-
我国甘肃、新疆、青海等西北地区,干旱少雨,地表蒸发量大,属严重缺水区域[1]. 尤其是黄土塬上的偏远村镇,没有可利用的地表水和地下水,资源性缺水更加严重[2-3]. 这些村镇不具备修建大型水利工程的条件,收集雨水是当地村民唯一的饮水方式,而水窖是最常用的雨水储存设施[4].
与河、库等地表水相比,雨水是一种水质较好的优质水源[5],但在收集饮用时同样面临着一定的水质污染风险. 集流面材料是影响雨水安全集蓄的一个关键因素. 常见的集流面有瓦屋面、沥青屋面和混凝土地面等. 其中,沥青屋面释放的污染物最多,获得的水质最差;混凝土地面应用最多,释放的碱性物质会显著提高雨水pH[6]. 此外,水窖周围环境是影响窖水水质的另一重要因素. 已有研究表明,建在厕所和牲畜棚旁边的窖水含有更多的污染物质[7].
新污染物是指具有环境稳定性、生物累积性和生物毒性的有毒有害化学物质,主要包括持久性有机污染物、内分泌干扰物、抗生素和微塑料四大类. 不同于常规污染物,新污染物浓度水平一般较低,但由于生物累积和生物放大作用,对人体和生态系统潜在威胁较大.
邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)和全氟化合物(PFCs)是两类典型的新污染物. PAEs是一种环境激素类内分泌干扰物,能够抑制雄性激素的生成,对人类的呼吸系统、生殖系统和内分泌系统均有损害. PFCs广泛应用于聚四氟乙烯生产,是重要的防水防油材料,也是灭火泡沫的主要成分. PFCs对人体肝脏功能、脂肪代谢和遗传发育均有不良影响[8]. 已有研究表明,两种污染物广泛存在于全球大气、土壤及水环境介质中[9-12]. 可以推断,在西北高海拔黄土塬区村镇,PAEs和PFCs两种新污染物同样存在,窖水也面临着相应的的污染风险. 然而,针对西北村镇窖水这种分散型饮用水源,还未有新污染物方面的报道.
窖水作为西北高海拔村镇唯一可用的饮用水源,其水质安全对当地村民身体健康有着重要意义. 本研究基于西北黄土塬区村镇饮水现状,以我国甘肃某县为代表区域,采集冬夏两季窖水进行水质分析,研究了15种目标PAEs和17种PFCs在冬夏两季窖水中的浓度水平和组成,讨论了两种新污染物来源,并利用模型计算了采样点覆盖区域内人群通过饮用窖水摄入PAEs和PFCs的健康风险,为西北高海拔黄土塬区村镇窖水的饮用处理提供了基础数据支撑.
-
研究区域所在县隶属甘肃省,为典型的黄土高原丘陵沟壑区,总体地势西北高、东南低,海拔1136—2089 m,常年干旱少雨,是典型的资源型缺水地区[13]. 该区以农业和畜牧业为主导产业,对水资源量的需求较高. 集雨水窖是当地村户最主要的饮用水渠道,雨季将雨水收集储存起来,仅依靠窖水的自然沉淀,未经其它处理,就直接进行生活饮用.
本次调研覆盖该县整个纵向区域,于2021年12月和2022年7月分两次,自北向南每间隔约10 km取水窖样品. 冬季窖水采样时距上次降雨约4个月,夏季窖水采样时正是雨天,具体采样点分布如图1所示,冬季共采集8个(a—h)窖水样品,所有窖水样品均进行了常规指标的检测,用于检测新污染物的窖水b、d、e、f用玻璃瓶密封,其它用聚乙烯瓶密封. 夏季共采集10个(1—10)窖水样品,所有样品均采用聚乙烯瓶密封. 1和a、2和b、4和c、6和d、7和f、8和g、9和h分别对应同一窖水采样点. 每批样品运回实验室后置于4℃冷库中保存,并在一周内完成所有样品的检测分析. 这些样品分布在不同的自然村落中,所有水窖材质均为混凝土水窖,集雨面均为混凝土地面,水窖8(g)是供水规模较大的集体水窖,其余各水窖皆为单户水窖.
-
15种PAEs标准样品购自中国上海阿拉丁公司,如表1所列;17种PFCs标准样品,如表2所列,以及9种PFCs同位素内标(13C4PFBA、13C4PFHxA、13C4PFOA、13C4PFNA、13C4PFDA、13C4PFUdA、13C2PFDoA、18O2PFHxS 和13C4PFOS) 购自加拿大惠灵顿公司;色谱纯乙腈、色谱纯甲醇、色谱纯正己烷、色谱纯二氯甲烷均购自加拿大飞世尔科技公司;色谱级乙酸铵购自中国上海的麦克林公司;超纯水使用日本奥加诺株式会社的Milli-Q系统生成(电阻率>18.2 MΩ·cm).
-
温度、溶解氧(DO)、pH、总溶解固体(TDS)、氧化还原电位(ORP)采用美国哈希公司的HQ40d多参数分析仪在现场测定;浊度采用哈希2100Q便携式浊度仪在现场测定;总有机碳(TOC)和总氮(TN)采用日本岛津公司的 TOC-L 总有机碳分析仪测定.
样品中的PAEs用C18固相萃取柱提取,富集倍数为100倍. 将500 mL各样品经0.45 μm尼龙滤膜过滤后置于1 L玻璃烧杯中备用. 萃取前,依次用5 mL甲醇、5 mL二氯甲烷、5 mL正己烷和5 mL超纯水活化C18小柱. 活化后,开始进行萃取,水样通过C18小柱的流速控制在每秒1滴. 水样全部通过小柱且淋洗完成后,利用真空泵抽干残余水分,然后用5 mL正己烷洗脱,取适量洗脱液,用外标法在日本岛津公司的TQ8030三重四极杆气相色谱质谱联用仪上进行检测. 色谱柱:Agilent DB-5MS UI 30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm, Intuvo 气相色谱柱 (货号:122-5532UI-INT);GC 部分:进样口温度 260℃,不分流进样,进样时间1 min;总流量50 mL·min−1,吹扫流量3 mL·min−1,柱流量1.2 mL·min−1,载气为恒压72.8 kPa,程序升温为: 初始温度60℃保持1 min,以10 ℃·min−1升至220 ℃保持1 min,再以7 ℃·min−1 升至260℃,保持10 min,总时间为33.71 min;MS部分:离子源温度230℃,接口温度为260℃,溶剂延迟时间7 min;各物质定性离子对和定量离子对分别为:DMP 163.0>133.1、163.0>77.1 ; DEP 177.0>149.0、177.0>93.1 ; DIBP 149.0>65.0、149.0>93.1;DBP 149.0>65.1、149.0>93.1;DMEP 149.0>65.1、149.0>93.1;BMPP 149.0>65.1、149.0>93.1;DEEP 176.0>149.0、176.0>104.1;DPP 149.0>65.1、149.0>93.1;DNHP 149.0>65.1、149.0>93.1;BBP 206.0>149.0、206.0>93.1;DBEP为193.0>149.0、193.0>93.1;DCHP 167.0>149.1、167.0>93.0;DNOP 149.0>65.1、149.0>93.1;DEHP 167.0>149.0、167.0>93.0;DINP 293.0>149.0、293.0>93.0.
样品中的全氟化合物(PFCs) 用WAX固相萃取柱提取. 样品各取400 mL加入2ng内标后不经过滤直接萃取,以检测窖水中PFCs的总浓度并考察浊度对PFCs浓度的影响. 萃取前,WAX小柱依次用4 mL甲醇、4 mL氨水甲醇和4 mL超纯水活化. 水样全部通过小柱且淋洗完成后,利用真空泵抽干残余水分,然后依次用4 mL甲醇、4mL 0.1% 氨水甲醇洗脱,将洗脱液氮吹至近干,用甲醇复溶至200 μL,浓缩倍数为2000倍,最后在电喷雾离子源负离子模式(ESI-)下采用内标法在美国安捷伦公司1290 Infinity HPLC系统与Agilent 6460三重四极杆质谱系统联用的高效液相色谱串联质谱仪上检测. 检测方法在本课题组已有研究中给出,采用其所用的定性定量参数,流速改为0.2 mL·min−1[14].
-
为了保证测定结果的可靠,窖水样品中PAEs和PFCs的测定均设置有1个平行,1个方法空白、3个溶剂空白和1个现场空白(在现场用相同采样瓶,在相同时间装入娃哈哈纯净水),并进行了3个窖水样品和3个超纯水空白的加标回收.
PAEs的空白加标回收率为87.3%—103.7%,是在3份超纯水样品中加入1 μg·L−1混合标准样品测得的. PAEs的基质加标回收率为82.5%—101.6%,是在3份窖水样品中加入1 μg.L−1 混合标准样品测得的. 以信噪比S/N>3为检出限,PAEs检出限范围为0.09—0.19 μg·L−1,其中DIBP、DMEP、DBEP 3种物质的空白值达到了各自检出限分别为0.27、0.14、0.10 μg·L−1,在计算浓度时需进行差减扣除. 各物质相对标准偏差范围为1.27%—9.79%. PFCs检出限范围为0.01—0.09 ng·L−1,所有空白均未达到检出限. 各物质相对标准偏差范围为2.50%—12.82%. PFCs检测的空白加标回收率为80.5%—119.7%,是在3份超纯水样品中加入20 ng混合标准样品测得的. PFCs检测的基质加标回收率为75.3%—117.1%,是在3份窖水样品中加入20 ng混合标准样品测得的,检测中PAEs和PFCs的校准曲线回归系数(r2)均超过0.99.
-
采用US EPA 提供的健康风险评价模型来评价窖水中PAEs,该评价模型包括致癌和非致癌两个部分[15-16]. 非致癌风险用风险值HI来表示,计算公式如下:
式中,CDI是由于暴露造成的污染物长期日摄入剂量,
$ \mathrm{m}\mathrm{g}\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ ;RfD为各污染物的参考剂量,$ \mathrm{m}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ .致癌风险则用R表示,是长期日摄入剂量与致癌斜率因子的乘积,计算公式如下:
式中,SF是致癌斜率因子,
$ \left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)\cdot{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{g}}^{-1} $ .饮用水途径暴露造成的污染物长期日摄入剂量计算公式如下:
式中,C为水中目标污染物的质量浓度,mg·L−1;U为日饮用水量,L·d−1;EF为暴露频率,d·a−1;ED为暴露持续时间,a;BW为平均体重,kg;AT为平均暴露时间,d.
以上公式中的参数取值来自文献[17]和中国人群暴露参数手册(成人卷)[18] : 夏、冬两季U分别取3.1 L·d−1和1.9 L·d−1(甘肃省);EF取365 d·a−1;ED对于非致癌物取30 a,对于致癌物取70 a;BW取61.8 kg(甘肃省); AT对于非致癌物取10950 d,对于致癌物取25550 d.
根据人群的PFCs饮水途径每日摄入量(estimated daily intake, EDI)来评估甘肃该县村民每日通过饮水摄入PFCs的健康风险. EDI计算公式如下:
式中,Cf为窖水样品中PFCs的测定浓度,ng·L−1;Vwater为日饮水量,L·d−1;BW为平均体重,kg. 夏、冬两季Vwater分别取3.1 L·d−1和1.9 L·d−1(甘肃省);BW取61.8 kg(甘肃省).
把该县人群EDI值同美国卫生和公共服务部给出的PFOA、PFOS、PFHxS和PFNA人群每日可耐受摄入量参考值(分别为3、2、20 、3
$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ )进行对比,得出四种全氟化合物的健康风险水平. -
冬季7个窖水样品的常规指标检测结果如表3所示,水温5.4—8.5℃,浊度1.8—29.5 NTU,pH 8.0—9.7,DO 4.9—8.8 mg·L−1,ORP 154.5—223.5 mV,TDS 59.6—110.0 mg·L−1,TOC 0.58—2.61 mg·L−1,TN 0.64—2.25 mg·L−1. 7个窖水样品pH均大于8,最高达到9.7. 不同窖水浊度差异较大,除了d、e、f 3个采样点窖水样品浊度低于《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB5749-2022)中分散式供水所规定3 NTU,其它样品浊度均超出了标准中规定的限值.
夏季10个窖水样品的常规指标检测结果如表4所示,水温12.5—21.9℃,浊度4.7—58.5 NTU,pH 8.2—9.4,DO 2.9—7.6 mg·L−1,ORP 173.9—235.4 mV,TDS 46.4—238.0 mg·L−1,TOC 0.78—3.18 mg·L−1,TN 0.80—3.27 mg·L−1. 10个窖水样品pH均大于8,最高达到9.4.
夏季雨期采集的窖水样品TOC、TN、温度和浊度普遍高于冬季. 所有水窖样品浊度均超过GB5749-2022中分散式供水所规定限值,这是因为雨期水窖储水后没有经过自然沉淀,肉眼可见悬浮物较多. 同一采样点2(b)和8(g)样品浊度和TDS在各窖水样品中依然处于较高水平,实地调研发现2(b)水窖存在渗漏,8(g)水窖是集体水窖且位于道旁,两个水窖易受到周围环境的污染.
-
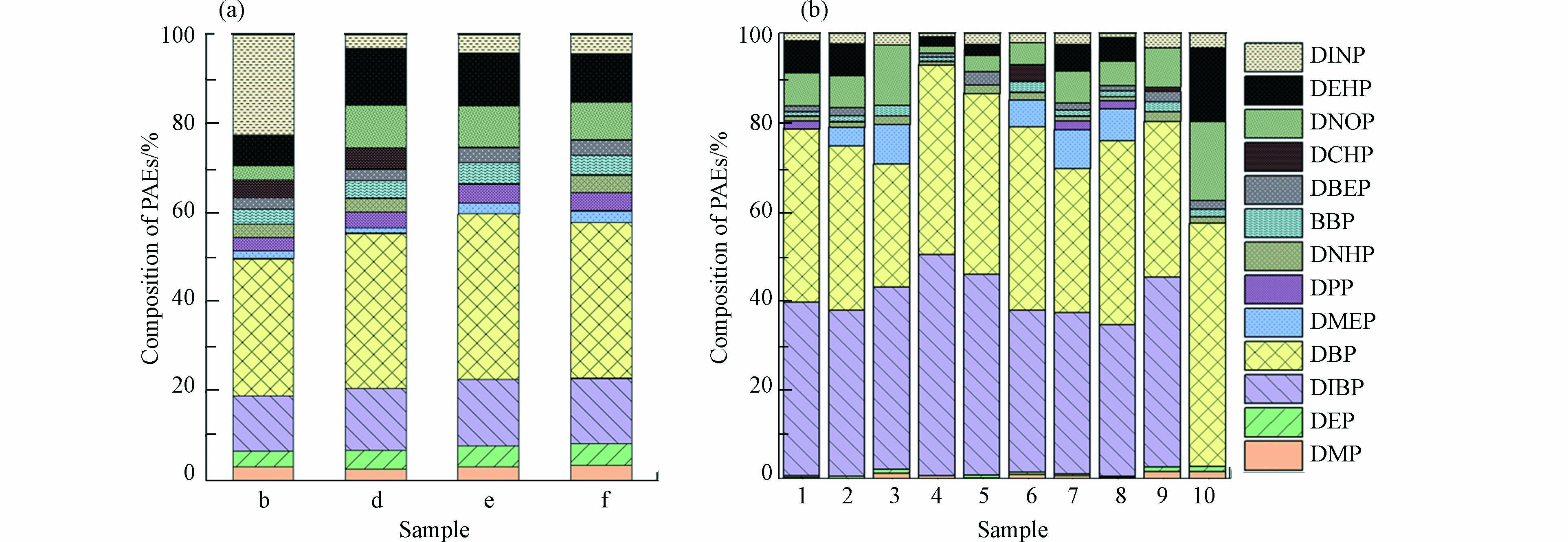
对冬季窖水样品b、d、e、f和夏季10个窖水样品进行PAEs组成及浓度的检测分析,结果如图2(a)、(b)所示. 15种目标PAEs中共有13种被检出,冬季样品总浓度平均值为3.12 μg·L−1. 其中DBP在各窖水样品中含量最高,平均值达到1.06 μg·L−1,其次是DIBP和DEHP,浓度平均值分别为0.43 μg·L−1和0.33 μg·L−1. 值得注意的是,b水窖中的DINP浓度较其它三口水窖高出约8倍,达到了0.84 μg·L−1. 夏季窖水样品总浓度平均值为4.56 μg·L−1,DBP和DIBP是各窖水样品的主要组成部分,浓度平均值分别为1.3μg·L−1和1.2 μg·L−1,两者占PAEs总量的64.5%—92.7%,高于冬季窖水两种物质比例43.5%—52.1%. 同一采样点2(b)、6(d)和7(f),夏季样品中DIBP浓度均显著高于冬季,而夏季样品中的DMP和DEP则略少于冬季. DIBP、DMP和DEP的LogP分别为4.46、1.64和2.70,与DMP和DEP相比,DIBP表现出更大的疏水性. 冬季窖水在长期自然沉淀过程中,疏水性更强的DIBP更易于随着颗粒物沉淀,而亲水性较强的DMP和DEP则在窖水中稳定存在,甚至会因颗粒物的释放,导致窖水中的溶解性PAEs含量上升,这可能是夏季窖水样品中DIBP浓度较冬季窖水低,而DMP和DEP浓度低于冬季的原因.
窖水中PAEs的可能来源:一是农村常使用塑料薄膜来建造温室大棚。塑料膜在使用及降解过程中,其含有的PAEs,最终可以水为介质进入环境中. 二是农村卫生状况相对较差,破损塑料膜、垃圾袋及包装纸等随意丢弃后,其中的PAEs可能通过降雨或径流进入到集雨水窖之中,带来水质风险[19].
通过与文献报道的其他水源中PAEs含量对比发现,一般地表水中的PAEs浓度范围波动较大,如三峡库区中6种优先控制PAEs(DMP、DEP、DBP、BBP、DEHP和DNOP)的总浓度为0.42—0.77 μg·L−1[20],远小于窖水中这6种PAEs的总浓度0.85—4.56 μg·L−1,而黄河甘肃兰州段干湿季PAEs的平均总浓度分别为3.24 μg·L−1和2.30 μg·L−1,与窖水中PAEs总浓度平均值相近[21]. 此外,窖水中的PAEs浓度普遍高于地下水,如东莞地区地下水中6种PAEs(DMP、DEP、DNBP、BBP、DEHP和DNOP)总浓度平均值为0.93 μg·L−1[22],湖北江汉地下水中PAEs总浓度平均值为0.98 μg·L−1[23],均小于此次窖水中的含量3.12 μg·L−1(冬季)和4.56 μg·L−1(夏季).
-
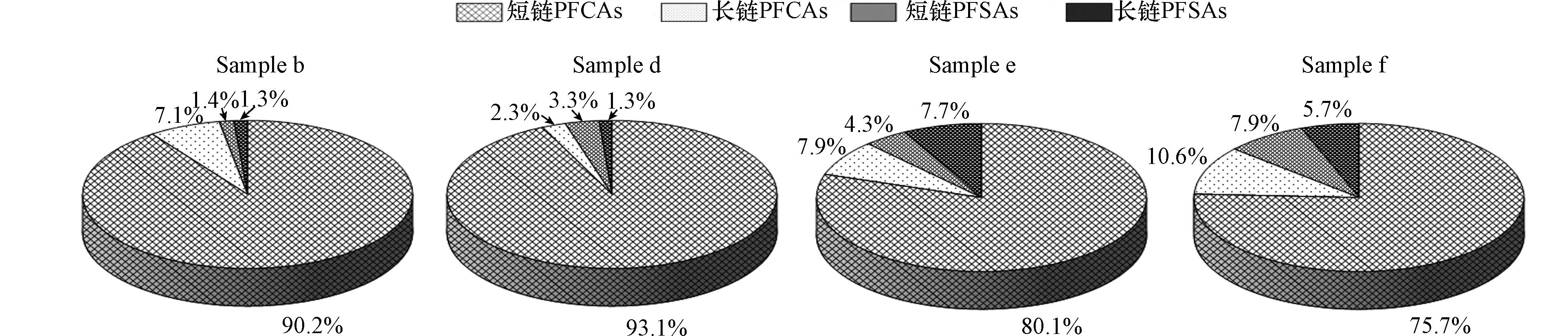
采用与PAEs测定相同的样品进行PFCs分析. 结果如图3和图4所示,所有窖水样品中,17种目标PFCs中共有14种被检出. 图3是冬季4个窖水样品PFCs组成情况,图4是夏季10个窖水样品PFCs组成情况,冬季PFCs总浓度范围为143.93—246.47 ng·L−1,夏季PFCs总浓度范围为275.90—405.51 ng·L−1,各窖水样品中的PFCs由PFCAs和PFSAs两部分组成. 其中PFCAs占窖水PFCs总量的80%以上,居于主体地位. PFCAs和PFSAs根据碳链长度可分为长链和短链,短链PFCAs占窖水PFCs总量的75%以上,全氟丁酸(PFBA)是短链PFCAs中含量最高的污染物,冬季窖水样品中平均浓度达到88.09 ng·L−1,而夏季窖水样品中平均浓度能达到214.98 ng·L−1.
同一采样点2(b)、6(d)和7(f),除PFPeA和PFHpA外,夏季雨期窖水PFCs浓度均高于冬季,尤其是PFOA和PFOS在所有PFCs中的浓度占比分别从6.7%和1.4%上升到了9.7%和15.1%. 这可能是由于夏季当地造纸、皮革和石油开采等氟化工产业扩大生产,提高产能,使得PFCs排放量上升,这些PFCs进入大气后随着降雨过程进入到水窖中,使得窖水PFCs浓度水平上升.
与地表水和地下水中的PFCs含量对比可知,相比于上海黄浦江和山东部分区域地表水中10种PFCs (PFBA、PFPeA、PFBS、PFHxA、PFHxS、PFHpA、PFOA、PFOS、PFNA、PFDA)总浓度(3.38—362.37 ng·L−1和35.71—1236.21 ng·L−1)[24-25],窖水10种PFCs总浓度121.82—395.16 ng·L−1处于中间水平,波动范围相对较小. 而地下水中的PFCs含量普遍较低,如天津市郊区和北京市部分地区地下水PFCs总浓度范围分别为0.32—8.30 ng·L−1和N.D.—165.80 ng·L−1[26-27],均低于窖水和地表水中的PFCs浓度. 可以发现,不同水环境中PFCs含量的差异与其所处区域周围工业活动以及水体自身特点密切相关. PFCs在工业发达地区水环境中检出率高,地表水作为工业废水处理后的受纳水体,易于受到污染. 而地下水由于经过渗流,水质一般较好. 水窖中的PFCs则可能来自于大气污染物湿沉降和集雨面径流,受间接污染.
-
根据美国环保署优先控制污染物名单和本次窖水检测出的污染物浓度水平,选择DMP、DEP、DIBP、DBP、DEHP和DNOP 等6种PAEs进行健康风险评价,除了对DEHP进行致癌风险评价外,其它5种PAEs均进行非致癌风险评价. 根据相关研究得到DMP、DEP、DIBP、DBP、DNOP等 5种PAEs的参考剂量RfD 分别为 0.1、0.8、0.098、0.1、0.02 mg·(kg·d)−1;DEHP的致癌斜率因子SF为0.014 (kg·d)·mg−1[28]. 将所有参数代入“1.5”中的公式(1)—(3),得到冬夏两季窖水中这6种PAEs的致癌和非致癌风险值. 非致癌风险值HI值小于1时,该污染物浓度不会存在非致癌风险,反之该污染物将存在非致癌健康风险. 致癌风险R值小于10−6 时,不会对人产生致癌风险;R为
$ {10}^{-6}—{10}^{-4} $ 时,存在潜在致癌风险;R大于10−4 存在致癌作用. 冬季水窖中DMP、DEP、DIBP、DBP、DNOP等 5种PAEs的HI为$ 4.75\times {10}^{-6}— $ $5.11\times {10}^{-4} $ . DEHP的R值为$ 1.11\times {10}^{-7}—1.86\times {10}^{-7} $ ;夏季水窖中这5种PAEs的HI为$1.11\times {10}^{-7}— 1.35\times {10}^{-3}$ . DEHP的R值为$ 3.39\times {10}^{-8}—2.99\times {10}^{-7} $ . 两季窖水样品中5种PAEs类的HI均小于1,DEHP的R值均小于10−6 ,检测窖水区域不存在非致癌和致癌风险.根据美国卫生和公共服务部提出的人群饮用水途径全氟化合物每日耐受量和两季窖水中全氟化合物的检出情况,选择PFOA、PFOS、PFNA和PFHxS等 4种PFCs进行EDI值的计算,来评估健康风险水平. 经计算,冬季PFOA的EDI平均值为0.35
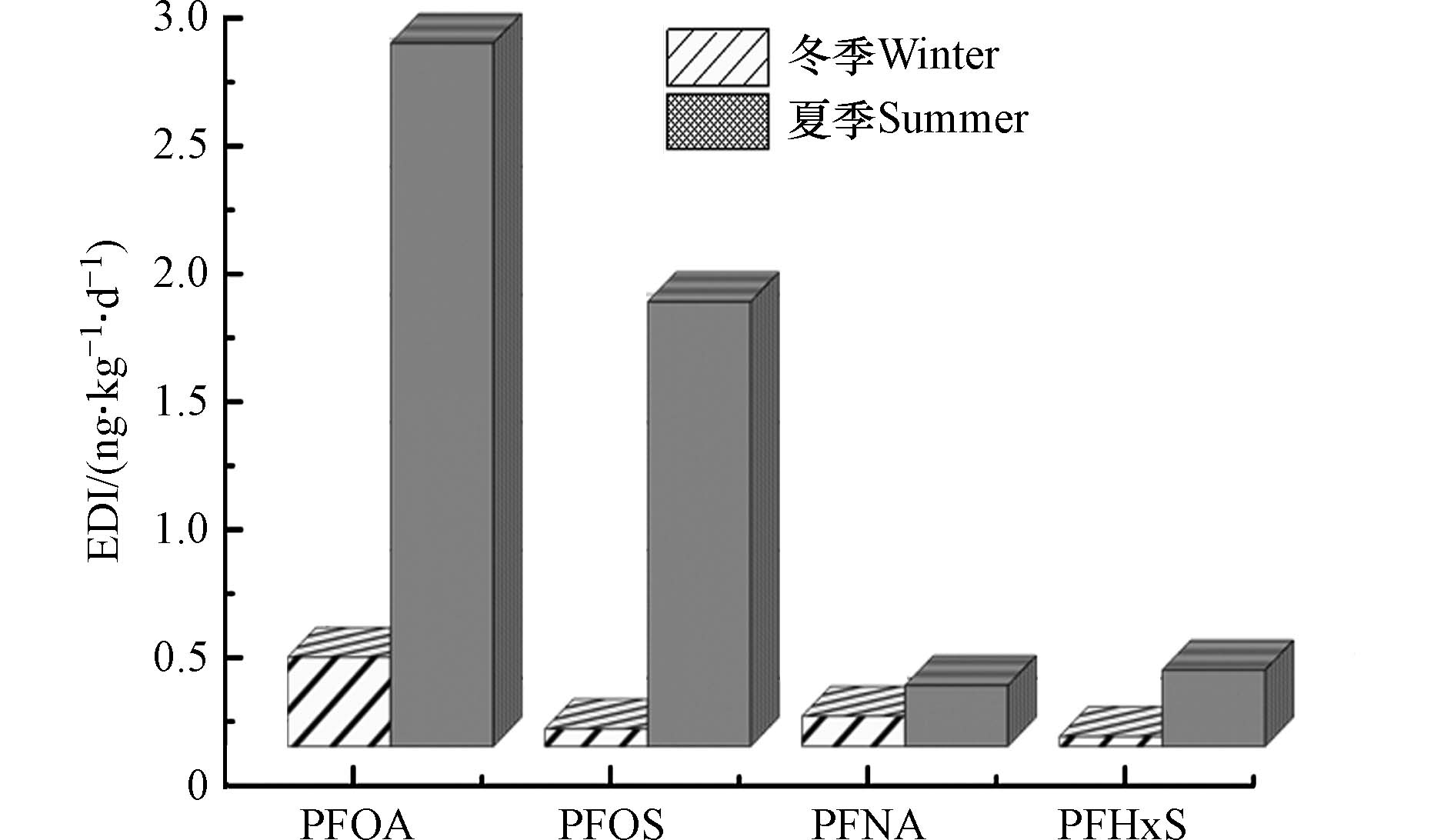
$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ ;PFOS的EDI平均值为0.07$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ ;PFNA的EDI平均值为0.12$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ ;PFHxS的EDI平均值为0.04$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ . 夏季PFOA的EDI平均值为2.75$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ ;PFOS的EDI平均值为1.74$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ ;PFNA的EDI平均值为0.24$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ ;PFHxS的EDI平均值为0.30$ \mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{ }\cdot{\left(\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}\cdot\mathrm{d}\right)}^{-1} $ . 如图5所示,两季窖水样品PFOA、PFOS、PFBA、PFHxS的EDI平均值均小于美国卫生和公共服务部给出的参考值,但也可以看到夏季雨期个别窖水样品EDI值超出了参考值,存在较高的健康风险. 结合夏季雨期窖水水质波动大、浊度普遍偏高的情况,建议当地村民在雨期集雨后,应进行必要的处理,至少要经过简单的沉淀. 浊度及其它常规指标对健康风险水平的影响方式和影响程度,仍需进一步研究. -
(1)甘肃该县冬、夏两季的窖水均呈现弱碱性(8.0≤pH≤9.7),浊度普遍偏高,且夏季雨期窖水浊度显著高于冬季.
(2)15种目标PAEs中共有13种在窖水中检出,冬季窖水中PAEs总浓度平均值为3.12 μg·L−1,夏季为4.56 μg·L−1. DBP和DIBP是各窖水样品的主要组成部分. 夏季雨期窖水中PAEs总浓度平均值明显高于冬季.
(3)17种目标PFCs中共有14种在窖水中检出,冬季PFCs总浓度范围为143.93—246.47 ng·L−1,夏季PFCs总浓度范围为275.90—405.51 ng·L−1. 窖水样品中的PFCs由PFCAs和PFSAs两部分组成,短链PFCAs中的全氟丁酸(PFBA)在PFCs中含量最高. 夏季雨期窖水PFCs浓度水平显著高于冬季,尤其是PFOA和PFOS在所有PFCs中的浓度占比显著上升.
(4)该县两季窖水中PAEs无致癌风险和非致癌风险;PFCs中的PFOA、PFOS、PFNA和PFHxS的平均EDI值均小于参考值. 此外,夏季窖水中PFOA和PFOS的EDI值大于冬季,且个别窖水EDI值超过参考值,应该予以重视.
甘肃某县窖水水质分析及健康风险评价
Water quality analysis and health risk assessment of water cellars in a county of Gansu
-
摘要: 本文以甘肃某县为代表,对区域内冬、夏两季窖水的常规指标、17种全氟化合物和15种邻苯二甲酸酯类进行了检测,对污染来源进行了探讨,并评估了两类新污染物的健康风险. 结果表明:该县窖水pH普遍偏高,夏季雨期窖水浊度显著高于冬季. 新污染的检测中,共检出13 种邻苯二甲酸酯类(PAEs)和14 种全氟化合物(PFCs). 冬季窖水中PAEs总浓度范围为2.65—3.71 μg·L−1,总浓度平均值3.12 μg·L−1. 夏季窖水中PAEs总浓度范围为1.85—9.26 μg·L−1,总浓度平均值为4.56 μg·L−1. 两季窖水中,邻苯二甲酸二丁酯和邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯是含量最高的成分,两种物质分别占窖水PAEs总浓度的47.8%和48.5%,窖水中PAEs没有致癌和非致癌风险. 冬季窖水中PFCs的总浓度为143.93—246.47 ng·L−1,夏季为275.90—405.51 ng·L−1. 检测出的PFCs包括全氟羧酸(PFCAs)和全氟磺酸(PFSAs)两大类,PFCAs占窖水PFCs总量的80%以上,是窖水中PFCs的主体. 两季窖水中全氟辛酸、全氟辛烷磺酸、全氟壬酸和全氟己烷磺酸的健康风险评价结果显示,除个别窖水样品,4种PFCs的浓度一般较低不构成健康风险.Abstract: In this study, the water quality conventional indexes, and the concentrations of 17 perfluorocarbons(PFCs) and 15 phthalates(PAEs) of cellar water in winter and summer were investigated in a typical county in Gansu Province. The pollution sources and the health risks of PFCs and PAEs were evaluated. Results showed that the pH values of cellar water in this area were generally high. The turbidity of cellar water in summer was obviously higher than that in winter. A total of 13 phthalates (PAEs) and 14 perfluorocarbons (PFCs) were detected in cellar water samples. The cellar water concentrations of PAEs in winter were in the range of 2.65—3.71 μg·L−1, with an average concentration of 3.12 μg·L−1. In summer, the concentration of PAEs ranged from 1.85 μg·L−1 to 9.26 μg·L−1, with an average of 4.56 μg·L−1. Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) were the main kinds of PAEs in cellar water, accounting for 47.8% and 48.5%, respectively. Based on human health risk assessment modeling, non carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks were found in the cellar water samples. The total concentration of PFCs in cellar water was 143.93—246.47 ng·L−1 in winter and 275.90—405.51 ng·L−1 in summer. The detected PFCs included perfluorocarboxylic acids (PFCAs) and perfluorosulfonic acids (PFSAs), and PFCAs accounted for more than 80% of the total PFCs in cellar water. Health risk assessment of Perfluorooctanoic acid, perfluorooctanesulfonic acid, perfluorononanoic acid and perfluorohexanesulfonic acid in winter and summer indicated that most water cellars had low concentration levels with low health risk, with the exception of individual water cellars with health risks.
-

-
表 1 检测的15种PAEs类型及化学式
Table 1. The type and chemical formulas of 15 PAEs in this study
化合物
Compouds英文名称
English name英文缩写
Abbreviation化学式
Chemical formulaCAS编号
CAS number邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 Dimethyl phthalate DMP C10H10O4 131-11-3 邻苯二甲酸二乙酯 Diethyl phthalate DEP C12H14O4 84-66-2 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 Diisobutyl phthalate DIBP C16H20O4 84-69-5 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 Dibutyl phthalate DBP C16H22O4 84-74-2 邻苯二甲酸二甲氧乙酯 Dimethylglycol phthalate DMEP C14H16O6 117-82-8 双(4-甲基-2-戊基)邻苯二甲酸酯 Bis(4-Methyl-2-pentyl)phthalate BMPP C20H30O4 146-50-9 双(2-乙氧基)邻苯二甲酸酯 Bis(2-ethoxyethyl) phthalate DEEP C16H22O6 605-54-9 邻苯二甲酸二戊酯 Di-n-pentyl phthalate DPP C18H26O4 131-18-0 邻苯二甲酸二己酯 Di-n-hexyl phthalate DNHP C20H30O4 84-75-3 邻苯二甲酸苄酯 Mono-Benzyl phthalate BBP C15H12O4 2528-16-7 双(2-正丁氧基乙酯)邻苯二甲酸酯 Bis(2-butoxyethyl) phthalate DBEP C20H30O6 117-83-9 邻苯二甲酸二环己基酯 Dicyclohexyl phthalate DCHP C20H26O4 84-61-7 邻苯二甲酸二辛酯 Di-n-octyl phthalate DNOP C24H38O4 117-84-0 双(2-乙基己基)邻苯二甲酸酯 Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate DEHP C24H38O4 117-81-7 邻苯二甲酸二异壬酯 Diisononyl phthalate DINP C26H42O4 68515-48-0 表 2 检测的17种PFCs类型及化学式
Table 2. The type and chemical formulas of 17 PFCs in this study
化合物
Compouds英文名称
English name英文缩写
Abbreviation化学式
Chemical formulaCAS编号
Chemical formula对应内标
Inner standard全氟丁酸 Perfluorobutanoic acid PFBA C3F7COOH 375-22-4 13C4PFBA 全氟戊酸 Perfluoropentanoic acid PFPeA C4F9COOH 2706-90-3 13C4PFOA 全氟己酸 Perfluorohexanoic acid PFHxA C5F11COOH 307-24-4 13C4PFHxA 全氟庚酸 Perfluoroheptanoic acid PFHpA C6F13COOH 375-85-9 13C4PFHxA 全氟辛酸 Perfluorooctanoic acid PFOA C7F15COOH 206-397-9 13C4PFOA 全氟壬酸 Perfluorononanoic acid PFNA C8F17COOH 375-95-1 13C4PFNA 全氟癸酸 Perfluorodecanoic acid PFDA C9F19COOH 335-76-2 13C4PFDA 全氟十一酸 Perfluoroundecanoic acid PFUnDA C10F21COOH 218-165-4 13C4PFUdA 全氟十二酸 Perfluorododecanoic acid PFDoDA C11F23COOH 307-55-1 13C2PFDoA 全氟十三酸 Perfluorotridecanoic acid PFTrDA C12F25COOH 276-745-2 13C2PFDoA 全氟十四酸 Perfluorotetradecanoic acid PFTeDA C13F27COOH 376-06-7 13C2PFDoA 全氟十六酸 Perfluorohexadecanoic acid PFHxDA C15F31COOH 67905-19-5 13C2PFDoA 全氟十八酸 Perfluorooctadecanoic acid PFODA C17F35COOH 16517-11-6 13C2PFDoA 全氟丁烷磺酸 Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid PFBS C4F9SO3H 375-73-5 18O2PFHxS 全氟己烷磺酸 Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid PFHxS C6F13SO3H 355-46-4 18O2PFHxS 全氟辛烷磺酸 Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid PFOS C8F17SO3H 1763-23-1 13C4PFOS 全氟癸烷磺酸 Perfluorodecanesulfonic acid PFDS C10F21SO3H 335-77-3 13C4PFOS 表 3 冬季窖水样品常规指标检测结果
Table 3. Test results of general parameters of cellar water samples in winter
地点
Position温度/℃
Temperature浊度/NTU
TurbiditypH 溶解氧/(mg·L−1)
DO氧化还原电位/mV
ORP总溶解固体/(mg·L−1)
TDS总有机碳/(mg·L−1)
TOC总氮/(mg·L−1)
TNa 8.5 11.7 9.7 6.9 154.5 61.4 0.69 0.99 b 7.8 29.5 8.0 7.7 207.0 92.4 2.61 2.25 c 7.9 4.2 8.8 6.2 223.5 67.7 1.02 0.78 d 6.1 1.8 9.0 4.9 207.7 59.6 0.58 1.00 e 5.8 3.2 8.6 5.6 196.3 62.4 0.62 1.02 f 6.2 2.3 8.4 5.2 213.3 65.6 0.73 1.23 g 5.4 6.1 8.6 8.8 185.4 110.0 1.62 0.64 h 7.2 5.3 8.3 5.9 218.6 68.0 0.98 0.68 表 4 夏季窖水样品常规指标检测结果
Table 4. Test results of general parameters of cellar water samples in summer
地点
Position温度/℃
Temperatur浊度/NTU
TurbiditypH 溶解氧/(mg·L−1)
DO氧化还原电位/mV
ORP总溶解固体/(mg·L−1)
TDS总有机碳/(mg·L−1)
TOC总氮/(mg·L−1)
TN1 18.8 30.6 8.8 5.9 193.2 51.3 1.91 2.07 2 21.3 58.5 9.4 6.3 211.7 223.0 3.18 3.27 3 12.5 4.7 9.0 7.6 176.5 62.9 0.78 1.38 4 17.0 18.8 8.5 6.0 204.0 60.0 1.39 0.98 5 21.9 14.1 8.5 4.8 188.2 68.7 1.19 0.80 6 20.2 11.8 8.4 6.5 226.7 61.6 1.18 1.97 7 19.3 15.1 8.6 5.1 189.7 51.7 1.34 0.99 8 21.6 19.6 8.5 4.3 235.4 238.0 1.56 2.45 9 19.5 8.8 8.3 2.9 228.0 46.4 1.22 2.05 10 18.2 19.0 8.2 5.6 173.9 53.7 1.51 1.68 -
[1] 史康立, 刘愿英, 万亮婷, 等. 试论西北地区的缺水问题及其对策 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2006, 24(2): 178-182,194. SHI K L, LIU Y Y, WAN L T, et al. Discussion on water shortage and countermeasures in northwest regions of China [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2006, 24(2): 178-182,194(in Chinese).
[2] SUN S A, ZHOU X, LIU H X, et al. Unraveling the effect of inter-basin water transfer on reducing water scarcity and its inequality in China [J]. Water Research, 2021, 194: 116931. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.116931 [3] 翟自宏. 解决甘肃水资源短缺的有效途径 [J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2016(12): 106-108. ZHAI Z H. An effective way to solve the shortage of water resources in Gansu [J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2016(12): 106-108(in Chinese).
[4] 徐强, 王小贞, 魏奋子. 西北黄土高原地区农村集雨窖水饮水安全保障研究 [J]. 甘肃科技, 2020, 36(17): 54-57, 32. XU Q, WANG X Z, WEI F Z. Study on drinking water safety guarantee of rural rainwater collection cellar in Northwest Loess Plateau [J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2020, 36(17): 54-57, 32(in Chinese).
[5] LEE M J, KIM M, KIM Y, et al, Consideration of rainwater quality parameters for drinking purposes: A case study in rural Vietnam[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 200: 400-406. [6] MAO J, XIA B Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Effect of roof materials and weather patterns on the quality of harvested rainwater in Shanghai, China [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 279: 123419. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123419 [7] 卢晓岩, 朱琨, 梁莹, 王亚军. 西北黄土高原地区雨水集流的水质特点 [J]. 兰州交通大学学报, 2004, 23(6): 15-18. LU X Y, ZHU K, LIANG Y, et al. Characteristics of rainwater quality harvested at loess plateau of northwest China [J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2004, 23(6): 15-18(in Chinese).
[8] CHEN R Y, LI G W, HE Y T, et al. Field study on the transportation characteristics of PFASs from water source to tap water [J]. Water Research, 2021, 198: 117162. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117162 [9] LE T M, NGUYEN H, NGUYEN V K, et al. Profiles of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in bottled water, tap water, lake water, and wastewater samples collected from Hanoi, Vietnam [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 788: 147831. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147831 [10] SUJA F, PRAMANIK B K, ZAIN S M. Contamination, bioaccumulation and toxic effects of perfluorinated chemicals (PFCs) in the water environment: A review paper [J]. Water Science and Technology:a Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 2009, 60(6): 1533-1544. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.504 [11] CHEN S, JIAO X C, GAI N, et al. Perfluorinated compounds in soil, surface water, and groundwater from rural areas in Eastern China [J]. Environmental Pollution (Barking, Essex:1987), 2016, 211: 124-131. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.12.024 [12] LEE Y M, LEE J E, CHOE W, et al. Distribution of phthalate esters in air, water, sediments, and fish in the asan lake of Korea [J]. Environment International, 2019, 126: 635-643. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.059 [13] 宋小三, 张国珍, 何春生, 等. 水窖集雨水水质规律研究 [J]. 兰州交通大学学报, 2011, 30(3): 129-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2011.03.029 SONG X S, ZHANG G Z, HE C S, et al. Research on the harvested rainwater quality rule of water cellar [J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2011, 30(3): 129-131(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2011.03.029
[14] CHEN R Y, LI G W, YU Y, et al. Occurrence and transport behaviors of perfluoroalkyl acids in drinking water distribution systems [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 697: 134162. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134162 [15] 弥启欣, 国晓春, 卢少勇, 等. 千岛湖水体中邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)的分布特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 1966-1975. MI Q X, GUO X C, LU S Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological and health risk assessment of phthalic acid esters in surface water of Qiandao Lake, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 1966-1975(in Chinese).
[16] 开晓莉, 张维江, 邱小琮, 等. 清水河污染物对儿童所致健康风险评估 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(12): 2809-2819. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018060402 KAI X L, ZHANG W J, QIU X C, et al. Health risk evaluation of children caused by water pollutants in Qingshui River [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(12): 2809-2819(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018060402
[17] 贺小敏, 施敏芳. 梁子湖水体和沉积物中邻苯二甲酸酯分布特征及生态健康风险评价 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2021, 37(2): 115-127. HE X M, SHI M F. Distribution characteristics and ecological and health risk assessment of phthalic acid esters in surface water and sediment of liangzi lake, China [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2021, 37(2): 115-127(in Chinese).
[18] 赵秀阁, 段小丽. 中国人群暴露参数手册(成人卷)概要[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2014. ZHAO X G, DUAN X L. Highlights of the Chinese exposure factors handbook(adults)[M]. China Environment Publishing Press, 2014(in Chinese).
[19] WANG Y, WANG F, XIANG L L, et al. Risk assessment of agricultural plastic films based on release kinetics of phthalate acid esters [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(6): 3676-3685. [20] 王瑞霖, 冉艳, 黄维, 等. 三峡库区御临河邻苯二甲酸酯类的空间分布特征及关键环境影响因子[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文), 2022, 44(8): 193-200. WANG R L, REN Y, HUANG W, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and key environmental impact factors of phthalates in Yulin River in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area [J]. Journal of civil and Environmental Engineering (Chinese and English), 2022, 44(8): 193-200(in Chinese).
[21] ZHAO X, SHEN J M, ZHANG H, et al. The occurrence and spatial distribution of phthalate esters (PAEs) in the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(16): 19724-19735. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08443-7 [22] 张英, 孙继朝, 陈玺, 等. 东莞地下水邻苯二甲酸酯分布特征及来源探讨 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2011, 33(8): 57-61. ZHANG Y, SUN J C, CHEN X, et al. The distribution characteristics and source of phthalic acid esters in groundwater of Dongguan [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2011, 33(8): 57-61(in Chinese).
[23] ZHANG D, LIU H, LIANG Y, et al. Distribution of phthalate esters in the groundwater of Jianghan plain, Hubei, China [J]. Frontiers of Earth Science in China, 2009, 3(1): 73-79. doi: 10.1007/s11707-009-0017-5 [24] SUN R, WU M H, TANG L, et al. Perfluorinated compounds in surface waters of Shanghai, China: Source analysis and risk assessment [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 149: 88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.012 [25] ZHANG G, PAN Z, WU Y, et al. Distribution of perfluorinated compounds in surface water and soil in partial areas of Shandong Province, China [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:An International Journal, 2019, 28(5): 502-512. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2019.1635079 [26] 高杰, 李文超, 李广贺, 等. 北京部分地区地下水中全氟化合物的污染水平初探 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2016, 11(2): 355-363. GAO J, LI W C, LI G H, et al. Preliminary investigation on perfluorinated compounds in groundwater in some areas of Beijing, China [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2016, 11(2): 355-363(in Chinese).
[27] QI Y J, HUO S L, HU S B, et al. Identification, characterization, and human health risk assessment of perfluorinated compounds in groundwater from a suburb of Tianjin, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(5): 1-12. [28] 昌盛, 樊月婷, 付青, 等. 北江清远段地表水及沉积物中酞酸酯的分布特征与风险评估 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(4): 822-830. CHANG S, FAN Y T, FU Q, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of phthalic acid esters in surface water and sediment of Qingyuan section of Beijiang River [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(4): 822-830(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: