-
自1929年发现青霉素来,抗生素作为一种能够有效对抗细菌感染的药物已被广泛应用于人类和牲畜疾病的预防与治疗. Klein等[1]的研究表明,在2000年至2015年间,全球抗生素的消费量增加了65%,并且预测在没有政策干预的情况下,2030年全球抗生素消费量可能比2015年高出200%. 由抗生素大量使用诱导产生的抗生素耐药问题是人类面临的重要公共卫生挑战之一. 据估计,每年死于抗生素耐药性问题的人数高达70万,如果不采取适当的预防措施,到2050年,每年的死亡人数将接近1000万,超过癌症的死亡人数[2]. 存在于抗生素耐药菌(antibiotic resistant bacteria, ARB)中的抗生素抗性基因(antibiotic resistance genes, ARGs),作为一种新污染物,与传统污染物不同,可以通过细菌的繁殖,进行垂直基因转移(vertical gene transfer, VGT),在环境中大量扩增,也可以通过水平基因转移(horizontal gene transfer, HGT)在不同细菌间扩散,进一步诱导抗生素耐药性的产生,因而引起了广泛的关注[3-4].
覆盖地球71%表面积的海洋对人类的生存和发展具有重要意义,反过来也受到了人类活动的广泛影响,它不仅是各类陆源污染物的汇,同样也是ARGs的重要天然储库. 海洋环境中的ARGs可以存在于细菌等微生物体内,也可以在微生物死亡后释放到海水和沉积物中并长期存在[5-6]. 这些ARGs可以在海洋生物之间传播,也可以在海洋生物与人类之间传播,显然海洋介质在ARGs的传播中发挥着重要作用,但这种作用在很大程度上无法量化[6-7]. 全球约40%的人口居住在海岸线100 km2以内的沿海地区,海洋环境中ARGs的存在会对这一区域的人类健康带来前所未有的挑战[8]. 但目前人们对于海洋环境中ARGs的来源、组成和影响因素,仍缺乏系统的认识. 本研究在总结国内外最新研究的基础上,重点讨论了海洋环境中ARGs的主要来源,对比分析了不同海域ARGs的优势类型、浓度水平,以及多个影响因子对海水和沉积物中ARGs的潜在影响,探讨了海洋环境中ARGs的传播扩散路径以及潜在影响等,为深入研究和治理海洋环境ARGs污染,降低ARGs的生态和健康风险提供参考.
-
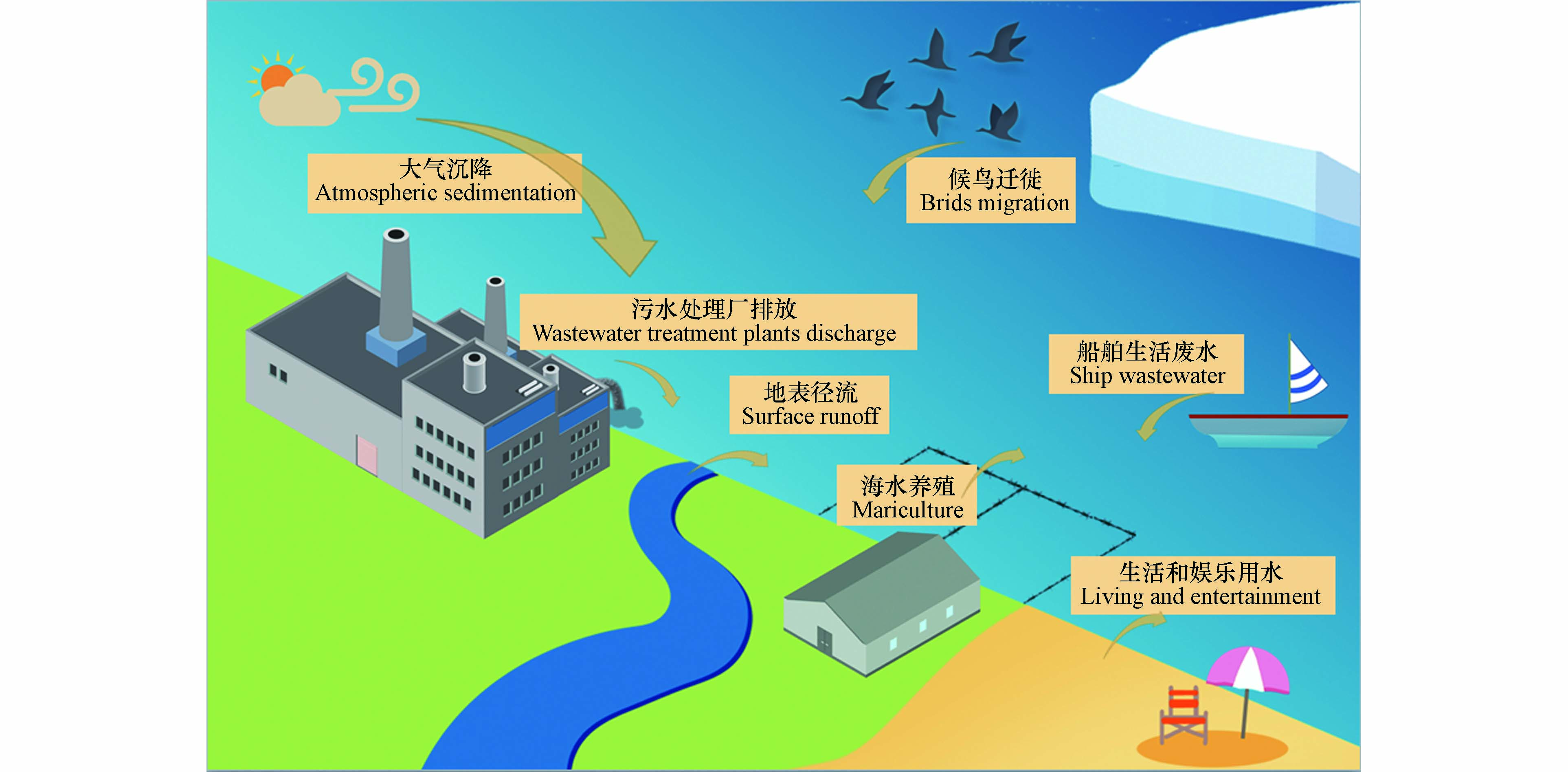
海洋环境中的污染物往往存在着复杂的来源,如污水处理厂排放、地表径流、船舶污染、人类近岸活动、大气远距离传输和候鸟迁徙等过程,这些过程给海洋环境带来了大量的污染物[9-12],其中就包括ARGs.
大多数污水处理厂的现有水处理方法不能有效地去除抗生素和ARGs,残留的抗生素和ARGs会通过污水处理厂的出水口排放到环境中,是河口和近海环境中ARGs的一大来源[13-15]. 在国内外许多海域,近海污水处理厂的废水排放是ARGs的重要来源之一. Huang等[16]的研究发现,市政污水处理厂的废水可能是福建九龙江口和闽江口的主要ARGs污染源. Makkaew等[17]的研究表明,污水直排输入会提高泰国邦盛和芭提雅海滩附近海水中ARGs的丰度. Fonti等[18]研究发现,在中亚得里亚海排放入海的废水中存在大量的ermB、qnrS、sul2和tetA等ARGs.
除此之外,地表径流也是海洋环境中ARGs的一个重要来源,人类和动物疾病治疗残留的大量抗生素和诱导产生的ARGs随着人为排放、雨水冲刷等途径直接入海或者进入河流,最终将排放到河口和近海环境中[13,19]. Dewi等[20]研究发现,澳大利亚悉尼海滩附近海水中的碳青霉素烯耐药菌很可能是通过雨水和其他淡水径流从陆源输入的. 河流排放是渤海[21]ARGs的重要来源之一,而胶州湾的ARGs则可能来自于河水和/或陆地废水排放[22].
包括近海海水养殖、居民生活、娱乐用水等的人类活动也会给海洋环境带来ARGs污染. 为了治疗和预防动物疾病,海水养殖过程中往往会投加大量的抗生素,这些抗生素将会导致海洋环境的ARGs污染[23-24]. 与自然海域相比,海水养殖场中ARGs丰度更高[25]. 在土耳其爱琴海居鲁克湾[26]进行的观测表明,水产养殖区具有更高的抗生素耐药风险. 韩国巨济附近海水中ARGs来源可能是沿海地区的港口和造船厂活动,而莞岛附近海水中ARGs的来源可能是水产养殖或农业活动[27].
候鸟尤其是海鸟在迁徙的过程中,也会携带ARGs并将其传播到更远的区域. 在美国东北部沿海水域,海鸟中分离出来的细菌的耐药性比在海洋哺乳动物中更普遍[28]. 斯瓦尔巴群岛朗伊尔城繁殖区的北极燕鸥泄殖腔内存在大量β-内酰胺类和喹诺酮类耐药菌[29]. 这些存在于海鸟体内的ARGs,将会随着海鸟的长距离迁移,传播到更远的区域.
除此之外,大气远距离传输和船舶生活污水排放等途径也将给海洋环境尤其是远洋环境带来ARGs污染,但目前仍缺乏相应的研究,人们对这些来源的贡献以及影响这些传播途径的因素知之甚少(图1).
-
对于海洋环境中微生物抗生素耐药性的检测,主要包括传统的微生物培养-药敏试验的方法和采用分子生物学技术的聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction, PCR)、定量PCR(quantitative real-time PCR, qPCR)、高通量qPCR(high-throughput qPCR, HT-qPCR)以及宏基因组检测等方法. 前者仅能检测海洋环境中可培养的ARB,而后者分析的对象则包括了可培养和不可培养的微生物,并可以进一步检测海洋环境中的ARGs,使得到的结果更为全面.
在一些早期的研究中,大多采用细菌培养-药敏试验的方法对海洋环境中细菌的耐药性进行检测[30-32]. 这种方法较为简单,且成本较低,可以检测细菌的耐药率,鉴别多重耐药菌. 其中,药敏试验部分主要包括纸片扩散法(K-B琼脂法)和稀释法,前者主要通过测量含抗生素在琼脂平板培养基上形成的抑菌环的直径,测定细菌的耐药强度;后者则是通过配置药物浓度梯度稀释的培养基,测定抗生素的最小抑菌浓度(minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC),进而得到细菌耐药强度[33].
一些研究会对得到的细菌进行进一步的DNA提取,并进行PCR检测,以进一步鉴定其中的ARGs种类[34-36]. 也有一些研究直接对海水或沉积物进行DNA提取,进一步PCR检测[37-38]. PCR检测主要是对特定DNA片段进行指数扩增,再采用琼脂糖凝胶电泳对扩增产物进行检测,以鉴别原始样品中是否存在目标DNA片段,这种检测方法耗时短、准确性强,能够定性分析海水和沉积物中的ARGs,但不能对其定量. 因此,近年来的许多研究采用了qPCR方法,对ARGs进行定量检测[39-41]. qPCR检测是在PCR检测的基础上,通过分析荧光信号在特定DNA片段指数扩增过程中的累积,对目标DNA片段进行定量的检测方法,这种方法可以更直观的表征海洋环境中ARGs组成和丰度的变化. 随着检测技术的发展,也有一些新的研究采用微滴式数字PCR(droplet digital PCR, ddPCR)[42]和HT-qPCR[43-44]对海洋环境中ARGs的组成进行分析,这些方法的灵敏度和检测效率更高.
随着测序技术的逐步发展,越来越多的研究采用了宏基因组检测的方法对海洋环境中ARGs的组成进行分析[45-47]. 宏基因组又名微生物环境基因组或环境基因组,主要是从环境中直接提取全部的DNA,并构建宏基因组文库,进行测序,更全面地识别出环境中ARGs的组成;也可通过基因克隆,构建文库进行筛选分析,发现新的ARGs[48].
-
海洋环境中的污染物既会受到附近人为污染源的强烈影响,也会随着海洋环流不断扩散,对遥远的大洋和极地产生影响,并长期存在于海水和沉积物中(图2). 因此,不同区域海水中ARGs的组成和丰度往往存在较大的差异,但总的来说,多药耐药基因,β-内酰胺类抗性基因和磺胺类抗性基因是常被检出的类型(表1).
河口和近海生态系统是陆源抗生素和ARGs入海的起点[39,49-50]. 对于印度洋附近海域,科钦河口肠外致病性大肠杆菌对β-内酰胺类抗生素氨苄西林耐药性最强(23.07%),其次是四环素(19.23%)[51]. 对于大西洋附近海域,西西里岛西北部近海地区的海水中β-内酰胺类抗性基因bla-TEM的检出率最高[38],亚得里亚海东部卡什泰拉湾的海水中β-内酰胺类抗生素耐药最强,其中检出率最高的抗性基因是bla-TEM[52],黑海近海地区海水中万古霉素类抗性基因vanB(2×10−1±1×10−1)和β-内酰胺类抗性基因bla-SHV(4×10−2±1×10−2)是相对丰度最高的ARGs[53],英吉利海峡和北海海域磺胺类抗性基因sul1占主导[54]. 在太平洋沿岸海域,泰国邦盛和芭堤雅海滩的海水中,bla-TEM在所有样品中均能检测到,磺胺类抗性基因sul1检出率为97.6%,四环素类抗性基因tetQ检出率为85.4%[17];我国通向南海的河口中,β-内酰胺类抗性基因和磺胺类抗性基因占主导[55-56];在渤海湾检出率最高的ARGs为磺胺类抗性基因sul1、sul2,β-内酰胺类抗性基因bla-TEM和四环素类抗性基因tetB,四者检出率均为100%[6]
而与近海环境相比,更开阔且受人类活动影响较小的大洋区域,ARGs的丰度相对较低. 在相对封闭的地中海,检测到的ARGs的平均相对丰度明显高于开阔的南大西洋[57]. 对于不同大洋区域,ARGs丰度也存在差异,西太平洋海水中ARGs的丰度((3.0×106±1.6×106) copies·mL−1)高于南大洋((1.7×106±1.0×106) copies·mL−1),ARGs丰度从最远的采样点到靠近陆地的采样点呈增加趋势,与人类活动或人为污染源有关[58]. 而对于同一区域,西太平洋中层和深层海水中观察到的ARGs丰度与在浅海中的差异并不显著,表明深海也是ARGs的汇[58]. 此外,在大西洋和北海的海水中,sul2基因在40年间无显著变化,但造成这一奇怪现象的原因仍不清楚[42].
极地通常被认为是脆弱且受人类影响最小的区域,但极地海洋环境中仍有ARGs的存在,不过南极海水中ARGs的丰度比地中海中低3—5个数量级,bla-TEM和tetW是地中海中最丰富的ARGs,而bla-TEM和bla-CTX-M-1是南极海域最丰富的ARGs,这种差异主要与人为污染有关. 地中海海水中ARGs的丰度更高,主要是由于受到沿岸人类活动带来的高抗生素选择压力和人类粪便污染的影响[63]. 在南极洲菲尔德斯地区,多肽、多药耐药和β-内酰胺抗性基因在海水中的含量也较为丰富.
-
与流动的海水环境相比,沉积物更具有区域稳定性,因此ARGs更倾向于在沉积物中积累,沉积物中的ARGs丰富且持久[21,60](表2),所以沉积物的再悬浮也是海水中ARGs的一种重要来源[17,49,64]. 总的来说,多药耐药基因和磺胺类抗性基因是海洋沉积物中常被检出的类型(表2和图2).
对于印度洋周边海域,在科威特附近海域沉积物中β-内酰胺类、头孢菌素类和青霉素类抗性基因被频繁检出[65],而在库奇湾、康巴特湾和阿拉伯海的沉积物中,多药耐药抗性基因的占比几乎>40%[66]. 对于太平洋周边海域,多药耐药基因是东中国海九龙江口和闽江口主要的ARGs类型[16],氨基糖苷类、多药耐药和磺胺类耐药是渤海湾西部海河河口3种最主要的耐药类型,其主要的耐药机制为抗生素失活和外排泵(共占81.4%)[43].
在大洋区域的沉积物中,情况与近海不同,ARGs的检出率和种类数目明显低于海水中. Su等[67]在西太平洋雅浦海沟的一个沉积物样品中检出了杆菌肽抗性基因,在另外两个沉积物样品中则未检出任何ARGs,而在海水样品中则检出了包括万古霉素、大环内酯和多药耐药等多种ARGs,这可能与海沟的极端深度和远离人为污染有关.
在极地海洋沉积物中也检出了ARGs. 在北极和亚北极的白令海北部区域,sul1、sul2和sul3是最普遍存在的ARGs,但其丰度与渤海湾的海河河口和其他受人类严重影响的海域相比低约2—5个数量级[68].
-
除污水处理厂的排放、地表径流、船舶污染、人类近岸活动等常见ARGs污染源的影响外,海洋环境中ARGs的组成还受到多种生物和环境因素的影响.
微生物作为ARGs的直接宿主,其群落组成会对ARGs的组成产生重要影响,但在不同区域,ARGs往往有着不同的潜在宿主. 蛭弧菌门(Bdellovibrionota)、蓝细菌(Cyanobacteria)和Margulisbacteria是西太平洋和南大洋海水中ARGs的主要潜在宿主[58]. γ‐变形菌(Gammaproteobacteria)和α-变形菌(Alphaproteobacteria)是西太平洋和深海ARGs的主要潜在宿主[70]. 而拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)和厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)与黄海沉积物中大部分ARGs正相关,可能是其潜在宿主[71]. Yang等[57]通过对Tara Oceans项目收集的全球132个海水样品中ARGs组成分析发现,海杆菌(Marinobacter)、交替单胞菌(Alteromonas)、黄杆菌(Flavobacterium)和假交替单胞菌(Pseudoalteromonas)是这些样品中ARGs的主要潜在宿主. 这种差异可能是不同区域理化因子和优势菌群的差异导致的. 与大多数化学污染物不同,ARGs不仅能够长期存在于海洋环境中,而且还能够通过VGT随着宿主的增殖进一步扩增. Li等[72]对龟山岛附近浅海热液口海水的调查显示,细菌群落和物理化学因素对ARGs的组成存在较强的共同影响,细菌群落介导的VGT过程可能对浅海生态系统中ARGs的组成存在重要影响. 此外,它们还能通过HGT作用在不同细菌之间传递,在环境中逐渐增加[73-74]. 包括质粒、转座子、整合子等在内的可移动遗传元件(Mobile Genetic Elements, MGEs)通过接合、转化、转导等方式实现HGT[75]. 许多研究都发现intI1能够促进海水和沉积物中一些基因的传递[43,58-59,76]. 例如,Na等[77]研究显示,1类整合子intI1与sul1和sul2显著相关,表明1类整合子可以促进黄海海水和沉积物中这两种抗性基因的传播. 而亚得里亚海沉积物中,具有β-内酰胺抗性的大肠杆菌菌株则与IncF质粒之间表现出显著相关[78].
此外,抗生素作为诱导产生ARGs的直接驱动力,是许多区域ARGs组成和丰度的重要影响因素. 例如,在一些海水养殖区,抗生素的浓度与一些相应ARGs丰度呈显著正相关关系[64,79]. 在厦门西溪河口和台州椒江口也发现了相同的情况[44]. 在珠江口的沉积物、北黄海的海水和渤海湾水和沉积物中,sul1和sul2都与磺胺类抗生素均呈显著正相关[56,59,77],此外,在渤海湾的海水和沉积物中,tetW与土霉素也呈显著正相关[59]. 但这种情况并非是绝对的,同样是在黄、渤海沉积物中,Lu等[60]的研究则发现,ARGs与相应抗生素间无明显相关关系. 在辽河河口海水、泰国沿海海水、香港沿岸沉积物中,抗生素浓度也与ARGs无明显相关关系[39,80-81]. 这可能与抗生素浓度和水文动力学过程对污染物的影响有关,在抗生素浓度高的养殖等区域,对ARGs存在更强的选择压力,并且海水的运动也会稀释近海水体中的抗生素和ARGs,减弱二者的相关性[39].
非抗生素污染因素也可以通过共同选择过程等影响ARGs的组成和丰度[39,82]. 越来越多的证据表明,重金属[39]、微塑料[46]、有机污染物(包括苯扎氯铵消毒剂[83]、多环芳烃(polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, PAHs)[84]、多氯联苯(polychlorinated biphenyls, PCBs)[85]、杀虫剂[86]、等离子液体[87]、纳米粒子[88]等在内的多种因素都会影响环境中ARGs的组成和丰度. Yang等[46]研究发现,与海水相比,微塑料和大塑料中ARGs和MRGs的相对丰度均较高,塑料是ARGs的重要载体. Wang等[84]研究发现,PAHs促进了海水中intI1介导的ARGs的共轭转移. Li等[50]研究发现,有机污染物PAHs、PCBs和六溴环十二烷的浓度也与ARGs丰度呈正相关,这一结果可以通过上述污染物对intI1的上调来解释. 此外,也有许多研究表明,海水和沉积物中的重金属与ARGs间存在显著正相关,这与共选择机制作用有关[39,44,50].
与淡水环境相比,海洋具有独特的物理化学性质,包括pH、盐度、营养盐和微量元素水平等,这些因素也会影响ARGs的组成. Zhang等[6]研究表明,海水中溶解氧(dissolved oxygen, DO)和sul2、bla-TEM有强负相关,DO是表示海水自净能力的重要因素,ARGs与DO呈负相关,表明海水的自净能力越低,ARGs的丰度越高,即在低氧海水环境中,ARGs具有更高的浓度. 盐度是衡量海水性质的重要指标,不同研究区域地理位置和盐度变化范围存在差异,对ARGs的影响也就不同. 在大洋海域,盐度高且变化小,而河口和近海区域盐度低且变化幅度大[58]. 在西太平洋和南大洋海水中,盐度和ARGs丰度呈正相关关系[58]. 而在太平洋海域的南海珊瑚礁海域的海水中、渤海湾海河河口沉积物中、厦门西溪河口沉积物中,以及大西洋海域英吉利海峡和北海海水中,盐度和ARGs丰度则呈现负相关关系[43-44,90]. 这可能与污水排放和地表径流对海水的冲淡有关,携带有大量ARGs的污水和河水盐度较低,但会带来大量的ARGs输入,因而导致了这种负相关关系. 与盐度类似,不同海域海水和沉积物中ARGs与不同理化因子的关系也不同. 渤海和黄海海水中ARGs的组成主要受铵盐、硝酸盐和海水盐度的影响[60]. Lu等[44]研究表明,沉积物中ARGs的相对丰度与沉积物粒径和总有机碳(total organic carbon, TOC)含量呈正相关,与沉积物pH和氧化还原电位呈负相关,其中,沉积物粒径是影响ARGs丰度的主要因子. 英吉利海峡和北海海水中sul1与DO、pH和浊度显著正相关[54]. 福建闽江口沉积物中ARGs与TOC、总氮(Total Nitrogen, TN)和总磷(total phosphorus, TP)显著正相关,而九龙江口沉积物中ARGs则与TOC显著正相关,与TN和TP显著负相关[16]. 西太平洋和渤海海水中的糖肽、三氯生、磷霉素和大环内酯-林可酰胺-链阳菌素抗性基因与亚硝酸盐、硝酸盐、叶绿素a、DO呈正相关,而糖肽、三氯生、大环内酯-林可酰胺-链阳菌素和β-内酰胺抗性基因与盐度和DO呈负相关[70]. 总的来说,TOC与海水和沉积物中ARGs呈明显正相关,而不同区域营养盐和pH则对ARGs的组成呈现不同的影响. 有机碳作为微生物尤其是异养细菌的重要营养来源,可以影响微生物群落[90-91],因而与ARGs呈明显正相关;而不同区域营养盐浓度和微生物群落组成差异较大,因此对ARGs的影响也不同.
综上所述,ARGs与环境因子和生物因素的相关性存在区域差异,可能与不同环境中这些理化因子差异较大、以及微生物的适应过程不同有关. 在复杂的海洋生态系统中,存在多种影响ARGs组成和丰度的因素,但对此仍没有一致性认识,因此需要进一步的识别和量化,并揭示相关机制.
-
海洋微生物群落是地球上最丰富、最复杂的群落之一[92],因此海洋也成了ARGs巨大的汇. 虽然海洋环境中ARGs的污染目前可能是局部性的,但其后果具有全球相关性,这些首先存在于局域环境中的ARGs可以通过海洋环流运输、海鲜运输和消费、旅游等过程扩大污染范围,对公共卫生、生态系统功能和动物疾病防治等造成严重危害[93].
首先,沿海地区会受到ARGs污染,并给附近生活的人类造成健康威胁. 例如,公共海滩是潜在ARGs污染源,这些区域的休闲海水、沉积物和沙子中存在的ARGs会给海滩使用者带来潜在的健康风险[17,30,36,94-95]. 在大连的傅家庄海水浴场,海水中检出了多种抗生素耐药大肠杆菌,其中38%(26/69)的菌株对至少一种抗生素具有耐药性[96]. 在巴西的海滩,休闲水域的海水和沙子中,也检测出了多种ARGs[97].
其次,海洋环境中的ARGs可以通过洋流输送到遥远的地区,构成全球风险,最终对人类健康构成威胁. 例如,极地区域和深海中也检出了多种ARGs[47,63,70]. Tan等[68]研究发现,北极/亚北极区域存在多种ARGs,这些ARGs与人类特异性分子标记物显著相关,这意味着极地区域已受到人为源ARGs的污染,而这些人为源ARGs很可能是通过海洋环流等过程传输而来的. 除此之外,陆源ARGs可以通过大气传输影响海洋,而海洋环境中的ARGs也可以通过海-气交换进入大气环境,并通过大气长距离运输,进一步传播到更远的地区. 候鸟迁徙也是ARGs从海洋环境向外扩散的一个重要途径,多项研究表明,海鸟胃肠道和粪便中存在多种ARB和ARGs,它们即是环境中的被感染对象也是潜在的传播源[98-100].
此外,海水养殖设施对海水和沉积物中ARGs的积累和传播也具有重要作用. 随着海水养殖业的快速发展,使得大量投加抗生素治疗养殖生物的细菌感染等疾病成为了常态,这带来了大量的抗生素残留,而鱼、虾等海产品则会从海水养殖环境中摄取这些ARGs,并进一步通过食物链威胁人类健康[101-103]. 在不同国家的多种海产品中均检出了ARGs[104-106]. 例如,在印度孟买零售市场销售的海鲜中分离出了大肠杆菌,71.58%的菌株能够产生超广谱β-内酰胺酶[107]. 在中国12个沿海地区采集的虾的内脏中也检测到了114种ARGs,其中主要为多药耐药抗性基因(21.05%),其次是四环素类抗性基因(17.54%)[108]. 可见,这些存在于海水养殖环境及水产品中ARGs将会通过食用等途径,给人类健康带来风险.
-
抗生素耐药性问题是一个全球性的公共卫生问题,也是整个世界,尤其是发展中国家面临的一个亟待解决的重要问题. 而海洋环境作为人类活动产生的污染物的重要归宿,也是ARGs的一个天然储库. 海洋环境中存在着多种ARGs,但目前关于海洋环境中ARGs种类组成和传播途径的相关研究较少,对ARGs的归趋及其影响因素还缺乏系统的认识,对海水和沉积物中ARGs的扩散机制仍有待进一步探索.
因此,建议在以下4个方面强化研究,以深入认识海洋环境中的ARGs污染过程及防控措施:(1)开展各个海域、各种模式下海洋环境中ARGs的来源、组成和丰度的相关研究,深入解析不同人为源和自然源对海洋环境ARGs的贡献. (2)丰富海洋环境中ARGs的相关数据,建立海洋ARGs污染数据库,调查抗生素污染以及由此引发的ARGs对海洋微生物的长期和短期影响,并建立和完善海洋环境中ARGs的生态风险和人类健康风险评价指标体系,研发近海海洋环境ARGs污染基准,为制定相应环境标准、规范海水养殖和近海污水处理排放提供理论依据. (3)深入探究海洋环境中各类理化因子和污染物对ARGs的选择压力及机制,研究海洋环境中ARGs的降解机制,明确ARGs与海洋微生物群落之间的关系,细化海洋生态系统中ARGs的环境行为,从而制定相应策略,以期遏制ARGs在海洋环境中的扩散. (4)明确海洋环境中ARGs扩散和传播的分子机制,基于基因组学、大数据分析和数值模型,预测海洋环境介质中ARGs的变化趋势.
海洋环境中抗生素抗性基因研究进展
Antibiotic resistance genes in marine environment – A review
-
摘要: 抗生素抗性基因(antibiotic resistance genes,ARGs)作为一种危害人类和生物健康的新污染物,已成为21世纪人们面临的重大挑战之一. 海洋是人类活动产生的ARGs的潜在储库,但目前人们对海洋环境中ARGs的来源、污染水平、传播路径、健康影响等的认知较为缺乏,相关研究尚处于起步阶段. 本文在总结国内外最新研究的基础上,综述了国内外海洋环境中ARGs的研究进展,重点探讨了海洋环境中ARGs的来源、不同海域ARGs的污染现状、环境因素对海水和沉积物中ARGs组成的影响等,并进一步分析了海洋环境中ARGs的潜在生态和健康风险,以期为未来海洋环境中ARGs污染的相关研究和监管提供参考.Abstract: Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) have been identified as emerging pollutants that endanger human and animal health. In fact, ARGs have been listed as one of the major environmental and health challenges in the 21st century. The ocean acts as an important reservoir of ARGs, but knowledge gaps remain there, e.g., what are these ARGs’ sources and how they come there? how about their pollution levels, and health risks? This study reviews the studies of ARGs in marine environments of China and international hot studies on marine ARGs and focuses on four topics. The topics include the sources of marine ARGs, the abundances of ARGs in various oceanic zones, the composition of ARGs in seawater and sediments related to environmental factors, potential ecological and health risks of ARGs in marine environments. This study aims to service future studies of marine ARGs and policies making.
-
Key words:
- marine environment /
- antibiotic resistance genes /
- antimicrobial resistance /
- seawater /
- sediment.
-

-
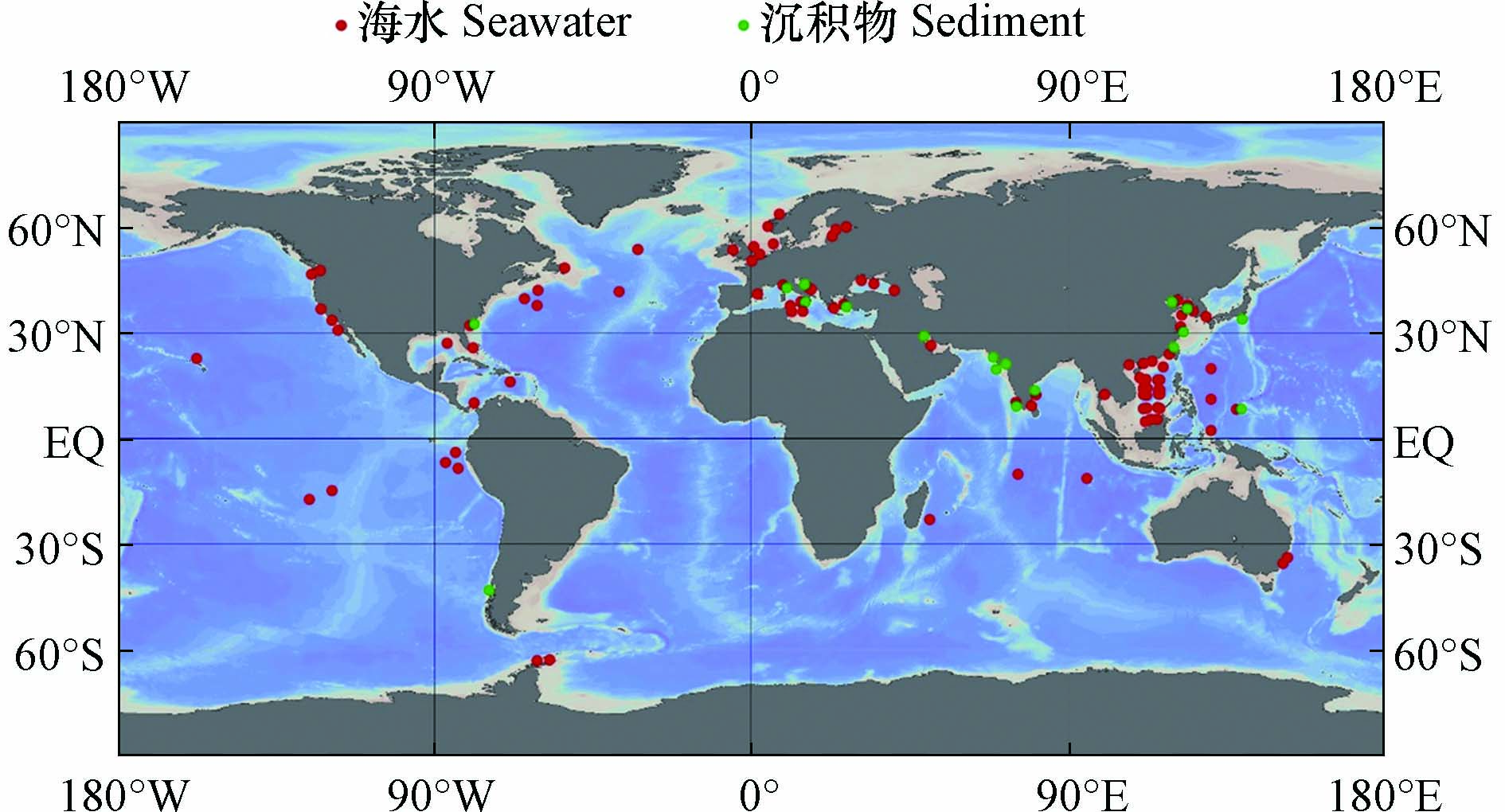
图 2 海水和沉积物中ARGs的相关研究(采用Ocean Data View[69]绘制)
Figure 2. Researches of ARGs in seawater and sediments (Draw with Ocean Data View)
表 1 不同海域海水中的ARGs的丰度
Table 1. Abundance of ARGs in seawater of different areas
海域
Sea area研究时间
Time研究方法
MethodARGs 相对丰度
(16S rRNA−1)
Relative abundance绝对丰度
Absolute abundance参考文献
Reference中国渤海湾 2015.07.12 qPCR tetM 5.15×10−5 [59] sul 10−5—10−3 泰国邦盛和芭堤雅海滩 2018.12,
2019.02—2019.08qPCR bla-TEM 2.08—4.12 lg copies·100 mL−1 [17] 中国黄海和渤海 2018.08.18—
2018.09.07qPCR sul1, sul2, tetB, tetG, tetX, ermF, ermT, qnrA, qnrB, qnrS 21.1—8.00×103 copies·mL−1 [60] 西太平洋和南大洋 2019.10.31—
2019.12.04qPCR tetA, tetB, tetBP, tetD, tetZ, sul1, ermB, blaTEM, qnrD, oqxA (3.0×106±1.6×106) copies·mL−1 [58] 爱尔兰海 2018.09—2019.10 qPCR bla-TEM 2.6×103—6.3×103 GC·100 mL−1 [41] sul1 3.7×102—4.8×103 GC·100 mL−1 黑海 2019.07—08 qPCR vanB 2×10−1±1×10−1 [53] bla-SHV 4×10−2±1×10−2 bla-CMY 1×10−2±3×10−3 mcr-1 3×10−2±2×10−2 ermB 1×10−3±5×10−4 vanA 1×10−5±5×10−4 悉尼港河口玫瑰湾 2019.08—09 qPCR sul1 (7.96×101±2.16×102) copies·100 mL−1 [61] qnrS (1.38×103±3.23×103) copies·100 mL−1 tetA (9.98×103±3.03×103) copies·100 mL−1
(2.87×105±2.50×105) copies·100 mL−1波罗的海 2008.08,
2009.09qPCR tetB 1.8×102—7.3×102 copies·L−1 [62] bla-SHV 2.5×102—1.0×103 copies·L−1 ermB 5.0×101—3.0×102 copies·L−1 tetM 4.2×101—7.8×103 copies·L−1 sul1 2.5×101—1.7×104 copies·L−1 英吉利海峡和北海海域 2020.01 qPCR tetA 2.24 lg copies·mL−1 [54] sul1 1.52—3.55 lg copies·mL−1 表 2 不同海域沉积物中的ARGs丰度
Table 2. Abundance of ARGs in sediment of different areas
海域
Sea area研究时间
Time研究方法
MethodARGs 相对丰度(16S rRNA−1)
Relative abundance绝对丰度(copies·g−1)
Absolute abundance参考文献
Reference中国渤海湾 2015.07.12 qPCR tetM 1.7×10−4 [59] sul 10−4—10−2 中国九龙江口和闽江口 2016.04 宏基因组 289种ARGs 1.05×10−1—2.93×10−1 [16] 中国黄海和渤海 2018.08.18—
2018.09.07qPCR sul1, sul2, tetB, tetG, tetX, ermF, ermT, qnrA, qnrB, qnrS 4.67×103—1.08×107 [60] 白令海北部 2007.05—06,
2016.07,
2015.11qPCR sul1, sul2, sul3, tetA, tetB, tetM, tetC, tetD, aacC2, aacC3, aacC4, qepA, qnrB, qnrA, qnrS, qnrD, ermC, blaOXA-1, blaTEM-1, blaOXA-2, blaDHA-1, blaVIM-1, ampC, blaCMY-2, blaOXA-10, blaSHV-1, blaGES-1, blaNDM-1, blaKPC 10−9—10−5 [68] 中国渤海附近
海河河口2018.05 HT-qPCR 85种ARGs 9.06×106—2.93×108 [43] -
[1] KLEIN E Y, van BOECKEL T P, MARTINEZ E M, et al. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015 [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(15): E3463-E3470. [2] O'NEIL J. Antimicrobial resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations / the review on antimicrobial resistance chaired by Jim O'Neill. [M]. London, UK: Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, 2014: 1-20. [3] SHAO S C, HU Y Y, CHENG J H, et al. Research progress on distribution, migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment [J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2018, 38(8): 1195-1208. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2018.1471038 [4] JIANG Q, FENG M B, YE C S, et al. Effects and relevant mechanisms of non-antibiotic factors on the horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in water environments: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150568. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150568 [5] 罗义, 周启星. 抗生素抗性基因(ARGs)——一种新型环境污染物 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(8): 1499-1505. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.08.002 LUO Y, ZHOU Q X. Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) as emerging pollutants [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28(8): 1499-1505(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.08.002
[6] ZHANG Y P, NIU Z G, ZHANG Y, et al. Occurrence of intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes in coastal areas of Bohai Bay (China) and the factors affecting them [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236: 126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.033 [7] HATOSY S M, MARTINY A C. The ocean as a global reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(21): 7593-7599. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00736-15 [8] SALE P F, AGARDY T, AINSWORTH C H, et al. Transforming management of tropical coastal seas to cope with challenges of the 21st century [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 85(1): 8-23. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.005 [9] 谷河泉, 陈庆强. 中国近海持久性毒害污染物研究进展 [J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(12): 6243-6251. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.12.056 GU H Q, CHEN Q Q. Persistent toxic substances in offshore zone of China: A review [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(12): 6243-6251(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.12.056
[10] 戈华清, 蓝楠. 我国海洋陆源污染的产生原因与防治模式 [J]. 中国软科学, 2014(2): 22-31. GE H Q, LAN N. Causes and prevention mode on marine pollution from the land-based activities or sources(MPLBA) in China [J]. China Soft Science, 2014(2): 22-31(in Chinese).
[11] 高会旺, 张英娟, 张凯. 大气污染物向海洋的输入及其生态环境效应 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2002, 17(3): 326-330. GAO H W, ZHANG Y J, ZHANG K. Atmospheric inputs of pollutants to the sea and their effects on marine environment and ecosystem [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2002, 17(3): 326-330(in Chinese).
[12] 林伟龙, 刘贝贝, 黄伟彬. 海洋环境陆源污染及船舶污染防治建议研究 [J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2018, 36(8): 123-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.08.041 LIN W L, LIU B B, HUANG W B. Study on marine environmental pollution from land sources and prevention and control of marine pollution [J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2018, 36(8): 123-125(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.08.041
[13] ZHENG D S, YIN G Y, LIU M, et al. A systematic review of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in estuarine and coastal environments [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 777: 146009. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146009 [14] GAO R, SUI M H. Antibiotic resistance fate in the full-scale drinking water and municipal wastewater treatment processes: A review [J]. Environmental Engineering Research, 2021, 26(4): 200324. [15] PAZDA M, KUMIRSKA J, STEPNOWSKI P, et al. Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems - A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 697: 134023. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134023 [16] HUANG J, ZHU J, LIU S G, et al. Estuarine salinity gradient governs sedimentary bacterial community but not antibiotic resistance gene profile [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 151390. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151390 [17] MAKKAEW P, KONGPRAJUG A, CHYEROCHANA N, et al. Persisting antibiotic resistance gene pollution and its association with human sewage sources in tropical marine beach waters [J]. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 2021, 238: 113859. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113859 [18] FONTI V, di CESARE A, ŠANGULIN J, et al. Antibiotic resistance genes and potentially pathogenic bacteria in the central adriatic sea: Are they connected to urban wastewater inputs? [J]. Water, 2021, 13(23): 3335. doi: 10.3390/w13233335 [19] ZHANG Q Q, YING G G, PAN C G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6772-6782. [20] RASMIKA DEWI D A P, GÖTZ B, THOMAS T. Diversity and genetic basis for carbapenem resistance in a coastal marine environment [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 86(10): e02939-19. [21] ZHANG Y X, LU J, WU J, et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in sediments in a semi-enclosed continental shelf sea [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 720: 137712. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137712 [22] DANG H Y, REN J, SONG L S, et al. Dominant chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in coastal marine waters of Jiaozhou Bay, China [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 24(2): 209-217. doi: 10.1007/s11274-007-9458-8 [23] JAHANGIRI L, ESTEBAN M. Administration of probiotics in the water in finfish aquaculture systems: A review [J]. Fishes, 2018, 3(3): 33. doi: 10.3390/fishes3030033 [24] TAMMINEN M, KARKMAN A, LÕHMUS A, et al. Tetracycline resistance genes persist at aquaculture farms in the absence of selection pressure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(2): 386-391. [25] JIA L, LIU H, ZHAO N, et al. Distribution and transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in coastal aquatic ecosystems of Bohai Bay [J]. Water, 2022, 14(6): 938. doi: 10.3390/w14060938 [26] ALTUĞ G, ÇARDAK M, TÜRETKEN P S Ç, et al. Antibiotic and heavy metal resistant bacteria isolated from Aegean Sea water and sediment in Güllük Bay, Turkey: Quantifying the resistance of identified bacteria species with potential for environmental remediation applications [J]. Johnson Matthey Technology Review, 2020, 64(4): 507-525. doi: 10.1595/205651320X15953337767424 [27] GERMOND A, KIM S J. Genetic diversity of oxytetracycline-resistant bacteria and tet(M) genes in two major coastal areas of South Korea [J]. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance, 2015, 3(3): 166-173. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2015.04.005 [28] ROSE J M, GAST R J, BOGOMOLNI A, et al. Occurrence and patterns of antibiotic resistance in vertebrates off the Northeastern United States coast [J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2009, 67(3): 421-431. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00648.x [29] AKHIL PRAKASH E, HROMÁDKOVÁ T, JABIR T, et al. Dissemination of multidrug resistant bacteria to the polar environment - Role of the longest migratory bird Arctic tern (Sterna paradisaea) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815: 152727. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152727 [30] MUDRYK Z, PERLIŃSKI P, SKÓRCZEWSKI P. Detection of antibiotic resistant bacteria inhabiting the sand of non-recreational marine beach [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2010, 60(2): 207-214. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.09.025 [31] VIGNESH S, MUTHUKUMAR K, ARTHUR JAMES R. Antibiotic resistant pathogens versus human impacts: A study from three eco-regions of the Chennai coast, southern India [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(4): 790-800. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.01.015 [32] LEVIN-EDENS E, SOGE O O, NO D, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Northwest marine and freshwater recreational beaches [J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2012, 79(2): 412-420. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01229.x [33] 吴楠, 杨静慧, 张伟玉, 等. 不同环境介质中抗生素耐药性的检测方法研究进展 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43(12): 2720-2729. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160034 WU N, YANG J H, ZHANG W Y, et al. Progress in detection methods of antibiotic resistance in different environmental matrices [J]. Microbiology China, 2016, 43(12): 2720-2729(in Chinese). doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160034
[34] DANG H Y, REN J, SONG L S, et al. Diverse tetracycline resistant bacteria and resistance genes from coastal waters of Jiaozhou Bay [J]. Microbial Ecology, 2008, 55(2): 237-246. doi: 10.1007/s00248-007-9271-9 [35] RAHMAN M H, NONAKA L, TAGO R, et al. Occurrence of two genotypes of tetracycline (TC) resistance gene Tet(M) in the TC-resistant bacteria in marine sediments of Japan [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(14): 5055-5061. [36] SOGE O O, MESCHKE J S, NO D B, et al. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. isolated from US West Coast public marine beaches [J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2009, 64(6): 1148-1155. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp368 [37] GRIFFIN D W, BANKS K, GREGG K, et al. Antibiotic resistance in marine microbial communities proximal to a Florida sewage outfall system [J]. Antibiotics (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 9(3): 118. [38] SUCATO A, VECCHIONI L, SAVOCA D, et al. A comparative analysis of aquatic and polyethylene-associated antibiotic-resistant microbiota in the Mediterranean Sea [J]. Biology, 2021, 10(3): 200. doi: 10.3390/biology10030200 [39] LU Z H, NA G S, GAO H, et al. Fate of sulfonamide resistance genes in estuary environment and effect of anthropogenic activities [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 527/528: 429-438. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.101 [40] XU K H, WANG J, GONG H, et al. Occurrence of antibiotics and their associations with antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial communities in Guangdong coastal areas [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 186: 109796. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109796 [41] SALA-COMORERA L, NOLAN T M, REYNOLDS L J, et al. Bacterial and bacteriophage antibiotic resistance in marine bathing waters in relation to rivers and urban streams [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 718234. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.718234 [42] DI CESARE A, PETRIN S, FONTANETO D, et al. ddPCR applied on archived continuous plankton recorder samples reveals long-term occurrence of class 1 integrons and a sulphonamide resistance gene in marine plankton communities [J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2018, 10(4): 458-464. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12665 [43] ZHAO Z, ZHANG K, WU N, et al. Estuarine sediments are key hotspots of intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes: A high-throughput analysis in Haihe Estuary in China [J]. Environment International, 2020, 135: 105385. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105385 [44] LU X M, PENG X, XUE F, et al. Distance dilution of antibiotic resistance genes of sediments in an estuary system in relation to coastal cities [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 281: 116980. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116980 [45] PORT J A, WALLACE J C, GRIFFITH W C, et al. Metagenomic profiling of microbial composition and antibiotic resistance determinants in Puget Sound [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(10): e48000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048000 [46] YANG Y Y, LIU G H, SONG W J, et al. Plastics in the marine environment are reservoirs for antibiotic and metal resistance genes [J]. Environment International, 2019, 123: 79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.061 [47] ZHANG T, JI Z Q, LI J, et al. Metagenomic insights into the antibiotic resistome in freshwater and seawater from an Antarctic ice-free area [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 309: 119738. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119738 [48] 王秋水, 刘悦, 邓婕, 等. 动物性水产品及其养殖环境中抗生素抗性基因的研究进展 [J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2022, 13(5): 1453-1461. WANG Q S, LIU Y, DENG J, et al. Research progress of antibiotic resistance genes in animal aquatic products and aquaculture environment [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2022, 13(5): 1453-1461(in Chinese).
[49] ZHU Y G, ZHAO Y, LI B, et al. Continental-scale pollution of estuaries with antibiotic resistance genes [J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2: 16270. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.270 [50] LI Q W, NA G S, ZHANG L X, et al. Effects of corresponding and non-corresponding contaminants on the fate of sulfonamide and quinolone resistance genes in the Laizhou Bay, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 128: 475-482. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.051 [51] SUKUMARAN D, MOHAMED HATHA A A. Antibiotic resistance and virulence genes of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli from tropical estuary, South India [J]. Journal of Infection in Developing Countries, 2015, 9(5): 496-504. doi: 10.3855/jidc.5627 [52] MARAVIĆ A, SKOČIBUŠIĆ M, CVJETAN S, et al. Prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from marine beach waters [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 90(1/2): 60-67. [53] PREKRASNA I, PAVLOVSKA M, DZHULAI A, et al. Antibiotic resistance in black sea microbial communities [J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10: 823172. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.823172 [54] BOURDONNAIS E, COLCANAP D, le BRIS C, et al. Occurrence of indicator genes of antimicrobial resistance contamination in the English channel and north sea sectors and interactions with environmental variables [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 883081. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.883081 [55] ZHOU L, XU P, GONG J Y, et al. Metagenomic profiles of the resistome in subtropical estuaries: Co-occurrence patterns, indicative genes, and driving factors [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 810: 152263. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152263 [56] CHEN B W, LIANG X M, NIE X P, et al. The role of class I integrons in the dissemination of sulfonamide resistance genes in the Pearl River and Pearl River Estuary, South China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 282: 61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.010 [57] YANG P S, HAO S G, HAN M Z, et al. Analysis of antibiotic resistance genes reveals their important roles in influencing the community structure of ocean microbiome [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153731. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153731 [58] JANG J, PARK J, HWANG C Y, et al. Abundance and diversity of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial communities in the western Pacific and Southern Oceans [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 822: 153360. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153360 [59] NIU Z G, ZHANG K, ZHANG Y. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the coastal area of the Bohai Bay, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 107(1): 245-250. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.03.064 [60] LU J, ZHANG Y X, WU J, et al. Occurrence and spatial distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea areas, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 450-460. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.143 [61] WILLIAMS N L R, SIBONI N, POTTS J, et al. Molecular microbiological approaches reduce ambiguity about the sources of faecal pollution and identify microbial hazards within an urbanised coastal environment [J]. Water Research, 2022, 218: 118534. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118534 [62] TIIRIK K, NÕLVAK H, OOPKAUP K, et al. Characterization of the bacterioplankton community and its antibiotic resistance genes in the Baltic Sea [J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2014, 61(1): 23-32. doi: 10.1002/bab.1144 [63] BLANCO-PICAZO P, ROSCALES G, TORIBIO-AVEDILLO D, et al. Antibiotic resistance genes in phage particles from Antarctic and Mediterranean seawater ecosystems [J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(9): 1293. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091293 [64] GAO Q X, LI Y L, QI Z H, et al. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes from mariculture sites of China’s coastline [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 630: 117-125. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.122 [65] HABIBI N, UDDIN S, LYONS B, et al. Antibiotic resistance genes associated with marine surface sediments: A baseline from the Shores of Kuwait [J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(13): 8029. doi: 10.3390/su14138029 [66] MOOTAPALLY C, NATHANI N M, PORIYA P, et al. Antibiotic resistome biomarkers associated to the pelagic sediments of the gulfs of Kathiawar peninsula and Arabian Sea [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 17281. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53832-9 [67] SU H L, WU C C, HAN P Y, et al. The microbiome and its association with antibiotic resistance genes in the hadal biosphere at the Yap Trench [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 439: 129543. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129543 [68] TAN L, LI L Y, ASHBOLT N, et al. Arctic antibiotic resistance gene contamination, a result of anthropogenic activities and natural origin [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 621: 1176-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.110 [69] SCHLITZER R. Ocean data view[EB/OL] [2022-06-22]. [70] ZHANG H K, WANG Y B, LIU P Y, et al. Unveiling the occurrence, hosts and mobility potential of antibiotic resistance genes in the deep ocean [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 816: 151539. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151539 [71] LU J, ZHANG Y X, WU J, et al. Fate of land-based antibiotic resistance genes in marginal-sea sediment: Territorial differentiation and corresponding drivers [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 288: 132540. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132540 [72] LI J W, ZHANG L P, LI Y F, et al. A comprehensive profile of antibiotic resistance genes in the water column of a shallow-sea hydrothermal vent ecosystem [J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(3): 1776. doi: 10.3390/su14031776 [73] LERMINIAUX N A, CAMERON A D S. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments [J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2019, 65(1): 34-44. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2018-0275 [74] LI W Y, ZHANG G S. Detection and various environmental factors of antibiotic resistance gene horizontal transfer [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 212: 113267. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113267 [75] 苏洁, 付韵涵, 明红霞, 等. 海洋环境中抗生素抗性基因的水平传播研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(7): 893-897,908. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2021.07.017 SU J, FU Y H, MING H X, et al. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in marine environment [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(7): 893-897,908(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2021.07.017
[76] LIN L, YUAN K, LIANG X M, et al. Occurrences and distribution of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in the Yangtze River Estuary and nearby coastal area [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 100(1): 304-310. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.08.036 [77] NA G S, ZHANG W R, ZHOU S Y, et al. Sulfonamide antibiotics in the Northern Yellow Sea are related to resistant bacteria: Implications for antibiotic resistance genes [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 84(1/2): 70-75. [78] CITTERIO B, ANDREONI F, SIMONI S, et al. Plasmid replicon typing of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli from clams and marine sediments [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 1101. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01101 [79] CHEN C Q, ZHENG L, ZHOU J L, et al. Persistence and risk of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in major mariculture sites in Southeast China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 580: 1175-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.075 [80] GUO F, LI B, YANG Y, et al. Impacts of human activities on distribution of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes and antibiotic resistance genes in marine coastal sediments of Hong Kong [J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2016, 92(9): fiw128. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiw128 [81] SUZUKI S, OGO M, TAKADA H, et al. Contamination of antibiotics and sul and tet(M) genes in veterinary wastewater, river, and coastal sea in Thailand [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 791: 148423. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148423 [82] CHAPMAN J S. Disinfectant resistance mechanisms, cross-resistance, and co-resistance [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2003, 51(4): 271-276. [83] TANDUKAR M, OH S, TEZEL U, et al. Long-term exposure to benzalkonium chloride disinfectants results in change of microbial community structure and increased antimicrobial resistance [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(17): 9730-9738. [84] WANG J, WANG J, ZHAO Z L, et al. PAHs accelerate the propagation of antibiotic resistance genes in coastal water microbial community [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 1145-1152. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.067 [85] GIUDICE A L, CASELLA P, BRUNI V, et al. Response of bacterial isolates from Antarctic shallow sediments towards heavy metals, antibiotics and polychlorinated biphenyls [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2013, 22(2): 240-250. doi: 10.1007/s10646-012-1020-2 [86] ANJUM R, KRAKAT N. Detection of multiple resistances, biofilm formation and conjugative transfer of Bacillus cereus from contaminated soils [J]. Current Microbiology, 2016, 72(3): 321-328. doi: 10.1007/s00284-015-0952-1 [87] LUO Y, WANG Q, LU Q, et al. An ionic liquid facilitates the proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes mediated by class I integrons [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2014, 1(5): 266-270. [88] MÜHLING M, BRADFORD A, READMAN J W, et al. An investigation into the effects of silver nanoparticles on antibiotic resistance of naturally occurring bacteria in an estuarine sediment [J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2009, 68(5): 278-283. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.07.001 [89] LIU S, SU H C, PAN Y F, et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes and ecological risks in the coral reef regions adjacent to two typical Islands in South China Sea [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 158: 111424. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111424 [90] 肖喜林, 咸淑慧, 张锐, 等. 海洋异养细菌利用溶解有机碳的定量评估 [J]. 微生物学报, 2020, 60(6): 1090-1105. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20200134 XIAO X L, XIAN S H, ZHANG R, et al. Quantification of biodegradable dissolved organic carbon in the ocean [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2020, 60(6): 1090-1105(in Chinese). doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20200134
[91] 张乃星, 宋金明, 贺志鹏. 海水颗粒有机碳(POC)变化的生物地球化学机制 [J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(7): 2328-2339. ZHANG N X, SONG J M, HE Z P. Biogeochemical mechanism of particulate organic carbon(POC) variations in seawaters [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(7): 2328-2339(in Chinese).
[92] LOVE C R, ARRINGTON E C, GOSSELIN K M, et al. Microbial production and consumption of hydrocarbons in the global ocean [J]. Nature Microbiology, 2021, 6(4): 489-498. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-00859-8 [93] SNEHA K G, ANAS A, JAYALAKSHMY K V, et al. Distribution of multiple antibiotic resistant Vibrio spp across Palk Bay [J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2016, 3: 242-250. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2015.11.004 [94] GABASHVILI E, KOBAKHIDZE S, CHKHIKVISHVILI T, et al. Metagenomic and recombination analyses of antimicrobial resistance genes from recreational waters of black sea coastal areas and other marine environments unveil extensive evidence for their both intrageneric and intergeneric transmission across genetically very diverse microbial communities [J]. Marine Genomics, 2022, 61: 100916. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2021.100916 [95] ROBERTS M C, SOGE O O, GIARDINO M A, et al. Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus spp. in marine environments from the West Coast of the USA [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2009, 107(1): 300-307. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04207.x [96] SU J, FAN J F, MING H X, et al. The municipal sewage discharge may impact the dissemination of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in an urban coastal beach [J]. Water, 2022, 14(10): 1639. doi: 10.3390/w14101639 [97] FURLAN J P R, RAMOS M S, dos SANTOS L D R, et al. Appearance of mcr-9, blaKPC, cfr and other clinically relevant antimicrobial resistance genes in recreation waters and sands from urban beaches, Brazil [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 167: 112334. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112334 [98] EWBANK A C, ESPERÓN F, SACRISTÁN C, et al. Occurrence and quantification of antimicrobial resistance genes in the gastrointestinal microbiome of two wild seabird species with contrasting behaviors [J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2021, 8: 651781. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.651781 [99] PRICHULA J, PEREIRA R I, WACHHOLZ G R, et al. Resistance to antimicrobial agents among enterococci isolated from fecal samples of wild marine species in the southern coast of Brazil [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 105(1): 51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.02.071 [100] EWBANK A C, ESPERÓN F, SACRISTÁN C, et al. Seabirds as anthropization indicators in two different tropical biotopes: A One Health approach to the issue of antimicrobial resistance genes pollution in oceanic Islands [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 754: 142141. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142141 [101] THIANG E L, LEE C W, TAKADA H, et al. Antibiotic residues from aquaculture farms and their ecological risks in Southeast Asia: A case study from Malaysia [J]. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 2021, 7(1): 1926337. doi: 10.1080/20964129.2021.1926337 [102] di CESARE A, VIGNAROLI C, LUNA G M, et al. Antibiotic-resistant enterococci in seawater and sediments from a coastal fish farm [J]. Microbial Drug Resistance (Larchmont, N. Y. ), 2012, 18(5): 502-509. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2011.0204 [103] WANG X T, LIN Y F, ZHENG Y, et al. Antibiotics in mariculture systems: A review of occurrence, environmental behavior, and ecological effects [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 293: 118541. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118541 [104] SU H C, HU X J, WANG L L, et al. Contamination of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in a typical marine aquaculture farm: Source tracking of ARGs in reared aquatic organisms [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 2020, 55(3): 220-229. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2019.1684747 [105] JEONG S H, KWON J Y, SHIN S B, et al. Antibiotic resistance in shellfish and major inland pollution sources in the drainage basin of Kamak Bay, Republic of Korea [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2021, 193(8): 471. doi: 10.1007/s10661-021-09201-z [106] MILANOVIĆ V, CARDINALI F, AQUILANTI L, et al. Quantitative assessment of transferable antibiotic resistance genes in zebrafish (Danio rerio) fed Hermetia illucens-based feed [J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2021, 277: 114978. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2021.114978 [107] SINGH A S, NAYAK B B, KUMAR S H. High prevalence of multiple antibiotic-resistant, extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli in fresh seafood sold in retail markets of Mumbai, India [J]. Veterinary Sciences, 2020, 7(2): 46. doi: 10.3390/vetsci7020046 [108] LI W, LI Y Y, ZHENG N G, et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the guts of shrimp from different coastal areas of China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815: 152756. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152756 -



 下载:
下载: