ${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ 1.7 1.7 0 表 3 各池体的初始设计
Table 3. The volumes of treatment tanks
构筑物名称 有效体积/m3 运行参数 厌氧池 1 816 无曝气 前缺氧池 3 496 无曝气 前好氧池 6 224 700个曝气头,额定曝气 后缺氧池 1 472 101个曝气头,关闭曝气 后好氧池 736 54个曝气头,额定曝气 表 4 不同水温条件下的初始模拟外排水尾水情况
Table 4. The modelling results based on default parameters under different temperature
mg·L−1 水质指标 京标A Bardenpho工艺 超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺 12 ℃ 25 ℃ 10 ℃ 12 ℃ 25 ℃ 10 ℃ 12 ℃ 25 ℃ COD 20 20 27 27 26 14 14 14 BOD5 4 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 SS 5 5 2 2 2 1 1 1 TN 10 10 13.3 12.8 11.8 36.2 36.2 34.7 ${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ 1.5 1 0.45 0.22 0.04 0.07 0.05 0.02 TP 0.2 0.2 3.9 4.2 5.2 2.4 2.4 2.5 难降解CODmf / / 24 24 23 13 13 13 表 5 Bardenpho工艺设计参数优化情景的模拟结果
Table 5. The scenario simulation results for the optimization of the Bardenpho process
情景
编号内回
流/%外回
流/%前缺氧
池碳源/
(t·d−1)后缺氧
池碳源/
(t·d−1)PAC/
(L·d−1)排泥/
(m3·d−1)SRT/
d前好氧
池曝气/
(Nm3·d−1)后好氧
池曝气/
(Nm3·d−1)DO/
(mg·L−1)COD/
(mg·L−1)BOD5/
(mg·L−1)SS/
(mg·L−1)TN/
(mg·L−1)${{\rm{NH}}_4^ + }$
(mg·L−1)TP/
(mg·L−1)${{\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }}$
(mg·L−1)1 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 83 57.5 90 720 6 998 0.6 27 1 2 12.8 0.22 4.22 4.16 2 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 83 57.5 108 864 8 398 1.2 24 1 2 17.7 0.09 5.38 5.33 3 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 83 57.5 136 080 10 498 4.3 23 1 2 21.1 0.06 5.69 5.65 4 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 166 33.9 90 720 6 998 0.7 26 1 1 14.6 0.29 3.32 3.27 5 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 249 24.1 90 720 6 998 0.9 25 1 1 15.6 0.40 2.43 2.39 6 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 332 18.7 90 720 6 998 1.2 24 1 1 16.4 0.62 1.60 1.56 7 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 249 24.1 108 864 8 398 1.5 22 1 1 19.2 0.14 4.67 4.64 8 400 100 0.0 0.0 0 249 24.1 81 648 6 299 0.5 26 1 1 16.0 3.21 1.39 1.34 9 400 100 0.0 0.0 676 249 22.4 90 720 6 998 0.9 25 1 2 15.6 0.40 0.17 0.01 10 400 100 9.0 0.0 676 249 23.3 90 720 6 998 0.5 33 1 1 9.9 2.16 0.07 0.01 11 400 100 0.0 4.5 676 249 22.3 90 720 6 998 0.7 28 1 2 8.4 0.75 1.17 1.00 12 400 100 0.0 4.5 976 249 21.7 90 720 6 998 0.8 28 1 2 8.7 0.47 0.22 0.01 13 400 100 0.0 4.5 876 332 17.1 90 720 6 998 1.0 27 1 2 9.2 0.73 0.20 0.01 14 400 100 0.5 4.0 976 249 21.8 90 720 6 998 0.9 29 1 2 10.3 0.49 0.21 0.01 15 400 50 0.0 0.0 0 249 17.2 90 720 6 998 1.3 24 1 1 22.5 1.39 0.55 0.53 16 400 50 0.0 4.5 676 249 16.0 90 720 6 998 1.0 26 1 1 8.2 1.24 0.91 0.76 17 200 100 0.0 4.5 676 249 22.3 90 720 6 998 0.9 28 1 2 9.1 0.46 1.09 0.92 18 200 50 0.0 4.5 676 249 16.0 90 720 6 998 1.1 26 1 1 8.6 0.91 0.87 0.72 19 200 50 0.0 4.2 876 249 15.7 90 720 6 998 1.1 26 1 1 9.2 0.77 0.19 0.01 表 6 好氧池池容的优化数据
Table 6. The optimization results of the capacity of the aeration tank
情景
编号池容
削减/%模拟值/(mg·L−1) COD BOD5 SS TN ${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ TP 1 0 14 1 1 36.2 0.05 2.43 2 10 14 1 1 35.9 0.05 2.42 3 20 14 1 1 35.5 0.05 2.41 4 30 14 1 1 35.0 0.06 2.40 5 40 14 1 1 34.1 0.09 2.38 6 50 14 1 1 32.6 0.18 2.36 7 60 14 1 1 25.7 0.83 2.37 8 70 16 1 1 26.8 7.38 1.74 9 80 18 1 1 36.2 24.37 0.97 表 7 超磁分离-Bardenpho工艺设计参数优化情景模拟结果
Table 7. The scenario simulation results for the optimization of the magnetic separation-Bardenpho process
情景
编号内回
流/%外回
流/%后缺氧
池碳源/
(t·d−1)PAC/
(L·d−1)排泥/
(m3·d−1)SRT/d 前好氧
池曝气/
(Nm3·d−1)后好氧
池曝气/
(Nm3·d−1)DO/
(mg·L−1)COD/
(mg·L−1)BOD5/
(mg·L−1)SS/
(mg·L−1)TN/
(mg·L−1)${{\rm{NH}}_4^ + )}$
(mg·L−1)TP/
(mg·L−1)${{\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }}$
(mg·L−1)1 400 100 0.0 0 83 43.0 90 720 6 998 2.9 14 1 1 32.6 0.18 2.36 2.35 2 400 100 0.0 0 83 42.9 72 576 5 599 2.1 14 1 1 25.7 0.77 2.38 2.37 3 400 100 0.0 0 166 25.3 72 576 5 599 3.4 15 1 1 28.2 3.86 1.64 1.62 4 400 100 0.0 876 83 33.7 72 576 5 599 2.1 14 1 1 25.7 0.77 0.15 0.02 5 400 100 6.5 276 83 39.5 72 576 5 599 2.0 18 2 1 8.9 0.56 0.78 0.70 6 400 100 6.5 376 83 38.4 72 576 5 599 2.0 18 2 1 8.9 0.55 0.40 0.30 7 400 100 6.5 476 83 37.5 72 576 5 599 2.0 18 2 1 8.7 0.55 0.12 0.01 8 400 100 6.3 476 83 37.5 72 576 5 599 2.0 18 2 1 9.3 0.54 0.12 0.01 9 200 100 6.3 476 83 37.4 72 576 5 599 2.1 18 1 1 8.5 0.26 0.12 0.01 10 400 50 6.3 476 83 29.7 72 576 5 599 2.3 18 2 1 10.1 1.83 0.11 0.01 11 200 50 6.3 476 83 29.6 72 576 5 599 2.3 18 2 1 7.5 0.66 0.11 0.01 12 100 50 6.3 476 83 29.8 72 576 5 599 2.3 17 2 1 11.4 1.60 0.11 0.01 13 200 50 5.8 476 83 29.5 72 576 5 599 2.4 17 2 1 9.2 0.70 0.11 0.01 14 200 50 5.8 376 83 30.1 72 576 5 599 2.4 17 2 1 9.3 0.71 0.35 0.26 注:水温均为12 ℃;碳源投加量(以COD计)为230 g·L−1;PAC(以Al计)投加量为53 g·L−1;排泥指二沉池排泥;MLSS和DO指前好氧池末端。 表 8 2条工艺路线的技术有效性比较
Table 8. The comparation of the two process on technical performances
工艺条件 好氧池池容/m3 内回流比/% 外回流比/% 碳源/(t·d−1) 三级处理PAC/(L·d−1) 初始值 6 960 400 100 0 0 Bardenpho路线 6 960 200 50 4.2 876 超磁分离-Bardenpho路线 3 480 200 50 5.8 476 工艺条件 排泥/(m3·d−1) 总曝气量/(Nm3·d−1) MLSS/(mg·L−1) 曝气池DO/(mg·L-1) 尾水超标指标 初始值 83 97 718 / / / Bardenpho路线 249 97 718 3 629 1.13 COD 超磁分离-Bardenpho路线 83 78 175 3 484 2.35 无 表 9 2条工艺路线的投资成本计算结果
Table 9. The comparation of investment costs of the two processes
万元 分项 Bardenpho路线 超磁分离-Bardenpho路线 相对差 超磁设备费 0 470.0 470.0 土建费 4 313.6 3 986.1 −327.5 用地费 657.0 637.4 −19.6 尾水臭氧设备 183.0 0 −183.0 小计 5 153.6 5 093.5 −60.1 表 10 2条工艺路线的运营成本计算结果
Table 10. The comparation of operational cost s of the two processes
万元·d−1 成本项目 Bardenpho路线 超磁分离-Bardenpho路线 相对差 电费(曝气+超磁) 0.312 0.372 0.06 商业碳源 0.840 1.160 0.320 三级PAC 0.140 0.076 −0.064 超磁PAC 0 0.288 0.288 超磁磁粉 0 0.064 0.064 超磁PAM 0 0.112 0.112 超磁活性炭 0 0.184 0.184 污泥处理 0.476 0.182 −0.294 超磁污泥处理 0.000 0.489 0.489 尾水臭氧 0.420 0 −0.420 小计 2.668 2.927 0.739 -
[1] 王斌. 关于水处理磁分离技术应用与研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2018, 43(6): 108-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.06.026 [2] 陈林虎. 磁分离技术在水处理工程中的应用工艺及发展趋势[J]. 环境与发展, 2017, 29(9): 78-79. [3] 朱凯, 王琳. 加载混凝-磁分离水处理技术应用研究[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(S1): 190-192. [4] 刘艳辉, 陈明阔, 刘媛, 等. 超磁分离技术在矿井水处理中的应用[J]. 给水排水, 2015, 51(4): 55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2015.04.015 [5] 郑利兵, 佟娟, 魏源送, 等. 磁分离技术在水处理中的研究与应用进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(9): 3103-3117. [6] 蒋长志. 磁混凝优化试验研究及工艺应用分析[D]. 武汉. 华中科技大学, 2017. [7] 郝二成, 马文瑾, 刘伟岩. 数学模拟技术在污水处理厂的应用方案[J]. 净水技术, 2019, 38(5): 97-102. [8] HENZE M, GRADY L Jr., GUJER W, et al. Activated Sludge Model No. 1[M]. London: IAWPRC Publishing, 1987. [9] ROELEVELD P J, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M. Experience with guidelines for Wastewater Characterisation in The Netherlands[J]. Water Science & Technology, 2002, 45(6): 77-87. [10] HUSLSBEEK J J W, KRUIT J, ROELVEDLD P J, et al. A practical protocol for dynamic modelling of activated sludge systems[J]. Water Science & Technology, 2002, 45(6): 127-136. [11] 何秋杭. 强化磁分离污水碳源浓缩资源化技术研究[D]. 北京. 清华大学, 2018. [12] 王哲晓, 吕志国, 张勤. 超磁分离水体净化技术在水环境领域的典型应用[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(12): 34-37. [13] 周建忠, 靳云辉, 罗本福, 等. 超磁分离水体净化技术在北小河污水处理厂的应用[J]. 中国给水排水, 2012, 28(6): 78-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4602.2012.06.021 [14] 王辰辰. A2/O工艺处理城镇污水的脱氮除磷性能研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2019. [15] 崔洪升, 刘世德. 强化脱氮Bardenpho工艺碳源投加位置及内回流比的确定[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(12): 22-24. [16] PLUMLEE M H, STANFORD B D, DEBROUX J-F, et al. Costs of advanced treatment in water reclamation[J]. Ozone:Science & Engineering, 2014, 36(5). doi: 10.1080/01919512.2014.921565 [17] 赵文玉, 张逢, 胡洪营, 等. 污水再生处理臭氧氧化系统运行费用分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011, 34(9): 126-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2011.09.029 -



 下载:
下载:













































