-
随着近代工业的发展,生态环境的污染问题日益严重,其中重金属造成的污染问题尤为突出。环境中的重金属可被农作物吸收,进而进入人体,对人体健康造成危害,因此重金属污染治理的相关研究日益成为热点。重金属污染治理常用的修复方法包括物理、化学和植物法。由于物理、化学方法对环境二次污染严重,成本高,存在一定的局限性。自1983年CHANEY et al[1]首次提出植物修复技术的概念,作为一种绿色的修复技术,近年来该领域受到科学家的广泛关注。该方法相比于化学、物理法等修复技术,对环境友好,并且还能创造额外的经济效益,在重金属污染处于低、中水平的地区有较好的应用效果[2]。基于此,近年来利用植物修复重金属污染的研究和应用日益广泛并产生了大量的研究成果,但对于这些数量庞大、内容庞杂的相关科研文献却缺少系统、科学的统计和分析。
文献计量学(Bibliometrics)是以已发表的文献体系和文献计量特征为研究对象,进行文献定量分析的一种研究方法[3-4]。目前,文献计量分析已广泛用于农林、环境工程与科学、生态学、食品安全等领域科研成果的定性、定量分析,且方法也较为成熟。通过文献计量学分析,不但可对某一领域的研究现状进行总结,还可在此基础上预测未来该领域科研的发展趋势,为该领域的科研工作者开展研究提供方向和参考。
本研究期望通过对近20年植物修复重金属污染的进行相关文献计量和可视化分析,清晰、直观、全面地分析当前该领域的研究成果,对该领域科研成果的特点、重点等进行总结,并对未来发展趋势进行展望。本研究可为重金属污染的修复工程提供理论支持,并为相关研究提供参考。
-
Web of Science(WoS)数据库是获取全球学术信息的重要数据库平台,Web of Science的3大引文索引(SCIE+SSCI+A&HCI)收录了全球12 400多种权威的、高影响力的国际学术期刊,内容涵盖自然科学、工程技术、社会科学、艺术与人文等学科领域[5]。为了探究重金属污染生物修复的研究情况,本研究以Web of Science(WoS)数据库作为英文相关文献检索的数据源,构建高级检索式:TS=("phytoextraction*"OR"phytoaccumulation*"OR"phytostabilization*"OR"phytovolatilization*"OR"phytofiltration*"OR"Hyperaccumulator*"OR"phytovolatilization*") AND TS = ("heavy metal "OR" cadmium" OR"Cd " OR"Mercury "OR"Hg"OR" arsenic"OR "As"OR " lead"OR"Pb"OR" chromium"OR "Cr" )。
本研究检索时间跨度为2000-01-01~2021-09-01,检索时间为2021-09-08,共检索出7 263篇文献,利用Citespace对数据进行除重处理后,进行计量可视化分析。运用WoS自带的分析功能,以及Citespace,Excel 2016等软件,对近20年间发表的有关重金属污染植物修复技术文献进行计量及可视化分析。分析内容包括发文量、发文作者、重要研究机构、关键词、来源期刊、支持基金等,术语来源根据所分析内容分别依次勾选标题、关键词、机构、国家等。时间节点设为 3年,阈值设置为top=50,算法设置为Pathfinder,利用Pruning sliced networks和Pruning the merged network,对网谱进行优化。
-
相关研究领域的发文量在一定程度上可以反映出该领域的研究热度、发展速度及水平。对于重金属污染植物修复的研究,虽然1983年即提出了生物修复的概念,直到90年代中后期,相关的研究才陆续得以开展,且在2000年之后进入了快速发展时期。国际与中国在2000~2010期间发文量均呈上升趋势,个别年份有小幅波动;2011~2020年国际学术界发文量整体而言上升趋势平稳,但中国尤其是最近几年上升趋势明显。这说明近年来全球范围对生态问题高度重视,政府科研投入增加,也促进了科研人员的科研积极性。尤其在国内,生态环境相关政策相继发布,国家和各级政府将生态治理和污染防治提上重点建设日程,随着各级政府的重视,该领域的科研得以迅速发展,见图1。
-
通过对重金属污染的植物修复文章发表的作者进行分析,并对该领域科研工作者发文量进行了排序,筛选出发文量前10的作者,见表1。
在发文量前10的作者中,发文量最高的科研人员为杨肖娥,作为该领域科研的领军人物,在检索时间范围内共发文110篇,H指数高达62。杨肖娥的主要研究内容包括植物营养与环境生态、污染环境植物修复、微量元素与健康等。发文量排第二位是马奇英,其发文量达到79篇,H指数达到57,其主要研究超积累植物在重金属土壤修复中的作用及机理。发文量排第3位的研究人员为骆永明,发文56篇,H指数达到50,主要研究内容为重金属植物修复及螯合剂的添加对植物修复效率的影响。
-
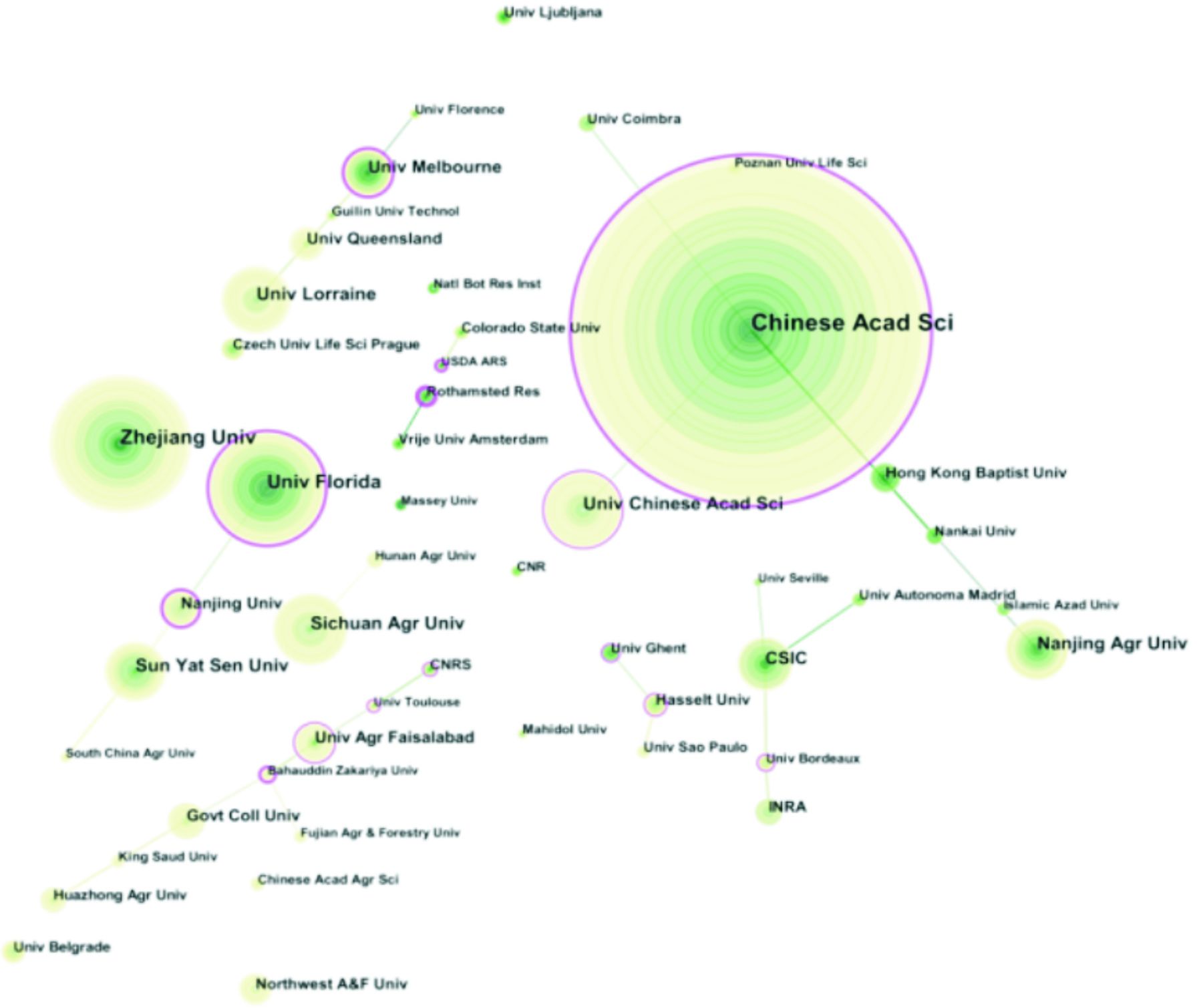
本研究使用Citespace软件对研究机构进行了共现分析,见图2。
图2中共有连线253条,节点243个。结果显示,从机构间合作关系上看,该领域研究机构形成了分别以(1)中国科学院(Chinese Academy of Sciences)、南京农业大学(Nanjing Agricultural University)、科英布拉大学(University de Coimbra);(2)浙江大学(Zhejiang University)、佛罗里达大学(University of Florida)、四川大学(Sichuan University);(3)法国洛林大学(University de Lorraine)、昆士兰大学(The University of Queensland)、墨尔本大学(The University of Melbourne);(4)西班牙国家研究委员会(CSIC)、根特大学(Ghent University)、法国国家农业科学研究院(INRA)、法国国家科学研究中心(CNRS)、图卢兹联邦大学(Federal University of Toulouse Midi-Pyrénées);(5)费萨拉巴德农业大学(University of Agriculture, Faisalabad)、巴哈丁扎卡里亚大学(Bahauddin Zakariya University)、华中农业大学(Huazhong Agricultural University) 5个紧密合作机构组合。另外从共现图上可以看出,中国科学院是发文量最多的科研机构。
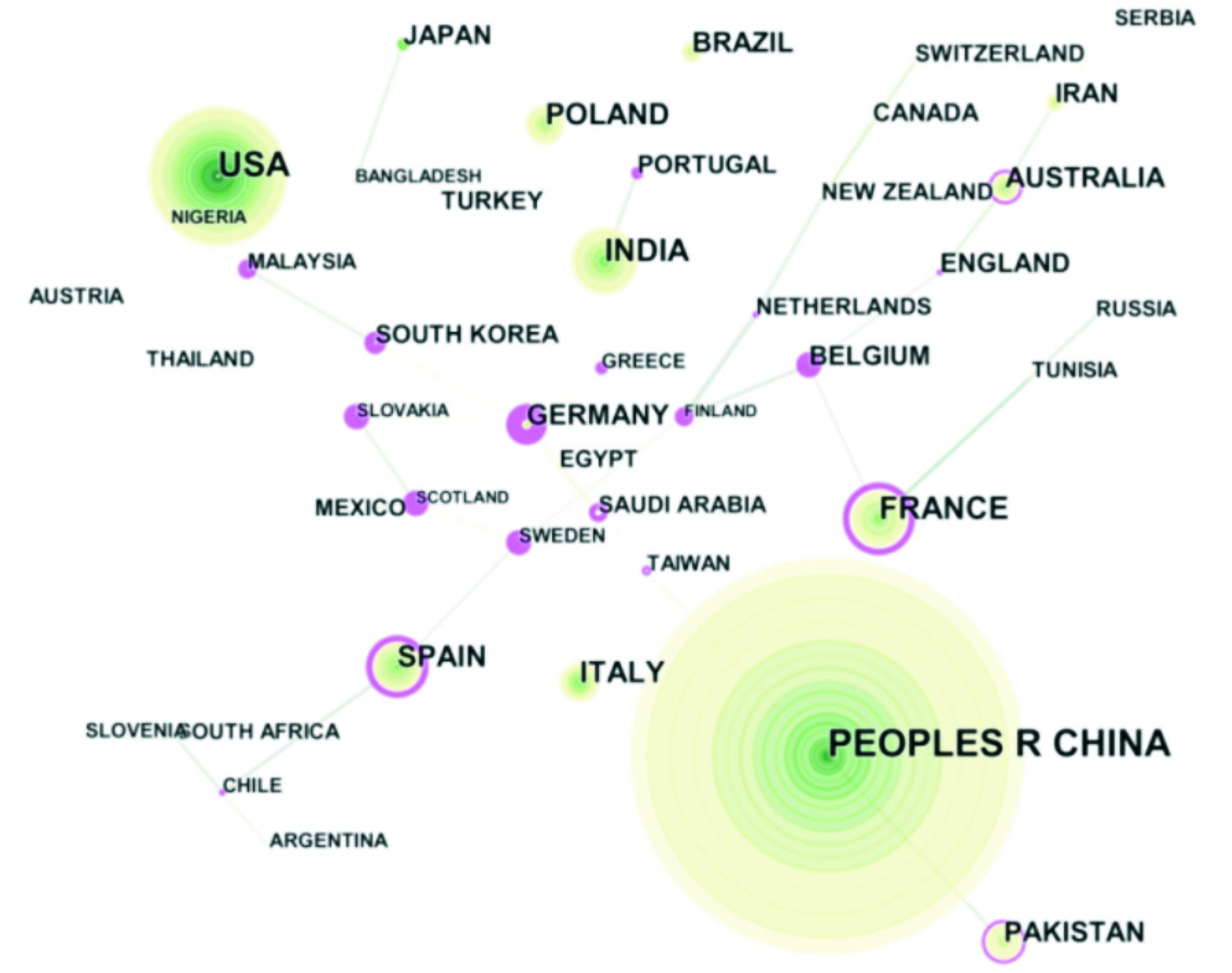
此外,关于发表重金属污染植物修复研究性论文总数前5的国家分别为是中国(CHINA)、美国(USA)、印度(INDIA)、法国(FRANCE)、西班牙(SPAIN),其中中国发文量排名第一,见图3。
该分析结果表明,我国对植物修复重金属污染研究十分重视,并进行了大量的科研工作。同时,图谱中共有连线47条,节点45个。而且,以中国,美国,法国,西班牙为中心的合作组合,也是国际上开展相关研究论文数较多的国家,表明国际合作在推进前沿科研中的重要作用。
-
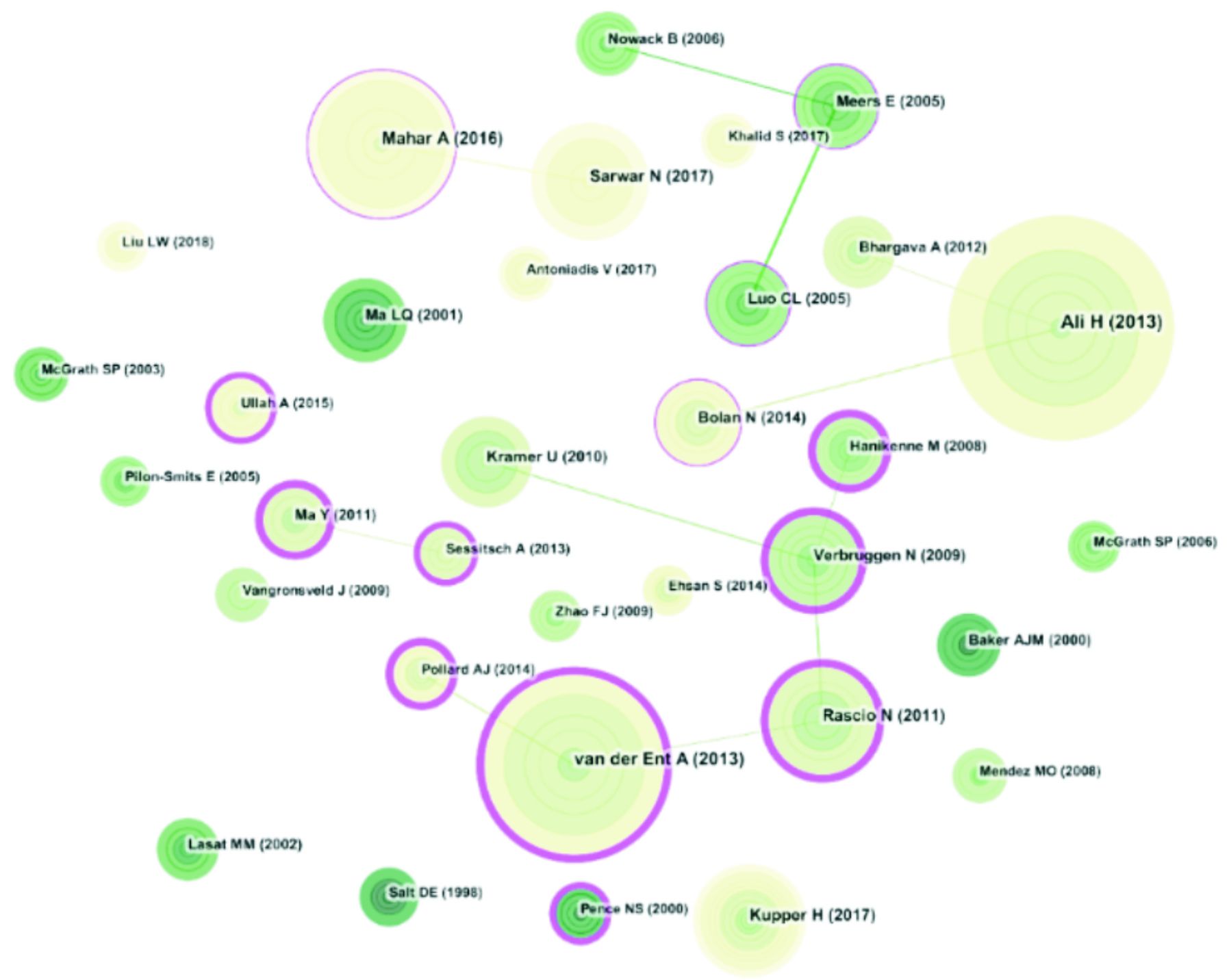
共被引分析是指两篇文献共同出现在第3篇施引文献的参考文献目录里,则这两篇文献形成共被引关系。通过分析文献共被引网络中的关键节点,可以分析该研究领域的经典文献,进而了解该领域的知识结构、知识基础[6]。共被引分析图谱中,共有连线199条,网络节点193个。
重金属植物修复被引频次排名前10文献,最高被引文献为“Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications”。该文献属于综述类文章,系统地总结了利用植物修复重金属污染的研究现状和研究热点,并阐述了植物修复重金属污染的优势和不足,对整个领域相关研究者而言具有很高的参考价值[7]见表3。与该文献联系较为紧密的为BOLAN N发表题目为“Differential Effect of Biochar on the Reduction-induced Mobility and Bioavailability of Arsenate and Chromate”的文章,两篇文章均对重金属的生物利用度进行了讨论。目前,虽然相关研究表明,生物炭、螯合剂等在提高土壤中重金属生物利用度有着显著的效果,但在大规模场地修复应用中,也存在着成本高,二次污染等问题。此外,另一篇高被引文献“Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements: Facts and fiction”与RASCIO N的“Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: How and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting?”以及VERBRUGGEN N的“Molecular mechanisms of metal hyperaccumulation in plants”作为共被引文献,都围绕超积累植物修复重金属污染以及相关分子机制进行了讨论和展望。由此可知,在利用植物修复重金属污染的研究和应用领域,如何利用超富集植物进行修复或如何提高其修复效率一直是研究的热点。如,利用基因工程技术对超富集植物重金属耐受性、富集率等进行改良可能对于提高超富集植物修复效率是个较为理想且技术上可可行的方案。然而,基于社会大众对于基因编辑植物的生物安全性的担忧,相关政策和制度保障机制的完善可能仍是关键,见图4。
-
载文期刊分析可以帮助科研工作者把握该领域核心期刊,追踪该领域最新研究情况。发文量前10的载文期刊,见表4。
表4可知,International Journal of Phytoremediation、Environmental Science and Pollution Research、Chemosphere、Environmental Pollution、Journal of Hazardous Materials在所检索文献中排名前5,是相关科研人员的潜在投稿期刊。其中杂志International Journal of Phytoremediation发文量第1,占所检索期刊的8.019%,但其H指数为49,IF为2.528,属中科院3区期刊,在前10期刊中处于较低水平。该结果说明虽然该期刊发文量高,但可能由于其文章偏向方法研究或创新性等问题,导致H指数与IF偏低。期刊Journal of Hazardous Materials,发文量仅为第5,但其H指数为235,IF为9.52,同为最高,属中科院1区期刊。该结果说明此期刊在植物修复重金属研究领域有着较大的影响力,收录文章水平较高且研究方向具有前沿性,了解该期刊的相关文章有助于科研人员进一步了解该领域最新研究进展及热点问题。
-
关键词作为文献研究内容的高度提炼,通过对关键词聚类分析以及突发性分析,有助于进一步挖掘近年相关研究领域的热点问题。
-
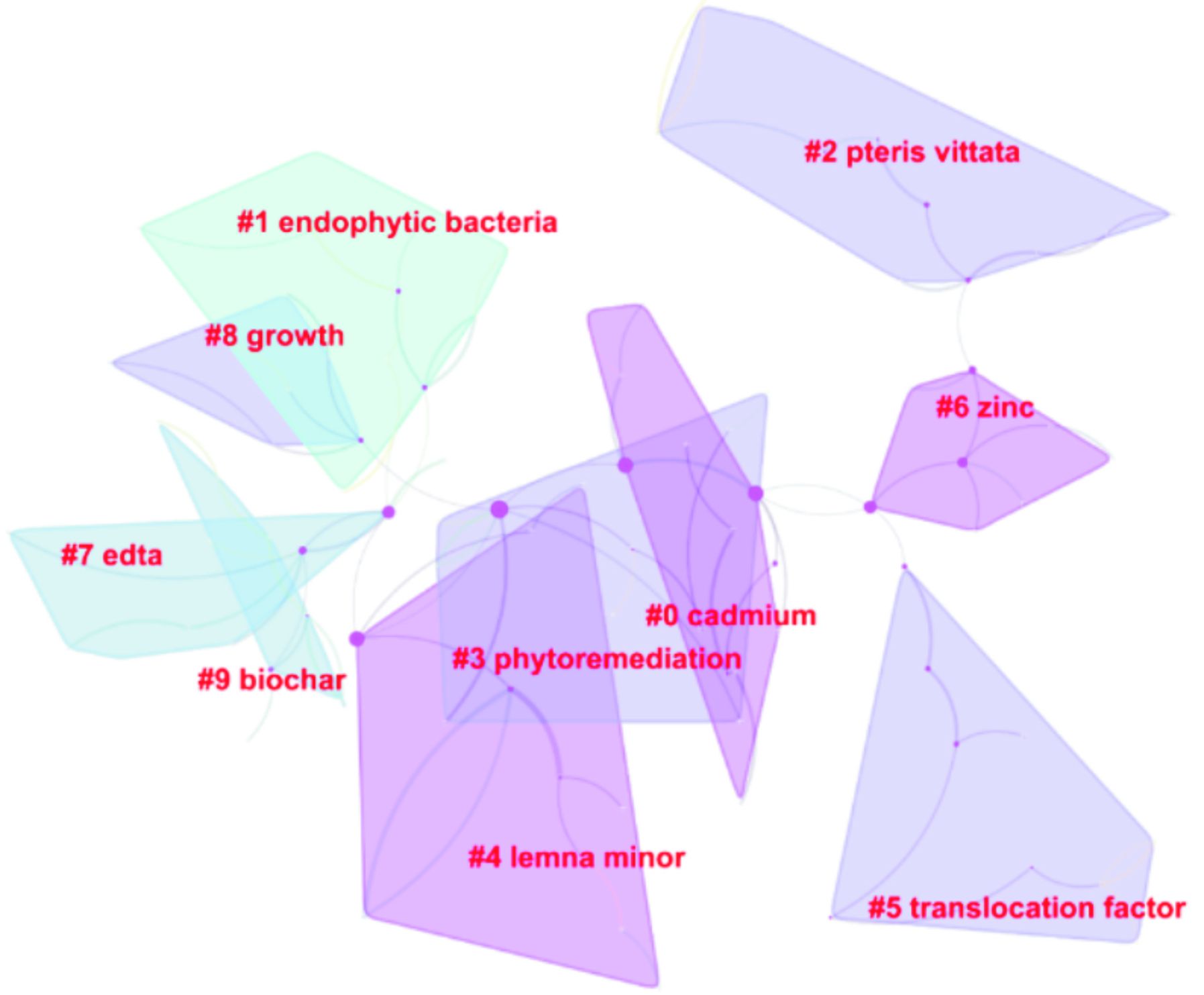
关键词聚类分析通过对该领域特征明显的词进行聚类归纳,有助于探究研究领域之间的相互联系,以及交叉学科等热点问题。关键词聚类分析,见图5。
图5可见,图谱中共出现10个聚类,分别为重金属镉(Cadmium)、植物内生菌(Endophytic bacteria)、植物修复(Phytoremediation)、浮萍(lemna minor)、蜈蚣草(Pteris vittata)、生物炭(Biochar)、转移系数(Translocation factor)、乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)、金属锌(Znic)和植物生长(Growth)。其中金属螯合剂EDTA,常被用于植物稳定修复。在修复过程中,螯合剂通过与重金属形成强水溶性复合物从土壤固相中解吸有毒金属,再利用植物根际吸收或利用植物根系分泌物、酶等物质与重金属螯合,降低土壤中重金属迁移性和生物有效性,从而有效降低重金属淋溶到地下水并进一步污染环境的风险。但大规模的施用金属螯合剂必然造成环境的二次污染,因此,如何合理利用螯合剂在提高重金属生物有效性的前提下,避免对环境的二次污染成为研究的关键。“蜈蚣草”和“浮萍”,这两个关键词聚类的重点都集中于超富集植物。自BROOKS提出了超富集植物的概念以来,目前已发现400多种植物对土壤中重金属具有吸收提取的作用[9-10]。CHEN et al[11]首次在中国境内发现重金属As超富集植物蜈蚣草,为我国利用超累积植物进行重金属污染修复奠定了基础。此外,相关研究也发现中国蕨类植物有作为对砷和铊复合污染土壤进行修复的优选植物物种的潜力。但目前而言,利用植物修复铊污染土壤的相关研究却鲜有发表,因此从细胞和基因水平上对中国蕨类对铊吸收、积累的功能和机制的相关研究可能是未来的一个很有潜力的研究方向。
“生物炭”也是聚类的一个关键词,自HILTON等人发现生物炭在土壤中对非草隆等农药有较好的吸附效果以来,生物炭对水土中各类污染物的治理应用一直是研究热点[12]。目前研究认为,在重金属污染土壤中添加相应的生物炭能够提高土壤的pH值和有机质含量,改变其氧化还原电位和土壤微生物群落构成,以此降低重金属的生物可利用性[13]。ZHANG et al[14]通过水相还原成功制备了活性生物炭A-BC-NZVI复合材料,该材料具有固定铀U(Ⅵ)的有效吸附能力,A-BC-NZVI在对含有铀U(Ⅵ)的污水治理应用中具有广阔的前景。尽管生物炭在修复重金属方面有着良好的效果,但持久有效性低也导致实际修复周期短,不宜作为主要修复材料。在今后的研究中,生物炭配合植物共同修复重金属污染仍有可能是研究的重点。生物炭一方面作为重金属的吸附材料,另一方面作为土壤养分改良剂,在改善修复植物初期生存率低,生长缓慢等方面可能具有不错的效果。
-
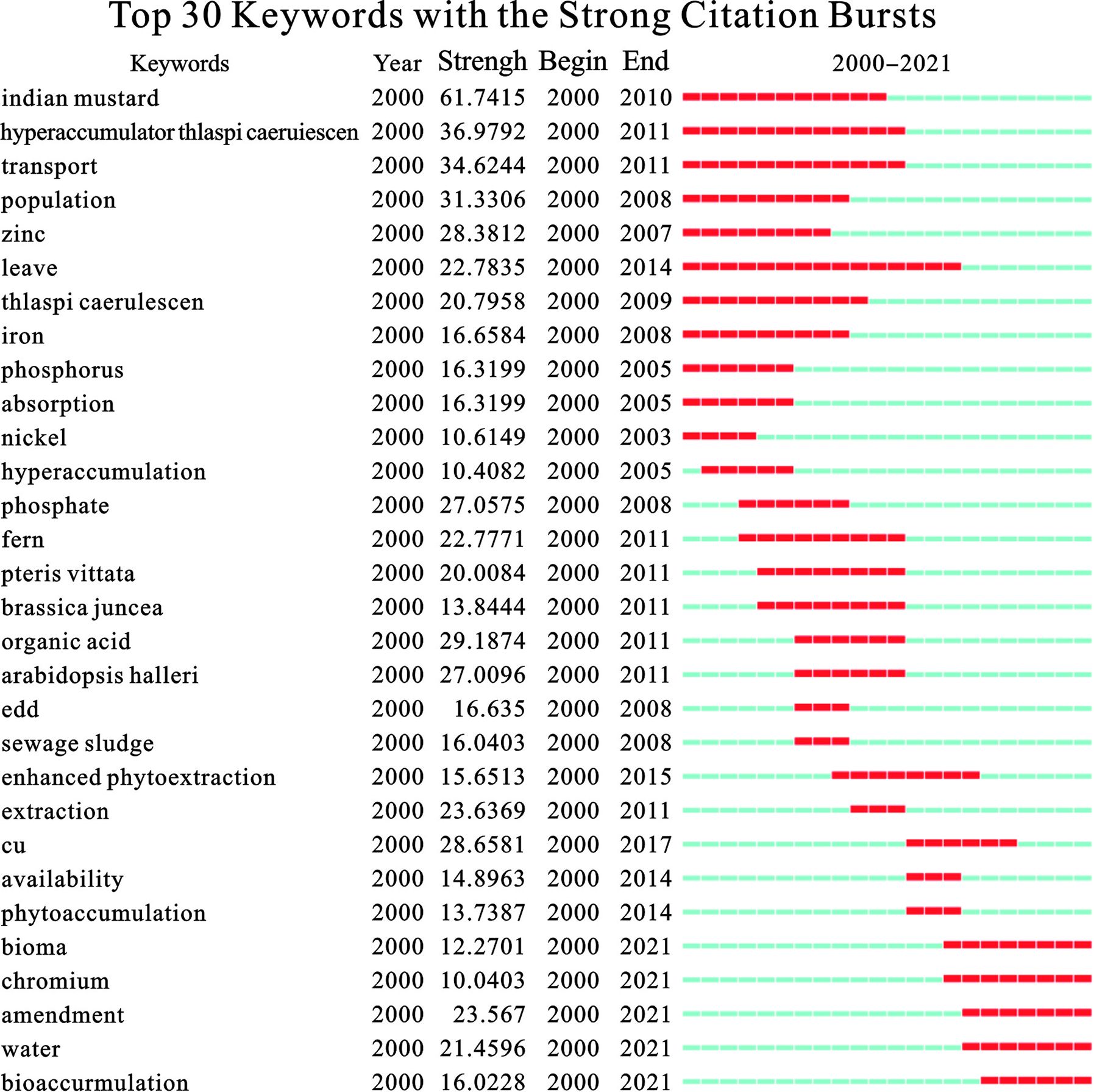
关键词突发性分析提供了特定关键词与出现频率激增相关联的证据,关键词的爆发表明一个潜在的话题已经或正在引起研究人员在特定时期特别的关注。因此关键词的突发性被认为是高度活跃研究领域的重要指标,可被用于指导研究领域新兴趋势的探索[7]。
本研究对植物修复重金属污染的前30个关键词突现进行分析后发现,“Indian mustard”的突现强度为61.7415,“transport”的突现强度为34.6244,“pollution”的突现强度为31.3306。分析结果表明,作为突现强度最高词,“Indian mustard”可被视为这一时期的研究热点,随着近年来基因测序等技术的成熟和成本下降,原本不属于模式植物的Indian mustard的相关基因组信息逐步得以了解,因此针对其与重金属相关的基因功能、生理生化、细胞等相关研究得以迅速的发展。而持续时间最长的突现词是“leave”,持续时间是从2000~2014年。植物虽然是通过根系将重金属从土壤中吸收到植物体内,但如果想实现重金属污染土壤问题的根本解决,还是需要将根部的重金属转入植物的地上部分,尤其是草本植物的叶片部位,以利于后期的收割、回收。因此,进入叶片等器官的重金属的比率(转移率)是实现植物修复的一个关键指标。突现时间最晚的突现词是“pollution”,首次突现于2017年,这可能与生物修复由概念、基础科研向实用性转化的趋势有关,见图6。
-
(1)从重金属污染植物修复的相关文献的检索及分析过程可以发现,文献的数量逐年增加,表明重金属污染植物修复研究已经越来越受到国内外学术界的关注。其中发文量前3的期刊分别为International Journal of Phytoremediation、Environmental Science and Pollution Research、Chemosphere,发文量前3的国家分别为中国、美国、印度。我国对于土壤重金属污染植物修复的研究十分重视,并对该领域的科研发展做出了显著的贡献。
(2)从总联系强度看,该领域的科研力量已经形成以中国、美国、法国、西班牙为中心的合作组合。国际合作开展科研是该领域研究的趋势也是重要推动力量。我国科学家杨肖娥作为发文量和H指数最高的科研人员,属于该领域科研的领军人物。
(3)文献共被引及关键词强度分析结果表明,当前植物修复重金属污染领域的研究热点为利用重金属离子螯合剂、生物炭等新型材料与超富集植物联合修复重金属污染的方法及机理的研究。此外,利用新的超富集模式植物从遗传、分子的角度对其吸收、转运、富集基因及机理的研究也是一个新的趋势。
植物修复重金属污染相关研究的文献计量分析
Bibliometric analysis of research on phytoremediation of heavy metal pollution
-
摘要: 基于Web of Science数据作为数据源,借助Citespace文献计量工具对2000~2021年植物修复重金属污染领域的相关文献从发文量、发文国家、载文期刊、关键词等方面进行计量分析,以探究分析国内外该领域的研究现状、前沿热点及未来发展趋势。结果表明:2000~2021年该领域发文量在近年来呈总体上升趋势,发文量排前3位期刊分别为International Journal of Phytoremediation, Environmental Science and Pollution Research, Chemosphere;发文数量前3位的国家分别是中国、美国、印度;杨肖娥是发文量和H指数最高的科研人员,属于该领域领军人物。文献共被引及关键词强度分析表明,当前该领域研究热点为利用重金属离子螯合剂、生物炭等新型材料或超富集植物等对重金属污染进行的联合修复。
-
关键词:
- 植物修复 /
- 重金属污染 /
- 计量分析 /
- Web of Science数据库
Abstract: Based on the Web of Science TM core collection database, bibliometric analysis of the articles related to phytoremediation of heavy metal contamination was performed, which had been published from 2000 to 2021. To clarify the status, research hot spots and the trends, the number, the original country, the source journal and the keywords of these publications were analyzed. The results showed that the publication number increased from 2000 to 2021. In terms of publication number, the top three journals were International Journal of Phytoremediation, Environmental Science and Pollution Research and Chemosphere, and the top three countries were China, the United States and India. Besides, Xiao E YANG was the scientist with the highest publication number. The literature co-citation and keyword strength analyses showed that the research focus in this field was applying materials such as heavy metal ion chelators, biochar or hyperaccumulation plants for the remediation of heavy metal pollution. -

-
表 1 发文量前10作者分析
作者 发文数量 H指数 中心性 杨肖娥 110 47 0.03 马奇英 79 73 0.07 骆永明 56 63 0.02 吴龙华 55 34 0.03 GUILLAUME Echevar 51 7 0.02 魏树和 48 28 0.02 SHAFAQAT Ali 47 58 0.01 林立金 45 19 0.00 仇荣亮 44 48 0.06 何振立 43 52 0.02 李廷强 43 37 0.02 表 3 重金属植物修复被引频次排名前10文献
文献题目 t/a 出版期刊 作者 总被引频次 中心性 Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications 2013 Chemosphere ALI H 252 0.09 Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements:
Facts and fiction2013 Plant Soil ANTONY 203 0.84 Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review 2016 Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety MAHAR A 167 0.11 Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives 2017 Chemosphere SARWAR N 132 0.05 Lead Toxicity in Plants 2017 Metal Ions in Life Sciences KUPPER H 131 0.04 Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: How and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? 2011 Plant Science RASCIO N 123 2.94 Molecular mechanisms of metal hyperaccumulation in plants 2009 New Phytologist VERBRUGGEN N 107 0.9 Metal Hyperaccumulation in Plants 2010 Annual Review of Plant Biology KRAMER U 104 0.08 A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic 2001 Nature LENA Q Ma 8 0.1 Comparison of EDTA and EDDS as potential soil amendments for enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals 2005 Chemosphere MEERS E 96 0.16 表 4 重金属污染植物修复相关发文量前10的期刊
载文期刊 发文量 占比 IF H指数 中科院分区 International Journal of Phytoremediation 582 8.019 2.649 49 3 Environmental Science and Pollution Research 453 6.231 3.33 82 3 Chemosphere 409 5.626 6.195 212 2 Environmental Pollution 246 3.392 7.314 194 2 Journal of Hazardous Materials 218 2.997 9.52 235 1 Science of The Total Environment 218 2.997 7.137 205 2 Plant and Soil 217 2.984 3.537 163 2 Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 192 2.642 5.248 110 2 Water Air and Soil Pollution 145 1.998 2.019 100 4 Environmental and Experimental Botany 119 1.643 4.173 105 2 注:H指数指在所有发表的论文中,有至少H篇论文分别被引用了至少H次,那么这份期刊或会议的H指数就是H。影响因子(IF)是某一期刊的文章在特定年份或时期被引用的频率,是衡量期刊的质量及影响力的重要指标,一般来说,期刊的影响因子越高,影响力越高[8]。 -
[1] CHANEY R L. Plant uptake of inorganic waste constituents[C]//Land Treatment of Hazardous Wastes. Noyes Data Corporation. New Jersey, 1983: 50-76. [2] ZHAO S P, YE X Z, ZHANG Q, et al. Soil contaminated by heavy metals: Comparison of bioremediation methods[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin. 2020, 36(20): 83-91. [3] GAO Y F, XU Y N, ZHU Y X, et al. An analysis of the hotspot and frontier of mine eco-environment restoration based on big data visualization of VOSviewer and CiteSpace[J]. Geological Bulletin of China. 2018, 37(12): 2144-2153. [4] LI Y Y, HU Z P, DU C D, et al. Bibliometric analysis of the research status and hot-spots on Aconitum L. [J]. Journal of Modern Medicine & Health. 2020, 36(16): 2490-2493. [5] 吕茜倩. “双一流”背景下理性应用WOS系列数据库助推学科服务[J]. 大学教育, 2020(6): 3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3437.2020.06.060 [6] CHEN B, ZHANG Y, RAFIQ M T, et al. Improvement of cadmium uptake and accumulation in Sedum alfredii by endophytic bacteria Sphingomonas SaMR12: Effects on plant growth and root exudates[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 117: 367 − 373. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.078 [7] HAZRAT A L, EZZAT K, MUHAMMAD A S. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91(7): 869 − 881. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075 [8] MOREIRA L F P, et al. The archives and the publication of its first impact factor[J]. Arquivos Brasileiros De Cardiologia, 2010, 95(1): 1 − 2. doi: 10.1590/S0066-782X2010001100001 [9] BROOKS R R, LEE J, REEVES R D, et al. Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1977, 7: 49 − 57. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(77)90074-7 [10] 张文博, 王彩虹, 刘艳萍. 重金属富集植物的超积累机理研究进展[J]. 云南化工, 2020, 47(12): 9 − 11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-275X.2020.12.03 [11] CHEN T B, WEI C Y, HUANG Z C, et al. Arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. and its arsenic enrichment characteristics[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002(3): 207 − 210. [12] 姜时欣. 生物炭对水体及其沉积物中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附效果研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学 2020. [13] KOBYA M. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto hazelnut shell activated carbon: kinetic and equilibrium studies[J]. Bioresource technology, 2004, 91(3): 317 − 322. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2003.07.001 [14] ZHANG Q, WANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Active biochar support nano zero-valent iron for efficient removal of U(VI) from sewage water[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 852(25): 156993. -



 下载:
下载: