-
城镇污水处理厂站提标改造中多采用移动床生物膜反应器(moving bed biofilm reactor,MBBR)及膜生物反应器(membrane bio-reactor,MBR)等工艺[1-2]。这些工艺存在一次性投资大、原生化池改造难度大、后期运行能耗大、费用高等问题[3-4]。近年来,膜曝气生物膜反应器(membrane aerated biofilm reactor,MABR)工艺以其对高氨氮进水处理性能高、曝气效率高和电耗低的特点,逐步在污水处理项目中受到关注[5-6]。MABR工艺与传统活性污泥系统相比,能耗可降低75%以上,在降低运行成本方面有较大优势[7]。目前,MABR工艺在一体化分散式污水处理装置中应用较多,在河道整治项目中也有应用,但在污水处理厂站提标改造中却应用较少[8-11]。
本文结合MABR工艺在北方地区某污水处理站提标改造工程中的应用,重点阐述了MABR系统的工艺特点、设备配置和设计参数,对调试运行期间主要污染物的处理效果进行了验证,同时亦对该工艺的投资和运行费用进行了分析,以期为后续该工艺在类似工程项目的应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
该污水处理站原设计处理规模为1 000 m3·d−1,实际运行处理规模为800 m3·d−1。污水处理站原设计出水水质满足《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准(GB 18918-2002)》中“一级B”标准,实际进出水水质见表1。升级改造后,污水处理站出水水质要求达到“一级A标准”,本次升级改造设计进出水水质见表2。
-
原污水处理站工艺流程为:提升泵站和格栅→曝气沉砂池→循环式活性污泥(cyclic activated sludge technology,CAST)池→紫外消毒渠→排放。污泥处理工艺流程为:CAST池→污泥储池→污泥脱水间→外运。核心生化工艺为CAST工艺,原设2组,每组由进水区、生物选择区和主反应区3部分组成。进水区土建尺寸为5.0 m×1.0 m×5.8 m,生物选择区土建尺寸为5.0 m×3.0 m×5.8 m,主反应区土建尺寸为5.0 m×9.5 m×5.8 m,有效水深均为5.0 m。进水区水力停留时间为1.2 h,生物选择区水力停留时间为3.6 h,主反应区水力停留时间为11.4 h,主反应区污泥负荷(以每千克MLSS消耗的BOD5(kg)计,下同)为0.07 kg·(kg·d)−1。生物选择区设有潜水搅拌器,主反应区设有潜水搅拌器、内回流泵、剩余污泥泵、滗水器和微孔曝气系统,采用离心鼓风机供气。
-
原设计对进水水量水质的波动性考虑不足,对进水水质各项指标预测偏低,实际进水总氮和氨氮较高,碳源不足,导致CAST池污染物负荷高且稳定性差,出水不达标。另外,原设计中未设置碳源投加和化学除磷设施、生物选择区设置过小、好氧区曝气量偏小、硝化液回流量偏小,也是导致出水不达标的原因。
因此,污水处理站改造的核心任务包括:提高生化系统的生物脱氮除磷能力;由于场地有限,需在原池体基础上进行改造,避免扩建生化池体;缩短系统改造工期,以减少不达标废水的外运处理费用。
1.1. 处理规模和水质情况
1.2. 原处理工艺流程
1.3. 污水处理站改造核心任务
-
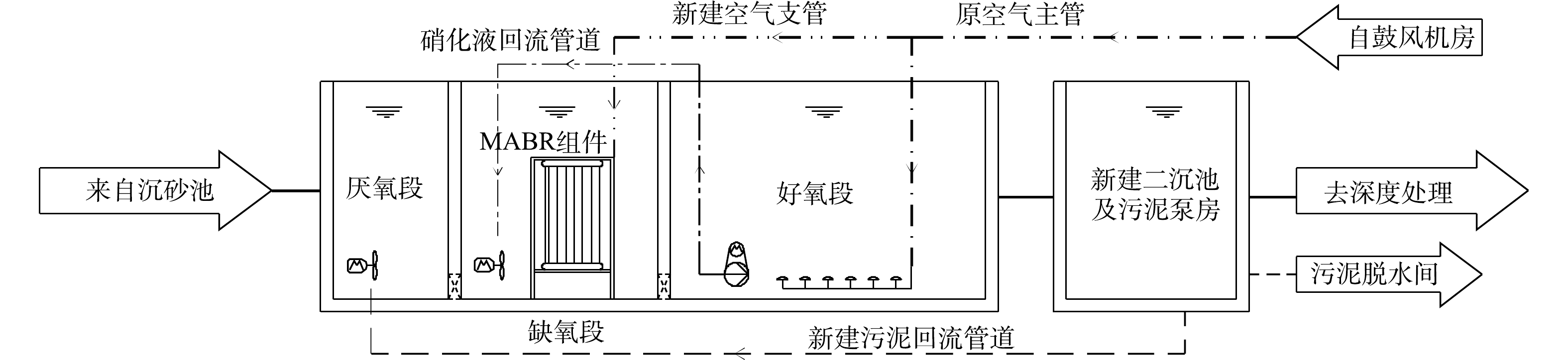
MABR是一种依靠膜材料曝气传氧和提供载体的具有硝化反硝化功能的生物膜反应器。空气中的氧气通过膜材料表面的膜孔扩散到膜材料表面附着的生物膜。生物膜依次形成好氧层、兼氧层和缺氧层,并同步实现有机物降解和营养物去除。生物膜内硝化菌为优势菌,好氧硝化作用为主导,氨氮去除率高[5-7]。实际工艺流程中,通常在缺氧段设置MABR膜组件,与后续好氧曝气段和二沉池形成一个工艺组合系统(见图1)[8],悬浮活性污泥系统与生物膜系统相辅相成。该工艺组合系统中,硝化反应发生在好氧曝气段,也发生在缺氧段MABR生物膜上,并通过设计各自的硝化反应贡献率来决定MABR膜的投入量。
-
1)在原CAST池的生物选择区中吊装MABR膜组件,即原2格生物选择区每格吊装2组MABR膜组件,形成缺氧段。原CAST池进水区定义为厌氧段,原CAST池主反应区定义为好氧段。
2)从原CAST池的主空气管接出支管,作为MABR组件的供气管路,提供工艺气和擦洗气。
3)保留原CAST池中潜水搅拌器、硝化液回流泵和管路,取消滗水器,改造剩余污泥泵和管路作为新增硝化液回流系统。
4)新建二沉池及污泥泵房,为MABR系统提供污泥回流。
-
1) MABR主工艺单元的改造,不涉及原池体的土建改造和新增附属设备,最大化利用原曝气系统和工艺设备。因此,CAST池不进行土建改造,厌氧段水力停留时间为1.2 h,缺氧段为3.6 h,好氧段为11.4 h。
2)生化系统设计污泥负荷0.155 kg·(kg·d)−1,污泥质量浓度 3.5 g·L−1,污泥产率系数(以每千克BOD5对应污水中的挥发性悬浮物(volatile suspended solids,VSS)质量计,下同)0.5 kg·kg−1,运行调试初期,污泥回流比为100%,好氧区混合液溶解氧控制在3~4 mg·L−1,后期MABR生物膜成熟后可控制在2~3 mg·L−1。
3)生化系统硝化功能要由好氧段悬浮活性污泥和MABR膜表面的生物膜承担,整个系统设计硝化量(以氨氮计)36 kg·d−1,MABR生物膜设计硝化能力占整个系统的9.5%,生物膜的设计硝化负荷(以氨氮计)为2.6 g·(m2·d)−1,设计MABR膜面积为1 382.4 m2。由于MABR膜表面的氧气利用效率远高于好氧段微孔曝气系统,故原曝气系统供气量可满足新增MABR组件硝化需氧量,无需新增鼓风机。
4) MABR投加初期,硝化液回流比控制在200%左右。MABR生物膜成熟后,可适当降低硝化液回流比。
5)新建矩形二沉池1座2格,平面尺寸为8.35 m×4 m,表面负荷1.00 m3·(m2·h)−1。
6) MABR系统共使用4组膜组件。膜组件采用中空纤维膜丝,材质为聚丙烯(PP),具有压力小、曝气效率高的特点。系统的理论曝气效率为23~26 kg·(kW·h)−1,中空纤维膜有效长度为2.2 m,外径1.2 mm,壁厚0.78 mm;由中空纤维膜丝组成的单个膜头的有效膜面积为1.2 m2,每个膜组件由288个膜头组成,每个膜组件供气量为6 m3·h−1。
2.1. 改造的基本思路
2.2. 改造的实施内容
2.3. 设计和运行参数
-
MABR主体工艺运行调试大致分为3个阶段:初始投加阶段(0~15 d);生物膜形成阶段(16~50 d);生物膜成熟阶段(51~90 d)。调试期间水温为12~23 ℃。MABR主体工艺稳定后,总体进出水水质情况见表3。其中,进水取样点为MABR生化系统进水,出水取样点为二沉池出水,主要出水水质指标可达到设计出水水质要求,总磷和SS指标配合后续深度处理也可稳定达标。
-
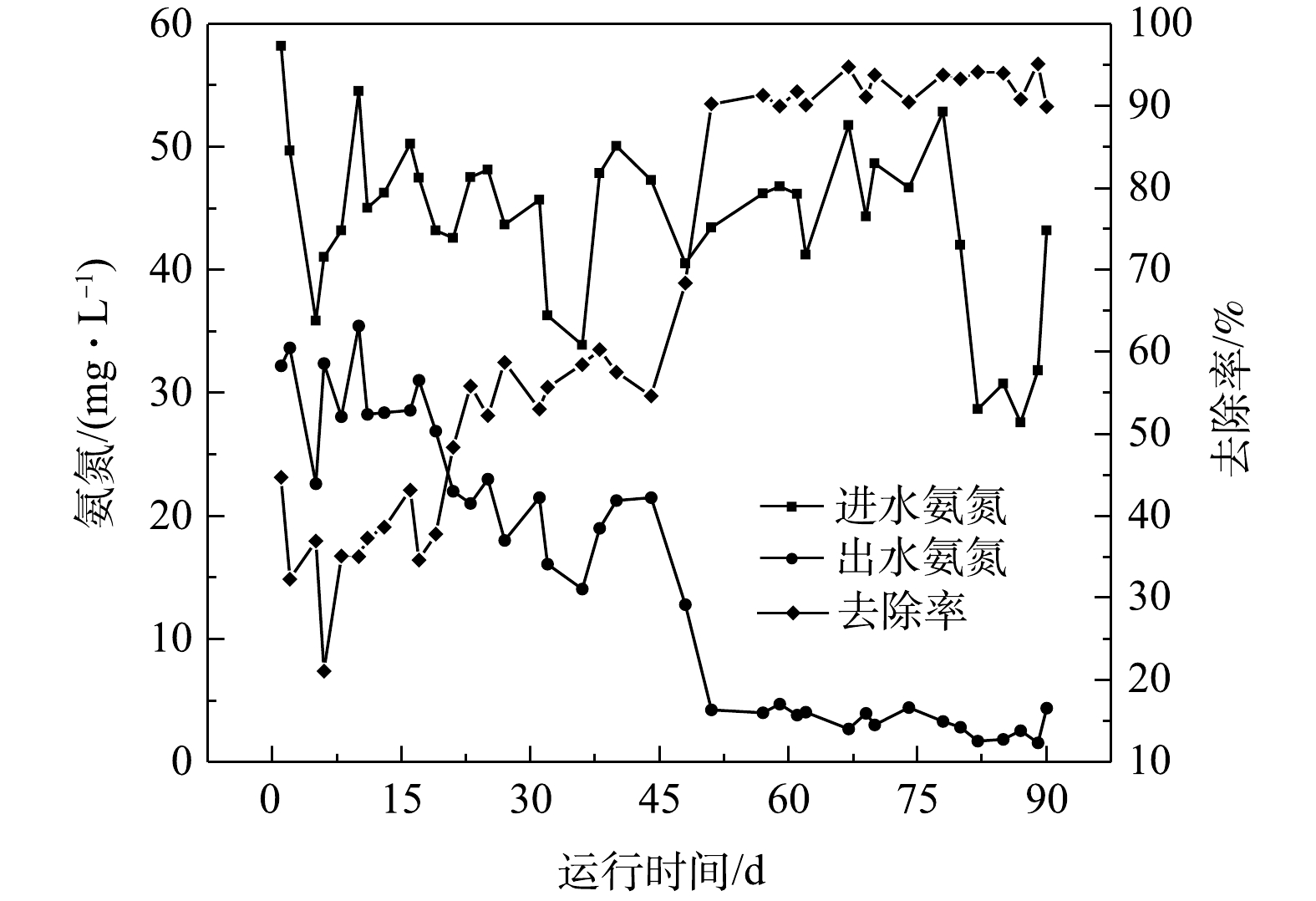
调试运行阶段生化系统进水氨氮波动较小,进水均值为44 mg·L−1。MABR膜组件初始投加阶段(0~15 d),氨氮进水均值为47 mg·L−1,出水均值为30 mg·L−1,平均去除率为36%;MABR工艺生物膜形成阶段(16~50 d),氨氮进水均值为44 mg·L−1,出水均值为19 mg·L−1,平均去除率为57%;生物膜成熟阶段(51~90 d),氨氮进水均值为39 mg·L−1,出水均值为3 mg·L−1,平均去除率为92%。整个调试运行阶段去除率不断增大。各阶段进出水氨氮指标变化情况见图2。由图2可知,MABR膜组件投入初期(0~15 d)出水氨氮较高,去除率较小。这可能是原生化系统由CAST工艺向MABR工艺转变过程中生物种类发生变化和生物量减少所致。由于MABR传氧膜使得绝大部分氧气通过膜直接进入生物膜,附着在膜表面内层以好氧自养细菌(硝化细菌)为主,氧气促进了细菌的硝化作用。随着MABR膜组件上生物膜的形成,其硝化能力快速增加,氨氮去除率在(15~50 d)快速增大。
已有研究表明,生物膜的氨氮负荷(以氨氮计)可达到0.5~2.5 g·(m2·d)−1[12-13]。MABR稳定运行期间,对生化系统缺氧区进出水氨氮进行测定发现,氨氮去除量为2.3~4.5 mg·L−1,一周平均值为3.5 mg·L−1;缺氧区投加的MABR膜表面积为1 382.4 m2,MABR生物膜的实际硝化负荷(以氨氮计)约为2.0 g·(m2·d)−1,氨氮去除贡献率约为9.6%,接近本工艺的设计参数。同期污泥浓度(即悬浮固体颗粒的质量浓度,mixed liquor suspended solids,MLSS)均值为3 500 mg·L−1,每千克MLSS的硝化负荷(以氨氮计,下同)为0.026 kg·(kg·d)−1。
在生物膜成熟阶段,虽然出水氨氮已达标,但受进水高负荷冲击影响明显。这说明MABR抗冲击能力需要进一步提升。如果进水氨氮冲击负荷较高,需要考虑保留好氧硝化,合理平衡厌氧段生物膜硝化负荷和好氧段活性污泥硝化负荷。
-
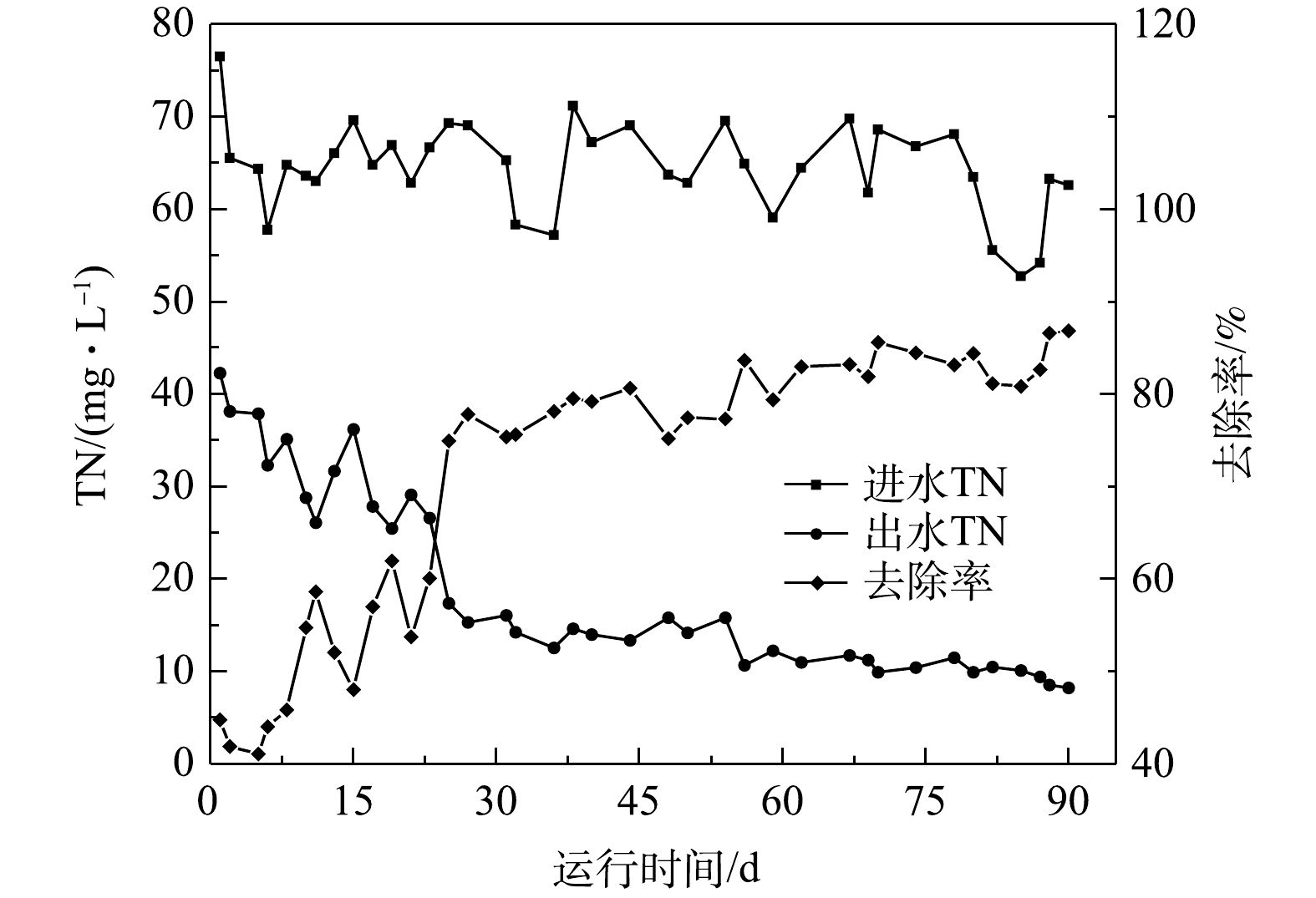
调试运行阶段生化系统进水TN波动性较小,进水均值为65 mg·L−1。MABR膜组件初始投加阶段(0~15 d)TN进水均值为66 mg·L−1,出水均值为35 mg·L−1,平均去除率为47%;生物膜形成阶段(16~50 d)TN进水均值为65 mg·L−1,出水均值为18 mg·L−1,平均去除率为73%;生物膜成熟阶段(51~90 d)TN进水均值为63 mg·L−1,出水均值为11 mg·L−1,平均去除率为83%。整个调试运行阶段去除率稳步增大,各阶段进出水TN变化见图3。原CAST系统的TN去除率约为55%,出水TN无法达标。系统改造稳定后,TN去除率达到83%。其主要原因可能是系统硝化能力增强,氨氮去除率明显增大;同时新增的二沉池延长了生化时长,生化系统硝化反硝化能力整体增强。
-
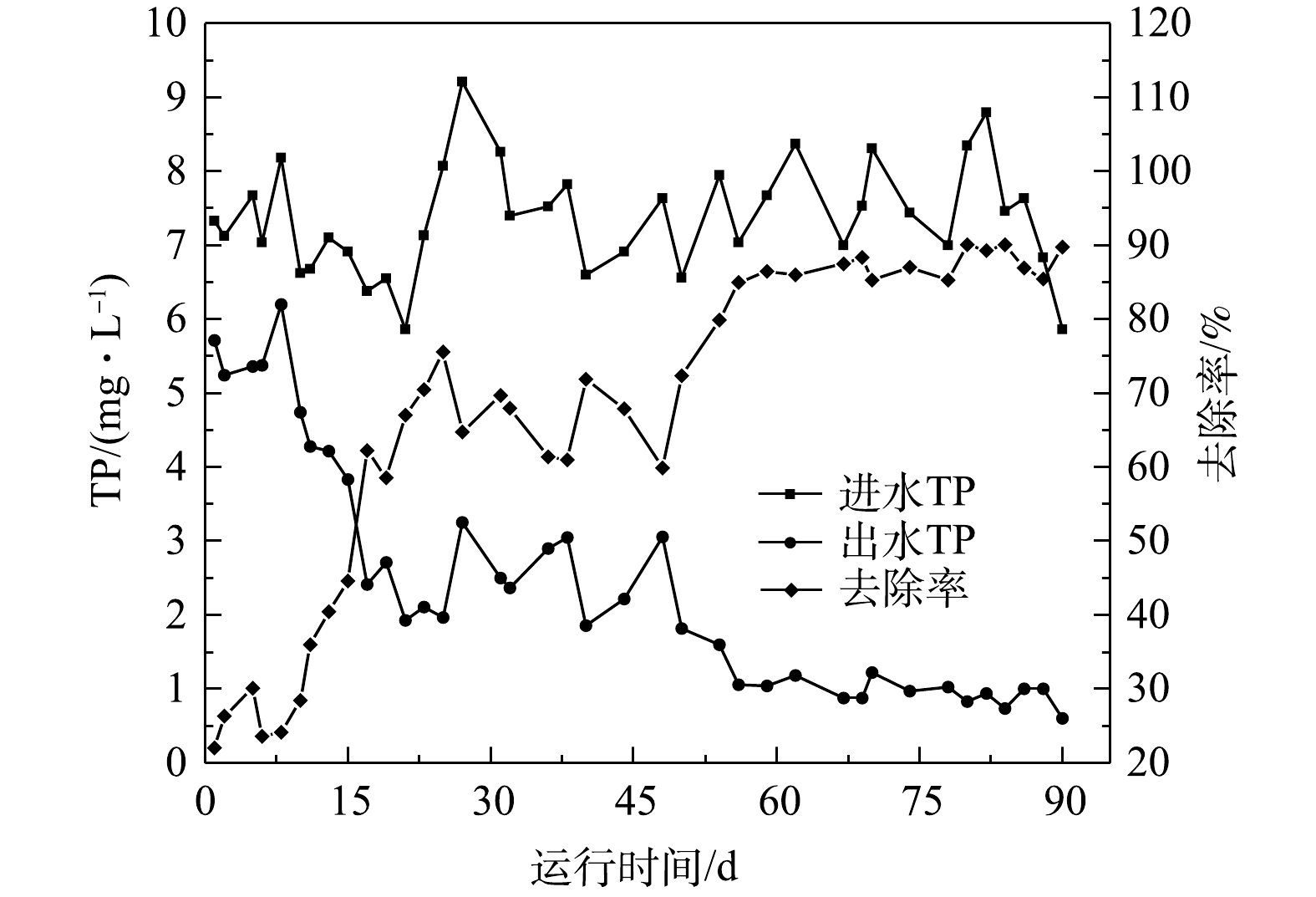
调试运行阶段生化系统进水TP进水均值为7.4 mg·L−1。MABR膜组件初始投加阶段(0~15 d)TP进水均值为7.2 mg·L−1,出水均值为5.2 mg·L−1,平均去除率为28%;生物膜形成阶段(16~50 d)TP进水均值为7.3 mg·L−1,出水均值为2.4 mg·L−1,平均去除率为66%;生物膜成熟阶段(51~90 d) TP进水均值为7.5 mg·L−1,出水均值为0.9 mg·L−1,平均去除率为88%。调试期间进出水TP情况见图4。原CAST系统TP的去除约为31%,出水TP无法达标。系统改造稳定后TP去除率达到88%。这是由于系统改造后将进水区变为厌氧区,为聚磷菌创造了有利释磷条件;同时,新建的二沉池可排出剩余污泥,也能提升生化系统生物除磷效果。
-
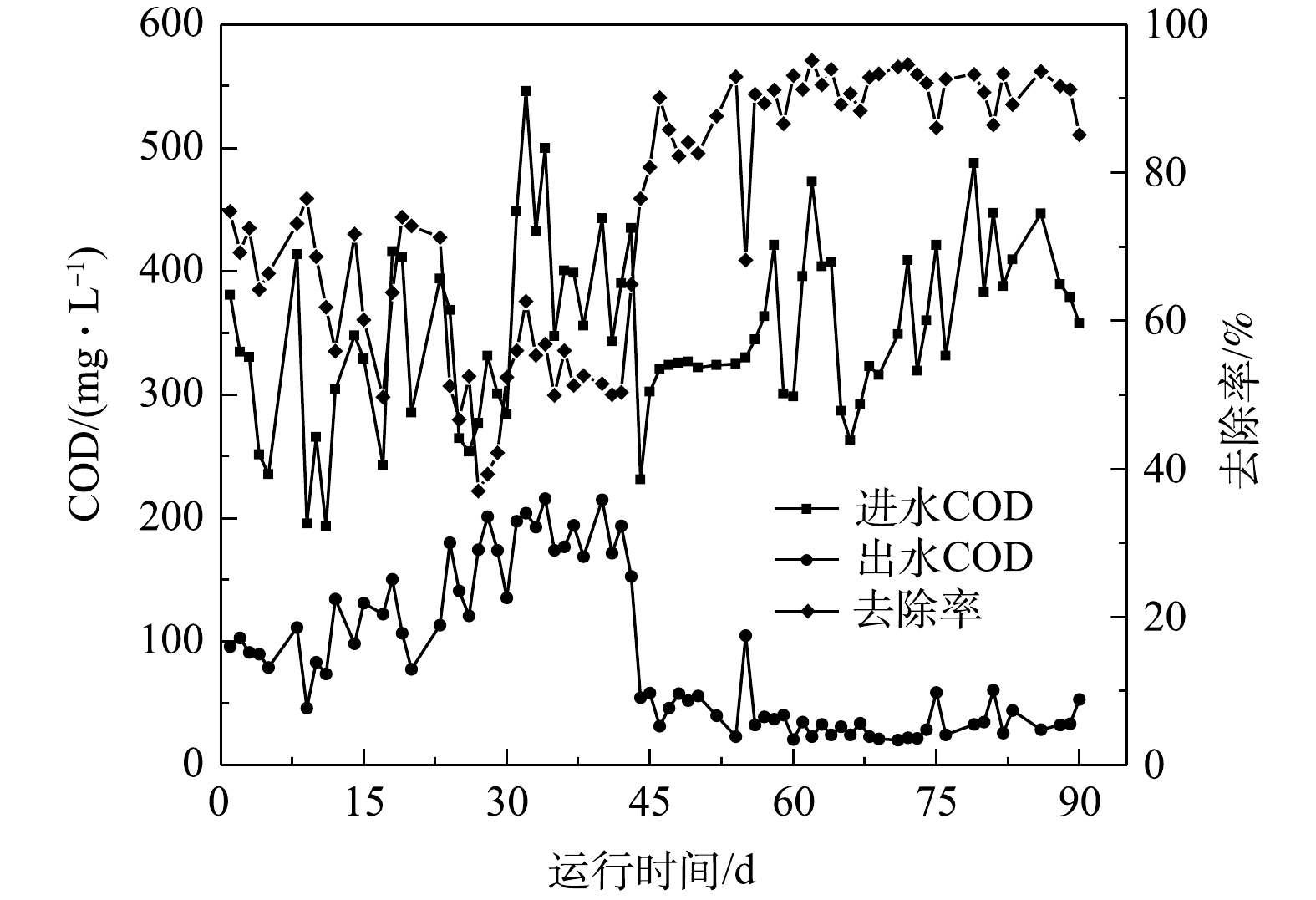
调试运行阶段生化系统进水COD波动性较大,进水均值为351 mg·L−1。MABR膜组件初始投加阶段COD进水均值为342 mg·L−1,出水均值为139 mg·L−1,平均去除率为59%;生物膜形成阶段进水均值为332 mg·L−1,出水均值为87 mg·L−1,平均去除率为75%;生物膜成熟阶段进水均值为367 mg·L−1,出水均值为35 mg·L−1,平均去除率为90%。各阶段进出水COD变化见图5。由图5可知,初始投加阶段出水COD较高,去除率下降。这主要是由于生化系统由CAST工艺向MABR工艺转换过程中厌氧段MABR生物膜尚未形成,好氧段活性污泥浓度较低,整个系统生物量不足所致。生物膜形成后期至成熟阶段,系统COD去除率快速增大,这是由于好氧段生物量增加所致。
-
提标改造后工程的处理规模为800 m3·d−1。生化段由CAST工艺改造为MABR工艺,改造投资强度为850 元·m−3。改造前CAST工艺段运行能耗为0.65 kW·h·(m3·d)−1,电价以0.5 元·(kW·h)−1计,电费0.32 元·(m3·d)−1;改造后MABR工艺段运行能耗为0.61 kW·h·(m3·d)−1,电费0.31 元·(m3·d)−1。在满足出水水质的前提下,使用MABR工艺用膜面积较少,MABR降低能耗的比例不突出,而随着MABR膜产品价格的不断降低,MABR工艺在降低能耗上的优势更明显。在药剂费方面,改造前CAST工艺段未设置碳源补充和碱度补充设施,改造为MABR工艺段后新增了碳源和碱度补充设施。运行调试期间,BOD5与总凯氏氮之比约为5,进水剩余碱度大于70 mg·L−1,亦无需再投加碳源和补充碱度。
3.1. 改造后的工艺调试阶段
3.2. MABR主工艺系统对氨氮的去除情况
3.3. MABR主工艺系统对TN的去除情况
3.4. MABR主工艺系统对TP的去除情况
3.5. MABR主工艺系统对COD的去除情况
3.6. MABR主工艺的系统投资及运行费用
-
采用MABR工艺对原CAST工艺进行了改造,改造后的生化系统出水氨氮、TN、TP和COD均能稳定达标,MABR工艺对主要污染物质的去除效果得到了初步验证。值得注意的是,MABR生化系统氨氮去除率水平较高,体现了其硝化速率高的优势;但该系统抗冲击负荷能力较差,系统工艺设计需要进一步研究和优化。同时,整个提标改造项目工期较短,后期运行成本较低,也体现了MABR工艺系统简单、高效节能的优势。



 下载:
下载: