-
随着我国经济水平的提高,城镇污水处理无论在数量还是质量上都得到了迅速发展。截至2017年12月,我国已运行污水处理厂5 006座,处理能力近1.85×108 m3 ·d−1,预计2016—2020年城镇生活污水排放量仍将保持6%的快速增长趋势[1-2]。随着人们对环境质量要求的逐渐提高,政府对城镇污水处理厂排放标准的要求也进一步提高。虽然目前部分地区出台了更加严格的地方标准,但是目前《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》 (GB 18918-2002)一级A排放标准(以下简称一级A标准)(或一级B)仍是我国大部分城镇污水处理厂执行的主要标准。由于进水水质或污水处理厂运行调控水平等原因,城镇污水处理厂出水的稳定达到标准(一级A标准)仍存在较大难度。
在城镇污水处理厂运行过程中,总氮(TN)和总磷(TP)是影响稳定达标的重要指标。氮的去除完全依靠生物代谢过程,脱氮效果受环境因素影响较多,故脱氮效果较难控制。与此相比,磷的去除可以借助化学除磷药剂,去除难度较小。因此,总氮是制约城镇污水处理厂出水稳定达标的关键指标。
本研究针对出水执行一级A排放标准的城镇污水处理厂,构建了总氮超标逻辑分析方法,借助污水处理厂全流程分析手段,应用于某城镇污水处理厂,实现了出水水质的达标排放。
全文HTML
-
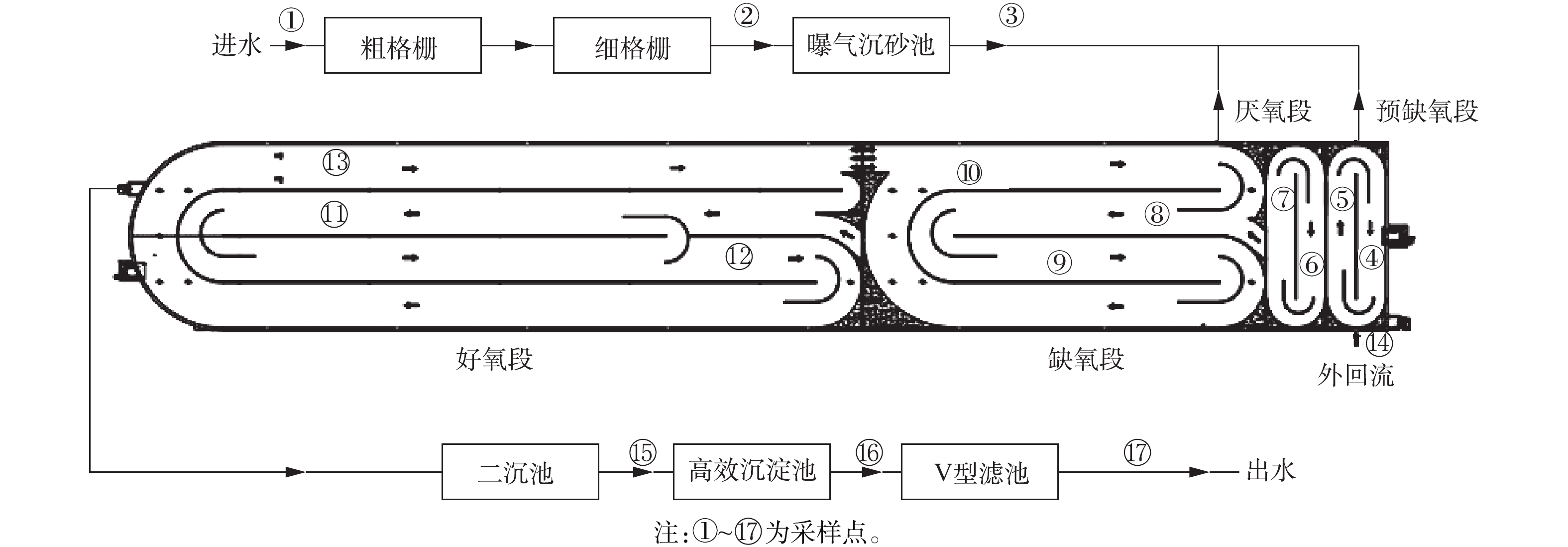
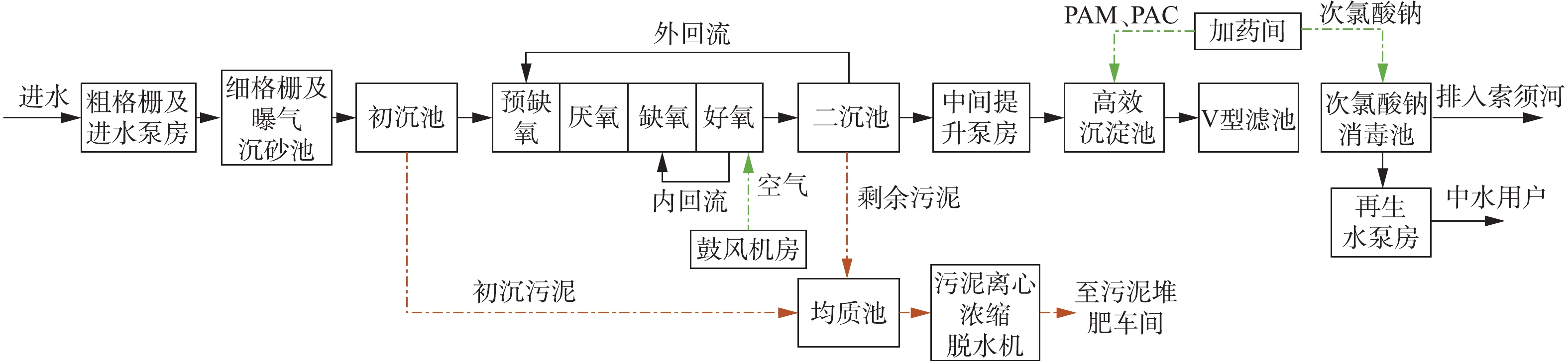
某污水处理厂设计规模为5×104 m3·d−1,实际运行进水量为4×104 m3·d−1,工艺流程如图1所示。设计出水水质执行《贾鲁河流域水污染物排放标准》(DB 41/908-2014)郑州区排放限值(以下简称贾鲁河排放标准),排放标准如表1所示。该污水处理厂自2018年3月开始调试运行,至2018年7月,出水TN仍未实现达标排放。
借助全流程分析手段,可对污水处理厂各功能单元的处理效果进行科学评估,为TN超标逻辑分析方法的应用提供重要数据,并为生物处理工艺的调整和优化提供建设性意见。此次全流程分析在该厂各单元总共设置了17个采样点,具体分布如图2所示。
-
本研究测定的水质指标包括:化学需氧量(COD)、溶解性化学需氧量(SCOD)、TN、溶解性总氮(STN)、氨氮(
${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N)、${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N、总磷(TP)、溶解性总磷(STP)、磷酸盐(${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P)、混合液悬浮固体浓度(MLSS)、混合液挥发性悬浮固体浓度(MLVSS)。上述指标采用标准方法[3] 测定。SCOD、STN和STP均为污水经0.45 μm玻璃纤维滤膜所得水样的COD、TN与TP浓度。另外,使用WTW牌便携式水质分析仪Multi 3430监测了水中pH、DO和氧化还原电位(Eh)。测定反硝化潜力时,首先,取8 L缺氧池活性污泥泥水混合液,搅拌至其溶解氧浓度为0。之后,向泥水混合液中加入1.20 g的硝酸钾,以保证初始
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度。根据实验目的加入适量无水乙酸钠2 g,分别在0、1、3、5、10、15、20、30、45、60、90和120 min取20 mL混合液,使用0.45 μm玻璃纤维滤膜过滤水样,并测定滤后水样的${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度。测定释磷潜力测试时,首先,取8 L好氧池中段活性污泥混合液,沉淀后撇去上清液,并加入蒸馏水,反复清洗3次,消除硝态氮对厌氧释磷的影响,最终保留8 L泥水混合液,搅拌并维持溶解氧浓度为0。之后,向泥水混合液中加入2 g乙酸钠,分别在0、10、20、30、40、50和60 min取20 mL混合液,使用0.45 μm玻璃纤维滤膜过滤水样,并测定滤后水样
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P浓度。
1.1. 某城镇污水处理厂基本情况
1.2. 测试方法
-
基于微生物脱氮原理及大量实际工程经验,构建了图3所示的城镇污水处理厂总氮超标逻辑分析方法。针对城镇污水处理厂出水总氮超标问题,首先须对污水厂出水总氮(TN)成分进行分析,然后对出水中
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N、${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N或不可氨化有机氮过高导致的出水TN超标进行针对性分析判断。溶解性有机氮是一类含氮化合物的总称。从生物可利用性角度看,溶解性有机氮可分为易生物降解有机氮和难生物降解有机氮,污水处理工艺对溶解性有机氮的去除效果有限[4-5]。因此,为保证污水处理厂正常生产,若发现出水有机氮突然升高,应对上游排污企业取样排放,以明确污水中有机氮的来源[6]。
出水
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度过高是城镇污水处理厂最易发现的问题。当出水${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度过高时,须先确定缺氧池末端和好氧池末端${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度,以判断是否是由于运行参数不合理引起以上问题。之后,结合实际情况,对生物系统的反硝化菌群相对丰度、水温、缺氧池DO和进水碳源条件逐一排查,最终确定造成出水${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度过高的真正原因。当城镇污水处理厂出水
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度大于11 mg·L−1时,须先确定缺氧池末端与好氧池末端${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N浓度,以此确定缺氧池反硝化效率是否达到最大。前者远小于后者,则须适当加大内回流,提高缺氧池脱氮化效率;若前者与后者相近,则说明缺氧池反硝化效果不佳。造成缺氧池反硝化效果不佳的主要原因为:活性污泥中反硝化菌群较低的丰度限制了缺氧池的脱氮效果;缺氧池内环境抑制了反硝化细菌的活性。影响反硝化细菌活性的环境因素包括水温、DO和碳源水平等[7]。反硝化潜力可反映活性污泥中微生物的活性和菌群相对丰度。若反硝化潜力较低,应检查是否存在污泥老化、污泥中毒和池底积泥现象,并采取相应措施。若反硝化潜力在正常水平,则表明环境因素是造成缺氧池脱氮不佳的主要原因,应进一步检测缺氧池内水温、DO和进水碳源条件。
通过实验可知,反硝化细菌生长的最适温度为25~35 ℃,当水温超过这一范围,则细菌活性下降明显[8-9]。若生物池水温过低(小于10 ℃),可通过投加适量碳源来提高反硝化菌活性;另外,还可通过适当加大外回流比等措施,增大单位容积内的生物量[10],以提高缺氧池脱氮效率的上限。
DO对缺氧池的反硝化反应影响较大,若缺氧池DO>0.5 mg·L−1,不利于反硝化细菌的脱氮反应,可通过适当减小内回流比、降低好氧池内回流口附近曝气量,及适当提高进水量等措施进行调节[11]。
生物脱氮反应须利用进水中的易降解有机物作为电子供体,污水处理工艺进水C/N较低会严重影响脱氮效果[12]。若进水BOD5/TN≤4,缺氧池内反硝化过程将会因有机物浓度过低而受限[13],因此,应在合适的位点采取外加优质碳源的措施,提高缺氧池脱氮效率。
城镇污水处理厂出水
${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N浓度主要受进水${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N浓度、好氧池pH和好氧池水温等因素影响。针对该问题须分别检测城镇污水处理厂进水${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N浓度、好氧池pH和好氧池水温等来排查问题。之后,通过交叉曝气实验,进一步寻找抑制好氧池硝化细菌活性的其他因素。在考察进水
${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N浓度的过程中,当城镇污水处理厂出水${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N浓度超过2 mg·L−1时,表明好氧池硝化效果不佳。应检测好氧池pH和水温,确认好氧池内微生物所处环境是否正常。硝化细菌对pH的变化较敏感,若生物池pH<6.80或pH>8.50,则应投加相应化学药剂调节pH[14-15]。若水温低于10 ℃,温度便成为限制硝化细菌硝化速率的主要原因,可通过增加外回流比、适当增大曝气量、延长SRT等措施提高硝化效率[16]。若好氧池内pH和水温均正常,则应进一步检测进水${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N浓度。若进水${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N浓度高于设计值1.5倍以上,则应适当减少进水量,以增大污水在好氧池内的停留时间,提高好氧池的脱氮效率,并排查上游高浓度${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N排放企业。若好氧池pH和水温与进水${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N浓度均正常,则应进行交叉曝气实验做进一步分析。交叉曝气实验是将出水
${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N正常的污水处理厂与目标污水处理厂的活性污泥和进水作为4个实验对象,两两配对进行的曝气实验。通过交叉曝气实验可确定好氧池是否存在DO较低、HRT不足和污泥中毒等问题[17-18]。确定好氧池存在问题后,可参考图3中提出的应对措施,制定具体解决方案,最终实现出水达标的目的。 -
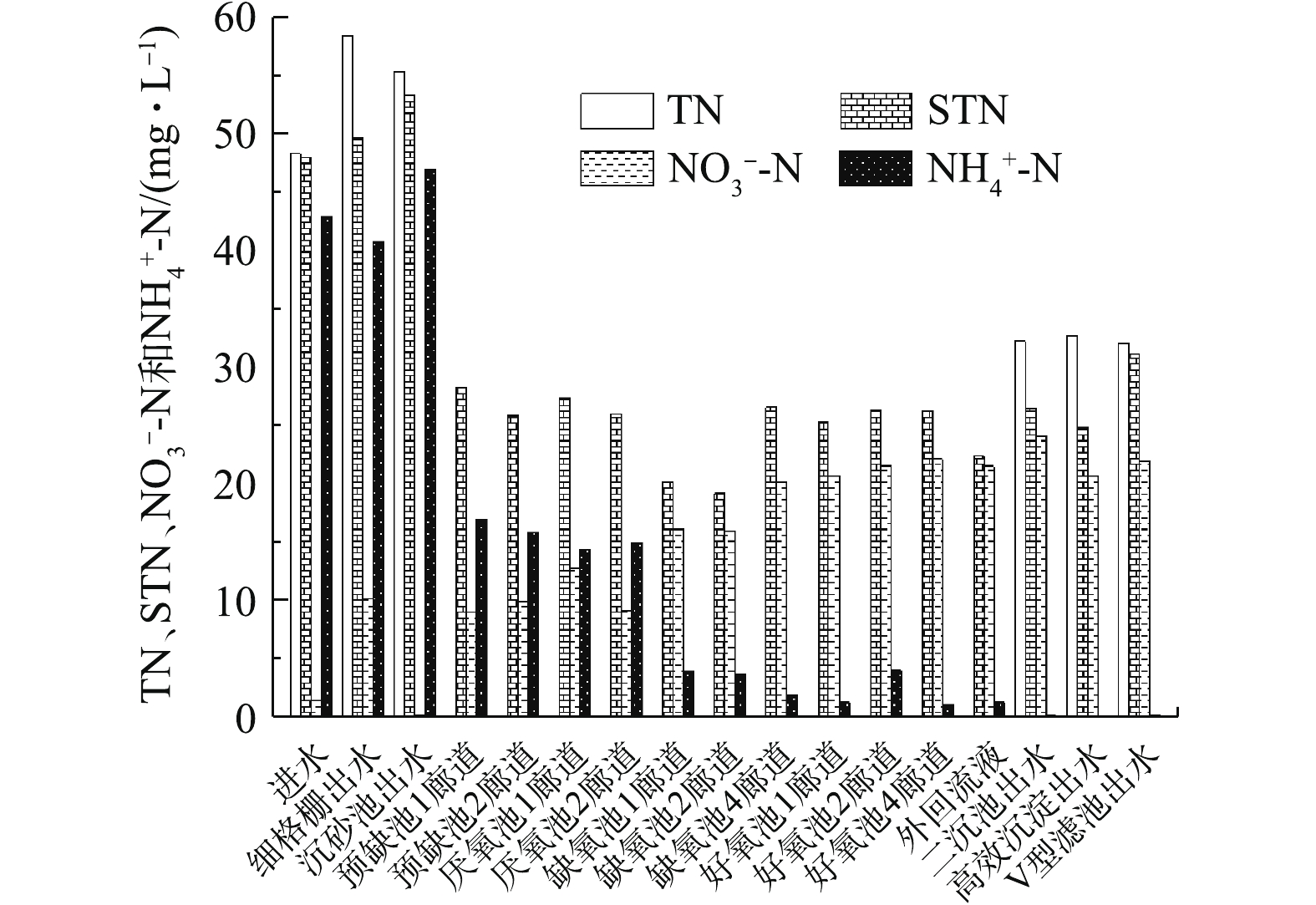
1)某城镇污水处理厂TN、
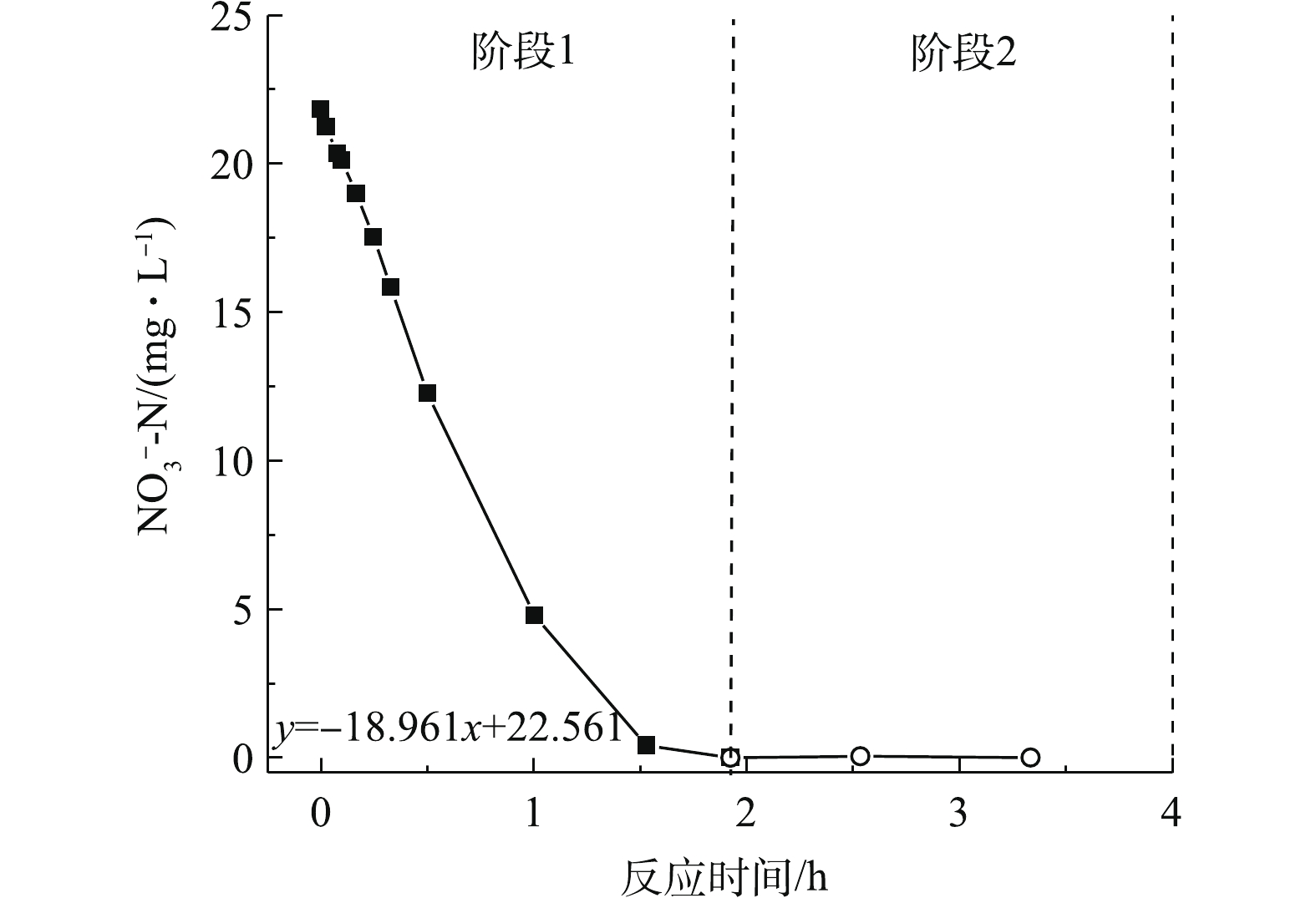
${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N和${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N的全流程分析。在图4中,进水TN浓度略高于STN和${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N浓度,${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N为0,表明该污水处理厂进水有机氮浓度较低。预缺氧池至厌氧池硝态氮浓度在8 mg·L−1以上,表明预缺氧池脱氮效果较差,不能为厌氧池内的聚磷菌提供适宜的释磷环境。缺氧池至好氧池STN浓度变化较小,该污水处理厂最终出水TN为31.04 mg·L−1,${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N为0.25 mg·L−1,表明生物系统反硝化效果较差,但硝化效果较好。该厂出水TN超标是由${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N较高造成的,因此,缺氧池并未实现良好的反硝化功能,有必要进行反硝化潜力实验,以检测该污水处理厂活性污泥中的反硝化菌群相对丰度是否在正常水平。2)某城镇污水处理厂活性污泥反硝化潜力的确定。污水处理厂活性污泥在使用进水碳源进行反硝化过程中,会受到进水pH、有机物浓度和内回流溶解氧等因素影响。通过实验模拟反硝化细菌的最适环境,可判断该厂活性污泥中的反硝化菌群相对丰度是否处于正常水平或该厂所用工艺是否还有提高脱氮率的空间。由图5和表2可知,反硝化潜力为8.96 mg·(g·h)−1。以生活污水为主的污水处理厂活性污泥反硝化潜力在8 mg·(g·h)−1左右[19],因此,该厂反硝化菌群相对丰度处于正常水平。
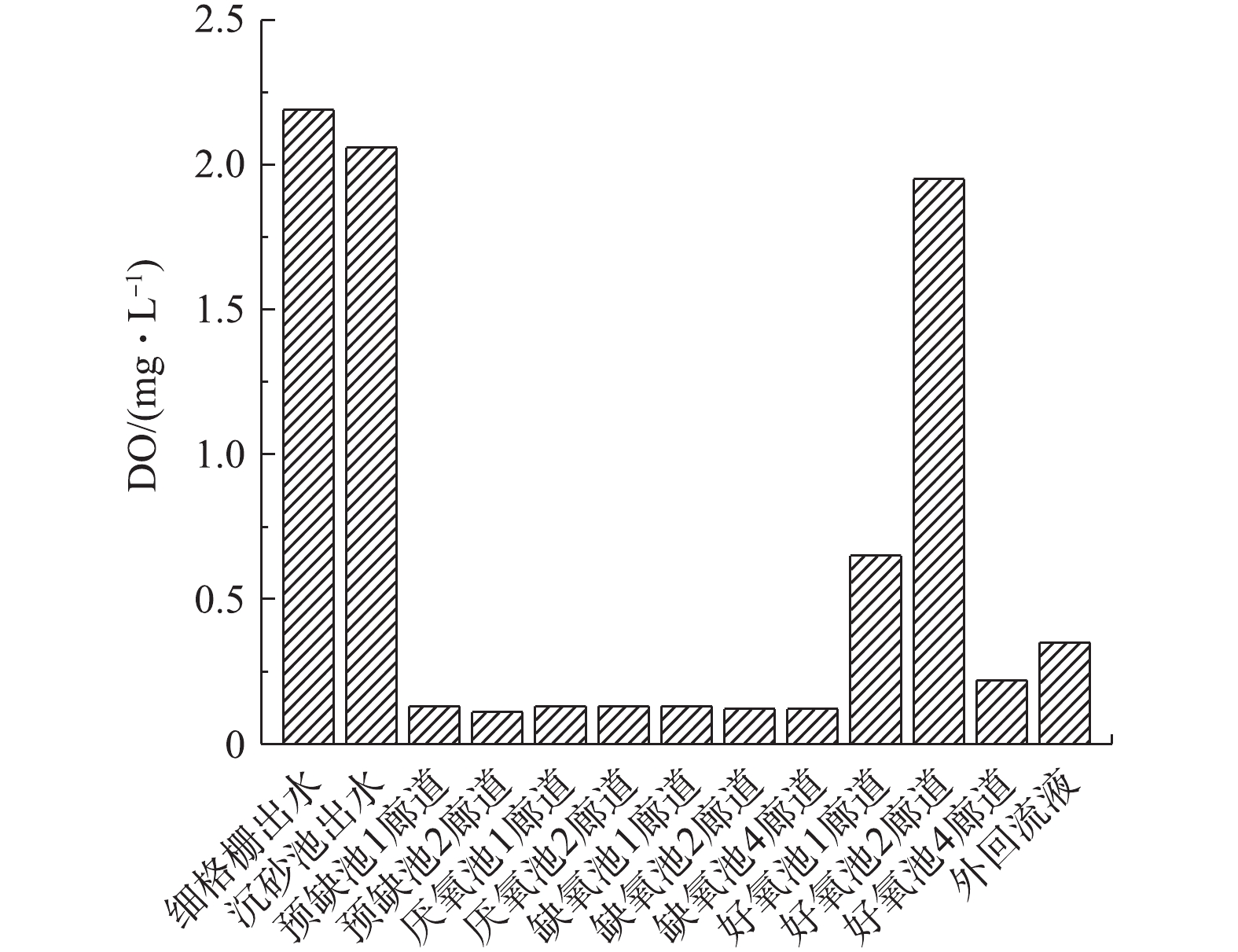
3)缺氧池反硝化条件的分析。本次实验于7月份进行,水温在25 ℃左右。由上述实验可知,水温并未对反硝化菌活性造成负面的影响。由图6可知,该污水处理厂好氧池之前的功能区DO控制良好,缺氧池DO浓度均在0.10 mg·L−1左右,具备缺氧条件。沉砂池出水DO浓度为2.06 mg·L−1,此较高的DO浓度进水会使部分易降解有机物被无效消耗,可降低后续生物脱氮的碳源利用率。
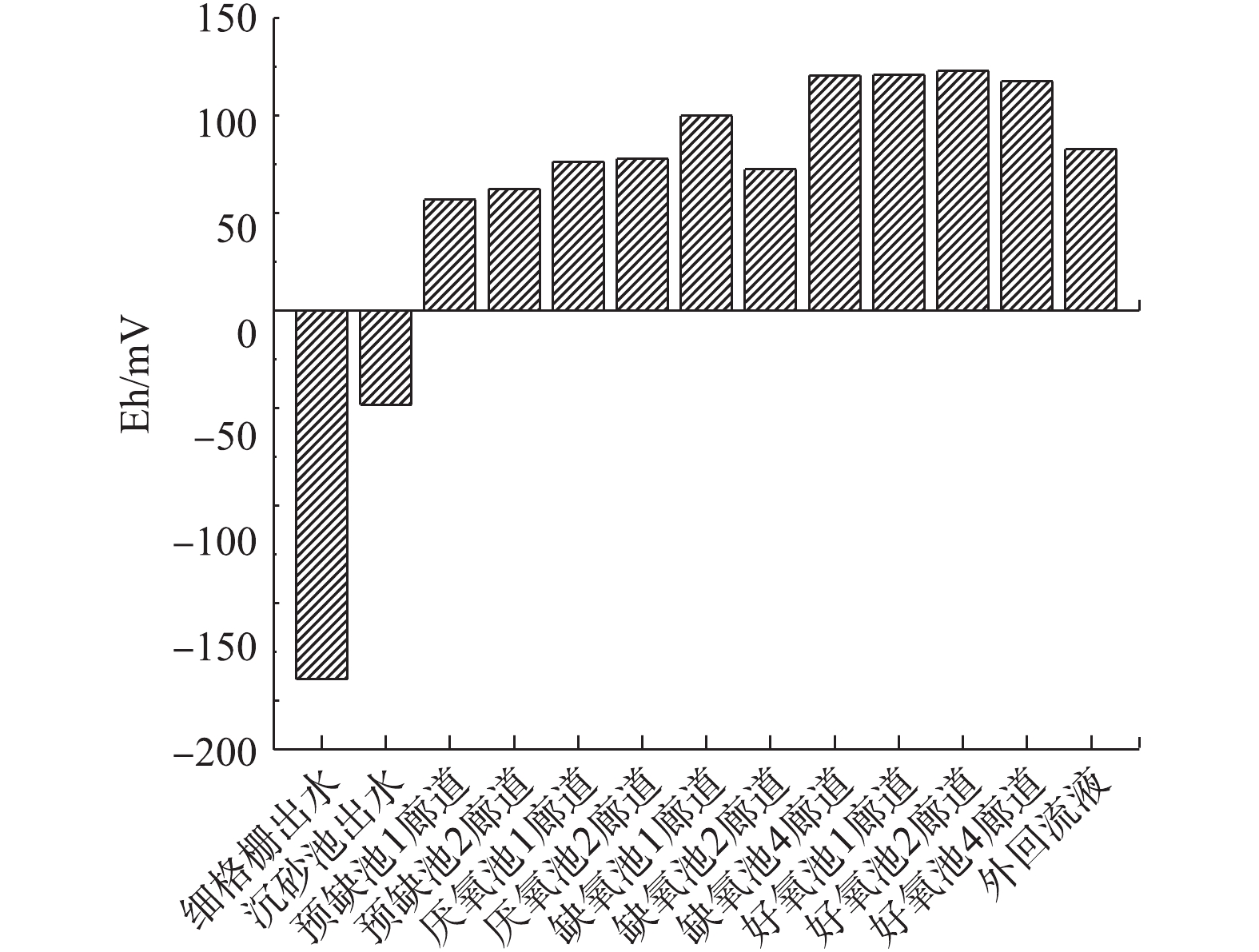
Eh是水质中一个重要指标,它用来反映水呈现出的整体宏观氧化-还原性。电位为正表示溶液显示出一定的氧化性,为负则说明溶液显示出还原性[20-21]。如图7所示,相比于细格栅出水,曝气沉砂池出水Eh升高明显,说明曝气沉砂池消耗了部分的碳源,致使水体表现出氧化性,使后续生物池可用于生物脱氮的碳源减少。
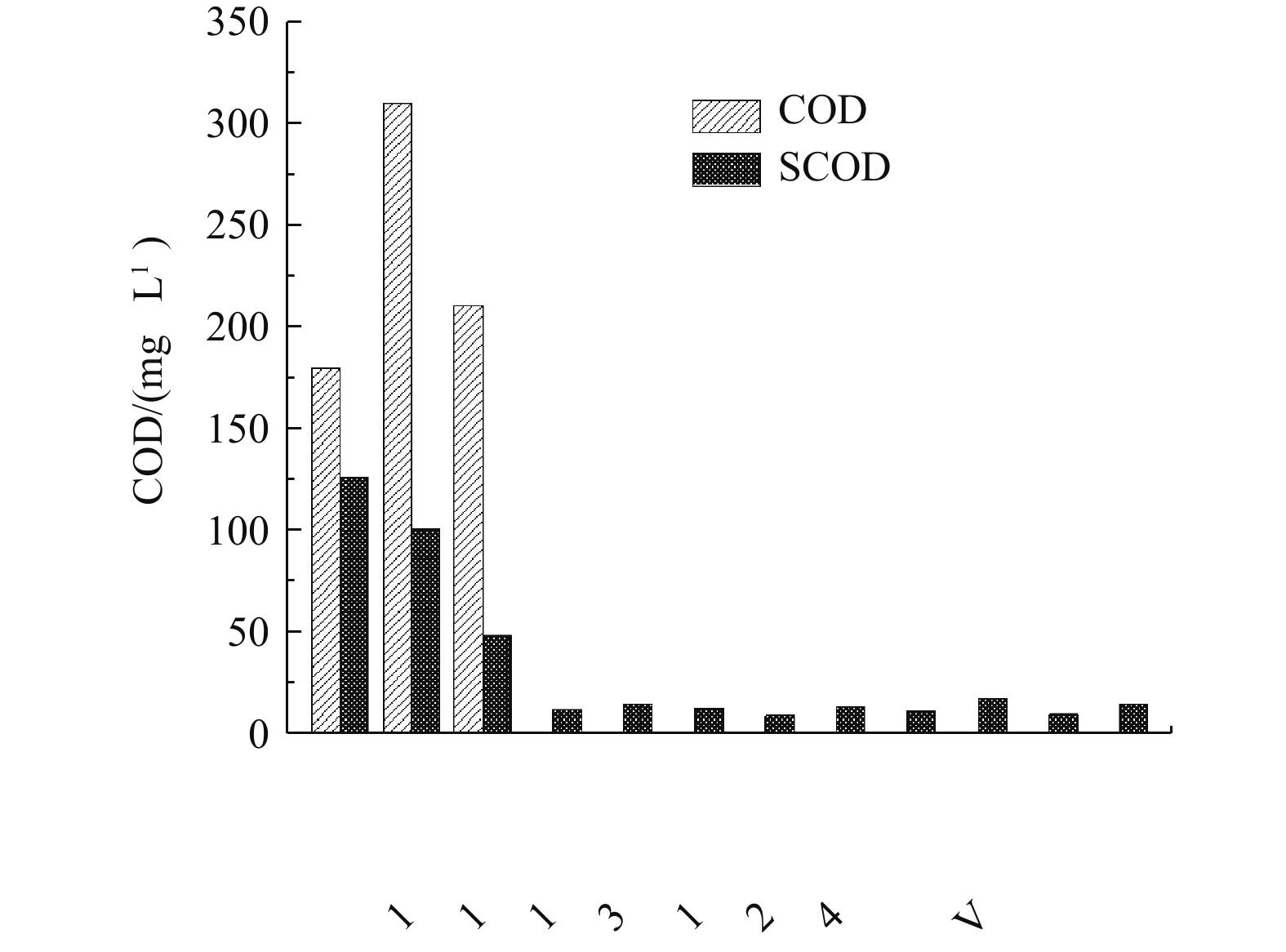
由图8可知,污水处理厂进水COD为150~300 mg·L−1,但SCOD仅为48.40 mg·L−1,故可供微生物直接利用的易降解有机物较少,属于低C/N进水。因此,在应后续生物池中,可采取碳源投加措施。在运行调试初期,该厂已对缺氧池采取了碳源投加的措施,碳源投加量为10 t·d−1,投加位点为缺氧池4廊道,但反硝化效果并不理想。考虑到缺氧池4廊道为内回流廊道,易携带溶解氧,造成碳源的无效损失,故须调整碳源投加位点。
4)优化措施及其效果。根据现有条件,该厂可以考虑采取2种方法补充后续生物段所需碳源:关闭或降低沉砂池曝气系统,使细格栅出水越过沉砂池直接进入前缺氧池;优化碳源投加位点。具体措施如下。
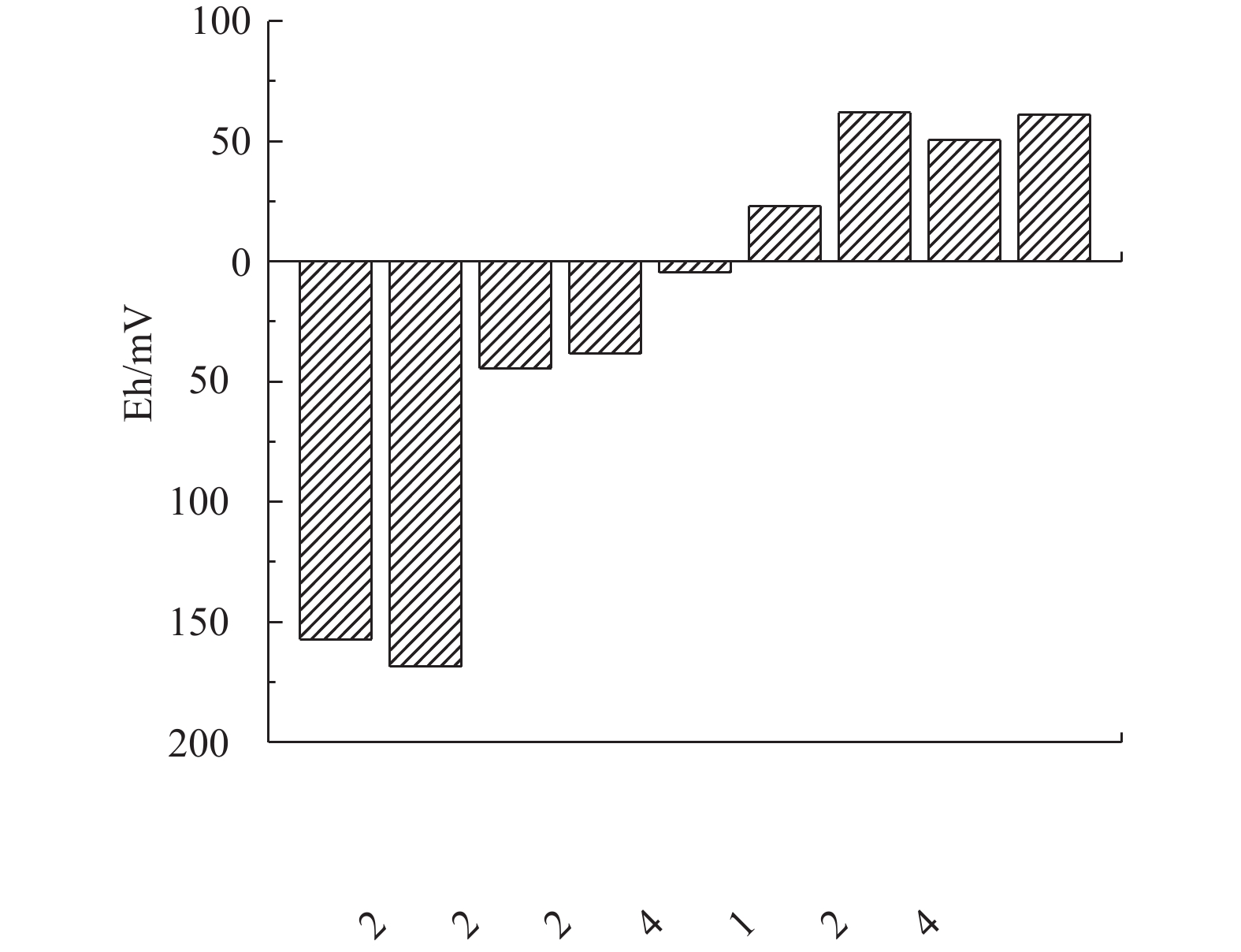
①关闭沉砂池曝气系统。本研究所依托的污水处理厂,由于沉砂池设计存在缺陷,导致沉砂池基本丧失截留进水无机颗粒和有机颗粒的能力,因此,采取了停止曝气沉砂池的措施。与图7相比,图9中前缺氧池、厌氧池、缺氧池Eh均由正值变为负值,变化幅度为101.30 mV。这表明沉砂池关闭曝气系统后有效提高了后续生物池中有机物的含量,为提高污水厂脱氮效率奠定了基础。
②优化碳源投加位点。该厂前期虽已进行碳源投加工作,但缺氧池4廊道为内回流廊道,易携带大量的溶解氧。在该位置投加碳源,反硝化菌群在与大量以氧气作为电子受体的异养微生物竞争碳源时处于劣势,因此,缺氧池脱氮效率没有显著提高。由于厌氧池的主要功能为生物释磷,若将碳源投加位点提前至厌氧池,在强化缺氧池生物脱氮效率的基础上,还可强化厌氧池生物释磷功能。
由图10可知,在采取以上优化措施后,前缺氧池与厌氧池
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N均低于0.12 mg·L−1,为厌氧释磷提供了良好的环境;其他各功能区TN浓度与图4相比,均有不同程度的降低,最终出水TN降至12.74 mg·L−1,可满足贾鲁河标准出水要求。
2.1. 出水TN超标逻辑分析方法
2.2. TN超标逻辑分析方法在污水处理厂的实际应用
-
1)通过将总氮去除原理与大量工程实践相结合,构建了以一级A排放标准为目标的污水处理厂总氮超标逻辑分析方法。该方法借助于污水处理厂全流程测试手段,分析各影响因素和生化功能区TN、
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N、${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N浓度的变化,在逐步查找原因的同时,提供了相应的解决方案,可操作性强。2)将TN超标逻辑分析方法在某污水处理厂进行实际应用,在进行出水TN成分和各功能单元COD、TN、
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N、${\rm{NH}}_4^ +$ -N、DO和Eh等指标变化情况分析、反硝化菌群相对丰度和碳源投加位点判断等一系列因素评估后,通过采取关闭沉砂池曝气系统和调整碳源投加位点的措施,最终解决了该厂出水总氮超标的问题。





 下载:
下载: