-
近年来,随着乡村经济的发展和农户生活水平的提高,农村生活污水对水环境的威胁日益严重[1]。为了有效整治农村人居环境,推进“美丽乡村”建设,以人工湿地(CW)主的污水生态处理工艺被广泛用于农村生活污水的处理[2-3]。CW种类多样,包括表面流人工湿地(SFCW)、水平潜流人工湿地(HFCW)、垂直人工湿地(VFCW)和潮汐流人工湿地 (TFCW)等[4]。其中HFCW对氮磷营养盐、有机物、总悬浮颗粒物(TSS)和病原体等污染物均有良好的去除效果,故成为农村生活污水处理中最常用的湿地类型[5-6]。通常认为,HFCW对TSS和有机物具有较理想的去除效果,但其对氮磷营养盐的去除效果却不甚理想[5-7]。究其原因,则应主要归因于进水中相对不足的有机碳源、HFCW较差的复氧能力及其填料有限的磷素吸附容量等[8-9]。鉴于此,亟需采用相应的技术手段或者调控措施对HFCW的脱氮除磷性能进行强化,以便使其能够高效稳定的处理农村生活污水。
利用电化学技术强化CW的脱氮除磷性能已成为当前CW强化脱氮的研究热点之一[4],先后有研究尝试将该技术与CW工艺耦合,以期提高CW系统的净化效能[10-11]。当利用电化学技术进行污水的处理时,污水中的N素可以通过电催化氧化法和电催化还原法来实现。前者可以直接或间接氧化污水中的氨氮,后者可以高效地去除污水中的硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐[12]。而基于牺牲阳极的电絮凝技术则可以利用铁或铝等阳极材料在电解时产生的金属阳离子生成高活性的多形态聚铁或聚铝絮凝剂,将水中磷酸盐予以去除[13]。
为了实现HFCW对农村生活污水的高效处理,本研究将电化学技术与前期构建而成的三级串联水平潜流人工湿地进行耦合,构建了E-HFCWs。然后考察了E-HFCWs的脱氮除磷性能和电解措施对其他水质指标的影响,分析了各级CW填料的全磷含量及其磷素形态和填料样品的微生物群落结构,以期为新型人工湿地工艺的研发和应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
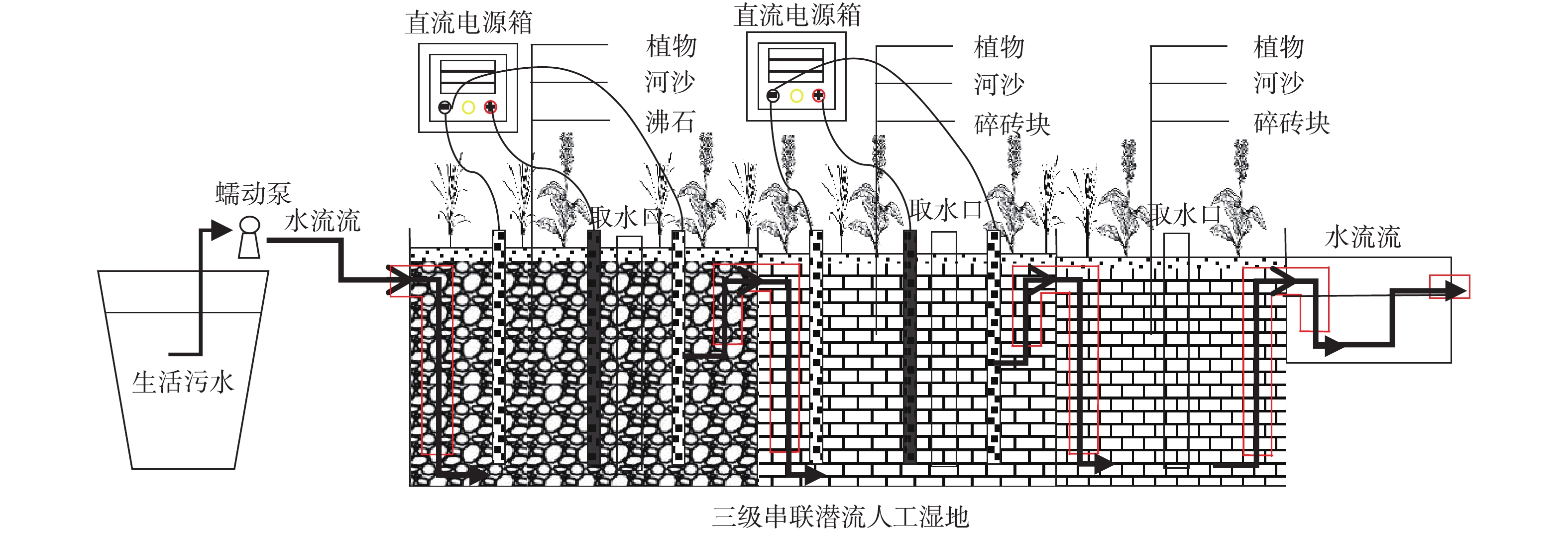
E-HFCWs实验装置如图1所示,装置(L×W×H=1 500 mm×540 mm×348 mm)由厚度为8 mm的钢化玻璃构建而成。该系统包含3个串联的湿地单元(L×W×H=1 264 mm×540 mm×348 mm)和1个出水池(L×W×H=237 mm×310 mm×150 mm),各湿地单元之间均使用管径为35 mm的PVC管进行连接。第1级湿地(H1)基质以沸石为主(粒径为3~8 mm,基质层厚度为220 mm),其主要成分是SiO2,表面粗糙,孔径均匀,吸附能力强,对COD 和氮素具有良好的去除效果。第2级(H2)和第3级(H3)湿地中的基质以红壤烧制而成的废砖块为主(粒径为10~50 mm,基质层厚度为220 mm),其铁、铝含量较高,具有较大的比表面积和多孔结构,有利于生物膜的生长。表层均用河砂(粒径为2 mm以下,厚度为30 mm)覆盖,基质层总厚度为250 mm。在H1和H2中安装电解装置,装置的电极材料均使用纯铁,阳极(L×W×T=250 mm×150 mm×0.3 mm、表面打孔、孔径为20 mm、孔距为20 mm)设置在湿地单元的中心,阴极均匀地设置在阳极的两侧,各极板相距为120 mm。使用铜线(直径为2 mm)将电极与直流稳压电源(eTM-305F、0~30 V、0~5 A)相连,为电解装置提供恒定电流。湿地植物选用生长正常、株型大小基本一致的芦苇和美人蕉,混种密度为76株·m−2。系统由蠕动泵、微电脑时控开关和液体流量计共同定时定量连续进水,以水平推流方式从另一端排出。植物移栽后,加入自来水至基质饱和。待植物成活、系统稳定后开始实验。
-
该装置的HLR(水力负荷)为0.30 m3·(m2·d)−1,污水在系统中的水力停留时间(HRT)为3 d,即系统处理污水量为20 L·d−1。稳压直流电源每天以恒流模式输出8 h。本研究的实验时段为2018年4月至2019年9月,可分为3个阶段:第1阶段(2018年4—9月,电流强度为0 mA);第2阶段(2018年10月—2019年2月,电流强度为100 mA);第3阶段(2019年4—9月,电流强度为50 mA)。在实验开始前,装置先连续运行30 d,使湿地植物和基质微生物适应环境,并开始生长繁殖。接种污泥来自合肥市望塘城市污水处理厂。实验进水来自安徽农业大学园区内生活污水,原水经沉淀处理后,取上清液作为系统的进水。其污水水质如表1所示。
-
实验装置的每个CW单元中用四周开孔的PVC管各设置1个固定的取水口(图1),进水的采样点设在污水桶,出水采样点设在出水池。每周二09:00用取样瓶从各采样点取水样并进行测定,测定取3次重复。各级湿地水质指标采样点的编号分别为H1、H2、H3。
-
水样的测定指标包括pH、温度、溶解氧(DO)、氧化还原电位(Eh)、TN、
${\rm{NH}}_4^{\rm{ + }}$ -N、${\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ -N、${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N、TP、${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P、Fe2+和总溶解铁(TDFe)。上述部分水质指标测定时均参照《水与废水水质测定方法》[14],水中Fe3+的含量由TDFe含量减去Fe2+含量获得,pH、温度和Eh则分别采用便携式水质分析仪进行测定。在实验结束后,对各级湿地中填料样品的全磷含量及磷形态进行测定。填料中的全磷使用硫酸/高氯酸消解-钼锑抗分光光度法进行测定,有机磷的测定则采用马弗炉灼烧-钼锑抗分光光度法。填料中各种形态的无机磷首先利用不同化学浸提剂加以逐级分离,而后采用钼锑抗分光光度法测定,不同形态无机磷分离方法参照《土壤农化分析》[15]。直流稳压电源输出的电流、电压和电功率由其内置的4位数显电表测得。填料截留的磷素总量、TP去除量、TN去除量的计算如式(1)~式(3)所示。式中:q为各级湿地的填料对溶液中P的吸附总量,mg;q2为各级湿地对溶液中P的去除量,mg;q3为各级湿地对溶液中P的吸附量,mg;ΔC为湿地填料的全磷变化量,mg·g−1;C0为初始TP浓度,mg·L−1;C2为经过电解处理后TP浓度,mg·L−1;C1为初始TN浓度,mg·L−1;C3经过电解处理后TN浓度,mg·L−1;V为装置中的污水体积,L;m为装置中填料的质量,g。
-
1)样品采集。装置稳定运行17个月后,采集了湿地单元的基质样品,用于高通量测序,分析其微生物群落结构。样品采集的具体过程如下:移除湿地表层凋落物和腐殖质后,使用梅花点阵法随机确定取样点。H1表层和底层极板间基质样品的编号分别为A1和a1,极板四周表层和底层的基质样品编号分别为A2和a2,H2表层和底层极板间基质样品的编号分别为B1和b1,极板四周表层和底层的基质样品编号分别为B2和b2,H3表层的基质样品编号为C1,底层基质样品编号为c2。共10个混合样品,各样品经充分混合后放入无菌袋中。
2) PCR扩增和测序。采用Illumina MiSeq技术平台进行测序,将湿地填料样品放至−80 ℃低温环境下,送至百迈客基因生物科技有限公司进行高通量测序。结果数据经过预处理和质量控制后,进行OTU聚类和注释,从而获得特定环境样品的细菌或古菌的物种组成及丰度信息;再通过多样性分析,从而寻找样品间的差异信息。分析湿地单元表层和底层以及电极之间的微生物群落结构和功能群的变化特征,以及其对污水的处理效果的影响。
-
本实验选择铁作为阳极材料,电催化和电絮凝反应过程中的化学方程式如下。其中电催化氧化分为直接氧化和间接氧化。直接氧化是指污染物在阳极表面通过电子传递被氧化(式(4))。间接氧化是指污染物被电解产生的活性物质如·OH等氧化(式(5)和式(6))。在电解过程中,系统会将
${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ 和${\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ 电催化还原成${\rm{NH}}_4^{\rm{ + }}$ -N(式(7)),然后通过电催化转化为N2(式(8))。P去除依赖于阳极产生的Fe2+,通过生成难溶于水的FePO4沉淀下来。其反应过程如式(9)~式(11)所示。电催化脱氮反应见式(4)~式(8),电絮凝除磷反应见式(9)~式(11)。 -
实验数据的计算和处理使用Excel 2018完成,用Pearson检验方法和配对T检验来进行相关性分析和差异性分析,检验数据间相关水平的统计分析通过SPSS 20.0进行。利用GraphPad Prism 8软件作图,图中相关数据均为平均值±标准差。
1.1. 实验装置
1.2. 实验条件和模拟废水
1.3. 采样点设置
1.4. 水质测定与分析方法
1.5. 微生物群落分析
1.6. 电化学反应机理
1.7. 数据处理
-
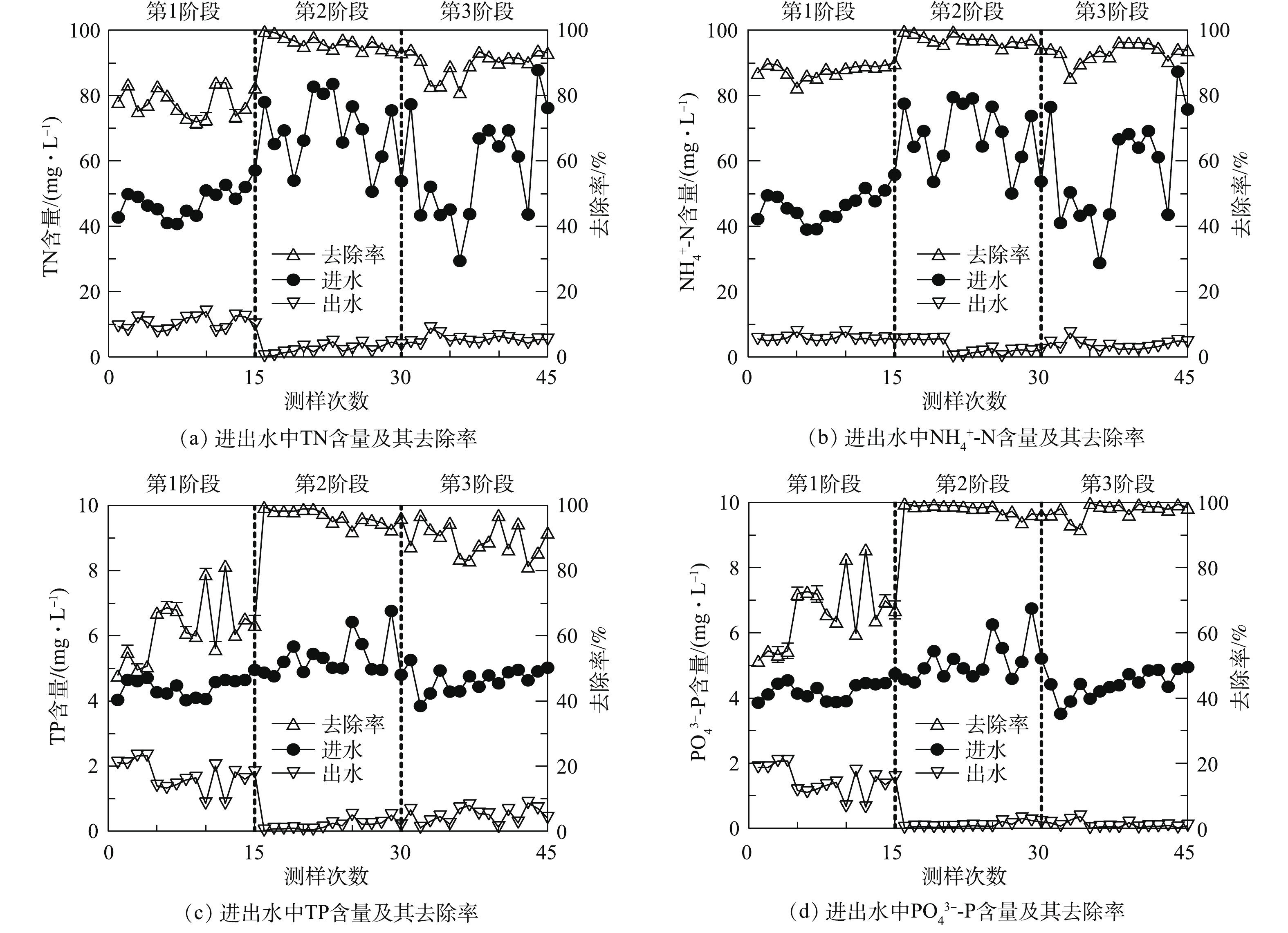
E-HFCWs在不同实验阶段对氮、磷的净化效果如图2所示。系统进水中N、P的浓度均有所波动。在第1阶段(即未电解阶段),系统出水中TN、
${\rm{NH}}_4^{\rm{ + }}$ -N、TP和${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P的平均含量分别为(10.35±2.06)、(5.59±0.63)、(1.68±0.45)和(1.45±0.44) mg·L−1,平均去除率分别为(78.11±4.44)%、(87.81±1.99)%、(62.26±9.74)%和(65.89±10.15)%。而在第2、3阶段,电解强化人工湿地系统出水中TN、${\rm{NH}}_4^{\rm{ + }}$ -N、TP和${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P的平均含量分别为(4.03±1.96)、(2.74±1.49)、(0.34±0.25)和(0.10±0.09) mg·L−1,平均去除率分别为(92.99±4.51)%、(95.22±3.04)%、(93.13±5.22)%和(97.84±1.96)% (如图2所示)。在第2阶段中,装置在秋冬季节运行,环境温度整体较低,人工湿地中植物和微生物作用较弱,因此,选择的电流强度为100 mA;出水中TN、
${\rm{NH}}_4^{\rm{ + }}$ -N、TP和${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P含量分别为(2.60±1.42)、(1.83±0.97)、(0.19±0.14)和(0.11±0.09) mg·L−1,去除率分别为(96.19±1.99)%、(97.10±1.58)%、(96.66±2.23)%、(98.00±1.57)%。而在第3阶段,装置主要在春夏时节运行,环境温度较高,人工湿地中植物和微生物作用较强,因此,选择的电流强度为50 mA。出水中TN、${\rm{NH}}_4^{\rm{ + }}$ -N、TP和${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P 的含量分别为(5.47±1.25)、(3.65±1.36)、(0.49±0.24)和(0.10±0.10) mg·L−1,去除率分别为(89.78±4.03)%、(93.28±2.90)%、(89.59±4.95)%、(97.69±2.30)%。第2阶段系统的氮磷去除能力要明显优于第3阶段。系统进出水中的${\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ -N和${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N含量相对较少,但作为硝化和反硝化作用的中间产物,会在各级湿地中有不同程度的积累。而在电解阶段,${\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ -N和${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ -N的积累量随电流强度越大而减少,且主要积累于未电解的H3中。由此可见,电化学技术与CW的结合大大提高了系统对氮磷营养盐的净化能力,且电解系统随着电流强度的增加,出水中氮磷含量持续下降,去除率显著升高。使出水达到了《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。
-
各级湿地出水中的N、P、Fe的含量及pH如表2所示。阳极铁片电解产生Fe2+,Fe2+在CW表面和植物根附近的有氧环境中易被氧化成Fe3+,而Fe3+在CW中下层的厌氧环境中被还原为Fe2+[16]。虽然Fe离子的引入能够强化N和P的去除[17],但是如果Fe离子含量较多,同样会污染水体。第2、3阶段系统出水的TDFe含量分别为(2.91±1.75) mg·L−1和(2.55±1.89) mg·L−1,均以Fe3+为主,且前后Fe离子含量没有显著性差异(n=15,P>0.05)。在第2阶段中,H1的TDFe的平均含量为(5.32±3.89) mg·L−1,且随着实验的进行缓慢地升高。而H2中的TDFe含量为(10.54±3.99) mg·L−1,显著高于H1(n=15,P<0.05),且H2中铁离子含量的上升速度明显快于H1。H1和H2具有相同的电解条件,但由于H1中的填料为沸石,而沸石独特的分子筛结构,对铁离子具有较强的吸附能力,故将电解产生的Fe2+直接吸附在填料的表面和孔隙中。H3中未添加电解装置,因此,TDFe含量较低,为(4.17±3.37) mg·L−1。在第3阶段电流强度降低,各级湿地的TF含量分别为(5.65±3.40)、(7.15±5.25)、(3.92±3.90) mg·L−1。除H1外,H2和H3中的Fe离子含量均显著降低(n=15,P <0.05)。除第2阶段H2中的Fe2+含量高于Fe3+铁以外,其他各级湿地均是Fe3+含量高于Fe2+。
E-HFCWs中出水相较于进水,出水的温度和pH均在上升,DO、Eh均在下降(表2和表3)。第1阶段进水的pH为6.18~7.51,出水为7.62~8.03。第2阶段进水pH为4.59~7.64,出水为7.06~8.17。第3阶段进水pH为4.65~7.71,出水为7.26~8.41。H1在第2阶段中的平均pH(6.90±0.57)要低于进水(7.21±0.81),然而在第1阶段和第3阶段,H1的碱度在增加(表2)。这可能是因为第2阶段环境温度较低,电流强度较大,产生的铁盐含量较多,其水解引起了碱度消耗所致。3个阶段进水的DO分别为6.67~7.77、7.82~9.15、6.85~7.94 mg·L−1,出水分别为0.61~0.91、0.43~0.71、0.60~0.83 mg·L−1。与未电解HFCWs相比,电解的效果可以诱导更为碱性和更加缺氧的环境。各阶段进水的Eh分别为−29.70~45.75、−45.15~140.22、−45.35~136.66 mV,出水分别为−64.16~−35.05、−72.67~−6.73、−86.74~−18.61 mV。
-
P在CW中的去除依赖于填料的吸附和沉淀、微生物的转化与吸收、植物的吸收与同化[6]。其中填料的吸附和沉淀作用被证明是最主要的去除方式[18]。为了探究填料对系统中P的去除贡献率和去除机理,测定了本实验前后各级CW中填料的全P含量及其P形态的情况,如表4所示。整个实验过程中,系统共截留P素23 609.82 mg,填料的吸附和沉淀作用占P去除贡献率的70%以上。H1、H2和H3的填料各截留了3 758.18、12 644.35、7 207.28 mg。H2中的全P含量最高,其次是H3和H1,全P的变化量分别为0.211、0.126、0.047 mg·g−1,分别占各自全P含量的67.32%、55.28%和43.85%。因此,废砖块作为E-HFCWs中的填料,对P有更好的吸附和沉淀能力。
在各基质样品中,无机P含量最高,其中Al-P和Fe-P为填料沉淀磷素的主要途径,分别占无机磷总量的90.48%、85.24%和83.80%,水溶性P、O-P和Ca-P占比较少。H1和H2的填料样品均是Fe-P的截留量高于Al-P,而H3则完全相反。这是由于H1和H2中的铁片电极在电解过程中产生的Fe2+,而其能与水中O2或电解过程中产生的·OH和H2O2形成Fe3+,生成高活性的絮凝基团,具有极强的吸附能力[19],可将废水中的磷酸盐吸附共沉,生成难溶性的FePO4进而固定下来[20],在湿地中形成黄褐色的沉淀物。而H3中没有电解装置且平均pH=7.62,容易与废砖块在水体中释放的Al3+,生成AlPO4沉淀下来[21]。
-
本项目共完成10个样品的测序,共获得 1 115 342对序列,为了研究样品的物种组成及多样性信息,将相似性达到97%的序列聚类成一个OTU,各样品的OTUs数量和α多样性指数统计结果如表5所示。H3的OTUs数目>H2>H1,且各样品间共有597个相同的OTUs,并没有特有的OTUs。α多样性指数主要反映单个样品的物种丰度及其多样性,衡量指标包括Chao1、Ace、Shannon、Simpson。由表5可以看出,样品的覆盖率最低为99.1%,说明此次测序的结果能够准确且完整地反映E-HFCWs中微生物样品的真实状况。在这10个样品中,C1的ACE、Chao1和Shannon指数最大,而Simpson指数最低,说明C1样品群落中物种丰度和多样性最高。而A1的ACE、Chao1和Shannon指数最低,而Simpson指数最高,即说明A1样品群落中物种丰度和多样性最低。H3的微生物物种丰度和多样性最高,其次是H2和H1。而在H1和H2的各样品中,除了b1和b2外,其余样品均是电极之间的物种丰富度和多样性要低于电极四周。这可能是由于电解作用降低了微生物群落中的物种丰富度和多样性。
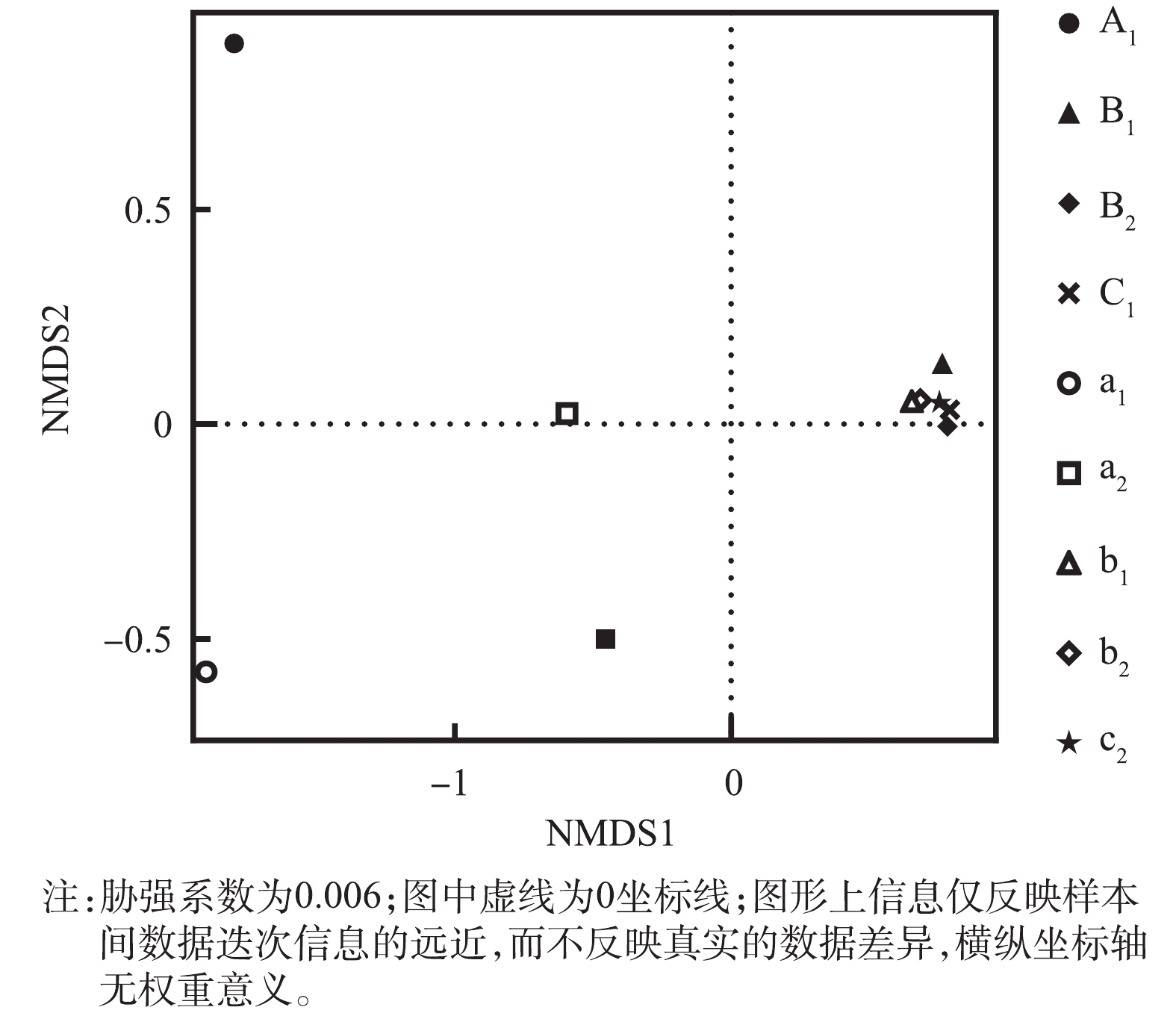
为了进一步分析样品间物种多样性差异,依据不同微生物样品的OTUs 组成,对样品进行了非度量多维标定法(NMDS)分析。如图3所示,胁强系数远小于0.2,这说明NMDS分析可以准确反映样本间的差异程度。A1、A2、a1、a2的差异程度较大,其余样品间的差异程度较小且聚集在一个共同的区域。这说明在H1中,无论在表层还是底层,电极之间与电极四周的菌群组成有较大的差异,且在表层更为显著。
-
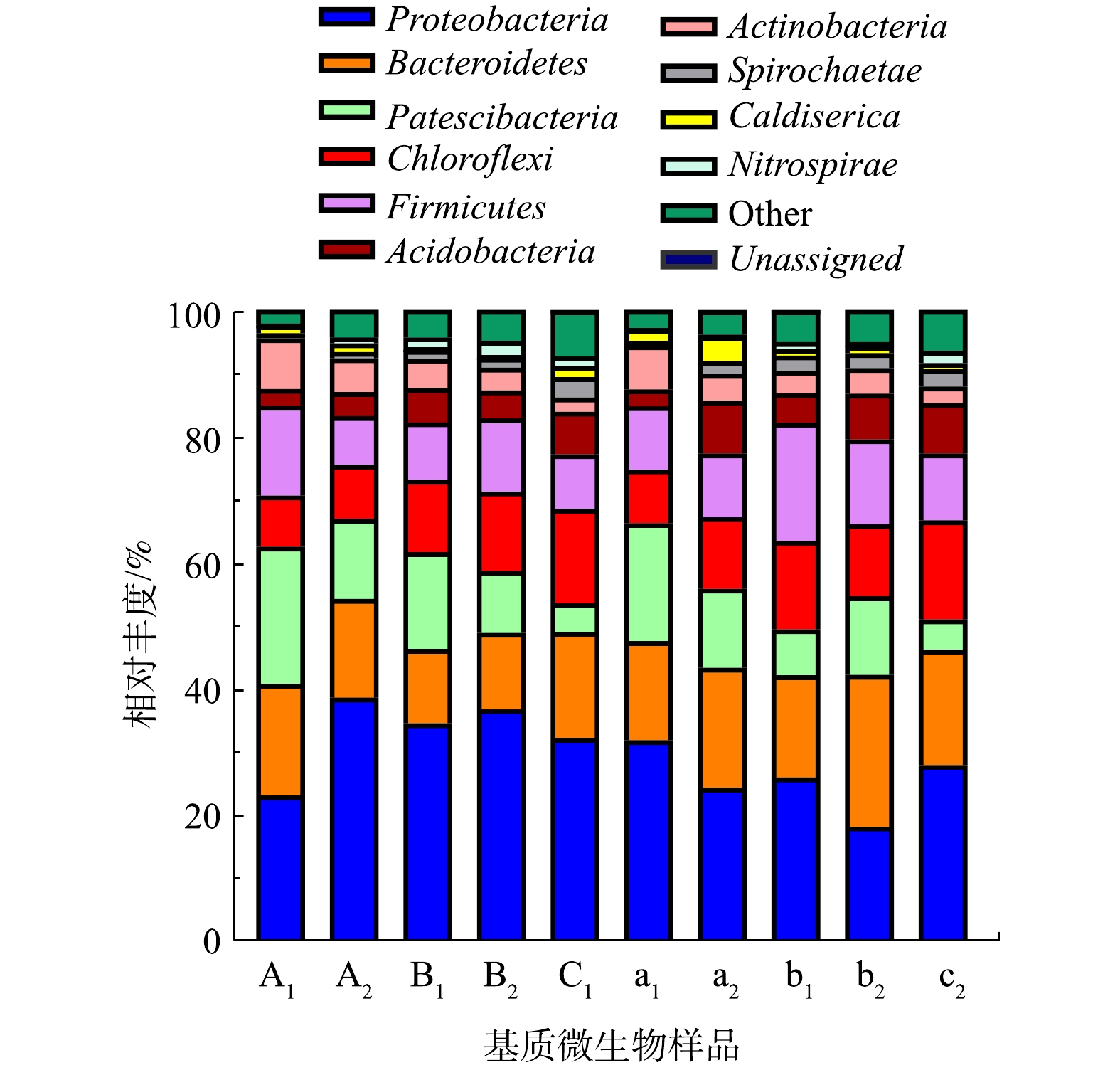
通过对OTU进行去低含量筛除(物种丰度小于0.005%),10个样品中共统计出2界、40门、91纲、192目、313科、501属、524属。为了方便分析,筛选出相对丰度前十的菌门,如图4所示,分别是变形菌门、拟杆菌门、Patescibacteria、绿弯菌门、厚壁菌门、酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)、放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、螺旋体门(Spirochaetae)、嗜热菌门(Caldiserica)、硝化螺旋菌门(Nitrospirae)。前5个菌门是系统中的优势菌门,在各级CW中的相对丰度超过80%。其中变形菌门、拟杆菌门和Patescibacteria在前两级湿地中的相对丰度超过60%,在H3中超过56%。在各样品中,变形菌门的相对丰度最高,且CW表层相对丰度高于底层。在H1、H2表层电极之间的变形菌的相对丰度要低于四周,而在底层分布规律完全相反。有研究[22-23]表明,变形菌在人工湿地微生物氮磷去除中起到主要作用。其次是拟杆菌门,底层相对丰度大于表层,电极四周高于电极之间。Patescibacteria在前两级湿地广泛分布,平均相对丰度分别为16.42%和11.19%,而在H3中则分布较少(4.65%),且其在电极之间的相对丰度较高,因此,该类微生物的富集可能与电解作用有关。绿弯菌门主要分布在后两级湿地,能利用有机物进行光合作用,还可利用
${\rm{NH}}_4^{\rm{ + }}$ -N和有机N作为N源生长[24]。厚壁菌门在H2中分布较多(13.20%),且底层(16.03%)大于表层(10.37%),其次H1(10.52%)和H3(9.67%)。厚壁菌门中部分菌属具有反硝化的作用,对N和有机物具有良好的去除作用[25]。 -
为了进一步的分析电解对CW的影响,对数据进行了相关分析性和差异性分析。我们发现在第2、3阶段中,N和
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P的去除率与进水的DO和Eh呈极显著负相关(n=15,P<0.01),与进水pH和温度呈极显著正相关(n=15,P<0.01)。第2阶段的环境温度较低,TP去除率与进水的DO成极显著负相关,与进水温度呈极显著正相关(n=15,P<0.01)。而在第3阶段,环境温度较高,TP去除率与进水的DO呈显著正相关,与进水温度无关(n=15,P<0.01)。在第2阶段,各级湿地水体中Fe2+和TDFe含量与其对应P的去除率呈极显著负相关(n=15,P<0.01)。除H2外,Fe3+含量与其对应的P去除率也呈极显著负相关(n=15,P<0.01)。H1和H2中Fe离子的含量均与其对应的TN去除率呈显著负相关(n=15,P<0.05)。在第3阶段,各级湿地水体中Fe2+含量与其对应${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P的去除率呈显著负相关(n=15,P<0.01)。各级湿地水体中Fe3+和TDFe含量与其对应TP的去除率呈显著负相关(n=15,P<0.01),Fe离子的含量与其对应N的去除率无关(n=15,P>0.05)。2、3阶段系统中出水的${\rm{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ -P含量及其去除率均没有显著性差异(n=15,P>0.05),但在第2阶段,当电流强度为100 mA时,N和P的去除率均高于第3阶段。
2.1. 电解对脱氮除磷的影响
2.2. 电解对其他主要水质指标的影响
2.3. 各级湿地中填料的TP含量及其P的形态
2.4. 各湿地单元的多样性分析
2.5. 湿地单元基质微生物的群落结构
2.6. 电解阶段水质指标间的相关性分析
-
1)当水力负荷为0.30 m3·(m2·d)−1时,3个阶段中系统对TN和TP的平均去除率分别为(78.12±4.38)%、(96.19±2.03)%、(89.85±4.20)%,(62.27±9.86)%、(96.66±2.28)%、(89.59±5.06)%。电解强化了系统对N、P营养盐的净化能力。使第2阶段和第3阶段的出水达到了《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。
2)在整个实验过程中,系统共截留P元素23 609.82 mg,填料的吸附和沉淀作用对P的去除贡献率占70%以上。各级湿地的填料中无机P含量最高,其中Al-P和Fe-P为填料沉淀磷素的主要途径。
3)各级湿地中的基质微生物种群和相对丰度均具有差异。共发现10个共同的优势菌门,分别是变形菌门、拟杆菌门、Patescibacteria、绿弯菌门、厚壁菌门、酸杆菌门、放线菌门、螺旋体门、嗜热菌门、硝化螺旋菌门。前5个菌门是系统中的优势菌门,在各级CW中的相对丰度均超过80%。其中,变形菌门、拟杆菌门和Patescibacteria在前两级湿地中的相对丰度超过60%,在H3中超过56%。在各样品中,变形菌门的相对丰度最高,对人工湿地N、P去除中起到主要作用。





 下载:
下载: