-
固定床吸附装置广泛应用于大气污染防治、军事护学及核电等领域的有毒有害气体防护及净化,其可靠性和有效性决定了净化效果的好坏,以及系统效能的实现。由于吸附装置内的吸附材料 (通常为活性炭) 装填不密实、密封材料老化破裂、运输安装不当等因素造成的内部结构损坏,均会引起吸附装置发生机械泄露[1-4]。机械泄露的情况一旦发生,有毒气体将瞬时穿透防护层,导致吸附装置净化效能降低甚至失效[5-7]。因此,吸附装置机械泄露的非破坏性评价已引起国内外研究者重视。
机械泄露非破坏性评价的关键是根据吸附材料选择合适的示踪剂 (气体) 。利用示踪气体的吸附穿透时间与机械泄露的瞬时穿透之间的时间间隔可判断吸附装置是否存在机械泄露,并在测试结束后采用气流反向吹扫脱附的方法将残留在吸附装置内部的示踪剂完全脱除,从而不会对吸附装置的净化性能造成影响。氟利昂11的化学式为CCl3F,分子量137.37 g·mol−1,在1.01×105 Pa (1个标准大气压) 下沸点为23.7 ℃,水溶量为0.000 11 g·g−1。该化合物具有化学性质稳定、低浓度易检测、易脱附、无毒无害等特点,并且在吸附材料上具有一定的吸附容量,可作为机械泄露非破坏性检测的示踪气体。美国萨瓦那河实验室曾使用氟利昂11进行碘吸附器泄漏实验[8-9],发现氟利昂11可用于碘吸附器的出厂实验及现场测试。中国核辐射防护研究院对碘吸附器泄露试验中氟利昂11在活性炭床层的解吸行为进行了研究[10],提出了有利于氟利昂11在活性炭床层解吸的方法及条件。王坤俊等[11]开展了碘吸附器脉冲式氟利昂法泄露的检测技术研究,取得了与连续法进样一致的结果,并发现脉冲式进样更节省示踪剂用量。标准《M48A1过滤吸收器性能指标》(MIL-PRF-32137)[12]、《M98过滤吸收器性能指标》(MIL-PRF-51525B)[13]、《气相吸附过滤吸收器滤芯单元性能指标》(MIL-PRF-32016)[14]等均规定将氟利昂类物质作为此类吸附装置机械泄露非破坏性检测的示踪剂。目前,我国相关领域固定床吸附装置机械泄露的非破坏性检测方法尚未建立起来,相关的标准长期处于空白。
氟利昂类气体在吸附装置的吸脱附行为是建立机械泄露非破坏性评价的基础,目前鲜有研究报道[3]。本课题组基于前期研究成果[15-16],系统研究了低浓度氟利昂11气体在专用浸渍炭材料上的吸附穿透和脱附行为,并采用Wheeler方程、Yoon-Nelson方程、LDF方程以及Freundlich方程等动力学模型研究其吸脱附动力学,揭示氟利昂11在浸渍炭床层的吸脱附规律,以期为我国相关领域固定床吸附装置的研发及机械泄露非破坏性检验方法的建立提供参考。
-
采用山西新华化工有限责任公司生产的柱状浸渍活性炭作为吸附材料。该材料为微孔吸附剂,含有少量中孔,其比表面积和孔结构参数见表1。本课题组对该材料表面含氧官能团表征分析的研究表明,其表面含氧官能团以羟基、醚基为主,含有少量的羰基、醌基、羧基、酯基等基团[11]。测试前将浸渍炭样品置于干燥箱中在110 ℃条件下预处理12 h,以去除样品表面的水分和杂质。实验所用吸附质为氟利昂11气体 (23 546.49 mg·m−3标准气体,由北京海普气体有限公司提供) 。
-
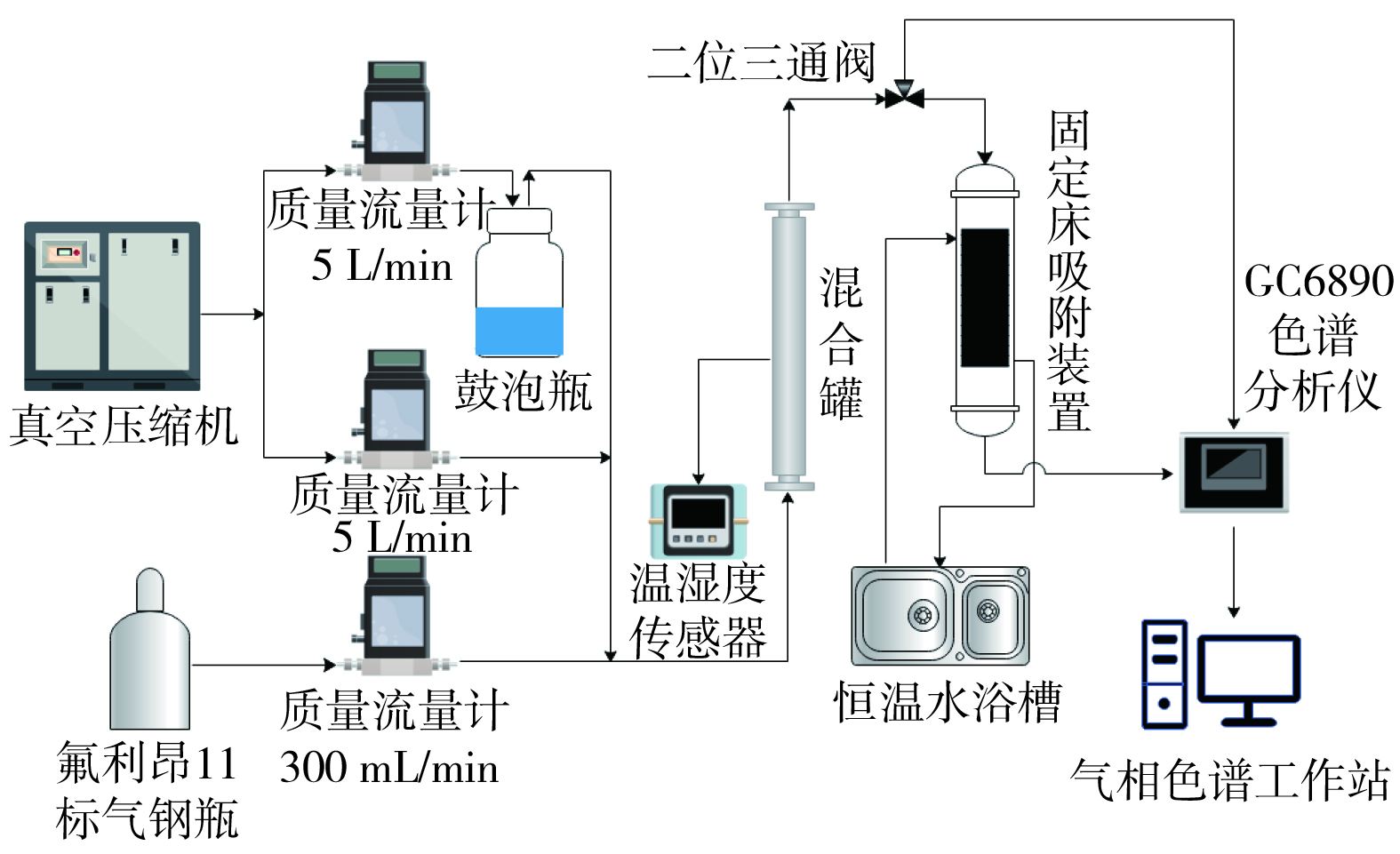
实验装置 (图1) 主要由氟利昂11气体发生系统、固定床吸附系统和气体检测系统3部分组成。使用半径1 cm、长度10 cm的不锈钢动力管作为固定床吸附装置,其实验温度调控通过恒温水浴 (F12,德国优莱博科技公司) 循环加热实现。氟利昂11气体的发生通过空气压缩机 (QWWJ-100,上海曲晨机电技术有限公司) 产生的气体作为背景气和氟利昂11标气2条气路混合进行,分别由质量流量计 (D08-1F,北京七星华创电子股份有限公司) 控制流量,发生质量浓度为588.66 mg·m−3的氟利昂11气体。另一路采用鼓泡法通过调节吹扫气体的流量控制发生气流的相对湿度。三路气体在混合罐内混匀,气体温度和相对湿度由温湿度传感器 (HMP130,芬兰维萨拉公司) 在线监测。气体经过混合罐后,由二位三通阀进行切换,由气相色谱仪 (GC6890,美国安捷伦科技公司) 对氟利昂11气体初始浓度和吸附装置尾气浓度进行在线检测。
-
1) 吸附穿透曲线测试。采用图1所示实验装置测试不同气流比速和气流湿度条件下氟利昂11在浸渍炭床层的穿透曲线。首先,考察气流比速对氟利昂11吸附穿透的影响,条件为氟利昂11初始质量浓度588.66 mg·m−3、实验温度20 ℃、床层厚度3 cm,气流湿度<1%,控制气流比速为0.5、0.8、1、1.2 L·min−1·cm−2;然后,考察气流相对湿度对氟利昂11吸附穿透的影响,条件为氟利昂11初始质量浓度588.66 mg·m−3、实验温度25 ℃、床层厚度3 cm,气流比速为1 L·min−1·cm−2,控制气流相对湿度为(<1%、30%、44%、60%、74%)。
通过对穿透曲线积分计算得到饱和吸附容量,计算公式[17]见式(1)。利用Wheeler方程和Yoon-Nelson方程对穿透曲线进行拟合,通常被用来研究床层的吸附动力学,以反映气体吸附质在固定床的传质过程[18]。Wheeler方程能描述气体在床层的低浓度透出阶段的穿透行为[19]。Yoon-Nelson方程能较为准确地描述S型穿透曲线中浓度达到50%阶段由吸附剂的活性位和吸附质分子数共同控制的准二级吸附动力学过程[20]。方程表达式分别为式(2)和式(3)。
式中:qe为饱和吸附量,mg·g−1;F为气体流速,mL·min−1;C0和Ct分别表示床层入口和出口气体浓度,mg·m−3;M是吸附质分子质量,g·mol−1;ts为达到完全穿透的时间,min;m为吸附剂的质量,g;V为实验温度下的气体分子体积,L·mol−1。
式中:tb为达到穿透分率Cx/C0的时间,min;C0和Cx分别为床层入口和出口质量浓度,mg·m−3;Q为体积流量, cm3·min−1;W为炭吸附剂的重量,gc;ρb为床层的堆密度,gc·cm−3;Wc为饱和吸附量,g·gc−1;kv为吸附速率系数,min−1。
Yoon-Nelson方程见式(3)。
式中:t为穿透时间,min;τ为50%穿透时间,min;k′为吸附速率常数,min−1;C0和Cx分别为床层入口浓度和出口质量浓度,mg·m−3。
2) 空气吹扫脱附实验。分别研究了气流比速、温度及床层含水率等因素对脱附行为的影响,以确定机械泄露吹扫脱附的最佳操作条件。测试了不同气流比速、温度及床层含水率条件下氟利昂11在浸渍炭床层的脱附曲线。首先,将质量浓度为588.66 mg·m−3的氟利昂11气体以脉冲进样方式在固定床内吸附3 min。控制吸附实验条件为氟利昂11质量浓度588.66 mg·m−3,气流比速0.5 L·min−1·cm−2,温度20 ℃,床层厚度3 cm。在吸附结束后,以一定流量的洁净空气对床层进行反向吹扫脱附。在研究气流比速对脱附的影响时,调节气流比速分别为0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2 L·min−1·cm−2,控制脱附气流的相对湿度<1%,脱附温度30 ℃;在研究脱附温度对脱附的影响时,设置脱附温度分别为20、25、30、35、40 ℃,控制脱附气流比速0.8 L·min−1·cm−2,脱附气流相对湿度<1%;研究床层含水率对脱附的影响时,先对床层进行预吸附水处理,即采用1 L·min−1的流量分别发生<1%、30%、48%、70%不同相对湿度的气流,吹扫床层12 h,使床层含水率分别达到0%、5%、10%、22%[15]。接着,分别对不同含水率的床层进行吹扫脱附实验,其条件为脱附温度30 ℃,脱附气流比速为0.8 L·min−1·cm−2,气流相对湿度<1%。
采用线性驱动力LDF模型和Freundlich动力学模型来描述浸渍炭床层氟利昂11气体的热脱附动力学。LDF模型主要用来描述涉及主要机制单一的受扩散控制的动力学过程。方程如式(4)所示。Freundlich动力学模型描述了一系列反应机制的过程,主要用于描述吸附能随表面饱和度的增加呈指数衰减的过程,其方程如式(5)所示[21-25]。
式中:Qt为在时间t时的脱附量,mg·g−1;Qe为平衡脱附量,mg·g−1; k为脱附动力学常数,h−1。
式中:C为吸附质的质量浓度,mg·m−3;A和B为脱附动力学常数,h−1。
-
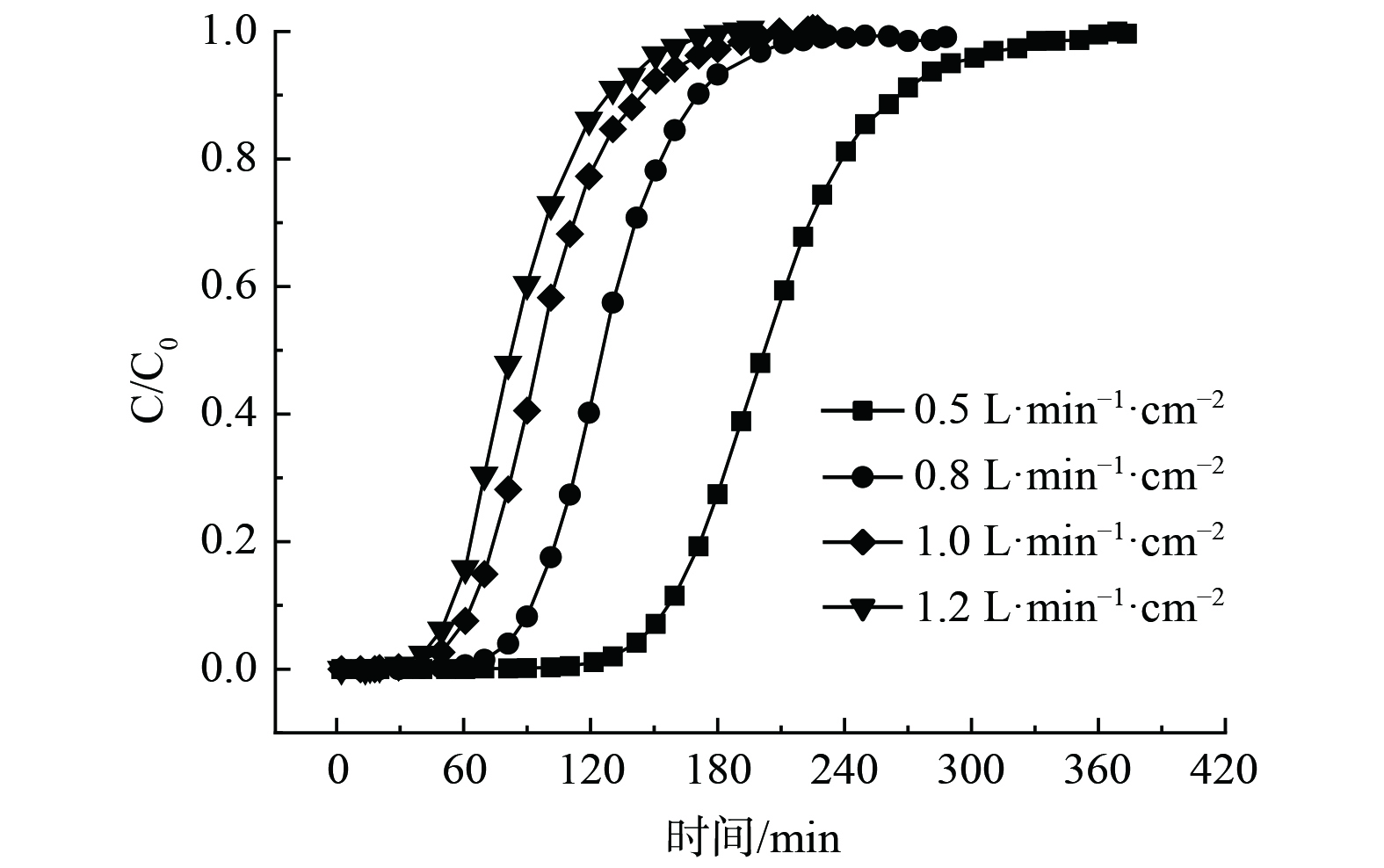
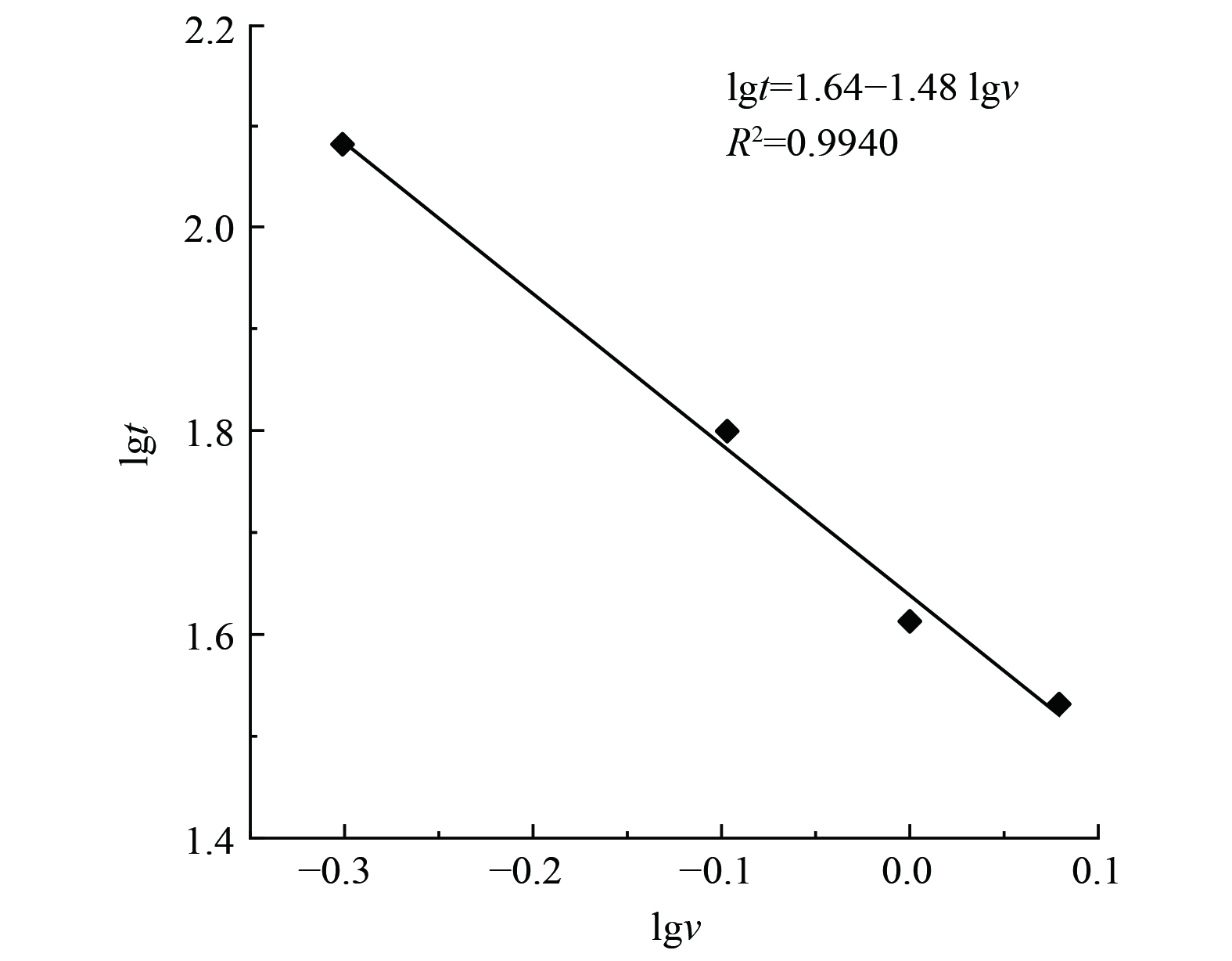
不同气流比速条件下氟利昂11在浸渍炭床层的吸附穿透曲线为图2。采用Wheeler方程和Yoon-Nelson对穿透曲线进行了拟合计算,拟合结果见表2。随着气流比速的逐渐增大,吸附过程的穿透时间和达到吸附平衡的时间依次缩短。改变气流比速,吸附床层的饱和吸附量变化不大,当氟利昂11初始质量浓度588.66 mg·m−3时,不同比速下动态饱和吸附容量维持在约30 mg·g−1。吸附速率常数随气流比速的提高逐渐增大,在低浓度穿透阶段,气流比速从0.5 L·min−1·cm−2提高到1.2 L·min−1·cm−2,氟利昂11的吸附速率增大了153%,这表明气体吸附速率主要受外扩散阶段控制。将吸附质出口质量浓度达到入口质量浓度的1%时视为穿透,对应时间定义为1%穿透时间。在不同气流比速下,浸渍炭床层对氟利昂11的穿透时间数据如表2所示。随着气流比速的增大,穿透时间减小,大体上呈负指数关系。分别用lgt (1%穿透时间) 与lgv (气流比速) 进行线性标绘,可得到很好的线性拟合结果 (图3) ,进而得出氟利昂11的1%穿透时间与气流比速的定量关系式:lgt=1.64-1.48lgv (1%穿透) 。
-
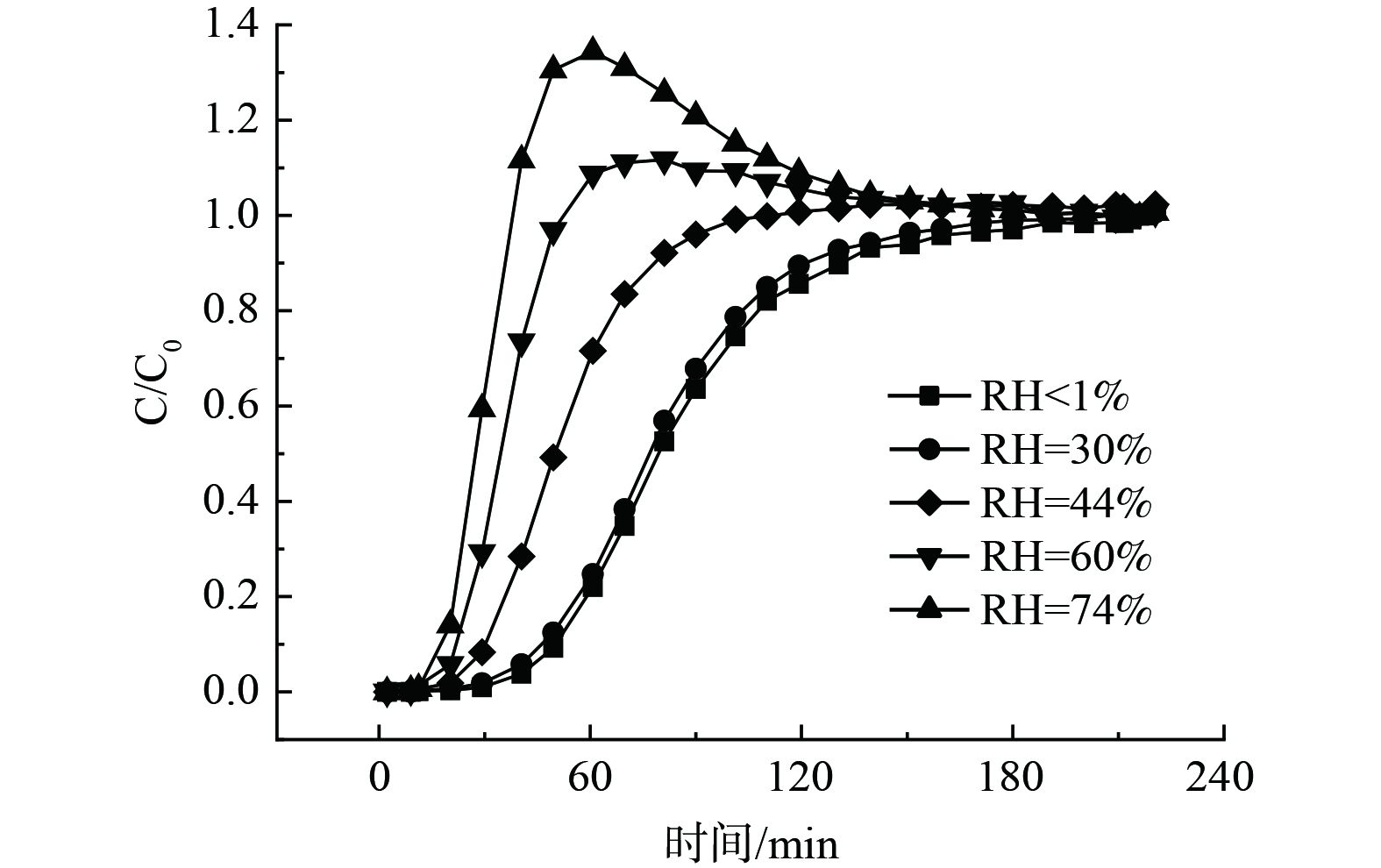
在不同气流湿度条件下,氟利昂11在浸渍炭床层的穿透曲线见图4。随着气流湿度的升高1%穿透时间依次缩短。在气流湿度低于30%时,气体吸附受影响较小,穿透曲线形状变化不明显,仍为S型曲线。当气流湿度从44%增大到74%时,穿透曲线出现卷起现象,且随着相对湿度的提高穿透曲线的卷起程度增大,这是由于水分子与氟利昂11分子发生竞争吸附所致。当气流湿度增大时,在初始穿透阶段,由于浸渍炭表面含有大量亲水基团,易与水分子结合,占据活性炭表面更多的有效吸附位点,使其表面吸附位点数减少,导致氟利昂11的1%穿透时间缩短。浸渍炭表面的含氧官能团与水分子结合成氢键的作用力强于吸附质分子与材料表面形成的范德华力,使得水分子相对于吸附质分子是强吸附组分[26-27]。随着气流湿度的增加,已被吸附的吸附质分子被后续进入的水分子替换,由气流带出,使得在氟利昂11达到完全穿透之前,床层出口端质量浓度比入口质量浓度要高,导致穿透曲线出现卷起的形状[28-29]。
采用Wheeler方程和Yoon-Nelson方程对湿度条件的穿透曲线进行拟合,计算结果列于表3中。随着气流湿度的升高,1%穿透时间缩短,动态饱和吸附容量显著下降,而吸附速率不断增大。气流湿度从30%增大到60%,对氟利昂11的吸附速率增大了1.2倍。气流湿度因素对饱和吸附容量的影响效果显著,气流湿度从30%增大到74%,氟利昂11的饱和吸附容量减少了92.1%。这可能是由于水分子吸附放热产生热效应使床层处于非等温状态,床层温度上升,导致吸附速率加快[16]。从吸附平衡的热效应来看,温度升高促使吸附质分子发生解吸,在床层尾端脱附被气流带出,导致氟利昂11饱和吸附量下降。
-
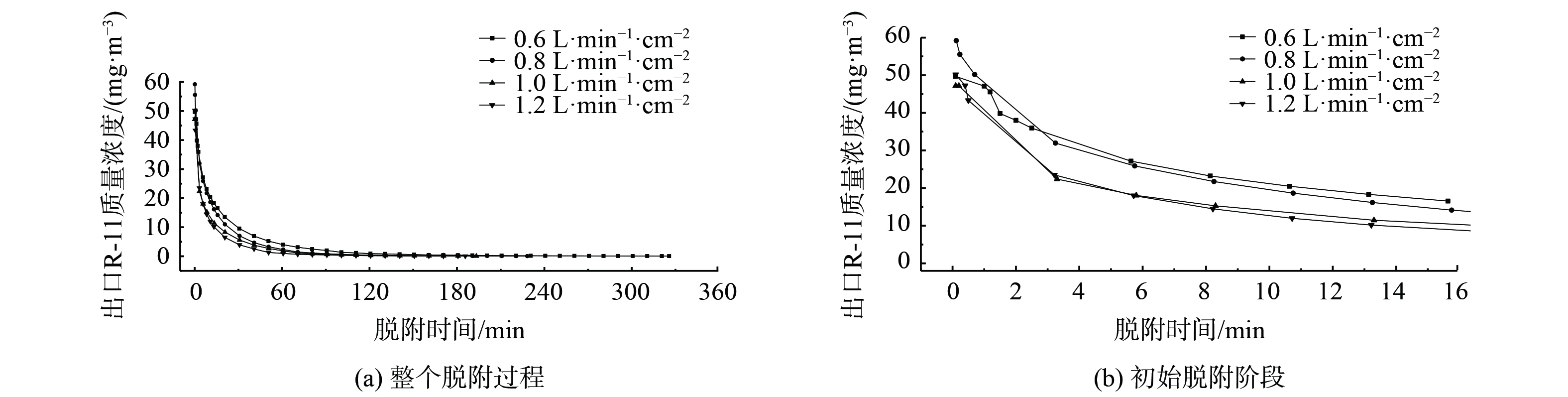
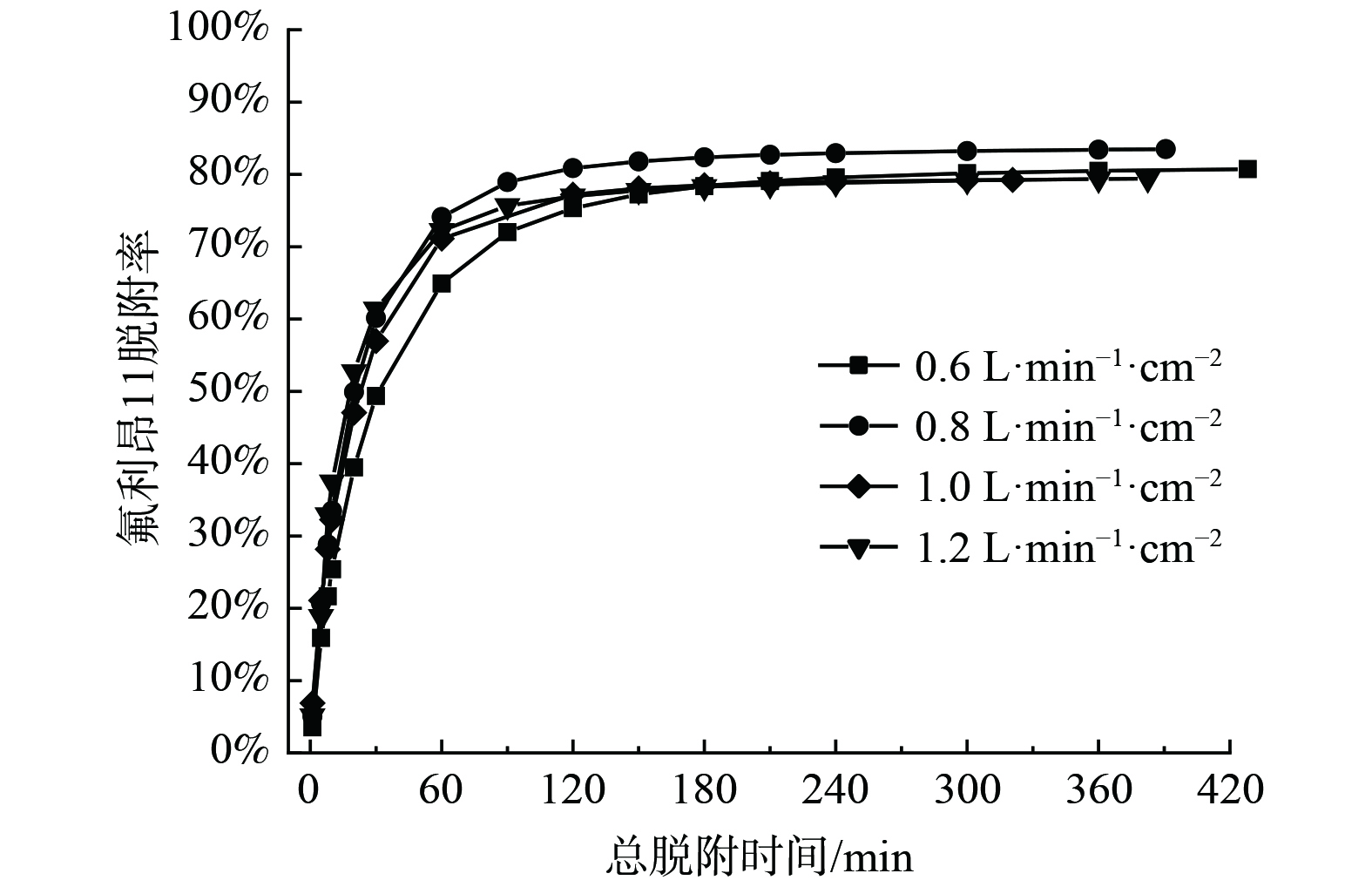
空气吹扫气流比速对氟利昂11脱附的影响见图5、图6和表4,出口气流中氟利昂11质量浓度随时间的变化关系呈半抛物线关系。浸渍炭床层对氟利昂11的脱附经过先快速后慢速的过程,床层出口端氟利昂11质量浓度在脱附操作开始阶段很快达到浓度峰值。在接近脱附平衡阶段,脱附曲线表现出拖尾的特征。反向吹扫脱附造成靠近脱附气流进口端床层被吸附的吸附质分子被吹扫脱附后随气流方向向下扩散,从而被再次吸附。同时,部分吸附在弱吸附位点上的吸附质分子随气流流出,并且在强吸附位点上吸附的吸附质分子脱附速度偏慢。因此,随着脱附过程的进行,氟利昂11质量浓度缓慢减小并呈现拖尾的趋势。
通过对脱附曲线进行积分,利用式(1)求得不同脱附时间下对应的脱附量,进而得到氟利昂11气体脱附操作时间和床层中氟利昂11脱附效率的关系曲线 (图6) 。在不同气流比速下,床层中氟利昂11脱附率的变化情况基本一致。经过一段时间的处理后,床层中氟利昂11气体的去除率达到约80%。当脱附气流比速为0.8 L·min−1·cm−2和1.2 L·min−1·cm−2时,在吹扫脱附的初始阶段,床层中氟利昂11的脱附速度相较于其他气流比速条件更快。另外,在0.8 L·min−1·cm−2气流比速下,氟利昂11脱除效果较好,脱附率达到83.49%。因此,在研究其他因素对床层中氟利昂11气体的脱除效率影响时,选取0.8 L·min−1·cm−2的脱附气流比速为实验条件。
采用LDF方程和Freundlich方程对脱附曲线进行拟合 (表4) ,计算得到脱附速率常数k随气流比速的升高而增大。这是由于随着脱附气流比速的增大,脱附的氟利昂11分子外扩散阻力降低,传质速率加快[21]。当气流比速从0.8 L·min−1·cm−2提升至1.2 L·min−1·cm−2时,出口氟利昂11质量浓度达到0.588 7mg·m−3所需时间texp由140.6 min缩短至70.7 min。表4表明,受脱附气流比速单个因素影响,床层中气体吸附质脱附曲线较为符合LDF脱附动力学方程,相关系数达到0.98以上。然而,Freundlich方程拟合得到的相关系数偏低,为0.953 0~0.972 9,这与Freundlich模型适用于描述多个影响因素控制的过程有关。
-
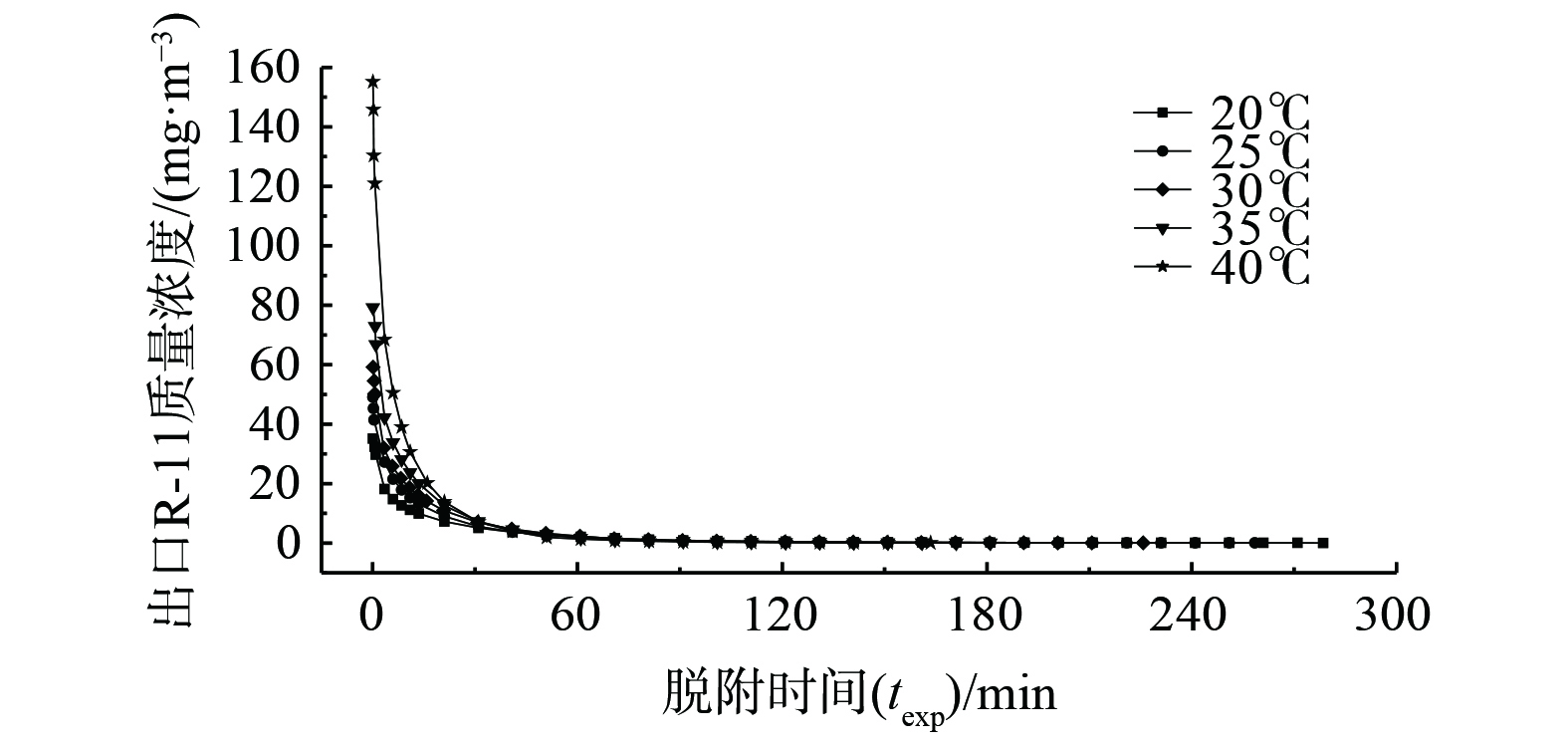
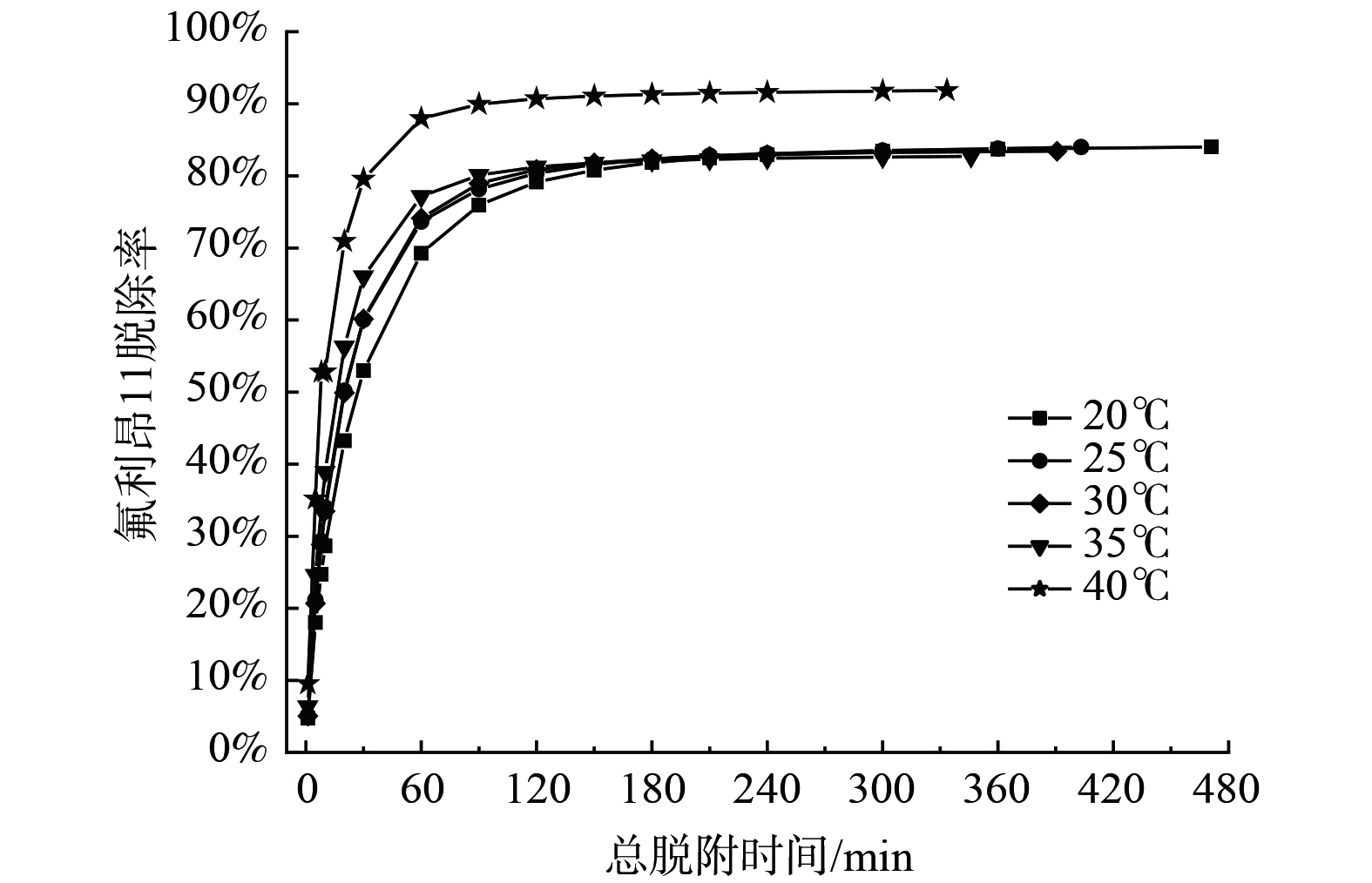
吹扫脱附温度对氟利昂11脱附的影响见图7、图8和表5。随着脱附温度上升,出口氟利昂11浓度峰值依次增大,且开始一段时间内脱附曲线的浓度变化较快。特别是脱附温度为40 ℃时,脱附曲线最高点质量浓度达到155.16 mg·m−3,操作过程的脱附曲线浓度下降得很快,这有利于脱附操作的快速进行[30]。床层中吸附质脱附率随脱附操作时间变化曲线图8显示。在20~35 ℃时,平衡脱附率基本一致;在40 ℃时,脱附速率和平衡脱附率大大提高,平衡脱附率为91.84%。
为研究不同脱附温度下的脱附动力学,采用LDF方程和Freundlich方程对脱附曲线进行拟合分析,计算结果列于表5。相比于Freundlich方程,LDF方程能更好拟合温度条件的脱附数据。LDF方程对实验结果拟合的相关系数为0.989 7~0.996 9,而Freundlich方程拟合的相关系数范围为0.926 8~0.982 5。随着脱附温度的升高,脱附速率常数依次增大,是由于脱附是吸热反应,提高温度有利于反应的进行,内部分子的热运动加剧,导致脱附速率增大。另外,当脱附温度从20 ℃提升至30 ℃时,出口氟利昂11质量浓度达到0.588 7 mg·m−3 所需时间texp由116.0 min缩短至98.3 min。由于工业上机械泄露现场测试一般在常温下进行,25 ℃和30 ℃时的脱附处理时间texp接近,氟利昂11脱除率均达到83%,故工业上进行机械泄露测试对氟利昂11的最佳脱附温度为25~30 ℃。
-
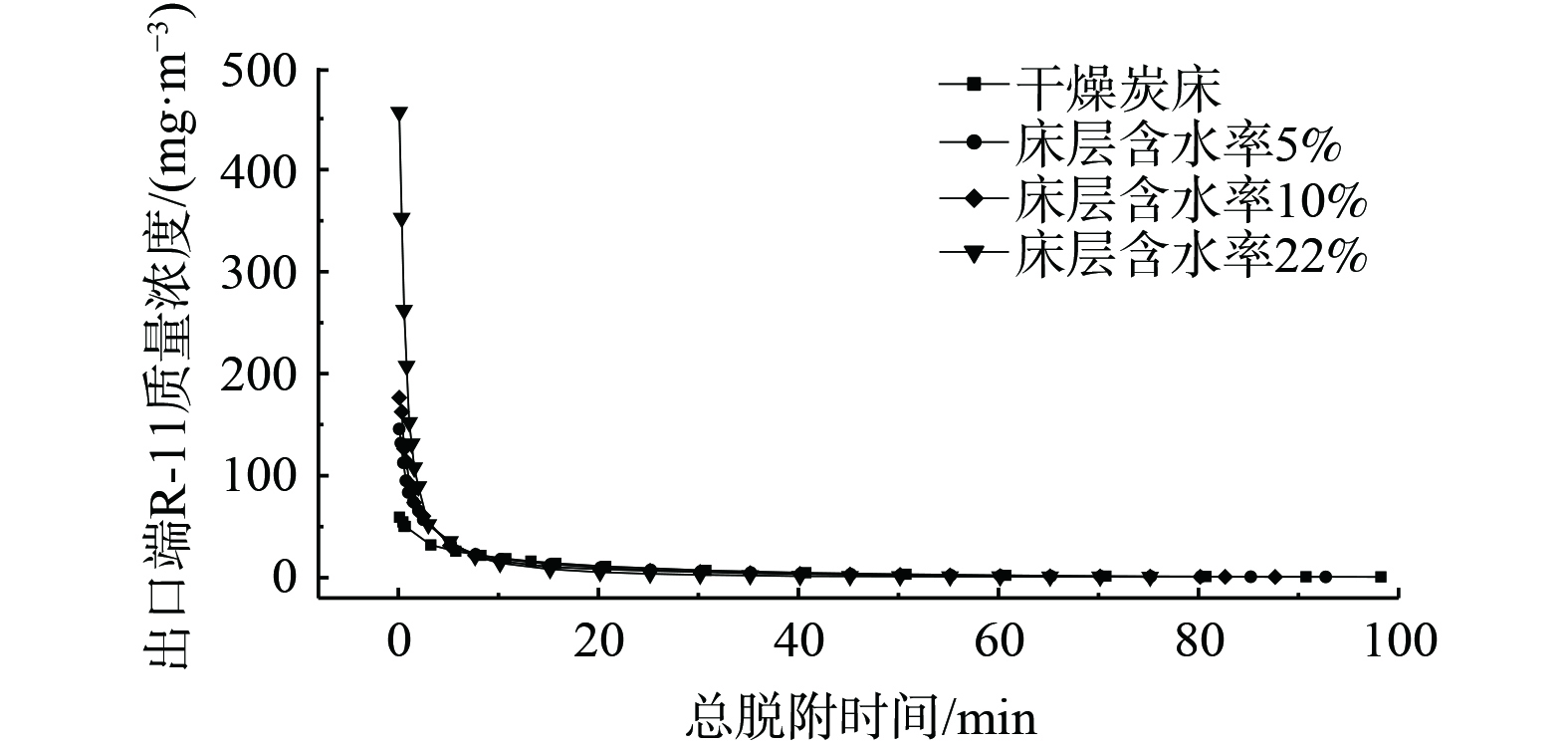
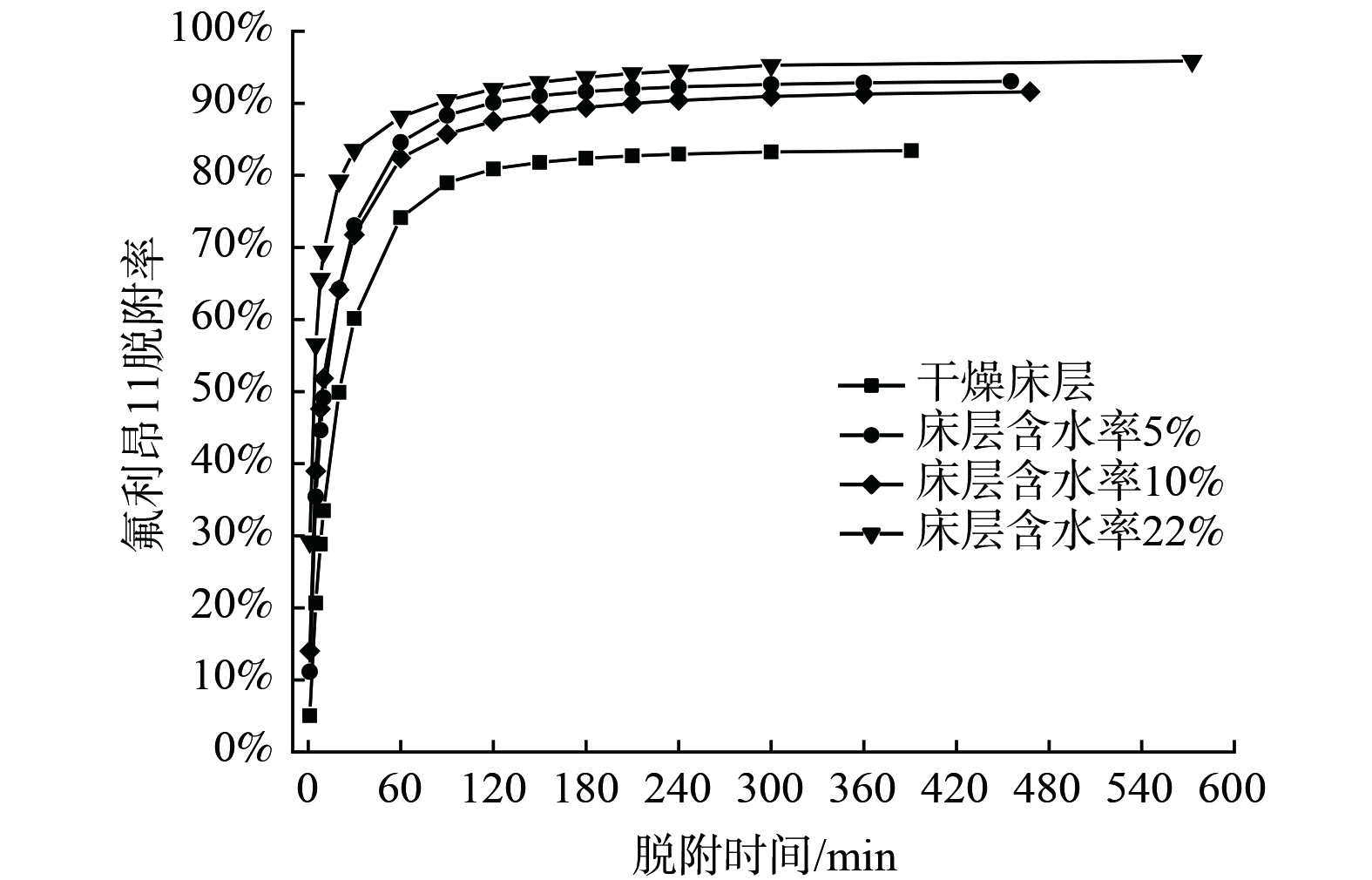
床层含水率对氟利昂11在浸渍炭床层脱附行为的影响见图9、图10和表6。床层含水率对吹扫脱附影响效果显著。氟利昂11出口浓度峰值随床层含水率的增大而升高,当床层含水率从0%增加到22%时,脱附气体中氟利昂11质量浓度峰值从50.62 mg·m−3增至 387.34 mg·m−3,而脱附时间texp从98.3 min缩短到75.2 min,随床层含水率的增加变化幅度不大。相比于干燥床层,含水床层对气体吸附质的脱除效果更好。干燥床层对氟利昂11的脱附率为83.49%,而床层含水率22%时对氟利昂11的脱附率达到了95.86%。分析可能是由于水分子占据强吸附位点,由于氢键作用和活性炭之间相互作用力更强,所需脱附能量高,而氟利昂11占据弱吸附位点,脱附能量低,相比于水分子更容易发生脱附[31]。较高的床层含水率导致脱附能垒低的弱吸附位点上的吸附质分子更容易发生脱附,故随着床层含水率升高,氟利昂11的平衡脱附率提高。
由线性驱动力LDF模型和Freundlich动力学模型的分析结果可发现:在含水率较低时,LDF动力学模型的拟合度高;当高含水率时,Freundlich模型的拟合度更高。含水率从5%增加到22%时,LDF模型拟合的相关系数从0.981 3下降到0.936 5。与Freundlich模型的拟合结果相比较,含水率为22%时拟合度为0.984 6,拟合度高于LDF方程。这是由于随着含水率的升高,多因素控制的影响效果更显著。
-
1) 浸渍炭对氟利昂11的吸附动力学主要受外扩散控制,随着气流比速的增大,吸附速率加快,饱和吸附容量保持不变。浸渍炭床层对低浓度氟利昂11的1%穿透时间与气流比速的定量关系为lgt=1.64-1.48lgv。
2) 随着气流湿度的升高,水分子和吸附质分子的竞争吸附加剧,穿透曲线卷起程度变大,吸附速率不断增大,穿透时间逐渐缩短,饱和吸附容量显著降低。
3) 浸渍炭对氟利昂11的脱附速率与气流比速、脱附温度和床层含水率呈正相关,气流比速为0.8 L·min−1·cm−2时,氟利昂11的脱除效果最佳,工业上进行机械泄露测试对氟利昂11的脱附温度推荐25~30 ℃。
4) LDF方程能够较好的拟合温度或气流比速单因素条件下氟利昂11的脱附曲线。对于床层含水率条件的脱附数据,低床层含水率时,LDF方程的拟合度高,而含水率较高时,Freundlich方程的拟合效果较好。
氟利昂11在浸渍活性炭床层的吸脱附行为
The adsorption and desorption behavior of freon 11 on impregnated activated carbon bed
-
摘要: 对低浓度氟利昂11气体在浸渍活性炭 (浸渍炭) 上的吸脱附行为进行了研究。考察了不同的气流比速和气流湿度条件对氟利昂11在浸渍炭床层吸附穿透的影响,利用Wheeler方程和Yoon-Nelson方程描述了吸附动力学过程。探讨了脱附温度、气流比速及床层含水率等影响因素对氟利昂11脱除效果的影响机制,运用LDF和Freundlich脱附动力学模型对脱附过程进行了描述。结果表明:氟利昂11在浸渍炭上的吸附动力学主要受外扩散控制,确定了其1%穿透时间与气流比速的定量关系;气流湿度对氟利昂11吸附行为的影响体现在与水分子发生竞争吸附,从而导致穿透曲线出现卷起现象;氟利昂11的脱附速率大小与脱附温度、气流比速和床层含水率呈正相关;当脱附温度为25~30 ℃,气流比速为0.8 L·min−1·cm−2时为最佳机械泄露测试脱附条件。本研究可为有毒有害气体净化用固定床吸附装置的设计,以及机械泄露非破坏性检验应用方法的建立参考。Abstract: The adsorption and desorption behavior of low concentration freon 11 gas on impregnated activated carbon was studied. The effects of air flow rate and air flow humidity on the adsorption penetration of freon 11 on impregnated carbon bed were investigated, and the adsorption kinetics was described by Wheeler equation and Yoon-Nelson equation. The influence mechanism of desorption temperature, air flow rate and bed water content on freon 11 removal was discussed. LDF and Freundlich desorption kinetics models were used to describe the desorption process. The results showed that the adsorption kinetics of freon 11 on impregnated carbon was mainly controlled by external diffusion. The quantitative relationship between 1% penetration time and air flow rate was determined. The influence of humidity effect on the adsorption behavior of freon 11 was reflected in the curl of the breakthrough curve caused by competition between freon 11 and water molecules. The desorption rate of freon 11 was positively correlated with the desorption temperature, air flow rate and bed water content. A desorption temperature at 25~30 ℃ and a air flow rate of 0.8 L·min−1·cm−2 were the best conditions for mechanical leakage test of desorption. The research results can provide important theoretical basis and technical support for the establishment of the application method of non-destructive inspection of mechanical leakage in fixed bed adsorption device for the purification of toxic and harmful gas .
-
Key words:
- adsorption /
- desorption /
- impregnated carbon /
- freon 11 /
- filter leakage
-

-
表 1 浸渍炭比表面积和孔结构参数
Table 1. Specific surface area and pore structure parameters of impregnated carbon
吸附剂 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 总孔容/(cm3·g−1) 微孔孔容/(cm3·g−1) 中孔孔容/(cm3·g−1) 微孔百分比(%) 浸渍炭 541.5 0.276 0.232 0.044 84.06% 表 2 不同气流比速下浸渍炭床层对氟利昂11的吸附动力学参数
Table 2. Adsorption kinetic parameters of freon 11 by impregnated carbon bed at different air flow rates
比速/
(L·min−1·cm−2)饱和吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)1%穿透时间/min Wheeler方程吸附速率
常数kv/(min−1)Yoon-Nelson方程吸附速率
常数k’/(min−1)0.5 29.87 120.5 2 170.39 0.041 7 0.8 30.26 63.0 2 940.35 0.061 0 1.0 28.94 41.0 3 096.80 0.061 5 1.2 30.47 34.0 3 452.43 0.064 0 表 3 不同气流湿度下浸渍炭床层对氟利昂11的吸附动力学参数
Table 3. Adsorption kinetic parameters of freon 11 on impregnated carbon at different air humidity
相对湿度 饱和吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)1%穿透时间/min Wheeler方程吸附速率
常数kv/(min−1)Yoon-Nelson方程吸附速率
常数k’/(min−1)<1% 24.91 28.5 2480.67 0.061 2 30% 24.71 24.8 2506.84 0.064 4 44% 15.28 18.4 2609.11 0.091 9 60% 5.80 14.8 2997.95 0.160 3 74% 1.95 13.5 3165.32 0.389 0 表 4 不同气流比速下拟合方程参数和实验值
Table 4. Parameters of the fitting equation and experimental values at different air flow rates
比速/
(L·min−1·cm−2)实验结果 LDF拟合结果 Freundlich拟合结果 Qexp/(mg·g−1) texp/min ηe/% k/h−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) R2 拟合方程 R2 0.6 0.333 140.6 80.74 1.73 0.340 0.989 9 lnc=−0.55lnt+1.70 0.953 0 0.8 0.344 98.3 83.49 2.46 0.345 0.996 9 lnc=−0.43lnt+3.73 0.926 8 1.0 0.327 88.3 79.26 2.61 0.330 0.995 6 lnc=−0.52lnt+3.51 0.972 9 1.2 0.328 70.7 79.41 3.24 0.328 0.989 5 lnc=−0.52lnt+3.39 0.964 9 注:texp为氟利昂11气体质量浓度降到0.588 7 mg·m−3时对应的时间;ηe为达到脱附平衡时的脱附率;Qexp为实验条件下平衡脱附量;Qe为LDF方程拟合得到的平衡脱附量。 表 5 不同温度下拟合方程参数和实验值
Table 5. Parameters of the fitting equation and experimental values of the fitting equation at different temperatures
温度/ ℃ 实验结果 LDF拟合结果 Freundlich拟合结果 Qexp/(mg·g-1) texp/min ηe/% k/h-1 Qe/(mg·g-1) R2 拟合方程 R2 20 0.347 116.0 84.00 2.06 0.338 0.989 7 lnc=−0.53lnt+3.70 0.960 9 25 0.346 101.0 83.98 2.44 0.338 0.994 4 lnc=−0.54lnt+3.84 0.952 3 30 0.344 98.3 83.49 2.46 0.345 0.996 9 lnc=−0.43lnt+3.73 0.926 8 35 0.341 81.0 82.69 3.73 0.336 0.996 9 nc=−0.56lnt+4.03 0.951 9 40 0.379 71.0 91.84 5.49 0.373 0.9897 lnc=−0.66lnt+4.20 0.982 5 表 6 不同床层含水率下拟合方程参数和实验值
Table 6. Parameters of fitting equation and experimental values under different bed water content
床层含水率 实验结果 LDF拟合结果 Freundlich拟合结果 Qexp/(mg·g−1) texp/min ηe/% k/h−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) R2 拟合方程 R2 0 0.344 98.3 83.49 2.46 0.345 0.996 9 lnc=−0.43lnt+3.73 0.926 8 5% 0.366 92.7 93.04 4.48 0.355 0.981 3 lnc=−1.41lnt+5.29 0.926 9 10% 0.344 87.7 91.60 5.18 0.330 0.966 6 lnc=−1.42lnt+5.52 0.949 0 22% 0.324 75.2 95.86 10.27 0.308 0.936 5 lnc=−1.46lnt+5.61 0.984 6 -
[1] 程代云, 史喜成. 集体防护装备技术基础[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008. [2] 张龙喜, 张忠良, 靳捷. 机械漏毒无损检测技术研究[J]. 测控技术, 2020, 39(10): 52-55. doi: 10.19708/j.ckjs.2020.06.260 [3] KARWACKJ C J, MORRISON R W. Adsorptive retention of volatile vapors for nondestructive filter leak testing[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1998, 37(8): 3470-3480. [4] 梁飞, 张计荣, 张渊, 等. 碘吸附器泄漏率检测的方法与影响因素探讨[J]. 辐射防护, 2018, 38(6): 496-501. [5] 俞杰, 吴振龙, 凌学会, 等. 碘吸附器有效性试验方法及评价[J]. 核安全, 2018, 17(2): 43-47. doi: 10.16432/j.cnki.1672-5360.2018.02.008 [6] 俞杰, 张伟, 杜建兴, 等. 环己烷法用于碘吸附器泄漏率检测技术研究[J]. 核科学与工程, 2019, 39(6): 980-985. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2019.06.019 [7] 俞杰, 杜建兴, 王龙江, 等. 环己烷在碘吸附器活性炭床上的解吸行为研究[J]. 辐射防护, 2018, 38(3): 222-227. [8] MUHLBAIER D R. DP-1053-nondestructive test of carbon beds for reactor containment applications progress report October 1964-January 1966 [R]. Dupont&Savannah River National Laboratory, Aiken, SC, 1966. [9] MUHLBAIER D R. DP-1082-nondestructive test of carbon beds for reactor containment applications progress report february-June 1966 [R]. Dupont&Savannah River National Laboratory, Aiken, SC, 1967. [10] 贾明, 路学诗, 郭亮天, 等. 碘吸附器泄漏试验中活性炭床上氟里昂-11的解吸实验研究[J]. 辐射防护, 1990, 10(5): 339-346. [11] 王坤俊, 马英, 李永国, 等. 碘吸附器的脉冲式氟利昂法泄漏检测技术实验研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2017, 42(8): 126-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2017.08.027 [12] Performance Specification Filter, Gas-particulate: NBC 100 CFM, M48A1: MIL-PRF-32137[S]. US. Army Edgewood Chemical Biological Center, 2003. [13] Performance Specification Filter, Gas, 200 CFM, M98: MIL-PRF-51525B[S]. US. Army Edgewood Chemical Biological Center, 2004. [14] Performance Specification Cell, Gas Phase, Adsorber: MIL-PRF-32016[S]. US. Army Edgewood Chemical Biological Center, 2002. [15] 郑超, 康凯, 周术元, 等. 水蒸气在浸渍活性炭上的吸附平衡[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版, 2021, 54(6): 617-626. [16] 郑超. 氟利昂134a和水蒸气在化学防护炭材料上的竞争吸附研究. [D]. 北京: 军事科学院防化研究院, 2021. [17] GUO M, LIU Q L, LU S C, et al. Synthesis of silanol-rich MCM-48 with mixed surfactants and their application in acetone adsorption: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies[J]. Langmuir, 2020, 36(39): 11528-11537. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c01933 [18] 程代云, 史喜成. 军用吸附技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012. [19] LODEWVCKX P, VANSANT E F. Influence of humidity on adsorption capacity from the Wheeler-Jonas model for prediction of breakthrough times of water immiscible organic vapors on activated carbon beds[J]. AIHAJ, 1999, 60(5): 612-617. doi: 10.1080/00028899908984480 [20] WEN T T, CHANG C Y, CHEN L Y. Adsorption properties and breakthrough model of 1, 1-dichloro-1-fluoroethane on activated carbons[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1999, 69(1): 53-66. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3894(99)00058-8 [21] 于颖, 邵子婴, 刘靓, 等. 热强化气相抽提法修复半挥发性石油烃污染土壤的影响因素[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(4): 2522-2527. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201510158 [22] 杨玉洁, 王春雨, 沙雪华, 等. 烃类污染土壤热强化气相抽提技术的脱附动力学[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 10(13): 2328-2335. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201905119 [23] FLETCHER A J, THOMAS K M. Adsorption and desorption kinetics of n-octane and n-nonane vapors on activated carbon[J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15(20): 6908-6914. doi: 10.1021/la9814992 [24] GHAFARI M, ATKINSON J D. Impact of styrenic polymer one-step hyper-cross-linking on volatile organic compound adsorption and desorption performance[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 351: 117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.051 [25] ZHANG X, GAO B, ZOU W, et al. Chemically activated hydrochar as an effective adsorbent for volatile organic compounds (VOCs)[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 218: 680-686. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.144 [26] 季闻翔, 许博文, 李清钞, 等. 甲苯和环己烷双组分在活性炭上竞争吸附特性[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2019, 35(5): 385-394. [27] 王稚真, 卢晗锋, 张波, 等. 水蒸气对改性椰壳活性炭吸附VOCs的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2010, 4(11): 2566-2570. [28] 张俊香, 黄学敏, 曹利, 等. 负载Cu改性活性炭吸附VOCs性能的研究[J]. 环境工程, 2015, 1: 95-99. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201501022 [29] 杜娟, 栾志强, 解强, 等. 蜂窝状ZSM-5型分子筛对丙酮和丁酮吸附性能研究[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(12): 4706-4711. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.12.027 [30] 韩忠娟, 罗福坤, 李泽清. 蜂窝状活性炭对VOCs的吸-脱附性能研究[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(12): 3662-3666. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.12.034 [31] 张智, 马修卫, 李津津, 等. 中高温环境下VOCs在活性炭上的吸附性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(12): 4811-4820. -



 下载:
下载: